Table of Contents
Nestled in the North Atlantic Ocean, between Norway and Iceland, lies a cluster of islands known as the Faroe Islands. This remote and picturesque archipelago, with its dramatic landscapes and close-knit communities, has captured the imagination of many. However, beneath the breathtaking scenery and the allure of its unique culture, the Faroe Islands are grappling with the complex challenges of modern life. In this article, we take a closer look at the daily realities faced by the people of the Faroe Islands as they navigate the demands of contemporary society.
Nestled in the North Atlantic Ocean, between Norway and Iceland, lies a cluster of islands known as the Faroe Islands. This remote and picturesque archipelago, with its dramatic landscapes and close-knit communities, has captured the imagination of many. However, beneath the breathtaking scenery and the allure of its unique culture, the Faroe Islands are grappling with the complex challenges of modern life. In this article, we take a closer look at the daily realities faced by the people of the Faroe Islands as they navigate the demands of contemporary society.
The Faroe Islands, with their rugged cliffs, lush green valleys, and pristine fjords, seem like a place frozen in time. Yet, like any other corner of the world, they are not immune to the forces of change brought about by globalization and technology. As we delve deeper into the lives of the islanders, we discover that their deep connection to the land and sea is both a source of sustenance and a challenge.
Fishing has been the lifeblood of the Faroe Islands for generations, providing not only food and livelihood but also a profound cultural identity. However, modern fishing practices and international regulations have posed challenges to this traditional way of life. Islanders must now navigate the complexities of sustainable fishing and changing market dynamics while preserving the integrity of their age-old traditions.
