Table of Contents
- Economists
- Marketers
- The Data-Driven Revolution
- Common Ground: Data Analysis
- Market Research
- Consumer Behavior Analysis
- Predictive Modeling
- Customer Segmentation
- Pricing Strategies
- Holistic Decision-Making
- Risk Mitigation
- Resource Optimization
- Innovation
- Challenges and Solutions
- Cross-Training
- Data Integration
- Regular Communication
In today’s data-centric business landscape, the roles of economists and marketers have evolved significantly. While their core objectives may seem distinct at first glance, there is an increasing need for these two disciplines to collaborate and bridge the gap for effective data-driven decision-making. This article explores how economists and marketers can join forces to harness the power of data and drive business success.
In the contemporary business ecosystem, the dynamic interplay between economists and marketers has become a critical determinant of success. The evolution of these two disciplines, while rooted in distinct objectives, has converged in the pursuit of data-driven excellence. Let’s delve deeper into the reasons behind this shift and how it holds the key to unlocking the full potential of businesses:
1. Convergence of Analytical Skills: Economists have long been equipped with analytical tools to decipher macroeconomic trends, while marketers have honed their skills in understanding consumer behavior at a micro-level. In today’s landscape, where data reigns supreme, the analytical prowess of both economists and marketers is coming to the forefront. Economists are adapting to microeconomic analysis, and marketers are increasingly delving into data analytics to uncover consumer insights. This convergence of analytical skills allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the business environment.
2. Data as the Common Language: Data has become the lingua franca of business decision-making. Economists and marketers now communicate through data, transcending the traditional language barriers that once separated these disciplines. They understand that data-driven insights can reveal the complex relationship between economic factors and consumer behavior, leading to more informed decisions.
3. The Holistic View of Business: As the business landscape grows more interconnected, economists and marketers realize that a narrow focus on their respective domains can limit growth opportunities. Collaborating enables them to take a holistic view of the business, considering both the broader economic context and the intricate intricacies of consumer preferences. This broader perspective leads to more balanced and sustainable strategies.
4. The Rise of Digitalization: The digital revolution has blurred the lines between macro and micro perspectives. Online platforms and e-commerce have created a wealth of data at both the macroeconomic and individual levels. Economists and marketers must work together to navigate this digital landscape effectively. For example, understanding how shifts in the economy impact online consumer behavior requires a unified effort.
5. Agility in Decision-Making: Rapid changes in the business environment demand agility in decision-making. By collaborating, economists and marketers can respond swiftly to economic shifts, consumer trends, and market dynamics. This agility is essential for staying competitive and seizing opportunities as they arise.
6. Enhanced Risk Management: Economic uncertainties and market volatilities are ever-present challenges. Economists are skilled in risk assessment, while marketers excel at risk mitigation through customer-centric strategies. Together, they can develop comprehensive risk management plans that protect the business against economic downturns and shifts in consumer sentiment.
7. Data-Backed Innovation: Collaboration between economists and marketers fosters a culture of innovation. Economists provide the economic context for innovation, while marketers identify opportunities for consumer-centric product or service enhancements. This synergy results in innovative solutions that resonate with customers while aligning with economic realities.
8. Optimized Resource Allocation: In an era where resources are finite, optimizing resource allocation is paramount. By combining their expertise, economists and marketers can ensure that investments in marketing campaigns, product development, and market expansion are strategic and economically sound.
In conclusion, the evolving roles of economists and marketers are driven by the recognition that data-driven decision-making is not a trend but a necessity in today’s business landscape. By collaborating and leveraging their respective strengths, these disciplines can create a powerful symbiosis that unlocks new possibilities for growth, innovation, and resilience in the face of ever-changing economic and market conditions. This harmonious convergence is not just an evolution; it’s a revolution in the way businesses navigate the complexities of the modern world.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Artificial intelligence (AI) applications for marketing: A literature …
Economists
Economists are experts in understanding the broader economic landscape. They analyze macroeconomic trends, study consumer behavior, and evaluate market dynamics. Their primary goal is to provide insights into how external factors impact business operations, helping organizations make informed financial decisions.
“Economists are experts in understanding the broader economic landscape. They analyze macroeconomic trends, study consumer behavior, and evaluate market dynamics. Their primary goal is to provide insights into how external factors impact business operations, helping organizations make informed financial decisions.
In the complex world of economics, economists play a crucial role as interpreters and navigators. Here are some key aspects of their contributions:
Forecasting and Planning: Economists use historical data and current trends to make forecasts about future economic conditions. These forecasts are invaluable for businesses as they plan for expansions, investments, and resource allocation. It’s like having a weather forecast for the financial climate.
Risk Management: Understanding economic trends helps organizations anticipate and mitigate risks. Economists can identify potential vulnerabilities in supply chains, assess currency exchange rate risks, and even predict shifts in consumer demand. This proactive risk management can save companies from unforeseen crises.
Policy Advocacy: Economists often engage in policy discussions at local, national, and international levels. They advocate for policies that promote economic stability, growth, and fairness. Their insights are instrumental in shaping government regulations and fiscal policies that can have a profound impact on businesses.
Resource Allocation: Businesses have limited resources, and economists assist in optimizing their use. They provide guidance on where to invest capital, how to price products and services, and when to expand or contract operations. This helps companies maximize their efficiency and profitability.
Consumer Insights: Economists delve deep into consumer behavior, analyzing spending patterns, preferences, and the psychology behind economic decisions. This knowledge helps businesses tailor their marketing strategies, product development, and pricing to better meet consumer needs.
Global Perspective: In today’s interconnected world, economists provide a global perspective. They help organizations navigate international markets, assess the impact of global events, and identify opportunities for expansion or risk mitigation on a global scale.
