Introduction
In a world driven by innovation and complex systems, the importance of risk management and standardization cannot be overstated. Businesses, industries, and organizations across the globe face a myriad of risks daily, ranging from financial and operational risks to those related to safety, security, and compliance. Implementing effective risk management strategies is crucial for identifying, assessing, and mitigating these risks, but it’s the role of standardization that provides the framework and guidelines to achieve consistency, safety, and quality.
Navigating Risk with Standardization: A Blueprint for Success
In a world where innovation reigns supreme, and complex systems intertwine, the significance of risk management and standardization stands as an unassailable truth. Across the vast landscape of businesses, industries, and organizations, a constant, churning sea of risks emerges daily. These risks come in multifarious forms, spanning financial perils that threaten stability, operational challenges that demand efficiency, and the unwavering demands of safety, security, and compliance. The linchpin in this intricate dance of risk and resilience lies in the effective implementation of risk management strategies. However, it’s the role of standardization that emerges as the silent orchestrator, providing the much-needed framework and guidelines to not just mitigate risks but to achieve a harmonious symphony of consistency, safety, and quality.
1. Setting the Baseline: Standardization begins by setting the baseline, the fundamental norms against which all actions and processes are measured. It forms the bedrock upon which risk management strategies are constructed. With standardized protocols in place, organizations can gauge deviations, identify vulnerabilities, and anticipate potential risks with precision.
2. Consistency Across Boundaries: In today’s interconnected world, organizations often operate across geographical and sectoral boundaries. Standardization ensures that risk management practices remain consistent, regardless of location or industry. This consistency is vital in mitigating risks that transcend borders and in maintaining a unified approach to risk across diverse operations.
3. Safety by Design: Safety is a non-negotiable priority, especially in industries where lives and well-being are on the line. Standardization not only codifies safety practices but embeds them into the very DNA of an organization. It dictates safety by design, where every action, process, or product adheres to established safety standards, minimizing the risk of accidents or harm.
4. Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory requirements are a formidable force in risk management. Compliance with industry-specific standards and regulations is often mandatory and is non-negotiable. Standardization acts as a compass, ensuring that organizations navigate the complex landscape of regulatory compliance with clarity and precision.
5. Quality Assurance: Quality and risk are inseparable bedfellows. Standardization elevates the pursuit of quality from a lofty aspiration to a measurable and attainable goal. It sets the benchmarks and performance metrics that organizations must meet to ensure not just quality but also the reliability that underpins risk management.
6. Scalability and Adaptability: Businesses are not static entities; they evolve and expand. Standardization provides the flexibility needed to scale operations while maintaining effective risk management. It is equally adaptive, allowing organizations to pivot and adjust their risk strategies in response to changing circumstances and emerging threats.
7. Streamlining Communication: Effective risk management relies on seamless communication. Standardized terminology, reporting formats, and risk assessment methodologies facilitate clear and concise communication within organizations. This streamlined communication ensures that risk-related information reaches the right stakeholders promptly.
8. Reducing Ambiguity: Ambiguity is the enemy of effective risk management. Standardization clarifies roles, responsibilities, and procedures, leaving no room for interpretation or uncertainty. This reduction in ambiguity empowers teams to take decisive and informed actions in the face of risks.
9. Fostering a Risk-Aware Culture: Beyond processes and protocols, standardization fosters a culture of risk awareness. It encourages individuals at all levels of an organization to understand, embrace, and contribute to risk management efforts. It’s not just a set of rules but a mindset that permeates an organization’s ethos.
In conclusion, standardization is the cornerstone upon which effective risk management strategies are built. It’s the silent but indispensable partner in the relentless pursuit of consistency, safety, and quality. In a world where risks abound and innovation surges, standardization remains the beacon guiding organizations through the labyrinthine landscape of uncertainty. It transforms risk from a nebulous threat into a calculated endeavor, where organizations can confidently navigate the tides of change, knowing that the guiding principles of standardization are their steadfast allies in the pursuit of success.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of …
In an era marked by rapid technological advancements, globalization, and interconnected markets, risks have evolved in complexity and severity. Organizations must navigate financial uncertainties, supply chain disruptions, cybersecurity threats, and regulatory changes, among others. Effective risk management serves as a protective shield, allowing businesses to proactively address potential threats and seize opportunities.
