Introduction
Food safety is a paramount concern for consumers worldwide. Ensuring that the food we consume is free from contamination and safe for consumption is a responsibility shared by governments, food producers, and regulatory bodies. One of the essential tools in this endeavor is the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) system. In this article, we will delve into the significance of food safety standards, with a particular focus on the HACCP system.
Food safety isn’t a matter of chance; it’s a meticulous process. It’s the product of rigorous standards, stringent inspections, and unwavering commitment to protecting the well-being of consumers. At the heart of this effort lies the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) system. This internationally recognized framework is the linchpin in ensuring that every step of the food production process is carefully monitored and controlled. From the farm to the table, HACCP identifies potential hazards, establishes critical control points, and implements measures to eliminate or reduce risks. By adhering to these meticulous standards, the food industry upholds its promise of delivering safe and wholesome products, earning the trust of consumers worldwide. Food safety is a continuous journey, and the HACCP system is our trusted guide, leading the way toward a healthier and safer future for all.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Consumers and food safety: A food industry perspective
Food safety is not merely a matter of quality; it’s a matter of public health. Contaminated or improperly handled food can lead to severe health issues, including foodborne illnesses, which affect millions of people each year. Ensuring food safety is crucial for preventing these illnesses, safeguarding consumer health, and maintaining public trust in the food industry.
Food safety is a paramount concern that transcends culinary delight. It’s a pledge to protect the well-being of individuals and communities. Every step in the food production and distribution chain plays a vital role in this commitment. From farmers and processors to retailers and consumers, we all share a collective responsibility to uphold the highest food safety standards. This vigilance not only shields us from harm but also reinforces the integrity and trustworthiness of the global food ecosystem.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Food safety

HACCP is a systematic, science-based approach to identifying, evaluating, and controlling food safety hazards. It stands for Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points. Developed initially for the NASA space program, HACCP has become the gold standard in food safety management.
HACCP is not just a set of rules; it’s a proactive system that empowers food businesses to ensure the safety of their products at every stage of production. It’s about identifying potential hazards, establishing preventive measures, and constantly monitoring and adjusting processes to guarantee food safety. In essence, HACCP is a dynamic and comprehensive strategy that prioritizes consumer well-being.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Consumers and food safety: A food industry perspective

HACCP revolves around seven core principles:
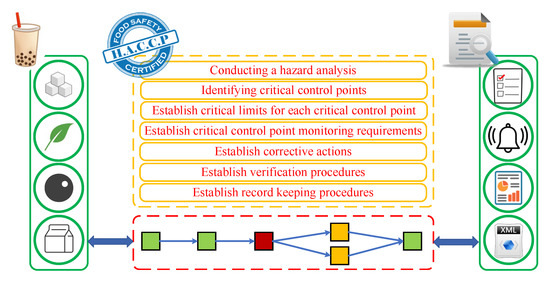
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) is a systematic and science-based approach to food safety that revolves around seven core principles. These principles serve as the foundation for developing and implementing effective food safety plans, ensuring that food products are safe for consumption from production to consumption:
Conduct Hazard Analysis: The first step in HACCP is to conduct a thorough hazard analysis. This involves identifying potential biological, chemical, and physical hazards that may occur at various stages of food production, processing, and distribution. Understanding these hazards is essential for effective risk management.
Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs): Once hazards are identified, the next step is to determine critical control points. CCPs are specific points or steps in the production process where control measures can be applied to prevent, eliminate, or reduce hazards to an acceptable level. Identifying CCPs is crucial for targeting interventions effectively.
Establish Critical Limits: At each CCP, critical limits are established. Critical limits are the maximum and minimum values, such as temperature, time, pH, or microbial load, that must be maintained to control the hazard effectively. These limits are based on scientific data and regulatory requirements.
Monitor CCPs: Continuous monitoring of CCPs is essential to ensure that critical limits are consistently met. This involves regular testing and observation to verify that the process is under control. Any deviations from critical limits must be addressed promptly.
Establish Corrective Actions: When monitoring reveals deviations from critical limits or other unexpected issues, corrective actions must be established. Corrective actions are specific steps taken to bring the process back under control, prevent product contamination, and ensure food safety. These actions must be documented and implemented as needed.
Verify and Validate: Verification and validation are critical steps to confirm the effectiveness of the HACCP plan. Verification involves ongoing activities, such as reviewing records and conducting audits, to ensure that the plan is working as intended. Validation, on the other hand, is a one-time process to confirm that the plan is scientifically sound and effective.
