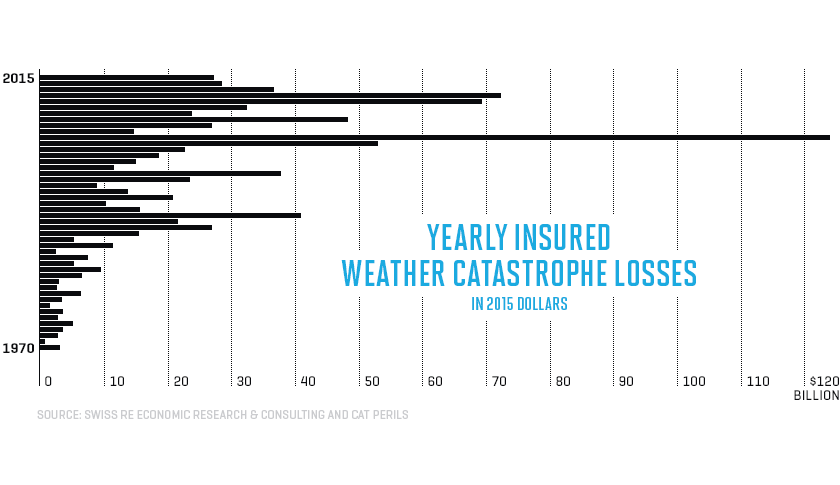
Introduction
The insurance industry plays a pivotal role in helping individuals, businesses, and communities recover from the financial impacts of unexpected events. However, the changing climate is introducing new challenges and complexities into the world of insurance and reinsurance. This article explores the ways in which climate change is affecting the insurance industry, the innovative approaches insurers are adopting, and the role of reinsurance in managing climate-related risks.
Climate change is reshaping the landscape of the insurance and reinsurance industries in profound ways. Here are some key points to consider:
Increased Frequency and Severity: Climate change has led to a rise in the frequency and severity of weather-related disasters. Events like hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and droughts are occurring more frequently, resulting in higher insurance claims. This increased exposure to climate-related risks has prompted insurers to reassess their pricing models and risk assessments.
Actuarial Challenges: The traditional actuarial models that insurers rely on to calculate premiums and assess risks are being challenged by the unpredictability of climate-related events. Historical data may no longer provide an accurate basis for predicting future losses. Insurers are increasingly turning to climate modeling and advanced data analytics to refine their risk assessments.
Resilience and Mitigation: Insurers are taking proactive steps to incentivize policyholders and businesses to adopt climate-resilient practices. This can include offering lower premiums to homeowners who invest in flood-resistant home improvements or providing discounts to businesses that implement climate mitigation measures. By encouraging resilience and mitigation, insurers aim to reduce the overall impact of climate-related events.
Innovative Products: To address emerging climate risks, insurers are developing innovative insurance products. These can range from parametric insurance, which pays out based on predefined weather conditions, to specialized coverage for renewable energy projects. These products are designed to provide financial protection in a changing climate landscape.
Reinsurance’s Role: Reinsurance companies, which provide insurance to primary insurers, play a crucial role in managing climate risks. They help spread the financial burden of catastrophic events across a wider pool of insurers. Reinsurers are increasingly involved in climate risk assessment and modeling, helping primary insurers better understand and manage their exposure.
Regulatory Pressure: Regulatory bodies and governments are increasingly recognizing the importance of climate risk disclosure and management. Insurers are under pressure to disclose their climate-related risks and demonstrate how they are addressing them. Compliance with evolving climate-related regulations is becoming a critical aspect of insurance operations.
Collaboration and Data Sharing: The insurance industry is also exploring collaborations with other sectors, such as academia and climate research institutions, to access valuable data and insights. This collaborative approach can lead to more accurate risk assessments and better-informed decisions.
