Table of Contents
- The Significance of Economic Impact Studies in Marketing
- Informed Decision-Making
- Resource Allocation
- Policy Development
- Job Creation
- Community Development
- Methodologies in Economic Impact Studies
- Input-Output Analysis
- Multiplier Analysis
- Surveys and Data Analysis
- Scenario Analysis
- Real-World Applications
- Tourism
- Sporting Events
- Manufacturing
- Retail
- Real Estate
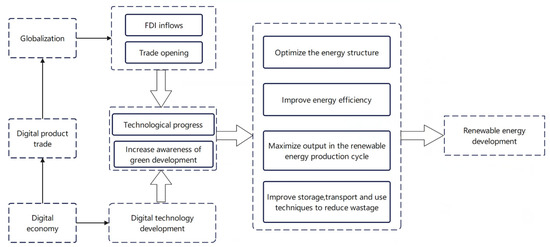
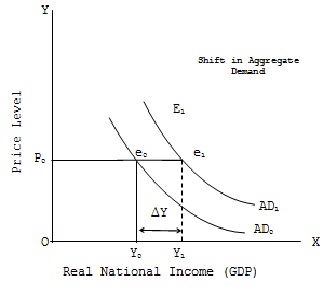
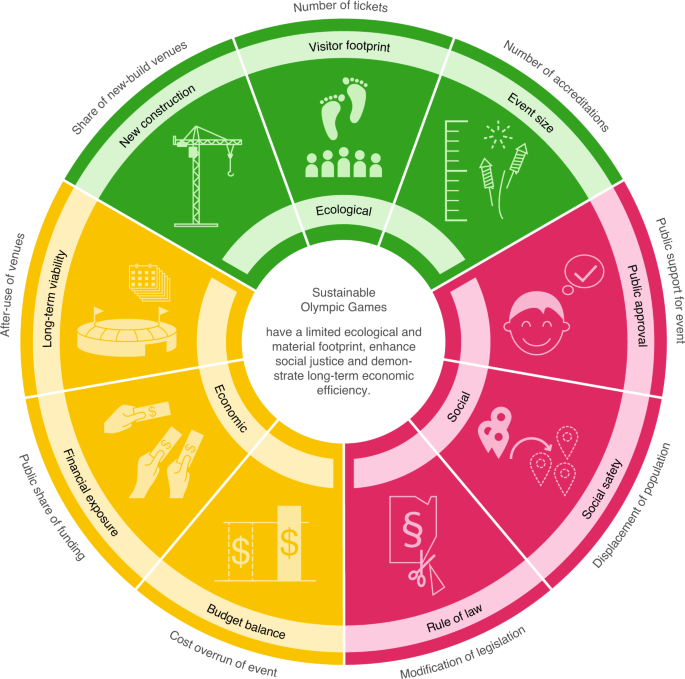
In today’s interconnected world, marketing isn’t just about promoting products or services; it’s about understanding the profound economic implications of these efforts. Economic impact studies have emerged as a vital tool for evaluating how marketing initiatives influence both local and global economies. This article explores the role of economic impact studies in marketing, highlighting their significance, methodologies, and real-world applications.
In today’s interconnected world, marketing has evolved beyond the traditional role of simply promoting products or services; it now encompasses a broader perspective that includes understanding the profound economic implications of these efforts. Economic impact studies have emerged as a vital tool for businesses and policymakers alike, allowing them to comprehensively evaluate how marketing initiatives influence both local and global economies. Let’s delve deeper into the role of economic impact studies in marketing and uncover their significance, methodologies, and real-world applications:
Significance of Economic Impact Studies in Marketing:
Economic impact studies in marketing serve as a bridge between the world of business and the broader economic landscape. They offer insights that go beyond sales numbers and profit margins, shedding light on how marketing initiatives ripple through society, impacting industries, jobs, and even government revenues. Here’s why they are significant:
Strategic Decision-Making: These studies empower businesses to make informed decisions by quantifying the economic consequences of marketing investments. They help in choosing the most effective strategies and allocating resources optimally.
Policy Development: For policymakers, economic impact studies inform the development of policies that encourage business growth and economic prosperity. Understanding the impact of marketing initiatives aids in crafting supportive regulatory frameworks.
Stakeholder Engagement: Economic impact studies provide valuable data for engaging with stakeholders. Businesses can demonstrate their contributions to local and global economies, fostering positive relationships with investors, communities, and governments.
Competitive Advantage: Companies that understand and communicate their economic impact effectively can gain a competitive advantage by highlighting their role in job creation, economic growth, and community development.
Sustainability Considerations: As sustainability becomes a central concern, these studies help evaluate the environmental and social implications of marketing efforts, aligning business practices with sustainability goals.
Methodologies Used in Economic Impact Studies:
Economic impact studies employ various methodologies to assess the ripple effects of marketing initiatives. These methodologies typically include:
Input-Output Models: These models examine how changes in one industry (in this case, marketing) affect other industries in the economy. They consider direct, indirect, and induced effects.
Surveys and Data Analysis: Surveys and data analysis collect information on spending patterns, employment, and other economic indicators to estimate the impact of marketing efforts.
Scenario Analysis: Economic impact studies often involve scenario analysis, which evaluates the potential economic outcomes of different marketing strategies or events.
Social Accounting Matrices (SAMs): SAMs are comprehensive data sets that provide insights into the interconnections between different sectors of an economy. They are useful in understanding how marketing impacts various industries.
Real-World Applications:
Economic impact studies in marketing find practical applications in a variety of contexts:
Tourism: They assess how marketing campaigns and events promote tourism, contributing to local economies through increased spending on accommodation, dining, and entertainment.
