Table of Contents
The Russian Arctic, a vast and pristine wilderness spanning the northernmost reaches of the country, is home to a diverse tapestry of indigenous cultures and resilient communities. These northern dwellers have forged a unique way of life amidst the extreme cold, polar nights, and stunning landscapes of the Arctic. In this article, we embark on a journey to explore the lives of Russia’s Arctic inhabitants, gaining insights into their rich cultures, time-honored traditions, and their unyielding connection to the Arctic environment.
The Russian Arctic, a sprawling and untamed expanse stretching across the northernmost realms of the nation, remains one of the last great frontiers on our planet. Within this seemingly inhospitable wilderness, a mosaic of indigenous cultures and tenacious communities has carved out an extraordinary existence. Their lives are intimately intertwined with the land, sea, and ice, a testament to the incredible resilience of the human spirit in the face of extreme cold, polar nights, and the breathtaking but harsh beauty of the Arctic.
Venturing into the heart of the Russian Arctic is akin to stepping into a world where time seems to have its own rhythm. Here, amidst the unspoiled landscapes and pristine wilderness, the indigenous peoples, including the Nenets, Evenki, and Chukchi, have maintained their unique ways of life for countless generations. These cultures are woven into the fabric of the Arctic, shaped by its unforgiving environment, and enriched by their deep-rooted connection to the land and its resources.
In this article, we embark on a captivating journey to delve into the lives of Russia’s Arctic inhabitants. We are drawn into their rich and diverse cultures, where traditions are more than mere customs; they are the threads that bind communities together. From the nomadic reindeer herders of the tundra, who have mastered the art of survival on the open plains, to the coastal communities whose lives revolve around the rhythms of the sea, each group offers a unique perspective on what it means to thrive in the Arctic.
One cannot help but be captivated by the stories of the Chukchi, who have been navigating the icy waters of the Bering Sea for centuries, relying on their remarkable seamanship to sustain their communities. Equally inspiring are the Nenets, who traverse vast distances with their reindeer herds, maintaining a sustainable existence that is both resilient and deeply respectful of the environment.
As we journey through this remote and rugged terrain, we begin to grasp the profound significance of the Arctic environment in shaping not just the livelihoods but also the identities of its inhabitants. The Arctic is more than just a geographic region; it is a way of life, a source of cultural richness, and a wellspring of spiritual connection. The relationship between the people of the Russian Arctic and their surroundings is a delicate dance, a partnership that has evolved over centuries.
In exploring the lives of those who call the Russian Arctic home, we gain not only a greater appreciation for the diversity of human cultures but also a deeper understanding of the urgent need to protect this pristine wilderness. It is a reminder that as we contemplate the future of the Arctic, we must do so with reverence for its enduring inhabitants, their traditions, and their unyielding connection to the land, sea, and ice. In their stories, we find inspiration and a call to action, urging us to preserve the Arctic for generations to come, ensuring that this remarkable tapestry of human and natural heritage endures.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Indigenous Peoples’ access to Health Services
The Russian Arctic: A Land of Contrasts
Russia’s Arctic territory encompasses the northernmost regions of the country, including the Yamal Peninsula, the Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Chukotka, and many others. Spanning thousands of miles, the region presents a tapestry of diverse landscapes, from tundra and taiga to the frozen Arctic Ocean.
nullDon’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Chapter 4: Sea Level Rise and Implications for Low-Lying Islands …

Harsh Climates
The Arctic climate is characterized by brutally cold winters, polar nights, and the awe-inspiring phenomenon of the Northern Lights. Despite these challenges, the people of the Russian Arctic have learned to adapt and thrive.
The Arctic climate presents a relentless array of challenges, with its brutally cold winters, seemingly endless polar nights, and the enchanting but often harsh Northern Lights dancing in the sky. Yet, amid these formidable conditions, the resilient inhabitants of the Russian Arctic have demonstrated an incredible capacity not only to adapt but to thrive in this extreme environment.
Winter in the Russian Arctic can be unforgiving, with temperatures plummeting far below freezing. But rather than succumbing to the cold, the Arctic communities have developed a deep understanding of how to not just survive but make the most of these harsh conditions. Traditional practices like ice fishing and hunting have been honed over generations, providing essential sustenance and maintaining a connection to the land.
