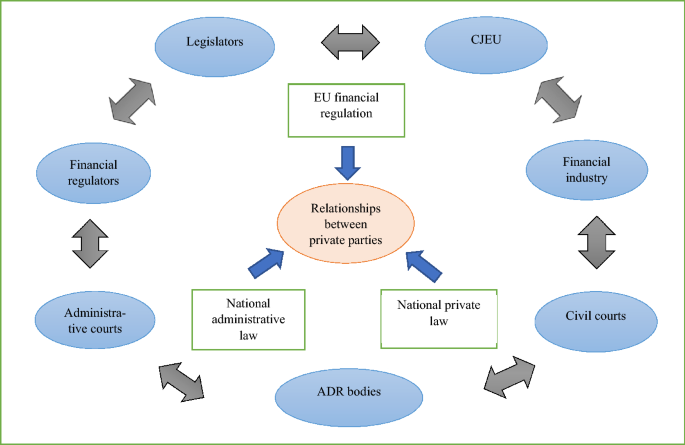
Introduction
European banking and financial regulations are the bedrock of a stable and secure financial landscape within the European Union (EU). These regulations serve as a framework for supervising and ensuring the integrity of the financial sector, protecting consumers, and maintaining economic stability. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of European banking and financial regulations, their evolution, and their pivotal role in maintaining a resilient financial ecosystem.
European banking and financial regulations have evolved significantly over the years to adapt to the changing dynamics of the financial industry and the broader economic landscape. These regulations encompass a wide range of areas, including prudential rules, consumer protection, anti-money laundering measures, and market integrity.
One of the fundamental objectives of European financial regulations is to safeguard the stability of the financial system. The 2008 financial crisis served as a wake-up call, prompting the EU to strengthen its regulatory framework to prevent similar crises in the future. The establishment of the European Banking Authority (EBA), the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA), and the European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA) marked a significant step towards harmonizing regulations across member states and enhancing supervisory mechanisms.
Moreover, European regulations prioritize consumer protection. Measures such as the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID) and the Payment Services Directive (PSD2) aim to ensure that financial products and services are transparent, accessible, and safe for consumers. These regulations empower consumers with greater control over their financial transactions and investments while fostering trust in the financial sector.
In the realm of anti-money laundering (AML) and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT), European regulations are robust. The EU’s AML/CFT framework obliges financial institutions to implement stringent due diligence measures, report suspicious activities, and cooperate with law enforcement agencies. This not only protects the financial system from illicit activities but also contributes to the global fight against financial crime.
Market integrity is another critical focus area of European financial regulations. Regulations like the Market Abuse Regulation (MAR) and the Benchmark Regulation aim to maintain fair and transparent financial markets by preventing market abuse, insider trading, and manipulation. These regulations help bolster investor confidence and ensure that financial markets operate efficiently.
As the financial industry continues to evolve with the advent of fintech innovations and digitalization, European regulations are adapting to these changes. Initiatives like the European Digital Finance Strategy and the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) are designed to harness the benefits of technological advancements while mitigating potential risks.
In summary, European banking and financial regulations play an indispensable role in safeguarding the financial stability, consumer protection, and market integrity within the EU. They are a dynamic and evolving framework that reflects the region’s commitment to maintaining a resilient and competitive financial ecosystem while adhering to the highest standards of ethics and responsibility.
The Evolution of European Banking and Financial Regulations
The history of European banking and financial regulations can be traced back to the formation of the European Economic Community (EEC) in the 1950s. However, the regulatory landscape truly began to take shape with the establishment of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) and the introduction of the euro as a common currency in 1999.
One of the landmark developments in European financial regulation was the creation of the European Central Bank (ECB) in 1998. The ECB, headquartered in Frankfurt, Germany, was entrusted with the responsibility of formulating and implementing monetary policy for the Eurozone. Its primary objective is to maintain price stability within the Eurozone by controlling inflation.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: report – final -1 – clean-fn-img
Key Regulatory Bodies
The regulatory framework in Europe is a collaborative effort involving various institutions, with the primary objective of safeguarding financial stability and fostering economic growth. Some of the key regulatory bodies include:
European Central Bank (ECB): As mentioned earlier, the ECB plays a central role in monetary policy formulation for the Eurozone. It supervises significant banks within the Eurozone and ensures they comply with prudential regulations.
European Banking Authority (EBA): The EBA is responsible for ensuring the effective and consistent application of prudential banking standards across the EU. It harmonizes regulations and conducts stress tests to evaluate the resilience of EU banks.
European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA): ESMA supervises securities markets, ensuring transparency and investor protection. It also plays a vital role in regulating credit rating agencies and trade repositories.
