Introduction
The story of American agriculture is not only one of abundant harvests and fertile lands but also a narrative of innovation and transformation. American farming techniques have played a pivotal role in shaping the global landscape of food production. From the mechanization of farming to the development of advanced crop management practices, this article explores how American agricultural innovation has influenced and continues to influence global food production.
The tale of American agriculture is a multifaceted narrative that extends far beyond the bountiful harvests and fertile landscapes that have defined it. It is a story of unwavering innovation and transformative change, with American farming techniques at the forefront of shaping the global landscape of food production. From the mechanization of farming to the development of cutting-edge crop management practices, this article delves into the profound impact of American agricultural innovation and how it continues to reverberate across the world of food production.
Mechanization and the Agricultural Revolution
One of the most pivotal chapters in the history of American agriculture is the mechanization of farming. It marked a dramatic shift from traditional manual labor to the use of machinery, greatly increasing efficiency and productivity. Innovations like the reaper, developed by Cyrus McCormick, and the cotton gin, invented by Eli Whitney, revolutionized crop harvesting and processing. These breakthroughs not only transformed American agriculture but also set a global precedent for the importance of mechanized farming techniques.
Crop Management and Scientific Advancements
American farmers have also been pioneers in adopting advanced crop management practices. The development and dissemination of scientific research in agriculture, led in part by institutions like land-grant universities, played a crucial role. Concepts such as crop rotation, soil conservation, and pest control were refined and widely adopted, leading to increased yields and sustainable farming practices. These methods have not only fed the nation but have also served as models for agricultural development worldwide.
Genetic Advancements and Biotechnology
In recent decades, American agriculture has witnessed another wave of innovation driven by genetic advancements and biotechnology. The development of genetically modified (GM) crops, such as insect-resistant and herbicide-tolerant varieties, has further increased crop yields and reduced the need for chemical pesticides. While GM crops have generated debates on safety and environmental concerns, they have undeniably impacted global agriculture by increasing food production in regions facing hunger and food security challenges.
Sustainable Agriculture and Environmental Stewardship
The evolving landscape of American agriculture also includes a growing emphasis on sustainable practices and environmental stewardship. Concerns about soil erosion, water quality, and the impact of industrial agriculture on ecosystems have led to a renewed focus on sustainability. American farmers are increasingly adopting precision agriculture techniques, using data and technology to optimize resource use and reduce environmental impact. These efforts resonate with global discussions on sustainable food production and responsible land management.
Global Influence and Challenges Ahead
American agricultural innovation has not only influenced domestic food production but has also had a lasting impact on global agriculture. The adoption of American farming techniques and technologies has improved food security and agricultural practices in many parts of the world. However, it is essential to address the challenges of modern agriculture, including issues of sustainability, climate change, and equitable access to resources. American agriculture continues to evolve, seeking solutions to these global challenges while maintaining its legacy of innovation and transformation.
In conclusion, the story of American agriculture is a remarkable journey of innovation and transformation that extends far beyond its borders. American farming techniques, from mechanization to biotechnology, have played a pivotal role in shaping the global landscape of food production. As we navigate the complexities of a growing global population and environmental concerns, American agriculture remains a source of inspiration and knowledge in the pursuit of sustainable, efficient, and equitable food production worldwide.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Sustainable Agriculture | Learn Science at Scitable
The foundations of American agricultural innovation were laid during the 18th and 19th centuries. As settlers pushed westward, they encountered a diverse range of climates and soil types. This diversity necessitated the development of adaptable farming practices, leading to an agricultural revolution.
The roots of American agricultural innovation run deep, intertwining with the nation’s pioneering spirit and its relentless pursuit of progress. The 18th and 19th centuries, marked by westward expansion, were pivotal in shaping American agriculture into a dynamic force of innovation. As settlers ventured into new territories, each presenting its unique challenges and opportunities, they forged a path toward an agricultural revolution that would forever transform the landscape of farming.