Effective risk management is not just about protection; it’s a strategic advantage. Here’s a deeper exploration of the importance of risk management in today’s dynamic business landscape:
Safeguarding Reputation: A solid reputation is one of the most valuable assets a business can have. Risk management helps protect that reputation by identifying and mitigating potential crises before they escalate. Whether it’s a product recall, data breach, or ethical dilemma, a well-prepared response can prevent lasting damage to a company’s image.
Enhancing Decision-Making: Risk assessment is integral to decision-making. When business leaders have a clear understanding of potential risks and their potential impact, they can make more informed choices. This includes everything from investment decisions to market expansion strategies. Risk management enables leaders to balance risk and reward effectively.
Promoting Resilience: Resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity. Effective risk management builds organizational resilience. It ensures that businesses have contingency plans in place for various scenarios, from natural disasters to economic downturns. These plans allow companies to weather storms and emerge stronger on the other side.
Fostering Innovation: Paradoxically, risk management can be a catalyst for innovation. When businesses are aware of potential risks, they are motivated to find creative solutions. This often leads to the development of new products, services, and processes that not only mitigate risks but also create competitive advantages.
Compliance and Ethics: In an increasingly regulated world, compliance with laws and ethical standards is non-negotiable. Effective risk management includes compliance as a core component. It ensures that businesses adhere to legal requirements and ethical principles, reducing the risk of costly fines, legal battles, and damage to brand reputation.
Supply Chain Stability: Global supply chains are intricate and vulnerable to disruptions. Risk management in supply chain operations helps identify weak points and diversify sourcing strategies. This ensures a more stable supply chain, even in the face of unexpected events like pandemics or geopolitical tensions.
Financial Resilience: Financial risks, from market volatility to credit risk, can severely impact a business’s stability. Risk management includes financial risk management, helping organizations protect their financial assets and maintain liquidity during challenging times.
Customer Trust: Trust is the foundation of customer relationships. Effective risk management practices, particularly in data privacy and cybersecurity, show customers that their information is secure. This fosters trust and loyalty, which are essential in competitive markets.
Environmental and Social Responsibility: Sustainability is increasingly a focus for consumers, investors, and regulators. Risks related to environmental impact and social responsibility are now central concerns. Effective risk management encompasses sustainable practices, helping businesses meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria.
Adapting to Change: Change is constant in today’s business environment. Risk management prepares organizations to adapt to change effectively. This can include everything from adapting to new technologies to responding to shifts in consumer behavior.
In sum, risk management is not just a defensive strategy; it’s a proactive approach to navigating today’s complex business landscape. It helps businesses protect their reputation, make informed decisions, foster innovation, and ensure compliance. By managing risks effectively, organizations position themselves for long-term success and sustainability.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: rma-risk-management-fundamentals.pdf

Standardization is the process of developing and implementing uniform practices, protocols, and specifications within an industry, sector, or organization. These standards are meticulously crafted to ensure consistency, quality, safety, and compliance across a range of activities. They provide a common language and framework that enable stakeholders to work together seamlessly while adhering to best practices.
Standardization stands as a fundamental pillar of modern society, a testament to human ingenuity and the quest for efficiency and reliability. It’s a multifaceted process that transcends boundaries, encompassing industries, sectors, and organizations to foster consistency, excellence, and trust.
At its core, standardization is about the meticulous crafting of guidelines and specifications that set the gold standard for performance, safety, and quality. These standards become the bedrock upon which industries and organizations build their operations. They are meticulously designed to leave no room for ambiguity or error, ensuring that every participant in a process understands the rules of engagement.
The value of standardization lies not only in its ability to establish a common language but also in its power to streamline operations. Imagine a symphony orchestra without a conductor, each musician playing their own interpretation of the score. Chaos would reign. Standardization is the conductor that ensures each note is played precisely as intended, resulting in a harmonious and coherent performance.
Moreover, standardization is the guardian of safety and compliance. In industries where precision is paramount, such as aviation and healthcare, adhering to established standards can be a matter of life and death. These standards leave no room for improvisation, requiring that each procedure, component, or operation meets exacting criteria. This stringent adherence is the linchpin of safety.
