Introduction
In the vast and intricate world of the food industry, ensuring the safety, quality, and integrity of food products is paramount. Regulatory compliance and adherence to industry standards are the cornerstones of this commitment. This article delves into the multifaceted realm of regulatory compliance and how it shapes the global food industry.
Within the expansive and intricate domain of the food industry, safeguarding the safety, quality, and integrity of food products stands as an absolute imperative. At the heart of this commitment lie the fundamental pillars of regulatory compliance and adherence to industry standards. This article embarks on a comprehensive exploration of the multifaceted landscape of regulatory compliance, unveiling its profound significance and far-reaching impact on shaping the global food industry.
In a world where the food supply chain traverses borders and continents, ensuring that every step of the journey meets rigorous regulatory standards is essential. From the farm to the processing facility, through transportation, and ultimately to the consumer’s plate, a web of regulations and guidelines guides each stage of food production and distribution. These regulations are not arbitrary; they are meticulously crafted to safeguard public health, consumer rights, and environmental sustainability.
One of the paramount aspects of regulatory compliance is food safety. Foodborne illnesses can have severe consequences, both in terms of human health and economic repercussions. Regulatory bodies worldwide establish stringent guidelines to minimize the risks associated with foodborne pathogens, contaminants, and hazards. Compliance with these guidelines is not just a legal obligation; it’s a moral and ethical responsibility to protect the well-being of consumers.
Moreover, regulatory compliance extends to food quality and authenticity. Consumers have the right to expect that the products they purchase meet the promised standards of quality, taste, and composition. Whether it’s the purity of organic products, the authenticity of regional specialties, or the accuracy of nutritional labeling, adherence to these standards fosters trust between consumers and food producers.
The global food industry is a complex tapestry of stakeholders, from multinational corporations to local artisans. Regulatory compliance ensures a level playing field, where all participants adhere to the same rules and standards. This fairness not only promotes competition but also safeguards consumers from deceptive practices and subpar products.
Furthermore, compliance with regulations is a fundamental aspect of international trade in food products. It enables the smooth flow of goods across borders, facilitates global market access, and supports economic growth. It’s not just about meeting the minimum requirements; it’s about striving for excellence and exceeding regulatory expectations to gain a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
However, navigating the labyrinth of food regulations can be daunting for businesses. Compliance demands an intricate understanding of local and international standards, rigorous record-keeping, and a commitment to continuous improvement. It’s a dynamic landscape that evolves in response to emerging risks, scientific advancements, and changing consumer expectations.
In conclusion, regulatory compliance is the bedrock upon which the global food industry stands. It ensures the safety, quality, and integrity of food products while promoting fairness, trust, and economic prosperity. This multifaceted realm of compliance is not just a legal obligation; it’s a commitment to the well-being of consumers, the sustainability of the industry, and the global movement toward a safer and more transparent food supply chain.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: The Complex Regulatory Landscape for Natural Flavor Ingredients
The food industry operates within a web of regulations and standards that vary from one region to another. These regulations are established by government bodies, such as the FDA in the United States or the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in Europe. They are designed to safeguard public health, prevent foodborne illnesses, and maintain the integrity of food products.
The intricate tapestry of regulations and standards that envelop the food industry serves as a vital safeguard for consumers and a cornerstone of public health. These regulations, meticulously crafted and enforced by government bodies like the FDA in the United States or the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in Europe, represent a commitment to ensuring the safety, quality, and integrity of the food supply chain.
One of the primary objectives of these regulations is the prevention of foodborne illnesses. They lay out stringent guidelines for food handling, storage, transportation, and preparation, with a focus on minimizing the risk of contamination and the spread of pathogens. This emphasis on food safety extends from farm to fork, encompassing all stages of production and distribution.
To achieve these goals, regulatory agencies employ a multifaceted approach. They conduct inspections, audits, and sampling of food products, ensuring compliance with established standards. They also enforce labeling requirements, allergen declarations, and nutritional information to empower consumers with transparent and accurate data about the foods they purchase.
Additionally, regulations play a pivotal role in protecting consumers against food fraud and deceptive practices. They set the bar for ingredient authenticity, labeling accuracy, and product claims. For example, regulations may specify the minimum percentage of a particular ingredient in a product for it to be labeled as such. This level of precision ensures that consumers receive the products they expect and pay for.