The islands’ isolation, which once protected their unique culture, now presents a different set of challenges. Younger generations are drawn to mainland Europe for education and job opportunities, raising concerns about depopulation and the preservation of Faroese heritage. The Faroe Islands must find a delicate balance between encouraging their youth to explore the world and ensuring that their vibrant culture endures.
Furthermore, the Faroe Islands, like many other remote regions, are grappling with environmental concerns and the impacts of climate change. Rising sea levels, changing weather patterns, and ocean pollution affect the delicate balance of their ecosystems, impacting not only the environment but also the islanders’ traditional ways of life.
Despite these challenges, the people of the Faroe Islands are resilient, adapting to modernity while fiercely protecting their cultural heritage. They are finding innovative ways to sustain their fishing industry, embracing renewable energy sources, and fostering a sense of community that transcends geographical boundaries.
As we journey through the daily lives of the Faroese people, we gain a deeper appreciation for their unwavering commitment to preserving their unique identity amidst the complexities of the modern world. Their story is a testament to the human spirit’s ability to adapt, cherish tradition, and find harmony with the ever-evolving landscape of contemporary society.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Meet the psychologist exploring unconscious bias—and its tragic …
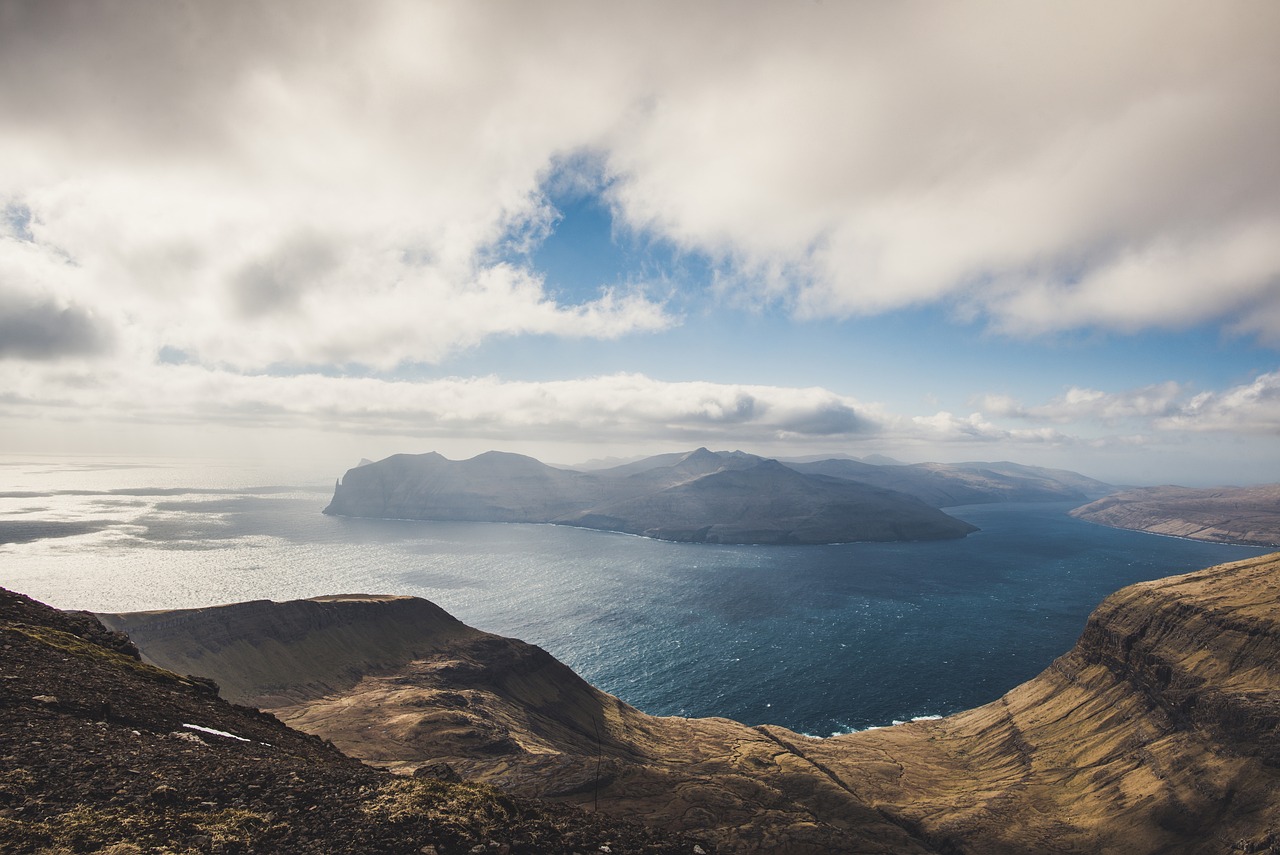
Isolation and Accessibility
The Faroe Islands’ isolation presents both beauty and challenges. While the remote location adds to the islands’ allure, it also poses accessibility issues. With no bridge or tunnel connecting the 18 major islands, travel between them often requires ferry rides or helicopter flights. This limited connectivity can hinder the movement of people and goods, impacting daily life and economic opportunities.