Standardization also facilitates interoperability, allowing different systems, products, or services to seamlessly work together. In the digital age, where various devices and platforms must communicate effortlessly, adherence to common standards becomes the bridge that connects disparate elements. It ensures that your smartphone can connect to your Wi-Fi network, your car’s engine can run on standard gasoline, and your email can be read on any compatible device.
Furthermore, standardization serves as a powerful tool for innovation. It sets the baseline against which progress can be measured. By defining what constitutes excellence or compliance, standards provide a target for improvement. Innovators and engineers, armed with a clear understanding of what’s achievable and what’s required, can push the boundaries of technology and performance.
In essence, standardization is the quiet architect of progress. It lays the foundation for industries to flourish, organizations to thrive, and individuals to trust in the products and services they rely upon. Whether it’s the ISO standards that guide global industries, the healthcare protocols that save lives, or the technical specifications that enable your everyday devices to function flawlessly, standardization is the invisible force that shapes the world around us.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Management system standards – ISO

The marriage of risk management and standardization is a potent strategy for modern organizations. Here’s how they complement each other:
The synergy between risk management and standardization is a dynamic force that modern organizations harness to navigate the complexities of today’s business landscape. Together, they form a formidable strategy that not only addresses the challenges of uncertainty but also fosters a culture of excellence and adaptability. Let’s explore how these two pillars complement each other and contribute to an organization’s success:
Enhanced Predictability: Standardization lays the foundation for consistency and predictability in processes and operations. By establishing uniform practices and protocols, organizations can minimize variations and uncertainties. This predictability is essential for effective risk assessment, as it provides a stable baseline against which potential risks can be measured.
Risk Identification: Standardization creates a structured environment in which potential risks become more apparent. When processes are well-defined and standardized, deviations or anomalies are easier to detect. This heightened visibility enables organizations to proactively identify and assess risks before they escalate into larger issues.
Risk Mitigation: Once risks are identified, standardized procedures and protocols offer a roadmap for risk mitigation. These established practices not only guide how risks should be managed but also ensure that mitigation efforts are consistent and effective across the organization. Standardization acts as a safety net, preventing risks from spiraling out of control.
Streamlined Compliance: In regulated industries, compliance with industry-specific standards is essential. Standardization aligns an organization with these regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties. It also simplifies the process of demonstrating adherence to regulations through clear documentation of standardized procedures.
Continuous Improvement: Standardization and risk management are not static concepts; they evolve in response to changing circumstances and new insights. By integrating risk management into standardized processes, organizations foster a culture of continuous improvement. They can identify areas where standardization can be enhanced to mitigate risks more effectively.
Adaptability: In an ever-changing business environment, organizations must remain adaptable. Standardization and risk management can be tailored to accommodate changing conditions. Standardized procedures can be updated to reflect emerging risks, and risk management strategies can be adjusted to meet evolving needs.
Resilience: The combined approach of risk management and standardization promotes organizational resilience. It equips organizations to anticipate and withstand unexpected disruptions, adapt to new challenges, and emerge stronger in the face of adversity.
Optimized Resource Allocation: Risk management helps organizations prioritize resources where they are most needed. Standardization enables efficient resource allocation by ensuring that resources are used consistently and effectively in risk mitigation efforts.
Cultural Alignment: The adoption of standardized risk management practices fosters a culture of risk awareness and responsibility throughout the organization. This cultural alignment ensures that risk management is not a siloed function but a collective effort that involves all stakeholders.
Competitive Advantage: Organizations that successfully integrate risk management and standardization gain a competitive advantage. They can respond to risks more effectively, meet regulatory requirements with ease, and deliver consistent quality, all of which enhance their reputation and position in the market.
In essence, the marriage of risk management and standardization is a strategic alliance that empowers organizations to thrive in an environment of uncertainty and change. Together, they create a robust framework for not only managing risks but also optimizing operations, fostering resilience, and achieving sustained success. As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape, this partnership remains a cornerstone of their strategic approach.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: AI Risk Management Framework | NIST

Standardization helps organizations identify risks by establishing clear benchmarks and expectations. When processes, products, or systems adhere to standardized norms, deviations and anomalies become more apparent, making it easier to spot potential risks.
Standardization is a powerful tool in the realm of risk management and mitigation. By setting clear benchmarks and expectations for processes, products, or systems, standardization illuminates the path to identifying and addressing potential risks.