Adapting to Diverse Environments: The westward expansion of the United States brought settlers face-to-face with an astonishing array of climates, soil types, and geographical features. From the fertile plains of the Midwest to the arid landscapes of the Southwest, American farmers encountered diverse ecosystems that demanded adaptive farming practices. This necessity to thrive in vastly different environments became a driving force for innovation.
Pioneering Crop Varieties: In response to the varying conditions, American farmers began experimenting with crop varieties. They sought to identify and cultivate plants that could thrive in specific regions. This experimentation gave rise to the development of hardy, regionally adapted crop varieties, each tailored to the unique demands of its environment. From drought-resistant grains to cold-tolerant fruits, these new varieties revolutionized American agriculture.
Innovative Farming Techniques: The quest for agricultural adaptability extended beyond crop selection. Farmers developed innovative techniques to maximize productivity and sustainability. Practices such as crop rotation, contour farming, and terracing emerged as effective strategies to combat erosion, conserve soil fertility, and optimize water usage. These methods became invaluable tools for managing the diverse range of landscapes they encountered.
Machinery and Mechanization: The 19th century witnessed significant advancements in agricultural machinery. Inventions like the steel plow, reaper, and threshing machine revolutionized the efficiency of farming operations. These labor-saving devices allowed farmers to cultivate larger areas and increase their yields, laying the foundation for a more mechanized agriculture.
Transportation and Access to Markets: The expansion of transportation networks, including canals, railroads, and roads, facilitated the movement of agricultural products to distant markets. This not only increased the reach of American farmers but also stimulated the growth of commercial agriculture. It transformed farming from subsistence agriculture to a more market-oriented enterprise.
Scientific Advances: Scientific knowledge and research also played a pivotal role in American agricultural innovation. Land-grant universities, established under the Morrill Acts, became centers of agricultural research and education. Farmers had access to the latest scientific insights, from soil chemistry to pest management, enabling them to make informed decisions and adopt best practices.
Agriculture as a National Identity: The American spirit of innovation in agriculture became a defining aspect of the nation’s identity. It symbolized the resilience and adaptability of American farmers who could turn barren land into fertile fields. This spirit of innovation persists today, with American agriculture at the forefront of sustainable practices and technological advancements.
In conclusion, the foundations of American agricultural innovation, laid during the westward expansion of the 18th and 19th centuries, continue to shape the nation’s agricultural landscape. The adaptability, ingenuity, and determination of American farmers, coupled with advancements in science and technology, have propelled American agriculture to new heights. It remains a symbol of both the nation’s heritage and its commitment to feeding the world through innovation and sustainable practices.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Agriculture Technology

One of the most significant contributions of American agriculture to the world was the mechanization of farming. Eli Whitney’s cotton gin, patented in 1793, revolutionized cotton production and laid the groundwork for large-scale agriculture. Later innovations like the steel plow, reaper, and combine harvester greatly increased the efficiency of planting, harvesting, and processing crops. These inventions not only boosted productivity but also reduced the need for manual labor, fundamentally transforming agriculture.
The mechanization of farming in America stands as a testament to innovation’s power in revolutionizing agriculture and, by extension, transforming societies. Eli Whitney’s groundbreaking invention, the cotton gin, marked the beginning of this agricultural revolution, but it was far from the sole innovation in this transformative journey.
Eli Whitney’s cotton gin, patented in 1793, was a game-changer for the cotton industry. Prior to its introduction, the labor-intensive process of separating cotton fibers from seeds was a slow and arduous task, limiting the production of cotton. With the cotton gin, this process became significantly more efficient, enabling the processing of large quantities of cotton in a fraction of the time. This innovation not only spurred the growth of the cotton industry but also had profound economic and social implications, including the expansion of cotton plantations and the institution of slavery.
However, the cotton gin was just the beginning. American inventors and engineers continued to pioneer agricultural innovations. The development of the steel plow, credited to John Deere, revolutionized soil cultivation. Its durable and efficient design allowed farmers to work in tough, previously uncultivated terrains, expanding arable land and increasing agricultural output.