Moreover, regulations extend their reach to aspects beyond safety. They encompass quality standards, such as the grading of meats or the classification of olive oils. These standards serve to maintain consistency and uniformity in food products, helping consumers make informed choices based on product attributes and quality.
In the global food market, regulations also facilitate trade by providing a common framework for safety and quality. Harmonized standards, like the Codex Alimentarius, are developed to promote international consistency, making it easier for food products to move across borders while upholding rigorous safety measures.
While regulations may at times seem complex and burdensome, they are fundamentally a reflection of society’s commitment to upholding the integrity of the food supply chain. They underscore the importance of transparency, accountability, and responsibility among all stakeholders, from food producers and distributors to retailers and consumers.
As the food industry continues to evolve, so too will the landscape of regulations and standards. Emerging technologies, changing consumer preferences, and global trade dynamics will necessitate ongoing adjustments and refinements. Nonetheless, the core mission of these regulations—to safeguard public health and ensure food safety and quality—will remain unwavering, serving as a bedrock upon which the food industry can build a future that is both innovative and secure.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Handbook on Product Standards and International Trade …

Food safety regulations are the bedrock of the food industry. They encompass a wide range of requirements, from the handling and processing of food to labeling and packaging standards. These regulations address critical aspects of food safety, including hygiene, sanitation, temperature control, and microbiological standards.
Comprehensive Food Safety Regulations: Safeguarding Consumer Health
Food safety regulations stand as the cornerstone of the food industry, acting as the guardians of public health and consumer trust. They constitute a comprehensive framework that leaves no aspect of food production, processing, and distribution to chance. Here, we delve deeper into the multifaceted world of food safety regulations and their pivotal role in ensuring the integrity of the global food supply.
1. The Spectrum of Food Safety
Food safety regulations encompass a spectrum of requirements that leave no room for compromise. They cover everything from the initial sourcing of raw materials to the final presentation of products to consumers. At every step, meticulous attention is paid to preventing contamination, ensuring hygiene, and maintaining the highest standards of quality.
2. Hygiene and Sanitation
Hygiene and sanitation are non-negotiable elements of food safety. Regulations dictate stringent measures for food handlers, including proper handwashing, the use of protective clothing, and the regular disinfection of surfaces and equipment. These measures are crucial in preventing the spread of pathogens that can cause foodborne illnesses.
3. Temperature Control
Temperature control is a critical aspect of food safety, particularly in the storage and transportation of perishable goods. Regulations stipulate precise temperature ranges for various food products, ensuring that they remain safe for consumption. This is especially vital for items like dairy products, meat, and seafood.
4. Microbiological Standards
Microbiological standards form the backbone of food safety. Regulations define acceptable levels of bacteria, yeasts, molds, and other microorganisms in food products. Stricter standards are imposed on products that are susceptible to rapid spoilage or the growth of harmful pathogens.
5. Contamination Prevention
Preventing contamination is a primary goal of food safety regulations. This involves strict separation of raw and cooked foods, rigorous cleaning and disinfection practices, and the use of food-safe packaging materials. Additionally, regulations require thorough cooking and reheating processes to eliminate harmful bacteria.
6. Labeling and Allergen Control
Food safety goes hand in hand with accurate labeling. Regulations mandate that food labels provide comprehensive information about ingredients, nutritional content, allergens, and expiration dates. Clear and informative labels empower consumers to make safe choices and avoid allergens that may harm their health.
7. Global Harmonization
In an increasingly interconnected world, global harmonization of food safety standards is a pressing concern. International organizations like the Codex Alimentarius Commission work tirelessly to establish common ground among nations, ensuring that food safety standards are consistent and globally recognized.
8. Challenges and Compliance
Achieving and maintaining compliance with food safety regulations is a continuous challenge for the food industry. It demands a commitment to rigorous testing, monitoring, and documentation. Food businesses invest significantly in training and technology to meet these requirements and safeguard the health of consumers.