Strategic Decision-Making: Whether it’s a startup evaluating market entry or a multinational corporation considering mergers and acquisitions, economists offer invaluable input for strategic decision-making. They consider not only the immediate financial implications but also the long-term sustainability of these choices.
Measuring Economic Impact: Economists can quantify the impact of external factors, such as policy changes or market trends, on a business’s bottom line. This quantification enables organizations to assess the effectiveness of their strategies and make adjustments as needed.
In essence, economists are the interpreters of the economic symphony that surrounds businesses. They provide the sheet music, helping organizations create harmonious financial strategies in an ever-changing economic landscape. Their insights are not just about understanding the economy but about leveraging that understanding to drive business success.”
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: bridging-the-digital-gender-divide.pdf

Marketers
Marketers, on the other hand, focus on promoting products or services, building brand awareness, and driving sales. They are responsible for crafting marketing strategies, conducting market research, and understanding customer preferences to create effective campaigns.
nullFor additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Marketing & Sales Big Data, Analytics, and the Future of Marketing …

The Data-Driven Revolution
The digital age has ushered in an era of data abundance. Businesses have access to vast amounts of information, from customer behavior on websites to market trends in real-time. This wealth of data can be overwhelming, but it also presents an opportunity for both economists and marketers to enhance their decision-making processes.
The digital age has indeed ushered in an era of data abundance. Businesses today find themselves in possession of an unprecedented wealth of information, ranging from granular insights into customer behavior on websites to the ability to track market trends in real-time. This deluge of data can be overwhelming at first glance, but it also presents an extraordinary opportunity for economists and marketers alike to transform and elevate their decision-making processes.
Economic Insights: Economists can harness this data to gain a deeper understanding of economic systems and behaviors. With access to real-time data on consumer spending, employment trends, and supply chain activities, economists can create more accurate models and forecasts. This enhanced understanding can help governments and businesses make more informed policy decisions and adapt quickly to economic shifts, such as the disruptions caused by global events like pandemics.
Consumer-Centric Economics: In the past, economic theories often relied on aggregated data and assumptions about consumer behavior. Today, economists can access individual-level data, allowing for a more consumer-centric approach. This means understanding how individual choices and preferences drive economic outcomes, which can lead to more effective policies and market strategies.
Precision Marketing: Marketers are using this data abundance to refine their strategies with unprecedented precision. They can analyze customer behavior, preferences, and engagement across various digital channels. This level of insight enables marketers to create highly targeted and personalized campaigns that resonate with specific segments of their audience, resulting in better conversion rates and customer loyalty.
Real-Time Adjustments: The availability of real-time data allows both economists and marketers to be agile in their decision-making. Economists can adjust economic policies in response to immediate changes, and marketers can tweak campaigns on the fly to optimize results. This agility is a powerful tool in an ever-changing landscape.
Cost Reduction: For both economists and marketers, data abundance can lead to cost reduction. Economists can identify inefficiencies in economic systems more easily, leading to cost-saving measures. Marketers can allocate their budgets more efficiently, reducing wasted spending on ineffective strategies.
Innovation Acceleration: Access to data abundance fosters innovation. Economists can explore new economic theories and models based on real-world data. Marketers can experiment with novel approaches to engage customers and reach untapped markets, leading to product and service innovations that meet evolving consumer needs.
Ethical Considerations: With great data abundance comes the responsibility to handle data ethically. Both economists and marketers must navigate the complex landscape of data privacy and security, ensuring that they use data in ways that respect individuals’ rights and expectations.
In conclusion, the digital age’s data abundance is a double-edged sword, offering both challenges and opportunities. For economists, it opens up new avenues for understanding and shaping economic systems. For marketers, it provides the means to connect with customers on a deeper level. By embracing this data-driven era and using it responsibly, both economists and marketers can make more informed decisions that benefit society, businesses, and consumers alike.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: BBVA-Selects-AWS-to-Accelerate-Its-Data-Driven-Transformation
Common Ground: Data Analysis
Data analysis is the common ground where economists and marketers can collaborate effectively. Here’s how:
Data analysis is the common ground where economists and marketers can collaborate effectively. Here’s how:
Market Research and Consumer Behavior: Economists can contribute by analyzing macroeconomic data, such as inflation rates, GDP growth, and employment figures, to provide marketers with a broader understanding of the economic environment in which they operate. Marketers, in turn, can leverage this information to tailor their strategies to consumer behavior trends influenced by these economic factors.
Demand and Pricing Strategies: Economists excel at modeling demand curves and assessing price elasticity. By collaborating with marketers, economists can help determine optimal pricing strategies that maximize revenue while considering consumer preferences and market conditions.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Both economists and marketers rely on data to make informed decisions. By working together, they can establish data collection and analysis protocols that provide actionable insights for better decision-making. This synergy leads to more effective marketing campaigns and sound economic strategies.
Predictive Analytics: Economists can apply their expertise in predictive modeling to anticipate economic trends and consumer behavior. Marketers can use these insights to develop proactive marketing campaigns that align with predicted market shifts, giving them a competitive edge.
Return on Investment (ROI) Analysis: Marketers often need to justify their budgets and expenses. Economists can help assess the financial impact of marketing initiatives, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently and generating a positive ROI.
Market Segmentation: Economists can provide valuable insights into market segmentation based on income, demographics, and other economic factors. Marketers can then tailor their messaging and targeting strategies to reach specific customer segments more effectively.
Regulatory Compliance: Economic regulations and policies can have a significant impact on marketing activities. Collaborating ensures that marketing efforts align with legal and regulatory frameworks, reducing the risk of legal issues and fines.
Resource Allocation: Both economists and marketers can work together to optimize resource allocation, considering factors like marketing spend, production costs, and market potential. This holistic approach maximizes the efficiency of resource utilization.
