Introduction
The labor market in Europe is a complex and dynamic landscape that reflects the economic, social, and political developments in the region. Understanding the trends and challenges within this market is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and job seekers alike. In this article, we will delve into the key labor market and employment trends in Europe, examining both the opportunities and challenges that shape the world of work on the continent.
The labor market in Europe is a multifaceted arena, constantly shaped by a confluence of factors ranging from economic shifts to social dynamics and political decisions. Its complexity is emblematic of the broader European context, where diverse nations and cultures intersect. To navigate this intricate landscape effectively, it’s imperative for policymakers, businesses, and job seekers to comprehend the prevailing trends and challenges that define the world of work in Europe.
One of the prominent trends in Europe’s labor market is the evolution of work arrangements. Traditional employment models are giving way to greater flexibility and diversity. The gig economy, remote work, and freelancing have gained prominence, offering new opportunities for both employers and workers. While these arrangements provide flexibility, they also raise questions about job security, social protections, and labor rights.
Another noteworthy trend is the growing demand for digital skills. As technology continues to reshape industries and business operations, proficiency in digital tools and technologies has become a prized asset. Europe is investing in upskilling and reskilling programs to ensure that its workforce remains competitive in the digital age. Bridging the digital skills gap is essential for fostering innovation and economic growth.
On the demographic front, Europe faces the challenges of an aging population and declining birth rates. This demographic shift has implications for labor supply, pension systems, and healthcare. It underscores the importance of workforce participation among older adults and immigration policies to address skill shortages and sustain economic vitality.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has left a lasting imprint on Europe’s labor market. Remote work became the norm for many, prompting a reevaluation of workplace practices and a potential shift in urbanization trends. The pandemic also highlighted the importance of healthcare and the role of essential workers, sparking discussions about wages and labor conditions.
Europe’s labor market trends also intersect with environmental considerations. The transition to a green economy and sustainability initiatives are driving job creation in renewable energy, environmental protection, and green technologies. This transition not only addresses climate change but also presents opportunities for a more sustainable and inclusive labor market.
In conclusion, Europe’s labor market is a dynamic and evolving arena, shaped by a multitude of factors and trends. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals seeking to navigate the world of work on the continent. By staying attuned to labor market trends and challenges, Europe can foster inclusive growth, social cohesion, and economic resilience in an ever-changing global landscape.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: THE IMPACT OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ON THE FUTURE OF …
Labor Market Flexibility
One of the defining characteristics of the European labor market is its flexibility. European countries vary in their approach to labor market regulations, with some favoring strict employment protections and others adopting more flexible arrangements. The gig economy, characterized by short-term contracts and freelance work, has gained prominence in recent years. While providing opportunities for flexible work arrangements, it also raises questions about job security and workers’ rights.
The European labor market’s flexibility is indeed a distinctive feature, with diverse approaches to labor regulations across countries. While some prioritize stringent employment protections, others embrace flexible arrangements. The gig economy, marked by its short-term contracts and freelance opportunities, has witnessed substantial growth. While it offers flexibility, it also sparks debates around job security and safeguarding workers’ rights, underscoring the need for a balanced approach that ensures both flexibility and protection in the evolving world of work.
Skills Mismatch
Europe faces a persistent challenge of skills mismatch in the labor market. Despite high levels of education and training, there is often a gap between the skills possessed by job seekers and the skills demanded by employers. This mismatch can lead to high youth unemployment rates in some regions while industries struggle to find qualified workers. Addressing this issue requires a concerted effort from educational institutions, employers, and policymakers to align skills development with market needs.
Certainly, let’s expand on that idea:
Skills Mismatch and its Remedies:
The issue of skills mismatch in Europe’s labor market underscores the importance of aligning educational and training programs with the evolving demands of industries. As the Fourth Industrial Revolution ushers in technological advancements and automation, traditional skills are rapidly evolving. To bridge this gap, several strategies are being implemented:
Education and Training Reforms: European nations are revising their education systems to emphasize not only academic knowledge but also practical, job-relevant skills. Vocational and technical education programs are gaining prominence, offering students hands-on experience and industry-specific training.