In conclusion, the insurance and reinsurance industries are at the forefront of managing the financial risks associated with climate change. As the climate continues to evolve, these sectors will need to embrace innovation, data-driven decision-making, and collaborative efforts to ensure they can effectively protect individuals, businesses, and communities in a changing climate landscape.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: The Fed – Climate Change and Financial Stability
Climate change is leading to more frequent and severe weather events, including hurricanes, wildfires, floods, and droughts. These events result in a growing number of insurance claims, straining the resources of insurance companies. Here’s how climate change is impacting the insurance landscape:
“Insurance companies are having to reassess risk models, underwriting practices, and pricing strategies to account for the increased likelihood of extreme weather events. Additionally, some regions may see insurance becoming less affordable or available, creating challenges for homeowners and businesses.”
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Impacts of Climate Change and Remote Natural Catastrophes on …

Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns contribute to an uptick in claims for weather-related damages, such as property damage, crop losses, and infrastructure repairs.
The increase in claims for weather-related damages due to rising temperatures and shifting weather patterns has far-reaching consequences. Here are some key considerations:
Property Damage: As extreme weather events become more frequent and severe, property owners face a higher risk of damage to homes, buildings, and infrastructure. This leads to increased insurance claims, potentially causing premiums to rise for property owners.
Crop Losses: Farmers and agricultural businesses are particularly vulnerable to weather-related damages. Droughts, floods, heatwaves, and unseasonal frosts can devastate crops and livestock. The resulting financial losses impact both individual farmers and global food supply chains.
Infrastructure Repairs: Weather-related events, such as hurricanes, heavy rainfall, and wildfires, often result in the need for extensive infrastructure repairs. Roads, bridges, utilities, and public facilities require significant investments to restore functionality and safety.
Insurance Industry Challenges: The surge in weather-related claims presents challenges for the insurance industry. Insurers must accurately assess and price climate-related risks while managing their own exposure. This involves using advanced modeling and data analytics to better understand and anticipate weather-related losses.
Economic Impact: The economic consequences of weather-related damages are substantial. Beyond insurance claims, there are indirect costs related to lost productivity, supply chain disruptions, and government expenditures on disaster relief and recovery efforts.
Government Response: Governments at various levels must allocate resources for emergency response and long-term recovery. This can strain public budgets and lead to debates about how to prioritize spending in the face of increasingly frequent weather-related disasters.
Climate Adaptation: Rising claims for weather-related damages underscore the importance of climate adaptation strategies. These include building climate-resilient infrastructure, implementing better land-use planning, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices to reduce vulnerability to climate-related risks.
Business Resilience: Businesses must factor in the increased likelihood of weather-related disruptions when planning their operations. This includes considering supply chain diversification, disaster preparedness, and risk management strategies to ensure business continuity.
Individual Preparedness: Individuals also play a role in mitigating weather-related risks. Homeowners can invest in resilient building materials and design, while communities can implement flood control measures and emergency response plans to protect residents.
Long-Term Planning: The trends in rising claims for weather-related damages underscore the need for comprehensive, long-term planning at local, national, and global levels. Mitigating the impacts of climate change and building resilience to extreme weather events are critical priorities for ensuring a sustainable future.
In summary, the increase in claims for weather-related damages due to climate change has multifaceted implications, from financial challenges for individuals and businesses to the need for proactive climate adaptation and resilience-building efforts. Addressing these challenges requires a coordinated and sustained effort across sectors and levels of society.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: The State of the Reinsurance Property Catastrophe market | Swiss Re

Extreme weather events are not only more frequent but also more severe, leading to higher claim payouts and greater financial strain on insurers.
Extreme weather events are not only more frequent but also more severe, leading to higher claim payouts and greater financial strain on insurers. This trend is pushing insurance companies to reassess risk models, increase premiums, and explore innovative solutions to manage and transfer risk effectively. Furthermore, it underscores the urgency of climate action to reduce the long-term financial impact on both the insurance industry and society at large.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: REPORT TO THE PRESIDENT Extreme Weather Risk in a …

Insurance companies must reevaluate their risk assessment models to accurately price policies in a changing climate. This can lead to higher premiums for policyholders.