Consumer Surveys and Feedback: Economists can design and analyze surveys to gain insights into consumer preferences, while marketers can use this data to create more relevant and appealing products, services, and marketing campaigns.
Scenario Planning: By combining economic scenario analysis with marketing scenario planning, businesses can be better prepared for unexpected events or economic downturns. This collaboration helps develop contingency plans and adaptive marketing strategies.
Competitive Analysis: Economists can analyze industry and market competition to provide marketers with a broader view of their competitive landscape. This information aids in crafting competitive marketing strategies and differentiating from rivals.
Long-Term Strategic Planning: Collaboration between economists and marketers supports long-term strategic planning. By aligning economic insights with marketing goals, businesses can develop robust strategies that withstand market fluctuations and uncertainties.
In conclusion, the synergy between economists and marketers through data analysis creates a powerful foundation for informed decision-making. By bridging the gap between economic principles and marketing strategies, businesses can navigate the complex landscape of consumer behavior, market dynamics, and economic forces more effectively, ultimately driving growth and success.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Quantitative Marketing: Data-Driven Strategies and Challenges …
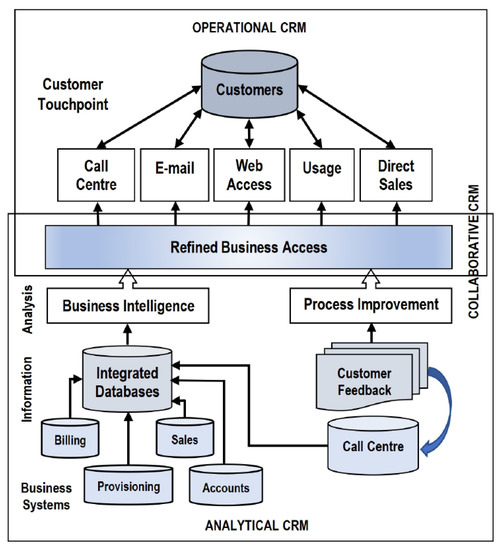
Market Research
Economists can provide valuable insights into economic indicators that affect markets. They can help marketers understand the broader economic context in which they operate. This information can influence pricing strategies, product development, and target market selection.
Economists play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between economic theory and practical business decisions. Here’s an extended perspective on how economists can provide invaluable insights into the economic landscape and how these insights can influence various facets of marketing:
In-Depth Economic Analysis: Economists are trained to dissect complex economic indicators and trends. Their expertise goes beyond surface-level observations, enabling them to uncover nuanced insights that may be overlooked by those without their analytical skills.
Macro and Micro Perspectives: Economists offer both macroeconomic and microeconomic perspectives. They can provide a broad view of national or global economic trends and drill down to the micro-level to understand the intricacies of consumer behavior and market dynamics.
Market Research Enhancement: Economists complement market research efforts. They can contextualize market data within the broader economic environment, shedding light on how economic shifts may impact consumer sentiment, purchasing power, and buying behaviors.
Pricing Strategy Optimization: Understanding economic indicators is crucial for pricing strategies. Economists can guide businesses in setting prices that consider factors like inflation, consumer income levels, and price elasticity, ensuring that pricing aligns with market realities.
Product Development Alignment: Economists can help align product development with economic conditions. They can identify product features or offerings that are particularly relevant during economic downturns or upswings, ensuring that product development remains agile.
Target Market Selection: Economic insights can influence target market selection. Economists can identify demographic groups or geographic regions that are poised for growth or have specific economic characteristics that align with a product’s value proposition.
Competitive Advantage: Businesses armed with economic insights have a competitive edge. They can anticipate economic shifts, adapt strategies proactively, and outperform competitors who may react belatedly.
Budget Allocation: Marketing budgets can be optimized based on economic forecasts. Economists help businesses allocate resources to marketing channels and campaigns that are likely to yield the best returns given economic conditions.
Risk Mitigation: Understanding the economic environment allows businesses to assess risks more comprehensively. This includes anticipating potential economic shocks, policy changes, or disruptions that could impact marketing strategies.
Strategic Planning: Economists contribute to long-term strategic planning. They assist businesses in setting realistic growth targets, evaluating market expansion opportunities, and aligning strategic goals with economic realities.
Consumer Behavior Prediction: Economic indicators often correlate with shifts in consumer behavior. Economists can provide insights into how changes in economic conditions may influence consumers’ preferences, purchasing power, and brand loyalty.
Market Entry Decisions: When considering entering new markets, businesses can rely on economists to assess the economic viability of expansion. This includes evaluating market stability, growth potential, and regulatory considerations.
Sustainability Integration: Economists can also guide sustainability efforts. They can help businesses incorporate environmental and social responsibility into their strategies, aligning with evolving consumer expectations.
In essence, economists serve as indispensable advisors, helping businesses navigate the complex and ever-changing economic landscape. Their insights ripple through every aspect of marketing, from understanding consumer behavior to informing pricing strategies, and from market expansion decisions to long-term strategic planning. By harnessing the expertise of economists, businesses can make informed decisions that not only drive short-term success but also foster resilience and sustainability in the face of economic uncertainties.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Bridging the Gap Between Research and Practice: Predicting What …
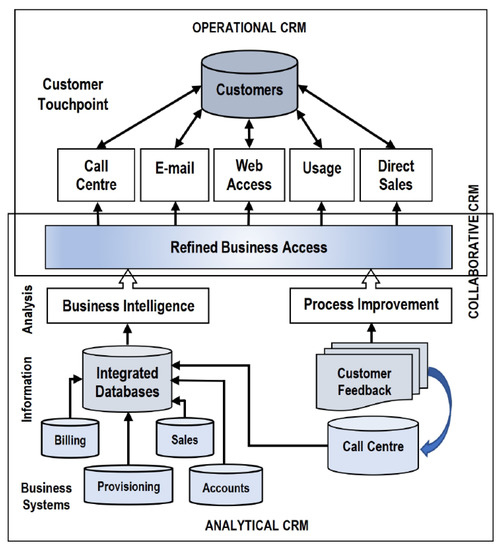
Consumer Behavior Analysis
Marketers are experts in tracking and interpreting consumer behavior. They can help economists gain a more granular understanding of how economic trends translate into real consumer choices. By merging economic data with customer behavior analysis, businesses can refine their strategies.
