Table of Contents
- I. Prevention Strategies
- Proper Warm-Up and Stretching
- Conditioning and Strength Training
- Proper Technique and Coaching
- Appropriate Equipment
- Rest and Recovery
- II. Treatment Approaches
- R.I.C.E Method
- Physical Therapy
- Medication
- Surgery
- III. The Role of Rehabilitation
- Customized Programs
- Progressive Training
- Monitoring and Support
- Return to Play
Participation in sports offers numerous physical and mental health benefits, but it also comes with the risk of injuries. From sprains and strains to more severe trauma, sports injuries can be a setback for athletes of all levels. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the world of sports injuries, focusing on prevention strategies, effective treatment approaches and the crucial role of rehabilitation in getting athletes back in the game.
Engaging in sports is undeniably a gateway to a plethora of physical and mental health advantages, yet it is not without its share of risks. Sports injuries, ranging from minor sprains and strains to more severe traumas, can affect athletes across all skill levels. In this comprehensive article, we will embark on a journey into the realm of sports injuries, delving into the critical aspects of prevention, effective treatment modalities and the indispensable role of rehabilitation in facilitating the triumphant return of athletes to their chosen arena.
The Importance of Prevention: Prevention is the cornerstone of minimizing sports injuries. We will explore the strategies and practices that athletes, coaches and healthcare professionals can employ to reduce the risk of injuries. This section will include discussions on proper warm-up routines, conditioning exercises and injury-specific prevention techniques.
Recognizing and Managing Injuries: It is crucial for athletes and their support teams to recognize the signs of an injury promptly. We will delve into the different types of sports injuries, from common ones like sprains and fractures to less frequent but more severe incidents like concussions. Understanding the nature of these injuries and the initial steps in injury management can significantly impact recovery outcomes.
Effective Treatment Approaches: Beyond recognition, the timely and appropriate treatment of sports injuries is paramount. We will discuss various treatment approaches, including rest, ice, compression and elevation (RICE), physical therapy, medications, and, in some cases, surgical interventions. Highlighting the importance of a multidisciplinary approach, we will emphasize the role of healthcare professionals in providing expert care.
The Psychological Impact: Sports injuries often come with a psychological toll, affecting an athlete’s mental health and well-being. This article will explore the emotional aspects of injury, including the frustration, anxiety and depression that can accompany the recovery process. Strategies for maintaining a positive mindset and accessing mental health support will also be discussed.
Rehabilitation: The Road to Recovery: The journey back to the field or court is a critical phase for injured athletes. Rehabilitation plays a pivotal role in restoring strength, flexibility and functionality. We will explore the components of effective rehabilitation programs, from tailored exercise routines to monitored progress assessments.
Preventing Recurrence: Preventing re-injury is as vital as the initial injury prevention. We will delve into strategies for athletes to avoid recurrence and return to their sport with confidence, including gradual reintegration and ongoing injury prevention techniques.
Case Studies and Success Stories: Real-life examples of athletes who have successfully overcome sports injuries will provide inspiration and insight. Their stories will illustrate the challenges they faced, the strategies they employed and the triumph of returning to peak performance.
The Role of Technology: Technological advancements, such as wearable devices and digital health tools, are transforming sports injury prevention, diagnosis and treatment. We will explore how these innovations are reshaping the landscape of sports medicine and injury management.
By delving into the multifaceted world of sports injuries, we aim to equip athletes, coaches, healthcare professionals and sports enthusiasts with the knowledge and resources needed to navigate the complex terrain of sports-related injuries. From prevention to rehabilitation and beyond, our comprehensive exploration will empower individuals to enjoy the immense benefits of sports while minimizing the risks and repercussions of injuries.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Prevention Aiming at Functioning—Describing Prevention in the …
I. Prevention Strategies
Preventing sports injuries is the first line of defense for athletes. By following these strategies, athletes can reduce the risk of injury:
Preventing sports injuries is not only the first line of defense for athletes but also a fundamental pillar of athletic performance and longevity. Implementing these strategies not only reduces the risk of injury but also enhances overall athletic well-being and success:
Proper Warm-Up and Stretching: Before engaging in physical activity, athletes should dedicate time to a thorough warm-up. This prepares the body for exercise by increasing blood flow to muscles and improving flexibility. Incorporating dynamic stretching and mobility exercises can further enhance joint range of motion and reduce the risk of muscle strains and sprains.
Strength and Conditioning: A well-rounded strength and conditioning program tailored to the specific demands of the sport can bolster an athlete’s resilience to injury. Strengthening core muscles, stabilizers and muscle groups relevant to the sport not only enhances performance but also provides a protective shield against injuries.
Technique and Form: Proper technique and form are critical in sports. Athletes should receive coaching and guidance to ensure that they are executing movements correctly. This not only optimizes performance but also reduces the risk of overuse injuries and traumatic accidents resulting from poor form.
Gradual Progression: Athletes should avoid sudden spikes in training intensity, duration or load. Gradual progression allows the body to adapt to increased demands, reducing the risk of overtraining injuries. Coaches and athletes should work together to create well-structured training plans.
Rest and Recovery: Adequate rest and recovery are essential components of injury prevention. Rest days allow the body to repair and regenerate tissues. Athletes should prioritize sleep, incorporate active recovery techniques and listen to their bodies to avoid overtraining and burnout.
Nutrition and Hydration: Proper nutrition fuels athletic performance and supports recovery. Athletes should maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients, stay hydrated and consider consulting with a sports nutritionist for personalized guidance.
Footwear and Equipment: Choosing the right footwear and equipment for the sport is crucial. Ill-fitting shoes or equipment can lead to discomfort, instability and injury. Athletes should invest in quality gear and ensure it is well-maintained.
Injury Awareness: Athletes should be educated about common sports injuries and their risk factors. Understanding the signs of an impending injury allows for early intervention and preventive measures.
Cross-Training: Engaging in cross-training activities can reduce the risk of overuse injuries by diversifying the physical demands on the body. Incorporating activities like swimming, cycling or yoga can help athletes maintain overall fitness while reducing the strain on specific muscle groups or joints.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals: Athletes should establish a relationship with healthcare professionals, such as sports medicine doctors, physical therapists and athletic trainers. Regular check-ups and consultations can help identify potential issues and receive guidance on injury prevention.
Mental Preparation: Sports injuries can also result from mental stress and anxiety. Incorporating mental preparation techniques, such as visualization, mindfulness and stress management, can help athletes maintain focus and reduce the risk of injury-inducing mistakes.
Listen to the Body: One of the most critical aspects of injury prevention is listening to the body. Athletes should be attuned to signs of fatigue, pain or discomfort. Ignoring these signals can lead to overuse injuries. When in doubt, it’s better to rest and seek professional advice.
Incorporating these injury prevention strategies into an athlete’s routine not only safeguards against injuries but also supports consistent and sustainable athletic performance. By prioritizing health and well-being, athletes can enjoy their sport to the fullest while minimizing the setbacks and challenges associated with injuries.
You can also read more about this here: Prevention Aiming at Functioning—Describing Prevention in the …