The reaper, another transformative invention, was introduced by Cyrus McCormick in the 1830s. It mechanized the harvesting of crops, such as wheat, dramatically reducing the labor required for harvesting. This innovation not only made harvesting faster and more efficient but also allowed farmers to cover larger expanses of land.
The combine harvester, later perfected by inventors like Hiram Moore and Jerome Increase Case, represented the pinnacle of agricultural mechanization. It combined the processes of harvesting, threshing, and winnowing into one machine, further increasing efficiency. The combine harvester’s adoption revolutionized grain farming, enabling large-scale operations to feed growing populations.
The impact of these innovations extended beyond the United States. American agricultural machinery, known for its reliability and efficiency, became sought-after worldwide. It played a pivotal role in global food production and trade, contributing to food security and economic development in numerous countries.
Perhaps one of the most profound consequences of these innovations was their ability to reduce the need for manual labor in agriculture. This, in turn, spurred urbanization as agricultural workers moved to cities in search of employment in burgeoning industries. It transformed the labor landscape, diversified the economy, and contributed to the growth of American cities.
In conclusion, American agriculture’s contributions to the world, particularly through mechanization, are a testament to the transformative power of innovation. From Eli Whitney’s cotton gin to the steel plow, reaper, and combine harvester, these inventions not only increased productivity but also reshaped the agricultural and economic landscapes. They propelled American agriculture to a position of global leadership and played a significant role in shaping the modern world.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: ADOPTION OF TECHNOLOGIES FOR SUSTAINABLE FARMING …

American farmers were among the early adopters of scientific farming techniques. They embraced crop rotation, soil testing, and pest control measures, improving the sustainability of farming practices. The establishment of land-grant universities and agricultural extension services further disseminated knowledge and best practices to farmers across the country and around the world.
American farmers have long been at the forefront of adopting scientific farming techniques, demonstrating their commitment to sustainable agriculture and their willingness to embrace innovative practices. This dedication to improving farming methods not only enhanced the productivity of American agriculture but also had far-reaching effects on global food production and sustainability.
Crop rotation was one of the fundamental practices that American farmers embraced. By alternating the types of crops grown in a specific field over successive seasons, they not only optimized soil fertility but also reduced the risk of pest and disease buildup. Crop rotation was a game-changer, as it improved both soil health and crop yields, contributing to long-term agricultural sustainability.
Soil testing emerged as another critical tool in the farmer’s arsenal. Through soil analysis, farmers gained insights into the nutrient composition of their fields. Armed with this knowledge, they could apply fertilizers and soil amendments more precisely, minimizing waste and environmental impact. Soil testing became a cornerstone of modern agronomy, illustrating how science could be harnessed to optimize agricultural practices.
Pest control measures, such as the introduction of biological controls and the use of pesticides, were also integral to American agriculture’s sustainable evolution. Farmers adopted integrated pest management strategies, balancing chemical interventions with biological controls and cultural practices. This holistic approach minimized the ecological impact of pest management and helped preserve beneficial organisms within the farming ecosystem.
The establishment of land-grant universities and agricultural extension services played a pivotal role in disseminating knowledge and best practices to farmers. These institutions were instrumental in bringing cutting-edge research and scientific advancements to agricultural communities across the nation. Farmers gained access to research-based recommendations, technical expertise, and educational resources, empowering them to make informed decisions and continually improve their farming practices.
The impact of American farmers’ embrace of scientific farming techniques extended far beyond national borders. As the United States became a leader in agricultural innovation, its practices and knowledge were shared with the world through international agricultural development initiatives. American expertise in sustainable agriculture played a crucial role in helping other nations boost their food production and agricultural sustainability, ultimately contributing to global food security.
Furthermore, the adoption of sustainable farming practices helped mitigate environmental degradation, demonstrating that productivity and environmental stewardship could go hand in hand. American farmers became exemplars of responsible land management, showcasing the potential for agriculture to coexist harmoniously with the environment.
