Introduction
In today’s competitive business landscape, maintaining consistent quality in products and services is paramount. Quality not only ensures customer satisfaction but also boosts the reputation and success of a company. This is where Quality Management Systems (QMS) come into play, with ISO 9001 being one of the most recognized and globally adopted standards.
“ISO 9001 is not just a certification; it’s a commitment to quality excellence. Implementing an ISO 9001 Quality Management System goes beyond obtaining a badge; it’s about building a culture of continuous improvement and customer satisfaction within your organization. Let’s explore how ISO 9001 can benefit your business and pave the way for long-term success.”
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: What is ISO 9001:2015? ISO 9001 Certification Step by Step
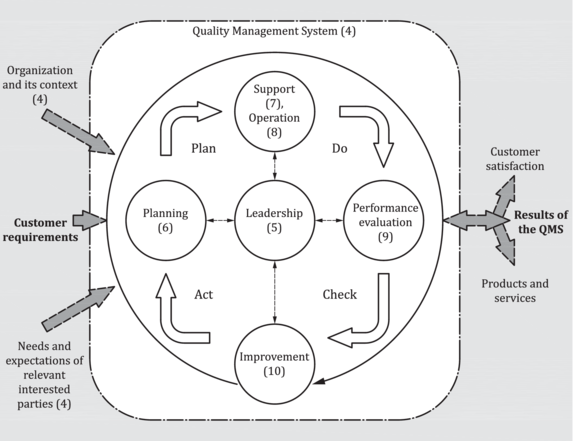
A Quality Management System is a structured approach to managing and improving the quality of products, services, and processes within an organization. Its primary goal is to meet or exceed customer expectations while ensuring efficiency and compliance with regulatory requirements. QMS provides a systematic framework for organizations to identify, measure, control, and continually improve their quality-related activities.
Implementing a Quality Management System (QMS) involves several key steps and considerations. Here’s a breakdown to guide organizations on their journey towards improved quality and customer satisfaction:
Assessment and Planning: Begin by assessing your organization’s current quality processes and identifying areas that need improvement. Establish clear quality objectives and set measurable targets.
Leadership Commitment: Top management should demonstrate a strong commitment to quality improvement. Leadership sets the tone for the entire organization’s approach to quality.
Employee Engagement: Involve all employees in the QMS implementation. Provide training and resources to ensure everyone understands their roles and responsibilities in maintaining quality.
Process Mapping: Document your organization’s key processes, from product development to customer service. This helps identify potential bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
Risk Management: Analyze potential risks that could affect product quality or customer satisfaction. Develop strategies to mitigate these risks.
Resource Allocation: Ensure you have the necessary resources, including personnel, technology, and infrastructure, to support your QMS.
Quality Metrics: Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of your QMS. Regularly monitor and analyze these metrics to identify trends and areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement: Implement a culture of continuous improvement. Encourage employees to identify and report quality issues and suggest improvements. Use tools like root cause analysis to address the underlying causes of problems.
Supplier Management: Assess the quality of your suppliers and establish clear criteria for supplier selection and evaluation. Good supplier relationships are crucial to maintaining product quality.
Customer Feedback: Gather and analyze customer feedback to understand their needs and expectations better. Use this information to make necessary adjustments to your products and services.
Compliance: Ensure your QMS aligns with relevant industry standards and regulatory requirements. Stay up-to-date with changes in regulations that may affect your organization.
Documentation and Record Keeping: Maintain clear and organized documentation of all QMS processes, procedures, and activities. Proper record keeping is essential for compliance and audits.
Internal Audits: Conduct regular internal audits to assess the effectiveness of your QMS. Identify non-conformities and take corrective actions as needed.
External Certification: Depending on your industry and customer requirements, you may seek external certification of your QMS, such as ISO 9001. Certification demonstrates your commitment to quality.
Communication: Effective communication is vital throughout the QMS implementation process. Keep all stakeholders informed about progress, changes, and the benefits of the QMS.
Celebrating Success: Recognize and celebrate achievements related to quality improvement. This boosts employee morale and reinforces the importance of the QMS.
By following these steps and maintaining a strong commitment to quality, organizations can establish and continually improve their Quality Management Systems to meet customer expectations, enhance efficiency, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
You can also read more about this here: What are core elements of a quality management system (QMS …