nullTo expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Anti-Racist Shakespeare

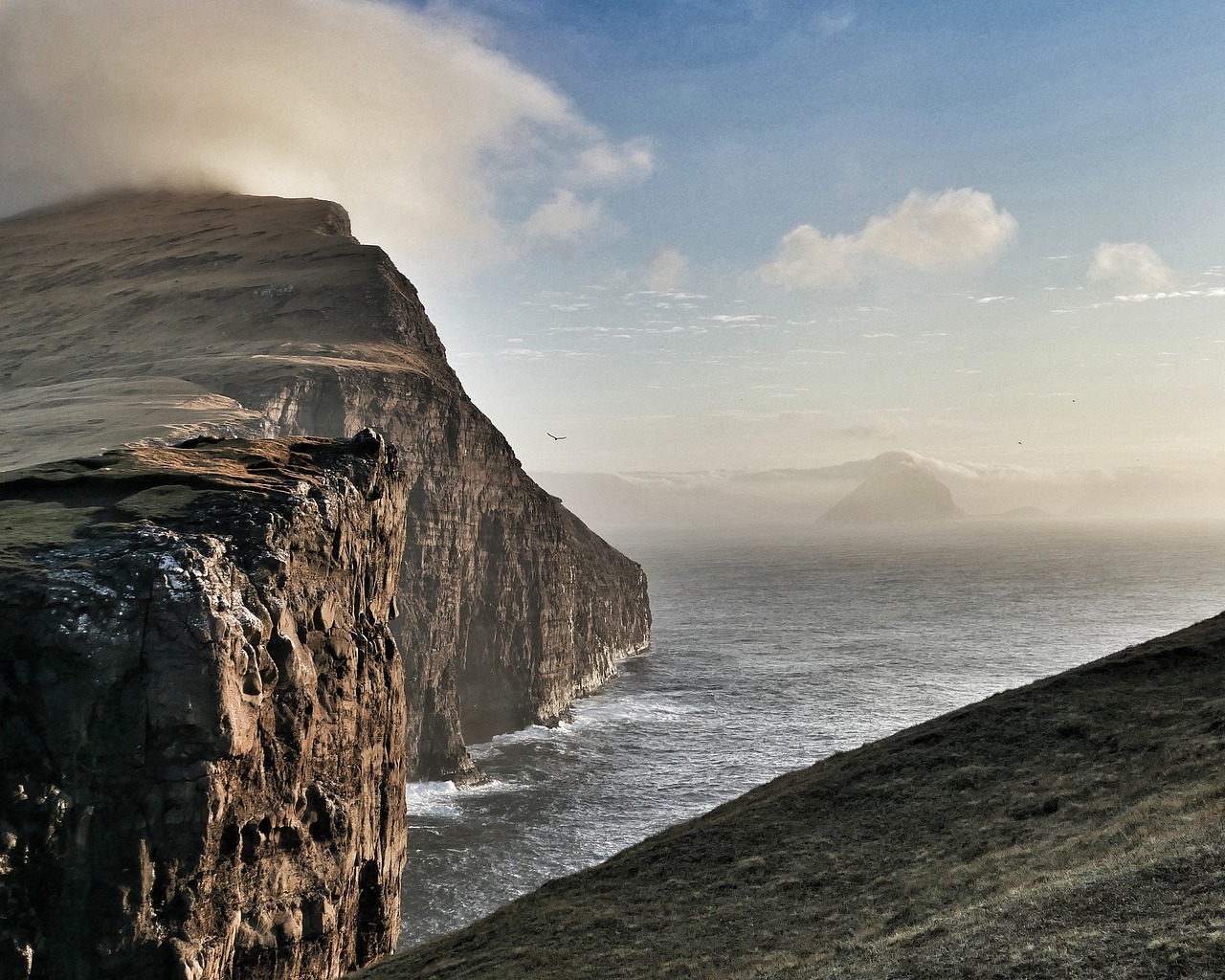
Weather and Climate
The Faroe Islands’ climate is characterized by its unpredictability. Rain, fog, and wind are common companions, which can disrupt daily routines, outdoor activities, and even transportation. The rugged terrain and harsh weather make agricultural activities challenging, influencing the availability and cost of locally produced food.
The Faroe Islands, with their stunning landscapes and unique cultural heritage, are indeed a place where the weather takes center stage in daily life. Unpredictable climate patterns dominate the island chain, where residents often say, “If you don’t like the weather, wait five minutes.” Rain, fog, and gusty winds are steadfast companions, capable of disrupting the best-laid plans, whether it’s a casual stroll or an important voyage.
The rugged terrain, characterized by steep cliffs and rocky outcrops, combined with the harsh and ever-changing weather conditions, poses formidable challenges for agriculture. The traditional Faroese practice of sheep farming and the cultivation of root vegetables like potatoes and turnips are not for the faint of heart. Farming in these conditions requires tenacity and innovation, as crops and livestock must contend with the elements year-round.