Sports and Events: Such studies evaluate the economic impact of hosting sports events, festivals, or conferences, including ticket sales, hospitality, and tourism revenue.
Industry Growth: Economic impact studies help industries, like tech or manufacturing, understand how marketing efforts influence job creation, investments, and supply chain activities.
Regional Development: They play a crucial role in regional development planning, helping communities attract businesses and investments through marketing strategies.
Public Policy: Policymakers rely on these studies to make informed decisions about incentives, regulations, and infrastructure development to support economic growth.
In conclusion, economic impact studies in marketing have evolved to become indispensable tools for businesses and policymakers navigating the complex terrain of the global economy. They provide a holistic understanding of the far-reaching effects of marketing initiatives, guiding strategic decisions, fostering stakeholder engagement, and contributing to sustainable economic development on both local and global scales. As the world of marketing continues to evolve, these studies will play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of business and economic landscapes.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Economic impacts of artificial intelligence (AI)
The Significance of Economic Impact Studies in Marketing
Economic impact studies aim to measure and quantify the economic effects of various activities, including marketing campaigns. They provide valuable insights into how marketing initiatives impact economies on multiple levels, from local communities to the global marketplace. Here are some key reasons why these studies are crucial:
nullFor additional details, consider exploring the related content available here The Economics of Local Food Systems
Informed Decision-Making
Businesses and governments rely on economic impact studies to make informed decisions about marketing investments, resource allocation, and policy development. Understanding the economic repercussions of marketing decisions ensures that these choices align with broader economic goals.
“Businesses and governments alike turn to economic impact studies as invaluable tools in the pursuit of informed, strategic decision-making. These studies provide a comprehensive view of the economic consequences that stem from various marketing investments, resource allocation decisions, and policy development choices. By embracing the insights offered by these studies, both entities can ensure that their actions harmonize with broader economic goals and aspirations.
Resource Allocation: Economic impact studies play a pivotal role in resource allocation. They offer a data-driven perspective on where investments should be directed for optimal economic returns. Businesses can determine which marketing strategies yield the highest economic benefits, enabling them to allocate budgets with precision. Similarly, governments can allocate resources to sectors or initiatives that promise economic growth and stability.
Evidence-Based Policy Development: For governments, crafting effective policies hinges on understanding their potential economic effects. Economic impact studies serve as roadmaps for policymakers, helping them gauge the consequences of various policy options. Whether it’s tax incentives for businesses, regulations to protect consumers, or investments in infrastructure, these studies provide the empirical evidence needed to make informed choices.
Maximizing Economic Growth: Both businesses and governments share an interest in fostering economic growth. Economic impact studies shed light on which actions have the greatest potential to drive growth. Businesses can invest in strategies that contribute not only to their own success but also to the overall economic prosperity of the regions in which they operate. Governments can leverage these studies to identify growth catalysts and make targeted interventions.
Risk Mitigation: In the world of marketing and policy, risks are inherent. Economic impact studies offer a proactive approach to risk mitigation. By assessing the potential economic consequences of various scenarios, entities can develop contingency plans, adjust strategies, and minimize the negative impacts of unforeseen events.
Aligning with Broader Goals: Economic impact studies ensure that marketing, resource allocation, and policy decisions align with broader economic objectives. Whether it’s achieving sustainability, reducing unemployment, or enhancing the overall well-being of a population, these studies provide the compass that keeps choices on course.
Transparency and Accountability: For governments, the use of economic impact studies enhances transparency and accountability. It demonstrates a commitment to evidence-based decision-making, fostering trust among citizens. Businesses, too, benefit from transparency as stakeholders can assess the economic rationale behind their choices.
In summary, economic impact studies are indispensable tools for businesses and governments navigating the complex landscape of marketing, resource allocation, and policy development. These studies empower decision-makers with data-driven insights, ensuring that their choices not only benefit their immediate interests but also contribute to broader economic goals. By leveraging the power of economic impact analysis, entities can navigate the challenges and opportunities of today’s dynamic world with greater confidence and foresight.”
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Michigan K-12 Standards for Social Studies

Resource Allocation
For businesses, marketing expenditures represent a significant portion of their budgets. Economic impact studies help optimize resource allocation by identifying which marketing strategies generate the most substantial economic returns, enabling companies to allocate resources more efficiently.
Indeed, for businesses, marketing expenditures can be substantial, and making the most of these investments is paramount. Economic impact studies play a pivotal role in this optimization process by providing deeper insights and benefits:
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Economic impact studies rely on rigorous data collection and analysis. This data-driven approach allows businesses to make decisions based on facts and figures rather than intuition or guesswork. By relying on concrete data, companies can allocate resources with greater precision, minimizing the risk of wasted spending.
ROI Maximization: Return on investment (ROI) is a critical metric in marketing. Economic impact studies help identify which marketing strategies generate the highest ROI. Businesses can then focus their resources on these strategies to maximize returns, ensuring that every marketing dollar spent yields the greatest economic benefit.
Budget Allocation Transparency: Economic impact studies bring transparency to budget allocation. When stakeholders, including executives and investors, can see the tangible economic impact of marketing strategies, they gain confidence in the allocation of resources. This transparency enhances accountability and fosters trust in the decision-making process.
Risk Mitigation: Not all marketing strategies yield the same level of economic returns. Some may carry higher risks than others. Economic impact studies assess and quantify these risks, enabling businesses to make informed choices that align with their risk tolerance. This risk mitigation approach safeguards against potential financial losses associated with ineffective marketing efforts.