nullIf you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Marketing & Sales Big Data, Analytics, and the Future of Marketing …
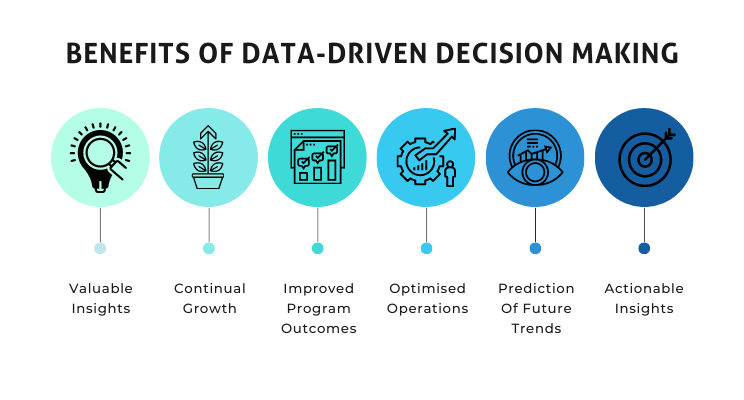
Predictive Modeling
Both economists and marketers can benefit from predictive modeling. Economists can use predictive analytics to forecast economic trends, while marketers can predict consumer preferences and anticipate market shifts. By sharing their modeling techniques, they can develop more accurate predictions.
Both economists and marketers can reap the rewards of predictive modeling. Economists can harness the power of predictive analytics to forecast economic trends, enabling governments and businesses to make informed decisions and allocate resources wisely. On the other hand, marketers can employ these models to anticipate and adapt to ever-changing consumer preferences, gaining a competitive edge in the marketplace.
What’s even more advantageous is the potential synergy between these two fields. By fostering collaboration and knowledge-sharing, economists and marketers can enhance the accuracy of their predictions. For instance, economists can provide valuable insights into broader economic indicators that can influence consumer behavior, while marketers can offer real-world data and insights that refine economic models. This interdisciplinary approach not only leads to more precise forecasts but also facilitates a deeper understanding of the intricate relationship between economic factors and consumer behavior, ultimately benefiting both professions and society as a whole.
You can also read more about this here: Bridging the gap: why, how and when HR analytics can impact …
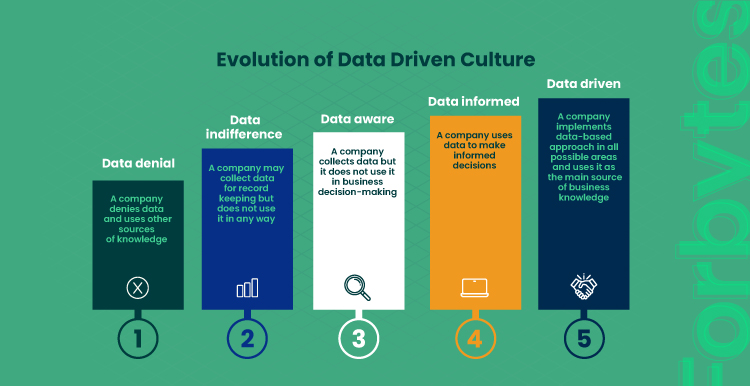
Customer Segmentation
Economists can assist marketers in segmenting the market based on economic variables, such as income, inflation rates, or unemployment levels. Marketers can then tailor their campaigns to address the specific needs and preferences of each segment.
Collaboration between economists and marketers, particularly in market segmentation, brings about a powerful synergy that enhances the precision and effectiveness of marketing strategies. Here’s an extended exploration of how economists can assist marketers in leveraging economic variables for targeted campaigns:
Macro-Market Analysis: Economists specialize in analyzing macroeconomic indicators like GDP growth, inflation rates, and unemployment levels. By closely monitoring these variables, they can provide valuable insights into the overall economic health of different regions or markets. Marketers can leverage this data to identify areas with economic stability or growth potential for market expansion.
Segmentation by Income Levels: Income is a fundamental economic variable that often correlates with consumer purchasing power. Economists can help marketers segment markets based on income brackets. This segmentation allows for the creation of tailored marketing strategies, product pricing, and promotional offers that align with the financial capacity of each segment.
Consumer Behavior in Economic Context: Economists can shed light on how consumer behavior changes in response to economic shifts. For example, during economic downturns, consumers may prioritize cost savings and value-driven purchases. In contrast, during periods of economic growth, they may be more inclined toward premium products and experiences. Marketers can adjust their messaging and product offerings accordingly.
Inflation and Pricing Strategies: Inflation rates can significantly impact pricing strategies. Economists can help marketers anticipate and respond to inflation by recommending pricing models that maintain profitability while accommodating consumer budget constraints. This proactive approach ensures that businesses remain competitive even in inflationary environments.
Unemployment and Targeted Messaging: High unemployment rates can create economic uncertainty and affect consumer sentiment. Economists can collaborate with marketers to craft messaging that resonates with consumers during times of economic uncertainty. This might involve emphasizing job security, value-driven purchases, or support for local communities.
