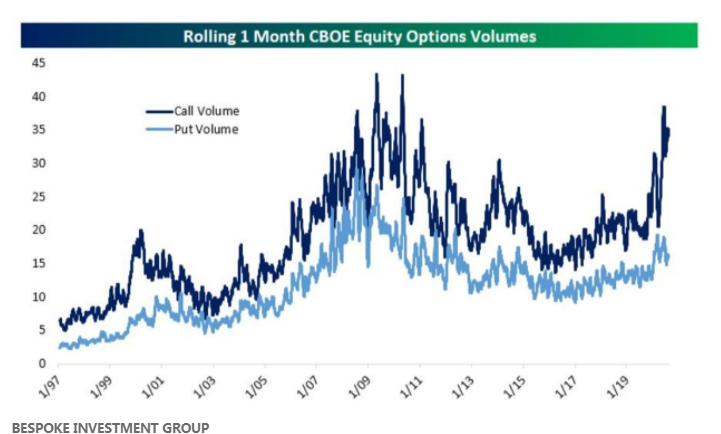
Introduction
Options trading has traditionally been the domain of professional traders and institutions. However, in recent years, there has been a noticeable surge in the participation of retail investors in the options market. This phenomenon has been driven by various factors, including increased access to information, user-friendly trading platforms, and the allure of potential high returns. In this article, we will delve into the rise of options trading among retail investors, explore some common strategies employed, and discuss the associated risks.
Options trading, once the exclusive territory of professional traders and institutions, has undergone a remarkable transformation in recent years. The surge in participation by retail investors has redefined the landscape of the options market. This seismic shift can be attributed to a confluence of factors, each playing a crucial role in democratizing options trading and making it more accessible to a wider audience.
One of the primary drivers of this shift is the democratization of information. In today’s digital age, retail investors have access to an unprecedented wealth of information and educational resources. Online tutorials, webinars, and easily accessible financial news have empowered individuals to grasp the complexities of options trading and develop a deeper understanding of the strategies involved. This newfound knowledge has emboldened many to venture into the world of options trading with confidence.
Furthermore, the emergence of user-friendly trading platforms has played a pivotal role in enabling retail investors to participate in options trading. These platforms offer intuitive interfaces, robust analytical tools, and real-time data, allowing individuals to execute complex options strategies with ease. The elimination of barriers to entry, such as high trading fees and complex order routing, has made options trading more appealing and financially viable for retail investors.
The allure of potential high returns has also been a driving force behind the surge in options trading. Options offer unique opportunities for profit, including leverage and the ability to profit from both rising and falling markets. Retail investors, drawn by the prospects of substantial gains, have increasingly embraced options as a key component of their investment portfolios.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the phenomenon of options trading among retail investors. We will explore some of the common strategies employed, ranging from simple covered calls to more complex spreads and straddles. Additionally, we will discuss the associated risks, emphasizing the importance of risk management and a well-defined trading plan.
While the rise of retail participation in options trading is undeniably promising, it’s crucial to approach this market with diligence and a commitment to ongoing education. Options can be powerful tools for wealth generation, but they also carry inherent complexities and risks. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of options trading and adopting prudent risk management strategies, retail investors can navigate this evolving landscape with confidence and potentially reap the rewards it offers.
You can also read more about this here: Regulatory Notice 22-08 | FINRA.org
The democratization of finance, aided by the internet and commission-free trading platforms, has opened the door for retail investors to engage in options trading. Retail traders now have access to a wide array of educational resources, webinars, and communities that facilitate learning and information exchange. As a result, the number of retail investors trading options has grown significantly.
The democratization of finance, fueled by the internet and the proliferation of commission-free trading platforms, has brought about a revolution in the world of options trading. This transformation has reshaped the landscape of financial markets, breaking down longstanding barriers and empowering retail investors to participate in options trading like never before.
In this new era, retail traders are no longer confined to traditional investment instruments. Options, once considered the realm of institutional investors and seasoned professionals, are now accessible to the everyday investor. This democratization has been further facilitated by the wealth of educational resources available at the fingertips of retail traders.
Online platforms offer a treasure trove of resources to help retail investors understand the intricacies of options trading. Comprehensive guides, interactive tutorials, and video lessons cover everything from the basics of call and put options to more advanced strategies like spreads and straddles. These resources empower individuals to build a strong foundation of knowledge and develop the confidence to engage in options trading effectively.
