Introduction
In an increasingly interconnected world, the journey of food from farm to plate often spans continents and crosses borders. While this global supply chain has brought a diverse array of culinary delights to our tables, it has also highlighted the critical importance of food safety and quality assurance. In this exploration, we delve into the complex web of food safety measures and quality assurance practices that safeguard the global food supply and protect consumers from potential risks.
In today’s globally interconnected world, the remarkable journey that food undertakes from farm to plate is often a transcontinental odyssey that transcends borders and boundaries. This intricate global supply chain has bestowed upon us an astonishing array of culinary treasures, enriching our tables with flavors and ingredients from far-flung corners of the Earth. However, this global culinary tapestry has also cast a spotlight on an issue of paramount importance: the assurance of food safety and quality.
The complex web of food safety measures and quality assurance practices is the vigilant guardian of our global food supply. It comprises an extensive network of checks and balances designed to uphold the highest standards of food safety, ensuring that the products we consume are free from contaminants and adhere to strict quality benchmarks.
At the heart of this safeguarding process lies rigorous testing and inspection protocols. These protocols encompass every facet of the food supply chain, from the cultivation of crops and the rearing of livestock to the processing, packaging, and transportation of food products. Laboratories equipped with cutting-edge technology play a pivotal role in this journey, meticulously examining food samples to detect the presence of pathogens, allergens, or any other potential hazards.
Furthermore, stringent regulations and guidelines are enacted and enforced by governmental bodies and international organizations to maintain the integrity of the global food supply. These regulations set forth standards for hygiene, labeling, and packaging, ensuring that consumers have access to clear and accurate information about the products they purchase. Food producers and distributors must adhere to these regulations, with inspections and audits serving as key tools for compliance.
In addition to governmental oversight, various industry stakeholders and associations also contribute to the assurance of food safety and quality. They develop best practices, share knowledge, and engage in collaborative efforts to address emerging challenges and innovate solutions. This collective commitment to excellence in food safety extends to the development of technologies such as blockchain, which can provide transparent and traceable supply chain data to further enhance consumer confidence.
Ultimately, the complexities of the global food supply chain are met with a resounding commitment to protect consumers from potential risks. Food safety and quality assurance are not just principles but a global imperative. They reassure us that, regardless of where our food originates, it has undergone a rigorous journey of scrutiny and care to ensure it nourishes and delights, safeguarding both our health and culinary experiences.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: The Importance of Public-Private Partnerships to Advance Food Safety
The globalization of the food industry has led to a remarkable diversity of food products on store shelves. However, it has also introduced challenges related to traceability, as products may traverse multiple countries before reaching consumers. Ensuring the safety and quality of these products requires rigorous oversight and coordination.
The globalization of the food industry has led to a remarkable diversity of food products on store shelves. However, it has also introduced challenges related to traceability, as products may traverse multiple countries before reaching consumers. Ensuring the safety and quality of these products requires rigorous oversight and coordination.
The availability of diverse food products from around the world has expanded culinary horizons and enriched the diets of people everywhere. Exotic spices, unique ingredients, and international cuisines have become easily accessible to consumers, contributing to cultural exchange and culinary innovation.
Nevertheless, the global food supply chain can be complex and extensive, with products often passing through numerous intermediaries, ports, and distribution centers across borders. This complexity can pose challenges for tracking and monitoring the journey of food items from their source to the consumer’s plate.
To address these challenges, modern technology plays a crucial role. Advances in traceability systems, such as blockchain and RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification), enable real-time tracking of food products throughout the supply chain. Each step of a product’s journey, from farm to fork, can be recorded, providing transparency and accountability.
These traceability systems not only enhance food safety but also facilitate rapid responses to food recalls or outbreaks of foodborne illnesses. In the event of a safety concern, authorities can quickly identify affected products and their sources, preventing further distribution and consumption.
Moreover, traceability systems support sustainability efforts by allowing consumers to make more informed choices about the origins of their food. Concerns about ethical sourcing, environmental impact, and fair labor practices have become increasingly important to consumers. Traceability empowers consumers to support products that align with their values and beliefs.
