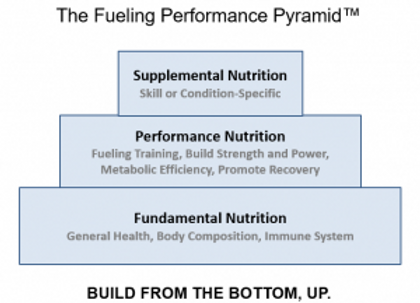
Introduction
Sports nutrition is a dynamic field that blends the principles of nutrition and exercise science to optimize athletic performance and enhance post-exercise recovery. In this article, we’ll explore the essential elements of sports nutrition, how it fuels performance, and its role in promoting recovery.
Indeed, sports nutrition is a fascinating and ever-evolving field that serves as a critical cornerstone of athletic excellence. By harmonizing the realms of nutrition and exercise science, it empowers athletes to unlock their full potential, both on the field and during the crucial recovery phase. Let’s delve deeper into the multifaceted world of sports nutrition, understanding its pivotal role in optimizing performance and promoting recovery:
Fueling Athletic Performance: At its core, sports nutrition is about fueling the body effectively to support optimal performance. Athletes require a precise balance of macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—tailored to their specific needs and activity levels. Carbohydrates serve as the primary energy source, providing the endurance needed for prolonged efforts. Proteins are essential for muscle repair and growth, while fats contribute to overall energy stores and endurance.
Hydration and Electrolytes: Proper hydration is a linchpin of sports nutrition. Dehydration can quickly impair performance, leading to fatigue, cramps, and decreased focus. Maintaining proper fluid balance is crucial, and athletes must replenish not only water but also electrolytes lost through sweat. Hydration strategies are tailored to the individual, considering factors like climate, intensity, and duration of exercise.
Timing and Meal Planning: The timing of nutrition intake is pivotal for athletes. Pre-workout meals provide the energy necessary for peak performance, while post-workout nutrition supports muscle recovery and replenishes glycogen stores. Meal planning takes into account these windows of opportunity, ensuring that the body is adequately fueled before, during, and after exercise.
Supplementation: In some cases, athletes may benefit from supplements to address specific nutrient deficiencies or optimize performance. Common supplements include vitamins, minerals, protein powders, and energy gels. However, supplementation should always be approached cautiously and under the guidance of a qualified sports nutritionist or healthcare provider.
Nutrient Dense Foods: Sports nutrition emphasizes the consumption of nutrient-dense foods. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health and well-being. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats not only optimizes athletic performance but also contributes to long-term health.
Individualization: Every athlete is unique, and sports nutrition plans are tailored to individual needs, goals, and preferences. Factors such as body composition, training intensity, sport type, and metabolic rate all influence nutritional requirements. Nutritionists work closely with athletes to design personalized plans that align with their specific athletic pursuits.
Recovery and Muscle Repair: Post-exercise nutrition is instrumental in the recovery process. Consuming a balanced mix of protein and carbohydrates shortly after exercise helps repair muscle tissue, replenish glycogen stores, and reduce muscle soreness. This phase is essential for the body to adapt and grow stronger.
Mental Performance: Sports nutrition extends beyond physical nourishment; it also encompasses mental performance. Proper nutrition can enhance cognitive function, focus, and decision-making abilities, all of which are crucial in competitive sports.
In summary, sports nutrition is a multifaceted discipline that plays a pivotal role in the world of athletics. It is the art and science of optimizing the body’s nutritional needs to support performance, endurance, and recovery. Athletes who embrace the principles of sports nutrition can unlock their full potential, setting the stage for peak physical and mental performance, while also promoting long-term health and well-being.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Sports Nutrition Program | Beef Loving Texans
Macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—are the cornerstone of sports nutrition. Each plays a vital role in fueling athletic performance:
nullFor additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Fueling and Hydrating Before, During and After Exercise

Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for athletes. They are stored in the muscles and liver as glycogen, which provides readily available energy during exercise. Maintaining adequate carbohydrate stores is crucial for endurance and high-intensity activities.
