Introduction
Food waste is a global problem that not only impacts our environment but also exacerbates issues of food scarcity and hunger. In a world where millions go to bed hungry, the wastage of edible food is an ethical and economic dilemma. To address this issue, innovative approaches rooted in the concept of a circular economy are gaining momentum. In this article, we will explore the significance of food waste reduction and the circular economy initiatives that aim to transform our food systems.
In a world where abundance and scarcity coexist, the paradox of food waste emerges as a stark reminder of the ethical and economic dilemmas we face. It’s a global problem that transcends borders, impacting not only the environment but also deepening the wounds of food scarcity and hunger. As millions go to bed hungry every night, the wastage of edible food becomes an unsettling contradiction that challenges our conscience and our commitment to building a more equitable world.
The magnitude of food waste is staggering. It encompasses everything from the misshapen vegetables left unharvested in fields to the perfectly good groceries discarded from store shelves and the leftovers abandoned on restaurant plates. At every stage of the food supply chain, from production to consumption, edible food is lost, squandering precious resources and contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
The environmental toll of food waste is undeniable. When edible food ends up in landfills, it decomposes and emits methane, a potent greenhouse gas that exacerbates climate change. The water, land, and energy used to produce, transport, and prepare this wasted food also represent a staggering inefficiency, especially in a world where resource conservation is increasingly paramount.
Yet, the most profound impact of food waste is felt by those who struggle to secure their next meal. Food scarcity and hunger persist as intractable challenges in many regions, and the sheer volume of wasted food underscores the stark disparities that persist in our global food systems. It’s a painful irony that in a world of plenty, millions still face the gnawing pangs of hunger.
To address this ethical and environmental crisis, innovative approaches rooted in the concept of a circular economy are gaining momentum. The circular economy model seeks to eliminate waste and ensure that resources, including food, are used efficiently and sustainably. It challenges the linear “take-make-dispose” paradigm, advocating instead for a circular flow of resources where products are designed for longevity, repair, and reuse.
In the context of food waste reduction, circular economy initiatives are transformative. They envision a world where surplus food is rescued and redistributed to those in need rather than being discarded. They promote practices that encourage consumers to buy what they need, reduce plate waste, and creatively repurpose leftovers. They support innovative solutions for transforming food waste into valuable resources, such as compost and bioenergy, rather than sending it to landfills.
Furthermore, circular economy principles drive changes throughout the food supply chain. They encourage farmers to minimize losses by adopting more efficient harvesting and storage practices. They challenge retailers to rethink their inventory management and donation programs. They inspire restaurants and foodservice providers to design menus that reduce waste and celebrate the beauty of imperfect produce.
In this evolving landscape, food waste reduction is not merely an aspiration; it is an imperative. It represents a commitment to equity, sustainability, and responsible resource management. By embracing the principles of the circular economy and reimagining our relationship with food, we can pave a path toward a more just and sustainable world—a world where abundance is shared, waste is minimized, and the ethical dilemmas of hunger and environmental degradation are confronted with unwavering resolve.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Towards a more resource-efficient and circular economy The role of …
The scale of food waste is staggering. Every year, approximately one-third of all food produced globally is lost or wasted. This accounts for 1.3 billion tons of food, worth around $1 trillion. Such waste contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, depletes natural resources, and strains the global food supply chain.
The scale of food waste is staggering. Every year, approximately one-third of all food produced globally is lost or wasted. This accounts for 1.3 billion tons of food, worth around $1 trillion. Such waste contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, depletes natural resources, and strains the global food supply chain.
Addressing food waste is not only an environmental imperative but also a moral and economic one. At its core, food waste represents the inefficiency and inequity in the way food is produced, distributed, and consumed. It’s a stark paradox that while millions of people go hungry, vast quantities of perfectly edible food end up in landfills.
One of the primary contributors to food waste is the lack of proper infrastructure and storage facilities, especially in developing countries. Without adequate cold storage and transportation systems, perishable food items often spoil before they can reach consumers. Investing in better infrastructure can help mitigate these losses and ensure that food reaches those who need it most.
Consumer behavior also plays a significant role in food waste. In many affluent societies, there’s a tendency to discard food based on cosmetic imperfections or arbitrary expiration dates. Educating consumers about the true shelf life of products and promoting responsible shopping and meal planning can significantly reduce household food waste.
Restaurants and food service establishments are also important stakeholders in the fight against food waste. They can implement practices such as portion control, better inventory management, and creative ways to repurpose leftovers. Donating surplus food to charitable organizations can also make a significant impact.