Proper Warm-Up and Stretching
A thorough warm-up routine and proper stretching before physical activity can increase flexibility and reduce the risk of muscle strains.
A comprehensive warm-up routine and effective stretching are not mere preparatory rituals before physical activity; they are essential components of injury prevention and performance enhancement. When done correctly, these practices can have a profound impact on the body’s readiness for exercise and overall well-being.
First and foremost, a well-structured warm-up serves as a transition phase for the body, gently shifting it from a state of rest to one of heightened activity. This gradual increase in heart rate and blood flow primes the cardiovascular system, ensuring that the heart and lungs are ready to meet the increased demand for oxygen during exercise. As a result, the risk of sudden stress on the heart is minimized.
Moreover, a proper warm-up initiates a series of physiological responses that prepare the muscles, tendons and ligaments for the upcoming physical exertion. Muscle temperature rises, leading to increased elasticity and improved muscle contraction efficiency. This not only enhances athletic performance but also reduces the risk of muscle strains, tears and other injuries that can occur when the muscles are not adequately prepared.
Stretching, when incorporated into the warm-up routine, adds another layer of injury prevention. Dynamic stretching, in particular, helps increase joint range of motion and muscle flexibility. This dynamic stretching routine mimics the movements of the activity you’re about to engage in, ensuring that your muscles are stretched and lengthened in a way that’s relevant to the upcoming exercise. This targeted approach reduces the likelihood of overstretching or straining muscles during physical activity.
In addition to reducing the risk of injury, proper stretching can enhance overall athletic performance. It allows for a greater range of motion, facilitating more efficient and powerful movements. Improved flexibility can also lead to better posture and muscle balance, reducing the chances of developing chronic conditions related to muscle imbalances.
In conclusion, a thorough warm-up and proper stretching are essential components of a safe and effective exercise regimen. They not only prepare the body for physical activity but also contribute to enhanced performance and injury prevention. Incorporating these practices into your routine demonstrates a commitment to your long-term well-being, ensuring that you can enjoy physical activity while minimizing the risk of injuries that can disrupt your active lifestyle.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: CURRENT CONCEPTS IN MUSCLE STRETCHING FOR …

Conditioning and Strength Training
Building strength and endurance through regular training can improve overall stability and reduce the risk of overuse injuries.
Committing to regular training goes beyond just improving specific skills or physical performance; it’s a pathway to enhancing overall stability and significantly reducing the risk of overuse injuries.
When we engage in consistent training routines, we progressively build not only strength and endurance but also a strong foundation of stability. This stability is vital for maintaining proper posture and body mechanics during physical activities, preventing unnecessary strain on muscles and joints.
Moreover, regular training allows our bodies to adapt and become more resilient. As we gradually increase the intensity and duration of our workouts, our muscles, tendons and ligaments grow stronger and more flexible. This adaptive process helps protect against the wear and tear that can lead to overuse injuries.
Overuse injuries often occur when repetitive motions or excessive stress are placed on certain areas of the body without adequate recovery time. By incorporating varied exercises and giving our bodies the rest they need, we mitigate the risk of these injuries. Additionally, training that includes mobility and flexibility work can help prevent muscle imbalances that might otherwise lead to overuse injuries.
The benefits of regular training extend beyond physical improvements. It can boost confidence and mental resilience, which can be especially valuable when facing physical challenges or pushing through plateaus. It fosters discipline and dedication, encouraging individuals to stick with their fitness routines over the long term.
In conclusion, building strength and endurance through regular training isn’t just about achieving specific fitness goals; it’s about creating a solid foundation of stability and resilience. This foundation helps safeguard against overuse injuries, allowing individuals to enjoy a physically active lifestyle while minimizing the risk of setbacks. It’s an investment in both immediate well-being and long-term physical health.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Understanding Sports Medicine: A Comprehensive Guide

Proper Technique and Coaching
Learning and practicing correct techniques under the guidance of knowledgeable coaches can significantly reduce the risk of injuries, especially in contact sports.
Learning and practicing correct techniques under the guidance of knowledgeable coaches is not just about excelling in sports; it’s a fundamental aspect of ensuring the safety and well-being of athletes, particularly in contact sports. The importance of proper technique cannot be overstated when it comes to minimizing the risk of injuries.
In contact sports like football, rugby and martial arts, the potential for physical contact and impact is high. Without the right skills and techniques, athletes are more susceptible to injuries ranging from sprains and strains to more severe concussions or fractures. Coaches play a pivotal role in imparting the essential skills needed to navigate these challenges safely.
These coaches possess a wealth of experience and expertise, honed through years of involvement in their respective sports. They understand the nuances of body positioning, movement and timing that can make all the difference between a successful play and a potentially devastating injury. Their guidance ensures that athletes not only perform at their best but also do so in a way that minimizes risk.
Proper technique isn’t just about individual performance; it also encompasses the importance of teamwork and communication. Coaches emphasize the significance of coordinated efforts and strategic plays, reducing the likelihood of collisions or accidents on the field. In contact sports, where teamwork is paramount, well-coached teams are not only more successful but also safer.
Beyond the physical aspects, coaches instill a sense of discipline and respect for the rules of the game. They emphasize the importance of fair play and sportsmanship, which not only contribute to the overall safety of the sport but also shape athletes into responsible individuals both on and off the field.
Moreover, coaches keep abreast of the latest developments in sports science and injury prevention techniques. They ensure that their athletes are equipped with the most up-to-date knowledge and strategies for staying safe in a dynamic and ever-evolving sports landscape.
In essence, the role of coaches in teaching correct techniques goes beyond skill development; it’s about fostering a culture of safety and excellence. Athletes who learn and practice under their guidance not only perform at their best but also minimize the risks associated with contact sports. This combination of skill and safety ultimately creates an environment where athletes can thrive, push their limits and enjoy their chosen sport to the fullest.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Injury Prevention, Safe Training Techniques, Rehabilitation, and …