Behavioral Economics Insights: The field of behavioral economics, which combines psychology and economics, offers valuable insights into consumer decision-making. Economists can help marketers understand cognitive biases, decision heuristics, and the emotional factors that influence consumer choices. This knowledge can inform persuasive marketing strategies.
Data-Driven Campaigns: Economists can assist in the collection and analysis of economic data to inform data-driven marketing campaigns. For example, they can identify seasonal economic patterns or economic indicators that correlate with specific consumer behaviors. Marketers can then use this data to optimize the timing and targeting of their campaigns.
Global Market Expansion: Economists provide a crucial perspective for businesses looking to expand into international markets. They can analyze global economic trends, currency exchange rates, and trade policies to assess the economic feasibility and risks associated with international expansion.
Market Forecasting: Economists excel in forecasting economic trends. Marketers can leverage these forecasts to anticipate changes in consumer behavior and market dynamics. This foresight enables businesses to adapt their strategies preemptively and stay ahead of market shifts.
Sustainability and Economic Impact: Economic sustainability and corporate responsibility are growing concerns for consumers. Economists can assess the economic impact of sustainability initiatives and help marketers communicate these efforts effectively, resonating with environmentally conscious consumers.
Incorporating economic expertise into marketing strategies not only enhances targeting precision but also fosters adaptability in an ever-changing business landscape. By collaborating closely with economists and incorporating economic variables into their campaigns, marketers gain a competitive edge in understanding consumer behavior and responding to economic shifts with agility and relevance. This interdisciplinary approach bridges the gap between economics and marketing, enabling businesses to thrive in diverse economic contexts.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Marketing & Sales Big Data, Analytics, and the Future of Marketing …

Pricing Strategies
Economists can provide insights into pricing strategies that consider factors like elasticity of demand and market competitiveness. Marketers can implement these strategies effectively by understanding customer perceptions and willingness to pay.
The collaboration between economists and marketers in crafting pricing strategies is a dynamic synergy that harmonizes economic theory with real-world consumer behavior. Economists bring valuable insights to the table, considering factors such as elasticity of demand and market competitiveness, while marketers use this knowledge to craft and implement strategies that resonate with customers’ perceptions and willingness to pay. This partnership yields several noteworthy advantages:
Elasticity-Informed Pricing: Economists excel at assessing price elasticity, which measures how sensitive demand is to price changes. This information is vital for determining whether a product is price-sensitive or price-inelastic. Marketers can then adjust pricing strategies accordingly, such as implementing dynamic pricing for elastic products and value-based pricing for inelastic ones.
Optimal Pricing Points: Economists can identify the pricing sweet spot where maximum profit can be achieved. By combining economic insights with market research and consumer feedback, marketers can determine the price that not only maximizes revenue but also aligns with customer perceptions of value.
Competitive Positioning: Economic analysis aids in understanding market competitiveness. Marketers can leverage this understanding to position their products or services strategically. Whether as a cost leader, differentiator, or niche player, the choice of pricing strategy is influenced by the economic context and competitive landscape.
Consumer Segmentation: Economists’ insights can guide marketers in segmenting the customer base effectively. Different segments may exhibit varying price sensitivities, allowing for tailored pricing strategies that address each group’s unique preferences and willingness to pay.
Psychological Pricing: Economists shed light on the psychological aspects of pricing, such as the charm of $9.99 instead of $10.00. Marketers can leverage these psychological pricing tactics to influence consumer perceptions and entice them to make a purchase.
Value Communication: The collaboration between economists and marketers enables effective communication of product value. Marketers can use economic insights to highlight the cost savings, utility, or unique features that justify a particular price point, aligning it with customer expectations.
Dynamic Pricing Algorithms: Economists contribute to the development of sophisticated dynamic pricing algorithms. Marketers can deploy these algorithms in real-time to adjust prices based on changing market conditions, competitor pricing, and demand fluctuations, ensuring optimal revenue generation.
Revenue Maximization: By optimizing pricing strategies, businesses can aim for revenue maximization rather than merely focusing on cost recovery. This approach considers both short-term and long-term revenue goals, helping businesses thrive in competitive markets.
Market Entry and Expansion: Economists guide decisions related to market entry and expansion. Marketers can use economic data to assess the viability of entering a new market, understanding how pricing dynamics may differ from their current market.
Ethical Considerations: Collaboration between economists and marketers also involves ethical considerations. Ensuring fair and transparent pricing practices is crucial for maintaining customer trust and long-term brand integrity.
In essence, the symbiotic relationship between economists and marketers forms a powerful alliance that optimizes pricing strategies for businesses. Economists provide the analytical rigor, while marketers infuse these insights with customer-centric approaches. This interdisciplinary collaboration results in pricing strategies that not only align with economic principles but also resonate with customers, driving profitability and enhancing the overall customer experience.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Artificial intelligence (AI) applications for marketing: A literature …

Holistic Decision-Making
By working together, economists and marketers can create a more comprehensive view of the business environment. This holistic approach enables organizations to make decisions that consider both economic factors and consumer behavior, resulting in more robust strategies.
nullExplore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: bridging-the-digital-gender-divide.pdf

Risk Mitigation
Collaboration helps in identifying potential risks early. Economists can signal economic downturns or inflationary pressures, while marketers can adjust strategies to mitigate these risks. Together, they can develop contingency plans to navigate uncertain times.
Collaboration helps in identifying potential risks early. Economists, armed with their understanding of macroeconomic indicators and trends, can often serve as early warning systems, signaling economic downturns or inflationary pressures on the horizon. When they collaborate with marketers, it creates a synergy that can be incredibly beneficial.
Marketers, closely tuned in to consumer behavior and market dynamics, have the agility to adjust strategies swiftly in response to economic signals. For instance, if economists predict an economic downturn, marketers can reallocate budgets, refine messaging, or target different customer segments to mitigate these risks. Likewise, in the face of inflationary pressures, marketers can make pricing adjustments or seek cost-effective advertising channels.