European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA): EIOPA focuses on the insurance and pension sectors, working to ensure their stability and consumer protection.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: European System of Financial Supervision (ESFS) | Fact Sheets on …

Regulatory Objectives
European banking and financial regulations have several key objectives:
Financial Stability: The primary goal is to maintain the stability of the financial system, preventing crises and ensuring the banking sector’s resilience.
Consumer Protection: Regulations aim to protect consumers from unfair practices, ensuring they have access to transparent and safe financial products and services.
Market Integrity: Maintaining fair and transparent financial markets is crucial for trust and confidence in the system.
Competition: Regulations promote healthy competition among financial institutions, fostering innovation and efficiency.
European banking and financial regulations are designed to achieve multiple vital objectives, safeguarding the integrity and sustainability of the financial sector:
Financial Stability: Ensuring the stability of the financial system is paramount. Regulations establish robust risk management practices, capital adequacy standards, and stress tests to prevent financial crises. The goal is to safeguard the broader economy from systemic shocks and maintain public trust in the financial sector.
Consumer Protection: Regulations prioritize the interests of consumers. They mandate transparency in financial products, ensuring that consumers can make informed decisions. Rules against predatory lending, fraudulent practices, and transparent disclosure requirements help protect individuals from financial harm.
Market Integrity: Upholding the integrity of financial markets is essential. Regulations prohibit market manipulation, insider trading, and other fraudulent activities that can erode trust in the system. Transparent reporting, surveillance, and enforcement mechanisms help maintain fair and orderly markets.
Competition: Encouraging healthy competition is another core objective. Regulations prevent anti-competitive behavior, such as monopolistic practices or market collusion. Promoting competition fosters innovation and efficiency, benefitting consumers and the broader economy.
Financial Inclusion: In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on financial inclusion. Regulations are evolving to ensure that underserved populations have access to banking and financial services, reducing disparities and promoting economic equity.
Cybersecurity: As digitalization accelerates, regulations increasingly address cybersecurity risks. They mandate robust data protection measures and require financial institutions to invest in cybersecurity to safeguard customer data and maintain trust in the digital age.
Sustainability: There is a growing recognition of the need to integrate sustainability considerations into financial regulations. European regulations are evolving to incorporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, aligning financial activities with sustainable development goals.
International Cooperation: Given the global nature of finance, European regulations often align with international standards. Cooperation with global bodies and coordination among European nations is essential to address cross-border financial challenges.
Innovation: Regulations also encourage innovation by providing a framework for fintech and digital financial services. They promote responsible innovation while safeguarding against emerging risks.
Adaptability: Regulations need to adapt to evolving market dynamics and technological advancements. Regulators continuously review and update rules to address emerging risks and challenges in the financial sector.
In summary, European banking and financial regulations are a multifaceted framework designed to protect the financial system’s stability, ensure consumer protection, foster market integrity, and promote competition. They are evolving to address contemporary challenges, including digitalization, sustainability, and global interconnectedness, while maintaining the core principles of a resilient, transparent, and equitable financial ecosystem.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Recent Trends in UK Financial Sector Regulation and Possible …
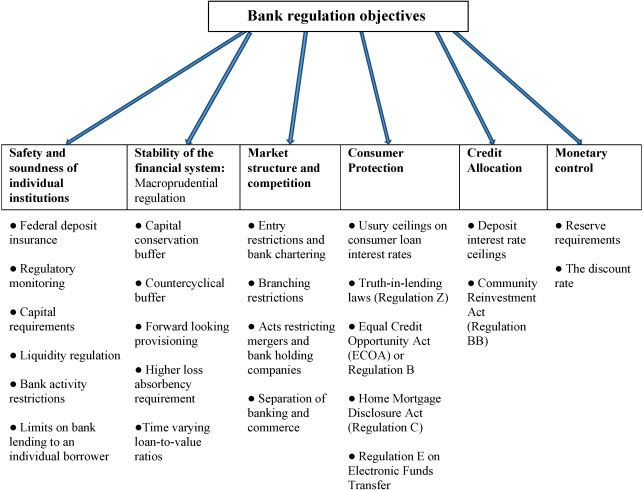
Challenges and Future Considerations
Despite the robust regulatory framework in Europe, challenges persist. Rapid technological advancements, such as fintech innovations and digital currencies like cryptocurrencies, have prompted regulators to adapt and develop new frameworks. Cybersecurity threats, Brexit-related changes, and the impact of global economic shifts also require continuous monitoring and adjustment of regulations.
Moreover, the transition toward sustainable finance is a key consideration. The EU has introduced the European Green Deal and the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) to align financial activities with environmental and social objectives.
While European banking and financial regulations have undoubtedly made significant strides in maintaining stability and protecting consumers, several ongoing challenges and emerging trends warrant close attention.