Resource Reallocation: Economic impact studies often reveal opportunities for resource reallocation. If certain marketing channels or campaigns consistently demonstrate a higher economic impact, businesses can reallocate resources from underperforming areas to capitalize on these opportunities. This agility ensures that marketing budgets remain adaptable in the face of changing market conditions.
Competitive Advantage: Businesses that leverage economic impact studies to optimize resource allocation gain a competitive edge. They can outmaneuver competitors by investing strategically in marketing initiatives that deliver quantifiable economic benefits, enhancing market share and brand visibility.
Long-Term Sustainability: The insights gained from economic impact studies promote long-term sustainability. By consistently optimizing resource allocation based on economic impact, companies can maintain financial stability and endure economic fluctuations, ensuring their marketing efforts contribute to sustainable growth.
Customer-Centric Strategies: Economic impact studies often highlight the importance of customer-centric strategies. Businesses discover which marketing approaches resonate most with their target audience, allowing them to tailor their efforts to meet customer needs effectively. This customer-centric approach enhances brand loyalty and long-term customer relationships.
In conclusion, economic impact studies in marketing are not merely tools for analysis; they are catalysts for informed decision-making and resource optimization. By identifying the most economically impactful marketing strategies, companies can ensure that their marketing budgets are invested wisely, yielding measurable returns and fortifying their competitive position in the market. As businesses continue to navigate dynamic market conditions, the role of economic impact studies in resource allocation remains indispensable for achieving financial efficiency and sustainable growth.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: An Introduction to the Main Types of Economic Evaluations Used for …
Policy Development
Governments and regulatory bodies use economic impact studies to craft policies that promote economic growth and sustainability. These studies inform decisions related to taxation, industry regulations, and economic development incentives.
Governments and regulatory bodies use economic impact studies as powerful tools to shape policies that foster not only economic growth but also long-term sustainability and stability. These studies are instrumental in guiding decisions that have far-reaching effects on a nation’s economic landscape, and their applications extend beyond taxation, industry regulations, and economic development incentives.
Infrastructure Investments: Economic impact studies play a crucial role in infrastructure development. Governments rely on these studies to assess the potential benefits of investing in infrastructure projects such as roads, bridges, and public transportation systems. By quantifying the expected economic returns, decision-makers can prioritize projects that offer the greatest economic and social value, reducing congestion, improving accessibility, and stimulating economic activity.
Environmental Policies: Sustainable economic growth requires careful consideration of environmental factors. Economic impact studies help governments design policies that strike a balance between economic development and environmental protection. For example, these studies can evaluate the economic consequences of implementing green energy initiatives, emissions reduction targets, or conservation efforts. By doing so, they inform policymakers about the economic feasibility and benefits of environmentally conscious policies.
Labor Market Planning: Labor market policies, including minimum wage adjustments and workforce training programs, are areas where economic impact studies provide valuable insights. Governments can assess the potential effects of these policies on employment rates, wage distribution, and overall economic well-being. Such studies aid in crafting policies that support both workers and businesses while maintaining a competitive economic environment.
Trade Agreements: Economic impact studies are integral to trade negotiations and agreements. Governments use these studies to assess the potential gains or losses associated with trade deals. They evaluate how changes in trade policies might affect domestic industries, employment, and overall economic growth. This analysis informs negotiation strategies and helps ensure that trade agreements benefit the nation’s economy.
Healthcare and Education: Government policies related to healthcare and education significantly impact economic outcomes. Economic impact studies are employed to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of healthcare interventions, the return on investment in education, and the long-term economic benefits of a healthy and educated workforce. This information aids in crafting policies that improve public well-being and enhance a nation’s economic competitiveness.
Crisis Management: In times of economic crises, such as recessions or natural disasters, economic impact studies provide critical insights. Governments can assess the severity of the crisis, identify the most affected sectors, and formulate targeted policies to mitigate the economic downturn’s impact and facilitate a quicker recovery.
In conclusion, economic impact studies are versatile tools used by governments and regulatory bodies to make informed decisions across a wide spectrum of policy areas. They facilitate the development of policies that not only promote economic growth but also ensure sustainability, fairness, and resilience in the face of evolving challenges. By harnessing the insights provided by these studies, governments can steer their nations toward economic prosperity while addressing complex societal and environmental issues.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Do Social and Economic Policies Influence Health? A Review – PMC
Job Creation
Marketing initiatives can have a direct impact on job creation. Economic impact studies quantify how marketing activities lead to employment opportunities, providing valuable data for policymakers and job seekers.
nullShould you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: THE IMPACT OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ON THE FUTURE OF …
Community Development
At the local level, marketing efforts can contribute to community development by boosting tourism, attracting businesses, and increasing local revenue. Economic impact studies help communities understand how marketing can enhance their economic well-being.
Certainly, let’s explore the idea of how marketing efforts at the local level can contribute to community development and economic well-being in more detail:
“At the local level, the influence of effective marketing efforts extends beyond promoting products and services; it becomes a catalyst for holistic community development. Marketing, when strategically harnessed, can positively impact communities in various ways, ultimately leading to a more prosperous and vibrant local economy. Here are some key facets of this idea:
1. Tourism Promotion: Marketing plays a pivotal role in enticing tourists to visit a locality. Through compelling campaigns that showcase the unique attractions, culture, and experiences a community has to offer, marketing can boost tourism. Increased tourism not only brings in visitors but also stimulates local businesses such as hotels, restaurants, and shops. These establishments benefit from the influx of tourists, thereby generating additional revenue and employment opportunities for residents.