Appropriate Equipment
Wearing the right protective gear and ensuring that it fits properly is essential, whether it’s a helmet for football or the right footwear for running.
“Wearing the right protective gear and ensuring that it fits properly is essential, whether it’s a helmet for football or the right footwear for running. This attention to detail not only enhances safety but also plays a crucial role in performance and overall well-being.
In contact sports like football, hockey or rugby, a well-fitted helmet can be a lifesaver. It provides a critical layer of protection for the head, reducing the risk of head injuries and concussions. However, it’s not enough to simply wear any helmet; it must fit snugly and be properly fastened to offer the intended protection. Athletes, coaches and parents should prioritize regular helmet checks and replacements when necessary to ensure optimal safety on the field.
Footwear is another area where proper fit matters significantly, especially for runners. Ill-fitting shoes can lead to a host of issues, from blisters and discomfort to more serious injuries like sprains and stress fractures. Choosing the right running shoes, tailored to your gait and foot shape, can prevent these problems and enhance your running experience. Regularly replacing worn-out shoes is equally important to maintain proper support and cushioning.
Beyond safety concerns, well-fitted gear contributes to overall comfort and performance. In sports and activities that demand agility, mobility or precise movements, improperly fitting equipment can hinder an athlete’s ability to perform at their best. Conversely, gear that fits well promotes confidence and allows athletes to focus on their skills and technique.
Moreover, wearing the right protective gear sets a positive example for younger athletes and encourages safe practices. When children and teenagers see their role models prioritizing safety and taking care to wear the appropriate gear, it reinforces the importance of these practices from an early age. It instills a culture of safety and responsibility within sports communities.
In conclusion, the importance of wearing well-fitted protective gear cannot be overstated. It is a fundamental aspect of safety, performance and injury prevention in various sports and activities. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or a novice, taking the time to ensure that your gear fits properly is an investment in your well-being, comfort and success in your chosen pursuit.”
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Preventing Sports Injuries | Johns Hopkins Medicine

Rest and Recovery
Adequate rest between training sessions is crucial to allow the body to recover and reduce the risk of overtraining injuries.
“Adequate rest between training sessions is not just a suggestion; it’s a fundamental requirement for any athlete striving for peak performance and long-term well-being. This crucial aspect of training extends beyond the need for a good night’s sleep; it encompasses a broader approach to recovery that includes rest days, active recovery and periodization.
Rest Days: Incorporating scheduled rest days into your training regimen is essential. These days provide an opportunity for your body to repair and regenerate. Muscles that are subjected to intense training need time to heal and joints require a break from constant stress. Without adequate rest, the risk of overuse injuries such as stress fractures, tendonitis and muscle strains significantly increases.
Active Recovery: Active recovery involves low-intensity activities that promote blood flow and aid in muscle recovery. Activities like swimming, yoga or light cycling can alleviate muscle soreness and reduce the risk of stiffness. It’s a way to stay active while allowing the body to recover from intense workouts.
Periodization: Professional athletes and coaches understand the importance of periodization in training. This concept involves varying the intensity and volume of workouts throughout the training cycle. By incorporating periods of lower intensity and reduced training load, athletes give their bodies much-needed breaks while still making progress. Periodization helps prevent overtraining and burnout.
Nutrition and Hydration: Recovery isn’t just about rest; it’s also about fueling your body with the right nutrients. Adequate nutrition and hydration are vital components of the recovery process. Consuming a balanced diet with sufficient protein, carbohydrates and essential vitamins and minerals aids in muscle repair and growth. Proper hydration supports the body’s functions and helps flush out toxins.
Mental Recovery: Resting the mind is as crucial as resting the body. Mental fatigue can lead to decreased motivation and increased risk of injury. Techniques like mindfulness meditation, visualization and relaxation exercises can help athletes recharge mentally and maintain a positive mindset.
In summary, adequate rest and recovery are non-negotiable elements of any successful training program. They not only reduce the risk of overtraining injuries but also contribute to overall performance improvements. The right balance of training, rest and recovery techniques ensures that athletes can sustain their passion and commitment to their sport for the long haul, achieving their goals without compromising their health.”
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Sports Injuries: Types, Treatment and Prevention

II. Treatment Approaches
Despite best efforts in prevention, injuries can still occur. When they do, prompt and appropriate treatment is crucial:
Navigating Injuries: The Imperative of Swift and Effective Treatment
Despite our most diligent efforts in injury prevention, the unpredictability of life and sports means that injuries can still occur. When they do, whether on the field, at home or in daily life, the course of action that follows is critical. Swift and appropriate treatment can make all the difference in the road to recovery and long-term well-being.
1. Minimizing Damage: Prompt treatment is often the key to minimizing the extent of injury. In many cases, early intervention can prevent a minor issue from developing into a more severe or chronic condition. Whether it’s a sprain, strain or even a fracture, getting the right treatment as soon as possible can significantly impact the healing process.
2. Managing Pain and Discomfort: Injuries often come with pain and discomfort. Effective treatment, whether through medication, physical therapy or other modalities, can help manage and alleviate these symptoms. This not only improves an individual’s quality of life during the recovery period but also aids in a faster return to regular activities.
3. Restoring Functionality: Rehabilitation and therapeutic interventions are central to injury treatment. These approaches aim not only to heal the injury but also to restore functionality. Whether it’s regaining range of motion after a joint injury or rebuilding strength and endurance, timely treatment plays a crucial role in achieving these goals.
4. Preventing Complications: Certain injuries, if left untreated or inadequately managed, can lead to complications. For instance, a seemingly minor wound can become infected if not treated promptly. Proper care and treatment are essential to preventing such complications and ensuring a smoother recovery process.
5. Psychological Well-being: Injuries can take a toll not just on the body but also on an individual’s psychological well-being. The frustration, anxiety or even depression that can accompany an injury can be mitigated through timely treatment and support. This holistic approach to care considers not only the physical but also the emotional aspect of recovery.
6. Enhancing Long-Term Outcomes: The effects of an injury can linger long after the initial incident. Swift and appropriate treatment can enhance long-term outcomes, reducing the risk of chronic pain, disability or recurrent issues. It ensures that individuals can return to their normal routines and activities with confidence and vitality.
7. Learning and Prevention: Each injury can serve as a learning opportunity for individuals and healthcare professionals alike. Understanding the cause and context of an injury can inform prevention strategies to reduce the risk of recurrence. This, in turn, contributes to improved overall health and safety.
In the realm of injuries, time is often of the essence. Whether it’s a sports injury, an accident or a health-related concern, the importance of prompt and appropriate treatment cannot be overstated. It not only accelerates the healing process but also promotes well-being and prevents complications. In the face of injuries, individuals and healthcare providers alike recognize that timely and effective treatment is the linchpin to a brighter and healthier future.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Great Challenges Toward Sports Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation

