Introduction
In recent years, blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary tool with the potential to transform various industries. One sector that stands to benefit significantly from this innovation is agriculture. With the growing global demand for safe, sustainable, and traceable food products, blockchain offers a solution that can enhance transparency and traceability across the agricultural supply chain.
In recent years, blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary tool with the potential to transform various industries. One sector that stands to benefit significantly from this innovation is agriculture. With the growing global demand for safe, sustainable, and traceable food products, blockchain offers a solution that can enhance transparency and traceability across the agricultural supply chain.
The Power of Blockchain in Agriculture
Blockchain’s potential in agriculture extends beyond just transparency and traceability; it has the power to revolutionize the entire ecosystem:
Secure Transactions: Blockchain’s cryptographic principles ensure that data recorded on the ledger is secure and tamper-proof. This not only prevents fraud but also creates a level of trust that can stimulate investment in agriculture. Farmers can access financial services more easily, and investors are more inclined to support agriculture-related projects, knowing that their investments are safeguarded.
Supply Chain Efficiency: Beyond just tracking the source of a product, blockchain can optimize the supply chain. It enables real-time monitoring of inventory levels, weather conditions, and transportation logistics. This data-driven approach can help prevent overstocking, minimize wastage, and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
Empowering Smallholders: Blockchain technology can empower smallholder farmers in developing regions by providing them with a direct link to global markets. By digitally recording their transactions and product history, these farmers can build a reputation for quality, attracting buyers from around the world. This can lead to increased income and improved livelihoods for those at the grassroots level of agriculture.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: The data generated by blockchain technology can be harnessed for data analytics and predictive modeling. Farmers can use this information to make informed decisions about crop planting, harvesting times, and resource allocation. This, in turn, can lead to higher crop yields and reduced environmental impact.
Sustainable Practices: With increased transparency, consumers can reward sustainable agricultural practices. Blockchain can document organic certifications, fair trade agreements, and sustainable farming methods, allowing consumers to choose products that align with their values. This, in turn, can incentivize more environmentally friendly and ethical agricultural practices.
Global Trade Facilitation: Blockchain can simplify international trade in agriculture. Smart contracts can automate customs processes, tariff payments, and compliance checks, reducing paperwork and speeding up the movement of goods across borders. This can open up new markets for agricultural products and stimulate global trade.
Reducing Food Waste: By providing real-time information on the status and location of food products, blockchain can significantly reduce food waste. Retailers can better manage their inventory, and consumers can make informed decisions about product freshness, resulting in fewer discarded items.
As we look to the future of agriculture, blockchain technology is poised to play a pivotal role in addressing the challenges of feeding a growing global population while ensuring food safety, sustainability, and equitable access. Its potential to transform the industry is not limited to a single aspect but encompasses the entire agricultural ecosystem, making it a beacon of hope for a more efficient, secure, and sustainable future in farming and food production.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Blockchain Technology for Agriculture: Applications and … – Frontiers
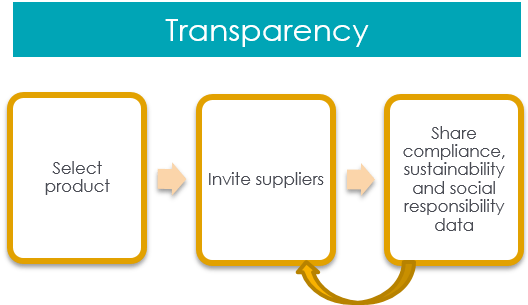
Transparency in agriculture has long been a concern. Consumers want to know where their food comes from, how it’s produced, and whether it meets certain quality and safety standards. Farmers, too, are keen to ensure that their products reach the market without being adulterated or counterfeited along the way. However, achieving these goals in a complex, globalized supply chain has been a considerable challenge.
Transparency in agriculture stands as a shared imperative for both consumers and farmers, reflecting the growing demand for a more intimate connection with our food systems. In an era where the journey from farm to fork traverses vast distances and myriad intermediaries, the need for clarity and trust has never been greater.
For consumers, the desire to know the origins of their food stems from a profound sense of responsibility – a desire to make informed choices that align with their values. It’s about understanding whether the food they consume adheres to ethical and environmental standards, or if it has been produced using practices that promote sustainability. Moreover, transparency empowers consumers to make health-conscious decisions, ensuring that the food they purchase aligns with dietary preferences, allergies, and nutritional requirements.
On the flip side, farmers are equally invested in transparency, seeking to protect the integrity of their products. They strive to guarantee that their hard-earned yields aren’t diluted, adulterated, or counterfeited during the complex journey through supply chains. Authenticity and the preservation of the unique qualities of their produce are not only a matter of pride but also a crucial component of their livelihoods.