2. Business Attraction: Effective marketing strategies can make a locality an attractive destination for businesses. When a community positions itself as business-friendly, with strategic advantages like a skilled workforce, accessible infrastructure, or incentives for companies, it can draw new businesses and investments. These incoming enterprises contribute to economic growth, provide job opportunities, and expand the local tax base, further benefiting the community.
3. Revenue Generation: Marketing campaigns, especially those promoting local events, festivals, or cultural activities, can draw attendees from both within and outside the community. These events generate revenue not only through ticket sales but also by encouraging spending at local businesses. This injection of funds into the local economy bolsters the financial well-being of both businesses and the community as a whole.
4. Branding and Identity: Effective marketing can help a community establish a unique brand and identity. This identity can be tied to its heritage, culture, or specific strengths, setting it apart from neighboring areas. A distinctive brand can attract not only tourists but also residents who value the community’s identity, leading to population growth and increased economic activity.
5. Quality of Life: Marketing efforts that highlight a community’s quality of life, amenities, and services can attract new residents. Individuals and families looking for a place to settle are drawn to areas that offer a high quality of life, good schools, recreational opportunities, and a sense of community. The influx of residents contributes to a vibrant local economy by increasing demand for housing, retail, and services.
6. Data-Driven Decision-Making: Economic impact studies are invaluable tools that communities can utilize to understand the tangible benefits of marketing efforts. By analyzing the economic impact of tourism, business attraction, and local events, communities can make data-driven decisions. These studies provide insights into the return on investment (ROI) of marketing initiatives and help communities allocate resources more effectively.
In conclusion, marketing at the local level transcends the promotion of products and services; it becomes a driving force for community development. By strategically positioning and marketing themselves, communities can attract tourists, businesses, residents, and investment. Economic impact studies serve as a compass, guiding communities toward informed decisions that enhance their economic well-being, making them more attractive and prosperous places to live, work, and visit.”
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: The territorial impact of COVID-19: Managing the crisis across levels …

Methodologies in Economic Impact Studies
Economic impact studies employ various methodologies to assess the effects of marketing activities. Common approaches include:
Economic impact studies employ various methodologies to assess the effects of marketing activities. Common approaches include:
Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA): This method evaluates the economic impact of marketing activities by comparing the costs incurred with the benefits generated. It helps in determining whether a marketing campaign or initiative is financially viable and whether the return on investment (ROI) justifies the expenses.
Input-Output Analysis: This approach examines the ripple effects of marketing activities throughout the economy. It assesses how spending on marketing leads to increased demand for goods and services in various sectors, creating a multiplier effect. Input-output models can provide insights into the indirect economic contributions of marketing efforts.
Consumer Surveys and Market Research: Understanding consumer behavior is crucial in assessing marketing impact. Surveys and market research allow researchers to gather data on consumer preferences, purchasing patterns, and brand perception. By analyzing this data, businesses can gauge the effectiveness of their marketing strategies.
Sales and Revenue Analysis: Examining changes in sales and revenue is a straightforward way to measure the economic impact of marketing. This method involves tracking sales figures before and after marketing initiatives to quantify the direct financial impact of marketing efforts.
Social Media and Web Analytics: In the digital age, online marketing plays a significant role. Web analytics tools can track website traffic, conversion rates, and social media engagement. These metrics help assess the online reach and effectiveness of digital marketing campaigns.
Econometric Modeling: Economists often employ statistical models to estimate the causal relationship between marketing activities and economic outcomes. Regression analysis and time-series modeling can identify key factors influencing sales, allowing businesses to refine their marketing strategies accordingly.
Scenario Analysis: By creating different scenarios based on varying marketing strategies, businesses can estimate potential economic impacts. This approach helps in decision-making by assessing the range of outcomes associated with different marketing approaches.
Geospatial Analysis: For location-based businesses or campaigns, geospatial analysis can be invaluable. It involves mapping marketing efforts against geographic regions to understand how marketing activities affect local economies and consumer behavior.
Competitive Benchmarking: Comparing the economic impact of marketing efforts with those of competitors provides valuable insights. This analysis can reveal opportunities for improvement and help businesses stay competitive in their industry.
Long-term Impact Assessment: Marketing doesn’t always yield immediate results. Assessing the long-term impact involves tracking customer loyalty, brand equity, and market share over an extended period to determine the sustained economic benefits of marketing investments.
In conclusion, economic impact studies use a diverse range of methodologies to evaluate the effects of marketing activities. The choice of method depends on the specific goals and circumstances of the study, but employing a combination of these approaches can provide a comprehensive understanding of how marketing strategies influence economic outcomes.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here A critical analysis of the impacts of COVID-19 on the global economy …

Input-Output Analysis
This method tracks the interdependencies between different sectors of an economy. It assesses how changes in one sector, such as increased marketing spending, ripple through the entire economy by affecting other industries.
This method, known as input-output analysis, serves as a dynamic lens through which economists examine the intricate web of relationships within an economy. It transcends the boundaries of individual sectors, allowing us to grasp the profound interdependencies that define economic systems. By assessing how changes in one sector, such as increased marketing spending, reverberate through the entire economy, affecting other industries, input-output analysis uncovers a wealth of insights with far-reaching implications:
Multiplier Effect: At its core, input-output analysis unveils the multiplier effect. When one sector experiences a change—be it an increase in spending or a dip in production—it triggers a chain reaction. This ripple effect extends across various sectors, amplifying the initial change and influencing overall economic activity.
Supply Chain Dynamics: Understanding the impact of changes in one sector on others is crucial for comprehending supply chain dynamics. For instance, increased marketing spending not only affects the advertising industry but also stimulates demand for raw materials, transportation services, and retail.
