Standards guide organizations in identifying and assessing information security risks. This involves evaluating potential threats, vulnerabilities, and their potential impact on operations.
Information security standards are essential for organizations as they provide a structured framework for identifying, assessing, and managing risks to protect sensitive data and maintain business continuity. This involves a systematic process of evaluating potential threats, vulnerabilities, and their potential impact on operations. By following these standards, organizations can proactively address security concerns, implement necessary safeguards, and create a robust security posture.
Furthermore, these standards often require organizations to conduct risk assessments periodically or in response to significant changes in their IT environment. This ongoing vigilance ensures that potential risks are continually monitored and mitigated, reducing the likelihood of security breaches and data compromises.
In a world where data is a valuable asset and cyber threats are ever-evolving, adherence to information security standards is crucial for safeguarding an organization’s reputation, customer trust, and bottom line. It’s not just a matter of compliance; it’s a strategic investment in protecting the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here NIST Risk Management Framework | CSRC
Standards promote the development of clear security policies and procedures that outline best practices for safeguarding data and systems.
The implementation of standards goes beyond mere adherence; it serves as a catalyst for developing robust security policies and procedures. Here’s how standards play a pivotal role in shaping and strengthening security measures:
Comprehensive Framework: Standards provide a comprehensive framework for addressing security concerns. They outline the fundamental elements that need to be considered in security policies, ensuring that nothing vital is overlooked.
Best Practices: Standards are often developed based on industry best practices. Incorporating these standards into security policies means that organizations are automatically adopting tried-and-true methods for safeguarding data and systems.
Risk Assessment: Standards often require organizations to conduct thorough risk assessments. This process identifies vulnerabilities and threats, allowing organizations to tailor their security policies to address their specific risks effectively.
Adaptability: Security threats are continually evolving. Standards are designed to be adaptable and responsive to these changes. As new threats emerge, standards are updated, ensuring that security policies stay relevant and effective.
Consistency: Standards provide a basis for consistency. When different organizations within an industry or sector follow the same standards, it creates a level playing field and promotes a unified approach to security.
Measurable Objectives: Standards often include specific requirements and metrics for compliance. This makes it easier for organizations to set measurable objectives within their security policies, helping them gauge their level of preparedness and track improvements.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: In many cases, compliance with security standards is a legal or regulatory requirement. Therefore, integrating these standards into security policies helps organizations remain compliant with the law, avoiding potential legal issues.
Auditing and Certification: Many organizations seek external audits and certifications to verify their security measures. Compliance with recognized standards is a significant factor in achieving these certifications, providing third-party validation of an organization’s security policies.
Continuous Improvement: Standards encourage a culture of continuous improvement. Organizations that incorporate standards into their security policies are more likely to regularly assess and enhance their security measures, staying ahead of emerging threats.
Customer Trust: Demonstrating adherence to well-established security standards can enhance customer trust. Customers feel more secure knowing that a company has implemented recognized security measures to protect their data.
Competitive Advantage: In some industries, adhering to robust security standards can be a competitive advantage. Organizations that prioritize security and demonstrate it through compliance with standards may attract more business and partnerships.
Global Reach: Many security standards have international recognition. This means that organizations can use these standards to ensure the security of their operations and data, whether they operate locally or globally.
In essence, standards serve as a blueprint for creating security policies and procedures that are effective, adaptable, and aligned with industry best practices. They provide organizations with the guidance and structure needed to build and maintain robust security postures in an ever-evolving threat landscape.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Enterprise Information Security Policies and Standards | Mass.gov

Controlling access to sensitive information is crucial. Standards define measures to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to critical data.
Absolutely, let’s extend that idea:
In today’s interconnected digital world, the safeguarding of sensitive information is paramount. The implementation of information security and cybersecurity standards is instrumental in controlling access to critical data. These standards provide a comprehensive framework for establishing access controls, encryption protocols, and user authentication processes. By adhering to these standards, organizations can confidently protect their digital assets, mitigate unauthorized access, and fortify their defenses against evolving cyber threats.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: SP 800-53 Rev. 5, Security and Privacy Controls for Information …
In the event of a security incident, standards outline procedures for rapid response, containment, and recovery to minimize damage and downtime.
Standards are essential in the realm of cybersecurity and incident management. They serve as a blueprint for organizations to follow in the event of a security incident. These standards provide clear guidelines for swift response, effective containment, and efficient recovery processes. By adhering to established cybersecurity standards, businesses can minimize the potential damage caused by security incidents, reduce downtime, and safeguard sensitive data. In a digital age where cyber threats are prevalent, having well-defined procedures and practices outlined by standards is crucial for protecting sensitive information and ensuring business continuity.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here A Cyber Incident Response and Recovery Framework to Support …
Standards provide guidance on identifying, patching, and mitigating vulnerabilities in software and systems to prevent exploitation by cybercriminals.
“Standards play a pivotal role in bolstering cybersecurity. They offer comprehensive guidance for identifying, patching, and mitigating software and system vulnerabilities, safeguarding against cybercriminal exploitation.”
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF)

