Table of Contents
Nestled in the icy expanses of Greenland’s northernmost regions, the Inughuit people have forged a unique way of life amidst some of the harshest conditions on Earth. These resilient Inuit communities, known for their deep connection to the Arctic environment and cultural traditions, offer a captivating glimpse into the lives of the northernmost Inuit. In this article, we embark on a journey to explore the history, culture, and daily existence of the Inughuit, shedding light on their remarkable adaptation to the Arctic’s unforgiving landscapes.
Nestled in the icy expanses of Greenland’s northernmost regions, the Inughuit people stand as a testament to human adaptability in the face of extreme conditions. Their unique way of life is a living testament to the indomitable spirit of indigenous cultures that have thrived in the harshest environments on Earth. As we embark on this journey to explore the history, culture, and daily existence of the Inughuit, we are drawn into a world where resilience, tradition, and a deep connection to the Arctic environment converge to create a captivating narrative.
History and Ancestry: The Inughuit, also known as the Polar Inuit, trace their lineage back thousands of years in the Arctic. Their ancestors, through generations, have navigated the challenges of the frozen North, carving out a distinct culture and heritage deeply intertwined with their surroundings. Their history is a tapestry woven with stories of exploration, survival, and a deep understanding of the Arctic’s rhythms.
Cultural Riches: The Inughuit’s culture is a treasure trove of traditions, stories, and artistic expressions. From their intricate clothing made from animal skins and furs, adorned with delicate beadwork and symbolism, to their mesmerizing throat singing and drum dances, every aspect of their culture reflects a profound connection to the land and its creatures. These traditions serve as a bridge between the past and the present, ensuring that the legacy of the Inughuit endures.
Harmonious Coexistence: Inughuit communities have honed a harmonious relationship with their environment over centuries. They possess an intimate knowledge of the Arctic’s flora and fauna, which has allowed them to thrive through hunting, fishing, and gathering. This sustainable way of life is a model of environmental stewardship, offering valuable lessons in the era of climate change and conservation.
Adaptation and Innovation: While the Inughuit hold fast to their ancestral practices, they also exhibit a remarkable ability to adapt and innovate. Modern technology, such as snowmobiles and radio communication, coexists with traditional methods of transportation and communication. This fusion of old and new demonstrates their pragmatic approach to life in the Arctic, where survival often hinges on embracing change without compromising core values.
Community and Resilience: Inughuit communities are tightly knit, where cooperation and mutual support are essential for survival. The harsh Arctic conditions demand unity, and the sense of community runs deep, serving as a source of strength in times of adversity. This resilience is a testament to the enduring spirit of the Inughuit people.
In conclusion, the Inughuit people, living at the northernmost reaches of Greenland, embody the essence of human adaptation and cultural preservation in one of the most challenging environments on Earth. Their history, culture, and daily existence provide a window into the unique world of Arctic indigenous communities. Through their stories and traditions, we gain not only a deeper understanding of the Inughuit but also valuable insights into the delicate balance between human existence and the pristine Arctic environment they call home.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: White Eskimo: Knud Rasmussen’s Fearless Journey into the Heart of …
Greenland’s Arctic Realm
Greenland, the world’s largest island, is renowned for its stunning landscapes, towering icebergs, and remote settlements. The island’s northernmost regions, known as Thule, are home to the Inughuit. Their lives are deeply entwined with the breathtaking but formidable environment.