Risk Assessment: Input-output analysis enables economists and businesses to assess economic risks more comprehensively. By tracing the ripple effects of potential disruptions, such as supply chain disruptions or market fluctuations, stakeholders can develop strategies to mitigate the impact on multiple sectors.
Policy Formulation: Policymakers rely on input-output analysis to formulate effective economic policies. They can gauge how policy changes, such as tax incentives or subsidies, will cascade through the economy, providing insights into potential outcomes and unintended consequences.
Resource Allocation: Businesses can optimize resource allocation by understanding the broader economic effects of their decisions. For example, when planning expansion, they can anticipate the demand generated in related sectors and allocate resources accordingly.
Economic Resilience: In times of economic turbulence, input-output analysis aids in building economic resilience. By identifying vulnerable sectors and assessing their interconnectedness, governments and businesses can implement measures to enhance stability and adaptability.
Environmental Impact: Beyond economic considerations, this analysis method helps assess environmental impacts. Changes in one sector may lead to increased resource consumption or emissions, prompting a deeper examination of sustainability practices.
Scenario Analysis: Input-output models facilitate scenario analysis. By simulating different economic scenarios, such as changes in consumer behavior or shifts in global trade, stakeholders can anticipate future challenges and opportunities.
Investment Planning: Investors and financial institutions use input-output analysis to inform investment decisions. They can evaluate the potential returns and risks associated with investments in specific industries based on their interconnections with other sectors.
Innovation Pathways: Understanding the ripple effects of innovation is crucial. By tracing how technological advancements affect various industries, businesses can identify innovation pathways that lead to broader economic benefits.
In essence, input-output analysis transcends traditional economic boundaries, offering a holistic view of economic systems. It demonstrates that every economic decision, whether in marketing, production, or policy, has repercussions that resonate far beyond the initial action. Embracing this analytical tool empowers us to navigate the complex web of economic interdependencies, fostering a deeper understanding of our interconnected world and enabling more informed decisions with far-reaching consequences.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: The labour market impact of international trade: Methodological …
Multiplier Analysis
Multipliers measure the indirect and induced economic effects of an initial change in economic activity. In marketing, this could be the impact of increased sales on suppliers, service providers, and related businesses.
nullTo expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: The labour market impact of international trade: Methodological …
Surveys and Data Analysis
Researchers gather data through surveys, interviews, and data analysis to estimate the economic effects of marketing campaigns, such as increased consumer spending and job creation.
The process of estimating the economic effects of marketing campaigns is a multifaceted and data-driven endeavor that relies on various research methods and analytical techniques. Researchers engage in a comprehensive approach to gather data, assess impacts, and provide valuable insights for businesses and policymakers. Let’s explore how this process unfolds in greater detail:
1. Survey Methodology: Researchers often kickstart their data collection process by conducting surveys. These surveys are meticulously designed to capture information related to consumer behavior, preferences, and spending patterns before and after exposure to a marketing campaign. Through carefully crafted questions and sampling techniques, surveys yield valuable data that shed light on how campaigns influence consumer decisions.
2. In-Depth Interviews: In addition to surveys, in-depth interviews with consumers, industry experts, and stakeholders play a crucial role in understanding the economic effects of marketing campaigns. These interviews provide qualitative insights that complement quantitative data, offering a richer perspective on the impacts of campaigns.
3. Data Analysis and Modeling: Once data is collected, researchers employ various analytical tools and econometric models to quantify the economic effects. This involves analyzing changes in consumer spending, job creation, sales revenue, and other relevant economic indicators. Econometric models enable researchers to establish causal relationships between marketing activities and economic outcomes.
4. Control Groups and Experiments: In some cases, researchers use control groups and experimental designs to isolate the impact of a marketing campaign. By comparing the behavior of a group exposed to the campaign with a control group that was not exposed, researchers can more confidently attribute changes in economic metrics to the campaign itself.
5. Market Research and Consumer Behavior Analysis: Market research data and consumer behavior analysis provide essential context for understanding the economic effects of marketing campaigns. Researchers delve into market trends, competitive landscapes, and consumer sentiments to connect the dots between campaign activities and shifts in economic behavior.
6. Measurement of Direct and Indirect Effects: Researchers not only measure the direct effects of marketing campaigns, such as increased sales, but also delve into the indirect effects. These can include supply chain impacts, job creation throughout the distribution network, and the broader economic ripple effects stemming from increased consumer spending.
7. ROI Assessment: An essential aspect of the research process is assessing the return on investment (ROI) of marketing campaigns. By comparing the costs of running a campaign to the economic benefits it generates, businesses can make informed decisions about future marketing investments.
8. Policy Implications: Beyond serving businesses, research on the economic effects of marketing campaigns can inform policy decisions. Policymakers use this data to understand the potential benefits of supporting certain industries or promoting specific types of campaigns that contribute to economic growth.
In summary, estimating the economic effects of marketing campaigns is a multifaceted endeavor that draws on a range of research methodologies and analytical tools. This comprehensive approach allows researchers to provide businesses and policymakers with valuable insights into the tangible impacts of marketing efforts. By quantifying the economic effects, businesses can fine-tune their marketing strategies, allocate resources effectively, and maximize the return on their marketing investments, ultimately contributing to economic growth and prosperity.
You can also read more about this here: Economic impacts of artificial intelligence (AI)

Scenario Analysis
Researchers create hypothetical scenarios to model the economic impact of different marketing strategies. This approach helps businesses assess the potential outcomes of various marketing investments.