The influence of this challenging environment extends beyond the farmstead. It directly impacts the availability and cost of locally produced food, as crops often yield limited harvests, and the rearing of livestock can be more demanding. As a result, the Faroese people have learned to adapt their diets and culinary traditions to the resources available. Fish, a staple of their diet for centuries, remains plentiful in the surrounding waters and has become a symbol of both sustenance and cultural identity.
In recent years, the Faroese have also harnessed modern technology to mitigate some of the climate’s challenges. Innovative methods such as indoor farming and the use of geothermal energy for greenhouse cultivation are helping to diversify food production and reduce the reliance on imports. These efforts underscore the Faroese people’s resilience and commitment to maintaining their way of life in harmony with the unique environment that surrounds them.
Moreover, the Faroese are no strangers to adaptability. Their seafaring heritage, which has spanned centuries, has instilled a sense of resourcefulness and preparedness in the face of the unpredictable. This adaptability has been a key asset in navigating the challenges of their climate and has allowed them to thrive in an environment where others might falter.
In conclusion, the Faroe Islands’ climate, characterized by its fickle and unpredictable nature, has left an indelible mark on the daily lives, agriculture, and food culture of its people. Yet, it is precisely this environment that has forged the resilience and adaptability that define the Faroese way of life. Their ability to embrace the challenges of their surroundings while preserving their cultural heritage is a testament to the human spirit’s capacity to thrive in the face of adversity.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: The impact of coronavirus (COVID-19) and the global oil price shock …

Economic Sustainability
Traditionally, the Faroese economy relied heavily on fishing and agriculture. While these sectors remain significant, the islands have diversified into areas like tourism, renewable energy, and technology. However, economic sustainability remains a concern, as the fishing industry faces fluctuating fish stocks, and job opportunities in other sectors may be limited.
Traditionally, the Faroese economy was firmly anchored in the twin pillars of fishing and agriculture, which sustained the livelihoods of its people for generations. While these sectors still play a vital role in the islands’ economic landscape, the Faroe Islands have embarked on a path of diversification to adapt to the changing global economic landscape.
One of the most notable sectors that have witnessed growth and diversification is tourism. The Faroe Islands’ breathtaking natural landscapes, including dramatic cliffs, cascading waterfalls, and rugged coastlines, have been a magnet for adventurous travelers seeking untouched beauty. In recent years, the islands have seen an influx of tourists eager to explore this remote archipelago. Tourism has not only created job opportunities in hospitality, travel services, and cultural experiences but has also introduced the Faroese way of life to a global audience.
Renewable energy is another area where the Faroese have made significant strides. With abundant wind and hydroelectric resources, the islands have invested in clean energy production. This transition not only aligns with global efforts to combat climate change but also enhances energy independence and reduces reliance on fossil fuels. The development of renewable energy projects has created jobs and stimulated innovation in the clean energy sector.
Additionally, the Faroese have ventured into the technology sector, leveraging their strategic location between Europe and North America to establish data centers and fiber-optic connections. This digital infrastructure has attracted businesses seeking secure and efficient data hosting solutions, contributing to the islands’ economic diversification and technology-driven job opportunities.
Despite these positive developments, economic sustainability remains a concern. The fishing industry, while still vital, grapples with the challenge of fluctuating fish stocks due to climate change and overfishing in neighboring waters. Sustainability measures are crucial to ensure the long-term viability of this sector and the preservation of traditional fishing practices.
Furthermore, the Faroe Islands face the challenge of job opportunities in emerging sectors. While tourism, renewable energy, and technology offer growth potential, the islands’ small population and remote location can limit the number of available positions. Balancing economic growth with the preservation of the Faroese way of life and environment is a delicate task.