Technology and innovation have a crucial role to play in combating food waste. Smart sensors and data analytics can help monitor food freshness and reduce spoilage throughout the supply chain. Food recovery apps connect surplus food from restaurants and events with organizations that can distribute it to those in need. These digital solutions not only reduce waste but also contribute to food security.
Furthermore, businesses and governments are increasingly setting targets and commitments to reduce food waste. This includes setting specific goals to halve food waste by a certain year, implementing waste-reducing practices, and measuring progress transparently. This shift toward accountability is a positive step toward reducing waste on a larger scale.
Reducing food waste isn’t just an environmental and economic opportunity; it’s also a moral imperative. By addressing the root causes of food waste, from production and distribution to consumer behavior and waste management, we can reduce the strain on the planet’s resources, help alleviate hunger, and create a more sustainable and equitable food system.
In conclusion, the scale of food waste is a global challenge with profound environmental, economic, and ethical implications. Addressing food waste requires a multi-faceted approach, involving infrastructure development, consumer education, technological innovation, and concerted efforts by businesses and governments. By working together to combat food waste, we can create a more sustainable and equitable food system for future generations.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Prevention of Waste in the Circular Economy: Analysis of Strategies …

The circular economy is a regenerative approach that focuses on reducing waste and maximizing the value of resources. When applied to the food industry, it emphasizes the following principles:
The concept of the circular economy, with its regenerative and waste-reducing principles, holds immense promise when applied to the dynamic and resource-intensive food industry. This transformative approach redefines how we view and manage resources, offering a sustainable path forward for food production and consumption. Within the context of the food industry, it emphasizes several key principles:
Reducing Food Waste: The circular economy in the food sector prioritizes minimizing food waste at every stage of the supply chain. This includes efforts to prevent overproduction, improve inventory management, and divert surplus food to those in need. Reducing food waste not only conserves valuable resources but also addresses the pressing issue of global hunger.
Optimizing Resource Use: Efficiency becomes paramount in a circular food economy. Resource optimization involves using ingredients, water, and energy more efficiently in food production processes. This not only conserves resources but also reduces the environmental footprint of food production.
Embracing Sustainable Sourcing: Circular food systems prioritize sustainable and ethical sourcing practices. This involves selecting ingredients and raw materials that are environmentally friendly, support local communities, and adhere to fair labor practices. Sustainable sourcing ensures that the food industry operates in harmony with both nature and society.
Implementing Closed-Loop Systems: In a circular food economy, closed-loop systems are essential. These systems aim to capture and repurpose byproducts and waste materials from food production. For example, food manufacturers can use food scraps and processing waste to create animal feed, biofuels, or compost, thereby reducing waste and adding value to resources.
Promoting Circular Packaging: Packaging is a significant source of waste in the food industry. Circular food systems encourage the use of sustainable, recyclable, and biodegradable packaging materials. Additionally, companies are exploring innovative packaging solutions, such as reusable containers and systems that facilitate packaging return and reuse.
Consumer Education and Engagement: The circular food economy recognizes the critical role of consumers in minimizing waste. Educating and engaging consumers about food waste reduction, responsible consumption, and sustainable choices are integral components of this approach. Consumers are encouraged to make informed decisions that align with circular principles.
Investing in Innovation: Embracing innovation is essential to advancing the circular economy in the food industry. This includes the development of new technologies and processes that support waste reduction, resource efficiency, and sustainable practices. Collaborative efforts among industry stakeholders, startups, and research institutions drive continuous innovation.
Measuring and Reporting Impact: To track progress and hold stakeholders accountable, measurement and reporting of circularity metrics are crucial. Companies are encouraged to transparently report their efforts in reducing waste, optimizing resource use, and embracing sustainability.
By adhering to these principles, the food industry can transition toward a circular economy that not only conserves resources and reduces waste but also fosters resilience, ethical practices, and long-term sustainability. It represents a profound shift in how we approach food production and consumption, offering a more holistic and responsible approach to nourishing the world’s growing population while safeguarding the planet for future generations.
You can also read more about this here: Circular Economy and Food | Ellen MacArthur Foundation

The first step is to minimize food waste at the source. This involves measures such as better inventory management, improved harvesting techniques, and consumer awareness campaigns to reduce food over-purchasing.
Minimizing food waste at its source is a critical and multifaceted endeavor that encompasses various strategies and collaborative efforts. Here are some key elements and extensions of this important initiative:
Inventory Management Excellence: Effective inventory management is pivotal in reducing food waste within the food industry. Food businesses can implement advanced forecasting systems that optimize inventory levels, helping them match supply with demand more accurately. This not only prevents over-purchasing but also reduces the risk of food spoilage.