Webinars and virtual workshops have also emerged as powerful tools for learning. Experts in the field conduct live sessions, sharing their insights, strategies, and real-world experiences. These interactive forums enable participants to ask questions, seek clarification, and gain valuable perspectives on options trading.
Community engagement plays a pivotal role in this transformation. Online forums, social media groups, and specialized communities have sprouted, allowing retail traders to connect, collaborate, and share their journeys. These communities serve as valuable platforms for information exchange, idea generation, and support. Novice traders can learn from the experiences of more seasoned counterparts, while experienced traders can refine their strategies through collective brainstorming.
The impact of this democratization is evident in the substantial increase in the number of retail investors actively participating in options trading. The once-daunting world of options has become more approachable and attainable, and this trend shows no signs of slowing down.
However, it’s essential to emphasize that options trading carries inherent risks, and investors should exercise caution and due diligence. While accessibility and education have expanded, the potential for losses remains, especially when complex strategies are employed. Retail investors must approach options trading with a well-defined strategy, risk management plan, and a commitment to continuous learning.
In conclusion, the democratization of options trading represents a monumental shift in the world of finance. Retail investors now have unprecedented access to knowledge, resources, and communities that empower them to explore this intricate and potentially rewarding realm. As this evolution continues, it’s crucial for individuals to embrace education, engage in responsible trading practices, and always be mindful of the risks associated with options trading.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Retail investors lose big in options markets, research shows | MIT …

One of the most conservative options strategies, retail investors use covered calls to generate income from their existing stock holdings. They sell call options against their stock positions, giving someone else the right to buy their shares at a specified price (the strike price) before a predetermined expiration date.
Covered calls represent a conservative yet powerful options strategy favored by retail investors seeking to enhance their investment returns while managing risk. This strategy leverages the ownership of underlying stocks to generate additional income, making it an attractive choice for those looking to make the most of their existing holdings.
At its core, the covered call strategy involves two essential components: owning the underlying stock and selling call options. Let’s delve deeper into how it works:
Stock Ownership: To initiate a covered call, you must first own the underlying stock. This ownership is what makes the strategy “covered” because you have the shares available to fulfill the call option contract if it’s exercised by the buyer.
Call Option Sale: Once you have the stock, you sell call options for those shares. These options give the buyer the right (but not the obligation) to purchase your shares at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, before a specified expiration date.
Here’s where the income-generation aspect comes into play:
Premium Income: In exchange for selling the call options, you receive a premium from the buyer. This premium represents immediate income that goes into your pocket. It’s yours to keep, regardless of what happens with the option.
Income and Risk Mitigation: The premium you receive from selling the call options effectively reduces your overall cost basis in the stock. This can provide some downside protection, as the premium income partially offsets potential losses if the stock’s price declines.
Profit Potential: If the stock’s price remains below the strike price by the option’s expiration date, the call option will expire worthless, and you keep both the stock and the premium. You can then choose to sell more call options if you wish to continue generating income.
Assignment Risk: If the stock’s price rises above the strike price and the buyer of the call option decides to exercise their right, you will be obligated to sell your shares at the strike price. While this may limit your potential gains if the stock continues to rise, you still benefit from the premium income and the sale of your shares at a profit.
Covered calls are an excellent strategy for investors seeking to add an income stream to their portfolio, particularly in sideways or slightly bullish markets. However, it’s essential to select strike prices and expiration dates carefully, taking into account your long-term investment goals and risk tolerance. By understanding the mechanics of covered calls and using them judiciously, retail investors can manage risk while potentially increasing their overall returns from their stock holdings.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Options Trading for Beginners

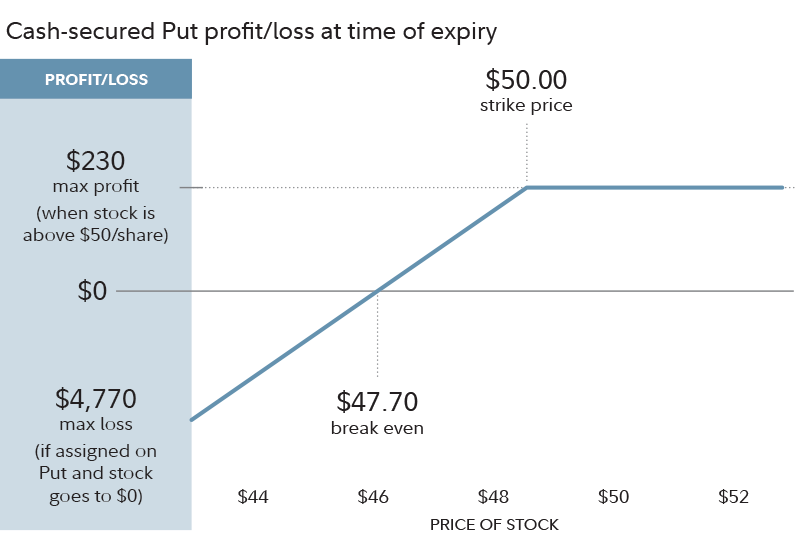
This strategy involves selling put options, backed by sufficient cash to buy the underlying stock if the options are exercised. Retail investors often use cash-secured puts to enter positions in stocks they want to own at a lower price.
