Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, has disrupted economies worldwide, and Europe has not been immune to its profound economic effects. The continent, home to diverse economies ranging from powerhouse nations to smaller, more fragile ones, has faced unique challenges in mitigating the pandemic’s economic fallout. In this article, we will delve into the multifaceted economic impact of COVID-19 in Europe, exploring the key areas of concern, government responses, and the road to recovery.
The COVID-19 pandemic has left an indelible mark on Europe’s economic landscape, ushering in an era of unprecedented challenges and transformative responses:
Diverse Economic Landscapes: Europe’s economies are a tapestry of diversity, with countries ranging from economic powerhouses to those grappling with fragility. This diversity translated into varying degrees of resilience in the face of the pandemic.
Economic Disruptions: COVID-19 triggered disruptions across sectors. Lockdowns and travel restrictions hampered industries like tourism and hospitality, while healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and technology sectors surged.
Employment and Labor Markets: Europe saw a surge in unemployment and furloughed workers. Governments implemented support measures, including wage subsidies and unemployment benefits, to cushion the impact and preserve jobs.
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs): SMEs, the backbone of many European economies, faced existential threats. Emergency loans and grants were rolled out to keep these businesses afloat.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Supply chains faced interruptions, impacting manufacturing and trade. Diversification and resilience in supply chain management gained importance.
Healthcare and Research: The pandemic underscored the importance of healthcare and research. Massive investments were made in healthcare infrastructure, vaccine development, and medical research.
Government Responses: European governments implemented extensive fiscal stimulus packages, monetary policies, and public health measures. The European Union’s NextGenerationEU recovery plan marked a landmark step in economic recovery and green transition.
Debt and Fiscal Sustainability: The crisis led to increased government debt levels, raising concerns about fiscal sustainability. Discussions on the issuance of joint EU bonds and the EU’s long-term fiscal framework gained prominence.
Digital Transformation: Digitalization accelerated, with remote work, e-commerce, and digital health becoming integral. Investments in digital infrastructure and skills were pivotal.
Green Transition: The pandemic offered an opportunity to align recovery efforts with sustainability goals. Europe embraced the Green Deal, emphasizing a green and digital recovery.
Vaccine Distribution: Vaccine distribution and access became paramount. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) played a pivotal role in approving and monitoring vaccines.
International Cooperation: Europe engaged in international cooperation, both in vaccine distribution and global economic support.
Economic Recovery: Europe embarked on a multifaceted path to recovery, focusing on investments in healthcare, digitalization, sustainable initiatives, and economic resilience.
Geopolitical Dynamics: The pandemic’s economic impact also had geopolitical implications, shaping Europe’s role in the global arena.
In conclusion, Europe’s journey through the COVID-19 pandemic has been one of resilience, adaptation, and transformation. While the challenges were immense, they catalyzed innovative responses and laid the foundation for a more sustainable and digitally-driven future. The road to recovery continues to evolve, with Europe at the forefront of shaping its economic destiny in a post-pandemic world.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic …
Unprecedented Economic Shock
COVID-19 brought an unprecedented economic shock to Europe. The rapid spread of the virus led to lockdowns, travel restrictions, and social distancing measures, resulting in a severe economic contraction. Businesses, particularly those in the tourism, hospitality, and retail sectors, experienced significant disruptions, leading to layoffs and closures.
The economic impact of COVID-19 in Europe reached far beyond immediate disruptions. As the pandemic persisted, it revealed deeper vulnerabilities in various sectors of the economy. The manufacturing industry faced supply chain disruptions, highlighting the need for diversification and resilience. Additionally, the shift towards remote work and digitalization accelerated, transforming the way businesses operate and emphasizing the importance of technology in a rapidly changing world. As Europe navigates the aftermath of the pandemic, policymakers and businesses are focusing on building resilience, adapting to new norms, and fostering innovation to ensure a robust and sustainable economic recovery.