nullFor a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: ARCTIC RESOURCE COMPILATION
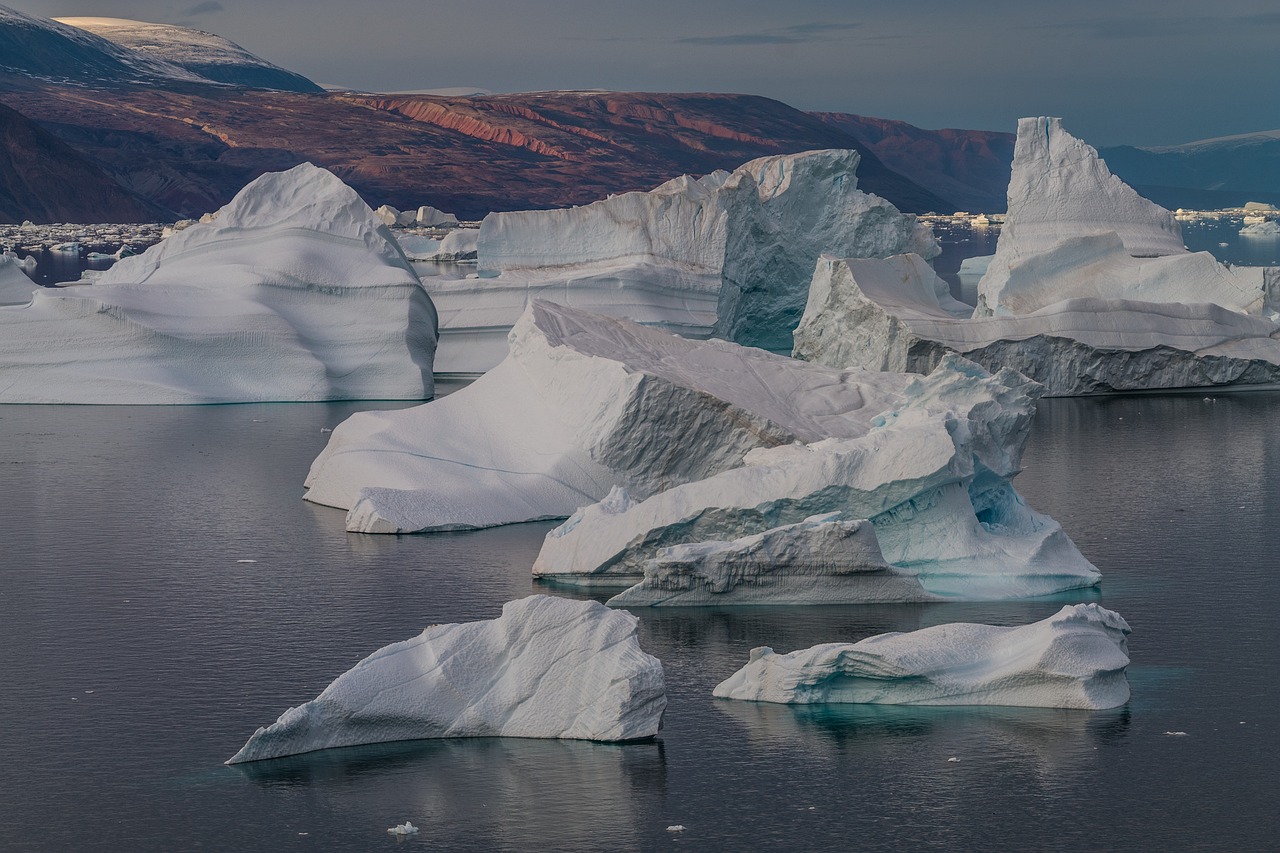

Arctic Extremes
The Arctic climate in Thule is characterized by extreme cold, with temperatures plummeting far below freezing. The region experiences polar night during the winter months, followed by the mesmerizing midnight sun in the summer.
The Arctic climate in Thule is characterized by extreme cold, with temperatures plummeting far below freezing. The region experiences polar night during the winter months, when the sun barely peeks above the horizon, casting the landscape into a long, enchanting twilight. This season brings challenges of darkness, cold, and isolation, but it also offers a unique opportunity to witness the ethereal dance of the Northern Lights, as they paint the night sky with vibrant colors, enchanting both residents and visitors alike.