Cash-secured puts are a strategic tool that offers retail investors an intriguing way to engage with the stock market, blending income generation and potential stock acquisition. Expanding on this idea reveals a deeper understanding of how this strategy works and why it’s favored by many:
Risk Mitigation: Cash-secured puts are often employed by investors who have a bullish outlook on a particular stock but want to be cautious. By selling put options, they generate income in the form of the premium received. Simultaneously, they set aside enough cash to cover the purchase of the underlying stock if the options are exercised. This prudent approach limits potential losses to the difference between the strike price and the stock’s current market value.
Income Generation: One of the primary attractions of cash-secured puts is the ability to generate income, typically through the option premium. Investors receive this premium upfront, which can provide an immediate boost to their portfolio’s cash flow. For income-seeking investors, this strategy can be an attractive way to supplement their returns.
Entry at a Discount: Investors often use cash-secured puts to establish positions in stocks they believe are undervalued but want to acquire at a lower price. By setting the strike price below the stock’s current market value, they essentially express their willingness to buy the stock at a discount, should the options be exercised. This aligns with the classic investment principle of “buy low.”
Portfolio Diversification: The cash-secured put strategy allows investors to diversify their portfolios by entering positions in a variety of stocks. This diversification can help spread risk across different sectors and industries, enhancing overall portfolio resilience.
Flexible Approach: Investors have flexibility with cash-secured puts. If the options are not exercised, they keep the premium income and can potentially repeat the strategy with different stocks. If the options are exercised, they acquire the stock at the predetermined price, and from that point, they can choose to hold, sell, or employ other strategies based on their investment goals.
Educational Opportunity: Engaging in cash-secured puts can also serve as an educational experience for investors. It encourages them to research and analyze stocks more deeply, consider their entry points carefully, and understand the dynamics of options trading.
Market Volatility Management: In times of market volatility, when stock prices may fluctuate significantly, cash-secured puts can provide a level of control. Investors have the power to set their desired entry price, potentially taking advantage of market dips while generating income during uncertain periods.
In summary, cash-secured puts are a versatile strategy that combines income generation, risk management, and stock acquisition. Retail investors often use this approach to carefully enter positions in stocks they believe have long-term potential. By understanding how cash-secured puts work and the benefits they offer, investors can expand their toolkit and make more informed decisions in their pursuit of financial goals.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Put Option: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Trade Them
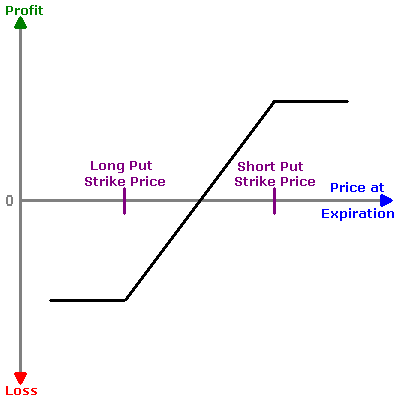
These strategies involve simultaneously buying and selling call (bull spread) or put (bear spread) options with different strike prices and expiration dates. Retail investors use these spreads to manage risk and potentially profit from directional price movements.
Options spreads are powerful tools that empower retail investors to manage risk and enhance their profit potential in the complex world of derivatives trading. Expanding on this concept delves deeper into the intricacies and benefits of options spreads:
Risk Management: Options spreads serve as a vital component of risk management for retail investors. By simultaneously holding multiple positions, such as buying one option and selling another, investors can mitigate potential losses. This helps establish a defined risk-reward profile, ensuring that they are well-prepared for various market scenarios.