ISO 9001 is an internationally recognized standard that outlines the requirements for implementing an effective Quality Management System. It is applicable to organizations of all sizes and industries and serves as a benchmark for demonstrating commitment to quality, consistency, and customer satisfaction.
ISO 9001 certification not only helps organizations improve their internal processes but also enhances their reputation in the global market. By adhering to ISO 9001 standards, businesses can gain a competitive edge and instill confidence in their customers, partners, and stakeholders. This commitment to quality can lead to increased trust, improved relationships, and ultimately, sustainable success in today’s competitive business landscape.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: What is ISO 9001:2015? ISO 9001 Certification Step by Step

ISO 9001 is built on a set of core principles that guide organizations in achieving quality excellence:
ISO 9001 is founded on a set of fundamental principles that serve as guiding pillars for organizations striving to achieve excellence in quality management:
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: What are core elements of a quality management system (QMS …
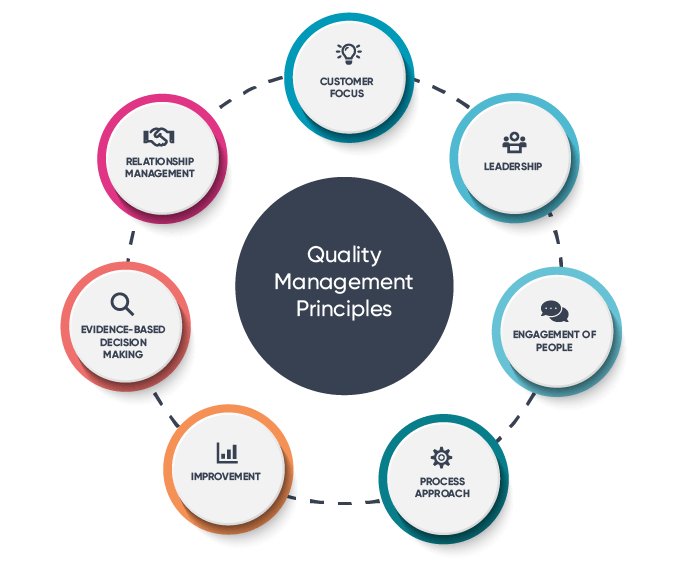
Meeting and exceeding customer needs and expectations is a central focus of ISO 9001. Understanding customer requirements and consistently delivering products or services that meet those requirements is key.
ISO 9001 places a strong emphasis on customer satisfaction. By actively seeking feedback, addressing concerns, and continuously improving processes, organizations can not only meet but also exceed customer expectations. This customer-centric approach not only enhances product and service quality but also builds long-lasting relationships and fosters business growth.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: What is ISO 9001:2015? ISO 9001 Certification Step by Step

Effective leadership is crucial for establishing a culture of quality within an organization. Leaders must be actively involved in QMS implementation and demonstrate their commitment to quality.
Leadership sets the tone for quality throughout the organization. Leaders should not only promote QMS but also be receptive to feedback, promote a culture of continuous improvement, and lead by example in embracing quality principles. Their dedication to quality encourages employees at all levels to take ownership of the QMS and work collectively toward achieving quality objectives. In essence, quality leadership is the cornerstone of a successful Quality Management System.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Key Elements of Quality Management System | Unichrone
ISO 9001 emphasizes the importance of involving and empowering employees at all levels. Engaged and motivated employees are more likely to contribute to the success of the QMS.
“ISO 9001 isn’t just about processes; it’s also about people. When employees are empowered and engaged, they become active participants in maintaining and improving the Quality Management System, driving its success.”
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: What is ISO 9001:2015? ISO 9001 Certification Step by Step

QMS encourages organizations to view their operations as a series of interconnected processes. Managing these processes systematically leads to better control and efficiency.
Implementing a Quality Management System (QMS) such as ISO 9001 not only enhances control and efficiency but also fosters a culture of accountability and transparency within an organization. When processes are viewed as interconnected, each employee understands their role in achieving the organization’s quality goals. This not only streamlines operations but also empowers employees to take ownership of their work, which can lead to improved overall performance and customer satisfaction. Through the lens of a QMS, the organization becomes a well-oiled machine, with each component working in harmony to deliver the highest quality products or services.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: What is ISO 9001:2015? ISO 9001 Certification Step by Step
ISO 9001 promotes a culture of continual improvement. Regularly assessing and enhancing processes and procedures is essential for maintaining and enhancing quality.
“ISO 9001 instills a mindset of perpetual progress within an organization. Through systematic internal audits, evaluations, and feedback loops, businesses can identify areas for improvement and make the necessary adjustments. This ongoing commitment to refinement ensures that quality remains a top priority, enabling companies to adapt to changing market dynamics and customer expectations effectively.”
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: What is a Quality Management System (QMS)? | ASQ