Reevaluating risk assessment models in the context of a changing climate is a necessity for insurance companies, but it can indeed have significant implications for policyholders. Here’s a more detailed exploration of this idea:
Risk-Based Pricing: Insurance premiums are traditionally based on actuarial risk assessments that rely on historical data to predict future losses. However, as climate change disrupts historical patterns, insurers face a dilemma. To accurately reflect the increased risks associated with climate-related events, they may need to raise premiums for policyholders in high-risk areas. This could mean higher costs for homeowners, businesses, and individuals, particularly those living in regions prone to hurricanes, floods, wildfires, or other climate-related disasters.
Affordability Challenges: While insurers have a responsibility to manage their risks, higher premiums can make insurance less affordable for many policyholders. This can result in a protection gap where a significant portion of the population is underinsured or lacks coverage altogether. For individuals and businesses, affordability challenges can translate into financial vulnerability when disaster strikes.
Equity Concerns: The burden of increased insurance costs is not distributed equally. Vulnerable communities, often disproportionately affected by climate change, may face the greatest challenges in affording higher premiums. This raises equity concerns, as those who contribute less to climate change may bear a more substantial financial burden in adapting to it.
Mitigation and Resilience Incentives: On the positive side, higher premiums can incentivize policyholders to invest in climate-resilient measures. For homeowners, this could mean strengthening their properties against hurricanes or flooding. For businesses, it might involve adopting energy-efficient technologies to reduce exposure to climate-related risks. By encouraging mitigation and resilience, insurers aim to reduce the overall impact of climate events.
Government Intervention: Governments may step in to address affordability concerns, especially for essential insurance coverage like flood insurance. Subsidies and incentives for climate-resilient practices can help policyholders adapt to higher premiums while still ensuring financial protection.
Data-Driven Solutions: Advanced data analytics and climate modeling can help insurers refine their risk assessments, potentially leading to more precise pricing. This can benefit policyholders by ensuring that premiums align more closely with their actual risk exposure.
In conclusion, the reevaluation of risk assessment models in response to climate change is a complex challenge for insurance companies. While it can lead to higher premiums for policyholders, it also highlights the critical role of insurance in promoting climate resilience. Striking a balance between accurate pricing and affordability, along with government intervention and data-driven solutions, is essential to ensure that insurance remains accessible and effective in a changing climate landscape.
You can also read more about this here: The Fed – Climate Change and Financial Stability
To address the challenges posed by climate change, the insurance industry is embracing innovative approaches:
“One innovative approach is parametric insurance, which pays out based on predetermined triggers like wind speed or rainfall, rather than traditional claims assessment. This can expedite payouts to policyholders in the aftermath of disasters. Additionally, the insurance industry is investing in climate modeling and data analytics to better understand and manage climate-related risks, ultimately improving their ability to serve customers in a changing world.”
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Insuring Nature to Ensure a Resilient Future

Insurers are investing in advanced risk modeling techniques that incorporate climate data to assess the potential impact of climate change on insured assets.
The insurance industry recognizes the significance of climate change and its potential impact on insured assets. To address this, insurers are adopting advanced risk modeling techniques that incorporate climate data in several ways:
Climate Risk Assessment: Insurers are increasingly integrating climate risk assessment into their underwriting processes. They utilize climate data to evaluate the likelihood and severity of weather-related events, such as hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and heatwaves. By factoring in these risks, insurers can more accurately price policies and assess the potential impact on their portfolios.
Historical Data Analysis: Insurers analyze historical climate data to identify trends and patterns in weather-related losses. This data-driven approach helps insurers understand the evolving risk landscape and make informed decisions about coverage and pricing.
Catastrophe Modeling: Catastrophe modeling has become a vital tool for insurers. These models use climate data to simulate various scenarios and assess potential losses from natural disasters. By running simulations based on climate projections, insurers can estimate the financial impact of future extreme events and develop strategies to manage and mitigate these risks.
Geospatial Analysis: Geospatial technology allows insurers to pinpoint areas at higher risk of climate-related events. This information helps insurers tailor policies and pricing based on the specific climate risks associated with a particular location, which can be crucial for homeowners, businesses, and agricultural operations.
Policy Design and Pricing: Climate data influences policy design and pricing. Insurers may offer more flexible policies that adapt to changing climate conditions, such as flood coverage or wildfire protection. Climate risk assessments also play a role in determining premium rates to align them with the anticipated risk.