The use of hypothetical scenarios as a modeling tool in marketing research is a valuable practice that offers businesses a forward-looking perspective on the economic impact of their marketing strategies. It’s akin to a test run in a controlled environment, enabling companies to anticipate and evaluate potential outcomes before committing resources. Expanding on this idea, let’s explore the benefits and nuances of using hypothetical scenarios for economic impact assessment:
Risk Mitigation: Hypothetical scenarios allow businesses to assess the potential risks associated with new marketing strategies or campaigns. By modeling different scenarios, companies can identify and mitigate potential pitfalls and challenges, reducing the likelihood of unforeseen setbacks.
Cost-Efficient Planning: Modeling scenarios is a cost-effective way to plan marketing strategies. Instead of implementing a strategy blindly and adjusting on the fly, businesses can simulate various scenarios to determine which course of action is most likely to yield favorable economic results.
Strategic Decision-Making: These scenarios empower businesses to make more informed strategic decisions. When faced with multiple marketing options, companies can create and evaluate scenarios for each, helping them choose the strategy that aligns best with their financial objectives and constraints.
Resource Allocation: Businesses can use scenario modeling to optimize resource allocation. It helps in determining where to allocate marketing budgets and human resources for maximum economic impact. This approach ensures that resources are distributed efficiently.
Market Response Analysis: Hypothetical scenarios can be used to predict and analyze how the market is likely to respond to various marketing initiatives. By adjusting key variables in the scenarios, companies can gauge customer behavior and market dynamics, aiding in strategy refinement.
Sensitivity Analysis: Scenario modeling facilitates sensitivity analysis, where businesses can assess the impact of changing key variables or assumptions. This allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of strategy robustness in different market conditions.
Long-Term Planning: Beyond short-term campaigns, hypothetical scenarios are valuable for long-term planning. Companies can project the economic impact of sustained marketing efforts over time, helping them set realistic and achievable goals for growth and profitability.
Competitive Positioning: Scenario modeling can also be used to assess competitive positioning strategies. Businesses can simulate scenarios where they compete head-to-head with rivals, allowing for strategic adjustments to gain a competitive edge.
Market Expansion: When considering entering new markets or expanding product lines, hypothetical scenarios provide a valuable tool for assessing the economic viability of these endeavors. Companies can gauge the potential return on investment and risks associated with expansion.
Continuous Improvement: Scenario modeling is an iterative process. As data and market conditions change, businesses can update and refine their scenarios, ensuring that their marketing strategies remain adaptive and aligned with their economic goals.
In conclusion, the use of hypothetical scenarios in economic impact assessment is a proactive and strategic approach to marketing planning. It enables businesses to explore different potential futures, anticipate challenges, and make data-driven decisions that optimize their marketing investments. By leveraging scenario modeling, companies can navigate the complex and ever-evolving marketing landscape with greater confidence, positioning themselves for economic success and sustainable growth.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here GlobalTrends_2040.pdf

Real-World Applications
Economic impact studies in marketing find applications across various sectors:
Economic impact studies in marketing are versatile and find applications across various sectors, making them invaluable tools for both businesses and policymakers. These studies serve as a lens through which the intricate web of economic interactions can be understood and harnessed to drive informed decision-making and sustainable growth.
Tourism and Hospitality: In the tourism and hospitality sector, economic impact studies are instrumental in assessing the contributions of hotels, restaurants, and attractions to local and regional economies. By quantifying the economic benefits generated by tourism, these studies aid in destination marketing, infrastructure development, and strategic planning for tourism growth.
Retail and Consumer Goods: Retailers leverage economic impact studies to measure the ripple effects of their operations on local communities. These studies reveal how retail establishments create jobs, stimulate consumer spending, and bolster the overall economic vitality of an area. This information helps retailers make location decisions and tailor marketing strategies.
Real Estate and Property Development: Economic impact assessments are pivotal for real estate developers and property investors. They provide insights into the potential economic benefits and drawbacks of new developments. This information guides decisions on land use, zoning, and property investment by evaluating how projects will affect property values, tax revenues, and local economies.
Sports and Entertainment: The sports and entertainment industry relies on economic impact studies to gauge the financial repercussions of events, stadiums, and venues. These studies help event organizers, teams, and municipalities assess the economic gains from hosting sporting events, concerts, and cultural festivals, influencing future investment and marketing strategies.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals: Healthcare providers and pharmaceutical companies conduct economic impact studies to understand their contribution to regional economies. These studies highlight job creation, research investments, and healthcare spending, demonstrating how the healthcare sector bolsters economic stability while guiding marketing strategies for healthcare services and products.
Higher Education: Educational institutions conduct economic impact studies to quantify their role in regional and national economies. These studies assess the value of education, research, and innovation, informing marketing efforts to attract students, faculty, and research partnerships.
Environmental Initiatives: Economic impact studies are increasingly used to assess the economic benefits of sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. Companies that invest in green technologies and eco-friendly products can use these studies to market their commitment to sustainability and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Nonprofit Organizations: Nonprofits can benefit from economic impact studies by showcasing the social and economic value they bring to communities. These studies can help nonprofits secure funding, engage donors, and communicate their impact effectively through marketing campaigns.
Government and Public Policy: Policymakers use economic impact studies to inform decisions related to taxation, infrastructure development, and regulatory changes. These studies help shape public policy and enable governments to market their regions as attractive places for business investment and economic growth.
Technology and Innovation: Tech companies and startups employ economic impact assessments to demonstrate how their innovations can boost productivity, create jobs, and stimulate economic growth. These studies support marketing efforts by highlighting the broader societal and economic benefits of technology advancements.