Carbohydrates, often referred to as the body’s “fuel of choice,” play a central role in an athlete’s performance and overall physical well-being. Let’s delve further into the significance of carbohydrates as the primary energy source for athletes and how maintaining optimal carbohydrate stores is pivotal for athletic success:
Energy Reservoir: Carbohydrates are the body’s preferred energy source due to their efficient and rapid conversion into glucose, the body’s primary fuel. When you consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose and stored as glycogen in the muscles and liver. This stored glycogen serves as a readily accessible reservoir of energy.
Endurance and Stamina: For athletes engaging in endurance activities like long-distance running, cycling, or swimming, carbohydrates are essential. The body taps into its glycogen stores to sustain energy levels over extended periods, allowing athletes to go the distance without fatigue setting in prematurely.
High-Intensity Performance: Carbohydrates are also crucial for high-intensity, anaerobic activities such as sprinting, weightlifting, and intense interval training. These activities demand rapid bursts of energy, and glycogen provides the quick, explosive power needed for peak performance.
Preventing Fatigue: Depletion of glycogen stores can lead to premature fatigue, commonly referred to as “hitting the wall” in endurance sports. Ensuring an ample supply of carbohydrates helps delay this point, allowing athletes to maintain their pace and mental focus.
Cognitive Function: Carbohydrates not only fuel the muscles but also support cognitive function. The brain relies heavily on glucose for energy, and during strenuous exercise, maintaining stable blood glucose levels is vital for decision-making, concentration, and overall mental acuity.
Muscle Recovery: Carbohydrates play a role in muscle recovery after exercise. Post-workout, consuming carbohydrates helps replenish glycogen stores, facilitating muscle repair and reducing the risk of overtraining and injury.
Protein Sparing: Adequate carbohydrate intake “spares” protein, meaning it prevents the body from breaking down muscle tissue for energy. This preservation of lean muscle mass is especially crucial for athletes aiming to build or maintain their strength and power.
Individualized Needs: Athletes have varying carbohydrate requirements based on their sport, training intensity, duration, and personal factors like age, gender, and metabolism. Tailoring carbohydrate intake to meet individual needs is essential for optimizing performance.
Nutrient Timing: Timing carbohydrate intake strategically is a key component of sports nutrition. Consuming carbohydrates before, during, and after workouts can help maintain energy levels, prevent glycogen depletion, and support recovery.
Balanced Diet: While carbohydrates are paramount, a well-rounded diet that includes protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals is crucial for overall athletic health. Carbohydrates should be part of a balanced nutrition plan that meets all nutrient requirements.
In essence, carbohydrates are the cornerstone of an athlete’s energy strategy, providing the power and stamina needed to excel in training and competition. Maintaining optimal carbohydrate stores through a combination of dietary choices and effective nutrition planning is a fundamental aspect of sports performance, helping athletes push their limits, achieve their goals, and reach their full athletic potential.
You can also read more about this here: High-Quality Carbohydrates and Physical Performance – PMC

Proteins are essential for muscle repair and growth. Athletes require slightly more protein than sedentary individuals to support muscle recovery and adapt to exercise. Protein intake should be timed strategically to optimize recovery.
Proteins are the building blocks of our body, and they play a crucial role in the realm of sports and fitness. They are not only essential for muscle repair and growth but also have several other vital functions that are particularly significant for athletes and active individuals.
Muscle Repair and Growth: One of the primary roles of protein in an athlete’s diet is to facilitate muscle repair and growth. When you engage in physical activity, especially strenuous exercise or strength training, your muscles undergo stress and microscopic damage. Protein provides the necessary amino acids to repair and rebuild these muscle fibers, making them stronger and more resilient. This process is essential for improving athletic performance and achieving fitness goals.