In the digital age, technology plays a pivotal role in addressing these transparency challenges. Blockchain, for instance, can provide an immutable ledger that traces every step of a product’s journey, from seed to sale. IoT (Internet of Things) devices can monitor storage conditions, ensuring the quality and safety of food along its path. Moreover, apps and websites offer consumers a window into the farms and practices behind their favorite products, fostering a sense of connection and trust.
Transparency in agriculture is not just a trend; it’s a transformation of our food systems. As we navigate this complex, globalized supply chain, it’s essential to embrace technological innovations, robust regulations, and a shared commitment to honesty and accountability. By doing so, we can create a more transparent, sustainable, and trustworthy food ecosystem that serves the interests of consumers, farmers, and the planet alike.
You can also read more about this here: Blockchain-based Traceability and Transparency in Agricultural …

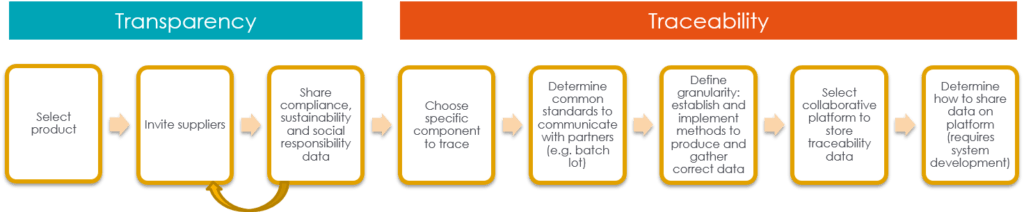
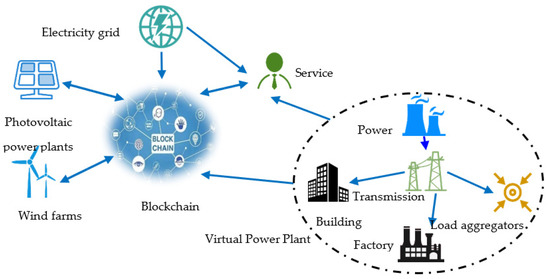
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Each “block” in the chain contains a batch of transactions, and once added, it cannot be altered without consensus from the network. This immutable record-keeping system has several implications for agriculture:
Blockchain technology, often associated with cryptocurrencies, has transcended its financial origins and found innovative applications in agriculture. Its decentralized and tamper-proof ledger system, which records transactions across a network of computers, presents a revolutionary paradigm for enhancing transparency, traceability, and efficiency throughout the agricultural supply chain.
Supply Chain Traceability: One of the primary advantages of blockchain in agriculture is its ability to provide end-to-end traceability. Each transaction or event in the supply chain, from planting and harvesting to processing and distribution, can be securely recorded in a blockchain. This transparency allows consumers to trace the journey of their food products, ensuring authenticity and provenance. For example, consumers can verify whether organic claims are legitimate, which is vital in an era of increasing food fraud and safety concerns.
Food Safety: Blockchain’s immutable ledger is a potent tool for enhancing food safety. In the event of a foodborne illness outbreak or contamination, authorities can quickly trace the source of the problem, pinpoint affected batches, and remove them from the market. This rapid response not only protects public health but also minimizes financial losses for growers and distributors.
Reduced Fraud: Agriculture is vulnerable to various forms of fraud, such as counterfeit seeds, adulterated fertilizers, and deceptive labeling. Blockchain helps reduce these fraudulent practices by creating a transparent and verifiable record of transactions. Smart contracts, a feature of blockchain, can automate payments and enforce quality control, ensuring that all parties in the supply chain adhere to their commitments.
Efficient Transactions: Traditional paperwork and manual record-keeping in agriculture can be time-consuming and error-prone. Blockchain streamlines these processes by automating data capture and verification. For instance, farmers can record crop yields and quality, which can then trigger automatic payments based on predetermined smart contract conditions.
Financial Inclusion: In regions with limited access to traditional banking and financial services, blockchain can empower farmers by providing a secure and transparent platform for financial transactions. This inclusion can open up new opportunities for credit access and insurance, improving the financial stability of small-scale farmers.
Market Access: For agricultural exports, blockchain-based certifications can streamline the approval process for meeting import regulations and standards. This simplification can lead to easier market access for agricultural products in international trade.
Data Ownership: Blockchain technology also addresses concerns about data ownership. Farmers and other stakeholders can have control over their data, deciding who has access and for what purposes. This control is particularly valuable as data-driven decision-making becomes increasingly prevalent in modern agriculture.
In summary, blockchain technology holds immense promise for agriculture by offering a secure, transparent, and efficient means of tracking and verifying transactions throughout the supply chain. Its potential to enhance food safety, reduce fraud, and promote transparency positions it as a transformative force in modernizing and safeguarding the agricultural industry. As adoption continues to grow, blockchain’s impact on agriculture will likely extend to other areas, ultimately shaping a more secure, sustainable, and accountable food system.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Blockchain in Agriculture Traceability Systems: A Review
Blockchain allows for the precise tracking of agricultural products from farm to table. Each step in the supply chain, from planting to harvesting, processing, and distribution, can be recorded on the blockchain. This ensures that consumers can access accurate information about the origin of their food.