In conclusion, American farmers’ early adoption of scientific farming techniques reflects their commitment to sustainable agriculture and innovation. These practices not only improved the efficiency and productivity of American farming but also had a profound influence on global agriculture. By disseminating knowledge and best practices, American farmers became ambassadors of sustainable farming, leaving a lasting legacy of responsible land management and agricultural progress that continues to resonate around the world.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here What is Sustainable Agriculture? | Sustainable Agriculture Research …

American scientists and farmers also played a crucial role in advancing crop genetics. The development of hybrid crops, such as hybrid corn, dramatically increased yields. Additionally, the Green Revolution of the mid-20th century, driven by American research, introduced high-yielding crop varieties and modern agricultural practices to countries facing food shortages, significantly increasing global food production.
The partnership between American scientists and farmers in advancing crop genetics has been a linchpin of agricultural progress that has reverberated around the world. Their collaboration has led to groundbreaking innovations, such as the development of hybrid crops like hybrid corn, that have profoundly impacted food production.
Hybrid crops, a product of careful crossbreeding and selection, have played a pivotal role in increasing agricultural yields. Hybrid corn, for example, brought about a dramatic transformation in corn production. These hybrid varieties combined the best traits of different corn lines, such as resistance to pests, adaptability to diverse climates, and increased yield potential. This breakthrough enabled farmers to produce more corn per acre, boosting their income and helping to meet the growing demand for food.
The impact of American innovation in agriculture extended far beyond hybrid crops. The mid-20th century witnessed the emergence of the Green Revolution, a global movement fueled by American research and expertise. At its core, the Green Revolution aimed to address food shortages and hunger in developing countries by introducing high-yielding crop varieties and modern agricultural practices.
American scientists like Norman Borlaug, often referred to as the “Father of the Green Revolution,” played instrumental roles in this transformative period. They developed new crop varieties, particularly high-yielding strains of wheat and rice, that were more resistant to pests and diseases and could thrive in a range of conditions. These new varieties, often referred to as “miracle crops,” significantly increased agricultural productivity and food security in countries facing chronic hunger.
The Green Revolution was not limited to crop development; it also promoted modern agricultural practices. These practices included the use of synthetic fertilizers, improved irrigation methods, and mechanization, which further contributed to increased crop yields. The adoption of these techniques allowed farmers to produce more food with less land and resources, easing the pressure on ecosystems and natural habitats.
Perhaps one of the most remarkable aspects of the Green Revolution was its global reach. American research and expertise were shared with countries around the world, enabling them to adapt and adopt high-yielding crop varieties and modern farming methods. This collaborative effort led to significant increases in food production and played a crucial role in alleviating hunger and poverty in many parts of the world.
The legacy of American innovation in crop genetics and agriculture continues to shape global food production and security. It serves as a testament to the capacity of science, technology, and collaboration to address complex global challenges. Moreover, it underscores the importance of sustainable agricultural practices that balance the need for increased food production with environmental stewardship and conservation.