Ensuring the safety and quality of globally sourced food products requires international cooperation and standards. Regulatory bodies, food safety agencies, and industry associations work together to establish guidelines and regulations that govern the global food trade. These standards cover everything from hygiene and labeling to packaging and transportation.
Additionally, certification programs, such as Fair Trade and organic certifications, provide consumers with assurance that products meet specific criteria related to ethical and environmental practices. These certifications help build trust between consumers and producers, fostering a sense of responsibility within the global food industry.
The globalization of the food industry has undoubtedly expanded choices for consumers and driven culinary innovation. However, it has also necessitated a commitment to rigorous oversight and coordination to ensure that the food we enjoy from around the world is safe, high-quality, and sourced responsibly. As technology continues to evolve and international cooperation strengthens, the global food supply chain can become even more transparent, resilient, and responsive to the evolving preferences and concerns of consumers.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Increasing transparency in the medicines supply chain | USP

Food safety is underpinned by a network of regulatory frameworks that vary from country to country. These regulations set standards for hygiene, labeling, and quality control. Adherence to these standards is essential to prevent foodborne illnesses and protect consumers’ health.
The foundation of food safety rests upon a complex network of regulatory frameworks that exhibit variability from one country to another. These regulations serve as the bedrock for ensuring that the food we consume is safe, wholesome, and of the expected quality. Their scope encompasses a range of critical aspects, including hygiene practices, accurate labeling, and stringent quality control measures. Adherence to these regulatory standards is not merely a matter of compliance; it is an absolute imperative in the ongoing battle to prevent foodborne illnesses and protect the health and well-being of consumers.
Hygiene standards stand at the forefront of these regulatory frameworks. They dictate the practices and protocols that food producers, processors, and handlers must adhere to at every stage of the food supply chain. This encompasses everything from the sanitary conditions of food production facilities to the hygiene practices of food handlers. Strict adherence to these standards is essential for mitigating the risk of contamination, which could otherwise lead to outbreaks of foodborne illnesses.
Accurate labeling is another crucial facet of food safety regulations. Clear and informative labeling not only empowers consumers to make informed choices but also ensures traceability in the event of a product recall or safety issue. It is through labeling that consumers can ascertain crucial information, including ingredient lists, allergen warnings, and nutritional facts. These labels not only safeguard those with specific dietary needs but also facilitate transparency and trust between producers and consumers.
Quality control measures represent yet another pivotal component of food safety regulations. These measures encompass a range of tests, inspections, and standards that food products must meet to ensure their safety and quality. This includes checks for microbial contamination, chemical residues, and physical defects. Stringent quality control processes serve as a bulwark against substandard or adulterated products from entering the market.
The significance of adhering to these regulatory standards cannot be overstated. Foodborne illnesses have the potential to inflict widespread harm, causing illness, economic losses, and damage to a brand’s reputation. Beyond the immediate health risks, outbreaks of foodborne diseases can strain healthcare systems and erode public trust in the safety of the food supply.
In conclusion, food safety regulations, though subject to variability from one region to another, share a common goal: safeguarding the health and well-being of consumers. These regulations encompass hygiene standards, labeling requirements, and quality control measures that serve as the cornerstones of a robust and resilient food safety framework. Adherence to these standards is not merely a regulatory obligation but a moral and ethical duty to protect the health and safety of those who rely on the food supply chain.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: who-global-strategy-food-safety-2022-2030.pdf

HACCP is a systematic approach to food safety that identifies and mitigates potential hazards at every stage of the food production process. It has become a global standard for ensuring the safety of food products and is employed by manufacturers, processors, and distributors worldwide.
HACCP, which stands for Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points, represents a systematic and proactive approach to food safety that has revolutionized the way we safeguard the quality and wholesomeness of our food supply. This comprehensive methodology is designed to identify, evaluate, and mitigate potential hazards at every critical stage of the food production process, from farm to fork. HACCP has not only become a global standard but also an indispensable tool employed by manufacturers, processors, and distributors worldwide to ensure the safety of food products.