“Blockchain technology has ushered in a new era of transparency and accountability in the agricultural industry, offering a comprehensive and unassailable means of tracking products from the moment they sprout in the fields to the moment they grace our tables. This revolutionary system captures every critical step in the supply chain, leaving no room for ambiguity or misinformation.
Farming Origins: At the very beginning of the journey, blockchain allows us to trace the roots of our food—literally. Each seed planted, each acre cultivated, and each farming practice employed can be recorded. This level of detail offers insights into the methods used, ensuring that sustainable and ethical farming practices are honored and rewarded.
Harvest to Table: As crops are harvested, blockchain technology continues to work its magic. The data trail extends to processing facilities, where the transformation of raw produce into consumer-ready products is meticulously documented. Whether it’s washing, cutting, packaging, or any other step in food processing, consumers can follow the journey of their food with complete confidence.
Distribution and Logistics: The blockchain ensures that nothing is lost in transit. Every movement, every stop, and every transfer in the distribution process is recorded. This not only enhances efficiency by identifying bottlenecks but also safeguards against issues like spoilage or contamination.
Authenticity and Quality Control: One of the most significant advantages of blockchain is its role in verifying the authenticity and quality of products. If a product carries a label of ‘organic,’ ‘fair trade,’ or ‘non-GMO,’ consumers can easily verify its legitimacy by checking the blockchain records. This kind of transparency empowers consumers to make choices that align with their values.
Food Safety and Recalls: In the unfortunate event of a food safety issue or recall, blockchain technology excels. By rapidly tracing the source of contamination, it enables targeted recalls, minimizing the impact on consumers and the reputation of the industry.
Consumer Empowerment: Ultimately, blockchain technology places the power in the hands of consumers. With a simple scan of a QR code or a few clicks on a website, consumers can access a wealth of information about the food they are about to consume. They can make informed decisions about their diet, supporting sustainable and ethical practices and rewarding responsible producers.
Global Impact: Blockchain’s global reach makes it an invaluable tool for international trade. It simplifies the verification of cross-border shipments, compliance with import regulations, and adherence to international standards, thereby facilitating the smooth movement of agricultural products across the globe.
In conclusion, blockchain technology is not just a ledger; it’s a game-changer for the agricultural industry. It enables precise tracking of agricultural products from their origins to our tables, ensuring that consumers have access to accurate and comprehensive information about the food they consume. This newfound transparency promotes sustainability, ethical practices, and informed choices, forging a brighter future for the agriculture and food industries.”
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Blockchain Technology for Agriculture: Applications and … – Frontiers

With all transactions recorded on a blockchain, the potential for fraud, such as counterfeit goods or false claims about a product’s organic status, is significantly reduced. Any attempt to manipulate data would require altering the entire chain, which is practically impossible due to the distributed nature of the technology.
The integration of blockchain technology into supply chains marks a significant leap forward in transparency and trustworthiness. This immutable ledger not only records every transaction but also offers unparalleled security against fraudulent activities.
One of the most notable advantages of blockchain is its ability to combat counterfeit goods effectively. As products move through the supply chain, each step is recorded and verified on the blockchain. This means that consumers and retailers can easily trace the origin and journey of a product, ensuring its authenticity. For example, in the luxury goods industry, where counterfeiting has long been a concern, blockchain provides an ironclad solution. Shoppers can be confident that the designer handbag or watch they purchase is indeed a genuine product, thanks to the unalterable blockchain record.
Moreover, blockchain adds an extra layer of security to claims about a product’s characteristics, such as its organic status. Mislabeling or false advertising can be rampant in various industries, including organic and sustainable products. However, with blockchain’s transparent and immutable ledger, consumers can verify the accuracy of these claims. They can access a complete history of the product’s journey, from its source to their hands, ensuring that the product aligns with the advertised standards.
The security of blockchain lies in its distributed nature. Any attempt to tamper with data would require altering every block in the chain, across all nodes in the network. This feat is not only exceptionally difficult but also highly impractical, making blockchain an incredibly robust tool against fraud.
As blockchain technology continues to gain traction in supply chains, it not only safeguards consumers but also encourages businesses to uphold high standards of transparency and authenticity. It is a pivotal step towards ensuring that the products we purchase are exactly what they claim to be, ultimately fostering a more honest and trustworthy marketplace for all.
You can also read more about this here: Blockchain Technology for Agriculture: Applications and … – Frontiers
In cases of foodborne illnesses or product recalls, blockchain can facilitate rapid and accurate traceability. Identifying the source of contamination becomes more efficient, reducing the time it takes to remove tainted products from the market and protecting public health.