Harvesting Innovations: Innovative harvesting techniques play a vital role in minimizing waste in agriculture. Technologies like automated sorting systems can identify and separate produce that may not meet strict cosmetic standards but are still perfectly edible. Such advancements help rescue surplus crops that would otherwise go to waste.
Farm-to-Table Partnerships: Collaborative efforts between farmers, distributors, and foodservice establishments can facilitate the efficient distribution of surplus or imperfect produce. Programs that connect local farmers with restaurants, food banks, and school cafeterias can ensure that excess food finds its way to those in need rather than being discarded.
Consumer Awareness Campaigns: Educating consumers about the impacts of food waste and providing practical tips on reducing waste at home are essential components of this initiative. Public awareness campaigns can encourage responsible shopping, meal planning, and food storage practices. They can also emphasize the value of embracing “ugly” or imperfect produce.
Dynamic Pricing Models: Retailers and foodservice providers can implement dynamic pricing models to incentivize the purchase of items nearing their expiration dates. Discounts on such items can motivate consumers to make more sustainable choices while reducing waste.
Donation Programs: Encouraging food businesses to establish donation programs can divert surplus food away from landfills. These programs can include partnerships with local food banks, shelters, and nonprofits, ensuring that edible but unsellable food goes to those who need it most.
Food Redistribution Platforms: Technology-driven solutions, such as food redistribution platforms and apps, connect surplus food with organizations and individuals in real-time. These platforms streamline the process of identifying available surplus food and facilitating its rapid distribution.
Waste Tracking and Analytics: The adoption of waste tracking systems and data analytics enables food businesses to identify patterns and areas of improvement in their operations. These insights can lead to more effective waste reduction strategies.
Packaging Innovations: Reducing food waste also involves reconsidering packaging. Eco-friendly packaging that extends the shelf life of perishable items can help prevent premature spoilage. Additionally, packaging that offers portion control can reduce overconsumption and waste.
Food Recovery Legislation: Governments and regulatory bodies can play a pivotal role by enacting food recovery and donation laws that protect businesses from liability when donating surplus food. These laws encourage food businesses to participate in food rescue efforts.
In summary, minimizing food waste at its source is a multifaceted effort that involves various stakeholders, from producers and distributors to retailers and consumers. Collaborative strategies, technological innovations, consumer education, and legislative support all contribute to reducing food waste and its associated environmental, economic, and social impacts. By addressing this issue holistically, we can make significant strides toward a more sustainable and responsible approach to food consumption and management.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Waste: Circular Economy

Edible surplus food can be redistributed to those in need through food banks and charitable organizations. Many initiatives are now connecting surplus food from restaurants, supermarkets, and events with individuals facing food insecurity.
The concept of redistributing edible surplus food represents a powerful and compassionate solution to combat food waste and address the pressing issue of food insecurity. In a world where vast quantities of food are wasted each year, the redirection of surplus food to those in need is not just a responsible choice but also a morally imperative one.
One of the critical mechanisms facilitating this process is the partnership between food establishments, such as restaurants and supermarkets, and charitable organizations and food banks. These collaborations are pivotal in bridging the gap between food surplus and food scarcity. Restaurants, for example, often find themselves with excess prepared food at the end of the day. Instead of discarding these edible leftovers, they can connect with local food banks or organizations specializing in food rescue.
Supermarkets, too, play a crucial role in this endeavor. They regularly manage inventory, and as a result, they may have surplus items nearing their expiration dates or produce with slight cosmetic imperfections that are still perfectly edible. By forming partnerships with food rescue organizations, supermarkets can ensure that these items don’t end up in the trash but are rather redirected to individuals and families who can benefit from them.
Food events, whether they are weddings, conferences, or large-scale gatherings, often generate surplus food that can be rescued and redistributed. Event organizers can collaborate with food rescue initiatives to ensure that the excess food is collected, safely stored, and distributed to those in need. This not only prevents food waste but also fosters a sense of responsibility and sustainability within the event industry.
Moreover, the advent of technology has facilitated the process of food redistribution. Mobile apps and online platforms have emerged, connecting donors, such as restaurants and grocery stores, with local charities and food banks in need. These digital tools streamline the logistics, making it easier for surplus food to find its way to those who require it most.
Beyond the immediate benefits of alleviating hunger and reducing food waste, these initiatives have broader positive implications. They contribute to building stronger communities by fostering cooperation between businesses, non-profit organizations, and individuals. Furthermore, they raise awareness about the environmental impact of food waste, prompting individuals and organizations to adopt more sustainable practices.