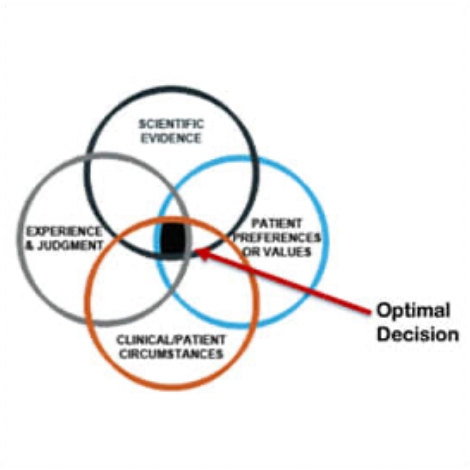
Informed decision-making based on data and evidence is a fundamental principle. ISO 9001 requires organizations to collect and analyze data to support their decision-making processes.
In today’s data-driven world, the importance of informed decision-making cannot be overstated. ISO 9001 recognizes this and places a significant emphasis on data and evidence-based decision-making as a cornerstone of effective Quality Management Systems (QMS). Here’s an extension of this idea:
Data-Driven Decision-Making in ISO 9001: Leveraging Insights for Continuous Improvement
ISO 9001, as a globally recognized standard for QMS, encourages organizations to adopt a proactive approach to decision-making. This involves the systematic collection and analysis of data related to various aspects of the organization’s processes, products, and services. Here are some key points to consider:
Data Collection: ISO 9001 mandates that organizations establish processes for collecting relevant data. This data can encompass a wide range of metrics, including product quality, customer satisfaction, process efficiency, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Data Analysis: Once collected, the data should be rigorously analyzed. Statistical tools and techniques can help identify trends, patterns, and anomalies. This analysis can provide valuable insights into the organization’s performance and areas that require attention.
Evidence-Based Insights: ISO 9001 recognizes that decisions made on a whim or without supporting evidence can be detrimental to quality and efficiency. By requiring organizations to base their decisions on data, it ensures that actions are taken with a clear understanding of the potential outcomes.
Continuous Improvement: The data collected and analyzed under ISO 9001 serves as a catalyst for continuous improvement. When organizations identify areas of non-conformance or opportunities for enhancement through data analysis, they can take corrective and preventive actions to address these issues.
Risk Management: Data-driven decision-making also plays a crucial role in risk management. By assessing potential risks and using data to make informed decisions about risk mitigation, organizations can avoid costly mistakes and disruptions.
Customer Focus: ISO 9001 places a strong emphasis on meeting customer requirements and enhancing customer satisfaction. Data collected from customer feedback and surveys helps organizations understand customer preferences and areas where improvements are needed.
Efficiency and Cost Reduction: Data analysis can reveal inefficiencies in processes and operations. By addressing these inefficiencies, organizations can reduce costs and enhance overall efficiency.
Compliance: In regulated industries, ISO 9001’s data-driven approach aids in ensuring compliance with relevant standards and regulations. Organizations can use data to demonstrate their adherence to quality and safety requirements.
Strategic Planning: Data-driven decision-making extends to strategic planning. Organizations can use data insights to formulate and adjust their long-term strategies, aligning them with changing market conditions and customer needs.
In summary, ISO 9001’s requirement for data and evidence-based decision-making is not just a compliance measure; it’s a powerful tool for organizations to drive continuous improvement, enhance customer satisfaction, manage risks, and achieve their strategic goals. By leveraging data-driven insights, organizations can adapt to a rapidly changing business landscape and thrive in competitive markets.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: What is a Quality Management System (QMS)? | ASQ
ISO 9001 helps organizations better understand and meet customer needs, leading to higher satisfaction rates.
Customer satisfaction is at the core of ISO 9001. By consistently meeting and exceeding customer expectations, organizations can foster loyalty, earn positive reviews, and build lasting relationships. ISO 9001’s customer-focused approach encourages businesses to listen to customer feedback, adapt to changing needs, and continuously improve their products and services. This customer-centric mindset not only boosts satisfaction rates but also contributes to long-term success and competitiveness in the market. In essence, ISO 9001 transforms customer satisfaction from a goal into a fundamental part of an organization’s DNA.
You can also read more about this here: The Future of Quality Management Is Business Success, Part 4 – The …
By streamlining processes and reducing errors, ISO 9001 can lead to increased efficiency and reduced operational costs.
By streamlining processes and reducing errors, ISO 9001 not only enhances operational efficiency and reduces costs but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement within an organization. This culture encourages employees to proactively identify areas for optimization, ultimately driving long-term financial sustainability. Additionally, the increased efficiency often leads to quicker product or service delivery, enhancing customer satisfaction and competitiveness in the market.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Q&A: driving supply chain excellence, and delivering value through …
ISO 9001 certification is often a requirement in various industries and can provide a competitive edge in the global market.
ISO 9001 certification is more than just a checkbox for compliance; it’s a strategic asset. In an increasingly competitive global market, having ISO 9001 certification sends a powerful message to customers and partners. It demonstrates your organization’s commitment to quality, efficiency, and continuous improvement. This can lead to increased trust, new business opportunities, and a strong competitive advantage, making ISO 9001 certification not just a requirement but a valuable investment in your company’s future.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: ISO 9001 and related standards — Quality management – ISO