Capital Adequacy: Insurers use climate modeling to assess their capital adequacy. By understanding potential losses related to climate change, they can ensure they have sufficient financial reserves to cover claims resulting from extreme weather events.
Engagement with Reinsurers: Reinsurance companies play a vital role in the insurance industry. Many insurers work closely with reinsurers to share the risk associated with climate-related events. Reinsurers also employ advanced climate modeling to evaluate their exposure and determine appropriate pricing.
Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory bodies are increasingly requiring insurers to disclose their climate risk exposure and mitigation strategies. Insurers must stay compliant with these regulations and demonstrate their commitment to managing climate risks effectively.
Customer Education: Insurers are also focused on educating their customers about climate-related risks and the importance of adequate coverage. This includes providing guidance on risk mitigation measures and the benefits of climate-resilient policies.
In summary, insurers are proactively incorporating climate data and advanced modeling techniques into their operations. By doing so, they aim to accurately assess climate-related risks, protect their policyholders, and ensure the long-term sustainability of the industry. As climate change continues to impact the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, the insurance sector’s ability to adapt and innovate will be critical in providing effective risk management solutions.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: The Fed – Climate Change and Financial Stability
Some insurers are offering products tailored to the needs of climate-conscious consumers, such as policies that promote energy-efficient home improvements or electric vehicle coverage.
Some insurers are offering products tailored to the needs of climate-conscious consumers, such as policies that promote energy-efficient home improvements or electric vehicle coverage. These specialized insurance products not only incentivize eco-friendly choices but also reflect a growing recognition of the role insurers can play in encouraging climate-resilient behaviors. As consumer preferences shift towards sustainability, insurance companies are adapting their offerings to align with these values and contribute to a greener future.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Capturing the climate opportunity in insurance | McKinsey

Insurance companies are increasingly aligning their investment portfolios with environmentally and socially responsible projects, contributing to climate mitigation efforts.
The alignment of insurance companies’ investment portfolios with environmentally and socially responsible projects is a significant development in response to climate change. Here’s a deeper exploration of this idea:
Impactful Investments: Insurers recognize the importance of using their substantial investment portfolios to make a positive impact on the environment and society. By directing their investments toward projects that promote climate mitigation and sustainability, they can contribute to global efforts to combat climate change. These investments may include renewable energy projects, green infrastructure, sustainable agriculture, and clean technology ventures.
Reducing Carbon Footprints: Insurance companies are not only addressing the risks posed by climate change but are also taking steps to reduce their own carbon footprints. This involves divesting from fossil fuels and industries with high environmental impacts. By shifting their investments away from carbon-intensive assets, insurers align their financial interests with climate-conscious goals.
Responsible Underwriting: Beyond their investment portfolios, insurers are incorporating climate-related considerations into their underwriting practices. They assess the climate resilience of policyholders, encouraging mitigation measures and offering incentives for climate-friendly practices. This approach helps reduce the overall risk exposure for both insurers and policyholders.
Positive Public Image: Aligning investments with environmental and social responsibility can enhance an insurance company’s public image. Consumers and stakeholders increasingly value companies that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. This can lead to increased trust and loyalty, which, in turn, can positively impact the company’s bottom line.
Financial Opportunities: Environmentally responsible investments are not just about ethics; they can also offer attractive financial returns. Many sustainable projects are economically viable and provide stable, long-term income streams. Insurance companies can benefit financially while simultaneously advancing climate goals.
Regulatory Compliance: As governments worldwide enact stricter environmental regulations and disclosure requirements, insurers are under pressure to ensure their investments are compliant. Aligning portfolios with responsible and sustainable projects helps insurance companies meet regulatory standards and avoid potential penalties.