Increased Protein Needs: Athletes and active individuals have slightly higher protein requirements than sedentary individuals. The additional protein is needed to support muscle recovery and adaptation to exercise. Adequate protein intake ensures that your body has the resources it needs to repair and build muscles efficiently. The exact protein needs can vary depending on the type, intensity, and duration of your physical activity, as well as your age, gender, and overall goals.
Timing Matters: While the total daily protein intake is crucial, the timing of protein consumption is equally important for optimizing recovery and performance. Many athletes benefit from consuming protein-rich foods or supplements within the first hour after exercise. This post-exercise window is when the body is most receptive to protein, and it can enhance muscle protein synthesis, helping you recover faster and rebuild muscle tissue more effectively.
Complete Protein Sources: Athletes should aim to incorporate a variety of protein sources into their diet to ensure they receive all essential amino acids. Complete protein sources, such as lean meats, fish, poultry, dairy products, and plant-based options like soy, quinoa, and tofu, provide a balanced profile of amino acids. Combining different protein sources in your meals can help you meet your protein needs more effectively.
Balanced Diet: It’s important for athletes to maintain a balanced diet that includes not only protein but also carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Carbohydrates provide energy for workouts, while fats play a role in overall health and endurance. Ensuring a well-rounded diet supports your overall fitness and enhances your performance.
Individualized Approach: It’s essential to remember that protein requirements can vary significantly from one athlete to another. Factors like age, training intensity, body composition goals, and dietary preferences all play a role in determining your specific protein needs. Consulting with a registered dietitian or sports nutritionist can help you develop a personalized nutrition plan tailored to your unique requirements.
In conclusion, proteins are indeed essential for muscle repair and growth, but their significance in sports nutrition goes beyond that. Athletes require slightly higher protein intake and should strategically time their protein consumption to optimize recovery and adaptation to exercise. By understanding your individual protein needs and incorporating a balanced diet, you can ensure that your body has the resources it needs to excel in your chosen sport and maintain overall health.
You can also read more about this here: American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Nutrition and …

Fats are a source of long-term energy, particularly during low to moderate-intensity activities. They also play a role in supporting overall health. Athletes should prioritize healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
Fats, often vilified in the past, are indeed essential components of a well-rounded athlete’s diet. They serve as a valuable source of sustained energy, particularly during low to moderate-intensity activities, and their role in supporting overall health cannot be overstated. Here’s a more in-depth look at the significance of healthy fats for athletes and why they should be at the forefront of dietary considerations:
1. Sustained Energy: Healthy fats are like the slow-burning logs in a metabolic fire. During endurance activities such as long-distance running, cycling, or hiking, your body relies on fat as a primary energy source. Unlike carbohydrates, which provide quick but short-lived energy, fats release energy steadily, ensuring you have the endurance to go the distance.
2. Endurance and Stamina: For athletes engaged in extended training sessions or competitions, fats are essential for maintaining endurance and stamina. The ability to tap into fat reserves helps delay the depletion of glycogen (stored carbohydrates), allowing you to push through prolonged efforts effectively.
3. Post-Exercise Recovery: After a strenuous workout, your body requires nutrients for recovery and repair. Healthy fats play a role in this process by aiding in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K. They also provide a source of calories necessary for muscle repair and growth.
4. Hormone Regulation: Fats are essential for hormone production and regulation. Hormones like testosterone, which plays a crucial role in muscle development, rely on the presence of dietary fats. Ensuring an adequate intake of healthy fats supports a balanced hormonal profile.
5. Joint and Tissue Health: Intense physical activity can put stress on joints and connective tissues. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in foods like fatty fish and flaxseeds, possess anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce exercise-induced inflammation and support joint health.
6. Cognitive Function: The brain is not exempt from the benefits of healthy fats. Omega-3s, in particular, are associated with improved cognitive function, memory, and concentration. Athletes often require sharp mental focus, and a diet rich in these fats can contribute to better mental acuity.
7. Immune Support: Strenuous exercise can temporarily suppress the immune system. Healthy fats, especially those from sources like nuts and seeds, contain essential vitamins and minerals that support immune function, helping athletes stay healthy and resilient.