The polar night, a phenomenon where the sun disappears below the horizon for an extended period, creates a unique set of challenges, including psychological ones. Yet, the people of the Russian Arctic have learned to embrace the polar night as a time for reflection, storytelling, and cultural preservation. It’s a period when communities come together, sharing stories, knowledge, and traditions that have been passed down through the ages. In doing so, they ensure that their cultural heritage remains vibrant, even in the darkest of times.
The Northern Lights, or Aurora Borealis, are not only a visual spectacle but also a source of wonder and inspiration. In Arctic folklore, these ethereal lights are seen as spirits dancing in the night sky. This connection to nature and the environment is deeply ingrained in the culture of the Russian Arctic, fostering a profound respect for the natural world.
Furthermore, the adaptability of the Russian Arctic communities is evident in their ability to integrate modern technology and innovations into their traditional way of life. Snowmobiles, modern fishing equipment, and advanced communication tools have become essential tools that complement age-old practices, making life in the Arctic more efficient and secure.
In essence, the people of the Russian Arctic have mastered the art of adaptation, drawing on a rich cultural heritage and a profound connection to their environment. They’ve not only survived but have thrived in one of the harshest climates on Earth. Their resilience, adaptability, and close-knit communities stand as a testament to the human spirit and the remarkable ways in which cultures can flourish in even the most challenging of environments.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Following the tracks of snowbirds: The Arctic Demography Index …

Indigenous Diversity
Indigenous peoples, such as the Nenets, Chukchi, and Yamal Nenets, have called these icy expanses home for centuries. Each group has its own unique languages, cultures, and traditions, making the Russian Arctic a mosaic of indigenous diversity.
The Russian Arctic, a realm of frozen tundra and vast expanses of ice, is not a barren wilderness but a vibrant tapestry woven with the diverse cultures and traditions of its indigenous peoples. Among them, the Nenets, Chukchi, and Yamal Nenets stand as guardians of their ancestral lands, having called this pristine wilderness home for countless generations.
Within this icy expanse, a rich mosaic of indigenous diversity unfolds. The Nenets, nomadic reindeer herders, traverse the Arctic tundra with their massive herds, maintaining a way of life that has endured for centuries. Their language, traditions, and intricate knowledge of the land reflect a profound connection to the rhythms of the Arctic.
In contrast, the Chukchi people inhabit the eastern fringes of the Russian Arctic, near the Bering Strait. Their culture, deeply rooted in hunting and fishing, is a testament to human adaptation to extreme conditions. Their unique linguistic and cultural traditions highlight their resilience in this harsh environment.
On the Yamal Peninsula, the Yamal Nenets lead a semi-nomadic life, herding reindeer and relying on the land for sustenance. Their language and customs, passed down through generations, are intrinsically tied to the seasonal migrations of their reindeer herds. They are stewards of a land that provides not just sustenance but also a cultural identity deeply intertwined with the Arctic’s frozen beauty.
Despite the challenges posed by the modern world and climate change, these indigenous communities persist, safeguarding their languages, cultures, and traditions. Their knowledge of the land and its delicate balance is invaluable in the face of rapidly changing environmental conditions.
In the Russian Arctic, these indigenous peoples are not just survivors; they are vibrant contributors to the rich tapestry of human diversity. Their presence reminds us of the importance of respecting and preserving the cultural heritage and wisdom of those who have thrived in the harshest of environments, and they offer a unique glimpse into the intricate relationship between humanity and the Arctic wilderness.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Indigenous Peoples’ access to Health Services

Indigenous Cultures of the Russian Arctic
The indigenous peoples of the Russian Arctic have rich cultural traditions that have been passed down through generations. These cultures are deeply rooted in their close relationship with the land, animals, and the Arctic Ocean.
The indigenous peoples of the Russian Arctic possess a profound and enduring heritage, with cultural traditions that have been lovingly nurtured and faithfully passed down through countless generations. These rich and vibrant cultures are intrinsically linked to their remarkable relationship with the pristine Arctic landscapes, the magnificent wildlife that roams its frozen expanses, and the ever-mysterious Arctic Ocean that defines their existence.