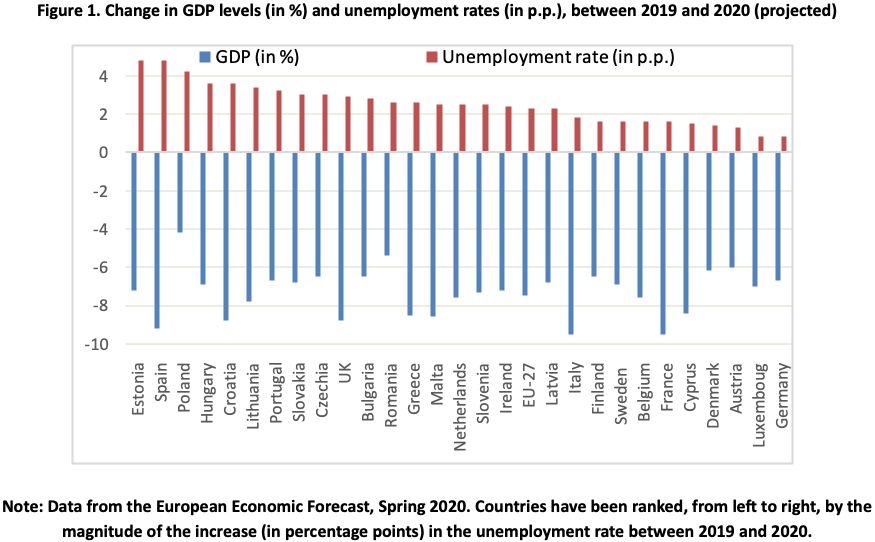
Soaring Unemployment
One of the most immediate consequences of the pandemic was a surge in unemployment across Europe. Lockdowns and business closures forced many companies to lay off workers, leaving millions unemployed. Governments scrambled to implement support measures such as wage subsidies to mitigate the impact on households.
The surge in unemployment that swept across Europe in the wake of the pandemic was not just a numerical statistic; it was a stark reflection of the human toll exacted by the crisis. As lockdowns shuttered businesses and economic activity ground to a halt, millions found themselves grappling with the sudden loss of jobs and livelihoods.
1. The Human Face of Unemployment:
- Behind the staggering numbers of job losses were individual stories of hardship and resilience. Families had to adapt to the new reality of reduced income, facing tough decisions on how to make ends meet.
2. Government Intervention and Support:
- Governments recognized the urgency of the situation and took swift action. Wage subsidies, unemployment benefits, and financial assistance programs were deployed to provide a lifeline to those impacted the most. These measures aimed not only at preserving financial stability but also at offering a glimmer of hope in uncertain times.
3. The Resilience of the Workforce:
- The pandemic highlighted the resilience and adaptability of the European workforce. Many individuals and businesses pivoted to remote work, demonstrating the ability to navigate new challenges and seize opportunities for growth in the face of adversity.
4. The Role of Digitalization:
- Digitalization played a significant role in mitigating unemployment in certain sectors. It enabled businesses to continue operations remotely and facilitated the growth of online industries, creating new job opportunities and transforming the way we work.
5. The Quest for Economic Recovery:
- As the pandemic evolved, discussions shifted from immediate relief to long-term recovery. Strategies for reemploying those who had lost their jobs became central to discussions at both national and European levels. Investments in reskilling and upskilling programs gained prominence, aiming to equip individuals with the tools needed to reenter the job market.
6. A Shared European Vision:
- The pandemic underscored the importance of solidarity within the European Union. Member states collaborated on economic recovery plans and initiatives, emphasizing the shared responsibility to support not only their own citizens but also the broader European community.
In retrospect, the surge in unemployment was a grim chapter in Europe’s response to the pandemic. Yet, it also revealed the resilience, adaptability, and collective spirit of its people. The swift government intervention and the transition to new modes of work demonstrate that even in the face of adversity, Europe’s workforce can weather the storm and emerge stronger, ready to face the challenges and opportunities of a rapidly changing world. The pandemic was not just a test of Europe’s economic stability but also a testament to its capacity to care for its citizens and chart a course toward recovery.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: World Economic Situation and Prospects: September 2022 Briefing …

Fiscal Responses
To counter the economic fallout, European governments unleashed a wave of fiscal stimulus packages. These measures included direct financial assistance to individuals and families, support for businesses, and enhanced healthcare funding. Additionally, the European Central Bank (ECB) implemented monetary policies to maintain liquidity and stabilize financial markets.
In response to the daunting economic challenges triggered by the various crises, European governments demonstrated resilience by deploying a sweeping wave of fiscal stimulus packages. These comprehensive measures went beyond mere financial support; they were a lifeline for individuals and families facing financial hardship. Governments swiftly provided direct financial assistance, helping people to meet their basic needs and keep their households afloat during times of economic uncertainty.