Enhanced Profit Potential: Beyond risk reduction, options spreads offer the opportunity for enhanced profit potential. Depending on the specific spread strategy employed, investors can benefit from price movements in their favor while keeping their capital requirements and overall exposure in check.
Flexibility and Versatility: Options spreads come in various forms, each tailored to specific market conditions and objectives. Investors can choose from vertical spreads, diagonal spreads, calendar spreads, and more, allowing them to adapt to changing circumstances and market sentiment.
Directional Bias: Bull spreads and bear spreads, as mentioned, enable investors to express their directional bias in the market. Bull spreads are suitable when anticipating upward price movements, while bear spreads work well for a bearish outlook. This flexibility enables investors to tailor their strategies to their market convictions.
Time Decay Mitigation: Options naturally suffer from time decay as expiration approaches. Options spreads can be structured to either benefit from or mitigate the impact of time decay, depending on the chosen strategy. For example, calendar spreads profit from time decay, while diagonal spreads may aim to reduce its impact.
Capital Efficiency: Options spreads are often more capital-efficient than outright option purchases. This allows investors to allocate their capital across a broader range of positions and strategies, diversifying their risk while potentially maximizing their overall return on investment.
Consistent Income: Some options spread strategies, such as credit spreads, are designed to generate consistent income. This can be appealing to investors looking for regular cash flow from their options portfolio.
Learning Opportunity: Engaging with options spreads offers valuable learning experiences. Retail investors can gain a deeper understanding of options pricing, volatility, and market dynamics by actively managing spread positions.
Risk-Reward Assessment: Options spreads require a thoughtful assessment of risk-reward ratios. Investors must analyze the potential rewards against the amount of risk they are taking on. This practice encourages disciplined decision-making and risk-conscious trading.
Market Conditions: Consider the broader market conditions when selecting options spreads. Volatility, interest rates, and economic events can all impact the performance of options. Investors should align their spread strategies with the prevailing market environment.
In conclusion, options spreads are versatile tools that empower retail investors to navigate the complexities of the options market. They provide an array of risk management and profit potential strategies that can be tailored to individual preferences and market outlooks. However, it’s crucial for investors to thoroughly understand the mechanics of options spreads, conduct thorough research, and practice responsible risk management to maximize their effectiveness in the world of derivatives trading.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Basic Vertical Option Spreads: Which to Use?
An iron condor involves selling both a put spread and a call spread on the same underlying security. This strategy profits from limited price volatility and is often used by retail investors who anticipate a sideways market.
An iron condor is a versatile options trading strategy that provides retail investors with a unique way to profit in situations where they expect a stock or underlying asset to exhibit limited price volatility, typically within a defined range. This strategy is often likened to a financial “credit spread” because it involves both selling (writing) and buying (purchasing) options contracts simultaneously, thereby generating a net credit.
Here’s how an iron condor works:
Identifying a Range: Retail investors typically initiate an iron condor when they anticipate that the price of the underlying security will remain relatively stable within a specific range over a certain period. They assess factors such as historical price movements, technical analysis, and market conditions to pinpoint this range.
Creating the Spread: The iron condor consists of two separate spreads – a put spread and a call spread:
Put Spread: Retail investors sell an out-of-the-money put option (with a strike price below the current market price) and simultaneously buy another put option with an even lower strike price. This creates a bear put spread, which limits potential losses if the price of the underlying security drops significantly.
Call Spread: Simultaneously, they sell an out-of-the-money call option (with a strike price above the current market price) and buy another call option with a higher strike price. This creates a bull call spread, which caps potential losses if the price of the underlying security rises significantly.
Profit Potential: By establishing both a bear put spread and a bull call spread, the retail investor collects premiums from the sale of the options. The net premium collected represents their potential profit. If the price of the underlying security remains within the specified range until expiration, all options contracts expire worthless, and the investor keeps the entire premium collected.
Limited Risk: The risk in an iron condor strategy is capped because of the defined range within which the investor expects the asset’s price to stay. However, it’s essential to note that while profits are limited to the net premium received, potential losses are also limited to the difference between the strike prices of the put and call spreads, minus the premium collected.
Time Decay and Theta: Retail investors who use iron condors benefit from the time decay (theta) of the options they sell. As time passes, the value of these options erodes, which can work in the investor’s favor, especially if the underlying security’s price remains within the expected range.
Adjustments: If the price of the underlying security moves significantly in one direction, the investor may choose to adjust their iron condor by rolling the spreads or closing out one side to mitigate potential losses.