R.I.C.E Method
Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation (R.I.C.E) is a standard method for treating many sports injuries, such as sprains and strains, in the initial stages.
Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation (R.I.C.E) is a standard method for treating many sports injuries, such as sprains and strains, in the initial stages. This simple yet highly effective protocol is often the first line of defense when an athlete encounters an injury on the field or during training. Let’s explore the components of R.I.C.E in more detail and understand why it remains a cornerstone of sports injury management:
Rest: Rest is the foundation of the R.I.C.E protocol. When an injury occurs, the affected area needs time to heal. Resting it allows damaged tissues to repair and prevents further damage. It’s essential to avoid putting weight or strain on the injured area, which may require using crutches, slings or other supportive devices, depending on the injury’s location and severity.
Ice: Applying ice to the injured area helps reduce pain and inflammation. Cold therapy constricts blood vessels, decreasing blood flow to the injured site, which can minimize swelling and tissue damage. It also numbs the area, providing pain relief. Ice should be applied for 15-20 minutes every 1-2 hours during the first 48 hours after the injury. It’s crucial to use a barrier, like a cloth, between the ice pack and the skin to prevent frostbite.
Compression: Compression involves wrapping the injured area with an elastic bandage or compression sleeve. This helps control swelling by applying gentle pressure, which prevents excess fluid buildup in the injured tissues. Be cautious not to wrap it too tightly, as it can impair blood circulation. Monitoring the area for any signs of numbness, tingling or color changes is essential.
Elevation: Elevation is the final component of the R.I.C.E protocol. Elevating the injured limb or area above the level of the heart whenever possible helps reduce swelling by facilitating the drainage of excess fluid away from the injured site. It’s particularly important for injuries in the extremities, such as ankle or knee sprains. Propping up the injured area with pillows or cushions during rest can assist in proper elevation.
The effectiveness of R.I.C.E lies in its ability to address the immediate impact of an injury. By reducing pain, swelling and the risk of further damage, it creates an optimal environment for the body’s natural healing processes to kick in. However, it’s essential to note that R.I.C.E is typically a first-aid measure for minor to moderate injuries. Severe injuries or those that don’t improve with R.I.C.E should be evaluated by a medical professional for a more comprehensive treatment plan, which may include physical therapy or surgery.
In summary, R.I.C.E is a tried-and-true method for managing sports injuries during their initial stages. It empowers athletes to take immediate action to minimize the damage and expedite the healing process. While it may not be a panacea for all injuries, its simplicity and effectiveness make it a valuable tool in an athlete’s arsenal for staying in the game and on the path to recovery.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: RICE and MEAT: Physical Therapy Terms You Need to Know for …

Physical Therapy
Many injuries require rehabilitation exercises to restore strength, flexibility and function. Physical therapists play a vital role in the recovery process.
In the intricate journey of healing and recovery, physical therapists emerge as indispensable guides, offering their expertise and unwavering support to individuals grappling with injuries. Their role extends far beyond the clinical setting, encompassing various facets of the rehabilitation process and contributing significantly to the restoration of strength, flexibility and function.
Tailored Rehabilitation Plans: Physical therapists are adept at crafting personalized rehabilitation plans that address the unique needs of each patient. They meticulously assess the nature and extent of injuries, taking into account factors like age, fitness level and long-term goals. This tailored approach ensures that recovery strategies align with individual capabilities and aspirations.
Restoring Physical Function: Whether it’s regaining the ability to walk after a lower extremity injury or restoring full range of motion in an injured joint, physical therapists are the architects of functional recovery. Their expertise in biomechanics and exercise physiology enables them to design exercises and interventions that gradually and safely rebuild physical capabilities.
Pain Management: Injuries often come with pain and discomfort. Physical therapists employ various techniques, such as manual therapy, modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation and targeted exercises, to alleviate pain and improve the overall sense of well-being during the recovery process.
Promoting Independence: Physical therapists empower patients to regain their independence. They not only facilitate physical recovery but also offer guidance on adapting daily activities and routines to accommodate any lingering limitations. This support fosters self-reliance and enhances overall quality of life.
Preventing Recurrence: Understanding the root causes of injuries is pivotal in preventing their recurrence. Physical therapists delve into biomechanical assessments and movement analysis to identify contributing factors. By addressing these underlying issues, they reduce the risk of reinjury and equip patients with tools for long-term wellness.
Education and Empowerment: Education is a cornerstone of the physical therapist’s role. They educate patients about their injuries, treatment options and the rationale behind specific exercises. This knowledge empowers patients to actively engage in their recovery journey and make informed decisions about their health.
Supporting Mental Health: Physical therapy is not solely about physical healing; it also addresses the psychological aspects of recovery. Physical therapists provide emotional support, motivation and encouragement, helping patients navigate the mental and emotional challenges that often accompany injuries.
Collaborative Care: Physical therapists work closely with a multidisciplinary team, including physicians, orthopedic specialists and sports trainers, to ensure comprehensive care. This collaborative approach maximizes the effectiveness of treatments and fosters a holistic view of patient well-being.
Continuous Improvement: Physical therapists stay up-to-date with the latest research and advancements in their field, ensuring that their practices are evidence-based and aligned with best practices. This commitment to continuous learning benefits patients by providing access to the most effective and cutting-edge rehabilitation methods.
In essence, physical therapists are the architects of recovery, guiding individuals from the depths of injury toward renewed strength, function and vitality. Their role extends beyond the clinical setting, encompassing elements of education, empowerment and holistic care. As champions of resilience, physical therapists empower patients to not only recover but also to thrive in the face of adversity, proving that the path to restoration is not just about healing the body but nurturing the spirit as well.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Sports Injuries: Types, Treatment and Prevention