You can also read more about this here: ADOPTION OF TECHNOLOGIES FOR SUSTAINABLE FARMING …
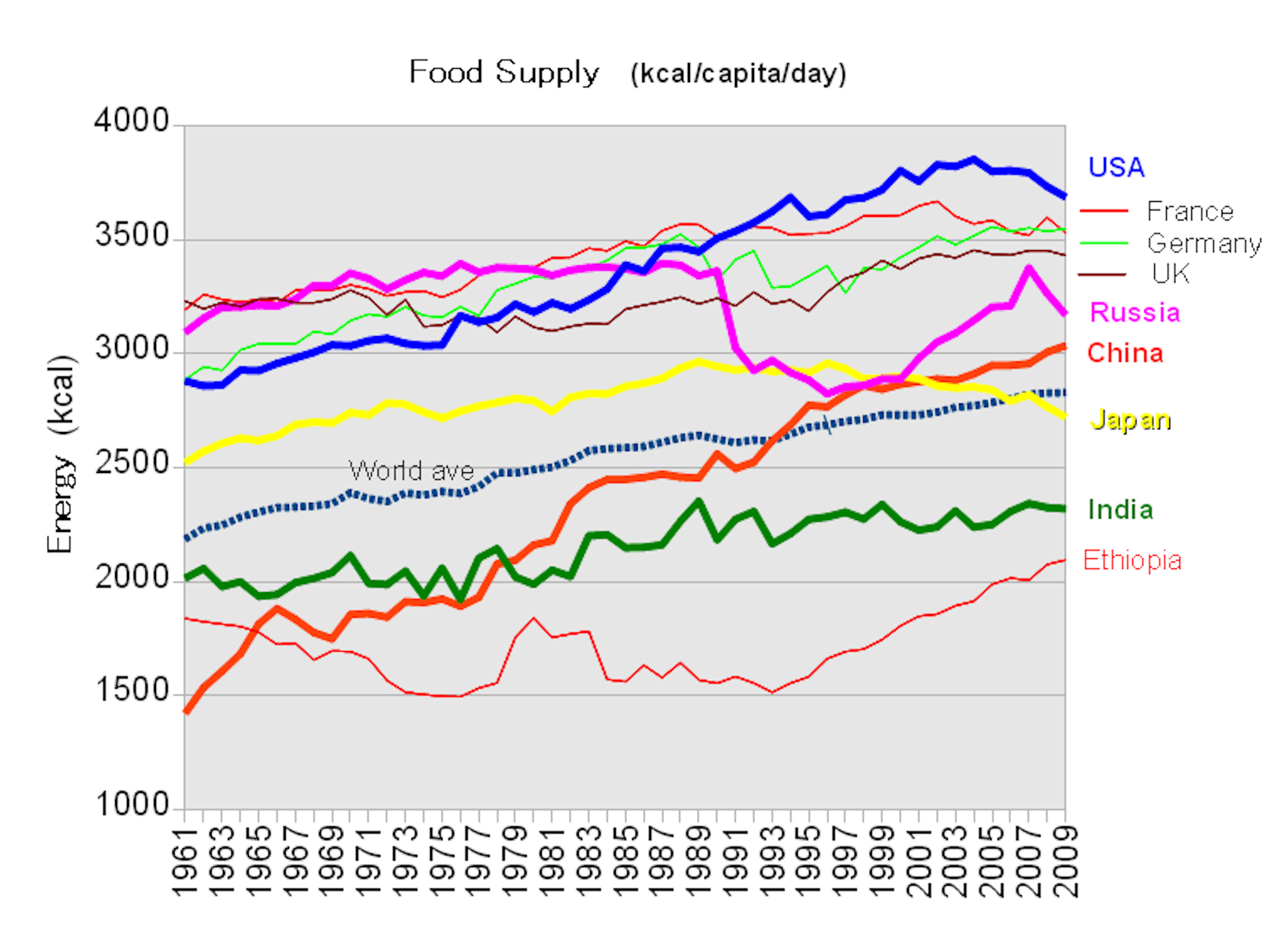
In the modern era, American agriculture has embraced technology to further optimize production. Precision agriculture, using GPS and data analytics, allows farmers to precisely manage their fields, conserve resources, and maximize yields. Drones, satellite imagery, and advanced irrigation systems have become integral tools for farmers, not only in the United States but also in regions facing food security challenges.
In the modern era, American agriculture stands as a testament to the relentless pursuit of efficiency and sustainability through the integration of cutting-edge technology. The transformation of farming practices, driven by innovations in precision agriculture, has not only empowered American farmers but has also become a beacon of hope for addressing global food security challenges.
Precision agriculture, often described as “farming with a surgical precision,” leverages a host of technological marvels to optimize every facet of the farming process. At the heart of this transformation are GPS and data analytics, which allow farmers to precisely manage their fields. Through the meticulous tracking of variables such as soil quality, moisture levels, and weather patterns, farmers can make data-driven decisions that enhance crop performance while minimizing resource waste.
Drones have emerged as invaluable tools in the farmer’s arsenal. Equipped with sophisticated sensors and cameras, these unmanned aerial vehicles can monitor crops from above, capturing detailed imagery and data that reveal crop health, pest infestations, or irrigation issues. Armed with this information, farmers can respond proactively, targeting specific areas with treatments or adjustments, thereby reducing the need for broad-scale interventions and minimizing environmental impacts.