In summary, the iron condor strategy is a favorite among retail investors seeking to profit from stable or sideways-moving markets while effectively managing risk. By understanding the dynamics of this strategy and its potential outcomes, investors can harness its power as a valuable tool in their options trading arsenal. However, as with any trading strategy, careful planning, risk management, and ongoing monitoring are crucial for success.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: 5 Options Trading Strategies For Beginners | Bankrate
Retail investors also engage in directional bets by buying call options (anticipating price increases) and put options (anticipating price decreases). This strategy offers potentially substantial returns but comes with higher risk.
Retail investors often delve into directional betting through options trading, a strategy that can lead to significant gains but entails elevated risk. Here’s an extended perspective on this approach:
Strategic Opportunity: Options trading provides a strategic avenue for retail investors to capitalize on their market predictions. Buying call options allows them to profit from anticipated price increases, while purchasing put options offers the potential to gain when they expect prices to fall. This versatility enables investors to align their strategies with market expectations.
Leveraged Returns: One of the key attractions of options is their leverage. A relatively small investment in options can control a more substantial underlying asset. This amplification of exposure can lead to substantial returns, often surpassing what would be possible with a direct investment in the underlying asset.
Defined Risk: Unlike some other speculative investments, options trading comes with a defined risk. The maximum loss is limited to the premium paid for the options contract. This feature can provide a level of comfort for investors, as they know the worst-case scenario upfront.
Portfolio Hedging: Options also serve as effective tools for risk management and hedging. Retail investors can use put options to protect their existing investments by offsetting potential losses in a declining market. This risk mitigation strategy can help safeguard their portfolios during market downturns.
Educational Value: Engaging in options trading often involves a learning curve. Retail investors are compelled to understand the intricacies of options, which can contribute to their overall financial education. This knowledge can be valuable for making more informed investment decisions in the future.
Market Insights: The options market can provide valuable insights into market sentiment. The volume and pricing of options contracts can offer clues about the collective expectations of market participants. This information can assist retail investors in fine-tuning their investment strategies.
Risk Management is Crucial: While the potential for substantial returns exists, retail investors must be acutely aware of the higher risks associated with options trading. Options can expire worthless, leading to a complete loss of the premium paid. To mitigate these risks, investors should have a well-thought-out strategy and consider employing risk management techniques.
Volatility’s Impact: Options are particularly sensitive to market volatility. When markets are highly volatile, options premiums tend to rise, increasing the cost of trading them. Retail investors should assess the market’s current volatility and its potential impact on their options positions.
Timing and Precision: Successful options trading often requires impeccable timing and precision. Predicting price movements is challenging, and being even slightly off in your predictions can lead to losses. Retail investors should exercise caution and thoroughly analyze their chosen strategies.
Diversification: As with any investment strategy, diversification is essential. Retail investors should consider how options trading fits within their overall investment portfolio. Spreading risk across various asset classes can help balance the potential rewards and risks associated with directional bets.
In summary, directional betting through options trading offers retail investors a unique opportunity to capitalize on market predictions. However, this strategy demands a nuanced understanding of options, diligent risk management, and a cautious approach. Retail investors should approach options trading with a comprehensive strategy aligned with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Regulatory Notice 22-08 | FINRA.org
Options offer substantial leverage, amplifying both gains and losses. Retail investors can quickly lose their entire investment if the market moves against them.
Options trading can be a double-edged sword, offering potential for significant gains but also carrying heightened risks. Here’s an extended perspective on this idea:
Amplifying Gains: Options provide an opportunity to amplify gains beyond what’s possible with traditional stock trading. By controlling a larger position with a relatively small investment, investors can benefit from magnified profits if the market moves in the anticipated direction.
Strategic Hedging: While options are often associated with speculative strategies, they also serve as effective tools for risk management. Investors can use options to hedge their existing positions, protecting themselves from potential losses if the market takes an unexpected turn. This strategic approach can be valuable in preserving capital.
Diverse Strategies: Options trading encompasses a wide array of strategies, from simple calls and puts to more complex combinations like straddles, strangles, and spreads. Retail investors can tailor their options strategies to align with their market outlook, risk tolerance, and investment objectives.
Time Sensitivity: Options contracts have expiration dates, introducing an element of time sensitivity. This feature can work in favor of investors who understand it well. Options can be used for short-term speculation or for longer-term investments, depending on the chosen strategy.