However, the true power of this collaboration lies in their ability to craft contingency plans together. By pooling their insights and expertise, economists and marketers can develop comprehensive strategies to navigate uncertain times. They can proactively identify opportunities even in challenging economic environments, such as targeting niche markets or promoting value-based propositions.
Furthermore, this collaboration doesn’t just end with the identification of risks and the crafting of contingency plans. It extends into the execution phase, where economists and marketers continue to work in tandem. Economists can provide ongoing economic updates, allowing marketers to fine-tune their strategies as the situation evolves. In return, marketers can supply data and customer insights that help economists refine their economic forecasts.
Ultimately, the collaboration between economists and marketers represents a proactive approach to risk management. It harnesses the strengths of both disciplines to not only foresee potential pitfalls but also to seize opportunities that may arise during uncertain times. In a rapidly changing world, this partnership can be a crucial element of a company’s resilience and adaptability, ensuring that it remains competitive and agile regardless of economic challenges.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Opinion Paper: “So what if ChatGPT wrote it?” Multidisciplinary …

Resource Optimization
Data-driven decision-making allows for better resource allocation. Economists and marketers can pinpoint which marketing channels, products, or services offer the highest returns on investment. This optimization leads to cost-efficiency and improved profitability.
Data-driven decision-making is the cornerstone of contemporary business strategy, providing a systematic approach to resource allocation that economists and marketers alike find invaluable. Let’s delve deeper into how this practice transforms resource allocation and enhances cost-efficiency and profitability:
Granular Insights: Data-driven decision-making offers granular insights into every aspect of your marketing efforts. It goes beyond high-level metrics, providing a detailed understanding of consumer behavior, channel performance, product preferences, and conversion patterns. Armed with this knowledge, you can allocate resources precisely where they will yield the greatest returns.
Channel Optimization: With data at your disposal, you can identify which marketing channels deliver the highest ROI. Whether it’s social media, email marketing, content marketing, or paid advertising, data allows you to assess the effectiveness of each channel. By allocating resources to the most effective channels, you maximize your marketing impact and minimize wastage.
Product and Service Focus: Data-driven insights extend to individual products and services. You can identify top-performing offerings and allocate resources accordingly. For instance, if a particular product category consistently outperforms others, you can invest more in its marketing, development, and promotion. This not only boosts sales but also streamlines resource allocation.
Customer Segmentation: Data enables sophisticated customer segmentation. You can pinpoint high-value customer segments and allocate marketing resources to target them more effectively. By tailoring your messaging and offers to specific customer groups, you enhance conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
Timing and Seasonality: Data-driven decision-making accounts for timing and seasonality. You can identify when your target audience is most active and allocate resources to coincide with peak engagement periods. This ensures that your marketing efforts are well-timed and maximize impact.
Budget Optimization: Instead of allocating a fixed budget to marketing channels without clear insights, data-driven decisions allow you to optimize your budget allocation. You can adjust spending in real-time based on performance, shifting resources to capitalize on emerging opportunities or address underperforming areas.
Risk Mitigation: Data-driven decisions also factor in risk mitigation. By monitoring the performance of marketing initiatives closely, you can identify and address issues early. This proactive approach reduces the risk of resource wastage on ineffective strategies.
Continuous Improvement: Data-driven resource allocation is a continuous improvement process. Regular analysis and optimization ensure that your strategies remain aligned with evolving market dynamics and consumer preferences. This adaptability keeps you ahead of competitors and fosters long-term profitability.
Competitive Advantage: Businesses that embrace data-driven decision-making gain a competitive advantage. They respond faster to market changes, identify hidden opportunities, and deliver personalized experiences that resonate with customers. This proactive stance fosters brand loyalty and enhances profitability.
Enhanced Profit Margins: Ultimately, data-driven resource allocation impacts the bottom line. By directing resources where they generate the most revenue and profit, you can enhance profit margins and achieve a more sustainable financial position.
Resource Efficiency: Resource allocation isn’t limited to budget alone; it also includes human capital and time. Data-driven decisions ensure that these resources are used efficiently, maximizing productivity and minimizing wasted efforts.
In conclusion, data-driven decision-making is a transformative force in resource allocation for economists and marketers alike. It empowers businesses to optimize marketing channels, products, and services, leading to enhanced cost-efficiency and improved profitability. By harnessing the power of data, organizations can make informed, strategic choices that drive success in an increasingly competitive business landscape.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: BBVA-Selects-AWS-to-Accelerate-Its-Data-Driven-Transformation

Innovation
The synergy between economists and marketers fosters innovation. It encourages businesses to explore new approaches, experiment with different market segments, and adapt to changing economic conditions. This culture of innovation can lead to a competitive advantage.
The collaboration between economists and marketers is indeed a catalyst for innovation in the business world. It goes beyond the traditional boundaries of these disciplines, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability. Here’s an extended exploration of this idea:
Data-Driven Insights: Economists bring their expertise in data analysis and macroeconomic trends, which, when combined with marketing insights, provide a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics. Data-driven decision-making becomes the norm, guiding businesses in optimizing strategies and resource allocation.
Market Expansion: The synergy between economists and marketers encourages businesses to explore new markets and market segments. Economists provide valuable insights into the economic conditions of different regions, helping marketers identify growth opportunities and assess market viability.
Risk Mitigation: Economists are well-versed in assessing economic risks, while marketers understand customer behavior and preferences. This collaboration enables businesses to develop risk mitigation strategies that account for both economic uncertainties and market dynamics.