Conclusion: A Commitment to Public Health
Food safety regulations represent a steadfast commitment to public health and consumer well-being. They are the invisible shield that protects consumers from the hidden dangers of contaminated food. In a world where food is an essential part of our daily lives, these regulations provide the assurance that the food we consume is safe, wholesome, and trustworthy.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Handbook on Product Standards and International Trade …

Quality standards are equally crucial in the food industry. They define the characteristics and attributes that food products must meet to be considered safe and of high quality. Quality control and assurance practices involve rigorous testing, inspections, and adherence to specifications throughout the production process.
In the intricate and essential world of the food industry, the establishment and maintenance of stringent quality standards stand as pillars of trust and assurance for consumers. These standards serve as the defining parameters that delineate the characteristics and attributes a food product must meet to be deemed safe, wholesome, and of impeccable quality. Quality control and assurance practices within the industry form an unyielding shield against compromise, encompassing a meticulous journey of testing, inspections, and unwavering adherence to precise specifications at every juncture of the production process.
Safety First: At the core of quality standards in the food industry is the unwavering commitment to safety. Ensuring that food products are free from contaminants, pathogens, and any potential hazards is paramount. Stringent safety measures, such as HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points), are implemented to identify and mitigate risks at every stage of production.
Consistency in Quality: Quality standards ensure that consumers receive food products that consistently meet their expectations. Whether it’s the taste, texture, appearance, or nutritional value, consumers rely on these standards to enjoy a familiar and reliable culinary experience every time they purchase a product.
Traceability and Transparency: Traceability is a fundamental aspect of quality control and assurance. Manufacturers and producers must be able to trace the origin of ingredients and components used in their products. This traceability not only aids in addressing safety concerns but also supports transparency, allowing consumers to make informed choices about the products they consume.
Compliance with Regulations: The food industry operates under a complex web of regulations and standards set by government authorities and industry organizations. These regulations ensure that food products meet minimum safety and quality requirements. Compliance is not optional; it’s a legal and ethical imperative for all food businesses.
Stringent Testing Protocols: Quality control involves rigorous testing protocols. Samples of products are regularly analyzed for a range of attributes, including microbiological safety, chemical composition, and sensory characteristics. These tests are conducted by specialized laboratories equipped with state-of-the-art technology.
Continuous Improvement: Quality assurance is not a static process; it’s a commitment to continuous improvement. Food businesses actively monitor and evaluate their processes to identify areas for enhancement. This dedication to improvement ensures that products evolve with changing consumer preferences and technological advancements.
Training and Education: Ensuring that all personnel involved in food production are well-trained and knowledgeable is essential. Training programs and ongoing education efforts instill a culture of quality throughout the organization, from farm to table.
Consumer Feedback Integration: Quality control and assurance practices actively incorporate consumer feedback. Whether through product reviews, surveys, or direct communication, consumer insights are invaluable for identifying areas of improvement and addressing any quality-related concerns.
Global Harmonization: In an increasingly interconnected world, there is a move toward global harmonization of food quality standards. This harmonization streamlines trade, ensures consistent quality expectations across borders, and enhances food safety on a global scale.
Public Trust and Brand Reputation: The meticulous adherence to quality standards not only protects public health but also safeguards the reputation and trust of food brands. Consumers gravitate toward brands known for their commitment to quality and safety.
In essence, quality standards in the food industry are not merely guidelines; they are the bedrock upon which consumer trust is built. They are the guardians of safety, consistency, and transparency, ensuring that every bite of food meets the highest standards of excellence. Quality control and assurance practices, with their unwavering dedication to precision, continue to be the unsung heroes of the food industry, guaranteeing that food remains a source of nourishment, pleasure, and unwavering confidence for consumers worldwide.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) Regulations – DataMyte
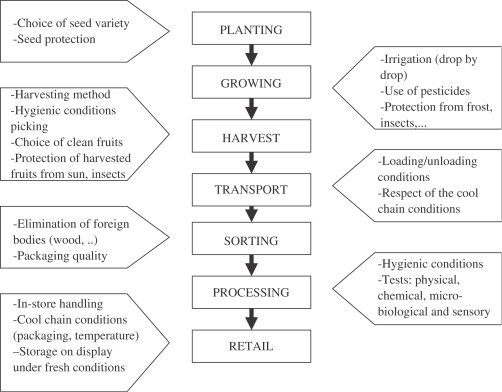
Food labeling regulations are essential for consumer transparency. They mandate accurate and informative labeling of food products, including ingredient lists, allergen information, nutritional content, and expiration dates. Clear labeling helps consumers make informed choices and ensures that products meet their dietary needs and preferences.