The fundamental principle of HACCP is its emphasis on prevention rather than reaction. Rather than relying solely on end-product testing and inspections, HACCP identifies potential hazards at various points in the food production chain and implements control measures to prevent their occurrence. These critical control points (CCPs) are carefully selected based on scientific analysis and risk assessment. They represent the stages where hazards can be effectively controlled, ensuring that the final food product is safe for consumption.
The HACCP system is founded on seven core principles, each of which plays a crucial role in ensuring food safety:
Conducting a hazard analysis: This initial step involves identifying potential biological, chemical, or physical hazards that could affect the safety of the food product.
Identifying critical control points: Once hazards are identified, critical control points are determined. These are specific points in the production process where control measures can be applied to prevent, eliminate, or reduce the identified hazards to an acceptable level.
Establishing critical limits: For each critical control point, critical limits are defined. These are measurable criteria that must be met to ensure that the hazard is under control. For example, a critical limit for cooking poultry might be a minimum internal temperature of 165°F (74°C).
Monitoring and controlling critical control points: Regular monitoring and verification activities are implemented to ensure that critical control points are operating within established limits. This involves ongoing measurement and observation to maintain control over hazards.
Establishing corrective actions: In the event that a critical control point deviates from its critical limits and a hazard arises, corrective actions are established to address the issue promptly and prevent unsafe food from reaching consumers.
Implementing verification procedures: Verification activities are conducted to confirm that the HACCP system is operating effectively. This includes periodic reviews, inspections, and audits to assess the system’s performance.
Maintaining records and documentation: Detailed records are kept to document the HACCP plan, hazard analysis, critical control points, monitoring results, corrective actions, and verification activities. These records provide a comprehensive history of the food safety efforts undertaken.
The success of HACCP lies in its adaptability and versatility, making it applicable to a wide range of food production processes, from farming and processing to distribution and preparation. It is a living system that evolves with changes in technology, production methods, and scientific understanding of food safety risks.
As global food supply chains continue to expand and consumer expectations for food safety remain high, HACCP remains a cornerstone of our efforts to protect public health and ensure that the food we consume is safe, wholesome, and free from hazards. Its widespread adoption reflects its proven effectiveness in preventing foodborne illnesses and contributing to the overall well-being of communities around the world.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Implementation of Food Safety Management Systems along with …

Transparency is a cornerstone of food safety and quality assurance. It involves the traceability of food products from their origin to the final consumer. Technologies like blockchain are increasingly used to provide real-time visibility into the movement of food products, enabling rapid response in case of contamination or recalls.
Transparency serves as an unshakable cornerstone in the realm of food safety and quality assurance. It is the bedrock upon which consumer trust is built and the foundation for ensuring that the food we consume meets the highest standards of safety and integrity. In an era where consumers demand accountability and information at their fingertips, transparency transcends mere buzzwords; it is a fundamental requirement.
At its core, transparency in the food industry entails the ability to trace the journey of food products from their inception, be it the farm, the factory, or the fishing boat, all the way to the hands of the final consumer. This means understanding not only the origin of ingredients but also the conditions under which they were grown, processed, and transported. It’s about unveiling the story behind each bite we take.
In this quest for transparency, technology has emerged as an invaluable ally, with blockchain technology at the forefront of this transformative wave. Blockchain, with its decentralized and immutable ledger, is increasingly harnessed to provide real-time visibility into the movement of food products within the supply chain. Each step in the journey of a food product is recorded on the blockchain, creating an unbroken and tamper-proof chain of information. This means that at any point in the supply chain, from farm to fork, stakeholders can access a wealth of data about a product’s journey, including its origin, processing, storage conditions, and transportation history.