8. Muscle Preservation: Healthy fats play a role in preserving lean muscle mass. In situations where energy needs are not met solely through carbohydrates, the body turns to fats to prevent muscle breakdown.
9. Satisfaction and Appetite Control: Including healthy fats in your diet can enhance satiety, helping you feel fuller for longer. This can be particularly beneficial for athletes looking to manage their weight or maintain a balanced diet.
In summary, healthy fats are not the enemy; they are your allies in achieving peak athletic performance and overall well-being. Athletes should prioritize sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil to ensure they receive the numerous benefits these fats offer. By embracing these dietary choices, athletes can enhance their energy reserves, support their physical and mental health, and optimize their performance in both training and competition.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Nutrition and …

Proper hydration is fundamental for performance. Even mild dehydration can impair physical and cognitive function. Athletes should monitor their fluid intake and replace lost fluids during exercise, especially in hot and humid conditions. Electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, are vital for maintaining fluid balance.
nullFor additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Role of nutrition in performance enhancement and postexercise …

Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, play essential roles in energy production and overall health. Athletes often have increased nutrient needs due to higher energy expenditure. For example, iron is critical for oxygen transport, and vitamin D is essential for bone health. Athletes should ensure they meet their micronutrient requirements through a balanced diet or supplements when necessary.
Micronutrients are the unsung heroes of our diets, operating behind the scenes to power our bodies and maintain our well-being. These tiny but mighty vitamins and minerals orchestrate a symphony of functions, from energy production to immune system support. For athletes, whose bodies are finely tuned machines, the demand for these micronutrients is even more pronounced due to their elevated energy expenditure.
1. Iron: The Oxygen Carrier: Iron, for instance, takes center stage in the athlete’s nutrient lineup. This humble mineral is the linchpin in the process of oxygen transport, an absolutely critical function, especially during intense physical activity. Insufficient iron can lead to fatigue and decreased athletic performance. Therefore, ensuring an adequate intake of iron through diet or supplementation is vital for athletes.
2. Vitamin D: The Bone Protector: Vitamin D, the sunshine vitamin, is a linchpin of bone health. Athletes, who often put their musculoskeletal system to the test, require strong and resilient bones. Vitamin D facilitates calcium absorption, ensuring that bones remain dense and robust. Insufficient vitamin D can lead to increased injury risk and hinder performance. Thus, athletes must seek sunlight exposure and dietary sources of vitamin D to maintain their bone strength.
3. B Vitamins: The Energy Boosters: The B-complex vitamins, including B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), and others, are instrumental in energy production. They assist in converting food into the fuel needed for exercise. Athletes benefit greatly from a balanced intake of these vitamins to sustain their energy levels during training and competition.
4. Antioxidants: The Cellular Defenders: Antioxidant vitamins like vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-carotene protect athletes from the oxidative stress induced by vigorous physical activity. These micronutrients help combat the free radicals produced during exercise, reducing the risk of cell damage and inflammation.
5. Calcium and Magnesium: The Muscle Supporters: Calcium and magnesium are vital for muscle contraction and relaxation. They play a pivotal role in preventing muscle cramps and spasms, which can be a significant hindrance to athletic performance.
6. Zinc: The Immune Guardian: Zinc is a cornerstone of immune function. Intense training can temporarily suppress the immune system, making athletes more susceptible to illness. Adequate zinc intake helps bolster the body’s defense mechanisms.
7. Hydration and Electrolytes: The Dynamic Duo: While not vitamins or minerals in the traditional sense, maintaining proper hydration and electrolyte balance is paramount for athletes. Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium ensure nerve and muscle function while proper hydration keeps athletes performing at their peak.