Educational Imperative: Due to their complexity, options require a solid understanding of market dynamics and strategy intricacies. Retail investors should commit to ongoing education and seek out resources to grasp the nuances of options trading fully.
Risk of Losing the Premium: It’s important for retail investors to recognize that options come with the risk of losing the premium paid for the contract. Unlike stocks, where the investment’s value can fluctuate but not disappear, an options premium can be entirely lost if the market doesn’t move as expected.
Volatility Impact: Options are particularly sensitive to market volatility. High volatility can increase the premiums of options contracts, making them more expensive to trade. Retail investors should consider market conditions and implied volatility when selecting options strategies.
Leverage Management: Managing leverage is crucial in options trading. While leverage can amplify gains, it can also magnify losses. Retail investors should set clear risk management rules, including stop-loss orders, to limit potential losses and protect their capital.
Risk-Reward Assessment: Before entering an options trade, investors should assess the potential risk and reward. This involves considering the probability of the market moving in the desired direction and the potential loss if it doesn’t. A well-defined risk-reward profile is essential for sound decision-making.
Paper Trading and Simulation: To gain experience and confidence in options trading, retail investors can start with paper trading or simulation platforms. These allow investors to practice without risking real capital, honing their skills and strategies.
Consulting a Financial Advisor: Given the complexities of options, retail investors may benefit from consulting a financial advisor or broker experienced in options trading. Professional guidance can help investors navigate the intricacies of options and make more informed decisions.
In summary, options trading offers both opportunities and risks for retail investors. While they can magnify gains and provide strategic hedging options, they also carry the potential for significant losses. Retail investors should approach options trading with a well-thought-out strategy, a commitment to ongoing education, and a focus on risk management to harness the benefits while mitigating the associated risks.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Joint Statement Regarding Complex Financial Products and Retail …

Options trading can be complex, with various strategies and factors to consider. Novice traders may make costly mistakes due to a lack of understanding.
Options trading is a nuanced financial activity that offers significant potential for profit, but it’s also rife with complexities and nuances that can trip up novice traders. Let’s explore this idea further:
Diverse Strategies: Options trading encompasses a vast array of strategies, each with its own set of rules, risks, and potential rewards. These strategies range from straightforward, such as buying a call option to speculate on a stock’s rise, to intricate multi-leg strategies like iron condors or butterfly spreads. Novice traders can easily become overwhelmed when trying to grasp the multitude of options available to them.
Risk Management: Effective risk management is paramount in options trading, and this includes understanding the potential for loss. Novice traders may underestimate the risks associated with options and engage in strategies that expose them to substantial losses. Without a solid understanding of how options work, they can find themselves in precarious financial situations.
Market Volatility: Options are sensitive to market volatility, and changes in factors like implied volatility can significantly impact option prices. Novice traders may struggle to gauge market conditions accurately, making it difficult for them to choose the appropriate strategies or understand how changing conditions affect their positions.
Time Decay: Options have a limited lifespan, and their value erodes over time due to a phenomenon known as time decay or theta decay. Novice traders might not grasp the implications of time decay and can be surprised by the rapid loss of value in their options contracts as expiration approaches.
Leverage and Margin: Options provide leverage, which can amplify both gains and losses. Novice traders may not fully comprehend how leverage works, leading to unexpected outcomes. Additionally, some options strategies may involve margin requirements, and traders must be aware of how margin impacts their risk exposure.
Lack of a Clear Strategy: Novice traders may not have a well-defined trading strategy or may deviate from their strategy due to emotional responses to market fluctuations. This lack of discipline can result in impulsive decisions and costly mistakes.
Educational Resources: The complexity of options trading underscores the importance of education. Novice traders can benefit immensely from comprehensive learning resources, courses, and mentorship to build a strong foundation in options trading concepts and strategies.
Paper Trading: Before risking real capital, novice traders can practice options trading through paper trading or simulated accounts. This allows them to gain experience and test strategies without the financial risk.
Seeking Guidance: Novice traders should consider seeking guidance from experienced traders, financial advisors, or professional mentors who can provide insights, share strategies, and help them navigate the complexities of options trading.
In summary, while options trading offers opportunities for profit and portfolio diversification, it’s not without its challenges, particularly for novice traders. A lack of understanding can lead to costly mistakes, making education, risk management, and practice critical components of successful options trading. By approaching options trading with a commitment to learning and discipline, novice traders can increase their chances of making informed decisions and achieving their financial goals.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: ESG Investing: Practices, Progress and Challenges

Options have expiration dates, and as they approach expiration, their value can erode rapidly due to time decay. Retail investors must be aware of this and factor it into their strategies.