Establish Record-Keeping and Documentation: Proper record-keeping is fundamental to HACCP. Accurate and comprehensive records provide evidence that the plan is being followed, and that critical limits are consistently met. Documentation also includes the HACCP plan itself, which outlines all of the above principles and serves as a guide for food safety.
These seven principles form a comprehensive and proactive approach to food safety. They are designed to prevent hazards rather than relying solely on testing and inspection of finished products. By applying these principles throughout the food production process, from farm to table, HACCP helps ensure the safety and quality of food products, protecting public health and building consumer confidence in the food supply chain.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: The Current US Food Safety System – Ensuring Safe Food – NCBI …

Identify and assess potential hazards in food production.
Identifying and assessing potential hazards in food production is a fundamental aspect of food safety standards like HACCP. This crucial step involves a comprehensive examination of each stage in the food production process to pinpoint potential risks to food safety. These hazards can encompass a wide range of factors, including biological (such as pathogens or bacteria), chemical (such as contaminants or additives), and physical (such as foreign objects or allergens) risks.
To achieve this, food producers, processors, and manufacturers employ a rigorous and systematic approach. They analyze the entire production process, from the sourcing of raw materials to the packaging and distribution of finished products. By doing so, they can identify critical control points (CCPs) where measures can be taken to prevent, reduce, or eliminate potential hazards.
This proactive hazard analysis not only enhances the safety of food products but also contributes to the overall quality and trustworthiness of the brand. Consumers have come to expect food that not only tastes good but is also safe to consume. Therefore, identifying and addressing potential hazards in food production is not just a regulatory requirement; it’s a commitment to ensuring public health and maintaining the reputation of the food industry.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF FOOD HYGIENE CXC 1-1969 Adopted …

Determine the key points in the production process where hazards can be controlled or prevented.
Identifying Critical Control Points (CCPs) in the production process is vital for ensuring food safety. These are specific stages where hazards can be controlled or prevented, minimizing risks to consumers. By pinpointing CCPs, businesses can implement targeted measures and quality controls, thus enhancing food safety and compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Hazard Analysis of Critical Control Points Principles
Set specific limits for each CCP to maintain control over potential hazards.
“Setting specific limits for Critical Control Points (CCP) is a fundamental aspect of hazard control in various industries, ensuring safety and quality.”
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Consumers and food safety: A food industry perspective
Develop systems to monitor CCPs to ensure hazards are kept in check.
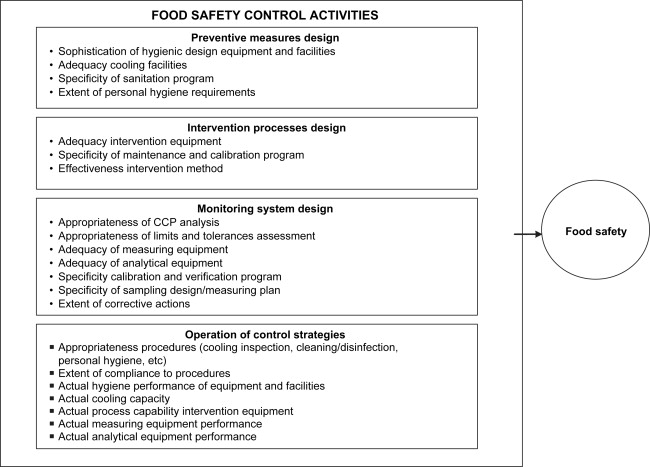
Developing robust monitoring systems for Critical Control Points (CCPs) is a fundamental aspect of ensuring the safety and quality of products and processes. CCPs are specific stages or points within a production or manufacturing process where control measures can be applied to prevent, eliminate, or reduce potential hazards. Here are some key considerations and benefits of implementing effective monitoring systems for CCPs:
Real-time Surveillance: Monitoring systems provide real-time surveillance of CCPs, allowing for immediate detection of deviations from established control measures. This timely feedback enables swift corrective action to be taken, preventing hazards from escalating.
Data Collection and Analysis: These systems collect valuable data related to CCPs, which can be analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and potential areas for improvement. Data-driven decision-making can lead to enhanced control strategies and more efficient hazard prevention.
Alerts and Alarms: Monitoring systems can be equipped with alerts and alarms that trigger when CCPs exceed established limits. These notifications ensure that responsible personnel are promptly informed, facilitating quick responses to mitigate risks.