Conversely, in the summertime, Thule undergoes a dramatic transformation as it enters the period of the mesmerizing midnight sun. During these months, the sun never sets, bathing the land in a perpetual, golden glow. It’s a time of remarkable contrast to the winter, as the region comes alive with vibrant life. The Arctic tundra blooms with colorful wildflowers, and wildlife, from caribou to migratory birds, make their return, taking advantage of the brief but intense burst of warmth and light.
This stark transition between the polar night and the midnight sun shapes the rhythm of life in Thule. It fosters a sense of resilience and adaptability among its inhabitants, who have learned to navigate the extremes and cherish the unique beauty of each season. The Arctic’s ever-changing face, from the icy depths of winter to the radiant abundance of summer, paints a portrait of nature’s awe-inspiring diversity, a testament to the enduring spirit of those who call this remote land home.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here i AMERICAN ARCTIC EXPLORATION A SOCIAL AND CULTURAL …

Inhospitable Terrain
The land is dominated by vast tundras, fjords, and ice-covered waters. The environment presents numerous challenges, including harsh weather, limited vegetation, and the ever-present threat of polar bears.
The Arctic environment of Thule, where the Inughuit people reside, is not just a stunning backdrop but also a formidable realm that shapes their daily lives in profound ways. Expanding on this idea:
Frozen Wilderness: Thule’s vast tundras stretch as far as the eye can see, covered in a thick blanket of snow for much of the year. These expansive plains are both beautiful and unforgiving, requiring a deep understanding of the land to navigate safely.
Majestic Fjords: Fjords, deeply carved into the coastline, are a defining feature of the landscape. These narrow, icy inlets are not only breathtaking but also serve as vital hunting and fishing grounds for the Inughuit. However, they can be treacherous to navigate, especially during the freezing winter months.
Ice-Covered Waters: The surrounding Arctic waters are a mosaic of ice floes and bergs, where seals and whales are abundant. While they offer sustenance, these icy waters can quickly turn perilous. Inughuit hunters skillfully navigate the frozen seas to secure their harvest, all while staying vigilant for changing ice conditions.
Surviving Harsh Weather: The Arctic climate is a formidable adversary. With bone-chilling temperatures, biting winds, and limited sunlight during the long polar nights, the Inughuit must rely on their traditional clothing, meticulously crafted to withstand the harshest of conditions.
Limited Vegetation: Vegetation in the Arctic is sparse, consisting mainly of hardy plants and mosses that can survive in the frigid climate. This scarcity means that the Inughuit cannot rely on agriculture, making hunting, fishing, and gathering essential for their sustenance.
Polar Bear Encounters: The ever-present threat of polar bears is a constant concern for the Inughuit. These formidable predators share their icy habitat and are known to venture into human settlements in search of food. Vigilance and protective measures are crucial to coexist safely with these powerful creatures.
Community and Camaraderie: Life in Thule is often centered around close-knit communities where neighbors rely on one another for support and safety. Sharing resources and knowledge is vital in the face of the Arctic’s challenges, reinforcing the bonds that hold these communities together.
In essence, the Arctic environment of Thule, with its stark beauty and unforgiving conditions, is a crucible that has forged the resilience and resourcefulness of the Inughuit people. It’s a place where survival relies not just on individual strength but on the collective wisdom and cooperation of a community that has learned to thrive in one of the world’s most extreme landscapes.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Cold Comforts: Women Making Inuit and Qallunaat Homes in the …

Inughuit Culture: Rich Traditions in the Arctic
The Inughuit people have maintained a rich cultural heritage for generations. Their traditions, passed down through storytelling, art, and everyday life, are deeply rooted in their Arctic surroundings.
The Inughuit people, a resilient and resourceful community inhabiting the frigid expanses of the Arctic, are custodians of a cultural heritage that spans countless generations. Within the heart of this remote landscape, their traditions have not only endured but thrived, shaped by the unique challenges and unparalleled beauty of their Arctic environment. These traditions, transmitted through the oral history of storytelling, the canvas of art, and the tapestry of daily life, are an integral part of the Inughuit identity, forging a profound connection between their culture and the land that sustains them.