The integration of blockchain technology into the food supply chain management system represents a significant leap forward in ensuring food safety, rapid response to contamination threats, and protecting public health. Here’s a more comprehensive exploration of how blockchain enhances traceability in cases of foodborne illnesses or product recalls:
Immutable Record-Keeping: Blockchain’s ledger system provides an immutable and transparent record of every step in the food supply chain, from farm to fork. This level of transparency ensures that data, once entered, cannot be altered or tampered with, guaranteeing the integrity of the information.
Real-Time Monitoring: Blockchain enables real-time monitoring of the supply chain. Data on product origin, handling, and transportation can be updated instantly, allowing stakeholders to track the movement of goods at every stage.
Swift Identification of Contamination Sources: In the event of a foodborne illness outbreak or contamination incident, blockchain allows for rapid identification of the source. By tracing back through the supply chain, authorities can pinpoint the origin of tainted products, helping to prevent further distribution and consumption.
Precision in Recalls: Traditional product recalls can be slow and imprecise, often resulting in mass recalls of products that may not be contaminated. With blockchain, recalls become highly targeted, as the system identifies affected batches with pinpoint accuracy. This reduces economic losses for producers and minimizes consumer anxiety.
Consumer Trust and Confidence: The transparent nature of blockchain instills trust and confidence in consumers. They can access detailed information about the products they purchase, including the source, handling, and safety measures implemented throughout the supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance: Blockchain simplifies regulatory compliance by providing a comprehensive and auditable record of each product’s journey. This helps businesses ensure that they meet all safety and quality standards.
Cost Reduction: Rapid and accurate traceability minimizes the financial impact of recalls. Businesses can limit the scope of recalls to affected products, reducing the financial burden associated with large-scale recalls.
Enhanced Accountability: All stakeholders within the supply chain, from producers to distributors and retailers, become more accountable for their role in food safety. The transparent nature of blockchain discourages irresponsible practices.
Global Impact: Blockchain’s benefits extend to global food trade. It facilitates cross-border traceability, ensuring that food safety standards are met across international supply chains.
Continuous Improvement: The data collected through blockchain can be analyzed to identify trends and areas for improvement in food safety practices. This information can inform policy decisions and drive continuous enhancements in food safety measures.
In summary, blockchain’s role in food traceability is revolutionary in its ability to enhance food safety and protect public health. By offering transparency, real-time monitoring, and immutable record-keeping, it minimizes the risks associated with foodborne illnesses and product recalls. As the global food supply chain becomes increasingly complex, blockchain technology stands as a beacon of progress in ensuring the safety and security of the food we consume.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Revolutionizing Agriculture and Food Supply Chains: The …

Blockchain can streamline supply chain operations by providing real-time visibility into inventory levels, shipment status, and demand forecasts. This can help optimize logistics, reduce waste, and lower costs.
Blockchain technology’s integration into supply chain operations offers a transformative potential that extends far beyond its initial applications in cryptocurrencies. It brings transparency, security, and efficiency to a complex web of interconnected processes, significantly impacting how goods are produced, distributed, and consumed.
Enhanced Transparency: Blockchain’s distributed ledger technology ensures that all stakeholders within the supply chain have access to the same information in real-time. This transparency minimizes the potential for fraud, errors, or discrepancies in the supply chain. Every transaction, from the production floor to the end consumer, is securely recorded, providing an unchangeable audit trail.
Inventory Management: One of the fundamental challenges in supply chain management is balancing supply with demand. Blockchain facilitates real-time monitoring of inventory levels, allowing companies to optimize stock levels more effectively. This prevents overstocking, which ties up capital, and understocking, which can lead to lost sales and disappointed customers.
Efficient Shipment Tracking: With blockchain, shipment tracking becomes a streamlined and tamper-proof process. Every stage of a product’s journey, from manufacturing to delivery, is recorded on the blockchain. This transparency enhances the ability to track and trace goods, leading to faster dispute resolution, reduced theft, and more reliable delivery times.
Demand Forecasting: Blockchain’s access to a wealth of data from various supply chain sources enables more accurate demand forecasting. Machine learning and data analytics can be leveraged to analyze this data and generate precise demand forecasts. This empowers companies to adjust their production schedules and inventory levels with greater precision, reducing waste and costs.
Smart Contracts: Blockchain introduces the concept of smart contracts, self-executing agreements that trigger actions when predefined conditions are met. In supply chain management, smart contracts can automate tasks like quality control inspections, payments, and customs clearances. This not only saves time but also reduces the potential for errors and disputes.
Improved Sustainability: Real-time visibility provided by blockchain enables better sustainability practices. Companies can monitor the environmental impact of their supply chain operations more effectively, making it easier to identify areas for improvement and reduce their carbon footprint.
Cost Reduction: By optimizing logistics, reducing waste, and automating processes, blockchain technology inherently lowers supply chain costs. It streamlines operations and minimizes the need for intermediaries and paperwork, resulting in significant savings for businesses.