Businesses, especially small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), found relief in these stimulus packages. Support measures ranged from grants and loans to tax deferrals and wage subsidy programs, ensuring that companies could retain their employees and weather the storm. This support was essential in preventing mass bankruptcies and job losses, thereby preserving the economic fabric of Europe.
Simultaneously, governments recognized the importance of healthcare in the battle against crises like the COVID-19 pandemic. They increased funding for healthcare systems, bolstering the capacity to respond to health emergencies effectively. This investment not only saved lives but also underscored the fundamental importance of a robust healthcare infrastructure in safeguarding a nation’s well-being.
Complementing these fiscal measures, the European Central Bank (ECB) played a pivotal role by implementing monetary policies designed to maintain liquidity and stabilize financial markets. These measures included interest rate cuts, asset purchase programs, and expanded lending facilities to banks. By ensuring the availability of credit and preventing a credit squeeze, the ECB helped avert a financial crisis of greater magnitude.
The combined efforts of governments and the ECB illustrated the resilience and adaptability of European institutions in the face of unprecedented challenges. These responses not only provided immediate relief but also laid the groundwork for a more stable and prosperous future. As Europe continues its journey towards recovery and resilience, the lessons learned from these measures will remain invaluable in shaping future policies and preparedness for unforeseen crises.

Uneven Impact
The pandemic’s economic impact was uneven across Europe. While countries like Germany and the Netherlands demonstrated resilience, others, including Italy and Spain, were hit harder due to their reliance on sectors heavily affected by the pandemic. Southern European nations, already grappling with high levels of debt, faced additional financial stress.
The pandemic’s economic impact indeed unveiled a stark contrast in resilience among European nations, reflecting their economic structures, preparedness, and exposure to pandemic-related shocks:
Resilient Economies: Countries like Germany and the Netherlands, with diversified economies and strong manufacturing sectors, weathered the storm relatively well. Their ability to adapt to remote work and their robust healthcare systems played pivotal roles.
Vulnerable Sectors: On the flip side, nations heavily reliant on sectors such as tourism, hospitality, and small-scale retail suffered immensely. Italy and Spain, both popular tourist destinations, faced severe economic setbacks due to travel restrictions and decreased tourist inflow.
Supply Chain Dependencies: The pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains. While some countries had diversified their supply sources, others found themselves reliant on specific regions for critical goods and faced disruptions.
Debt Levels: Southern European nations, including Italy and Greece, were already grappling with high levels of public debt before the pandemic. The economic downturn placed additional stress on their finances, raising concerns about debt sustainability.
Government Responses: Governments across Europe implemented various measures to cushion the economic impact. Resilient economies had more fiscal firepower to deploy stimulus packages and support businesses, while others faced limitations.
Fiscal Transfers: The EU’s response to the crisis included significant fiscal transfers, such as the NextGenerationEU recovery plan. These transfers aimed to support nations disproportionately affected by the pandemic and promote economic recovery.
Healthcare Disparities: Variations in healthcare infrastructure and preparedness also contributed to differences in outcomes. Countries with well-funded and robust healthcare systems coped better with the healthcare burden.
Regional Inequalities: The pandemic highlighted existing regional inequalities within countries. Urban centers often faced greater challenges than rural areas, leading to discussions about regional development and resilience.
Long-Term Implications: Beyond immediate economic impacts, there are long-term considerations. Nations that invested in digitalization, green initiatives, and healthcare infrastructure are likely to emerge stronger in the post-pandemic world.
International Cooperation: The crisis necessitated international cooperation. European nations collaborated on vaccine procurement and distribution, demonstrating solidarity in the face of a common challenge.
In summary, the pandemic underscored the economic disparities across Europe, with varying degrees of resilience and vulnerability. While some nations emerged relatively unscathed, others faced profound economic challenges exacerbated by their pre-existing conditions. The recovery process continues to be shaped by lessons learned during the crisis and the region’s collective efforts to build a more resilient and sustainable future.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Inequality and COVID-19 – IMF F&D

The Role of the European Union
The European Union played a significant role in coordinating responses to the economic crisis. The EU introduced initiatives like the NextGenerationEU recovery plan, which involves a substantial financial package to support member states’ recoveries. This plan includes the issuance of EU bonds, marking a historic step towards fiscal integration.
The European Union’s response to the economic impact of COVID-19 showcased a commitment to solidarity and cooperation among member states. The NextGenerationEU recovery plan, with its substantial financial package, not only provides much-needed support to struggling economies but also represents a significant leap in the direction of fiscal integration. The issuance of EU bonds as part of this plan is a historic moment, as it demonstrates the EU’s ability to act collectively in times of crisis.