In conclusion, athletes should view their nutritional intake as a performance-enhancing strategy. Meeting micronutrient requirements through a well-balanced diet is the foundation of athletic success. However, in cases where dietary needs cannot be fully met, supplements can be a valuable tool when recommended by healthcare professionals. By paying attention to these micronutrients, athletes can optimize their energy levels, reduce the risk of injury, and enhance their overall health and performance on the track, field, or court.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Nutritional optimization for female elite football players-topical review

The timing of meals and snacks is critical for athletes. Consuming carbohydrates before exercise can boost glycogen stores and enhance endurance. Post-exercise nutrition, particularly the intake of carbohydrates and protein within the “recovery window” of 30 minutes to two hours after exercise, supports muscle glycogen resynthesis and muscle repair.
The timing of meals and snacks is indeed a critical aspect of sports nutrition, and it can significantly impact an athlete’s performance and recovery. Let’s delve deeper into the importance of timing and its specific effects on athletes:
**1. Pre-Exercise Nutrition:
Before embarking on a training session or competition, athletes need to provide their bodies with the right fuel. Carbohydrates are especially crucial in this context. Consuming carbohydrates 1 to 4 hours before exercise helps boost glycogen stores in the muscles and liver. This stored glycogen serves as a readily available energy source during physical activity, which can enhance endurance and delay the onset of fatigue. Choosing easily digestible carbohydrates like fruits, whole grains, or energy gels is ideal to ensure that energy is available when it’s needed most.
**2. Intra-Exercise Nutrition:
For longer-duration activities, especially those lasting more than an hour, it’s essential to consider intra-exercise nutrition. Athletes can benefit from consuming carbohydrates and electrolytes during prolonged exercise to maintain blood sugar levels and prevent dehydration. This is particularly relevant for endurance athletes like marathon runners and cyclists.
**3. Post-Exercise Nutrition:
The “recovery window” of 30 minutes to two hours after exercise is a critical period for nutrition. During this time, the body is highly receptive to nutrient uptake, making it an optimal opportunity to kickstart the recovery process. Consuming a combination of carbohydrates and protein is key during this phase:
Carbohydrates: Replenishing glycogen stores is a primary goal of post-exercise nutrition. Carbohydrates should be consumed to replace the energy expended during the workout. Including fast-digesting carbohydrates like sports drinks, fruits, or rice can accelerate glycogen resynthesis.
Protein: Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth. After exercise, the body is in a state of heightened protein synthesis, making it an ideal time to provide the necessary building blocks for muscle recovery. Including sources of high-quality protein like lean meats, dairy, or plant-based options is crucial.
**4. Recovery Nutrition Variability:
The exact nutrient requirements during the recovery period can vary depending on the type, intensity, and duration of exercise, as well as individual factors like body composition and fitness level. Athletes may need to adjust their post-exercise nutrition based on these variables to optimize recovery. Working with a sports nutritionist can help tailor a recovery plan that aligns with specific training goals and needs.
**5. Hydration as Part of Recovery:
Rehydration is a critical aspect of recovery, especially if the exercise resulted in significant fluid loss through sweating. Replenishing lost fluids and electrolytes helps restore hydration levels and supports overall recovery. Athletes should prioritize water intake alongside their carbohydrate and protein intake during the recovery window.
In summary, the timing of nutrition in an athlete’s regimen is a strategic component for maximizing performance and recovery. Pre-exercise nutrition primes the body for activity, intra-exercise nutrition sustains energy levels during prolonged efforts, and post-exercise nutrition initiates the recovery process. Athletes should be mindful of their individual needs, the type of exercise they engage in, and the duration of their activities when planning their nutrition strategies. By optimizing meal and snack timing, athletes can unlock their full potential and maintain peak performance while reducing the risk of injury and fatigue.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Sporting performance and food – Better Health Channel

While a well-balanced diet should provide most of an athlete’s nutrition needs, supplements may be used strategically. Common supplements include creatine for strength and power athletes, caffeine for endurance, and protein supplements for those who struggle to meet their protein needs through food alone. It’s important to consult with a sports nutritionist or healthcare provider before incorporating supplements into an athlete’s regimen.