At the heart of these cultural traditions lies a profound connection to the land, which is not merely the backdrop to their lives but an integral part of their identity. The land provides sustenance, shelter, and spiritual meaning. It’s the canvas upon which their stories, legends, and rituals are etched. The indigenous peoples of the Russian Arctic have an intimate understanding of the land’s rhythms, its secrets, and its unpredictable nature. This knowledge is passed down through oral histories, songs, and the wisdom of elders, ensuring that the link between the people and their environment remains unbroken.
Equally vital is their relationship with the Arctic’s unique fauna, from the majestic polar bear to the graceful reindeer. These animals have sustained the indigenous peoples for millennia, serving as sources of food, clothing, and materials for their art and crafts. This profound connection goes beyond mere survival; it’s a testament to the respect and reverence these cultures hold for the natural world. Each animal is seen as a partner in the intricate dance of life, and their stories are woven into the fabric of the indigenous cultures.
The Arctic Ocean, with its frozen expanses and powerful currents, plays a central role in shaping the lives and cultures of these indigenous peoples. It’s not just a body of water but a source of sustenance through fishing and hunting marine mammals. It’s a route of travel, connecting communities across vast distances. And it’s a place of spiritual significance, where rituals and ceremonies are performed to honor the ocean’s bounty and seek protection for those who venture upon its icy surface.
In essence, the rich cultural traditions of the indigenous peoples of the Russian Arctic serve as a testament to the profound interdependence between humanity and the environment. Their way of life, deeply rooted in the land, animals, and the Arctic Ocean, offers valuable lessons in sustainability, resilience, and the enduring power of cultural heritage. As we celebrate their traditions, we also recognize the urgent need to protect the fragile Arctic ecosystems and ensure that these unique cultures continue to thrive for generations to come.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Arctic design: revisiting traditional fur clothing within the daily routine …
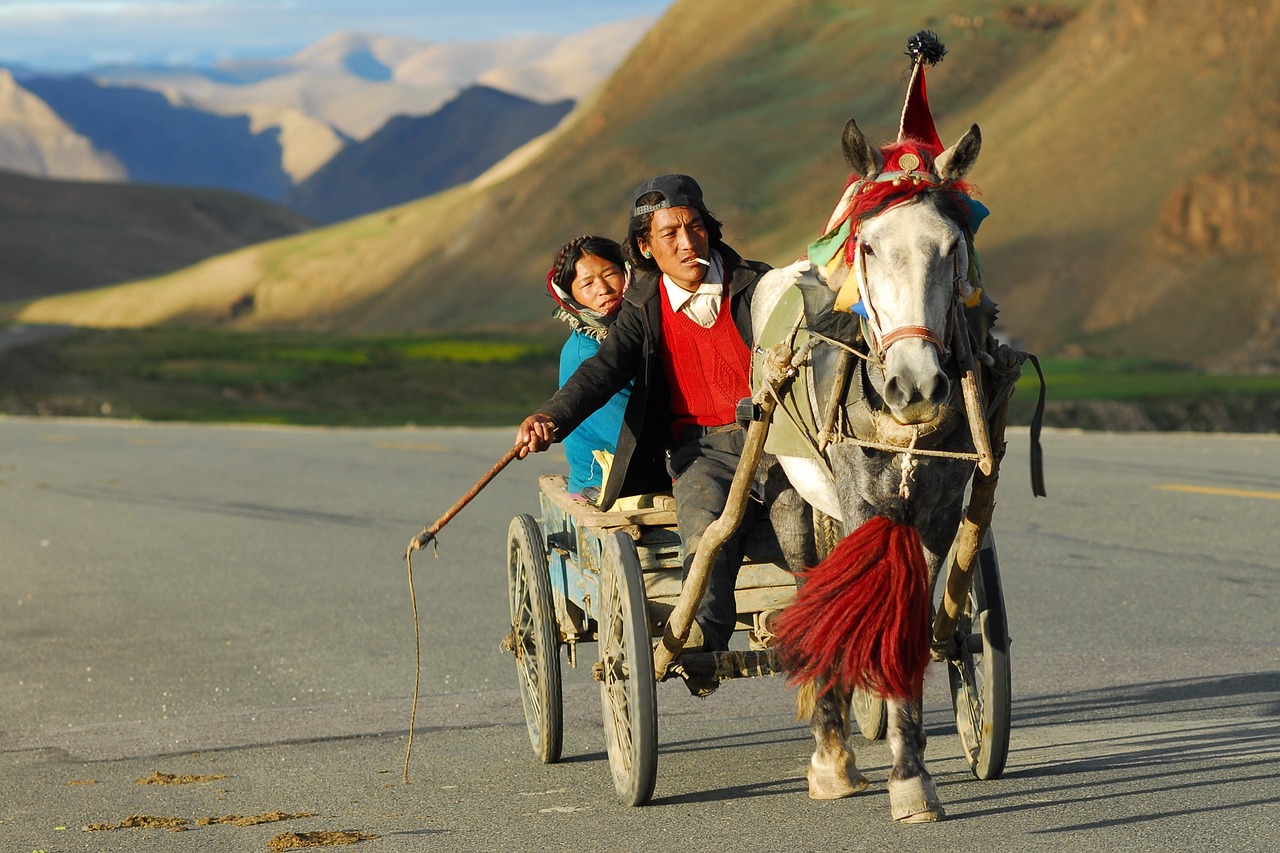

Nomadic Traditions
Many Arctic communities, such as the Nenets and Chukchi, have historically practiced nomadic lifestyles. They follow herds of reindeer, hunt marine mammals, and move with the changing seasons, living in harmony with the natural world.
nullLooking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Arctic design: revisiting traditional fur clothing within the daily routine …

Traditional Clothing