Storytelling serves as the lifeblood of Inughuit culture, a timeless tradition through which wisdom, values, and the shared experiences of their people are meticulously preserved. Gathered around the warmth of communal fires, under the enchanting glow of the Northern Lights, the Inughuit elders pass down tales that have spanned generations. These stories not only entertain but also educate, imparting the knowledge and survival skills necessary to navigate the extreme challenges posed by the Arctic climate. The oral tradition binds the community together, ensuring that the rich history and folklore of the Inughuit remain vivid and relevant in the modern world.
In addition to their captivating narratives, Inughuit culture finds expression in their art, which is deeply influenced by the ethereal Arctic landscapes. Whether it’s intricately carved bone and ivory artifacts, vibrant textile work, or evocative paintings, their art serves as a testament to the profound connection between creativity and the environment. Each piece is a reflection of the land’s stark beauty, the wildlife that sustains them, and the traditions that define them. It also provides a window into the Inughuit worldview, revealing their reverence for the natural world and the interdependence of all living things.
Moreover, the Inughuit way of life itself is a canvas where traditions are painted into every aspect of daily existence. From subsistence hunting and fishing practices to the construction of their resilient and efficient homes, every facet of their lives reflects a deep-rooted connection to the Arctic environment. The ingenious design of their dwellings, such as the iconic igloos, showcases the synergy between human ingenuity and the demands of the harsh climate. These traditional practices, handed down through the ages, are not just functional but also cultural expressions that highlight the resilience and adaptability of the Inughuit people.
In an era marked by rapid change and environmental challenges, the Inughuit people stand as a testament to the enduring power of culture and tradition. Their ability to maintain and celebrate their rich heritage amid the stark beauty and relentless conditions of the Arctic is a source of inspiration. It serves as a reminder of the profound connection between human cultures and the natural world, and the importance of preserving both in the face of a changing global landscape.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Arctic Studies Center Newsletter 2020

Hunting and Gathering
Traditional Inughuit life revolves around hunting and gathering. Seal, whale, caribou, and fish are staples of their diet. The Inughuit’s profound knowledge of animal behavior and ice conditions is passed down through generations.
nullTo delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Arctic Studies Center Newsletter 2020

Thule Culture
The Inughuit are part of the Thule culture, one of the most ancient Inuit cultures. Their ancestors, the Thule people, migrated to Greenland over a thousand years ago, bringing with them advanced hunting techniques and tools.
The Inughuit, a resilient and culturally rich community in Greenland, are an integral part of the Thule culture, which stands as one of the most ancient and enduring Inuit cultures. To understand the Inughuit’s way of life and their profound connection to the land, it’s essential to delve into their ancestral roots.
Over a thousand years ago, the Thule people embarked on an extraordinary journey, migrating from what is now Alaska to the vast and challenging terrain of Greenland. This migration was a testament to their adaptability, resourcefulness, and unparalleled knowledge of Arctic survival. It’s worth noting that this migration took place long before the age of modern transportation and technology, making it an awe-inspiring testament to their resilience.
The Thule people brought with them a wealth of advanced hunting techniques and tools, revolutionizing how they interacted with the Arctic environment. These innovations, which included refined methods of hunting seals, whales, and other marine mammals, allowed them to thrive in a landscape that was seemingly inhospitable to outsiders.
One of the most significant contributions the Thule people made was the development of the iconic Inuit kayak. These slender, agile watercrafts were ingeniously designed for hunting and navigating the treacherous Arctic waters. Their sleek design allowed hunters to approach seals and other prey with stealth and precision, further emphasizing the intricate relationship between the Thule people and their natural surroundings.
The Inughuit, as descendants of the Thule culture, carry forward this legacy of ingenuity and adaptability. Their connection to the land is deeply rooted in the knowledge and traditions passed down through generations. Hunting, fishing, and gathering are not merely activities but a way of life that reflects their profound respect for nature and the resources it provides.