Lifelong Learning: Encouraging a culture of lifelong learning is vital. Workers are encouraged to upskill and reskill throughout their careers to adapt to changing job requirements. Online courses, workshops, and industry certifications are becoming more accessible.
Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between governments, educational institutions, and businesses is fostering stronger connections between the classroom and the workplace. These partnerships ensure that curricula are aligned with industry needs, providing students with the skills required for today’s job market.
Labor Market Intelligence: Utilizing data-driven insights into labor market trends, governments and institutions can make informed decisions about skills development. By identifying areas of high demand and skills shortages, resources can be directed more effectively.
Supporting Career Guidance: Effective career guidance can help individuals make informed choices about their education and career paths. It also promotes awareness of emerging industries and job opportunities.
Cross-Border Mobility: Encouraging labor mobility within the European Union is another approach. Workers can move to regions where their skills are in demand, reducing unemployment disparities across the continent.
In addressing the challenge of skills mismatch, Europe aims not only to reduce unemployment but also to enhance its workforce’s overall adaptability and competitiveness in the global economy. Through these strategies, Europe is working to ensure that its labor market remains resilient and responsive to the demands of the future.
Digital Transformation
The ongoing digital transformation is reshaping industries and job roles across Europe. Automation, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things are changing the way work is done, affecting both routine and specialized tasks. While automation has the potential to improve productivity and efficiency, it also raises concerns about job displacement. To thrive in this digital era, workers must adapt and acquire digital skills relevant to the evolving job market.
“The evolving digital landscape in Europe is ushering in a new era of work. As automation and AI redefine industries, workers must embrace lifelong learning to stay relevant. Upskilling and reskilling are not just options; they are essential for career resilience in the digital age.”
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: The global digital skills gap: Current trends and future directions

Aging Workforce
Europe is experiencing demographic shifts, with an aging population and a declining birth rate. This demographic trend has significant implications for the labor market. As the workforce ages, there is a growing need to ensure that older workers can continue to participate in the labor force. Policies promoting age-friendly workplaces and supporting the retraining of older employees are essential for harnessing the potential of this demographic group.
The demographic landscape of Europe is undergoing a profound transformation characterized by two interconnected trends: an aging population and a declining birth rate. These demographic shifts hold significant implications for Europe’s labor market, as they reshape the composition and dynamics of the workforce.
The aging population, while emblematic of longer life expectancies and improved healthcare, poses both opportunities and challenges for the labor market. On one hand, older workers bring a wealth of experience, skills, and institutional knowledge to the workplace. Their contributions are invaluable in maintaining productivity and mentoring younger colleagues. However, ensuring that older workers can continue to participate in the labor force effectively requires proactive policies and measures.
Age-friendly workplaces have emerged as a critical component of addressing this demographic shift. These are workplaces that recognize and accommodate the needs of older employees, whether it be through ergonomic adjustments, flexible work arrangements, or phased retirement options. By creating environments that support the well-being and productivity of older workers, businesses can retain valuable talent and promote intergenerational collaboration.
Moreover, retraining and upskilling initiatives are indispensable in facilitating the continued labor force participation of older individuals. As technology and job requirements evolve, it’s crucial to equip older workers with the skills needed to remain competitive. Lifelong learning programs, vocational training, and career development opportunities can empower older employees to adapt to changing industries and seize new career prospects.
Additionally, policies that combat age discrimination are fundamental to ensuring that older workers are not sidelined or marginalized in the labor market. Enforcing anti-discrimination laws and promoting inclusive hiring practices foster a work environment where talent is recognized and valued, regardless of age.
Harnessing the potential of an aging workforce is not just a matter of social responsibility but also economic prudence. Europe’s labor market can benefit immensely from the wealth of knowledge and experience older workers bring to the table. By implementing age-friendly policies, investing in skills development, and fostering inclusive workplaces, Europe can turn demographic challenges into opportunities, ensuring a resilient and productive labor force that contributes to the continent’s economic prosperity and social well-being.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: The future of work in Europe | McKinsey
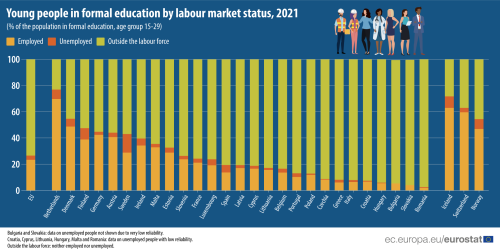
Green Jobs and Sustainability
Sustainability and climate change have become top priorities for Europe. The transition to a green economy has opened up opportunities in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and environmentally friendly technologies. Green jobs, which focus on reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability, are on the rise. These jobs not only contribute to environmental goals but also offer employment prospects in a rapidly changing economic landscape.