Satellite imagery takes this concept a step further, providing a comprehensive view of entire fields and even entire farms. This “bird’s-eye” perspective allows farmers to detect patterns and trends that might be invisible from the ground. Whether it’s monitoring crop growth, assessing the effectiveness of irrigation systems, or detecting early signs of stress, satellite imagery equips farmers with a level of insight and oversight that was inconceivable in the past.
Advanced irrigation systems represent another breakthrough in modern agriculture. Water is a precious resource, and efficient water management is essential for sustainable farming. Smart irrigation systems, often controlled remotely through mobile apps, enable farmers to deliver the right amount of water to each plant at the right time. By minimizing water wastage, these systems contribute to resource conservation and cost reduction.
The implications of these technological advancements in American agriculture extend far beyond national borders. In regions facing food security challenges, such as water scarcity and unpredictable climate conditions, these innovations offer a lifeline. By sharing knowledge and technology, American farmers and organizations are helping empower communities around the world to improve agricultural practices, enhance yields, and bolster food security.
Furthermore, the data-driven nature of modern agriculture opens doors to ongoing research and innovation. The vast datasets generated by precision agriculture enable scientists and researchers to gain a deeper understanding of crop behavior and ecosystem dynamics. This knowledge serves as a foundation for further innovations that can drive agricultural sustainability.
In conclusion, modern American agriculture is a testament to the power of technology and innovation to address the world’s pressing challenges. Precision agriculture, driven by GPS, data analytics, drones, and advanced irrigation systems, has revolutionized farming practices, making them more efficient, sustainable, and adaptable. These technological advancements not only benefit American farmers but also hold the promise of alleviating global food security challenges and fostering a more resilient and sustainable future for agriculture worldwide.
You can also read more about this here: ADOPTION OF TECHNOLOGIES FOR SUSTAINABLE FARMING …
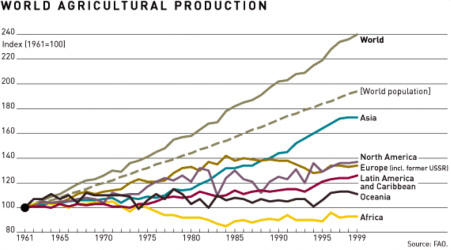
As American agriculture expanded, it faced environmental challenges. The recognition of these issues led to the development of sustainable farming practices, including organic farming, no-till farming, and integrated pest management. American innovation continues to drive efforts to balance increased food production with environmental stewardship.
The expansion of American agriculture, while pivotal in meeting the growing demand for food, was not without its environmental consequences. As the nation’s agricultural footprint expanded, it encountered a range of environmental challenges that threatened soil health, water quality, and biodiversity. Recognizing these issues, American farmers, researchers, and policymakers embarked on a journey towards sustainable farming practices, marking a profound shift in the way we cultivate our food.
One of the most notable developments in sustainable agriculture was the rise of organic farming. Organic farming prioritizes natural and holistic approaches to crop cultivation and livestock management, eschewing synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms. This shift towards organic methods aimed to reduce the ecological footprint of agriculture by minimizing soil erosion, protecting water quality, and promoting biodiversity. The organic farming movement not only gained popularity among consumers seeking healthier and environmentally friendly food options but also served as a model for sustainable agriculture practices.
Another innovative approach was the adoption of no-till farming. Traditional farming methods often involved plowing and tilling, which disrupted soil structure and contributed to erosion. No-till farming, on the other hand, minimizes soil disturbance, leaving crop residues on the field to protect against erosion and promote soil health. This conservation practice not only reduced the environmental impact of agriculture but also improved soil fertility and water retention, making farms more resilient to climate variability.