Documentation and Record-keeping: Effective monitoring includes the documentation of observations and actions taken at CCPs. This documentation serves as a valuable record for compliance, audits, and traceability, providing transparency and accountability.
Continuous Improvement: Regularly monitoring CCPs encourages a culture of continuous improvement. By analyzing data and performance trends, organizations can refine their control measures, enhance process efficiency, and further reduce risks.
Compliance with Regulations: In many industries, adherence to monitoring CCPs is a legal requirement to ensure consumer safety and regulatory compliance. Failure to monitor and control CCPs can result in non-compliance issues and potential legal consequences.
Enhanced Product Quality: Effective monitoring not only prevents hazards but also contributes to consistent product quality. This can lead to increased customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
Reduced Costs: Proactive hazard prevention through monitoring can lead to cost savings by minimizing the need for corrective actions, recalls, or product losses.
Traceability and Recall Management: In the event of a product recall, accurate and detailed monitoring data can facilitate the identification and isolation of affected products, reducing the scope and impact of recalls.
Risk Mitigation: Ultimately, the primary goal of monitoring CCPs is risk mitigation. By systematically identifying and controlling hazards, organizations can protect the safety of consumers, uphold their reputation, and ensure the overall integrity of their processes and products.
In summary, the development of monitoring systems for CCPs is a critical aspect of quality control and risk management in various industries. These systems offer real-time surveillance, data-driven insights, and proactive hazard prevention, ultimately contributing to safer products, compliance with regulations, and the continuous improvement of processes.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: The Current US Food Safety System – Ensuring Safe Food – NCBI …
Plan for actions to be taken if a CCP falls outside the critical limits.
When a Critical Control Point (CCP) falls outside its defined critical limits, it’s not merely a deviation; it’s a call to action. Prompt and precise responses are essential to safeguard the integrity of the food production process. Here’s how to effectively plan for and execute these actions:
Immediate Correction: The first step is swift correction. When a CCP goes awry, corrective actions must be taken immediately to bring the process back within control. This might involve adjusting equipment settings, modifying procedures, or addressing any issues that caused the deviation.
Assessment of Affected Product: Determine the extent of product affected by the deviation. This assessment helps in deciding whether the affected product can be safely reprocessed, reworked, or if it must be discarded.
Traceability and Record-Keeping: Effective traceability is crucial. You should be able to trace the affected product back to its source and identify any other potentially affected products. Detailed records of the deviation, actions taken, and product disposition should be maintained for future reference and audits.
Preventive Actions: Investigate the root cause of the deviation to prevent its recurrence. This may involve equipment maintenance, employee training, process redesign, or other measures to address underlying issues.
Communication: Timely communication is vital, both internally and externally. Internally, inform all relevant personnel about the deviation and the actions taken. Externally, if necessary, notify regulatory authorities and customers to ensure transparency and compliance.
Reverification: After corrective actions, it’s essential to verify that the process is back in control. Regular monitoring and testing should resume to ensure the continued safety and quality of the food product.
Documentation: Document all actions taken during and after the deviation. This documentation is essential for auditing, compliance reporting, and continuous improvement.
By diligently planning for these actions and having clear protocols in place, the food industry can respond swiftly and effectively to deviations at CCPs, ensuring the safety and integrity of the food supply chain.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Consumers and food safety: A food industry perspective
Verify the effectiveness of the HACCP system through regular checks and reviews.
Regular verification of the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) system is a cornerstone of food safety. It involves a meticulous process of ongoing checks and reviews to ensure that the system remains effective. These evaluations encompass monitoring critical control points, assessing records, and conducting periodic audits.
Through this rigorous oversight, any deviations or potential hazards can be promptly identified and addressed, preventing food safety risks from escalating. It’s a proactive approach that not only upholds the quality and safety of food products but also instills confidence in consumers and regulatory authorities that stringent safety measures are in place. In the ever-evolving landscape of food production, the commitment to verify and refine the HACCP system remains essential in safeguarding public health.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: HACCP Principles & Application Guidelines | FDA
Maintain comprehensive records to track the entire HACCP process.