In any organization, there are countless variables at play. These variables can pertain to production processes, supply chains, software systems, or even safety protocols. Without a standardized framework, it can be challenging to discern deviations or anomalies that might signal the presence of risks. However, when these processes adhere to established standards, any departure from the norm becomes glaringly apparent.
Consider, for instance, a manufacturing facility that adheres to strict quality standards for its products. These standards dictate everything from materials to production methods and testing procedures. As a result, the production process becomes highly predictable and repeatable. Any deviation from these standards, no matter how minor, immediately raises a red flag. This level of scrutiny ensures that even the slightest variation in product quality is detected and addressed before it can pose a risk to consumers or the organization’s reputation.
In the realm of information technology, standardization plays a crucial role in cybersecurity. Cyber threats are continually evolving, and organizations must remain vigilant in safeguarding their digital assets. Standardized security protocols and practices, such as those outlined in ISO 27001 for information security management, provide a structured approach to risk assessment and mitigation. They help organizations identify vulnerabilities, set security controls, and monitor for any deviations that might signal a security breach. In this context, the slightest anomaly in network traffic or user behavior can trigger alerts, allowing organizations to respond swiftly to potential cyber threats.
Moreover, standardization aids in risk assessment by providing a common language and framework for evaluating and comparing risks across different departments or areas of operation. This consistency allows organizations to prioritize risks, allocate resources effectively, and implement mitigation strategies that align with their overall risk tolerance.
In essence, standardization is the foundation upon which effective risk management is built. It helps organizations establish clarity and visibility into their operations, making it easier to spot potential risks early on. By adhering to standardized norms, organizations can proactively address deviations and anomalies, mitigating risks before they escalate into significant issues. Whether in manufacturing, cybersecurity, or any other domain, standardization is a formidable ally in the ongoing quest to identify, assess, and mitigate risks effectively.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Risk Management Guide for Information Technology Systems
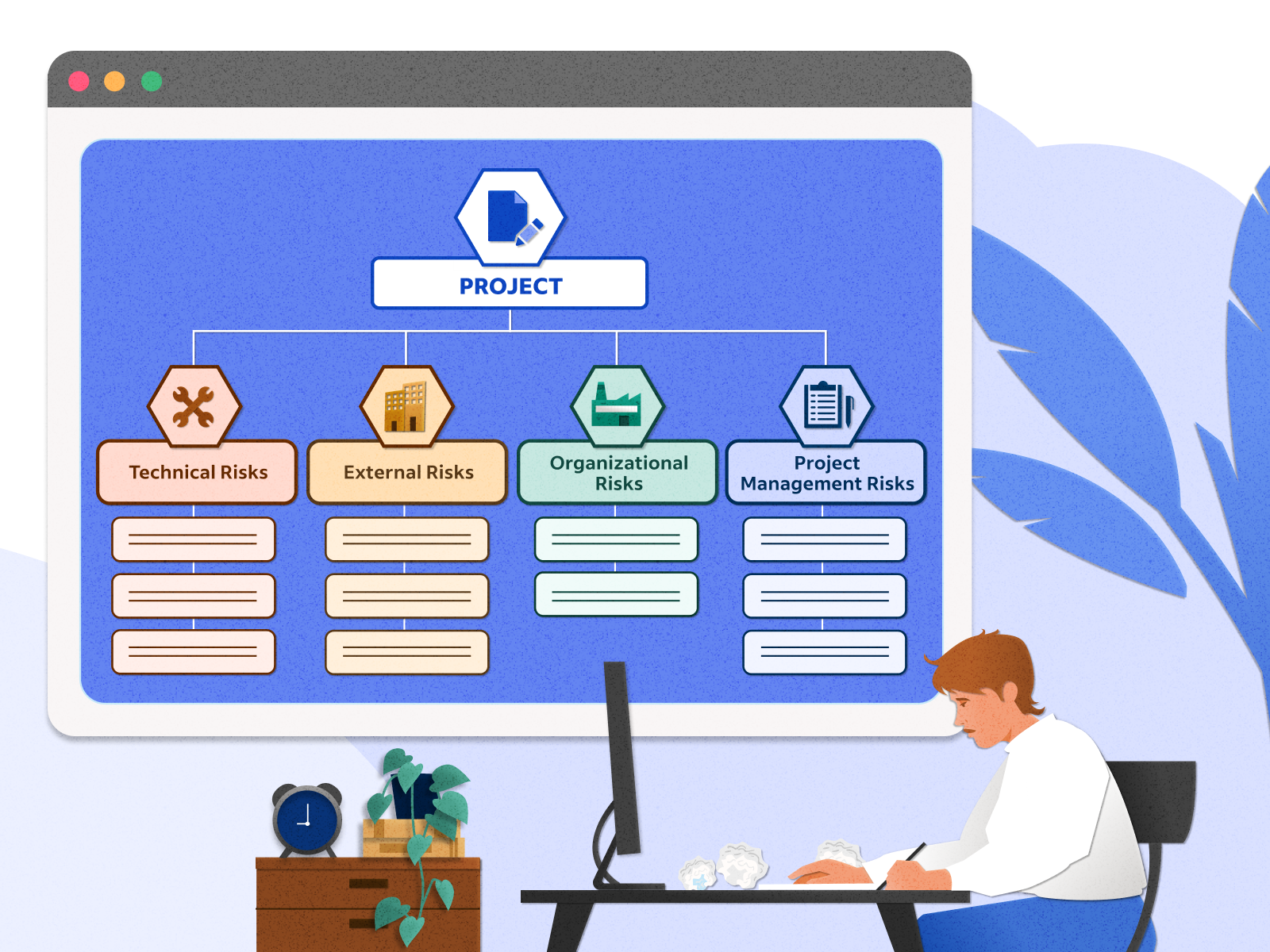
Once risks are identified, risk management methodologies can be applied more effectively. Standardized processes provide a consistent baseline for risk assessment, enabling organizations to evaluate the impact and likelihood of risks more accurately.
The integration of standardized processes and risk management methodologies in organizations creates a robust framework for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. Here’s a deeper exploration of this synergy:
Risk Identification: Standardized processes establish a structured environment where potential risks can be systematically identified. These processes define roles, responsibilities, and workflows, making it easier for employees to recognize potential risks as they occur. Whether it’s operational, financial, strategic, or compliance-related risks, standardized procedures provide a clear lens through which risks can be spotted, allowing for early intervention and proactive risk management.