Today, the Inughuit continue to honor their heritage while adapting to the challenges of the modern world. Their resilience, cultural richness, and the enduring legacy of the Thule culture remind us of the remarkable human capacity to not only survive but thrive in even the harshest of environments, leaving an indelible mark on the history and heritage of Greenland and the Arctic.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Assessment of Cultural Heritage Monuments and Sites in the Arctic

Oral Traditions
Storytelling is a cherished Inughuit tradition. Elders share stories of the past, myths, and legends that connect the people to their history and the natural world around them.
Storytelling among the Inughuit, an indigenous community residing in the Arctic regions of Greenland and Canada, is not merely a means of communication; it is a profound cultural cornerstone. This age-old tradition transcends generations, serving as a sacred thread that weaves together the tapestry of their identity, history, and deep connection to the natural world.
Elders within the Inughuit community are the custodians of these treasured stories. They possess a wealth of knowledge, garnered from a lifetime of experiences, and they hold the key to the rich oral history of their people. With each narrative they share, they breathe life into the past, allowing younger generations to walk in the footsteps of their ancestors.
These stories encompass a wide range of themes, from myths and legends that explain the origin of natural phenomena to historical accounts of survival in the unforgiving Arctic environment. Through these narratives, the Inughuit maintain an intimate bond with their surroundings, acknowledging the land, sea, and sky as not just physical entities but as living, breathing entities with their own stories to tell.
Inughuit storytelling is a communal endeavor, often taking place in gatherings where listeners of all ages come together to absorb the wisdom and heritage passed down through generations. As they listen to these tales, they are not just learning history; they are forging a deeper connection to their cultural roots and the environment that sustains them.
In a world that is rapidly changing, the tradition of storytelling remains a constant, a resilient bridge that connects the past to the present and guides the way to the future. It reminds the Inughuit that they are not just isolated individuals but part of an enduring legacy that has withstood the test of time. It is a testament to the enduring power of human storytelling, a testament that is written not on paper but etched into the hearts and minds of the Inughuit people, ensuring that their culture, history, and connection to the natural world will continue to thrive for generations to come.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Arctic Studies Center Newsletter 2020
Art and Crafts
Inughuit art is celebrated for its intricate designs and symbolism. Carvings, sculptures, and textiles are crafted with precision and creativity, reflecting the environment and their cultural identity.
Inughuit art, a vibrant and cherished tradition of the Inuit people of Northern Greenland, stands as a testament to the profound connection between artistry and the natural world. Celebrated for its intricate designs and deep symbolism, it serves as a visual language that tells stories of the land, the sea, and the spiritual essence of their culture.
One of the most captivating aspects of Inughuit art is its ability to breathe life into seemingly ordinary materials. Carvings, meticulously shaped from materials such as soapstone and bone, are marvels of precision and creativity. These sculptures depict a wide range of subjects, from wildlife like seals, polar bears, and whales, to representations of everyday life and mythological figures. Each carving is a work of art but also a vessel for cultural stories and values, preserving the memory of their ancestors and the beauty of the Arctic landscape.
Similarly, Inughuit textiles are a testament to the skill and creativity of their artisans. Traditional garments like the anorak and mittens are not only functional in the harsh Arctic climate but also richly adorned with intricate patterns and designs. These patterns often carry deep cultural and spiritual meanings, linking the wearer to their environment and heritage. The vibrant colors used in these textiles reflect the vivid beauty of the Arctic, with blues, whites, and earthy tones mirroring the icy landscapes, snowy horizons, and the ever-present dance of the Northern Lights.
Moreover, the symbolism embedded within Inughuit art goes beyond aesthetics; it is a way of preserving and transmitting cultural identity. The art serves as a bridge between generations, passing down stories, values, and traditional knowledge. Through each carving stroke or textile stitch, the Inughuit people reaffirm their place within the natural world, maintaining a spiritual connection to their ancestors and their homeland.