Maintaining detailed records is not just a requirement; it’s a fundamental aspect of successful HACCP implementation. These records serve as a roadmap of your food safety journey, documenting critical control points, monitoring activities, corrective actions, and verification procedures. They provide a clear picture of your commitment to food safety, ensuring transparency and accountability at every step. Additionally, these records are invaluable assets when it comes to audits, inspections, and continuous improvement efforts, helping you refine your processes and strengthen your commitment to producing safe and high-quality food products.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: HACCP Principles & Application Guidelines | FDA

The HACCP system is highly versatile and applicable across various sectors of the food industry, including:
The HACCP system’s versatility and applicability span across a wide spectrum of sectors within the food industry, showcasing its effectiveness in ensuring food safety and quality. Some of the key sectors where HACCP is prominently utilized include:
Food Manufacturing: HACCP plays a crucial role in food manufacturing, where it helps identify potential hazards and critical control points in various processes. Whether it’s a bakery producing bread, a dairy plant producing cheese, or a meat processing facility, HACCP is applied to prevent contamination, control hazards, and maintain product consistency.
Agriculture and Farming: From field to fork, HACCP principles are increasingly being integrated into agricultural practices. Farmers implement HACCP-based strategies to address potential risks associated with crop cultivation, livestock raising, and the handling of fresh produce. This ensures that agricultural products are safe and meet quality standards.
Seafood Industry: The seafood industry relies heavily on HACCP to manage risks related to fish and shellfish processing. This includes everything from catching or farming seafood to processing, packaging, and distribution. HACCP helps ensure the safety of seafood products and minimizes the risk of contamination, particularly in the case of seafood that is often consumed raw, such as sushi.
Food Service and Catering: Restaurants, cafeterias, and catering services also implement HACCP principles to maintain food safety and hygiene. From receiving food supplies to storage, preparation, and serving, HACCP helps prevent foodborne illnesses and ensures that customers can enjoy meals without concerns about safety.
Retail and Supermarkets: Grocery stores and supermarkets use HACCP guidelines to manage the safety of perishable products like meat, dairy, and deli items. HACCP plans help maintain product freshness, prevent cross-contamination, and reduce food waste through proper handling and storage.
Beverage Production: HACCP is applicable not only to solid foods but also to beverage manufacturing, including soft drinks, juices, and alcoholic beverages. It ensures that the ingredients used are safe and that the production processes are sanitary and controlled.
Food Packaging and Distribution: Companies involved in food packaging and distribution are not exempt from HACCP requirements. They use HACCP to safeguard the integrity of packaged foods, prevent contamination during transportation, and maintain proper storage conditions to extend shelf life.
Food Import and Export: In an increasingly globalized food market, HACCP compliance is essential for international trade. It helps exporters meet the food safety standards of importing countries, ensuring that food products meet regulatory requirements and consumer expectations.
Food Research and Development: HACCP is also applied in food research and development laboratories to test new products, ingredients, and processes for safety and quality. This proactive approach helps create innovative and safe food products.
Food Safety Training and Education: Beyond industry sectors, HACCP has found a place in food safety training and education programs. It equips food handlers, inspectors, and auditors with the knowledge and skills needed to ensure the safety of food products.
In essence, HACCP’s adaptability makes it a cornerstone of food safety management across diverse sectors. Its principles provide a structured framework for identifying, evaluating, and controlling hazards, ultimately contributing to the production of safe and high-quality food products worldwide.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Consumers and food safety: A food industry perspective

Ensuring the safety of processed foods, from meats to dairy products.
Ensuring the safety of processed foods, ranging from meats to dairy products, is a paramount objective of food safety standards like Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP). Processed foods constitute a significant portion of the modern diet, and consumers rightly expect them to be not only convenient but also safe for consumption.
In the context of HACCP, addressing the safety of processed foods involves a meticulous evaluation of each step in the manufacturing and processing stages. Here’s how it works:
Raw Material Sourcing: The process begins with the sourcing of raw materials, be it meat, dairy, grains, or other ingredients. At this stage, potential hazards like biological contaminants (e.g., bacteria or parasites), chemical residues (e.g., pesticides or antibiotics), and allergens are identified.
Hazard Analysis: Food safety experts conduct a hazard analysis to identify critical control points (CCPs) in the production process. CCPs are stages where control measures can be applied to prevent or eliminate hazards. For example, in meat processing, cooking or pasteurization is a CCP to ensure the destruction of harmful bacteria.
Monitoring and Control: Robust monitoring procedures are put in place at CCPs to ensure that control measures are consistently effective. This often involves real-time data collection and regular testing to confirm that hazards are being managed.