Time Decay and the Art of Options Trading: Maximizing Strategy Effectiveness
Options trading is a dynamic arena where understanding the concept of time decay is crucial. As options approach their expiration dates, their value can decline rapidly due to this phenomenon. Retail investors can navigate this challenge by incorporating time decay considerations into their strategies. Here’s a deeper exploration:
1. The Time Decay Factor:
Time decay, also known as theta decay, is an intrinsic characteristic of options. It signifies the reduction in the option’s value as it gets closer to its expiration date. This reduction occurs at an accelerated rate, particularly during the final weeks or days leading up to expiration.
2. Option Premium Erosion:
For option buyers, time decay is a critical consideration. As each day passes, the option’s premium diminishes. This can significantly impact the profitability of the trade. Retail investors buying options with a long time horizon should be aware of this premium erosion and its potential impact on their positions.
3. Planning and Strategy:
To mitigate the effects of time decay, retail investors need to approach options trading with a clear plan and strategy. This includes setting specific goals, understanding the time horizon of the trade, and selecting options with appropriate expiration dates.
4. Short-Term vs. Long-Term Strategies:
Different strategies require different approaches to time decay. For short-term trades, such as day trading or swing trading, options with near-term expirations may be suitable. In contrast, long-term investors may opt for options with extended expiration dates to give their positions more time to develop.
5. Regular Monitoring:
Active monitoring of options positions is crucial, especially as they near expiration. Retail investors should assess whether the trade is progressing as expected and whether adjustments are necessary to account for time decay and other market factors.
6. Strategies to Combat Time Decay:
Several options trading strategies are designed to combat the impact of time decay. These include strategies like covered calls, which involve selling call options against stock positions to generate income from premium decay.
7. Options Spreads:
Options spreads, such as calendar spreads or diagonal spreads, can also help manage time decay. These involve the simultaneous purchase and sale of options with different expiration dates. These strategies aim to benefit from the differing rates of time decay in the options involved.
8. Education and Simulation:
Retail investors are encouraged to educate themselves thoroughly on options trading, including time decay dynamics. Using paper trading or simulation platforms allows investors to practice options strategies without risking real capital, helping them become more adept at managing time decay.
9. Risk Management:
Given the potential rapid loss of value due to time decay, risk management is paramount. Retail investors should determine their risk tolerance, set stop-loss orders, and be prepared to exit positions that are not performing as expected.
In summary, understanding and managing time decay is an essential aspect of effective options trading. Retail investors can enhance their trading success by incorporating time decay considerations into their strategies, selecting appropriate expiration dates, and regularly monitoring their positions. With a well-informed and disciplined approach, investors can harness the power of options while navigating the challenges posed by time decay.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: What are Options? Types, Spreads, Example, and Risk Metrics

When selling options, there’s the risk of being assigned (obligated to fulfill the contract). This can result in unexpected stock purchases or sales.
Indeed, selling options can be a lucrative strategy, but it’s vital to grasp the concept of assignment risk. Going beyond the basics, let’s delve deeper into this aspect of options trading:
Assignment Mechanism: When you sell a call option, you give the buyer the right to purchase the underlying stock at the strike price before or on the expiration date. Conversely, when you sell a put option, you grant the buyer the right to sell the underlying stock to you at the strike price. Assignment can occur at any time before expiration, and it’s at the discretion of the option holder.
Managing Assignment Risk: To manage assignment risk effectively, consider several factors. First, timing plays a crucial role. Close monitoring of your options positions and understanding when assignments are more likely can help you make informed decisions. Second, be selective in choosing strike prices and expiration dates to align with your risk tolerance and investment objectives. Third, having a plan in place for handling assignments is essential. This might involve having sufficient cash or margin in your trading account or being prepared to take ownership of the stock if assigned.
Covered and Uncovered Positions: If you sell a covered call, you own the underlying stock, reducing the risk of an unexpected stock purchase. Conversely, selling an uncovered or “naked” call leaves you exposed to the possibility of buying the stock at the market price if assigned. For put options, selling uncovered puts obligates you to purchase the stock if assigned, which can be a substantial capital commitment.