In summary, economic impact studies transcend industry boundaries, offering a panoramic view of how businesses and organizations influence economies. Whether in tourism, retail, healthcare, or other sectors, these studies empower decision-makers to make informed choices, allocate resources effectively, and craft marketing strategies that align with their economic contributions while fostering sustainable development and growth.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Economic impacts of artificial intelligence (AI)

Tourism
Tourism boards use these studies to evaluate the impact of marketing efforts on visitor spending, job creation, and local businesses.
nullFor a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: A critical analysis of the impacts of COVID-19 on the global economy …

Sporting Events
Organizers of major sporting events assess how marketing and sponsorship deals impact the host city’s economy, including hotel bookings, restaurant revenue, and infrastructure development.
Organizing major sporting events is a colossal undertaking that extends far beyond the boundaries of the stadium. These events have the power to transform host cities and their economies in profound ways. Let’s delve deeper into how organizers evaluate the economic impact of marketing and sponsorship deals, considering not only immediate gains but also long-term sustainability and development:
1. Immediate Economic Boost: The influx of visitors for major sporting events brings an immediate economic boost to host cities. Marketing and sponsorship deals play a pivotal role in attracting spectators, sponsors, and media attention. This translates into increased hotel bookings, bustling restaurants, and a surge in retail and entertainment spending. The vibrancy of these economic activities during the event contributes significantly to the host city’s revenue.
2. Tourism and Hospitality: Major sporting events are magnets for tourists. Marketing campaigns and sponsorship agreements help position the host city as a desirable destination, attracting visitors not only for the event but also for extended stays. This surge in tourism not only boosts hotel bookings and restaurant revenue during the event but often has a lasting impact as tourists return for future visits.
3. Infrastructure Development: Hosting a major sporting event often necessitates significant infrastructure development. Marketing and sponsorship deals may include commitments to fund or enhance stadiums, transportation networks, and other facilities. These investments leave a lasting legacy that benefits the city’s economy long after the event concludes. Improved infrastructure can attract new businesses, residents, and events, driving economic growth.
4. Branding and Image Enhancement: Marketing and sponsorship deals extend beyond financial gains. They provide opportunities to enhance the host city’s brand and image. Positive associations with major events can attract new businesses, investors, and residents, fostering economic development over the long term. A favorable city image can lead to increased tourism, foreign investment, and job creation.
5. Community Engagement: Successful marketing and sponsorship strategies often involve community engagement initiatives. These programs can have a profound impact on the local economy by promoting inclusivity, diversity, and social responsibility. They may support local businesses, create jobs, and improve the overall quality of life in the host city.
6. Research and Analysis: Organizers use economic analysis tools to measure the impact of marketing and sponsorship deals comprehensively. This involves assessing not only direct revenue streams but also indirect and induced economic effects. Economists analyze data on hotel occupancy rates, restaurant sales, tax revenues, and employment figures to quantify the event’s economic impact.
7. Long-Term Planning: Economic analysis goes beyond the event’s duration. Organizers consider the long-term implications of hosting major sporting events. By understanding how marketing and sponsorship deals can stimulate economic growth, cities can develop sustainable strategies that leverage the event’s legacy for years to come.
8. Stakeholder Collaboration: Successful economic impact assessments involve collaboration with various stakeholders, including local businesses, governments, and community organizations. This collaborative approach ensures that the benefits of major sporting events are distributed equitably and that the host city’s economy is strengthened holistically.
In conclusion, major sporting events are not merely spectacles; they are powerful economic engines that can reshape host cities. Marketing and sponsorship deals are instrumental in driving economic growth by attracting visitors, enhancing infrastructure, and improving the city’s image. Through comprehensive economic analysis, organizers can navigate the complexities of these events, ensuring that the economic impact extends far beyond the final whistle or finish line, benefiting host cities for years to come.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic …
Manufacturing
Manufacturers analyze the economic impact of their marketing strategies on the supply chain, employment, and regional economic development.
Manufacturers’ economic analysis of their marketing strategies extends beyond the immediate sales and profitability considerations. It encompasses a broader perspective that takes into account the interconnectedness of their operations with the supply chain, employment landscape, and regional economic development. Here’s an expanded view of how this analysis plays a vital role:
Supply Chain Optimization: Manufacturers recognize that their marketing strategies can have a ripple effect throughout the supply chain. Economic analysis helps them assess how marketing decisions, such as product launches, pricing changes, or distribution methods, impact the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the supply chain. By optimizing the supply chain in response to marketing dynamics, manufacturers can reduce costs, improve delivery times, and enhance overall competitiveness.
Employment Dynamics: The manufacturing sector is a significant contributor to employment in many regions. Economic analysis enables manufacturers to gauge the potential impact of their marketing strategies on employment levels. This analysis helps companies make informed decisions about workforce planning, including hiring, training, and labor allocation. Manufacturers can also assess the potential for job creation or, conversely, the need for workforce adjustments in response to shifts in market demand.
Regional Economic Development: Beyond their immediate operations, manufacturers understand that they play a crucial role in the economic development of their regions. Economic analysis allows companies to evaluate how their marketing strategies contribute to or influence regional economic growth. This perspective extends to assessing the potential for attracting suppliers, fostering local businesses, and promoting community development through partnerships or investments.
Environmental Considerations: Economic analysis doesn’t stop at financial metrics. It also considers environmental impacts. Manufacturers increasingly assess the sustainability and ecological footprint of their marketing strategies. By understanding the environmental costs and benefits, companies can make more informed decisions regarding product design, packaging, transportation, and resource management, all of which influence both the economy and the environment.
Market Expansion: Manufacturers use economic analysis to evaluate the feasibility of expanding into new markets or regions. This includes assessing the economic dynamics, consumer behaviors, and regulatory environments in potential target areas. By considering the economic implications of market expansion, companies can make informed decisions about resource allocation and growth strategies.