Corrective Actions: In case a hazard is not adequately controlled or an issue arises, corrective actions are implemented promptly. This might involve adjustments to the production process, removal of affected products, or sanitation procedures.
Record Keeping: Detailed records of monitoring, control, and corrective actions are maintained. This documentation not only aids in ensuring compliance but also provides valuable insights for continuous improvement.
Verification and Validation: Food safety plans are periodically verified and validated to confirm their effectiveness. This involves comprehensive reviews and, at times, external audits to assess compliance with food safety standards.
Consumer Education: While not a direct part of HACCP, educating consumers about safe food handling and storage is crucial. It empowers individuals to play their part in maintaining food safety once the product leaves the manufacturer’s control.
By systematically addressing potential hazards at every step of the processing journey, food safety standards like HACCP significantly reduce the risks associated with processed foods. This, in turn, contributes to safeguarding public health and upholding the integrity of the food industry.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: How we ensure food safety | Nestlé Global

Implementing safe food handling practices in foodservice establishments.
Safe food handling practices are the cornerstone of foodservice establishments, ensuring the well-being of customers and compliance with food safety regulations. Staff training, proper handwashing, temperature control, cross-contamination prevention, and hygiene protocols are essential components of safe food handling. These practices not only protect consumers from foodborne illnesses but also uphold the reputation and success of foodservice businesses. By prioritizing food safety, establishments can create a trusted and enjoyable dining experience while reducing the risk of incidents that can harm public health and their bottom line.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Leftovers and Food Safety | Food Safety and Inspection Service

Controlling hazards in seafood production, from fishing to processing.
“Controlling hazards throughout the seafood production chain, from fishing to processing, is essential for ensuring the safety and quality of seafood products.”
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Seafood Watch
The implementation of HACCP offers numerous benefits, including:
The implementation of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) is a systematic and proactive approach to food safety management. It offers a wide range of benefits that contribute to the overall quality and safety of food products. Here are some key advantages of implementing HACCP:
Enhanced Food Safety: HACCP is designed to identify and control potential hazards at critical points in the food production process. This leads to safer food products with reduced risks of contamination, foodborne illnesses, and recalls.
Prevention Over Inspection: Unlike traditional inspection-based methods, HACCP focuses on hazard prevention rather than detection. By addressing potential issues at critical control points, it minimizes the likelihood of hazards occurring in the first place.
Compliance with Regulations: HACCP is widely recognized and often required by regulatory authorities and food safety standards. Implementing HACCP helps food businesses meet legal requirements and demonstrate their commitment to food safety.
Improved Product Quality: The rigorous monitoring and control of critical control points in HACCP not only enhance food safety but also contribute to consistent product quality. This can lead to higher customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Efficiency and Cost Savings: HACCP can identify and eliminate unnecessary steps or processes that do not contribute to food safety. Streamlining operations can lead to cost savings and increased operational efficiency.
Risk Reduction: By systematically analyzing and controlling hazards, HACCP reduces the risk of product recalls, legal liabilities, and damage to a company’s reputation.
Consumer Confidence: HACCP-certified products are often viewed favorably by consumers, as they are seen as safer and of higher quality. This can lead to increased consumer trust and loyalty.
Global Market Access: Many international markets require HACCP certification for imported food products. Implementing HACCP can open doors to global trade opportunities.
Documentation and Traceability: HACCP requires detailed documentation of processes, procedures, and monitoring activities. This documentation provides a clear record of due diligence and assists in traceability during recalls or investigations.
Continuous Improvement: HACCP encourages a culture of continuous improvement in food safety. Regular reviews and updates of the HACCP plan allow organizations to adapt to changing conditions and emerging risks.
Supplier and Vendor Management: HACCP extends beyond a single organization and often involves the evaluation and monitoring of suppliers and vendors. This ensures that raw materials and ingredients meet safety standards.
Employee Training: HACCP requires training and awareness among employees regarding food safety practices. This investment in employee education contributes to a safer work environment and adherence to best practices.
In summary, the implementation of HACCP is a proactive and systematic approach to food safety that offers numerous benefits to food businesses and consumers alike. It enhances food safety, prevents hazards, ensures compliance with regulations, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Ultimately, HACCP helps safeguard public health and the reputation of the food industry.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: How the Moon Landing Led to Safer Food for Everyone | NASA Spinoff
HACCP helps identify and control potential hazards, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
The Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) system is a dynamic and systematic approach that plays a pivotal role in safeguarding the food supply chain and, in turn, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses. Here’s how HACCP achieves this:
Proactive Hazard Identification: HACCP takes a proactive stance by identifying potential hazards at various stages of the food production process. These hazards can include biological, chemical, or physical contaminants that may compromise food safety.