Supplements play a strategic role in an athlete’s nutrition regimen, serving as targeted tools to enhance performance and overall well-being. While a well-balanced diet forms the foundation, supplements offer specific benefits for different athletic pursuits. Here’s a more comprehensive exploration of the role of supplements in sports nutrition:
1. Creatine for Strength and Power: Creatine is a well-researched supplement that is particularly beneficial for strength and power athletes, such as weightlifters and sprinters. It enhances short-term, high-intensity performance by providing a rapid source of energy for muscle contraction. Creatine supplements are often used to boost power output and muscle strength during intense, brief efforts.
2. Caffeine for Endurance: Caffeine is a popular ergogenic aid among endurance athletes, including runners, cyclists, and triathletes. It can enhance endurance performance by increasing alertness, reducing perceived effort, and sparing glycogen stores. Caffeine is known for its ability to delay fatigue and improve focus during prolonged workouts or races.
3. Protein Supplements for Dietary Gaps: Protein supplements, such as protein shakes or bars, can be valuable for athletes who struggle to meet their protein needs through whole foods alone. Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth, making it crucial for athletes involved in strength training and muscle-building activities. Supplements help ensure an adequate protein intake, especially in situations where whole food sources may be limited or inconvenient.
4. Vitamins and Minerals: Certain vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D, calcium, iron, and magnesium, are critical for athletes’ overall health and performance. Athletes with specific dietary restrictions or those training at high volumes may benefit from targeted supplements to address potential deficiencies.
5. Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): BCAAs, including leucine, isoleucine, and valine, are amino acids that play a role in muscle protein synthesis and reducing muscle soreness. Athletes, particularly those engaged in resistance training or high-intensity workouts, may use BCAA supplements to support muscle recovery and reduce post-exercise muscle soreness.
6. Glutamine for Recovery: Glutamine is an amino acid that supports immune function and may help with post-exercise recovery. Athletes who train intensely and frequently might consider glutamine supplements to aid in muscle repair and reduce the risk of overtraining.
7. Fish Oil for Inflammation: Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil supplements have anti-inflammatory properties. They may be used by athletes to reduce exercise-induced inflammation and support joint health, especially in sports that place repetitive stress on joints.
8. Hydration and Electrolytes: Electrolyte supplements, such as potassium and sodium, are vital for maintaining fluid balance and preventing dehydration, particularly in endurance sports. Athletes may use electrolyte supplements during prolonged training sessions or races to replenish lost minerals and stay hydrated.
9. Pre-Workout Supplements: Some athletes opt for pre-workout supplements containing ingredients like beta-alanine, citrulline malate, or nitric oxide boosters to enhance energy, focus, and performance during training sessions. These supplements are designed to provide a pre-exercise energy boost and promote better workout outcomes.
10. Consultation with Experts: Before incorporating any supplements into an athlete’s regimen, it’s crucial to seek guidance from a sports nutritionist or healthcare provider. They can assess an athlete’s specific needs, recommend appropriate supplements, and ensure they are used safely and effectively.
In conclusion, supplements serve as valuable tools in sports nutrition when used strategically to address specific performance or dietary needs. However, their usage should always be individualized, informed by expert guidance, and integrated into a well-balanced diet. The key is to optimize an athlete’s nutrition regimen while prioritizing safety and overall well-being.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Fueling for Performance – PMC

Proper nutrition after exercise is crucial for recovery. Athletes should consume a combination of carbohydrates and protein to replenish glycogen stores and support muscle repair. Including antioxidant-rich foods can also help reduce inflammation and promote recovery.
nullTo delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Fueling for Performance – PMC

Every athlete is unique, and their nutrition needs should be tailored to their sport, goals, and individual characteristics. Working with a sports nutritionist can help athletes create personalized nutrition plans that optimize performance and recovery.
Indeed, the journey to peak athletic performance is a highly individualized one, where no two athletes are exactly alike. Just as each sport requires specific skills and strategies, the nutritional needs of athletes can also vary significantly based on factors like the type of sport they engage in, their personal goals, and their unique physiological characteristics.