In essence, blockchain’s impact on supply chain operations transcends mere optimization; it offers a paradigm shift in how we manage and view the supply chain. It creates a more connected, transparent, and efficient ecosystem that benefits all participants. As this technology continues to mature and gain wider adoption, its potential to revolutionize supply chain management becomes increasingly evident, promising a future where inefficiencies, fraud, and waste are greatly diminished.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: The Effect of Blockchain Technology on Supply Chain Collaboration …

Blockchain can automate agreements and contracts within the agricultural supply chain. Smart contracts execute predefined actions automatically when specific conditions are met, such as releasing payment to farmers upon successful delivery of produce to a processing facility.
Blockchain technology, with its inherent transparency and security, is revolutionizing the way agreements and contracts are managed within the agricultural supply chain. One of its most remarkable applications is the utilization of smart contracts, which streamline processes and reduce the risk of disputes while promoting trust and efficiency.
Smart contracts operate on the “if-then” principle, where predefined actions are executed automatically when specific conditions are met. In the context of agriculture, this means that every step of the supply chain can be seamlessly orchestrated. For instance, when a farmer delivers a batch of produce to a processing facility, a smart contract can verify the delivery through IoT sensors or other means. Once the conditions of successful delivery are confirmed, the smart contract automatically triggers the release of payment to the farmer.
This automation has several significant advantages. Firstly, it eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing administrative costs and the potential for errors or delays in payment processing. Farmers can receive payment promptly upon meeting their obligations, helping them maintain financial stability and invest in future crops or improvements to their operations.
Secondly, the transparency and immutability of blockchain ensure that all parties involved have access to the same data and can trust the accuracy of the information. This reduces the likelihood of disputes and the need for costly litigation. It also provides a transparent record of every transaction, which can be invaluable for traceability and accountability in the event of food safety issues or recalls.
Furthermore, smart contracts can be programmed to include various conditions beyond payment, such as quality standards and delivery timelines. If any of these conditions are not met, the contract can automatically trigger notifications, penalties, or other actions, ensuring that the supply chain operates smoothly and in compliance with agreed-upon terms.
As blockchain technology continues to mature and gain wider acceptance in the agricultural sector, it holds the potential to revolutionize not only contract execution but also traceability, food safety, and supply chain efficiency. By automating agreements and contracts through smart contracts, we can expect to see more streamlined, transparent, and trustworthy agricultural supply chains that benefit everyone from farmers to consumers.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Blockchain technology in supply chain operations: Applications …

Several initiatives have already demonstrated the potential of blockchain technology in agriculture. For instance:
Blockchain technology has proven to be a transformative force in the field of agriculture, offering innovative solutions to longstanding challenges. Let’s explore some pioneering initiatives that showcase the immense potential of blockchain technology in agriculture:
Supply Chain Transparency: Numerous initiatives have harnessed blockchain to enhance supply chain transparency. Through blockchain, consumers can trace the journey of agricultural products from farm to table with unprecedented accuracy. For instance, in the coffee industry, blockchain enables consumers to verify the origin of their coffee beans, supporting fair trade practices and ensuring that farmers receive equitable compensation for their produce.
Crop Traceability: Blockchain has empowered crop traceability efforts, allowing for the precise tracking of individual crops throughout their lifecycle. This is particularly valuable in identifying the source of foodborne illnesses and rapidly initiating targeted recalls when necessary, thereby bolstering food safety.
Smart Contracts for Fair Payments: In the realm of fair payments to farmers, blockchain-based smart contracts are revolutionizing how transactions are conducted. These contracts automatically execute payments to farmers when predefined conditions are met, ensuring that farmers are compensated fairly and promptly.
Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Blockchain is supporting climate-resilient agriculture by providing a secure platform for recording and sharing climate data. This information assists farmers in adapting their practices to changing weather patterns, mitigating the impact of climate change on crop yields.
Land Title Verification: In regions where land disputes are common, blockchain is used to establish and verify land ownership. This not only safeguards farmers’ land rights but also fosters investment in agriculture by providing secure collateral for loans.
Market Access for Smallholders: Small-scale farmers often face barriers when accessing markets due to limited resources and information. Blockchain platforms connect smallholders with larger markets, enabling them to sell their products at fair prices and access a broader customer base.
Reduction of Food Fraud: Blockchain’s immutable ledger system is a powerful tool in reducing food fraud. By recording every transaction and movement of agricultural products, it becomes exceedingly difficult for counterfeit or substandard goods to infiltrate the supply chain.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Blockchain facilitates the collection and sharing of agricultural data, which, when analyzed, can inform data-driven decision-making. Farmers can make informed choices regarding crop selection, planting times, and pest control, ultimately optimizing their yields.
Global Trade Facilitation: Blockchain streamlines international trade by reducing paperwork, verifying product authenticity, and enhancing trust among trading partners. This not only accelerates the movement of agricultural goods but also reduces trade-related disputes.