In the intricate dance between consumers and the food industry, food labeling regulations emerge as essential guardians of transparency. These regulations are not mere bureaucratic red tape; they are the threads that weave trust into the fabric of every food transaction, ensuring that consumers have the knowledge they need to make informed choices about the products they bring into their homes and onto their plates.
At the heart of food labeling regulations lies the principle of accuracy. They mandate that food products bear accurate and informative labels that leave no room for ambiguity or deception. Ingredient lists are a prime example of this commitment to clarity. Every component that contributes to a product’s composition must be disclosed, allowing consumers to know exactly what they are consuming.
Allergen information is another critical aspect of food labeling regulations. For individuals with food allergies or intolerances, this information is a lifeline. Clear and conspicuous allergen labeling can mean the difference between a safe, worry-free meal and a potentially life-threatening health crisis. It empowers consumers to make choices that align with their dietary restrictions and health needs.
Nutritional content labeling offers yet another layer of transparency. In an age where health-conscious consumers scrutinize nutritional profiles, these labels provide invaluable insights. They reveal the caloric content, macronutrient composition, and the presence of essential vitamins and minerals. Armed with this information, consumers can make choices that align with their dietary goals and preferences, whether they seek to maintain a balanced diet, reduce their sugar intake, or increase their fiber consumption.
Expiration dates, often overlooked but no less important, play a crucial role in ensuring food safety. Food labeling regulations mandate the inclusion of clear and accurate expiration dates, allowing consumers to gauge the freshness and safety of a product. This not only helps prevent foodborne illnesses but also reduces food waste by guiding consumers on when products should be consumed or discarded.
Food labeling regulations, in essence, empower consumers to take control of their dietary choices. They serve as a compass, guiding consumers through the labyrinth of food options and enabling them to navigate with confidence. Whether it’s a parent selecting a peanut-free snack for their child, an athlete assessing the protein content of an energy bar, or a health-conscious individual seeking to limit sodium intake, clear and accurate labeling ensures that products meet their specific needs and preferences.
Moreover, food labeling regulations foster a culture of accountability within the food industry. They signal to manufacturers and producers that honesty, accuracy, and transparency are non-negotiable standards. This not only safeguards consumers but also incentivizes the industry to innovate responsibly, creating products that not only taste good but also align with the health and dietary preferences of a diverse and discerning consumer base.
In conclusion, food labeling regulations are the unsung heroes of the modern food landscape. They are the guardians of consumer trust and transparency, ensuring that the products we purchase and consume are accurately represented and safe. They empower consumers to make informed choices, cater to dietary needs, and navigate a complex marketplace with confidence. In doing so, they contribute not only to the well-being of individuals but also to the integrity and sustainability of the entire food industry.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Exploring AI-Enabled Regulatory Compliance for Nutraceuticals …

In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical practices within the food industry. Regulations and industry standards now address issues such as responsible sourcing, eco-friendly packaging, and fair labor practices. These requirements reflect the increasing consumer demand for products that align with their values.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical practices within the food industry. Regulations and industry standards now address issues such as responsible sourcing, eco-friendly packaging, and fair labor practices. These requirements reflect the increasing consumer demand for products that align with their values.
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern food production and distribution. Responsible sourcing practices focus on ensuring that the ingredients used in food products are produced in ways that minimize harm to the environment and promote conservation. This includes efforts to reduce carbon emissions, protect biodiversity, and conserve natural resources. Consumers are not only looking for tasty and nutritious meals but also want assurance that their food choices have a positive impact on the planet.
Eco-friendly packaging has also gained prominence as consumers become more conscious of the environmental footprint of their food purchases. Food producers and retailers are exploring innovative packaging materials and designs that reduce waste, promote recyclability, and minimize single-use plastics. Packaging that is both functional and environmentally responsible has become a selling point for many consumers.
Fair labor practices are another critical aspect of ethical food production. Consumers increasingly want assurance that the people involved in producing their food are treated fairly and ethically. This includes fair wages, safe working conditions, and respect for human rights throughout the supply chain. Certifications and labeling schemes, such as Fair Trade, are helping consumers make informed choices about the products they purchase.