Consistency in Risk Assessment: When it comes to assessing risks, consistency is key. Standardization ensures that risk assessment criteria are uniform across the organization, preventing inconsistencies or biases in risk evaluations. This consistency not only enhances the accuracy of risk assessments but also promotes fairness and transparency in decision-making processes related to risk management.
Quantification of Risks: Standardized processes enable organizations to quantify risks more effectively. By having predefined risk categories and measurement criteria, organizations can assign numerical values to risks, assessing their potential impact and likelihood more objectively. This quantitative approach allows for a more precise understanding of the magnitude and significance of each risk, facilitating prioritization and resource allocation for risk mitigation efforts.
Efficient Risk Mitigation: Once risks are identified and assessed, standardized processes streamline the implementation of risk mitigation strategies. These processes define the steps and procedures required to mitigate risks effectively, ensuring that responses are consistent and aligned with organizational goals. This efficiency minimizes delays in responding to risks and reduces the likelihood of ad-hoc, inconsistent risk management approaches.
Enhanced Communication: Standardization fosters clear and effective communication within organizations regarding risks. When everyone follows established processes and uses a common risk management framework, it becomes easier to communicate risk-related information across different departments and teams. This transparency ensures that all stakeholders are well-informed about risks and mitigation strategies, promoting a collective effort in risk management.
Continuous Improvement: Standardized risk management processes facilitate a culture of continuous improvement. Organizations can track the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies over time and make adjustments as needed. By documenting lessons learned from past risk incidents, organizations can refine their risk management methodologies, enhancing their overall risk resilience.
Compliance and Reporting: Standardization is crucial for regulatory compliance and reporting requirements. Many industries and sectors have specific regulations related to risk management and reporting. Standardized processes ensure that organizations meet these obligations efficiently and accurately, reducing the risk of compliance violations and associated penalties.
In conclusion, the integration of standardized processes and risk management methodologies in organizations is a synergistic approach that enhances the effectiveness of risk identification, assessment, and mitigation. It brings consistency, objectivity, and efficiency to the risk management process, enabling organizations to proactively address potential risks and protect their long-term viability and success. Standardization doesn’t just provide a framework; it’s a strategic asset for navigating the complex landscape of risks in today’s dynamic business environment.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: rma-risk-management-fundamentals.pdf

Standardization often comes with built-in safety measures and best practices. By following established standards, organizations can proactively mitigate risks. For instance, in the aviation industry, adherence to standardized maintenance procedures is vital to ensuring passenger safety.