The real-time nature of blockchain technology offers a remarkable advantage in the realm of food safety. In the unfortunate event of contamination, outbreaks, or recalls, this system enables swift and precise action. When a potential issue arises, authorities and companies can pinpoint the affected batches of products within moments, sparing consumers from potential harm and preventing the spread of contaminated goods.
Moreover, blockchain technology enhances accountability and trust among all participants in the supply chain, from farmers and manufacturers to distributors and retailers. It incentivizes responsible practices and encourages rigorous quality control at every stage of production. By fostering transparency, it helps reduce the likelihood of food fraud and counterfeit products entering the market.
In conclusion, transparency is not a luxury but a necessity in the modern food industry. It empowers consumers to make informed choices about the food they eat and instills confidence that the products they purchase are safe, authentic, and of the highest quality. As technology continues to advance, the integration of blockchain and similar tools will further elevate transparency, transforming the way we perceive, produce, and consume food while ushering in an era of enhanced safety, accountability, and trust in the food supply chain.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here What Supply Chain Transparency Really Means
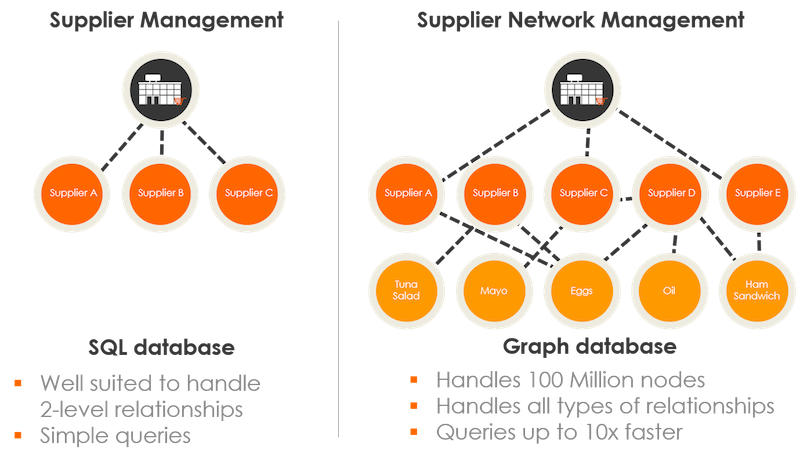
To maintain consumer trust, many companies subject themselves to third-party audits and certification programs. These programs verify that food safety and quality assurance measures are being followed, providing an extra layer of assurance for consumers.
In the complex world of food production and distribution, maintaining consumer trust is paramount. Consumers rightfully expect that the food they purchase is safe, high in quality, and free from contaminants. To meet these expectations and provide an extra layer of assurance, many companies voluntarily subject themselves to rigorous third-party audits and certification programs.
These audits and certification programs serve as a vital bridge of transparency and accountability between producers and consumers. They are conducted by independent entities with expertise in food safety and quality assurance, ensuring an objective and impartial evaluation of a company’s practices. The overarching goal is to verify that the highest standards of safety and quality are upheld throughout the food production and supply chain.
Food safety is a top priority, and third-party audits play a pivotal role in upholding these standards. They scrutinize various aspects of the food production process, from sourcing ingredients to handling and processing, to distribution and storage. The assessments include meticulous checks for compliance with regulatory requirements, industry best practices, and specific safety protocols.
Quality assurance is equally critical in maintaining consumer trust. Third-party audits evaluate factors such as product consistency, flavor, texture, appearance, and nutritional content. These assessments ensure that the food not only meets safety standards but also adheres to the promised quality levels, meeting or exceeding consumer expectations.
The value of third-party audits extends beyond the assurance of safety and quality. It also encompasses environmental and ethical considerations. Some certification programs evaluate a company’s sustainability practices, verifying that it adheres to environmentally responsible methods and ethical sourcing of ingredients. This broader perspective aligns with the growing consumer interest in supporting companies that demonstrate a commitment to the planet and ethical practices.