Medication
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or prescribed medications can help manage pain and inflammation.
The availability of pain relief options, both over-the-counter and prescription medications, plays a vital role in helping individuals manage pain and inflammation effectively. These medications offer not only relief from discomfort but also the potential for improved quality of life, especially for those dealing with chronic pain or acute injuries.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers like ibuprofen (Advil) and acetaminophen (Tylenol) are readily accessible and can be instrumental in alleviating mild to moderate pain and reducing inflammation. They are often the first line of defense against common ailments like headaches, muscle aches and minor injuries. OTC options empower individuals to take control of their pain management without the need for a prescription.
Prescribed Medications: For more severe or chronic pain conditions, healthcare providers may prescribe medications that target specific pain mechanisms. These prescription medications can include opioids for severe pain, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for inflammatory conditions and various other pain-modulating agents. Prescribed medications are tailored to an individual’s unique pain profile, taking into account factors like pain type, severity and underlying causes.
Management of Chronic Conditions: Prescription medications are indispensable for individuals grappling with chronic pain conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia or neuropathy. These conditions often require ongoing pain management strategies, which can involve the use of specialized medications. Pain management plans, created in consultation with healthcare providers, aim to enhance the individual’s quality of life by minimizing pain and maximizing function.
Balancing Benefits and Risks: It’s important to note that both OTC and prescribed medications carry potential risks and side effects. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in guiding patients toward the most suitable pain relief options while considering factors like allergies, interactions with other medications and overall health status. Ensuring that medications are used as directed and under medical supervision helps mitigate risks.
Complementary Approaches: In addition to medications, many individuals incorporate complementary approaches to pain management, such as physical therapy, acupuncture, mindfulness techniques or lifestyle modifications. These approaches can enhance the effectiveness of pain relief strategies and promote long-term well-being.
Improving Quality of Life: Effective pain management can significantly improve an individual’s overall quality of life. It can facilitate better sleep, enhance mobility and reduce the emotional burden associated with chronic pain. This, in turn, can empower individuals to engage in daily activities, maintain social connections and pursue their goals and aspirations.
Personalized Pain Management: The field of pain management continues to advance, emphasizing the importance of personalized approaches. Healthcare providers strive to tailor pain management strategies to the specific needs and preferences of each patient, recognizing that pain is a complex and individual experience.
In summary, both over-the-counter and prescription pain relievers are valuable tools in the toolbox of pain management. They offer relief from discomfort, reduce inflammation, and, when used appropriately and under medical guidance, contribute to improved well-being. The choice of pain relief method depends on the nature and severity of the pain and healthcare providers play a pivotal role in guiding individuals toward the most effective and safest solutions for their unique pain challenges.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Sports Medicine and Health Science | Journal | ScienceDirect.com …

Surgery
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair severe injuries, such as torn ligaments or fractures.
In the realm of sports and physical activity, injuries are an unfortunate but common occurrence. While many minor injuries can be managed through rest, rehabilitation and non-invasive treatments, there are instances when surgical intervention becomes a crucial and, at times, life-changing step in the journey to recovery. Here’s an exploration of the scenarios and significance of surgical intervention for severe injuries:
Complex Fractures: Severe fractures, such as compound fractures where the bone breaks through the skin, require surgical intervention. Surgeons can realign the broken bones, secure them with hardware like pins or plates and facilitate proper healing. This ensures that the affected limb or joint regains its strength and function.
Torn Ligaments: Injuries to ligaments, like a torn anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) in the knee, are common in sports. Surgical repair may be necessary to reconstruct the damaged ligament, providing stability to the joint and preventing long-term issues like chronic instability or arthritis.
Joint Dislocations: Dislocated joints, whether in the shoulder, elbow or elsewhere, often necessitate surgical intervention. Surgeons can carefully relocate the joint components to their proper positions and repair any associated soft tissue damage, promoting optimal function and minimizing the risk of recurrent dislocations.
Tendon Injuries: Tendon injuries, including complete ruptures, are another instance where surgery may be essential. Surgical repair reattaches the torn tendon to its anchor point, allowing for proper muscle function and joint movement. This is particularly vital in areas like the Achilles tendon or rotator cuff.
Complex Trauma: In cases of multiple injuries or trauma that involve various structures, surgery can be a comprehensive approach to address all aspects of the injury. Surgeons prioritize stabilizing and repairing damaged tissues to minimize complications and optimize recovery.
Nerve Damage: Severe injuries can damage nerves, leading to loss of sensation or function. Nerve repair surgeries, such as nerve grafts or transfers, are performed to restore nerve continuity and promote sensory and motor recovery.
Infections and Complications: Infections or complications that arise from injuries may require surgical intervention for drainage, debridement (removal of infected tissue) or revision of previous surgical procedures to address unforeseen issues.
Minimizing Long-Term Effects: Surgery is sometimes the most effective means of minimizing the long-term effects of a severe injury. Timely surgical intervention can prevent chronic pain, joint instability, muscle atrophy and functional limitations, allowing individuals to regain their quality of life.
Rehabilitation Partnership: Surgery is often followed by an extensive rehabilitation process. Surgeons work closely with physical therapists and healthcare professionals to ensure that post-operative rehabilitation is tailored to the individual’s needs, optimizing the chances of a successful recovery.
Individualized Approach: Surgical decisions are highly individualized, taking into account the nature of the injury, the patient’s overall health and their goals for recovery. Surgeons and patients collaborate to make informed choices that prioritize the best possible outcome.
In essence, surgical intervention for severe injuries is a critical step toward restoring function, minimizing long-term complications and helping individuals regain their active lifestyles. It represents a remarkable intersection of medical expertise, technology and patient determination, underlining the resilience of the human body and the dedication of healthcare professionals in the pursuit of recovery and well-being.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Prevention, treatment, and rehabilitation of anterior cruciate ligament …
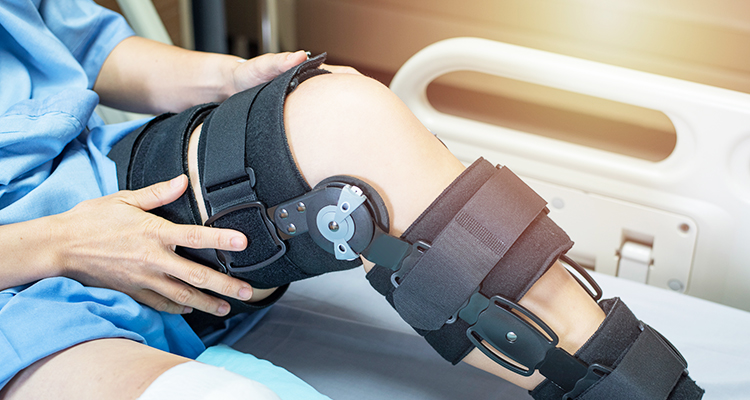
III. The Role of Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is a critical phase in the recovery journey of athletes:
Rehabilitation is a pivotal phase in the intricate and demanding journey of recovery that athletes undertake after facing injuries or physical setbacks. This phase represents not just the mending of physical wounds but the rekindling of hope and the restoration of dreams.
In the realm of sports, where athletes are often seen as symbols of strength and resilience, injuries can be particularly devastating. They not only bring physical pain but also emotional and psychological challenges. The road to rehabilitation is a grueling one, characterized by countless hours of therapy, exercises and setbacks. Yet, it’s this very phase that defines an athlete’s true mettle.
Rehabilitation is where the healing process becomes a story of unwavering determination. Athletes confront their limitations head-on, pushing themselves to the brink of their physical and mental capacities. They often work with a team of healthcare professionals, coaches and trainers who provide not just medical expertise but also emotional support. It’s a collaborative journey where trust and communication are as important as any exercise or treatment.
Moreover, rehabilitation is not just about getting back to where they were before the injury; it’s about emerging stronger, wiser and more resilient. Athletes learn to appreciate their bodies in a new light, gaining a profound understanding of their physicality and limitations. They develop mental fortitude that not only helps them recover but also prepares them for future challenges.
Rehabilitation, in its essence, is about rebirth. It’s a period of transformation where athletes evolve, not just physically but also as individuals. They emerge from this phase with a renewed sense of purpose, an appreciation for their sport and often, a deeper connection to their fans and supporters.
While the process of rehabilitation can be grueling and demanding, it is also a testament to the indomitable spirit of athletes. It showcases their ability to turn adversity into an opportunity for growth and transformation. In the end, rehabilitation is not just a phase; it’s a testament to the unwavering spirit of athletes who refuse to be defined by their injuries but instead choose to rise above them, emerging stronger and more resilient than ever before.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Athletic Training | NATA