Standardization’s integration of safety measures and best practices goes beyond mere adherence; it embodies a proactive commitment to risk mitigation. This proactive approach is exemplified in various industries, such as aviation:
Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Standardization involves a comprehensive evaluation of potential risks and vulnerabilities within a specific industry or process. By identifying these risks upfront, organizations can develop standardized protocols that address and mitigate them effectively. In aviation, rigorous safety standards and maintenance procedures are in place to reduce the likelihood of accidents caused by technical failures.
Consistency and Predictability: Standardization fosters consistency and predictability in operations. When every step of a process follows a standardized protocol, the chances of unexpected deviations or errors decrease significantly. In aviation, this translates to uniformity in aircraft maintenance, reducing the likelihood of human error and equipment failures.
Compliance and Accountability: Compliance with established standards is not just about adhering to guidelines; it’s about accountability. Organizations are held responsible for ensuring that their operations align with industry standards. This accountability encourages continuous monitoring, assessment, and improvement to maintain a high level of safety. In aviation, regulatory bodies rigorously enforce safety standards, holding airlines and maintenance providers accountable for the well-being of passengers.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Standardization often incorporates data-driven decision-making processes. In aviation maintenance, for instance, data on aircraft performance, component lifespan, and maintenance history inform standardized schedules and procedures. This data-driven approach ensures that maintenance is performed when needed, reducing the risk of in-flight failures.
Continuous Improvement: Standardization is not static; it evolves to incorporate lessons learned from past incidents and emerging technologies. In aviation, the industry constantly adapts its safety standards to reflect advancements in aircraft design, materials, and maintenance techniques. This commitment to continuous improvement is a hallmark of safety-focused standardization.
Cross-Industry Learning: Lessons learned in one standardized industry can often be applied to others. For example, safety practices and risk mitigation strategies developed in aviation have influenced standardization efforts in fields like healthcare and manufacturing. This cross-industry learning contributes to a broader culture of safety.
Public Trust: Perhaps the most significant benefit of standardized safety measures is the trust they instill in the public. Passengers board flights with confidence, knowing that rigorous standards are in place to protect their safety. This trust is a testament to the effectiveness of standardized safety practices in industries like aviation.
In summary, standardization not only defines best practices but also acts as a robust framework for proactively managing risks and ensuring safety. The aviation industry’s commitment to standardized safety procedures serves as a compelling example of how this approach can protect lives and uphold public trust. Across various sectors, adherence to standardized safety measures continues to drive progress in risk reduction and the promotion of overall well-being.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Risk Management Guide for Information Technology Systems
Standardization fosters clear communication within organizations and among industry stakeholders. This is crucial when addressing risks that affect multiple parties. For example, international safety standards for food production help prevent contamination risks in the global supply chain.
Standardization also serves as a foundation for comprehensive risk management frameworks. By establishing uniform processes, protocols, and assessment criteria, organizations can better identify, analyze, and mitigate risks across various aspects of their operations. This proactive approach not only enhances safety but also bolsters resilience, making organizations better prepared to navigate the complex landscape of modern risks, from cybersecurity threats to environmental challenges.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Risk Management Event Evaluation and Responsibilities …

Many industries are subject to stringent regulations. Compliance with these regulations is often achieved through adherence to industry-specific standards. Standardization simplifies the process of meeting legal requirements and reduces the risk of non-compliance.
Navigating Regulatory Waters with Standardization: A Shield Against Non-Compliance
In the ever-evolving landscape of industry regulations, compliance is not just a box to check; it’s a lifeline for businesses. Stringent regulations span various sectors, from healthcare and finance to manufacturing and environmental protection. These regulations are not just bureaucratic red tape; they are the safeguards that protect consumers, the environment, and the overall well-being of society. Ensuring compliance is not a mere formality; it’s a critical aspect of responsible corporate citizenship. This is where standardization steps in as the beacon of hope and efficiency.