Decentralized Marketplaces: Blockchain-powered decentralized marketplaces are emerging, where farmers can directly connect with consumers and bypass intermediaries. This empowers farmers to set fair prices for their products and establish direct relationships with their customers.
Crop Insurance: Blockchain-based crop insurance programs are increasing accessibility to coverage for smallholder farmers. The transparency and automation of blockchain facilitate efficient claims processing, reducing delays in payouts during times of crisis.
These initiatives underscore the versatile applications of blockchain technology in agriculture, from improving transparency and traceability to fostering fair trade practices and empowering smallholder farmers. As blockchain continues to evolve, it promises to revolutionize the agricultural landscape, making it more resilient, efficient, and sustainable for the benefit of farmers and consumers alike.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Systems | Free Full-Text | The Effect of Blockchain Technology on …
Walmart has partnered with IBM to implement blockchain in tracking leafy green vegetables. By using blockchain, they reduced the time it took to trace the source of contaminated produce from days to seconds.
The collaboration between Walmart and IBM to introduce blockchain technology into the realm of tracking leafy green vegetables represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of food safety and supply chain management. This innovative partnership is not just about reducing the time it takes to trace the source of contaminated produce; it’s a game-changer with far-reaching implications for food safety, transparency, and efficiency.
Revolutionizing Food Safety: In a world where foodborne illnesses are a significant concern, swift and accurate traceability is paramount. Blockchain’s immutable ledger allows for real-time tracking of each step in the supply chain, from farm to store shelf. This level of transparency enhances food safety by quickly identifying and isolating contaminated products. It helps prevent widespread outbreaks and protects consumers from potential health hazards.
Efficiency and Cost Savings: The traditional process of tracing the source of contaminated produce can be laborious, requiring days, if not weeks, of painstaking record-checking and communication among various stakeholders. With blockchain, this process is streamlined into a matter of seconds. This efficiency not only saves time but also reduces the economic impact of recalls on retailers, suppliers, and consumers.
Supplier Accountability: Blockchain’s transparency doesn’t just benefit consumers; it also holds suppliers and producers accountable for the quality and safety of their products. Knowing that every step of the supply chain is recorded and can be traced back to the source encourages best practices in agriculture and minimizes the risk of negligence.
Consumer Trust: In an era of increasing consumer demand for transparency and ethical sourcing, blockchain instills confidence in the food supply chain. Shoppers can access information about the origin and journey of their food with ease, fostering trust in retailers and food producers who prioritize safety and accountability.
Scaling the Solution: Walmart and IBM’s successful implementation of blockchain technology sets a precedent for the entire industry. As other retailers and food producers adopt similar systems, the collective impact on food safety and supply chain transparency becomes even more profound. It paves the way for a future where blockchain is an industry standard, ensuring the safety and quality of the food we consume.
Global Food Security: Beyond individual retailers, the use of blockchain in food tracking has the potential to contribute significantly to global food security. Rapid identification and containment of foodborne hazards can prevent contaminated products from reaching international markets, safeguarding the health of consumers worldwide.
In conclusion, the Walmart-IBM partnership represents a beacon of progress in the world of food safety and supply chain management. By embracing blockchain technology, they’ve not only reduced traceability time but also elevated the standards of accountability, transparency, and efficiency in the food industry. This innovative collaboration serves as a testament to the transformative power of technology in ensuring that the food on our tables is safe, trustworthy, and of the highest quality.
You can also read more about this here: IBM Supply Chain Intelligence Suite – Food Trust
Te-Food utilizes blockchain to trace the origin and journey of food products, with a particular focus on developing countries. This ensures that consumers have access to trustworthy information about the food they consume.
Te-Food’s innovative use of blockchain technology is nothing short of revolutionary, especially in the context of developing countries where food traceability is often a pressing concern. By leveraging blockchain, Te-Food not only traces the origin and journey of food products but also addresses a multitude of challenges that have long plagued the food supply chain in these regions.
1. Enhanced Food Safety: In many developing countries, food safety standards can be lax or inconsistently enforced. This can lead to foodborne illnesses and compromised consumer health. Te-Food’s blockchain solution provides a robust mechanism for tracking and verifying the safety of food products. It empowers consumers with real-time access to the history of the food they’re about to consume, instilling confidence and peace of mind.
2. Mitigating Food Fraud: Food fraud is a widespread issue globally, but it can be especially rampant in developing nations where regulatory oversight may be limited. Te-Food’s blockchain not only deters fraudulent activities by ensuring transparency but also acts as a powerful deterrent. The knowledge that each step in the supply chain is recorded and immutable discourages bad actors from engaging in deceptive practices.