Indigenous clothing reflects their environment. Fur-lined parkas, boots, and intricate designs are not only functional but also artistic expressions of their culture.
Indigenous clothing is a remarkable reflection of their deep connection to the natural world that surrounds them. It goes far beyond mere attire; it’s a testament to their enduring relationship with the environment and a vivid expression of their unique cultural identity.
Fur-lined parkas, adorned with intricate designs, serve as perfect examples of this synergy between function and artistry. These parkas are not just garments to keep warm in the harsh climates they inhabit; they are a fusion of practicality and aesthetics that has evolved over generations.
The use of fur in indigenous clothing is a testament to their resourcefulness and sustainable practices. It’s a way of making the most of what the environment provides while also ensuring that every part of the animal is utilized, minimizing waste. The choice of fur also speaks to their knowledge of the insulating properties of different animal pelts, which is crucial for staying warm in the extreme cold.
Furthermore, the intricate designs adorning these garments often hold deep cultural significance. They tell stories of their people’s history, beliefs, and traditions. These patterns and motifs are not merely decorative; they are a means of passing down ancestral knowledge and celebrating their heritage.
Beyond practicality and aesthetics, indigenous clothing is a source of pride and a symbol of resilience. It’s a tangible representation of their ability to adapt to the harshest of environments and thrive in harmony with nature. In a world where modernization often threatens traditional ways of life, the continuation of these clothing traditions becomes an act of cultural preservation and defiance against the erasure of indigenous identities.
As we admire the fur-lined parkas, boots, and intricate designs, we are invited to recognize the profound connection between indigenous communities and the environments they call home. Their clothing is a testament to their adaptability, resourcefulness, and the enduring beauty of their cultural expressions amidst the challenging landscapes of the world’s northern regions.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: The Roots of Russian Conduct

Connection to the Land
Indigenous cultures of the Russian Arctic maintain a deep spiritual connection to the land and its creatures. Practices such as shamanism and rituals are conducted to honor and seek harmony with the natural world.
Indigenous cultures of the Russian Arctic have nurtured an unbreakable bond with their pristine surroundings, rooted in a profound spiritual connection that transcends generations. Their ways of life are intertwined with the rhythms of the land and its creatures, and their practices, such as shamanism and age-old rituals, serve as a testament to this enduring relationship.