Furthermore, transparency in the food supply chain has become essential. Consumers are seeking detailed information about the origins of their food, its journey from farm to table, and the practices employed along the way. Labels and certifications that provide this information give consumers the confidence to make choices that align with their values.
The push for sustainability and ethical practices is not just consumer-driven; it’s also a response to global challenges such as climate change, resource scarcity, and social inequality. Governments and international organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of these issues and are enacting regulations and standards to promote responsible food production and distribution.
Moreover, food companies that prioritize sustainability and ethics are often seen as more attractive partners for collaborations and investments. Investors and stakeholders are increasingly considering environmental and social responsibility as key indicators of a company’s long-term viability and reputation.
In conclusion, the emphasis on sustainability and ethical practices within the food industry reflects both consumer demand and a broader recognition of global challenges. Responsible sourcing, eco-friendly packaging, fair labor practices, and transparency are no longer just trends but have become integral to the way food is produced, packaged, and distributed. This shift represents a positive transformation in the industry, where values-driven choices are driving meaningful change and shaping the future of food.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: How to Navigate the Ethical Risks of Doing Business in China

Given the global nature of the food industry, achieving harmonization of regulations and standards is an ongoing challenge. Organizations like the Codex Alimentarius Commission work to establish international food standards, guidelines, and codes of practice. These efforts aim to facilitate international trade and ensure consistent food safety and quality standards across borders.
In the intricate web of the global food industry, the quest for harmonization of regulations and standards is an ongoing and complex challenge. The sheer diversity of food products, production methods, and consumer preferences around the world necessitates a delicate balancing act. Fortunately, organizations such as the Codex Alimentarius Commission have stepped onto the international stage to tackle this formidable task head-on.
At its core, the Codex Alimentarius Commission is a beacon of collaboration among nations, working tirelessly to establish international food standards, guidelines, and codes of practice. These standards serve as a common language, transcending geographical boundaries and cultural nuances, to ensure that food products meet the highest standards of safety, quality, and fairness. In essence, they provide the building blocks for a global food safety and quality framework, fostering trust and transparency among nations engaged in international trade.
One of the primary objectives of the Codex is to facilitate the smooth flow of food across borders. Achieving this requires meticulous attention to detail. The Codex standards encompass a wide spectrum of aspects, from hygiene and labeling to pesticide residues and food additives. By providing a universal set of rules and regulations, the Codex eliminates the need for complex and often conflicting sets of standards in different countries, streamlining the process of international trade and promoting economic growth.
Beyond the economic implications, the work of the Codex holds immense significance for public health. The establishment of consistent food safety standards ensures that consumers worldwide can trust the safety of the food they consume. Whether it’s a staple grain, a processed product, or a culinary delicacy, the Codex standards create a safety net that transcends national borders, safeguarding the well-being of individuals and communities across the globe.
The Codex’s commitment to inclusivity is also noteworthy. It actively encourages participation from a wide range of stakeholders, including governments, food producers, consumers, and scientific experts. This multi-faceted engagement ensures that the standards are not only rigorous but also practical and applicable in the real world. It harnesses the collective wisdom of diverse perspectives to address the complex challenges of the global food industry.
As the food industry continues to evolve and globalize, the role of organizations like the Codex Alimentarius Commission becomes increasingly vital. They stand as beacons of cooperation and consistency in an increasingly interconnected world. While the challenges of harmonization remain formidable, the dedication of such organizations offers hope that, through collaboration and shared standards, the global food industry can continue to thrive, ensuring that safe, high-quality food reaches every corner of the globe.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Navigating the Complex World of Global Regulatory Affairs in …

Compliance with regulations and industry standards can be a complex and costly endeavor for food businesses. It requires dedicated resources for testing, inspections, and documentation. Moreover, staying current with evolving regulations and ensuring compliance across different markets can be a logistical challenge.
Navigating compliance with regulations and industry standards presents a multifaceted challenge for food businesses, requiring a meticulous approach and strategic resource allocation. This intricate process encompasses several noteworthy aspects:
Stringent Quality Control: Compliance necessitates rigorous quality control measures. Food businesses must conduct thorough testing and inspections of their products to ensure they meet safety and quality standards. This often involves investing in state-of-the-art laboratory equipment and specialized personnel with expertise in food safety.