Furthermore, the EU’s response emphasized the importance of a green and digital recovery. Funds allocated for green initiatives and digital transformation are expected to drive sustainable growth and innovation in Europe. The push towards a more digital and sustainable economy aligns with global trends and positions the EU to be a leader in these crucial areas.
While the economic impact of COVID-19 has been profound, the EU’s coordinated response reflects its determination to not only recover but also emerge stronger and more resilient in the face of future challenges. The lessons learned from this crisis are likely to shape European economic policies for years to come, emphasizing the value of unity and adaptability.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: EU response to COVID-19 | European Union

Long-Term Consequences
The long-term economic consequences of COVID-19 in Europe are still unfolding. Experts anticipate challenges such as increased public debt levels, changes in consumer behavior, and a potential restructuring of industries. The path to recovery will likely be protracted, with some sectors rebounding faster than others.
The long shadow cast by COVID-19 continues to shape Europe’s economic landscape, presenting both immediate challenges and lingering uncertainties. As we navigate the path to recovery, several key facets of the post-pandemic economic landscape come into view:
1. The Debt Dilemma:
- One of the most pressing concerns is the surge in public debt across Europe. Governments took on substantial debt burdens to finance relief measures and support their economies during the crisis. The challenge lies in finding a sustainable path to reduce this debt while simultaneously fueling economic growth.
2. Shifting Consumer Behavior:
- The pandemic fundamentally altered consumer behavior. E-commerce, remote work, and digital engagement became the norm, reshaping the retail and service sectors. Businesses are adapting by investing in digital infrastructure and rethinking their strategies to meet evolving customer expectations.
3. Resilience and Transformation:
- Certain industries, such as healthcare, e-commerce, and technology, thrived during the crisis. Others, such as tourism, hospitality, and traditional retail, faced unprecedented challenges. Recovery strategies must consider the need for sector-specific support and transformation.
4. The Remote Work Revolution:
- Remote work, once considered a niche trend, has become a fundamental shift in how we work. Employers are reevaluating office-centric models, while employees are seeking greater work-life balance. This shift has implications for office space demand, transportation, and urban planning.
5. Green and Sustainable Recovery:
- Europe has made a significant commitment to green and sustainable recovery. Investments in renewable energy, clean technologies, and sustainable infrastructure are central to both economic growth and addressing climate change.
6. Accelerating Digitalization:
- Digitalization has been accelerated across all sectors, from education to healthcare. Europe’s ability to embrace digital transformation will be a determinant of its economic competitiveness in the global arena.
7. International Collaboration:
- The pandemic highlighted the interconnectedness of the global economy. Collaboration with international partners on vaccine distribution, trade, and addressing global challenges is vital for Europe’s recovery.
8. Reskilling and Upskilling:
- Investing in reskilling and upskilling programs is crucial to helping individuals adapt to the evolving job market. Lifelong learning will be a key component of Europe’s economic resilience.
While the challenges are formidable, Europe’s history is marked by resilience and adaptability. The path to recovery will be protracted, but it also offers opportunities for innovation, sustainability, and transformation. Europe’s ability to navigate these challenges and seize these opportunities will determine its economic trajectory in the post-pandemic era. As we look ahead, Europe remains committed to charting a course toward economic prosperity, social well-being, and a sustainable future for its citizens.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: What is the EU doing in response to the COVID-19 coronavirus …
Resilience and Adaptation
Amid the economic turmoil, Europe showcased resilience and adaptability. Many businesses accelerated their digital transformations, governments embraced remote work solutions, and pharmaceutical companies raced to develop vaccines. These changes could shape the post-pandemic economic landscape.
In the midst of profound economic turmoil, Europe emerged as a resilient and adaptable region, marked by a spirit of innovation and cooperation. The challenges brought about by the crisis catalyzed a wave of transformative actions across various sectors, leaving an indelible mark on the trajectory of the post-pandemic economic landscape.
One of the most noticeable shifts occurred in the business world, where companies accelerated their digital transformations at an unprecedented pace. Forced to adapt to remote work, e-commerce, and digital services, businesses harnessed technology to maintain operations and even discover new avenues for growth. This rapid digitization not only ensured business continuity but also improved efficiency and accessibility, offering a glimpse into the potential of a more digitally-driven future.