Shamanism, in particular, holds a central place in the spiritual traditions of many Arctic Indigenous communities. Shamans, regarded as intermediaries between the physical and spiritual realms, play a pivotal role in preserving the delicate balance between humans and nature. Through ancient ceremonies, drumming, and trance-like states, shamans seek guidance from the spirit world to ensure the well-being of their people and the environment. This spiritual guidance is essential not only for individual harmony but also for the sustainability of their entire ecosystem.
Rituals, passed down through oral traditions and shared experiences, are another cornerstone of Indigenous cultures in the Russian Arctic. These rituals are not just ceremonies but profound expressions of gratitude and respect for the land, animals, and natural forces that sustain their communities. Whether it’s the celebration of the first catch of the season or the honoring of specific animals through ceremonies, these rituals reinforce their deep-seated belief in the interconnectedness of all living things.
Furthermore, the practice of seeking harmony with the natural world extends beyond spiritual rituals; it influences their everyday lives. Indigenous communities in the Russian Arctic have developed sustainable hunting and fishing practices that respect the cycles of nature. They understand that overexploitation of resources could disrupt the delicate equilibrium of their environment, and so they harvest only what is necessary for their immediate needs, ensuring that the land and its inhabitants continue to thrive.
In a world where modernization and climate change are challenging the very existence of Arctic ecosystems, the resilience of these Indigenous cultures serves as a beacon of hope. Their spiritual connection to the land fosters a deep commitment to its preservation, and their practices stand as valuable lessons in sustainable living and environmental stewardship. As we navigate an uncertain future, the wisdom of the Indigenous cultures of the Russian Arctic serves as an inspiration to us all, reminding us of the importance of living in harmony with the natural world.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: STATE OF THE WORLD’s INDIGENOUs PEOpLEs

Sustainable Practices
Sustainability is at the core of indigenous livelihoods. Practices such as reindeer herding and marine mammal hunting are carefully managed to ensure the continued health of animal populations.
Sustainability is at the core of indigenous livelihoods. Practices such as reindeer herding and marine mammal hunting are carefully managed to ensure the continued health of animal populations. These time-honored traditions, deeply rooted in respect for the environment, provide valuable lessons in how humans can coexist harmoniously with the natural world while meeting their essential needs.
Reindeer herding, practiced by indigenous groups like the Sami in northern Europe and various groups in Siberia, exemplifies the intricate balance between humanity and nature. These herders have honed their skills over generations, understanding the migratory patterns of reindeer and the delicate ecosystems they rely upon. They’ve developed sustainable practices that allow them to utilize reindeer resources for food, clothing, and shelter without jeopardizing the herds’ survival. The close connection between the herders and their reindeer not only ensures the animals’ well-being but also underscores the importance of maintaining traditional knowledge as a vital tool for preserving biodiversity.
Similarly, coastal indigenous communities, particularly those in the Arctic regions, have long relied on marine mammal hunting as a primary food source. This practice encompasses hunting seals, whales, and other marine animals. However, what sets these communities apart is their deep respect for these creatures and their environment. Indigenous hunters utilize every part of the animal, minimizing waste and demonstrating a profound understanding of the interconnectedness of all life in the ecosystem. They adhere to strict hunting quotas and seasonal restrictions, allowing animal populations to replenish and thrive.
These sustainable practices aren’t just about resource management; they represent a holistic worldview that recognizes the importance of maintaining a reciprocal relationship with the natural world. Indigenous cultures understand that their well-being is intricately tied to the health of the ecosystems in which they live. In doing so, they serve as guardians of biodiversity, demonstrating how human societies can thrive while ensuring the long-term vitality of the planet.
In an era where concerns about overexploitation and environmental degradation are paramount, the indigenous commitment to sustainability offers valuable insights. These practices emphasize the importance of preserving traditional knowledge and incorporating it into modern conservation efforts. Indigenous communities remind us that we can live in harmony with nature, not as conquerors, but as stewards, fostering a future where the world’s diverse ecosystems and cultures can thrive together. Their profound respect for the delicate balance of life on Earth serves as an inspiring example for all of humanity to follow.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Environmental justice in the context of urban green space …
Resilient Arctic Communities
Beyond indigenous cultures, the Russian Arctic is home to resilient communities that have adapted to the challenges of this remote environment.
nullIf you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: The Future of Arctic Cooperation in a Changing Strategic Environment

Economic Activities
Many Arctic communities engage in activities such as fishing, mining, and oil and gas production. These industries play a vital role in the regional economy and provide employment opportunities.