In conclusion, the Faroe Islands’ journey from traditional economic reliance on fishing and agriculture to diversification into tourism, renewable energy, and technology reflects their adaptability and resilience in the face of changing global trends. While these new sectors offer opportunities for growth and innovation, ensuring the sustainability of their economy and preserving their unique cultural heritage are ongoing challenges that the Faroese people continue to navigate with determination and ingenuity.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: About the OECD – OECD
Education and Employment
The Faroese education system is well-regarded, but higher education options are limited, leading many young Faroese to study abroad. Upon returning, finding suitable employment can be challenging, particularly in highly specialized fields. This phenomenon has led to a “brain drain” as talented individuals seek opportunities elsewhere.
The Faroese education system has garnered recognition for its commitment to providing quality education, and its emphasis on cultural preservation and sustainability. However, one noticeable challenge it faces is the limited higher education opportunities available within the Faroe Islands themselves. This constraint often compels many young Faroese students to seek higher education abroad, leading them to explore a world of knowledge and experiences beyond their isolated archipelago.
Pursuit of Excellence: The Faroese tradition of valuing education encourages many young talents to pursue higher studies in prestigious institutions around the world. This international exposure enriches their perspectives and equips them with valuable skills and qualifications.
Returnees and Challenges: However, upon returning to the Faroe Islands after completing their studies abroad, many of these well-educated and skilled individuals encounter a challenging reality. The Faroese job market may lack suitable employment opportunities, particularly in highly specialized fields such as cutting-edge technology, advanced healthcare, or specialized sciences. This disconnect between their qualifications and the local job market can be disheartening.
Economic Impact: The phenomenon of Faroese youth seeking opportunities elsewhere and the resulting “brain drain” have economic implications for the Faroe Islands. Losing talented individuals to other countries means the Faroe Islands may miss out on the potential for innovation and growth. The Faroe Islands invest in their education, and the departure of educated youth can hinder the return on this investment.
Cultural Implications: Beyond the economic aspect, the “brain drain” phenomenon also has cultural implications. The departure of highly educated individuals can lead to a loss of intellectual and creative capital within the Faroe Islands. This may affect the community’s ability to innovate and adapt to emerging global trends.
Finding Solutions: To address this challenge, the Faroese government and local businesses have begun to explore various solutions. Initiatives to diversify the local job market by attracting new industries and investments have been introduced. Furthermore, encouraging entrepreneurship and providing support for start-ups can create opportunities for highly skilled returnees.
Remote Work and Connectivity: In an increasingly interconnected world, remote work and digital connectivity have become more accessible. The Faroe Islands can leverage these trends to create opportunities for skilled individuals to work from within the archipelago while collaborating with global partners.
Balancing Tradition and Progress: The Faroe Islands face a delicate balancing act between preserving their unique cultural heritage and embracing progress. Encouraging skilled youth to return and contribute to their homeland while also acknowledging their experiences and aspirations gained abroad is a complex yet crucial endeavor.
In conclusion, while the Faroese education system continues to be highly regarded, the challenges associated with limited higher education options and subsequent “brain drain” underscore the need for innovative approaches to retain and harness the talents of their educated youth. The Faroe Islands’ ability to strike this balance will be instrumental in shaping their future as a resilient and innovative society.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Meet the psychologist exploring unconscious bias—and its tragic …

Language and Cultural Preservation
The Faroese language, rooted in Old Norse, is a cornerstone of Faroese identity. Efforts to preserve and promote the language are ongoing. However, as English becomes more prevalent in education and media, there are concerns about language erosion and its impact on cultural continuity.
nullYou can also read more about this here: 340 Fantasy Writing Prompts That Will Help You Leave Your …

Tourism Impact
The Faroe Islands’ stunning landscapes have attracted a growing number of tourists in recent years. While tourism brings economic benefits, it also presents challenges such as environmental impact, increased cost of living, and balancing tourism infrastructure with the preservation of the islands’ natural beauty.
The Faroe Islands’ stunning landscapes have indeed cast a captivating spell on travelers from around the world, leading to a steady rise in tourism in recent years. This influx of visitors has brought economic opportunities, cultural exchanges, and a newfound global appreciation for the archipelago’s remote beauty. However, as the islands grapple with the evolving tourism industry, they face a delicate balancing act, navigating the fine line between reaping the benefits of tourism and preserving the pristine allure of their natural environment.