Integrated pest management (IPM) emerged as a science-based approach to pest control that aimed to minimize the use of pesticides while effectively managing agricultural pests. IPM strategies incorporated a combination of techniques, such as biological controls, crop rotation, and the monitoring of pest populations. By reducing reliance on chemical pesticides, IPM helped preserve beneficial insects and mitigate the environmental risks associated with pesticide use.
American innovation played a central role in driving these sustainable farming practices forward. Research institutions, universities, and agricultural technology companies developed new tools and techniques to support sustainable agriculture. Precision agriculture, enabled by advancements in data analytics and sensor technology, allowed farmers to optimize resource use and minimize waste, further reducing the environmental footprint of agriculture.
Today, the journey towards sustainable agriculture continues to evolve as American innovation drives efforts to balance increased food production with environmental stewardship. Technologies like genetic engineering and precision breeding offer potential solutions for enhancing crop resilience and reducing resource inputs. Additionally, the growing emphasis on regenerative agriculture seeks to restore and enhance ecosystem services while maintaining agricultural productivity.
In conclusion, the recognition of environmental challenges in American agriculture led to a transformative shift towards sustainable farming practices. From organic farming to no-till methods and integrated pest management, these practices have helped mitigate the environmental impact of agriculture while ensuring food security. American innovation remains at the forefront of this ongoing journey, as the nation continues to pioneer new approaches to balance the imperative of feeding a growing population with the need to safeguard our natural resources and the environment.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Executive Order on Advancing Biotechnology and Biomanufacturing …

American farming techniques have had a profound influence on global food production. They have not only helped feed a growing world population but have also provided valuable knowledge and technology to farmers in other countries. However, challenges such as climate change, water scarcity, and changing dietary preferences present new hurdles that will require ongoing innovation and international collaboration to address.
American farming techniques have undoubtedly left an indelible mark on global food production, with far-reaching impacts that extend beyond simply meeting the demands of a growing global population. These techniques have played a pivotal role in shaping agricultural practices worldwide, offering not only sustenance but also knowledge, technology, and lessons in sustainability. However, as we navigate the complex challenges of climate change, water scarcity, and evolving dietary preferences, American agriculture stands at the forefront of addressing these pressing issues. Here are several key aspects to consider:
Yield Maximization: American farming techniques, characterized by the adoption of advanced machinery, precision agriculture, and biotechnological innovations, have significantly increased crop yields. This enhanced productivity has set a benchmark for global agriculture and helped ensure food security in regions grappling with population growth.
Knowledge Sharing: The United States has been instrumental in sharing agricultural knowledge and best practices with farmers worldwide. Through international agricultural development programs and partnerships, American expertise has empowered farmers in diverse regions, improving their agricultural techniques and livelihoods.
Technological Transfer: American agricultural technology, from genetically modified crops to irrigation systems, has been transferred to other countries, bolstering global food production capacity. These technologies have played a pivotal role in addressing food shortages and alleviating hunger in resource-constrained areas.
Sustainability Initiatives: American agriculture has increasingly embraced sustainability practices, such as conservation tillage, crop rotation, and reduced chemical usage. These initiatives serve as models for sustainable farming globally and are vital in preserving the health of ecosystems.
Climate Adaptation: Climate change poses a substantial threat to agriculture. American farmers have been at the forefront of adopting climate-resilient practices, such as drought-tolerant crop varieties and adaptive irrigation systems. These solutions provide a blueprint for mitigating the impact of climate change on global agriculture.
Water Management: American agriculture has pioneered water-efficient irrigation techniques and water resource management. These innovations are of paramount importance in regions grappling with water scarcity, offering solutions to maximize agricultural output while minimizing water usage.
Changing Dietary Preferences: As dietary preferences evolve towards greater emphasis on sustainability, health, and plant-based diets, American agriculture has been diversifying to meet these demands. It is producing a wider variety of crops and alternative protein sources, shaping global dietary trends.
Crop Diversity: The United States boasts diverse agricultural regions, each specializing in particular crops. This diversity has enriched global food trade by providing a wide array of agricultural products to meet diverse dietary needs.