In conclusion, the act of redistributing edible surplus food is a commendable endeavor that addresses both the ethical imperative of reducing food waste and the pressing need to combat food insecurity. The partnerships between food establishments and charitable organizations, supported by technology, form a dynamic force for good. As these initiatives continue to grow, they not only provide nourishment but also sow the seeds of compassion and sustainability in our society, ultimately creating a brighter and more resilient future for all.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here What is a circular economy? | Ellen MacArthur Foundation

Food waste that cannot be reduced or reused can be repurposed into other valuable products. For instance, food scraps can be transformed into compost or bioenergy through anaerobic digestion.
The issue of food waste presents not only a challenge but also a remarkable opportunity for innovation and sustainability. While the ideal scenario is to reduce or reuse food waste wherever possible, there are instances when waste is inevitable. In such cases, the concept of repurposing comes to the forefront as a means to extract value and minimize environmental impact.
One of the most promising avenues for repurposing food waste is through the process of composting. Food scraps, along with other organic materials like yard trimmings and leaves, can be transformed into nutrient-rich compost through controlled decomposition. This compost, often referred to as “black gold,” is a valuable resource for enriching soil, improving its structure, and enhancing its capacity to support plant growth. By diverting food waste from landfills and incinerators and instead converting it into compost, we not only reduce the volume of waste but also contribute to healthier soils and more sustainable agriculture.
Another innovative approach to repurposing food waste involves anaerobic digestion. This biological process breaks down organic materials, including food waste, in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas as a valuable byproduct. Biogas is a renewable energy source that can be used for electricity generation, heating, or even as a vehicle fuel. Anaerobic digestion not only diverts food waste from landfills but also harnesses its energy potential, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
Beyond composting and anaerobic digestion, food waste can also find new life as animal feed or ingredients in the production of pet food. In some cases, food waste can be transformed into new food products through upcycling. For instance, surplus fruits and vegetables that might not meet the cosmetic standards for retail can be processed into juices, sauces, or frozen products, minimizing waste and providing consumers with nutritious options.
Repurposing food waste is not only an environmental win but also a smart business strategy. It reduces disposal costs, minimizes the negative environmental impact of waste in landfills, and can even generate additional revenue streams through the sale of compost, biogas, or upcycled products.
However, it’s important to remember that repurposing food waste should be considered as a complementary approach rather than a primary solution. The first line of defense against food waste remains prevention, followed by reduction and reuse. Repurposing should be employed when these initial steps are not feasible.
In a world grappling with the challenges of resource scarcity and environmental sustainability, repurposing food waste is a beacon of hope and a testament to our ability to turn a problem into an opportunity. It showcases the ingenuity and commitment of individuals, businesses, and communities to create a more sustainable and circular food system, where waste is minimized, and every resource is valued and repurposed for the benefit of both people and the planet.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Circular economy action plan
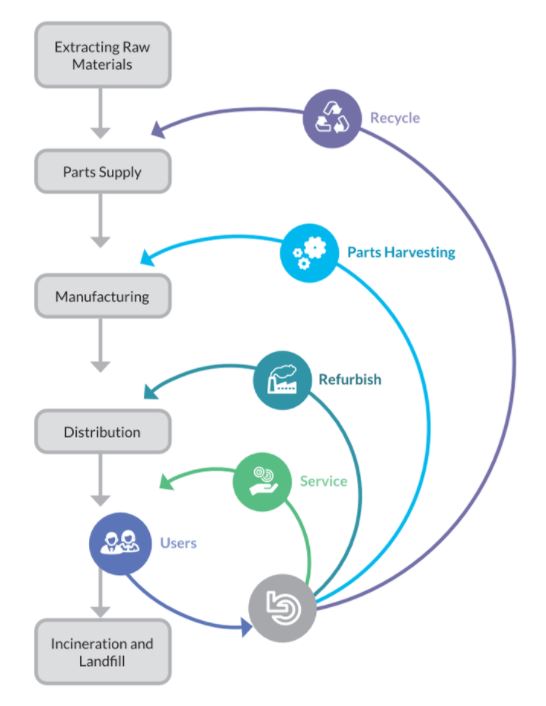
A key aspect of the circular economy is rethinking the way we approach food production and consumption. This includes embracing more sustainable farming practices, reducing plastic packaging, and supporting local and seasonal food systems.
Embracing sustainable farming practices is a pivotal element of the circular economy’s approach to food production and consumption. Here are some key strategies and considerations within this realm:
Regenerative Agriculture: Transitioning from conventional farming methods to regenerative agriculture is a fundamental shift in sustainable food production. This approach focuses on improving soil health, enhancing biodiversity, and reducing the need for synthetic inputs like pesticides and fertilizers. By adopting regenerative practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced tillage, farmers can create healthier ecosystems while producing food more sustainably.