Innovation in Pricing Strategies: Economists contribute to pricing strategies by analyzing price elasticity and consumer surplus, while marketers understand the psychology of pricing. Together, they innovate pricing models that maximize profitability while ensuring that customers perceive value.
Product Development: The integration of economic and marketing perspectives fuels innovation in product development. Businesses can create products that not only align with market demand but also consider the economic conditions that affect affordability and purchasing power.
Adaptation to Economic Shifts: Economists provide early warnings of economic shifts, such as recessions or inflationary trends. Marketers can proactively adjust their strategies to cater to changing consumer behavior during these economic transitions.
Economic Forecasting: Collaboration between economists and marketers enhances economic forecasting accuracy. This is particularly valuable in industries where demand is highly sensitive to economic conditions, such as real estate or luxury goods.
Sustainability Initiatives: Economists can help assess the economic implications of sustainability initiatives, while marketers communicate these efforts effectively to environmentally conscious consumers. The synergy supports the development and promotion of sustainable practices.
Global Expansion: For businesses eyeing international markets, the combined expertise of economists and marketers is instrumental in navigating complex global economic landscapes, regulatory frameworks, and cultural nuances.
Competitive Advantage: The culture of innovation cultivated by this collaboration often translates into a competitive advantage. Businesses that can adapt quickly to economic changes and align their marketing strategies accordingly are better positioned to outperform competitors.
Policy Advocacy: The collaboration between economists and marketers extends to policy advocacy. Businesses can leverage their collective expertise to engage in discussions on economic policies that directly impact their industries and consumers.
Thought Leadership: Businesses that foster collaboration between economists and marketers often become thought leaders in their respective industries. They publish research, whitepapers, and insights that contribute to a deeper understanding of economic and market dynamics.
In conclusion, the synergy between economists and marketers is a dynamic force that drives innovation, adaptability, and competitiveness in the business world. It encourages businesses to embrace data-driven decision-making, explore new horizons, and create strategies that resonate with both economic realities and consumer preferences. This collaboration ultimately positions companies for sustainable growth and success in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Artificial intelligence (AI) applications for marketing: A literature …

Challenges and Solutions
While collaboration between economists and marketers is beneficial, it may face challenges related to different terminologies and approaches. To overcome these challenges:
nullAdditionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Artificial intelligence (AI) applications for marketing: A literature …
Cross-Training
Encourage cross-training where economists gain marketing insights and vice versa. This promotes a shared understanding of each other’s roles and expertise.
Promoting cross-training between economists and marketing professionals can lead to a more holistic and collaborative approach to decision-making within organizations. Here’s an extended idea:
“Encourage cross-training where economists gain marketing insights and vice versa. This promotes a shared understanding of each other’s roles and expertise, ultimately fostering a more dynamic and strategic workforce. By breaking down the traditional silos that often separate these two disciplines, organizations can reap numerous benefits.
Enhanced Decision-Making: When economists gain marketing insights, they can make data-driven decisions that are not only financially sound but also align with customer preferences and market trends. Similarly, marketers who understand economic principles can develop campaigns and strategies that are not only creative but also financially viable.
Innovation: The intersection of economics and marketing is where innovation thrives. Economists can provide insights into emerging market dynamics, pricing strategies, and cost-benefit analyses, which can inspire marketers to come up with innovative product launches and marketing campaigns that capitalize on economic trends.
Customer-Centric Approach: Cross-training empowers economists to appreciate the value of customer-centricity, which is central to marketing. They can learn how consumer behavior drives market demand and tailor their economic models accordingly. On the other hand, marketers can better understand the economic constraints and factors that affect pricing and profitability.
Efficient Resource Allocation: Economists can help marketers make more efficient use of resources by providing insights into cost optimization and resource allocation. This leads to a more effective allocation of marketing budgets and resources, resulting in higher ROI.
Risk Management: An understanding of economics can help marketers anticipate and mitigate market risks. It allows them to develop marketing strategies that are not only focused on revenue generation but also on risk management, ensuring the long-term sustainability of the business.
Interdisciplinary Teams: Encouraging cross-training can lead to the formation of interdisciplinary teams where economists and marketers work closely together on projects. This collaborative environment encourages the exchange of ideas and promotes creative problem-solving, leading to more comprehensive and effective solutions.
Improved Communication: Cross-training fosters better communication between economists and marketers. They can speak a common language, making it easier to convey ideas, share insights, and collaborate on projects. This reduces misunderstandings and enhances overall team dynamics.
Professional Development: Cross-training offers professional development opportunities for employees. Economists and marketers can expand their skill sets and broaden their career prospects by gaining expertise in both disciplines, making them more valuable assets to their organizations.
In today’s rapidly changing business landscape, the synergy between economics and marketing is more crucial than ever. By encouraging cross-training, organizations can nurture a workforce that possesses a well-rounded understanding of both financial and customer-driven aspects, ultimately leading to more informed and strategic decision-making that drives sustainable growth and success.”
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Quantitative Marketing: Data-Driven Strategies and Challenges …

Data Integration
Invest in data integration tools and platforms that allow both teams to access and analyze data together. Unified data sources streamline collaboration.
Investing in data integration tools and platforms is not merely an option but a strategic imperative for businesses looking to leverage the combined expertise of economists and marketers. Here’s why these tools are essential and how they can foster seamless collaboration:
1. Streamlined Data Access: Data integration tools act as a bridge that connects various data sources and systems across the organization. For economists and marketers, this means easy access to the data they need without the hassle of navigating multiple platforms or departments. Whether it’s macroeconomic indicators, consumer behavior data, or sales figures, a unified data source provides a single point of entry.
2. Real-Time Data Sharing: In today’s fast-paced business environment, decisions often need to be made in real time. Data integration tools enable economists and marketers to access the most up-to-date information simultaneously. This real-time data sharing ensures that decisions are based on the latest insights, allowing for agile responses to market changes.