Global Initiatives: The insurance industry is actively participating in global initiatives related to sustainability and climate action. These collaborations allow insurers to leverage their resources and expertise to address climate challenges on a larger scale. Examples include joining the Principles for Sustainable Insurance (PSI) and supporting the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
In conclusion, the alignment of insurance companies’ investments with environmentally and socially responsible projects represents a proactive response to the challenges posed by climate change. This strategic shift not only contributes to climate mitigation but also benefits insurance companies, policyholders, and society at large. It reflects a growing recognition that the insurance sector has a crucial role to play in fostering a more sustainable and resilient future.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: AXA & Climate Change | AXA

Reinsurance plays a critical role in the insurance industry’s response to climate change:
“Reinsurance companies, which help insurers manage large risks, are developing climate-focused solutions and strategies to navigate the changing landscape. They are working closely with primary insurers to enhance risk assessment, provide access to capital, and share expertise in climate risk modeling. This collaborative effort between primary insurers and reinsurers is essential for ensuring the insurance industry’s resilience in the face of climate change and its ability to continue offering coverage to policyholders.”
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Global Reinsurers Grapple With Climate Change Risks | S&P Global …
Insurers often transfer a portion of their risk to reinsurers, which can help mitigate the financial impact of large and catastrophic claims resulting from extreme weather events.
The relationship between insurers and reinsurers is fundamental to the insurance industry, particularly when it comes to mitigating the financial impact of large and catastrophic claims resulting from extreme weather events. Here’s how this process works and its significance:
Risk Sharing: Insurers often face the challenge of accumulating substantial risk exposure, especially in regions prone to extreme weather events. By transferring a portion of their risk to reinsurers, insurers can spread the financial burden of potential large-scale losses. This risk-sharing mechanism helps insurers maintain financial stability and continue providing coverage to policyholders.
Catastrophe Reinsurance: Catastrophe reinsurance is a specialized type of coverage that specifically addresses the impact of catastrophic events, including natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods. Insurers purchase catastrophe reinsurance to protect themselves from the financial fallout of such events. Reinsurers, which are typically larger and more financially resilient than primary insurers, absorb a significant portion of the losses in the event of a catastrophe.
Diversification of Risk: Reinsurers often have a global presence and a diverse portfolio of clients. This diversification allows them to spread their own risk across various geographic regions and industries. When extreme weather events occur, reinsurers can draw on their diverse resources to cover losses, reducing the financial strain on individual insurers.
Capacity to Absorb Large Losses: Extreme weather events can result in substantial losses that may exceed the capacity of individual insurers to cover. Reinsurers, with their extensive financial resources and expertise in risk assessment, are better equipped to absorb these large losses. This capacity provides insurers with confidence in their ability to meet their obligations to policyholders.
Risk Management Strategies: The presence of reinsurers encourages insurers to adopt robust risk management strategies. Insurers may implement stricter underwriting guidelines, enhance risk assessment processes, and invest in disaster preparedness and mitigation measures. These efforts not only benefit insurers but also contribute to the overall resilience of communities and economies.
Access to Expertise: Reinsurers often have specialized expertise in assessing and managing complex risks, including those associated with extreme weather events. Insurers can leverage this expertise to improve their own risk modeling, underwriting practices, and disaster response strategies.
Policyholder Protection: Ultimately, the relationship between insurers and reinsurers helps protect policyholders. It ensures that insurers can honor their commitments even in the face of widespread and financially challenging events. Policyholders benefit from knowing that their claims will be paid promptly and fairly, which contributes to trust and confidence in the insurance industry.
In summary, the collaboration between insurers and reinsurers is a crucial element of the insurance ecosystem, especially in the context of extreme weather events. It allows insurers to manage their risk exposure effectively, maintain financial stability, and continue offering coverage to individuals, businesses, and communities. This partnership reinforces the insurance industry’s ability to respond to the challenges posed by climate change and extreme weather with resilience and confidence.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Insurance-Linked Securities

Reinsurers have substantial financial resources, enabling insurers to underwrite policies for climate-related risks that might otherwise be too financially burdensome.
Reinsurers have substantial financial resources, enabling insurers to underwrite policies for climate-related risks that might otherwise be too financially burdensome. In essence, reinsurers act as a safety net for primary insurers, providing them with the necessary support to cover extreme weather events and climate-related claims. This collaboration between insurers and reinsurers helps maintain stability in the insurance industry, ensuring that policyholders can access coverage even in the face of escalating climate risks. As climate change continues to shape the risk landscape, the relationship between insurers and reinsurers will be pivotal in safeguarding communities and businesses against its impacts.