Organic Farming: Organic farming eschews synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms in favor of natural methods for pest control and soil enrichment. By choosing organic products, consumers support farming practices that prioritize environmental stewardship and long-term sustainability.
Reducing Food Miles: Supporting local and seasonal food systems is another key aspect of the circular economy’s vision for food. Reducing the distance that food travels from farm to plate, commonly referred to as “food miles,” minimizes carbon emissions associated with transportation. Consumers can contribute by patronizing local farmers’ markets and participating in community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs.
Minimal Packaging: The excessive use of plastic packaging is a major environmental concern. Circular economy initiatives promote a reduction in packaging waste by encouraging businesses to adopt eco-friendly packaging alternatives. Biodegradable, compostable, and reusable packaging options are gaining popularity as part of this effort.
Upcycling and Reducing Food Loss: Innovations in food processing are finding creative ways to utilize food byproducts that would typically go to waste. This includes the creation of new products like snacks made from surplus grains or beverages crafted from imperfect fruits. By reducing food loss and finding value in previously discarded items, the food industry aligns more closely with circular economy principles.
Consumer Education: Educating consumers about the impact of their food choices is crucial. Empowered with knowledge about sustainable farming practices and the environmental implications of their choices, individuals can make more informed decisions when purchasing food products. This includes choosing foods with minimal packaging, supporting local farmers, and opting for products that align with their values.
Government Policies: Governments play a significant role in shaping agricultural practices through policies and regulations. Circular economy advocates call for policies that incentivize sustainable farming practices, reduce food waste, and promote equitable access to healthy food. Initiatives like subsidies for organic farming, restrictions on single-use plastics, and support for local food systems can be integral to this effort.
By rethinking our approach to food production and consumption in these ways, we can make meaningful strides toward a more sustainable and circular food system. This holistic approach not only benefits the environment but also supports the health and well-being of communities and future generations. It underscores the idea that the way we produce and consume food is deeply interconnected with the health of our planet.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Food Waste Solutions – Reduce Food Waste, Food Recycling …
Several initiatives and organizations are leading the charge in food waste reduction and circular economy efforts:
The global commitment to tackling the issue of food waste and promoting a circular economy has sparked the emergence of numerous initiatives and organizations dedicated to making a meaningful difference. These trailblazers are at the forefront of innovative strategies and collaborative endeavors aimed at reshaping the way we produce, distribute, and consume food. Their collective efforts represent a pivotal shift towards a more sustainable and responsible future.
Food Recovery Networks: Organizations like Food Rescue US and Second Harvest are spearheading food recovery efforts. They work closely with restaurants, supermarkets, and food producers to redirect surplus food to those in need rather than letting it go to waste. By facilitating the efficient redistribution of edible but unsellable food, they simultaneously alleviate hunger and reduce food waste.
Consumer Education Campaigns: Initiatives such as Love Food Hate Waste and Save the Food are on a mission to raise awareness among consumers. They provide valuable resources, tips, and information to help individuals make informed choices about food storage, portion control, and reducing waste in their own homes.
Innovative Food Tech Startups: The tech-savvy innovators in the food industry are creating cutting-edge solutions to prevent food waste. Apps like Too Good To Go connect consumers with surplus food from restaurants and grocery stores at discounted prices, reducing food waste while offering savings to consumers.
Circular Economy Alliances: Organizations like the Ellen MacArthur Foundation are leading the charge in promoting circular economy principles across various industries, including food. They advocate for a systemic shift towards regenerative agriculture, sustainable packaging, and responsible supply chain practices that minimize waste and environmental impact.
Zero-Waste Grocery Stores: Zero-waste grocery stores are gaining momentum worldwide. These innovative retailers, such as The Fillery and Unverpackt, encourage consumers to bring their reusable containers to shop for bulk items, significantly reducing single-use packaging and food waste.
Food Redistribution Platforms: Technology-driven platforms like OLIO and Food Cowboy connect businesses with surplus food to nearby charities and food banks. These platforms streamline the process of food donation, making it easier for food producers and retailers to contribute to the fight against hunger and waste.
Government Initiatives: Many governments are actively involved in food waste reduction efforts. They implement policies, regulations, and incentives to encourage businesses and individuals to reduce their food waste. Examples include tax incentives for food donations and strict landfill diversion targets.