1. A Regulatory Minefield: Navigating the complex labyrinth of regulations can be daunting. Regulatory bodies often release guidelines, rules, and directives in abundance, and keeping up with them is a formidable challenge. Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to legal consequences, fines, reputational damage, and even business closure. It’s a high-stakes game with no room for error.
2. The Role of Industry-Specific Standards: Within each industry, there exist industry-specific standards that serve as the bridge between regulatory requirements and practical implementation. These standards distill the regulatory jargon into actionable measures, providing organizations with a clear roadmap for compliance.
3. Standardization as the Translator: Standardization acts as the translator, converting the often intricate and convoluted language of regulations into tangible processes and practices. It simplifies the process of understanding what needs to be done to comply with regulations. Instead of deciphering legalese, organizations can turn to standardized protocols, which are designed to align with regulatory requirements.
4. Risk Mitigation: Non-compliance is a risk that no organization can afford to ignore. It comes with significant financial, legal, and reputational risks. Standardization, by providing a clear path to compliance, helps mitigate these risks. Organizations can systematically implement standardized processes and procedures, reducing the likelihood of compliance breaches.
5. Efficiency and Consistency: Compliance is not a one-time task; it’s an ongoing commitment. Standardized processes ensure that compliance efforts are not sporadic but built into the daily operations of an organization. This fosters efficiency, as employees know exactly what needs to be done to remain compliant. It also ensures consistency in compliance practices across different parts of the organization.
6. Adaptability to Change: Regulations are not static; they evolve in response to changing societal, environmental, and technological factors. Standardization is equally adaptable. When regulations change, organizations can rely on standardized frameworks to adjust their compliance efforts accordingly. It provides a flexible foundation that can accommodate new requirements without major disruptions.
7. Competitive Advantage: Beyond the baseline of compliance, standardization can also confer a competitive advantage. Organizations that excel in compliance often earn the trust of customers, partners, and investors. Demonstrating a commitment to adhering to industry-specific standards can set organizations apart from their competitors.
8. Reputation and Trust: Trust is a currency that organizations trade in, and compliance is a cornerstone of trust. When organizations consistently meet regulatory standards, they build a reputation for reliability and integrity. This trust extends to customers, who are more likely to choose products and services from compliant and trustworthy providers.
In a world where regulatory landscapes are in constant flux, where non-compliance can be financially devastating and ethically unacceptable, standardization emerges as the guiding light. It’s the tool that bridges the gap between regulatory requirements and practical implementation. It’s the shield that organizations wield to safeguard themselves against the risks of non-compliance. It’s the enabler that ensures that compliance is not just a legal obligation but a moral imperative. In the complex dance of regulations and standards, standardization is the partner that ensures every step is surefooted and every move is compliant, helping organizations navigate the regulatory waters with confidence and resilience.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Summary of the HIPAA Security Rule | HHS.gov

ISO 31000 is an internationally recognized standard that provides guidelines and principles for risk management. It assists organizations in developing a structured and comprehensive approach to risk. By integrating ISO 31000 with industry-specific standards, organizations can tailor their risk management processes to their unique needs while maintaining a global benchmark for excellence.
ISO 31000: A Universal Framework for Effective Risk Management
In the ever-evolving landscape of global business, the ability to manage risk effectively has never been more crucial. ISO 31000, an internationally recognized standard, serves as a guiding light for organizations seeking to navigate the complexities of risk management. Here’s a closer look at why ISO 31000 is a universal framework that transcends industries and geographies:
Global Consistency: ISO 31000 offers a universal language for risk management. Regardless of where an organization is located or what industry it operates in, ISO 31000 provides a common framework that ensures consistency in risk management practices. This standardization is particularly valuable for multinational corporations and industries with intricate supply chains.
Tailored Adaptability: While ISO 31000 provides a global benchmark, it is by no means a one-size-fits-all approach. Organizations have the flexibility to adapt its principles to their specific needs. By integrating ISO 31000 with industry-specific standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management or ISO 27001 for information security, organizations can create a tailored risk management system that aligns with their unique challenges and objectives.
Structured Approach: ISO 31000 offers a structured and systematic approach to risk management. It provides guidelines for risk identification, assessment, treatment, and monitoring. This structured methodology ensures that organizations don’t overlook critical risks and helps them prioritize actions to mitigate or capitalize on them.