Inughuit art is not only a form of creative expression but also a vital means of cultural preservation. It offers a window into a way of life that has endured for centuries, providing insights into the resilience and adaptability of the Inuit people in the face of a changing world. As we admire their artistry, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate tapestry of their culture and the enduring beauty of the Arctic environment that continues to inspire and shape their creative endeavors.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Cold Comforts: Women Making Inuit and Qallunaat Homes in the …

Survival in the Arctic
Adaptation and resilience are key to the Inughuit’s survival in this challenging environment.
nullExplore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Assessment of Cultural Heritage Monuments and Sites in the Arctic

Modern Technologies
While traditional practices persist, modern technologies, including snowmobiles, firearms, and GPS, have enhanced hunting and transportation efficiency.
While traditional practices continue to hold a significant place in the lives of indigenous communities in the Arctic, the integration of modern technologies has brought about a transformative shift in their way of life. These innovations, including snowmobiles, firearms, and GPS technology, have not only enhanced hunting and transportation efficiency but have also added a layer of complexity to the dynamic between tradition and modernity.
Snowmobiles, for example, have revolutionized transportation in remote Arctic regions. They have replaced traditional dog sleds as a primary means of travel, allowing for faster and more efficient movement across vast expanses of snow and ice. This transition has not only reduced the physical strain on hunters and gatherers but has also extended the reach of their activities, enabling them to cover larger areas in search of game and resources.
Firearms have similarly transformed hunting practices. While traditional tools like spears, bows, and harpoons remain culturally significant and are still used in some contexts, firearms have proven to be more efficient for hunting large game. They have increased the success rate of hunts and have provided a more reliable means of securing food for communities, particularly during harsh winters when resources can be scarce.
The integration of GPS technology into traditional hunting practices has added a layer of precision and safety. Hunters can now navigate the vast, featureless landscapes with greater accuracy, ensuring they reach their destinations and return home safely. This technology also aids in marking important locations, such as hunting grounds or campsites, which can be crucial in a nomadic lifestyle.
However, the introduction of modern technologies has not come without challenges. It has sparked debates within indigenous communities about the potential loss of traditional knowledge and skills. Some argue that as reliance on modern tools grows, the younger generations may not fully grasp the depth of traditional hunting techniques and the spiritual connection they hold with the land and its wildlife.
Moreover, there are concerns about the environmental impact of modern technologies, such as snowmobiles, on delicate Arctic ecosystems. Balancing the benefits of enhanced efficiency with the need to preserve the environment and traditional practices is a complex challenge faced by these communities.
In essence, the incorporation of modern technologies into traditional Arctic life represents a delicate balance between adaptation and preservation. It showcases the resilience of these communities in the face of a rapidly changing world while also emphasizing the importance of safeguarding their cultural heritage and the unique relationship they maintain with their challenging yet awe-inspiring Arctic environment.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Arctic Studies Center Newsletter 2020

Climate Change Challenges
The Inughuit face the impacts of climate change, including melting ice and altered animal migration patterns. These changes challenge their traditional way of life and require adaptation.
The Inughuit people, residing in the far reaches of the Arctic, confront a profound and urgent challenge: the relentless impacts of climate change. As global temperatures rise, the Arctic region is experiencing accelerated environmental transformations, and the Inughuit find themselves at the forefront of these shifts.
One of the most striking consequences of climate change in the Arctic is the rapid melting of sea ice. For generations, sea ice has been not only a vital platform for hunting and transportation but also a symbol of the Inughuit’s deep connection to the frozen expanse that surrounds them. As this ice diminishes, their ability to access hunting grounds and traditional resources is increasingly compromised. The loss of ice also means more dangerous conditions for hunters and the potential for isolation from neighboring communities.
Another profound impact of climate change is the alteration of animal migration patterns. The Inughuit have relied on the predictable movements of wildlife for centuries, and these shifts disrupt their hunting practices and food security. As species like seals, whales, and caribou adapt to changing temperatures and ocean currents, the Inughuit must also adapt, learning new hunting strategies and diversifying their diet to ensure their communities are adequately nourished.