Protecting networks from unauthorized access and intrusions is paramount. Standards define best practices for network security architecture and monitoring.
In an increasingly interconnected world, safeguarding networks from unauthorized access and potential intrusions is of utmost importance. Standards provide a vital framework for designing robust network security architecture and establishing effective monitoring protocols. These guidelines ensure that organizations can proactively defend their digital assets and sensitive information, thereby bolstering their cybersecurity posture. As the threat landscape continues to evolve, adherence to well-established standards remains a crucial element in the ongoing battle against cyber threats and data breaches.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: ISO/IEC 27001 Standard – Information Security Management Systems
Cybersecurity standards advocate for ongoing employee training to ensure that the human element does not become a weak link in the security chain.
In today’s digital age, the human factor is both an asset and a potential vulnerability in cybersecurity. Here’s why continuous employee training is essential:
Evolving Threat Landscape: Cyber threats are constantly evolving, becoming more sophisticated and adaptive. Employees need regular training to stay updated on the latest threats and attack techniques.
Phishing Prevention: Phishing attacks, where attackers trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, are prevalent. Training helps employees recognize phishing attempts and avoid falling victim to them.
Password Management: Weak passwords are a common entry point for cyberattacks. Training teaches employees how to create strong, unique passwords and employ password management tools effectively.
Data Protection: Employees need to understand their role in safeguarding sensitive data. Training reinforces the importance of data protection, including encryption, data classification, and secure file sharing.
Incident Response: In the event of a cyber incident, a well-trained workforce can respond promptly and effectively, minimizing damage and downtime.
Compliance Requirements: Many industries have regulatory compliance requirements related to cybersecurity. Ongoing training ensures that employees understand and adhere to these regulations.
Cultivating a Cybersecurity Culture: Regular training fosters a culture of cybersecurity within an organization. Employees become more vigilant, proactive, and committed to protecting the organization’s digital assets.
Remote Work Challenges: With the rise of remote work, employees access company systems from various locations and devices. Training helps them maintain security even outside the office environment.
Third-Party Risks: Employees who work with third-party vendors or partners need to be aware of the risks associated with sharing data or resources. Training covers best practices for secure collaborations.
Human Firewall: Ultimately, well-trained employees serve as a robust human firewall, strengthening an organization’s overall cybersecurity posture.
In summary, continuous employee training is not just a best practice but a critical component of a holistic cybersecurity strategy. It empowers employees to be vigilant, proactive, and capable defenders against ever-evolving cyber threats.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Security Awareness and Training | HHS.gov

Standards are increasingly incorporating AI and machine learning to detect and respond to threats more effectively.
Standards are embracing the power of AI and machine learning to proactively identify and address threats with greater precision and efficiency. This integration of advanced technology enhances safety measures, providing a robust defense against emerging risks in various industries.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Ethical and legal challenges of artificial intelligence-driven …
This approach assumes that no one, whether inside or outside the organization, should be trusted by default, and strict access controls are enforced.
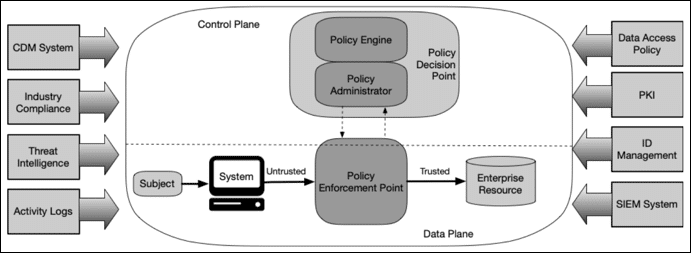
The principle of assuming zero trust is a fundamental shift in how organizations approach cybersecurity. In a traditional security model, there’s a default level of trust within an organization’s network once a user gains access. However, in the zero-trust model, this assumption is entirely discarded. Here, trust is never implied, and strict access controls are continuously enforced for all users, devices, and applications, regardless of their location – whether inside or outside the organization.
This approach recognizes that threats can originate both internally and externally, making it essential to scrutinize all activities and connections within the network. The zero-trust model operates on the premise that potential attackers might already be present within the network or can infiltrate it, requiring constant verification and authentication.
To implement zero trust, organizations adopt practices such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), continuous monitoring, strict identity verification, and micro-segmentation of the network. Each user and device must consistently prove their identity and adhere to predefined security policies. Any unusual or unauthorized activity triggers immediate responses, such as access denial or alerts to security teams.
By embracing the zero-trust model, organizations prioritize security at all levels and reduce the risk of insider threats, data breaches, and unauthorized access. It’s a proactive and adaptive approach to cybersecurity that aligns with the evolving threat landscape, ensuring that trust is never assumed and security remains a top priority.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: What is Zero Trust Security? Principles of the Zero Trust Model
More links
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: ISO/IEC 27001 Standard – Information Security Management Systems