3. Cross-Functional Insights: Unified data sources break down departmental silos and encourage cross-functional collaboration. Economists can gain a deeper understanding of consumer behavior trends, and marketers can access economic data that informs their strategies. This cross-pollination of insights results in more comprehensive and effective decision-making.
4. Enhanced Data Security: Data integration tools often come with robust security features, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected. This is crucial when economists and marketers need to access data from different parts of the organization. With proper access controls and encryption, data remains secure while remaining accessible to authorized personnel.
5. Data Quality Assurance: Data integration tools can include data quality checks and cleansing processes. This ensures that the data economists and marketers rely on is accurate and reliable. Data discrepancies and errors are flagged and resolved, preventing misinformation from influencing decision-making.
6. Customizable Dashboards: Many data integration platforms offer customizable dashboards tailored to the specific needs of economists and marketers. These dashboards can display key metrics, trends, and insights in a visually accessible manner. This customization empowers users to focus on the data that matters most to them.
7. Scalability: As businesses grow, so does their data. Data integration tools are designed to scale with the organization’s needs. Whether handling a small dataset or big data, these platforms can adapt to accommodate increasing volumes of information without compromising performance.
8. Collaboration Features: Some data integration tools incorporate collaboration features that facilitate communication and teamwork. Economists and marketers can annotate data, leave comments, and share findings within the platform. This collaborative environment encourages open dialogue and idea exchange.
9. Cost Efficiency: While there is an initial investment in data integration tools, the long-term cost savings can be substantial. The efficiency gained in data access and analysis, as well as the reduction in manual data handling, often justifies the expense.
10. Competitive Advantage: In a competitive marketplace, businesses that can harness data effectively gain a competitive edge. Unified data sources enable economists and marketers to make faster, more informed decisions, respond to market shifts swiftly, and capitalize on emerging opportunities. This agility and intelligence can set a business apart from its rivals.
In conclusion, data integration tools are the linchpin of effective collaboration between economists and marketers. They facilitate the seamless sharing of data, breaking down departmental barriers and fostering a culture of data-driven decision-making. In a data-centric world, businesses that invest in these tools are better positioned to thrive by leveraging the collective power of economists’ macro insights and marketers’ consumer-centric strategies. Unified data sources are not just tools; they’re enablers of innovation, efficiency, and success in the modern business landscape.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Artificial intelligence (AI) applications for marketing: A literature …
Regular Communication
Establish regular meetings or communication channels where economists and marketers can discuss findings, share insights, and brainstorm ideas.
“Establish regular meetings or communication channels where economists and marketers can discuss findings, share insights, and brainstorm ideas. This collaborative approach can bridge the gap between the analytical world of economics and the creative realm of marketing, leading to more effective strategies and informed decision-making.
Here’s how fostering this collaboration can benefit your organization:
Cross-Pollination of Ideas: Economists bring data-driven insights and a deep understanding of market forces, while marketers bring creativity and a keen sense of consumer behavior. When these two disciplines converge, it creates a fertile ground for innovative ideas that can drive marketing campaigns with a strong economic foundation.
Better Targeting: Economists can provide marketers with insights into the economic demographics and trends affecting target audiences. This knowledge enables marketers to tailor their campaigns more precisely, ensuring that their messages resonate with the right people at the right time.
Data-Driven Marketing: Marketers can leverage economists’ expertise in data analysis to refine their strategies. Economists can help them identify key performance indicators (KPIs) and design experiments to measure the impact of marketing initiatives accurately.
Risk Mitigation: By collaborating with economists, marketers can gain a deeper understanding of economic risks and how they might impact marketing campaigns. This knowledge allows for proactive risk mitigation strategies, helping organizations avoid costly missteps.
Long-Term Strategy Alignment: Economists focus on long-term economic trends, which can be instrumental in shaping marketing strategies for the future. Marketers can align their efforts with these trends to ensure sustained success and adaptability in a changing economic landscape.
Resource Allocation: Economists can provide valuable insights into resource allocation, helping marketers determine where to invest their budgets for the best return on investment. This ensures that marketing resources are used efficiently and effectively.
Evidence-Based Decision-Making: Collaboration between economists and marketers promotes evidence-based decision-making. Instead of relying solely on intuition or industry trends, decisions are grounded in empirical data and economic principles, reducing the risk of costly errors.
Competitive Advantage: Organizations that foster collaboration between economists and marketers often gain a competitive advantage. They are better equipped to anticipate market changes, respond to economic fluctuations, and adapt their marketing strategies in real-time.
To make this collaboration successful, it’s crucial to create a culture of openness and mutual respect between economists and marketers. Both parties should have the freedom to express their ideas and insights, and their contributions should be valued equally.
Regularly scheduled meetings or communication channels, such as shared documents or dedicated software platforms, can facilitate this ongoing exchange of knowledge. Additionally, training programs or workshops that promote cross-disciplinary understanding can further strengthen the relationship between economists and marketers.
In a world where data and creativity are both essential components of success, the synergy between economists and marketers can be a powerful catalyst for innovation and growth in any organization.”
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Regulating digital ecosystems: bridging the gap between …

Economists and marketers bring unique skills to the table, and when they collaborate, they create a formidable team for data-driven decision-making. In an era where data is king, the synergy between these disciplines is not just a competitive advantage; it’s a necessity. By leveraging their combined expertise and embracing the power of data, businesses can navigate complex economic landscapes, understand consumer behavior, and craft strategies that drive sustainable success. The bridge between economists and marketers is the pathway to informed, effective, and profitable decision-making in the digital age.
nullTo expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Bridging the Gap Between Research and Practice: Predicting What …
More links
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Bridging the gap: why, how and when HR analytics can impact …