One of the most pressing challenges arising from increased tourism is its environmental impact. The delicate ecosystems of the Faroe Islands are vulnerable to the surge in visitors. As foot traffic grows, erosion, littering, and disruption of fragile habitats become real concerns. Sustainable tourism practices and responsible visitor education are essential to minimize the ecological footprint of travelers and protect the islands’ unique flora and fauna.
The rising cost of living is another issue associated with tourism. As demand for goods and services surges, so do prices, affecting the affordability of everyday life for the local population. The challenge for the Faroese authorities is to strike a balance between catering to tourists’ needs and ensuring that residents can continue to enjoy a high quality of life.
Furthermore, the need to develop tourism infrastructure without compromising the islands’ natural beauty presents a significant dilemma. Constructing accommodations, transportation, and attractions to meet the growing demand must be done thoughtfully and sustainably. Striking this balance involves careful planning, adherence to strict environmental regulations, and community involvement to ensure that development aligns with the Faroese identity and values.
However, it’s worth noting that the Faroese are proactive in addressing these challenges. They have been exploring alternative forms of tourism that promote cultural exchange and authentic experiences while minimizing the negative impact on the environment. Initiatives like nature-friendly accommodations, hiking trails with Leave No Trace principles, and responsible whale-watching tours showcase their commitment to sustainable tourism.
In essence, the Faroe Islands stand at a crossroads, where the allure of their breathtaking landscapes meets the responsibility of safeguarding their natural and cultural heritage. As they navigate the complexities of tourism growth, the Faroese people exemplify the importance of finding a harmonious coexistence between economic benefits and the preservation of their beloved islands’ natural beauty.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: About the OECD – OECD
Environmental Conservation
As stewards of their pristine environment, the Faroese people face the responsibility of balancing resource extraction with environmental conservation. Sustainable practices are vital to ensure the long-term health of their ecosystems.
The Faroese people’s unique bond with their environment has deep roots in their cultural identity. They are not just inhabitants of these islands; they are stewards of a fragile and pristine ecosystem that has sustained their communities for generations. The responsibility they bear for balancing resource extraction with environmental conservation is not taken lightly, and sustainable practices are at the forefront of their efforts to ensure the long-term health of their ecosystems.
1. Sustainable Fisheries: Fishing is the lifeblood of the Faroese economy, and maintaining fish stocks is paramount. The Faroese government has implemented strict quotas and regulations to prevent overfishing, collaborating with scientific institutions to ensure sustainable practices. Innovative technology, such as eco-friendly fishing gear and selective fishing methods, is also employed to minimize bycatch and damage to marine ecosystems.
2. Renewable Energy: Recognizing the importance of reducing their carbon footprint, the Faroese have invested heavily in renewable energy sources. Wind turbines and hydroelectric power plants harness the region’s abundant natural resources to generate clean energy. This shift toward renewables not only reduces their impact on the environment but also positions the Faroe Islands as a global leader in sustainable energy production.
3. Responsible Tourism: As tourism continues to grow, the Faroese people are focused on responsible tourism practices. They promote low-impact tourism, emphasizing respect for local culture, wildlife, and natural habitats. Sustainable accommodations, eco-friendly transportation options, and guided tours that educate visitors about conservation efforts are becoming the norm.
4. Biodiversity Conservation: The islands’ unique ecosystems are home to diverse flora and fauna, some of which are endemic to the region. Conservation initiatives are in place to protect vulnerable species and their habitats. Strict controls on invasive species and habitat preservation measures help safeguard the delicate balance of these ecosystems.
5. Waste Management: The Faroese are acutely aware of the importance of proper waste management to prevent pollution. Recycling programs, waste reduction campaigns, and responsible disposal practices are encouraged. The rugged beauty of their natural surroundings serves as a constant reminder of the need to minimize human impact.