You can also read more about this here: REPORT TO THE PRESIDENT Extreme Weather Risk in a …

Reinsurers work closely with insurers to develop risk mitigation strategies, including encouraging policyholders to take preventive measures to reduce climate-related risks.
The collaboration between reinsurers and insurers in developing risk mitigation strategies for climate-related risks is a vital component of the insurance industry’s response to a changing climate. Here’s a more in-depth exploration of this idea:
Data-Driven Insights: Reinsurers bring extensive data and analytical capabilities to the table. They use historical climate data, catastrophe modeling, and risk assessment tools to provide insurers with valuable insights into the specific risks associated with climate change in various regions. This data-driven approach helps insurers make informed decisions about pricing, coverage, and risk management.
Tailored Risk Solutions: Reinsurers and insurers work together to create customized risk solutions that address climate-related challenges. This collaboration can lead to the development of innovative insurance products designed to cover new and emerging risks associated with extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and other climate-related perils.
Loss Prevention and Mitigation: One of the key strategies in managing climate risks is loss prevention and mitigation. Reinsurers often encourage insurers to promote risk reduction measures among policyholders. This can include providing incentives for property owners to invest in climate-resilient infrastructure, adopt sustainable practices, and implement disaster preparedness plans. By reducing the likelihood and severity of losses, insurers and reinsurers can help protect both policyholders and their own bottom lines.
Resilience Education: The collaboration extends to educating insurers and policyholders about the importance of climate resilience. Reinsurers share their expertise and research findings on climate change trends and their potential impacts. This knowledge transfer helps insurers better understand the evolving risks and empowers them to communicate effectively with policyholders about the need for climate-conscious choices.
Risk Pooling and Diversification: Reinsurers play a significant role in risk pooling and diversification. By spreading risks across a broad portfolio of insurers and geographic regions, reinsurers help stabilize the industry in the face of large-scale climate-related losses. This diversification ensures that insurers can continue to provide coverage even when faced with significant claims.
Innovative Risk Transfer: Reinsurers explore innovative risk transfer mechanisms to help insurers manage climate-related exposures. These may include catastrophe bonds, parametric insurance, and other financial instruments designed to transfer risks to the capital markets. Such solutions provide insurers with additional financial resources to cover claims in the event of a major climate-related catastrophe.
Adaptive Pricing: Reinsurers collaborate with insurers to develop adaptive pricing models that reflect changing climate risks. This approach allows insurers to adjust premiums based on the evolving threat landscape. It ensures that coverage remains affordable and accessible for policyholders while accurately reflecting the costs associated with climate risks.
In summary, the partnership between reinsurers and insurers is instrumental in addressing the challenges posed by climate change. Their joint efforts in risk assessment, loss prevention, education, and innovation contribute to a more resilient insurance industry. By working together, they enhance the industry’s ability to protect policyholders and communities in an increasingly unpredictable climate environment.
You can also read more about this here: The Fed – Climate Change and Financial Stability

Conclusion
Climate change presents complex challenges to the insurance industry, but it also offers opportunities for innovation and collaboration. Insurance companies and reinsurers are increasingly recognizing the importance of addressing climate-related risks. By leveraging advanced risk modeling, offering climate-resilient products, and embracing sustainable investments, the insurance industry is taking proactive steps to adapt to a changing climate and continue providing crucial financial protection to individuals and businesses worldwide.
“The insurance industry, amid the challenges posed by climate change, is positioned to be a key player in fostering resilience and sustainability. By leveraging innovative technologies, data analytics, and risk assessment models, insurers and reinsurers can better understand and manage climate-related risks. Moreover, the development of climate-resilient insurance products and the incorporation of sustainability criteria in investment portfolios demonstrate the industry’s commitment to addressing climate challenges. As climate change continues to reshape our world, the insurance sector is poised to play a pivotal role in mitigating its impact and helping individuals and businesses prepare for an uncertain future.”
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Climate change and increased risk for the insurance sector: a global …
More links
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: The Fed – Climate Change and Financial Stability