In the pristine and remote landscapes of the Arctic, many communities are uniquely positioned to harness the region’s abundant natural resources. While the Arctic’s breathtaking beauty and extreme conditions may be the first things that come to mind, it’s also a region of economic significance, where diverse industries have taken root to support both the local population and global demands.
One of the key pillars of economic activity in Arctic communities is fishing. The Arctic’s frigid waters teem with a rich variety of marine life, from cod and salmon to shrimp and crabs. These fisheries not only serve as a vital source of sustenance for local residents but also contribute to international markets, providing high-quality seafood to consumers around the world. The sustainable management of these fisheries is not only an economic necessity but also an environmental imperative, as preserving the delicate Arctic ecosystem is paramount.
Mining is another critical industry in the Arctic, with vast mineral deposits hidden beneath its frozen surface. Rich reserves of minerals like gold, diamonds, and rare earth elements are sought after for their economic value. The responsible extraction and processing of these resources have the potential to drive economic growth, create job opportunities, and bolster the economic resilience of Arctic communities. However, it’s essential that mining activities are conducted with the utmost consideration for environmental conservation and the well-being of local residents.
Oil and gas production is yet another sector that has gained prominence in the Arctic, given its vast reserves of hydrocarbons. These resources have global significance, providing a significant portion of the world’s energy needs. The revenue generated from oil and gas production plays a pivotal role in sustaining local economies, funding infrastructure development, and supporting social services in many Arctic regions. However, the industry is not without its challenges, as it must navigate the delicate balance between economic benefits and the preservation of fragile Arctic ecosystems.
While these industries undoubtedly provide much-needed employment opportunities and contribute to the regional economy, Arctic communities face unique challenges. Climate change, for instance, is altering the very landscapes upon which these industries depend, impacting both the environment and traditional ways of life. It’s a delicate dance that requires forward-thinking policies and a commitment to sustainability.
In conclusion, the Arctic is a region of great economic potential, where fishing, mining, and oil and gas production are integral to the livelihoods of its residents. Balancing economic development with environmental preservation and cultural continuity is a complex endeavor that demands responsible practices and a keen understanding of the delicate Arctic ecosystem. As the Arctic continues to evolve, these industries will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of this remarkable region.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: 2009 Conference Report Russia The Impact of Climate Change to …

Environmental Stewardship
As custodians of the Arctic, these communities actively participate in environmental monitoring and conservation efforts. They are committed to preserving the fragile Arctic ecosystem and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
As custodians of the Arctic, these communities play a pivotal role in safeguarding one of the Earth’s most fragile and vital ecosystems. Their commitment to environmental monitoring and conservation efforts is not just a responsibility; it’s a deeply ingrained part of their way of life.
Arctic communities are acutely aware of the profound changes occurring in their homeland due to climate change. Rising temperatures, melting ice, and shifting weather patterns threaten their traditional practices, livelihoods, and the very environment that sustains them. In response to these challenges, they have become active stewards of their land and seas.
Environmental monitoring is at the heart of their efforts. Local knowledge, passed down through generations, serves as a crucial tool in tracking changes. These communities closely observe the ice conditions, wildlife migrations, and weather patterns, providing invaluable data that contributes to our global understanding of climate change. Their insights are not only scientifically valuable but also culturally significant, as they bridge traditional wisdom with modern science.
Conservation is another cornerstone of their commitment. Arctic communities understand the interconnectedness of all life in their ecosystem. They advocate for sustainable practices in hunting, fishing, and gathering, ensuring that these activities do not harm the delicate balance of nature. By doing so, they are not just preserving their cultural heritage but also ensuring the survival of numerous species that rely on these ecosystems.
Furthermore, these communities actively engage in education and outreach programs. They share their experiences and knowledge with the wider world, raising awareness about the urgency of Arctic conservation and the global impacts of climate change. By doing so, they are powerful advocates for climate action and environmental protection on a global scale.