Holistic Perspective: In today’s interconnected world, risks often transcend traditional boundaries. ISO 31000 encourages organizations to take a holistic view of risk, considering both internal and external factors. This approach helps organizations identify emerging risks and opportunities that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Continuous Improvement: ISO 31000 promotes a culture of continuous improvement in risk management. Organizations are encouraged to regularly review and refine their risk management processes. This adaptability is crucial in a world where risks evolve rapidly, whether due to technological advancements, market shifts, or global events.
Stakeholder Engagement: Effective risk management isn’t an isolated activity—it involves engagement with stakeholders. ISO 31000 emphasizes the importance of involving relevant stakeholders in the risk management process. This engagement fosters a deeper understanding of risks and ensures that diverse perspectives are considered when making risk-related decisions.
Enhanced Decision-Making: With a robust risk management framework based on ISO 31000, organizations are better equipped to make informed decisions. Whether it’s strategic planning, investment choices, or operational decisions, risk considerations become integral to the decision-making process.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: ISO 31000 aids organizations in meeting legal and regulatory requirements related to risk management. By aligning with this international standard, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to adhering to best practices, which can be especially valuable in industries subject to stringent regulations.
In conclusion, ISO 31000 is not merely a set of guidelines; it’s a dynamic framework that empowers organizations to embrace risk as an opportunity rather than a threat. Its adaptability, structured approach, and global relevance make it an invaluable tool for organizations seeking to thrive in an uncertain world. ISO 31000 is not a destination; it’s a journey towards a more resilient and agile future.
You can also read more about this here: ISO 31000:2018(en), Risk management — Guidelines

In a world where risks are omnipresent, organizations must view risk management and standardization as integral components of their operations. Embracing standardized practices not only reduces risks but also enhances efficiency, quality, and safety. As industries continue to evolve, the symbiotic relationship between risk management and standardization will remain a powerful tool for organizations seeking sustainable success in an unpredictable world.
In today’s fast-paced and unpredictable world, the symbiotic relationship between risk management and standardization is more crucial than ever for the resilience and success of organizations. These two pillars, when integrated seamlessly into an organization’s operations, create a dynamic and adaptive framework that can withstand the challenges of an ever-changing landscape.
At the heart of this partnership lies the concept of risk mitigation. Standardization provides the solid foundation upon which risk management strategies can be built. It establishes clear guidelines, best practices, and benchmarks that allow organizations to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities with precision. With standardized processes in place, it becomes easier to assess and quantify risks accurately.
Standardization also fosters consistency, which is a key element in risk management. By implementing standardized practices, organizations ensure that every aspect of their operations adheres to a set of predetermined criteria. This consistency minimizes variations and uncertainties, reducing the likelihood of errors or unforeseen complications that can lead to risks.
Furthermore, standardization enhances transparency and accountability. It provides a clear framework for documentation, reporting, and monitoring of activities. This transparency is essential for effective risk management, as it allows organizations to track their progress in implementing risk mitigation strategies and identify areas that require improvement.
Risk management, on the other hand, complements standardization by offering a dynamic and adaptive approach to addressing risks. It involves continuously assessing, evaluating, and responding to emerging threats and opportunities. Risk management provides the agility needed to navigate the unpredictable nature of the business environment.
Incorporating risk management into standardization practices means that organizations can proactively identify potential risks that may arise from changes in technology, regulations, market conditions, or external events. By doing so, they can adjust their standardized processes accordingly, ensuring that they remain effective and resilient in the face of evolving risks.
Moreover, risk management encourages organizations to adopt a holistic view of risks. It encourages them to consider not only the immediate and tangible risks but also the long-term and strategic ones. This comprehensive approach helps organizations make informed decisions about where to invest in standardization efforts, ensuring that resources are allocated to areas with the greatest potential impact on risk reduction.
In conclusion, the symbiotic relationship between risk management and standardization is a powerful force that enables organizations to thrive in an unpredictable world. Standardization provides the solid foundation and consistency needed to identify, assess, and mitigate risks, while risk management offers the adaptability and agility required to address emerging challenges. Embracing these integral components as part of their operations, organizations can not only reduce risks but also enhance efficiency, quality, and safety, ultimately achieving sustainable success in an ever-changing environment.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Strengthening Forensic Science in the United States: A Path Forward

More links
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Federal Flood Risk Management Standard | FEMA.gov