6. Environmental Education: Education plays a pivotal role in fostering a culture of sustainability. The Faroese people are committed to raising awareness about environmental issues through schools, community programs, and public outreach. They aim to instill a sense of responsibility and stewardship in younger generations.
In conclusion, the Faroese people’s dedication to sustainable practices is not just a matter of economic necessity; it is an ethical commitment to preserving the natural beauty and ecological integrity of their islands. Their approach to balancing resource extraction with environmental conservation serves as a model for the world, demonstrating that even in remote and challenging environments, responsible stewardship can ensure the long-term health of ecosystems and the well-being of future generations.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Children growing up in Indian slums: Challenges and opportunities …

Mental Health and Well-being
The isolation, unpredictable weather, and limited daylight hours during winter can contribute to mental health challenges. Ensuring access to mental health services and fostering a supportive community environment is essential.
The remote Arctic regions, characterized by their isolation, unpredictable weather patterns, and the stark reality of limited daylight hours during the long winter months, pose unique challenges to the mental well-being of their inhabitants. In this austere environment, where nature’s forces can be both awe-inspiring and formidable, addressing mental health concerns becomes not just a necessity but a vital aspect of community resilience.
The isolation experienced by Arctic communities can be profound. Geographical remoteness, combined with the harsh conditions of the environment, often translates into limited access to medical and mental health services. The challenges of reaching healthcare facilities can be exacerbated during extreme weather events, leaving individuals and families feeling isolated and without the necessary support.
Moreover, the extended periods of darkness during the Arctic winter can have a profound impact on mental health. Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD), a condition characterized by symptoms of depression and low energy levels during the darker months, is a significant concern. The relentless polar nights, when the sun barely grazes the horizon or doesn’t appear at all, can lead to feelings of isolation, lethargy, and sadness.
In the face of these challenges, it becomes imperative to ensure that mental health services are not just available but also accessible to Arctic communities. Telehealth and telemedicine initiatives can bridge the geographical divide, providing remote consultations and counseling services. Furthermore, training community members in mental health first aid can empower them to recognize signs of distress and offer immediate support.
Fostering a supportive community environment is equally essential. Arctic communities, known for their resilience and close-knit relationships, have the potential to serve as powerful networks of emotional support. Strengthening these bonds and promoting open dialogue about mental health can break down stigmas surrounding mental health concerns, encouraging individuals to seek help when needed.
Traditional cultural practices, such as storytelling, art, and communal gatherings, can also play a crucial role in promoting mental well-being. These activities not only offer creative outlets for self-expression but also reinforce the sense of belonging and interconnectedness within the community.
Additionally, incorporating mental health education into school curricula can help destigmatize mental health discussions from an early age, creating a more inclusive and empathetic environment. It also equips the younger generation with essential tools to cope with the unique mental health challenges of Arctic living.
In conclusion, addressing mental health challenges in the Arctic requires a multifaceted approach that combines accessible healthcare services with a nurturing and empathetic community environment. The strength and resilience of Arctic communities can be harnessed as a powerful resource in promoting mental well-being. By ensuring access to support and fostering open conversations about mental health, we can empower these communities to thrive even in the face of the harshest environmental conditions.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here 340 Fantasy Writing Prompts That Will Help You Leave Your …

The Faroe Islands, with their breathtaking landscapes and rich cultural heritage, offer a unique but complex way of life. The challenges of modernity, such as accessibility, economic sustainability, and cultural preservation, are realities that Faroese people must confront daily. Yet, their resilience, strong sense of community, and commitment to preserving their heritage make them well-equipped to navigate these challenges. As they look toward the future, the people of the Faroe Islands continue to adapt and find innovative solutions to maintain the delicate balance between modernity and the preservation of their cherished way of life.
nullExplore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Ethics of the Attention Economy: The Problem of Social Media …
More links
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Could you live on $1.50 a day? Try it with Live Below The Line …