For instance, a long-distance runner may require a different nutrition plan compared to a weightlifter or a soccer player. The energy demands, macronutrient ratios, and timing of meals and supplements can all vary depending on the sport’s requirements. A sports nutritionist plays a pivotal role in deciphering these nuances.
One of the primary benefits of collaborating with a sports nutritionist is the creation of a personalized nutrition plan. By conducting a thorough assessment that considers an athlete’s age, gender, body composition, training intensity, and goals, the nutritionist can tailor a plan that optimizes energy levels, enhances recovery, and minimizes the risk of injuries or fatigue.
Furthermore, a sports nutritionist takes into account the specific nutrient needs that emerge during various phases of an athlete’s training cycle. Whether it’s the high-carbohydrate requirements leading up to a marathon, the protein intake needed for muscle recovery and growth after strength training, or the hydration strategy to combat heat exhaustion during intense summer workouts, a well-designed plan addresses these specific demands.
Moreover, a nutritionist helps athletes navigate the complex world of dietary supplements, ensuring that any additions to their diet are safe, effective, and align with their goals. They can advise on the appropriate use of supplements like protein powders, branched-chain amino acids, or electrolyte replacements.
Beyond the physical aspects, working with a sports nutritionist can also address psychological elements related to eating habits and body image. Athletes often grapple with these issues, and a nutritionist can provide guidance and support to cultivate a healthy relationship with food.
In conclusion, recognizing that every athlete is unique is the first step towards optimizing performance and achieving long-term success. The partnership between athletes and sports nutritionists is a dynamic collaboration aimed at fine-tuning nutrition plans to meet individual needs. Through this synergy, athletes gain a competitive edge, ensuring that their diet becomes a powerful ally in their pursuit of excellence on the field or in any sporting arena.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Nutrition – Stanford University Athletics

In sports with weight categories, such as wrestling or combat sports, athletes may need to manage their weight safely and effectively. A sports nutritionist can help develop strategies that prioritize performance while achieving weight goals in a healthy manner.
Navigating weight management in sports with weight categories is a delicate balancing act that requires careful planning and expertise. Athletes in disciplines like wrestling and combat sports must not only excel in their chosen sport but also ensure they meet weight requirements safely and effectively. This is where the expertise of a sports nutritionist becomes invaluable. Here’s how their guidance can make a difference:
Customized Nutrition Plans: Sports nutritionists tailor nutrition plans to the unique needs of individual athletes. They consider factors like body composition, metabolism, training intensity, and weight goals to create a plan that optimizes performance while meeting weight requirements.
Balanced Macronutrients: Achieving weight goals doesn’t mean sacrificing essential nutrients. Sports nutritionists ensure that athletes receive a balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to support energy levels, muscle maintenance, and overall health.
Hydration Strategies: Proper hydration is crucial for both performance and weight management. Nutritionists help athletes develop hydration strategies to maintain optimal fluid balance, especially during weight cuts and competitions.
Safe Weight Cutting: Weight cutting, if done incorrectly, can be harmful and impair performance. Nutritionists provide guidance on safe weight-cutting techniques, such as gradual reductions and rehydration protocols, to minimize the risk of health complications.
Monitoring Progress: Nutritionists closely monitor an athlete’s progress throughout the training and weight-cutting process. They make necessary adjustments to the nutrition plan to ensure that the athlete remains on track to meet weight goals safely.
Nutrient Timing: Timing is crucial in sports nutrition. Nutritionists help athletes understand when to consume specific nutrients to optimize energy levels, recovery, and muscle preservation during weight management.
Education and Awareness: Sports nutritionists educate athletes about the importance of proper nutrition in achieving their weight goals. They raise awareness about the potential risks of extreme weight cutting and encourage a long-term, sustainable approach to weight management.
Psychological Support: Weight management can be mentally challenging. Nutritionists offer psychological support to help athletes cope with the pressures of making weight while staying focused on their performance goals.