Adaptation is a concept deeply ingrained in Inughuit culture, and they are actively seeking innovative ways to preserve their traditional way of life in the face of these environmental challenges. This resilience is seen in their efforts to develop sustainable hunting practices, engage in collaborative research with scientists to better understand local ecosystems, and explore alternative economic opportunities that align with their cultural values.
The Inughuit’s journey in the age of climate change is not just about survival; it’s also about maintaining their cultural identity and heritage. They are striving to pass down their traditional knowledge to younger generations, ensuring that age-old practices, stories, and customs continue to thrive amidst the shifting Arctic landscape.
In conclusion, the Inughuit people’s struggle against the impacts of climate change is a poignant reminder of the profound and far-reaching consequences of global environmental shifts. Their adaptation efforts serve as an example of how resilience, innovation, and a deep respect for tradition can guide communities through these turbulent times. As the Arctic continues to transform, the Inughuit’s experience underscores the urgent need for worldwide action to mitigate climate change and support those who are most vulnerable to its effects.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Life in the Arctic – Arctic Bureau

Education and Connectivity
Improved access to education and communication technologies has enabled younger generations to balance their heritage with modern influences.
Improved access to education and communication technologies has empowered younger generations to skillfully navigate the delicate balance between preserving their heritage and embracing modern influences. In today’s interconnected world, the fusion of tradition and innovation is more achievable than ever before, creating a harmonious synergy that shapes the cultural landscape of our times.
Education, as a cornerstone of this transformation, equips younger generations with the tools to understand, appreciate, and carry forward their cultural legacies. Through formal education, workshops, and community initiatives, young individuals gain profound insights into the customs, languages, and histories of their ancestors. They not only become custodians of their heritage but also emerge as ambassadors capable of sharing it with a global audience.
Furthermore, communication technologies have shattered geographical boundaries, allowing young people to remain connected to their cultural roots even when living far from their ancestral lands. Social media, video conferencing, and digital archives facilitate the exchange of stories, traditions, and experiences among members of the same culture, regardless of where they reside. This virtual connectedness fosters a sense of belonging, reinforcing cultural ties and making heritage an intrinsic part of their modern lives.
However, the embrace of modernity doesn’t dilute the significance of tradition; instead, it amplifies it. Younger generations, armed with newfound knowledge and digital tools, can infuse their cultural practices with contemporary relevance. This dynamic evolution ensures that traditions remain vibrant and adaptable, resonating with today’s challenges and aspirations.
The interplay between heritage and modern influences is not a unidirectional process; it is a dialogue. Younger generations are not passive recipients of tradition but active participants who contribute fresh perspectives and innovations. They introduce new methods of storytelling, art forms, and interpretations of their heritage, enriching it in the process. This dynamic interaction generates a cultural fusion that speaks to the complexities of the present while honoring the wisdom of the past.
In essence, improved access to education and communication technologies serves as a bridge, facilitating the intergenerational transfer of knowledge and strengthening the connection between heritage and modernity. As young individuals continue to embrace their roots while embracing the opportunities of the digital age, they create a tapestry that is both ancient and contemporary, reminding us that culture is a living entity, constantly evolving and renewing itself in the hands of each generation.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Life in the Arctic – Arctic Bureau

Greenland’s Inughuit people are a testament to human adaptability and cultural richness in one of the world’s harshest environments. Their deep connection to the Arctic environment, profound cultural traditions, and ability to thrive in extreme conditions offer a valuable perspective on the resilience of indigenous communities worldwide. As the Arctic faces rapid changes due to climate shifts, the Inughuit’s way of life and their enduring relationship with the land serve as a reminder of the importance of preserving our planet’s most remote and fragile regions.
nullTo delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Arctic Pollution Issues: A State of the Arctic Environment Report
More links
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Arctic Pollution Issues: A State of the Arctic Environment Report