Collaborative Partnerships: Partnerships between food producers, retailers, nonprofits, and governmental agencies have become a driving force in food waste reduction. Collaborative initiatives bring diverse expertise and resources to the table, fostering innovative solutions and amplifying their impact.
Food Waste Challenges: Competitions and challenges, such as the Food Waste Reduction Challenge by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), incentivize businesses and entrepreneurs to develop novel technologies and strategies for minimizing food waste.
Certifications and Labels: Certifications like “Food Loss and Waste Standard” by the World Resources Institute and “Zero Food Waste” labels on products encourage businesses to adopt responsible practices and make food waste reduction a part of their brand identity.
These initiatives and organizations are not only tackling the pressing issue of food waste but also inspiring a global movement towards a more sustainable and circular approach to food production and consumption. Their collective efforts serve as a testament to the power of collaboration, innovation, and shared responsibility in addressing one of the most critical challenges of our time.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Sustainable Materials Management | US EPA

This organization champions the circular economy globally and works with businesses to redesign their operations, including those in the food sector.
At the heart of this global movement towards a circular economy lies a dynamic organization dedicated to championing this transformative vision. This organization serves as a beacon of change, rallying businesses across sectors, including the food industry, to rethink, redesign, and reimagine their operations in alignment with circular economy principles.
In the realm of food, the challenge is multifaceted, and the stakes are high. The traditional linear model of food production, distribution, consumption, and disposal has proven unsustainable, generating enormous food waste, depleting natural resources, and contributing to climate change. The organization recognizes that addressing these challenges requires a holistic approach, one that not only reduces waste but also regenerates ecosystems, fosters innovation, and enhances social and economic well-being.
To catalyze change within the food sector, the organization engages with businesses of all sizes, from multinational corporations to local enterprises, offering guidance, resources, and a roadmap for transformation. It begins by encouraging businesses to assess their entire value chain, identifying opportunities to reduce waste, improve resource efficiency, and enhance the overall sustainability of their operations.
One key area of focus is food loss and waste reduction. The organization works closely with food producers, manufacturers, retailers, and foodservice providers to implement strategies that minimize losses throughout the supply chain. This involves everything from optimizing harvest and storage practices on farms to implementing inventory management systems in supermarkets and hotels.
Additionally, the organization advocates for innovative solutions to repurpose food waste, diverting it from landfills and transforming it into valuable resources. Composting, for instance, can turn organic waste into nutrient-rich soil amendments, while anaerobic digestion can capture biogas for energy production.
Circular economy principles also drive product and packaging design in the food industry. The organization encourages businesses to create products that are not only functional and safe but also durable, repairable, and recyclable. This approach reduces the need for constant replacement and minimizes waste.
Moreover, the organization facilitates collaboration and knowledge sharing among businesses within the food sector. Through conferences, workshops, and industry partnerships, it fosters an environment of innovation and shared learning. Businesses can draw inspiration from one another, discovering new ways to embrace circularity and drive positive change.
Furthermore, the organization advocates for policies and regulations that support circular economy practices in the food industry. It engages with governments and policymakers to promote incentives for businesses to adopt sustainable practices and reduce waste.
In conclusion, this organization stands as a powerful force for change within the food industry and across sectors. It empowers businesses to embark on a journey towards circularity, reimagining their operations to minimize waste, conserve resources, and foster sustainability. In doing so, it not only champions a more sustainable and ethical future for the food sector but also contributes to a broader global shift towards a circular economy that benefits both people and the planet.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: CIRCULAR ECONOMY IN INDIA: RETHINKING GROWTH FOR …

This nonprofit organization in the United States recovers surplus produce from farms, farmers markets, and other sources, redistributing it to hunger relief agencies.
This nonprofit organization in the United States recovers surplus produce from farms, farmers markets, and other sources, redistributing it to hunger relief agencies. Their mission extends beyond the simple act of redistributing food; it’s about tackling food waste at its source while addressing the critical issue of food insecurity.
At the heart of their work is a commitment to reducing food waste within the agricultural supply chain. They collaborate closely with farmers to identify crops that might otherwise go to waste due to cosmetic imperfections, overproduction, or market fluctuations. By rescuing these surplus crops, they not only prevent them from ending up in landfills but also help farmers recoup some of their losses, contributing to the economic sustainability of local agriculture.
One of their innovative approaches is the use of gleaning, a practice that harks back to historical traditions. Volunteers are mobilized to harvest crops that may have been left unharvested due to labor shortages or the inability to find a market. This not only salvages nutritious food but also fosters community engagement and awareness about food waste issues.