Customized Programs
Rehabilitation programs are tailored to each athlete’s specific injury and recovery goals. They focus on restoring strength, mobility and function.
Rehabilitation programs stand as a cornerstone of an athlete’s journey back to peak performance, offering personalized pathways to recovery that go beyond just physical healing. These programs are meticulously designed to address not only the athlete’s specific injury but also their unique aspirations and the challenges they face. Here’s a deeper exploration of the comprehensive approach to rehabilitation, which encompasses not only restoring physical strength, mobility and function but also nurturing the athlete’s mental resilience:
Personalized Care: No two injuries are identical and athletes’ recovery needs are as diverse as their sports. Rehabilitation programs recognize this diversity and are tailored to each athlete’s specific injury, whether it’s a torn ligament, a stress fracture or a muscle strain. Customized care ensures that the rehabilitation journey is both effective and efficient.
Holistic Healing: Beyond physical recovery, rehabilitation acknowledges the importance of holistic healing. It addresses not only the injury site but also the interconnectedness of the body. Rehabilitation plans often encompass not just physical therapy but also elements such as nutrition, mental health support and sleep management to optimize the athlete’s overall well-being.
Mental Resilience: Sports injuries can take a toll on an athlete’s mental state. Rehabilitation programs incorporate psychological support to help athletes navigate the emotional challenges of recovery. Building mental resilience, confidence and a positive mindset is a fundamental part of the process.
Goal-Oriented Approach: Rehabilitation programs are goal-oriented. Athletes collaborate with their healthcare team to set clear, achievable recovery goals. These goals act as milestones that provide motivation and direction throughout the rehabilitation journey.
Progressive Conditioning: Rehabilitation involves a gradual progression of exercises and activities. Athletes start with gentle, controlled movements and gradually advance to more strenuous exercises as they regain strength and mobility. This progressive conditioning minimizes the risk of reinjury.
Functional Restoration: The ultimate aim of rehabilitation is not just to recover from the injury but also to restore function to pre-injury levels or even enhance it. Athletes work on sport-specific movements and skills to ensure they are ready to return to competition with confidence.
Patient Education: Athletes are actively involved in their rehabilitation process. They receive education on their injury, treatment options and preventive measures to reduce the risk of future injuries. Empowering athletes with knowledge helps them make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Long-Term Wellness: Rehabilitation programs often extend beyond the recovery phase to support the athlete’s long-term wellness. This may involve ongoing monitoring, maintenance exercises and lifestyle adjustments to promote continued health and performance.
Team Collaboration: Rehabilitation is a collaborative effort involving not just physical therapists but also sports medicine specialists, nutritionists, coaches and athletic trainers. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that every aspect of the athlete’s recovery is addressed comprehensively.
Return to Sport Readiness: The ultimate measure of a successful rehabilitation program is an athlete’s readiness to return to their sport safely and confidently. This readiness is assessed through a series of functional tests that evaluate strength, agility and performance-specific skills.
In conclusion, rehabilitation programs are not merely about regaining physical abilities; they are a holistic approach to healing that considers the athlete’s unique needs and aspirations. By addressing physical, mental and emotional aspects of recovery and providing personalized care, these programs play a pivotal role in helping athletes not only return to the field but also thrive in their future endeavors.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: CHRISTUS St. Vincent Sports Medicine & Therapy Services

Progressive Training
Rehabilitation involves gradual progression of exercises and activities to rebuild athletic capabilities while minimizing the risk of re-injury.
Rehabilitation is a meticulously designed journey that entails a systematic progression of exercises and activities, all carefully tailored to the individual’s unique needs and injury. This process is akin to a well-orchestrated symphony, where each note represents a step towards recovery and restored athletic capabilities.
Understanding the Gradual Progression: The cornerstone of successful rehabilitation is the principle of gradual progression. This gradual approach acknowledges that healing takes time and rushing the process can lead to setbacks or re-injury. Initially, rehabilitation often involves gentle movements and exercises aimed at reducing pain, swelling and stiffness. As the body responds positively to these initial steps, the rehabilitation plan advances, incorporating exercises that focus on strength, flexibility and balance.
Minimizing the Risk of Re-injury: One of the primary goals of rehabilitation is to not only recover but also to minimize the risk of re-injury. This is achieved through a combination of strengthening exercises, proprioceptive training (to improve awareness of body position) and functional activities that mimic the demands of the athlete’s sport or activity. By gradually rebuilding strength and agility while paying close attention to proper form and biomechanics, athletes are equipped with the tools to return to their sport with reduced vulnerability to re-injury.
The Role of Individualization: It’s essential to emphasize that rehabilitation is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Every athlete’s injury is unique, as are their goals and physical condition. Rehabilitation programs are, therefore, meticulously tailored to each individual. This individualization considers factors such as the type and severity of the injury, the athlete’s age, fitness level and long-term aspirations. This personalized approach ensures that the rehabilitation process addresses the specific needs and challenges of the athlete, fostering a more successful recovery.
Holistic Wellness: Beyond the physical aspect, rehabilitation also encompasses mental and emotional well-being. Athletes often experience a range of emotions during the rehabilitation process, including frustration, impatience and anxiety about returning to their sport. Rehabilitation programs often incorporate psychological support to help athletes cope with these challenges and maintain a positive mindset throughout their recovery.
In conclusion, rehabilitation is a multifaceted journey that prioritizes gradual progression and individualized care. It’s a process that not only rebuilds athletic capabilities but also minimizes the risk of re-injury, enabling athletes to return to their sport stronger and more resilient than before. It’s a testament to the resilience of the human body and spirit, showcasing the remarkable ability to overcome adversity and emerge even more formidable on the path to athletic excellence.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: HAMSTRING INJURY REHABILITATION AND PREVENTION OF …