Critical Control Points (CCPs): Through careful analysis, HACCP identifies critical control points where hazards can be controlled or eliminated. These are the key junctures in the production process where specific measures are applied to ensure food safety.
Risk Assessment: HACCP assesses the severity and likelihood of hazards occurring at each CCP. This systematic evaluation helps prioritize which hazards require immediate attention and which can be managed through other preventive measures.
Monitoring and Control: At each CCP, HACCP establishes monitoring procedures to track key parameters that ensure food safety. These procedures include temperature checks, microbial testing, and quality inspections. If parameters deviate from acceptable limits, immediate corrective actions are taken.
Preventive Measures: The emphasis on preventive measures is a hallmark of HACCP. By identifying potential issues before they become hazards, HACCP reduces the likelihood of foodborne illnesses. Preventive actions can include equipment maintenance, employee training, and process adjustments.
Documentation and Record-Keeping: HACCP requires thorough documentation of all steps, including hazard identification, CCPs, monitoring results, corrective actions, and preventive measures. This documentation is crucial for traceability, audits, and continuous improvement.
Verification and Validation: Regular verification ensures that the HACCP plan is effective and remains up-to-date. Validation confirms that the control measures in place are sufficient to eliminate or reduce hazards. These ongoing processes provide confidence in the system’s reliability.
Continuous Improvement: HACCP is not a static system; it encourages continuous improvement. By constantly monitoring and reviewing the process, organizations can adapt to new challenges, emerging hazards, and changing regulations.
Through its rigorous methodology and emphasis on prevention, HACCP is a powerful tool in reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses. It empowers food producers to proactively address potential hazards, maintain high food safety standards, and ultimately protect the health and well-being of consumers.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Health and Safety | USDA

It ensures compliance with food safety regulations and standards.
Compliance with food safety regulations and standards is not just a legal requirement; it’s a fundamental obligation to protect consumers and uphold the integrity of the food industry. Implementing and maintaining robust food safety practices is a multifaceted commitment that extends from farm to fork.
By adhering to these regulations and standards, food businesses demonstrate their dedication to producing safe, high-quality products. It’s a proactive stance that involves rigorous inspections, meticulous record-keeping, and ongoing training for personnel. This dedication to compliance not only mitigates risks but also fosters consumer trust, strengthens the reputation of food brands, and ensures that the global food supply chain remains reliable and safe.
In essence, compliance with food safety regulations and standards is a shared responsibility that transcends borders, and it serves as a cornerstone of public health and confidence in the food we consume.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: How we ensure food safety | Nestlé Global
By preventing contamination, HACCP can enhance the overall quality of food products.
Preventing contamination is not just about meeting regulatory requirements; it’s a cornerstone of producing high-quality food products. HACCP takes a proactive approach to quality by identifying potential hazards and implementing control measures to mitigate them. This not only safeguards consumer health but also ensures that your food products consistently meet or exceed quality standards.
When contaminants are effectively controlled, the result is improved taste, texture, and appearance of food items. This means happier customers who return for more and recommend your products to others. Furthermore, a reputation for quality can open doors to new markets and partnerships, allowing your business to thrive in a competitive food industry landscape.
In essence, HACCP isn’t just about compliance; it’s about elevating the overall quality of your food products, delighting customers, and building a brand known for excellence.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Food and Pesticides | US EPA
Consumers trust products with HACCP certification, knowing they meet rigorous safety standards.
Consumer trust is a cornerstone of any successful business, and in the realm of food safety, HACCP certification plays a pivotal role in fostering that trust. Here’s why consumers place so much value on products with HACCP certification and how it reinforces their confidence:
Assurance of Safety: When consumers see the HACCP logo or certification on a food product, it sends a clear message that the manufacturer has taken proactive steps to ensure its safety. This assurance is particularly important in an age where consumers are increasingly concerned about foodborne illnesses and contaminants.
Prevention of Foodborne Illness: HACCP is all about preventing rather than reacting to food safety issues. Consumers understand that this proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses, which can have severe health consequences. Knowing that their health is prioritized makes them more likely to choose products with HACCP certification.