For consumers, the presence of third-party certifications on food labels is a clear and trusted signal of a company’s dedication to delivering safe, high-quality, and responsibly produced products. It simplifies the decision-making process, allowing consumers to make choices that align with their values and preferences. It also provides peace of mind, knowing that an impartial and expert entity has independently verified the company’s claims.
In a world where information flows freely, and consumers are increasingly informed and discerning, the role of third-party audits and certification programs is more significant than ever. They offer an additional layer of trust and transparency, strengthening the bond between producers and consumers. As companies voluntarily subject themselves to these rigorous evaluations, they demonstrate a commitment to consumer safety, quality, and responsibility, fostering a mutually beneficial relationship built on trust and shared values.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: BlueNalu Announces Framework for Food Safety and Quality …

As supply chains grow more complex, so do the challenges. Food fraud, where products are misrepresented for financial gain, is a growing concern. Additionally, contamination risks, whether from pathogens or chemical substances, require continuous vigilance.
Navigating Complex Supply Chain Challenges: The Battle Against Food Fraud and Contamination
In an era of increasingly intricate global supply chains, the food industry faces a twofold challenge—combatting the rising tide of food fraud while maintaining rigorous vigilance against contamination risks.
1. Food Fraud: Unmasking Deceptive Practices
Food fraud, a clandestine deception perpetrated for financial gain, has emerged as a significant concern in our complex supply chain ecosystem. The deceptive practices involved can take various forms:
Counterfeiting: Fraudsters replicate high-demand products, often with subpar ingredients, passing them off as genuine.
Adulteration: Authentic foods are diluted or replaced with cheaper substitutes, compromising their quality and authenticity.
Mislabeling: Products are misrepresented in terms of origin, ingredients, or production methods, leading consumers to make decisions based on false information.
Food fraud not only undermines consumer trust but also poses health risks when counterfeit or adulterated products enter the market. To combat this, companies are increasingly turning to technologies like blockchain and DNA testing for traceability and verification.
2. Contamination Risks: The Constant Threat
Pathogens and chemical contaminants pose an ever-present risk in the food industry. Pathogens like Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria can cause widespread outbreaks of foodborne illnesses. Chemical contaminants, whether from pesticides, additives, or environmental pollutants, can compromise the safety and quality of food products.
Continuous vigilance and preventive measures are imperative:
Stringent Testing: Rigorous testing protocols are essential to identify and mitigate contamination risks. Regular inspections and audits of production facilities help maintain safety standards.
Safe Handling Practices: From farm to table, food must be handled with care to prevent contamination. This includes proper storage, hygiene, and temperature control.
Traceability: The ability to trace the origin of food products is vital for swift response in the event of contamination. Rapid recalls can prevent widespread harm.
Conclusion: Safeguarding the Integrity of the Global Food Supply Chain
In a world where supply chains are increasingly intricate, the challenges of food fraud and contamination are formidable foes. The battle to maintain the integrity of the global food supply chain requires collective efforts from producers, regulators, and consumers. It’s a commitment to transparency, rigorous testing, and responsible practices that ensures the food on our plates not only delights our taste buds but also nurtures our health and well-being.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Emerging Risks Related to Food Technology – PMC
Empowering consumers with knowledge about food safety is crucial. Labels that provide information about sourcing, production methods, and potential allergens enable consumers to make informed choices and demand transparency from manufacturers.
Empowering consumers with knowledge about food safety is not only crucial but also a fundamental right. In an era where food products come from diverse sources and undergo various production methods, providing consumers with comprehensive information is essential for their well-being. Labels, which serve as windows into the origins and composition of food items, play a pivotal role in this endeavor. They provide valuable insights into sourcing, production methods, and potential allergens, allowing consumers to make informed choices and, importantly, demand transparency from manufacturers.
One of the key aspects of food safety is knowing the source of the products we consume. Labels that specify the origin of ingredients or products help consumers trace the journey of their food from farm to table. For instance, a label indicating the country or region of origin can provide important information about food safety standards, quality controls, and potential risks associated with that source. Armed with this knowledge, consumers can make informed decisions about the products they purchase, opting for sources known for their stringent safety measures.