Biotechnology and Genetic Research: American biotechnology and genetic research have yielded crops with improved nutritional content, disease resistance, and adaptability to changing environmental conditions. These innovations are vital in addressing global food security challenges.
International Collaboration: The challenges facing agriculture today, particularly in the context of a growing global population and environmental concerns, necessitate international collaboration. American agricultural experts and institutions continue to engage in partnerships and research initiatives aimed at developing sustainable solutions on a global scale.
In conclusion, American farming techniques have not only been instrumental in feeding the world but have also disseminated knowledge, technology, and sustainable practices to benefit farmers worldwide. As we confront the multifaceted challenges of climate change, water scarcity, and shifting dietary preferences, American agriculture remains at the forefront of innovation and international collaboration. Together, we are working to ensure a sustainable and food-secure future for all.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: ADOPTION OF TECHNOLOGIES FOR SUSTAINABLE FARMING …

Conclusion
The history of American agriculture is a testament to human ingenuity and adaptability. From the mechanization of farming to the development of sustainable and technologically advanced practices, American innovation has been at the forefront of global food production. As the world faces new challenges and opportunities in agriculture, American farming techniques will continue to play a critical role in ensuring food security and sustainability for future generations on a global scale.
The history of American agriculture is a remarkable saga that underscores humanity’s capacity for innovation and adaptation in the face of evolving challenges. American farmers and agricultural scientists have consistently demonstrated their ability to pioneer new approaches and technologies to enhance food production and sustainability. Let’s explore further how this legacy of ingenuity continues to shape the future of agriculture:
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering: In recent decades, American agricultural innovation has extended to biotechnology and genetic engineering. The development of genetically modified (GM) crops, like insect-resistant Bt cotton and drought-tolerant maize, has not only increased crop yields but has also reduced the need for chemical pesticides and conserved water resources. American expertise in biotechnology is driving advancements that could lead to crops with improved nutritional profiles, further bolstering global food security.
Climate Resilience: As climate change poses increasingly complex challenges to agriculture, American farming techniques are evolving to build climate-resilient systems. Practices such as crop diversification, soil carbon sequestration, and precision climate data utilization are helping farmers adapt to shifting weather patterns and mitigate the impact of extreme events like droughts and floods.
Digital Agriculture and Big Data: The integration of digital technologies and big data analytics into American agriculture has ushered in the era of smart farming. Farmers now have access to real-time information about soil conditions, weather forecasts, and crop health. This data-driven approach empowers farmers to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and minimize waste, ultimately increasing agricultural productivity.
Global Collaboration: American agriculture is increasingly intertwined with global food production systems. American agribusinesses and research institutions collaborate with their counterparts worldwide, sharing knowledge, technologies, and best practices. This international cooperation is critical in addressing global challenges such as food distribution, access to resources, and sustainable farming methods.
Sustainable Practices: Sustainability has become a guiding principle in American agriculture. Practices like organic farming, no-till farming, and integrated pest management are gaining prominence, emphasizing soil health, biodiversity conservation, and reduced environmental impact. These approaches are not only environmentally friendly but also economically viable in the long term.
Rural Development and Community Engagement: American agriculture extends beyond food production; it contributes significantly to rural development and community engagement. Initiatives like local food movements and farmers’ markets promote the consumption of locally grown produce, support small-scale farmers, and foster stronger connections between urban and rural communities.
Education and Training: American agricultural institutions and extension services continue to provide education and training to farmers, both domestically and abroad. These programs equip farmers with the latest knowledge and technologies, enabling them to maximize their productivity and resilience in the face of global challenges.
In conclusion, the history of American agriculture is a testament to the spirit of innovation and adaptability that continues to drive the industry forward. American farming techniques, from mechanization to biotechnology and sustainable practices, have had a profound and lasting impact on global food production. As the world grapples with the complex interplay of population growth, climate change, and resource constraints, American agriculture remains a beacon of hope, offering solutions and leadership in ensuring food security and sustainability for generations to come.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Creating Shared Value and Sustainability Report 2022 | Nestlé
More links
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Agriculture’s technology future: How connectivity can yield new …