Documentation and Record-Keeping: Comprehensive documentation is a cornerstone of regulatory compliance. Food businesses are tasked with maintaining detailed records of their production processes, ingredient sourcing, and product testing results. This not only facilitates accountability but also streamlines audits and inspections.
Supply Chain Oversight: Ensuring compliance extends beyond the immediate production process. Food businesses must exercise oversight and traceability throughout their supply chains, from the sourcing of raw materials to the distribution of finished products. This may require partnerships with suppliers who meet the required standards.
Global Harmonization: For companies operating in multiple markets, the challenge of compliance is compounded by the need to harmonize with varying international regulations. This often entails adapting product formulations, labeling, and packaging to align with the specific requirements of each market.
Consumer Transparency: Regulatory compliance also encompasses transparency with consumers. This includes accurate labeling, clear allergen information, and nutritional disclosure. Meeting these requirements not only fosters trust but also ensures consumer safety.
Staying Abreast of Changes: Regulations and industry standards are not static; they evolve over time. Food businesses must stay vigilant and adaptable, continuously monitoring changes in regulations and adjusting their practices accordingly. This may involve attending industry conferences, subscribing to regulatory updates, and engaging with regulatory bodies.
Risk Mitigation: Non-compliance can have severe consequences, including product recalls, legal penalties, damage to brand reputation, and loss of consumer trust. Therefore, businesses must proactively identify potential compliance risks and implement robust risk mitigation strategies.
Investment in Training: Ensuring that employees are well-versed in compliance requirements is essential. Providing ongoing training and education on food safety and regulatory adherence is a critical component of achieving and maintaining compliance.
Third-Party Audits: Some food businesses opt for third-party audits and certifications to validate their compliance efforts. Achieving certifications such as ISO 22000 (Food Safety Management Systems) or GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) can enhance credibility and market access.
Ethical Considerations: Compliance also extends to ethical aspects, such as fair labor practices, sustainability, and responsible sourcing. Demonstrating ethical compliance can resonate with socially conscious consumers and investors.
In summary, achieving and sustaining compliance with regulations and industry standards in the food industry is a multifaceted endeavor that encompasses quality control, documentation, supply chain oversight, global harmonization, consumer transparency, adaptability, risk mitigation, training, third-party audits, and ethical considerations. While it poses significant challenges, it is a non-negotiable aspect of responsible and successful food business operations. Proactive and strategic compliance measures not only protect consumers but also safeguard the reputation and viability of food businesses in an increasingly complex and regulated global marketplace.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Navigating the complex landscape of regulatory requirements for …

Technology plays a pivotal role in regulatory compliance. Food businesses use advanced software and systems to track and document every stage of the production process, from sourcing raw materials to final distribution. This technology enables real-time monitoring, rapid traceability, and streamlined compliance reporting.
In the realm of regulatory compliance within the food industry, technology stands as a formidable ally, enabling businesses to meet and exceed stringent standards with unprecedented efficiency and precision. The integration of advanced software and systems has ushered in a new era of transparency, accountability, and agility across the entire food supply chain.
One of the key ways technology contributes to regulatory compliance is through the meticulous tracking and documentation of every facet of the production process. From the moment raw materials are sourced to the final distribution of food products, digital solutions provide an intricate digital thread that captures every detail. This digital thread acts as a comprehensive record, offering a real-time view of every step in the journey from farm to fork.
Real-time monitoring is a game-changer in regulatory compliance. With sensors, IoT devices, and data analytics, businesses can continuously assess conditions, detect deviations from safety and quality standards, and take immediate corrective actions. For example, temperature monitoring systems can ensure that perishable goods are stored at the right temperatures throughout transportation, reducing the risk of spoilage and foodborne illnesses. Any deviations trigger alerts, allowing for swift intervention to protect both consumers and brand reputation.
Rapid traceability is another invaluable asset made possible by technology. In the event of a food safety incident or a product recall, the ability to trace the origin of contaminated products swiftly is crucial. With digital tracking and batch management systems, businesses can trace the journey of every product back to its source within minutes, not days or weeks as in the past. This not only minimizes the impact of recalls but also enhances consumer trust and safety.