Production methods also significantly impact food safety. Labels that detail how a product was manufactured, processed, or handled provide consumers with insights into the potential risks associated with those methods. For example, labels may indicate whether a product has been pasteurized, irradiated, or produced using organic practices. This information is crucial for individuals with specific dietary preferences, ethical concerns, or health considerations. It empowers them to select products that align with their values and safety requirements.
Allergen information is another critical aspect of food safety. Many individuals have food allergies or intolerances, and the presence of allergenic ingredients in a product can have severe health consequences. Labels that clearly list potential allergens, such as peanuts, tree nuts, dairy, soy, wheat, or shellfish, serve as vital warning signs for those with allergies. This transparency enables consumers to avoid products that could trigger allergic reactions and make choices that protect their health.
Moreover, labels have the power to drive transparency in the food industry. When consumers demand clear and comprehensive labeling, manufacturers are incentivized to provide accurate and informative labels on their products. This, in turn, promotes accountability throughout the supply chain, encouraging producers, distributors, and retailers to uphold rigorous safety standards.
In essence, empowering consumers with knowledge through food labeling is a cornerstone of food safety and informed decision-making. Labels that offer insights into sourcing, production methods, and potential allergens not only guide consumer choices but also foster a culture of transparency and accountability within the food industry. As consumers increasingly prioritize health, ethics, and sustainability in their food choices, labeling remains a vital tool for bridging the gap between manufacturers and consumers, ultimately enhancing the safety and quality of the foods we consume.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: High-quality health systems in the Sustainable Development Goals …

Food safety and quality assurance in global supply chains are a shared responsibility among producers, regulators, and consumers. As our food supply chain becomes more intricate, the need for robust safety measures and quality control practices becomes even more apparent. It is a testament to our collective commitment to ensuring that the food on our plates is not only delicious but also safe and nourishing.
The realm of food safety and quality assurance in our complex, globalized supply chains is a collective endeavor, resting squarely on the shoulders of producers, regulators, and consumers alike. In an age where our food’s journey spans continents and cultures, the importance of steadfast safety measures and unwavering quality control practices has never been more conspicuous. It underscores a shared commitment to guaranteeing that the food adorning our plates not only tantalizes our taste buds but also serves as a testament to safety, nourishment, and culinary delight.
Producers play a pivotal role in this collaborative effort. From farmers tending to their crops to livestock keepers ensuring the well-being of animals, producers are the vanguards of food safety from the outset. They must adhere to meticulous hygiene standards, responsible farming practices, and ethical treatment of animals to cultivate the raw materials of our meals responsibly and sustainably.
Regulators, with their comprehensive frameworks and rigorous oversight, constitute another vital pillar of food safety. Governments and international bodies set and enforce standards, conduct inspections, and ensure compliance with regulations throughout the supply chain. Their dedication to monitoring and maintaining the highest levels of food safety instills trust in consumers, assuring them that the products they consume meet stringent safety criteria.
However, the role of consumers cannot be overstated. In this interconnected world, consumers possess the power to shape the direction of the food industry. Their choices—whether selecting organic produce, supporting sustainable practices, or demanding transparency in labeling—can influence the entire supply chain. Consumer awareness and education are critical components, empowering individuals to make informed decisions that align with their values and priorities.
As the global food supply chain continues to evolve and expand, so too must our commitment to robust safety measures and quality control practices. It is a recognition that food safety is not a static endeavor but an ongoing journey, an unbroken chain of responsibility that extends from the field to the kitchen table.
In essence, food safety and quality assurance are the fruits of a shared commitment—a pledge that transcends borders and cultures. They are a testament to our collective determination to savor the flavors of the world while upholding the highest standards of safety and nourishment. In this shared journey, we affirm our dedication to a future where every meal is a delectable celebration of culinary diversity, one that is safe, nourishing, and shared by all.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Responsibility & Sustainability
More links
You can also read more about this here: Increasing transparency in the medicines supply chain | USP