3. Empowering Smallholders: Many developing countries rely heavily on smallholder farmers and local food producers. Te-Food’s blockchain platform levels the playing field by granting them access to global markets. By establishing a transparent and traceable supply chain, it enables these smallholders to demonstrate the quality and authenticity of their products, which can lead to better market opportunities and improved livelihoods.
4. Reducing Food Waste: Food loss and waste are significant problems worldwide, with substantial losses occurring in the supply chain itself. Te-Food’s blockchain provides real-time visibility into product conditions and expiry dates, enabling more efficient inventory management and reducing the likelihood of food spoilage and waste.
5. Supporting Sustainability: With an increasing emphasis on sustainable and ethical food production, Te-Food’s blockchain helps consumers make informed choices. It highlights products that adhere to environmentally friendly and socially responsible practices, thus encouraging sustainability in food production.
6. Strengthening Supply Chains: In developing countries, supply chains can be fragmented and prone to disruptions. Te-Food’s blockchain adds resilience by providing accurate and up-to-date information, helping to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the supply chain, and ultimately improving its overall robustness.
In summary, Te-Food’s blockchain-driven approach transcends mere traceability; it empowers consumers in developing countries with a powerful tool for ensuring food safety, authenticity, and transparency. By addressing these critical issues, Te-Food contributes to healthier communities, more prosperous smallholder farmers, and a more sustainable and ethical global food system. This innovation is a beacon of hope for transforming food supply chains in regions that need it most.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: “Blockchain technology in food safety and traceability concern to …

AgriDigital uses blockchain to streamline the grain supply chain, providing farmers with secure and efficient digital solutions for managing their grain transactions, from delivery to payment.
AgriDigital’s innovative use of blockchain technology represents a transformative leap forward in the grain supply chain, introducing a new era of efficiency, transparency, and security for farmers and industry stakeholders alike. Their platform is not merely a technological marvel but a game-changer with far-reaching implications:
Seamless Transaction Tracking: AgriDigital’s blockchain solution creates an immutable ledger that meticulously tracks each grain transaction from the moment of delivery to the final payment. This transparency ensures that all parties involved have a real-time view of the transaction’s progress, eliminating the uncertainties and disputes that can often plague traditional supply chains.
Trust and Security: The blockchain’s inherent security features provide a level of trust that is unparalleled in the industry. Farmers can confidently deliver their grain knowing that their transaction data is cryptographically protected, reducing the risk of fraud or data manipulation. This newfound trust extends to all participants in the supply chain.
Payment Efficiency: AgriDigital’s platform streamlines the payment process, significantly reducing the time and administrative burden associated with grain transactions. Farmers receive faster and more secure payments, improving their cash flow and overall financial stability.
Data-Driven Insights: The wealth of data generated by blockchain transactions opens the door to powerful analytical insights. Farmers can leverage this data to make informed decisions about their grain production, optimize their operations, and adapt to changing market conditions, ultimately improving their profitability.
Supply Chain Sustainability: Blockchain technology can enhance supply chain sustainability by providing clear visibility into the provenance of grains. This transparency can help identify inefficiencies, reduce waste, and support sustainability initiatives, aligning with the global push for more environmentally responsible practices.
Global Accessibility: AgriDigital’s digital solutions are not limited by geographical boundaries. They offer farmers, regardless of their location, access to a global marketplace, creating opportunities to expand their customer base and compete on an international scale.
Industry Evolution: AgriDigital’s adoption of blockchain technology serves as an exemplar for the broader agricultural industry. As more stakeholders witness the benefits of secure, transparent, and efficient transactions, there is growing momentum for the integration of blockchain solutions throughout the entire supply chain.
In summary, AgriDigital’s blockchain-powered platform is more than just a technological innovation; it is a catalyst for positive change in the grain supply chain. It empowers farmers with the tools they need to thrive in an increasingly digital and competitive landscape, while also setting a precedent for greater transparency and efficiency in the broader agricultural sector. As this technology continues to evolve, it holds the potential to revolutionize not just grain transactions but the entire agricultural ecosystem, reshaping how we produce, distribute, and consume food globally.
You can also read more about this here: Blockchain Technology Revolutionizes Agriculture and Food …

While blockchain holds immense promise in agriculture, its widespread adoption faces challenges. These include concerns about data privacy, the need for industry-wide standards, and the costs associated with implementing blockchain solutions. However, as the technology matures and regulatory frameworks develop, these barriers are gradually being overcome.
While blockchain holds immense promise in agriculture, its widespread adoption faces challenges that require careful consideration and ongoing efforts to address. These challenges, ranging from data privacy concerns to the need for industry-wide standards and the associated costs of implementing blockchain solutions, present hurdles that the agricultural sector must navigate. However, as the technology matures and regulatory frameworks develop, these barriers are gradually being overcome, ushering in a new era of innovation and transparency.