1. Technological Advancements and Fintech Disruption: The rapid evolution of fintech innovations, including peer-to-peer lending, robo-advisors, and blockchain technology, has transformed the financial landscape. These advancements challenge traditional business models and demand regulatory adaptation to ensure innovation while preserving financial stability and security. Regulatory sandboxes and tailored frameworks for fintech firms are examples of regulatory responses to foster innovation without compromising safety.
2. Digital Currencies and Cryptocurrencies: The rise of digital currencies, including cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, presents a regulatory conundrum. While digital currencies offer potential benefits like faster and cheaper transactions, they also pose risks related to money laundering, fraud, and market volatility. European regulators are exploring ways to regulate and harness the potential of digital currencies while mitigating associated risks.
3. Cybersecurity Threats: With the increasing reliance on digital infrastructure, financial institutions face growing cybersecurity threats. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and other cybercrimes can compromise sensitive financial information. Regulatory bodies need to continuously update cybersecurity standards and encourage information sharing among financial institutions to protect against evolving threats.
4. Brexit-Related Changes: The United Kingdom’s exit from the EU has necessitated adjustments in financial regulations. The EU and the UK have had to redefine their financial relationship, including issues related to market access, equivalence decisions, and passporting rights. These ongoing negotiations require regulators on both sides to ensure financial stability amid changing dynamics.
5. Global Economic Shifts: Europe’s financial markets are not isolated from global economic developments. Trade tensions, geopolitical events, and shifts in international financial regulations can have ripple effects on the European financial system. European regulators must remain vigilant and adaptive to external economic forces.
6. Sustainable Finance Transition: The transition toward sustainable finance is a prominent agenda item for European regulators. The EU’s commitment to sustainability is evident in initiatives like the European Green Deal and the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR). These efforts aim to align financial activities with environmental and social objectives, encouraging investments in green projects and responsible business practices.
In conclusion, European banking and financial regulations are not static; they are continually evolving to address both longstanding challenges and emerging trends. The adaptability of regulatory bodies and their commitment to fostering innovation while preserving financial stability and consumer protection will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the European financial landscape. Meeting these challenges head-on will ensure that Europe remains a global leader in responsible and resilient financial governance.
Conclusion
European banking and financial regulations have come a long way, evolving to address the changing dynamics of the financial sector. They play a pivotal role in ensuring economic stability, consumer protection, and market integrity. As Europe faces new challenges and opportunities, these regulations will continue to adapt, underpinning the resilience and growth of the European financial ecosystem.
The evolution of European banking and financial regulations is a testament to their crucial role in shaping the financial landscape of the continent. Over the years, these regulations have demonstrated their ability to adapt and respond to the ever-changing dynamics of the financial sector. Here are some key facets of this evolution:
1. Safeguarding Economic Stability:
- European regulations have been instrumental in safeguarding economic stability, especially in the wake of the 2008 financial crisis. Stringent capital requirements, stress tests, and risk management practices have become pillars of financial stability.
2. Protecting Consumers:
- Consumer protection is a cornerstone of European financial regulations. Measures such as transparent fee structures, dispute resolution mechanisms, and robust anti-money laundering safeguards are in place to ensure the well-being of consumers.
3. Ensuring Market Integrity:
- Regulations like the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID II) aim to enhance market transparency and integrity. They require greater transparency in trading activities, leading to fairer and more efficient markets.
4. Fostering Innovation:
- While regulations are designed to mitigate risks, they also acknowledge the importance of innovation. Initiatives like the European Union’s fintech action plan promote innovation in financial services while maintaining regulatory oversight.
5. Embracing Digitalization:
- The rise of digital banking and fintech has prompted regulatory responses. Europe is moving toward harmonized rules for digital payments and open banking, allowing for innovation while safeguarding data privacy and security.
6. Navigating Brexit:
- The UK’s departure from the EU introduced complexities in the regulatory landscape. Negotiations led to agreements on financial services, but divergence in regulations remains a challenge to be managed.
7. Green Finance and Sustainability:
- Europe is at the forefront of integrating sustainability into financial regulations. The EU Taxonomy Regulation and the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation are examples of efforts to align finance with environmental objectives.
8. Global Collaboration:
- Europe actively collaborates with international counterparts to ensure regulatory consistency and address global financial challenges. Cooperation with organizations like the Financial Stability Board (FSB) is key to global financial stability.
As we look to the future, European banking and financial regulations will continue to evolve. They must strike a delicate balance between stability, innovation, and consumer protection. These regulations are not just rulebooks; they are the foundation upon which the European financial ecosystem is built. Their adaptability and resilience will be instrumental in shaping the future of finance in Europe, ensuring it remains robust, secure, and responsive to the needs of its citizens and businesses.
More links
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Global Financial Stability Report April 2015: Navigating Monetary …