Sustainability and addressing climate change have ascended to the forefront of Europe’s agenda. The shift toward a green economy has unlocked significant opportunities in sectors like renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and eco-friendly technologies. This transformation has given rise to green jobs, which center around minimizing environmental impact and advancing sustainability. Beyond their environmental benefits, these jobs are vital for economic growth and job creation, positioning individuals and industries to thrive in an ever-evolving economic landscape while contributing to a more sustainable future.

The Impact of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic had a profound impact on the European labor market. Lockdowns and restrictions led to job losses and disruptions across various industries. Remote work became the norm for many, highlighting the importance of digital skills. As Europe recovers from the pandemic, there is an opportunity to reshape the labor market with a focus on resilience, adaptability, and inclusivity.
Certainly, let’s explore this idea further:
Adapting to the Post-Pandemic Labor Market:
The COVID-19 pandemic served as a catalyst for transformation in Europe’s labor market. While it posed unprecedented challenges, it also accelerated certain trends and prompted a reevaluation of traditional work paradigms. Here are key considerations for reshaping the post-pandemic labor market:
Remote Work and Digital Skills: The pandemic underscored the importance of digital literacy and remote work capabilities. Many employees adapted to remote work, requiring proficiency in digital tools and online collaboration. To remain competitive, individuals and organizations must invest in upskilling and digital fluency.
Hybrid Work Models: The experience of remote work has led to a surge in interest in hybrid work models. This approach combines remote and office-based work, offering flexibility while maintaining the benefits of in-person collaboration. Companies are reevaluating their office spaces and adopting flexible policies.
Resilience and Adaptability: Resilience has emerged as a critical trait for individuals and organizations. Adapting to changing circumstances and acquiring new skills will be essential in a post-pandemic labor market. Lifelong learning and adaptability will be key drivers of success.
Inclusivity and Diversity: The pandemic exposed inequalities in the labor market, with certain groups disproportionately affected. To promote inclusivity, businesses are focusing on diversity and inclusion initiatives, equitable hiring practices, and ensuring that remote work opportunities are accessible to all.
Health and Well-being: Employee well-being has gained prominence. Mental health support, flexible work arrangements, and a focus on work-life balance are becoming integral to a healthy and productive workforce.
Green and Sustainable Jobs: Europe’s commitment to sustainability is shaping the labor market. Green jobs related to renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and environmental conservation are on the rise. The transition to a greener economy presents opportunities for job creation.
Government Support: Governments have played a crucial role in supporting the labor market during the pandemic. Continuing measures like job retention schemes, vocational training programs, and financial support for businesses will be pivotal in the recovery phase.
Entrepreneurship and Innovation: The pandemic has sparked entrepreneurial endeavors and innovation. Start-ups and small businesses are emerging as engines of job creation. Governments are providing support through funding and incubation programs.
As Europe navigates the aftermath of the pandemic, the labor market is poised for transformation. Adapting to new work models, prioritizing skills development, and fostering inclusivity will be central to shaping a resilient and adaptable labor force. The lessons learned during this period are guiding the way toward a more dynamic and responsive labor market in Europe.

Conclusion
The European labor market is a dynamic arena shaped by a multitude of factors, from technological advancements to demographic changes. Navigating these trends and challenges requires a collaborative effort between governments, businesses, educational institutions, and individuals. As Europe continues to evolve, so too will its labor market, offering both opportunities and responsibilities to all stakeholders involved. Adapting to these changes is essential for building a prosperous and inclusive future for European workers and businesses.
“The European labor market is undergoing a profound transformation. To harness its full potential, collaboration among governments, businesses, and individuals is paramount. With the right strategies in place, Europe can shape a labor market that embraces technological advancements, supports its workforce, and fosters inclusive growth.”
More links
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: The future of work in Europe | McKinsey