Furthermore, technology streamlines compliance reporting, significantly reducing the administrative burden on food businesses. Automated reporting tools can generate detailed compliance reports with a few clicks, saving time and resources. These reports not only demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements but also serve as invaluable resources for audits and inspections.
The benefits of technology in regulatory compliance extend beyond just meeting minimum requirements. Forward-thinking food businesses leverage data analytics to proactively identify potential risks and areas for improvement. By analyzing data collected throughout the supply chain, they can pinpoint trends, patterns, and anomalies, enabling them to enhance processes, reduce waste, and optimize resource allocation.
In a rapidly evolving regulatory landscape, technology also supports adaptability. Regulations are subject to change based on emerging risks, scientific discoveries, and shifting consumer expectations. Digital solutions provide the agility to update processes and documentation in real-time, ensuring ongoing compliance and competitiveness.
In conclusion, technology has become the linchpin of regulatory compliance in the food industry. It empowers businesses to maintain meticulous records, monitor conditions in real-time, swiftly trace product origins, automate reporting, and proactively manage risks. As technology continues to advance, it not only enables compliance but also drives innovation and excellence, elevating food safety and quality standards across the globe.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Brazil – Market Challenges
In a world where food is a fundamental part of daily life, regulatory compliance and adherence to industry standards are essential. They uphold the promise of safe, high-quality, and transparent food products for consumers. While navigating the intricate landscape of regulations and standards can be challenging, it is a commitment that ensures the continued trust and satisfaction of consumers in the global food industry.
In a world where food is not only a fundamental necessity but also an integral part of cultural heritage, social gatherings, and personal well-being, the importance of regulatory compliance and adherence to industry standards cannot be overstated. These standards and regulations are the cornerstones of a complex system that strives to uphold a fundamental promise: to provide consumers with safe, high-quality, and transparent food products that nourish their bodies and satisfy their tastes.
The intricate landscape of regulations and standards, though daunting, is a testament to the collective commitment to food safety and quality. At its core, this commitment is a reflection of the industry’s dedication to safeguarding public health and respecting the trust consumers place in the foods they consume. It is a pact between food producers, regulators, and consumers that transcends borders and cultures.
One of the paramount roles of regulations is to ensure food safety. In a world where foodborne illnesses can have widespread and devastating consequences, these regulations set forth rigorous guidelines for the handling, processing, and distribution of food. They require meticulous record-keeping, stringent sanitation practices, and the monitoring of critical control points to prevent contamination.
Industry standards, on the other hand, encompass everything from product quality and labeling to ethical sourcing and sustainability. They provide a framework that guides producers in their quest to deliver high-quality products that meet consumer expectations. For example, standards may dictate the precise attributes that define an extra-virgin olive oil or the specifications for the grading of meats.
Navigating this complex regulatory landscape can be a significant challenge for food producers and businesses. Compliance requires substantial investments in infrastructure, staff training, and ongoing quality control measures. It involves meticulous record-keeping, rigorous testing, and the ability to adapt swiftly to changes in regulations, technology, and consumer preferences.
Despite the complexities, regulatory compliance and adherence to industry standards are not just obligations; they are competitive advantages. Brands and businesses that prioritize safety, quality, and transparency position themselves as trustworthy partners in the eyes of consumers. They cultivate lasting relationships built on the assurance that the food products they provide are not only delicious but also safe and reliable.
Furthermore, these commitments resonate with the evolving values of today’s consumers. An increasingly informed and health-conscious public places a premium on transparency, sustainability, and ethical practices. By aligning with these values, food producers not only build trust but also contribute to the broader goal of promoting a more responsible and sustainable food industry.
In conclusion, regulatory compliance and adherence to industry standards are not mere bureaucratic necessities; they are the lifeblood of a global food industry that thrives on trust, reliability, and shared values. In a world where food plays such a fundamental role in our lives, these regulations and standards stand as the guardians of our well-being, ensuring that every meal we savor is not just a source of sustenance but a testament to the commitment to safety, quality, and transparency.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: High-quality health systems in the Sustainable Development Goals …
More links
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Ship recycling – navigating a complex regulatory landscape – DNV