1. Data Privacy Concerns: One of the foremost challenges in adopting blockchain technology in agriculture is data privacy. As the system records every transaction in a transparent and immutable manner, there are valid concerns about the exposure of sensitive information. Farmers, agribusinesses, and consumers need assurances that their data will be handled securely. Fortunately, advances in encryption and permissioned blockchains allow for data to be stored securely while still benefiting from blockchain’s transparency advantages.
2. Industry-Wide Standards: The lack of standardized protocols and industry-wide standards can hinder the seamless integration of blockchain into the agricultural supply chain. Various stakeholders, including government agencies, industry associations, and technology providers, must collaborate to establish common frameworks. These standards should cover data formats, interoperability between different blockchain platforms, and best practices for implementation, ensuring that blockchain solutions can work cohesively across the industry.
3. Implementation Costs: Implementing blockchain technology can be costly, especially for small-scale farmers and businesses. The initial investment required for hardware, software, and the training of personnel can be a barrier. However, as more use cases are proven and adoption increases, economies of scale may bring down these costs. Additionally, governments and international organizations can play a role in providing support, incentives, or subsidies to facilitate the adoption of blockchain in agriculture.
4. Education and Training: Blockchain technology is still relatively new, and many agricultural stakeholders may not fully understand its potential or how to use it effectively. Comprehensive education and training programs are essential to empower farmers, producers, and supply chain participants with the knowledge and skills needed to implement and benefit from blockchain solutions. Initiatives that offer guidance and resources can help bridge this knowledge gap.
5. Regulatory Frameworks: For blockchain technology to thrive in agriculture, clear and supportive regulatory frameworks must be established. These regulations should address issues such as data ownership, liability, and the legal recognition of blockchain records. Governments and international bodies need to work collaboratively to create a conducive environment for blockchain adoption, providing legal certainty and consumer protection.
6. Scalability and Energy Efficiency: Blockchain networks, particularly public ones like Ethereum, face scalability and energy efficiency challenges. As adoption grows, the need for faster and more energy-efficient blockchain solutions becomes apparent. Research and development efforts are ongoing to address these issues, potentially leading to the emergence of more sustainable and scalable blockchain platforms.
In conclusion, while blockchain technology in agriculture faces hurdles that demand attention and innovation, the potential benefits are too significant to ignore. As the technology continues to mature and stakeholders work together to address these challenges, we can anticipate a future where blockchain plays an integral role in enhancing transparency, traceability, and sustainability throughout the agricultural supply chain. With the right strategies, collaboration, and regulatory support, the agricultural industry can fully realize the transformative potential of blockchain, ushering in a new era of efficiency and trust in food production and distribution.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Blockchain technology in supply chain operations: Applications …
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain technology is poised to revolutionize the agricultural industry by enhancing transparency and traceability. As consumers increasingly demand knowledge about the origins of their food, and as the need for food safety and supply chain efficiency grows, blockchain provides a powerful tool for addressing these challenges. With ongoing innovation and collaboration, blockchain is set to play a pivotal role in creating a more transparent, secure, and sustainable food supply chain for the benefit of all stakeholders.
In conclusion, the adoption of blockchain technology within the agricultural sector promises a profound transformation, one that goes beyond mere enhancement of transparency and traceability. It represents a monumental step toward a smarter, more resilient, and sustainable food system that can meet the evolving needs and expectations of our modern world.
Blockchain’s impact on agriculture extends well beyond consumer curiosity. While consumers indeed seek knowledge about their food’s origins, the benefits of this technology ripple through the entire supply chain. Farmers, for instance, can leverage blockchain to secure fair compensation for their hard work and ensure the integrity of their produce. By providing an immutable ledger of transactions and certifications, blockchain can safeguard against fraudulent activities, mitigating issues such as counterfeit organic labels or misrepresentation of product quality.
Moreover, the food industry’s commitment to safety and sustainability finds a natural ally in blockchain. It enables rapid identification and mitigation of contamination or foodborne outbreaks, protecting public health and reducing the economic burden associated with such incidents. The real-time monitoring capabilities of blockchain technology can also enhance the efficiency of logistics, reducing food waste by optimizing storage and transportation conditions.
Furthermore, blockchain fosters global collaboration among stakeholders, encouraging knowledge sharing and innovation. Farmers, suppliers, distributors, and consumers all have a role to play in shaping a more secure and sustainable food supply chain. Blockchain’s decentralized nature encourages cooperation and transparency, allowing for more agile responses to emerging challenges, from climate change adaptation to emerging agricultural practices.
As we stand at the threshold of this technological revolution, it is clear that blockchain is not merely a tool but a catalyst for the agricultural industry’s evolution. With ongoing innovation, widespread adoption, and continued collaboration, blockchain is set to empower all stakeholders in the food supply chain, facilitating a future where transparency, security, and sustainability are not just goals but the very fabric of our global food system.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Blockchain in Agriculture: How It Can Help the Industry
More links
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: IBM Supply Chain Intelligence Suite – Food Trust