Quality Control: HACCP doesn’t just address safety; it also focuses on maintaining consistent product quality. Consumers appreciate the attention to detail in manufacturing processes that HACCP demands, which often translates to products that meet or exceed their quality expectations.
Transparency: HACCP principles emphasize transparency in food production. This means that manufacturers are required to document and record every step of the production process, from sourcing raw materials to packaging and distribution. These records are often available for consumers to review, enhancing trust by demonstrating accountability.
Compliance with Regulations: HACCP is often a regulatory requirement in many countries. When consumers see HACCP certification, they know that the product meets not only industry standards but also government regulations. This adds an extra layer of reassurance.
Global Recognition: HACCP is recognized internationally, making it applicable to both domestic and imported products. Consumers can rely on its credibility even when purchasing products from other countries, which is particularly relevant in today’s global marketplace.
Brand Reputation: Companies that invest in HACCP certification demonstrate a commitment to excellence and safety. This commitment positively impacts their brand reputation, which consumers associate with trustworthiness.
Reduction of Food Waste: HACCP’s emphasis on controlling processes and reducing the risk of contamination means that products are less likely to be recalled or discarded due to safety concerns. This contributes to reducing food waste, a concern that resonates with environmentally conscious consumers.
Peace of Mind: Ultimately, consumers want peace of mind when it comes to the food they consume and serve to their families. HACCP certification provides that peace of mind, allowing consumers to enjoy their meals without worry.
In a competitive food market where consumers have abundant choices, products with HACCP certification stand out as reliable and trustworthy options. This trust not only benefits consumers but also strengthens the reputation and market presence of the companies that invest in HACCP certification, creating a win-win situation for all stakeholders in the food industry.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Safer Food and Greater Consumer Confidence | by Tom Vilsack …

Conclusion
Food safety standards like HACCP are the backbone of ensuring that the food we consume is safe and of high quality. They protect public health, maintain industry integrity, and instill confidence in consumers. As we continue to prioritize food safety, systems like HACCP will remain essential tools in the global effort to provide safe and wholesome food for all.
Food safety standards, exemplified by systems like Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), are not just a bureaucratic requirement but rather the linchpin of ensuring the safety and quality of the food we consume. Here’s an extension of this crucial idea:
Upholding Public Health: At its core, food safety standards are about protecting public health. By systematically identifying, controlling, and mitigating hazards, these standards reduce the risks associated with consuming contaminated or adulterated food. This is particularly critical in a world where foodborne illnesses can have severe health consequences, affecting vulnerable populations disproportionately.
Industry Integrity and Credibility: Food safety standards are the bedrock of industry integrity. They signal to consumers that manufacturers are committed to producing safe and reliable products. This integrity extends to international trade, where adherence to recognized standards facilitates the smooth flow of goods across borders. It fosters trust among trading partners and ensures that consumers around the world can access safe food options.
Consumer Confidence: Food safety standards play a pivotal role in bolstering consumer confidence. When individuals see familiar certifications or labels like HACCP on food products, it instills trust. This trust translates into purchasing decisions, as consumers are more likely to choose products they perceive as safe and high in quality. In this way, food safety standards empower consumers to make informed choices about the foods they buy and consume.
Preventing Food Waste: Standards like HACCP also contribute to reducing food waste. By minimizing the risk of contamination or spoilage, they help extend the shelf life of products. This, in turn, reduces the amount of food that goes to waste, addressing both economic and environmental concerns associated with food waste.
Continuous Improvement: Food safety standards are not static; they evolve in response to emerging risks and scientific advancements. They encourage a culture of continuous improvement within the food industry, driving innovation in food safety technologies, practices, and systems.
Global Collaboration: In our interconnected world, where food is sourced and distributed globally, harmonized food safety standards are essential. They facilitate international trade, ensuring that food products meet the same safety and quality criteria regardless of their origin. This global collaboration benefits both producers and consumers, supporting economic growth and access to diverse food choices.
In conclusion, food safety standards like HACCP are the cornerstone of a safe, reliable, and thriving food industry. They protect public health, maintain industry integrity, and inspire confidence in consumers. As we continue to prioritize food safety in an increasingly complex global food system, these standards will remain indispensable tools in our collective effort to provide safe and wholesome food for all.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Consumers and food safety: A food industry perspective
More links
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: How we ensure food safety | Nestlé Global