Monitoring and Support
Skilled therapists monitor athletes’ progress and provide emotional support, helping them regain confidence and mental resilience.
In the realm of sports, the role of skilled therapists extends beyond physical recovery; it encompasses a profound journey of mental resilience and confidence-building. These therapists, often unsung heroes of an athlete’s comeback story, play a pivotal role in nurturing the athlete’s overall well-being and helping them rise to new heights in their respective sports.
Comprehensive Progress Tracking: Skilled therapists employ a multifaceted approach to monitor an athlete’s progress. This goes beyond the assessment of physical recovery and delves into the realms of mental and emotional well-being. Through careful observation, they track an athlete’s psychological response to setbacks, helping identify areas where support and intervention may be needed.
Emotional Support: In the world of sports, the mental and emotional aspects of recovery are just as crucial as the physical ones. Athletes often face the daunting challenge of overcoming not only their injuries but also the psychological toll that setbacks can bring. Skilled therapists are adept at providing the emotional support that athletes require during these trying times. They serve as a source of encouragement, lending a compassionate ear and offering strategies to cope with the stress and uncertainty that injuries may bring.
Confidence Restoration: Injuries can shake an athlete’s confidence to its core. Skilled therapists work tirelessly to rebuild that confidence by setting achievable milestones, celebrating small victories and instilling a sense of self-belief. They help athletes visualize their return to peak performance, inspiring them to push past doubts and fears.
Resilience Cultivation: Resilience is the bedrock upon which many successful comebacks are built. Skilled therapists help athletes develop resilience by teaching coping mechanisms, stress management techniques and mental toughness strategies. They create a safe and supportive environment where athletes can explore their mental fortitude and bounce back from adversity stronger than ever.
Tailored Interventions: Every athlete’s journey is unique and skilled therapists recognize the importance of tailored interventions. They work closely with athletes to understand their specific needs and preferences, customizing their support to align with individual personalities and circumstances. This personalized approach fosters a trusting and collaborative relationship between therapists and athletes.
Long-Term Well-Being: The impact of skilled therapists extends beyond the immediate recovery phase. They equip athletes with tools and techniques that can benefit their long-term well-being, both in sports and in life. These skills include stress management, mindfulness and techniques for maintaining mental health under the pressures of competition.
In conclusion, skilled therapists are instrumental in the holistic recovery of athletes. Their role transcends the physical aspects of rehabilitation, encompassing emotional support, confidence restoration and the cultivation of resilience. Through their expertise and compassion, they not only guide athletes back to peak physical condition but also empower them to face future challenges with newfound mental strength and unwavering confidence. The partnership between athletes and skilled therapists exemplifies the profound synergy between physical and mental well-being in the world of sports.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here 2022 Bern Consensus Statement on Shoulder Injury Prevention …
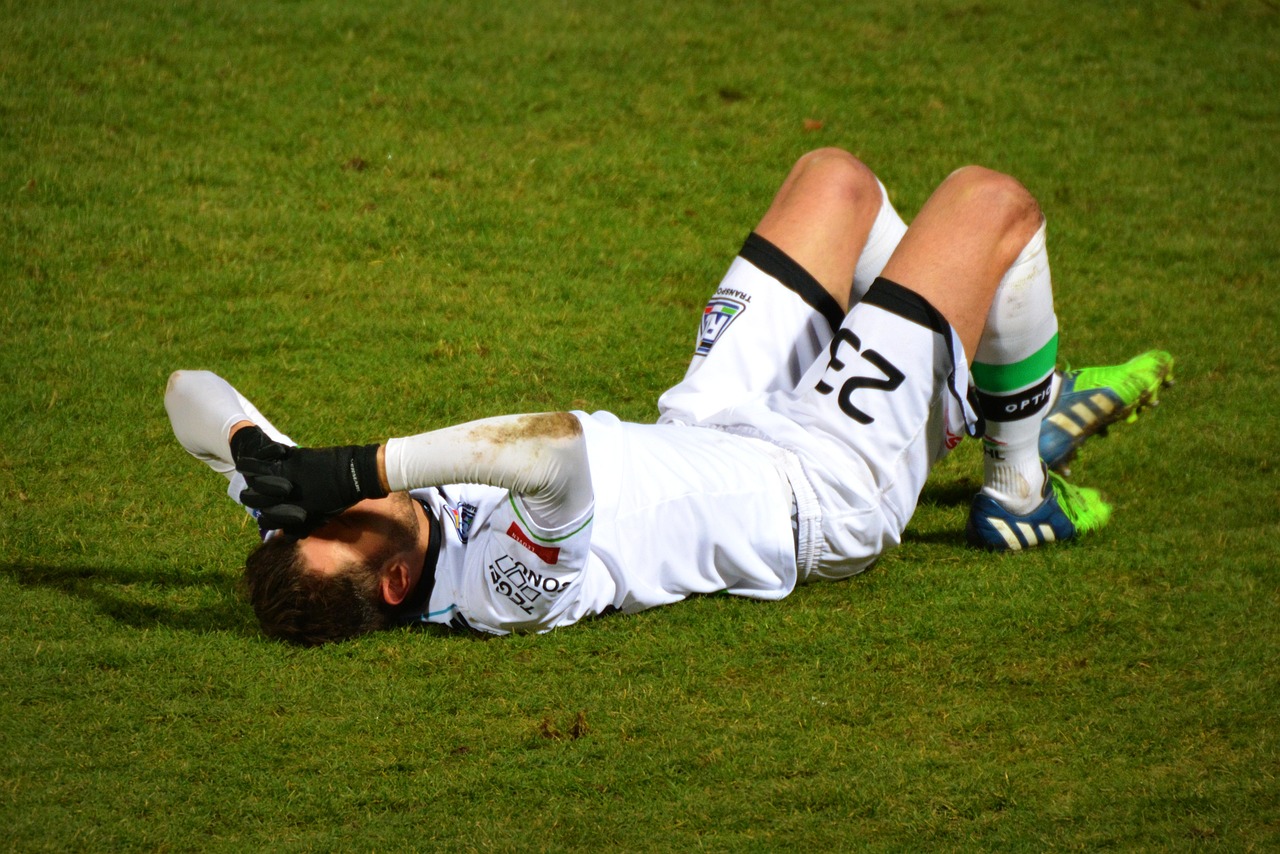