Their distribution network is a well-oiled machine that ensures rescued produce reaches those in need promptly. Partnering with hunger relief agencies, shelters, and community organizations, they bridge the gap between surplus food and individuals facing food insecurity. These partnerships are crucial in efficiently and equitably distributing food to the most vulnerable communities.
Furthermore, this organization actively engages in advocacy and education efforts. They work to raise awareness about food waste, its environmental consequences, and its impact on hunger. By advocating for policy changes and promoting responsible food consumption, they aim to create a more sustainable and equitable food system.
Their impact extends beyond food recovery. By addressing the root causes of food waste and food insecurity, they contribute to a more resilient and sustainable food system. Their work not only feeds the hungry but also inspires communities to rethink their relationship with food and strive for a world where surplus produce is never wasted while people go hungry.
In conclusion, this nonprofit organization in the United States stands as a shining example of how grassroots efforts can make a significant difference in the fight against food waste and hunger. Their holistic approach, encompassing food recovery, community engagement, advocacy, and education, exemplifies the potential for positive change within our food system. Through their tireless efforts, they not only salvage nutritious food but also sow the seeds of awareness and transformation in the way we value and share our resources.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here EU actions against food waste

In the UK, WRAP focuses on reducing food waste and promoting sustainability throughout the supply chain.
In the United Kingdom, the Waste and Resources Action Programme (WRAP) stands as a pioneering organization with a multifaceted mission that extends far beyond its borders. At its core, WRAP is a driving force dedicated to reducing food waste and championing sustainability throughout the intricate web of the supply chain.
One of WRAP’s most compelling contributions is its relentless pursuit of food waste reduction. In a world where millions go hungry while vast quantities of food are discarded, WRAP’s efforts serve as a beacon of hope. It collaborates with businesses, governments, and communities to tackle food waste at every juncture of the supply chain. This spans from the initial stages of production and distribution to the final moments when consumers make choices about food consumption and disposal.
WRAP’s approach is marked by innovation and pragmatism. It works closely with retailers, food manufacturers, and hospitality sectors to optimize processes, reduce overproduction, and minimize food losses. By sharing best practices, developing food waste reduction strategies, and promoting the use of surplus food to combat hunger, WRAP has played a pivotal role in reshaping the food industry’s approach to waste.
However, WRAP’s impact extends well beyond food waste alone. Sustainability is woven into the very fabric of its mission. It recognizes that food production and distribution are intrinsically linked to the environment and society. As such, WRAP places an emphasis on sustainability across the supply chain. This includes advocating for sustainable sourcing, responsible packaging, and energy efficiency within the food industry.
Moreover, WRAP operates at a systemic level, influencing policy, and driving transformative change. It collaborates with governments to shape regulations and standards that promote sustainability and reduce waste. This partnership approach is instrumental in creating an enabling environment for the adoption of circular economy principles in the food sector.
In the UK, WRAP’s influence has been profound. It has catalyzed a shift in mindset, inspiring businesses and consumers alike to embrace a more sustainable and responsible approach to food. The organization’s guidance and initiatives have led to tangible reductions in food waste and resource use, contributing to a more resilient and environmentally conscious food industry.
As the world grapples with the complex challenges of resource scarcity and environmental degradation, WRAP’s work serves as a testament to the power of collective action and a shared commitment to sustainability. Its ongoing efforts are not just shaping the UK’s approach to food waste and sustainability; they are setting an inspiring example for nations and organizations worldwide, illustrating how collaboration and innovation can drive positive change in the global pursuit of a more sustainable and responsible food system.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: WRAP – The Climate Crisis: Act Now
This industry association promotes the use of upcycled ingredients, which are created from food that would otherwise go to waste, in food products.
This industry association plays a pivotal role in advancing sustainable practices within the food industry by championing the use of upcycled ingredients. The concept of upcycled ingredients represents a powerful and innovative approach to combating food waste while simultaneously fostering creativity in food product development. Here are several key aspects and extensions of their mission:
Economic and Environmental Benefits: The promotion of upcycled ingredients is not only environmentally responsible but also economically advantageous. By utilizing ingredients that would otherwise be discarded, food businesses can reduce production costs and minimize their environmental footprint. This approach aligns with the principles of a circular economy, where resources are used efficiently and waste is minimized.
Diverse Applications: Upcycled ingredients offer versatility and can be integrated into a wide range of food products. From snacks and beverages to baked goods and sauces, these ingredients can enhance the nutritional profile, flavor, and texture of foods while reducing food waste.
Nutritional Enhancement: Upcycled ingredients often bring added nutritional benefits to food products. For instance, ingredients derived from surplus fruits and vegetables can enhance the vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber content of foods, contributing to healthier and more sustainable diets.