Mitigating Assignment: Investors often employ strategies to mitigate the risk of assignment. One common approach is to roll options positions forward, essentially closing out the current position and opening a new one with a later expiration date. This can delay assignment and provide more flexibility.
Dividend Risk: Another aspect to consider is dividend risk when selling covered calls. If you hold a covered call position on a stock that pays dividends, you risk being assigned just before the ex-dividend date. This could result in missing out on dividend income.
Understanding Tax Implications: Assignments can have tax implications, depending on your jurisdiction and holding period. It’s essential to be aware of the tax consequences of owning the underlying stock if assigned.
Continuous Learning: Options trading is intricate, and assignment risk is just one facet of it. Continuously educate yourself about options strategies and their associated risks. Many online resources, courses, and books are available to help you deepen your understanding.
In conclusion, while options trading provides opportunities for income generation and risk management, it also carries the potential for assignment, which can lead to unexpected stock purchases or sales. Managing assignment risk requires vigilance, planning, and a thorough understanding of options mechanics. By incorporating these considerations into your options trading strategy, you can navigate this aspect of the market more effectively and make informed decisions that align with your financial goals.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Risk: What It Means in Investing, How to Measure and Manage It
The fast-paced nature of options trading can lead to impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed. Emotional trading can lead to significant losses.
The high-speed world of options trading indeed poses a unique challenge: the potential for impulsive decision-making driven by powerful emotions like fear and greed. It’s crucial to recognize the consequences of emotional trading and take steps to mitigate its impact:
Risk Management: Emotions often cause traders to ignore well-thought-out risk management strategies. To counter this, establish clear risk parameters for each trade. Set stop-loss orders and profit targets in advance, and stick to them religiously, irrespective of emotional impulses.
Trading Plan: Develop a comprehensive trading plan that outlines your objectives, strategies, and risk tolerance. Having a written plan helps you stay disciplined and focused on your long-term goals, even when emotions threaten to derail your decisions.
Mindfulness and Emotional Control: Practicing mindfulness techniques can help you become more aware of your emotions while trading. Recognize the emotional triggers and reactions that may lead to impulsive decisions, and work on controlling these impulses through relaxation exercises or meditation.
Simulated Trading: If you’re new to options trading or struggle with emotional control, consider starting with simulated or paper trading. This allows you to gain experience and test strategies without risking real capital. It’s an excellent way to build emotional resilience.
Predefined Entry and Exit Points: Establish predefined entry and exit criteria for each trade. These should be based on technical analysis, market trends, and your trading plan. This reduces the temptation to deviate from your strategy due to emotional factors.
Use Automation: Automated trading systems or algorithms can execute trades on your behalf based on predetermined criteria. This minimizes the impact of emotions on your trading decisions, as the system follows a set of rules rigorously.
Continuous Learning: Educate yourself about options trading thoroughly. The more you understand the mechanics and risks, the more confidence you’ll have in your decisions, which can help mitigate emotional reactions.
Trade Size Control: Limit the size of your trades to a level that allows you to remain comfortable and emotionally detached. Overcommitting financially can amplify emotional stress during trading.
Journaling: Keep a trading journal to document each trade’s rationale and outcomes. Reviewing your journal can provide insights into emotional patterns and help you identify areas for improvement.
Take Breaks: If you find yourself overwhelmed by emotions, take a step back. Close your trading platform and step away from the market. A break can help you regain perspective and prevent impulsive actions.
Professional Guidance: Consider seeking guidance from a financial advisor or therapist who specializes in trading psychology. They can provide strategies and techniques to manage emotions effectively.
Remember that emotional trading is a challenge faced by both novice and experienced traders. It takes time and practice to develop emotional discipline. By implementing these strategies and recognizing the importance of emotional control, you can navigate the fast-paced world of options trading with greater confidence and resilience, ultimately reducing the risk of significant losses.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: 7 Tips Every Futures Trader Should Know | Charles Schwab

Conclusion
The rise of options trading among retail investors signifies a notable shift in the financial landscape. While options can offer opportunities for profit and risk management, they are not without their hazards. Retail investors must approach options trading with a clear understanding of the strategies involved and a disciplined approach to risk management. Seeking education, starting with simple strategies, and using a small portion of one’s portfolio for options trading are prudent steps for those looking to participate in this dynamic market. Ultimately, options trading can be a valuable tool for retail investors when used responsibly and with due consideration of the associated risks.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Introduction, Conclusions, and Historical Background Relative to E …
More links
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Options trading activity hits record powered by retail investors