Return to Play
The final phase of rehabilitation involves a comprehensive assessment to ensure the athlete is physically and mentally prepared to return to sports safely.
The concluding stage of the rehabilitation process represents a critical juncture, where an athlete’s readiness to resume sporting activities is rigorously evaluated to guarantee both their physical and mental preparedness. This phase serves as the bridge between recovery and competition, ensuring that the athlete can not only participate but thrive while minimizing the risk of reinjury.
Physical Proficiency: A comprehensive physical assessment is conducted to assess the athlete’s readiness. This evaluation encompasses a range of factors, including strength, flexibility, balance and agility. Specialists and physical therapists closely monitor the athlete’s progress, comparing it to predetermined benchmarks to gauge their ability to perform sport-specific movements and tasks without undue strain.
Functional Testing: Specific functional tests are employed to mimic the demands of the athlete’s sport. These evaluations ensure that the athlete can execute sport-specific actions and maneuvers safely and effectively. For example, a soccer player might undergo drills that mimic sprinting, cutting and jumping to verify their capability to perform these actions without risk.
Cardiovascular Fitness: Depending on the sport, cardiovascular fitness plays a vital role in an athlete’s return. Evaluations such as VO2 max testing can determine an athlete’s aerobic capacity and cardiovascular endurance, ensuring they have the stamina required for sustained performance.
Psychological Readiness: Beyond physical readiness, the mental and emotional well-being of the athlete is a crucial consideration. Sports psychologists or mental health professionals assess the athlete’s psychological readiness to return. This involves addressing any performance anxiety, fear of reinjury or mental hurdles that may hinder their confidence on the field.
Communication and Consent: Effective communication between the athlete, their healthcare team, coaches and trainers is paramount. The athlete’s input and concerns are carefully considered and their full understanding of the risks and benefits of returning to sports is ensured. Informed consent is a critical step to confirm that the athlete is making an informed decision.
Gradual Reintegration: In most cases, athletes are not immediately thrust back into full competition. Instead, a gradual reintegration plan is developed, allowing them to ease back into their sport in a controlled manner. This phased approach helps build confidence and assesses how the athlete responds to increasing levels of activity.
Monitoring Progress: Post-rehabilitation, ongoing monitoring is vital. Periodic check-ins with healthcare professionals and regular assessments ensure that the athlete continues to progress safely. Adjustments can be made to their training regimen or rehabilitation plan as needed.
Education and Injury Prevention: The final phase is also an opportunity to educate the athlete about the importance of injury prevention strategies. Proper warm-up routines, maintenance exercises and injury prevention programs are often integrated to reduce the risk of future injuries.
The culmination of these assessments and evaluations ensures that an athlete’s return to sports is a well-informed, calculated decision. It provides a safety net to help prevent potential setbacks or reinjury, allowing athletes to not only rejoin their teams and competitions but to do so with the confidence and assurance that their physical and mental readiness is at its peak.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Diagnosis, prevention and treatment of common lower extremity …

Sports injuries are an inherent part of athletic pursuits, but with proper prevention, timely treatment and effective rehabilitation, athletes can recover and return to the activities they love. Athletes should prioritize injury prevention and if injuries do occur, seek professional care for prompt and efficient recovery. Sports injuries may be setbacks, but they can also be opportunities for growth, learning and building resilience on the path to achieving athletic excellence.
Sports injuries, though unwelcome, are a shared experience for athletes across the spectrum of sports and skill levels. However, it’s essential to recognize that these injuries, while challenging, can be managed and even turned into opportunities for growth and resilience. Here’s a more comprehensive exploration of how athletes can navigate the journey from injury to recovery and beyond:
Mindset Matters: A positive mindset can make a significant difference in an athlete’s recovery journey. Viewing an injury as a temporary setback rather than a permanent obstacle is crucial. Athletes can use this time to focus on mental strength, setting new goals and refining their mental game.
Comprehensive Rehabilitation: Effective rehabilitation is key to a successful recovery. Athletes should work closely with physical therapists, sports medicine professionals and athletic trainers to create a tailored rehabilitation plan. This plan should address not only physical recovery but also psychological and emotional aspects.
Physical Recovery: Physical rehabilitation involves progressive exercises and therapies to regain strength, flexibility and mobility. Athletes should commit to their rehabilitation regimen, working diligently to rebuild their bodies and minimize the risk of reinjury.
Psychological Resilience: Coping with the emotional aspects of an injury is as critical as the physical aspect. Athletes may experience frustration, disappointment or even depression during recovery. Seeking support from sports psychologists or counselors can help them navigate these challenges and build resilience.
Learning Opportunities: Injuries can provide valuable learning opportunities. Athletes can use this time to analyze their training routines, technique and overall approach to their sport. Identifying weaknesses and making necessary adjustments can contribute to long-term success.
Setting New Goals: While recovering from an injury, athletes can set new goals and benchmarks. These goals may be related to rehabilitation milestones, skill development or even personal growth. Achieving these smaller goals can provide a sense of accomplishment and motivation.
Strengthening Weak Areas: Injured athletes often focus on strengthening the injured area, but it’s also an opportunity to address weaknesses in other parts of the body. Strengthening core muscles, improving balance and enhancing overall fitness can help prevent future injuries.
Nutrition and Recovery: Nutrition plays a vital role in the healing process. Athletes should ensure they are getting the right nutrients to support tissue repair and reduce inflammation. Consultation with a sports nutritionist can be beneficial.
Support System: A strong support system is invaluable during the recovery process. Athletes should lean on family, friends, coaches and teammates for encouragement and assistance.
Return with Caution: When cleared by medical professionals, athletes should ease back into their sport gradually. Rushing the return can lead to reinjury. Coaches and trainers can help plan a safe and effective return-to-play strategy.
Preventive Measures: Learning from the injury experience, athletes should prioritize preventive measures. This may include more thorough warm-ups, better conditioning and ongoing physical therapy to maintain optimal health.
Resilience and Perspective: In the grander scheme of an athletic career, injuries can provide a broader perspective. Athletes often emerge from injury with a newfound appreciation for their sport and a deeper well of resilience, which can serve them well in all aspects of life.
In conclusion, sports injuries are indeed challenges, but they are also opportunities for athletes to showcase their resilience and determination. By approaching injuries with a holistic perspective, focusing on both physical and mental recovery and using them as learning experiences, athletes can emerge stronger, more resilient and even more committed to their athletic pursuits. Ultimately, the journey from injury to recovery can be a transformative one, fostering growth and setting the stage for future athletic excellence.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: HAMSTRING INJURY REHABILITATION AND PREVENTION OF …
More links
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Sports Injuries: Prevention, Treatment and Rehabilitation, Fourth Edit