Risk Management: Economic analysis serves as a risk management tool. Manufacturers anticipate and assess potential economic risks associated with their marketing strategies, such as currency fluctuations, geopolitical events, or trade policy changes. This proactive approach enables companies to develop risk mitigation strategies and contingency plans to protect against adverse economic impacts.
Community Engagement: Manufacturers recognize the importance of being good corporate citizens. Economic analysis informs decisions related to community engagement and social responsibility. Companies may choose to invest in local initiatives, support educational programs, or participate in philanthropic activities that align with their economic goals and community well-being.
Long-Term Sustainability: Manufacturers take a long-term view of their economic impact. They consider how their marketing strategies today influence their future resilience and sustainability. Economic analysis helps companies plan for long-term growth, innovation, and adaptability in the face of changing economic conditions.
In conclusion, economic analysis for manufacturers goes far beyond profit and loss statements; it encompasses a holistic view of their impact on the supply chain, employment, and regional economic development. By analyzing the economic dimensions of their marketing strategies, manufacturers can make informed decisions that optimize their operations, contribute positively to their communities, and position themselves for sustained success in an ever-evolving economic landscape.
You can also read more about this here: A critical analysis of the impacts of COVID-19 on the global economy …

Retail
Retailers measure how marketing campaigns influence customer spending, foot traffic, and the overall economic health of shopping districts.
Retailers continually monitor and analyze the impact of their marketing campaigns, recognizing that these initiatives extend far beyond promoting products or services. The scope of measurement encompasses a broader spectrum of outcomes that collectively influence not only the retailer’s success but also the vibrancy of entire shopping districts. Here’s a more detailed exploration of how retailers assess the influence of marketing campaigns:
Customer Spending Patterns: Retailers closely examine how marketing campaigns affect customer spending patterns. By tracking changes in purchase behavior, such as increased average transaction values or higher sales volumes of specific products, they gain insights into the immediate impact of their promotional efforts.
Foot Traffic and Store Visits: Beyond sales, retailers pay attention to foot traffic and store visits. Marketing campaigns often aim to draw more customers into physical stores, and measuring foot traffic provides critical data on campaign effectiveness. Retailers assess whether these campaigns successfully drive in-store visits, contributing to potential sales conversions.
Customer Acquisition and Retention: Successful marketing campaigns not only attract new customers but also retain existing ones. Retailers measure the cost of customer acquisition against the value of those acquired, evaluating the long-term return on investment and customer lifetime value.
Online and Offline Convergence: In today’s omnichannel retail landscape, retailers analyze the synergy between online and offline marketing efforts. They examine how online promotions impact in-store visits and vice versa, aiming to create a seamless and complementary customer experience.
Brand Awareness and Loyalty: Marketing campaigns often aim to enhance brand awareness and foster customer loyalty. Retailers employ surveys, brand sentiment analysis, and customer feedback to gauge changes in brand perception and customer sentiment as a result of marketing initiatives.
Local Economic Impact: Retailers recognize their role as integral components of local economies. They measure how their marketing campaigns contribute to the overall economic health of shopping districts. Increased customer spending in one store can have a positive spillover effect on neighboring businesses, creating a thriving commercial ecosystem.
Competitive Positioning: Retailers assess their competitive positioning in the market by studying how marketing efforts influence market share, pricing power, and market penetration. They compare their performance against competitors to identify strengths and areas for improvement.
Seasonal and Event-Based Impact: Retailers often run targeted marketing campaigns during holidays or special events. They analyze how these campaigns influence consumer behavior during peak shopping periods, adjusting strategies for maximum impact.
Marketing Attribution Models: Retailers employ marketing attribution models to attribute sales and conversions to specific marketing channels or touchpoints. These models help allocate marketing budgets effectively and understand the contribution of each channel to overall performance.
Customer Feedback and Reviews: Customer feedback, online reviews, and social media sentiments are valuable sources of information for retailers. They provide qualitative insights into how marketing campaigns are perceived by customers and can highlight areas for improvement.
Long-Term Strategy: Retailers consider the long-term implications of marketing campaigns, looking beyond immediate results. They evaluate how sustained marketing efforts align with their overarching business goals and growth strategies.
Community Engagement: Marketing campaigns can also influence community engagement and social responsibility initiatives. Retailers assess their impact on community partnerships, sustainability efforts, and overall corporate citizenship.
In conclusion, retailers’ measurement of marketing campaign impact extends beyond immediate sales figures. It encompasses a comprehensive assessment of customer behavior, brand perception, competitive positioning, and contributions to local economies. By understanding these multifaceted outcomes, retailers can fine-tune their marketing strategies, cultivate stronger customer relationships, and contribute positively to the economic well-being of shopping districts and communities.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: NAFTA and the USMCA: Weighing the Impact of North American …

Real Estate
Developers assess the impact of marketing and branding on property values, local development, and housing markets.
nullFor a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Global Financial Stability Report
Economic impact studies in marketing are invaluable tools for assessing the broader economic consequences of marketing activities. They provide businesses, policymakers, and communities with data-driven insights that inform decision-making, resource allocation, and policy development. By understanding how marketing initiatives influence economies at the local and global levels, stakeholders can optimize their strategies and work toward sustainable economic growth and development. As marketing continues to evolve in a rapidly changing world, economic impact studies will remain indispensable for gauging the far-reaching effects of marketing efforts.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: The territorial impact of COVID-19: Managing the crisis across levels …
More links
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: The labour market impact of international trade: Methodological …