Identifying and mitigating risks is an integral part of ISO 9001, helping organizations anticipate and address potential issues.
Risk management is not merely a checkbox in ISO 9001 compliance; it’s a proactive approach that enhances an organization’s ability to navigate challenges effectively. By identifying potential risks early, organizations can develop mitigation strategies and contingency plans. This not only safeguards the quality of products and services but also bolsters resilience and adaptability in the face of unexpected disruptions. In essence, ISO 9001’s emphasis on risk management aligns quality management with long-term strategic planning, ensuring an organization’s capacity to thrive in an ever-changing business landscape.
You can also read more about this here: The Future of Quality Management Is Business Success, Part 6 – The …

ISO 9001 can aid in ensuring compliance with industry regulations and standards.
“ISO 9001 serves as a reliable compass for navigating the complex landscape of industry regulations and standards. By adhering to its principles and practices, organizations can not only achieve compliance but also streamline their operations for long-term success.”
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: What is a Quality Management System (QMS)? | ASQ

Conclusion
Quality Management Systems like ISO 9001 play a pivotal role in modern businesses. They provide a structured framework for maintaining and enhancing product and service quality, which ultimately leads to customer satisfaction and business success. As industries evolve, QMS will continue to adapt and drive excellence, making them a cornerstone of quality assurance and improvement in the corporate world.
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern business, the significance of Quality Management Systems (QMS) like ISO 9001 cannot be overstated. These systems serve as a linchpin for organizations striving to not only meet but exceed customer expectations. As industries grow more complex and customer demands become increasingly sophisticated, QMS adapts to these changes.
One of the key advantages of QMS is its adaptability. ISO 9001, for instance, is regularly updated to stay aligned with the latest industry trends, best practices, and technological advancements. This ensures that businesses can remain competitive and responsive to shifting market dynamics.
Furthermore, QMS fosters a culture of continuous improvement. By regularly monitoring and analyzing processes, organizations can identify areas for enhancement and make data-driven decisions. This culture of constant refinement is essential in an era where agility and adaptability are the keys to survival and success.
As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, the role of QMS will extend beyond traditional quality assurance. It will encompass data-driven decision-making, risk management, and even sustainability considerations. In this regard, QMS becomes a holistic framework for excellence that not only guarantees the quality of products and services but also supports a broader commitment to corporate responsibility and environmental sustainability.
In conclusion, Quality Management Systems like ISO 9001 are not merely tools for compliance; they are dynamic and adaptable frameworks that underpin success in a rapidly changing business landscape. Embracing QMS means not just meeting today’s quality standards but also preparing for tomorrow’s challenges, ensuring that businesses can thrive and excel in any environment.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Key Elements of Quality Management System | Unichrone
More links
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: What is a Quality Management System (QMS)? | ASQ