Governments, too, responded with agility, embracing remote work solutions for their own operations. This shift not only kept public services functioning but also demonstrated the feasibility of flexible work arrangements on a large scale. As remote work became the norm rather than the exception, it redefined traditional notions of work and office spaces, potentially leading to lasting changes in work cultures and urban planning.
In the race against the pandemic, pharmaceutical companies stood out as beacons of innovation. They worked tirelessly to develop and distribute vaccines at an unprecedented speed. The collaboration between governments, research institutions, and private industry paved the way for breakthroughs that could have far-reaching implications beyond the immediate health crisis. It highlighted the potential for rapid scientific advancements and international cooperation in addressing global challenges.
These changes in business, government, and healthcare are poised to shape the post-pandemic economic landscape in profound ways. Digitalization will continue to play a central role in business models and customer interactions. Remote work is likely to become a more integral part of the labor market, with implications for work-life balance and urban planning. The pandemic has also underscored the importance of preparedness and collaboration in addressing global crises, setting a precedent for how nations can come together to tackle shared challenges.
In essence, Europe’s resilience and adaptability in the face of economic adversity have not only enabled recovery but also opened doors to a future marked by innovation, flexibility, and a renewed sense of global cooperation. These transformative changes are likely to have a lasting impact on the continent’s economic landscape, shaping it into a more dynamic, digitally-driven, and resilient ecosystem.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Global Economy to Slow Further Amid Signs of Resilience and …

Conclusion
The economic impact of COVID-19 in Europe has been profound, affecting nations, industries, and individuals. While governments and international institutions have taken significant steps to mitigate the crisis, the road to recovery remains uncertain. Europe’s ability to adapt to new economic realities, invest in resilience, and foster innovation will be pivotal in shaping its economic future. As the continent strives to rebuild, lessons learned from this unprecedented challenge may pave the way for a more resilient and sustainable economy in the years ahead.
The profound economic impact of COVID-19 has left an indelible mark on Europe, highlighting the need for adaptability, resilience, and innovation in charting the path to recovery:
Nations in Transition: The pandemic exposed vulnerabilities and strengths across European nations. Some are already on a recovery trajectory, while others face ongoing challenges. The ability to pivot toward emerging economic opportunities will be key.
Digital Transformation: The pandemic accelerated digitalization across sectors. Europe’s commitment to harnessing the power of technology can lead to more efficient, competitive, and resilient economies. Investment in digital infrastructure and skills will drive economic growth.
Green Transition: Europe’s emphasis on sustainability and the Green Deal is a testament to its commitment to environmental responsibility. The recovery provides an opportunity to align economic growth with eco-friendly initiatives, fostering long-term sustainability.
Innovation and Research: Investment in research and innovation is essential for staying at the forefront of emerging industries and technologies. Europe’s focus on research and development can propel it into leadership roles in various sectors.
Education and Workforce: Preparing the workforce for the jobs of the future is vital. Education and training programs should align with evolving industry needs, ensuring a skilled workforce ready to embrace new economic realities.
Resilience to Shocks: Europe must enhance its resilience to future shocks, whether health-related or economic. Diversifying supply chains, bolstering healthcare systems, and reinforcing financial stability are crucial steps.
Global Collaboration: The pandemic has demonstrated the importance of international cooperation. Europe’s engagement in global efforts, from vaccine distribution to trade agreements, enhances its role on the world stage.
Inclusivity: Ensuring that recovery benefits all segments of society is paramount. Inclusivity in economic policies can reduce disparities and strengthen social cohesion.
Long-Term Planning: Governments and institutions should adopt long-term economic planning that takes into account demographic changes, climate challenges, and evolving technology landscapes.
Lessons Learned: The pandemic provided a crash course in resilience and adaptability. Lessons from this crisis will inform strategies for dealing with future challenges.
Europe stands at a pivotal juncture, where the choices made in the aftermath of the pandemic will shape its economic trajectory for years to come. The road to recovery is uncertain, but it also offers opportunities for transformation. By leveraging its strengths, embracing innovation, and staying true to its commitment to sustainability, Europe can emerge from this crisis as a stronger, more resilient, and sustainable economic powerhouse. The lessons learned will serve as valuable guideposts on this transformative journey.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: The territorial impact of COVID-19: Managing the crisis across levels …
More links
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: COVID-19: the EU’s response to the economic fallout