In their dedication to environmental preservation, Arctic communities also lead by example. Many have embraced renewable energy sources and sustainable technologies, reducing their carbon footprint and demonstrating the potential for sustainable living even in the harshest of environments. These efforts are a testament to their determination to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
In conclusion, as custodians of the Arctic, these communities are not passive observers of environmental change; they are active protectors and advocates for their homeland. Their commitment to environmental monitoring, conservation, and sustainable living serves as a beacon of hope in the face of the challenges posed by a warming world. They remind us that by valuing and preserving our planet’s most vulnerable places, we can collectively work towards a more sustainable and resilient future for all.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: 2009 Conference Report Russia The Impact of Climate Change to …
Modernization
Arctic communities are not isolated from the modern world. They have embraced technology and infrastructure development, enabling them to maintain connections to the broader Russian society.
Arctic communities, despite their remote locations, have not remained isolated from the modern world. In fact, they have shown remarkable adaptability by actively embracing technology and participating in infrastructure development. These efforts have allowed them to maintain essential connections with broader society, particularly in the case of Russian Arctic communities.
Digital Connectivity: Arctic communities have invested in digital infrastructure, ensuring that residents have access to the internet and modern communication tools. This connectivity not only facilitates communication with the outside world but also provides access to educational resources, telemedicine services, and opportunities for e-commerce. It has transformed the way people live, work, and interact in these remote regions.
Energy and Transportation: Infrastructure development includes improvements in energy generation and transportation. Sustainable energy sources such as wind and solar power have been harnessed to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, promoting environmental sustainability. Additionally, modern transportation infrastructure, including roads, airports, and ports, has improved access to essential goods and services.
Education and Healthcare: Arctic communities have invested in education and healthcare facilities, ensuring that residents receive quality services. Telemedicine, for instance, enables remote consultations with healthcare professionals, addressing the challenges posed by the vast distances between Arctic settlements and medical centers. Similarly, improved educational infrastructure empowers Arctic youth with opportunities for higher education and skill development.
Economic Diversification: By embracing technology and infrastructure development, Arctic communities have diversified their economies beyond traditional activities like fishing and hunting. They have explored opportunities in tourism, renewable energy, and even high-tech industries, contributing to economic growth and stability.
Cultural Preservation: Despite modernization, Arctic communities remain deeply committed to preserving their cultural heritage. They use technology and infrastructure to document and share traditional knowledge, languages, and artistic expressions with younger generations. Digital platforms and museums have become powerful tools for cultural preservation and dissemination.
Environmental Conservation: Arctic communities are keenly aware of the environmental challenges they face due to climate change. They have embraced technology to monitor and adapt to these changes, participating in research projects and advocating for sustainable practices that safeguard their unique ecosystems.
Collaboration with the Broader Society: Through their technological integration and infrastructure development, Arctic communities actively engage with the broader Russian society. They collaborate on regional development projects, share their experiences in adapting to the Arctic’s challenges, and contribute to national discussions on Arctic policy and sustainability.
In summary, Arctic communities have demonstrated resilience and adaptability by embracing technology and infrastructure development. These efforts have not only improved the quality of life for residents but have also enabled them to maintain meaningful connections with the broader Russian society. While they preserve their cultural heritage and traditional practices, they have successfully integrated modern tools and approaches to address the complex challenges posed by the Arctic environment and its changing dynamics.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Circumnavigation, Empire, Modernity, Race: “Meeting of Frontiers …

Russia’s Arctic inhabitants offer a captivating glimpse into the harmonious coexistence of humanity with the extreme environments of the far north. Their rich cultures, traditions, and deep-rooted connections to the land are a testament to human adaptability and resilience. As the Arctic faces unprecedented challenges due to climate change, these communities stand as guardians of their unique way of life and the pristine Arctic environment they call home. Their stories and insights into the Russian Arctic provide a valuable perspective on the importance of preserving our planet’s most remote and fragile regions.
nullFor additional details, consider exploring the related content available here GlobalTrends_2040.pdf
More links
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Following the tracks of snowbirds: The Arctic Demography Index …