Post-Weigh-In Strategies: After making weight, athletes need strategies to refuel and rehydrate effectively. Nutritionists design post-weigh-in plans that ensure athletes are in peak condition for competition.
Lifelong Skills: The knowledge and skills athletes acquire through working with a sports nutritionist extend beyond their competitive careers. They learn how to make informed nutritional choices for lifelong health and well-being.
In conclusion, the expertise of a sports nutritionist is instrumental in helping athletes safely manage their weight in sports with weight categories. By developing customized nutrition plans, promoting safe weight-cutting techniques, and offering ongoing support, nutritionists contribute not only to an athlete’s performance but also to their long-term health and well-rounded development as individuals.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Acute Weight Management in Combat Sports: Pre Weigh-In Weight …

Conclusion
In conclusion, the science of sports nutrition is a vital component of athletic success. By understanding the role of macronutrients, hydration, micronutrients, and timing in performance and recovery, athletes can optimize their nutrition regimens. Whether you’re a professional athlete or a recreational enthusiast, fueling your body with the right nutrients is key to achieving your athletic goals while maintaining overall health.
To summarize, the realm of sports nutrition stands as an indispensable pillar of athletic triumph. It serves as the compass guiding athletes toward the pinnacle of their performance potential. Through a comprehensive comprehension of the intricate interplay of macronutrients, the significance of optimal hydration, the micronutrients that serve as catalysts for success, and the precise timing of nutritional intake, athletes unlock the power to fine-tune their nutrition regimens.
1. A Personalized Approach: Sports nutrition is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor; it’s a highly personalized journey. Athletes can tailor their nutritional strategies to align with their unique physiology, training demands, and performance goals. This personalized approach ensures that each athlete maximizes their potential in a way that suits their individual needs.
2. Sustained Energy and Endurance: The strategic selection of macronutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, enables athletes to sustain energy levels and enhance endurance. Carbohydrates provide the necessary fuel for high-intensity workouts, while proteins aid in muscle repair and growth. The judicious inclusion of healthy fats contributes to long-lasting energy reserves.
3. Optimal Recovery: Recovery is as vital as performance itself. Sports nutrition plays a pivotal role in expediting post-exercise recovery. Proper nutrient intake following workouts replenishes glycogen stores, repairs muscle damage, and reduces inflammation. This accelerates recovery, reducing the risk of overtraining and injury.
4. Immune System Support: The micronutrients found in a well-balanced sports nutrition plan bolster the immune system. This is particularly crucial for athletes who subject their bodies to rigorous training routines, as intense exercise can temporarily suppress immune function. A robust immune system ensures that athletes remain in peak condition and can continue training consistently.
5. Injury Prevention: Adequate nutrition contributes to injury prevention. The right nutrients fortify bones, joints, and connective tissues, reducing the risk of injuries. Additionally, maintaining proper hydration is essential for joint lubrication and reducing the likelihood of strains and sprains.
6. Longevity in Sports: Sports nutrition is a lifelong pursuit. Its principles are applicable to athletes of all ages, from young talents embarking on their athletic journeys to seasoned veterans extending their careers. By sustaining healthy nutritional practices over the long term, athletes can enjoy a sustained and fulfilling athletic journey.
7. Holistic Health: Beyond athletic performance, sports nutrition fosters holistic health. It encourages athletes to maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients that promote overall well-being. This not only enhances athletic performance but also contributes to a high quality of life.
In closing, the science of sports nutrition is the compass that guides athletes toward the zenith of their potential. It is the roadmap to unlocking peak performance, fostering recovery, and nurturing long-term athletic careers. Whether an athlete competes on the world stage or engages in recreational pursuits, the mastery of sports nutrition is the key to achieving athletic aspirations while safeguarding overall health. It is a journey of self-discovery and optimization that empowers athletes to thrive, not only as competitors but as stewards of their own well-being.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: High-Quality Carbohydrates and Physical Performance – PMC
More links
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Gatorade Performance Partner: Fueling Athletic Performance