Consumer Appeal: Consumers increasingly value sustainability and responsible consumption. The use of upcycled ingredients in food products aligns with these values, making products more appealing to socially conscious consumers. Transparent labeling and communication about the use of upcycled ingredients can further enhance consumer trust.
Innovation and Collaboration: The promotion of upcycled ingredients encourages innovation within the food industry. It inspires chefs, food scientists, and product developers to think creatively about utilizing food resources efficiently. Additionally, it fosters collaboration between food businesses, suppliers, and organizations dedicated to reducing food waste.
Education and Awareness: The industry association can play a vital role in educating its members and the broader food industry about the benefits and opportunities associated with upcycled ingredients. This includes providing resources, case studies, and best practices for incorporating these ingredients into product formulations.
Regulatory Advocacy: The association can advocate for regulatory and policy changes that support the use of upcycled ingredients. This can include lobbying for incentives, tax breaks, or labeling standards that incentivize businesses to adopt sustainable practices.
Market Development: Promoting upcycled ingredients can help create a market demand for these products. Encouraging retailers, restaurants, and foodservice providers to offer products containing upcycled ingredients can stimulate market growth and investment in sustainable food solutions.
Research and Development: Investment in research and development of upcycled ingredients can lead to the discovery of novel applications and processing techniques. This can result in the development of even more innovative and sustainable food products.
In conclusion, the industry association’s commitment to promoting upcycled ingredients represents a significant step toward reducing food waste and advancing sustainability in the food industry. Their efforts encompass economic, environmental, and nutritional benefits, fostering innovation and collaboration within the industry while appealing to conscientious consumers. By continuing to advocate for and support the use of upcycled ingredients, the association contributes to a more sustainable and responsible food system that benefits both businesses and the planet.
You can also read more about this here: Defining upcycled food: The dual role of upcycling in reducing food …

Conclusion
The fight against food waste is a critical component of building a more sustainable and ethical food system. Circular economy initiatives offer a promising path forward by addressing food waste from multiple angles. By reducing, reusing, recycling, and rethinking how we produce and consume food, we can create a more resilient and responsible food ecosystem that benefits both people and the planet. It’s a journey that requires the collective efforts of individuals, businesses, and governments to achieve a future with less food waste and more responsible resource use.
The battle against food waste stands at the forefront of the global effort to construct a more sustainable, ethical, and responsible food system. It’s a multifaceted challenge that necessitates innovative solutions, and circular economy initiatives emerge as a promising pathway toward achieving substantial progress in this arena.
Circular economy principles center on the concept of regenerating, restoring, and renewing resources within a closed-loop system, thereby reducing waste and conserving valuable resources. When applied to the issue of food waste, these principles offer a comprehensive and holistic approach.
First and foremost, circular economy initiatives emphasize the importance of reducing food waste at its source. This involves a shift in mindset and practices across the entire food supply chain, from production to consumption. Farmers, for instance, can implement more precise farming techniques to minimize crop losses, while food manufacturers can optimize production processes to reduce overproduction and improve inventory management.
Secondly, the circular economy encourages the reuse of surplus food. This entails diverting edible surplus away from landfills and redirecting it to those in need through food banks and other charitable organizations. By reusing excess food, we not only combat food waste but also address the issue of food insecurity that plagues communities around the world.
Recycling is another crucial aspect of circular economy initiatives in the context of food waste. Organic waste can be repurposed into valuable resources like compost or bioenergy through advanced recycling techniques. This not only reduces landfill waste but also creates environmentally friendly alternatives for fertilizers and energy production.
Furthermore, rethinking the way we produce and consume food is essential. Innovations such as plant-based and lab-grown meat, sustainable packaging, and farm-to-table practices are examples of how circular economy principles can inspire novel approaches to food production and distribution.
Importantly, the journey towards a future with less food waste and more responsible resource use is a collective effort. Individuals can contribute by reducing food waste at home, supporting local food systems, and making sustainable food choices. Businesses can implement circular economy practices within their operations, from sourcing ingredients to managing surplus food responsibly. Governments play a pivotal role in setting policies and regulations that encourage and incentivize these practices.
In conclusion, circular economy initiatives hold the potential to revolutionize the way we approach food waste and create a more sustainable, resilient, and ethical food ecosystem. By reducing, reusing, recycling, and rethinking our food production and consumption patterns, we can contribute to a brighter future for both people and the planet. This journey toward responsible resource use requires the collective dedication of individuals, businesses, and governments, and it represents a critical step toward a more sustainable world.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Circular economy strategies for combating climate change and other …
More links
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Fighting food waste using the circular economy
