Introduction
The insurance industry is at the frontline of facing the consequences of climate change. As the Earth’s climate continues to evolve, the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and droughts, have increased. These changes have significant implications for insurers worldwide. In this article, we will explore the intricate relationship between the insurance industry and climate change, examining the challenges it poses, innovative solutions, and the industry’s role in mitigating the impacts of a changing climate.
The insurance industry’s position at the forefront of dealing with climate change consequences is emblematic of its pivotal role in our evolving world. The ongoing transformation of Earth’s climate has brought about a troubling surge in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, encompassing devastating hurricanes, catastrophic floods, raging wildfires, and debilitating droughts. These profound shifts in climate patterns carry profound implications for insurers on a global scale. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the intricate and symbiotic relationship between the insurance industry and climate change. We scrutinize the multifaceted challenges it confronts, the ingenious solutions it pioneers, and its indispensable role in curbing and managing the far-reaching impacts of our changing climate.
Risk Assessment and Pricing: Insurers grapple with the formidable task of recalibrating their risk assessment models and pricing strategies. The evolving climate landscape necessitates a more nuanced understanding of weather-related risks, requiring the industry to adapt its methodologies to accurately reflect the increased likelihood of extreme events.
Increased Payouts: The surge in extreme weather events translates to a surge in insurance payouts. The insurance industry faces mounting financial pressure as it strives to fulfill its obligations to policyholders affected by hurricanes, floods, and wildfires, posing solvency concerns.
Reinsurance and Risk Transfer: Reinsurance plays a pivotal role in the industry’s ability to manage climate-related risks. Reinsurers absorb a significant portion of the financial burden, allowing primary insurers to mitigate their exposure to large-scale weather-related claims.
Policy Coverage: Insurers are challenged to revisit policy coverage terms and limits to ensure they align with the changing climate reality. Policyholders must be adequately protected against the growing threat of extreme weather events.
Innovation and Data Analytics: The insurance industry leverages innovation and data analytics to enhance risk modeling and prediction capabilities. This enables more accurate underwriting, efficient claims processing, and proactive risk management.
Climate-Resilient Infrastructure: Insurers encourage climate-resilient infrastructure investments to mitigate future losses. They collaborate with governments, businesses, and communities to promote the construction of buildings, roads, and utilities that can withstand the impacts of climate change.
Climate Disclosure: The insurance industry increasingly recognizes the importance of climate disclosure and transparency. Investors, regulators, and stakeholders demand insight into insurers’ climate risk exposure and strategies for managing it.
Advocacy and Awareness: Insurers play an advocacy role in raising awareness about climate change and its implications. They advocate for policies that promote sustainability and emissions reduction, recognizing that a proactive approach benefits both their business and society.
Green Insurance Products: Insurers introduce green insurance products that incentivize policyholders to adopt sustainable practices, such as renewable energy installations and energy-efficient building designs.
Risk Pooling and Sharing: Climate change prompts insurers to explore novel risk-sharing mechanisms and partnerships. Collaborative approaches, such as risk pools and public-private partnerships, distribute the financial burden of extreme weather events more equitably.
Long-Term Resilience: The insurance industry recognizes that fostering long-term resilience is crucial. This entails supporting initiatives that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, protect ecosystems, and enhance community preparedness.
In conclusion, the symbiotic relationship between the insurance industry and climate change underscores the pivotal role insurers play in navigating an increasingly uncertain world. As climate patterns continue to shift, the industry’s ability to innovate, adapt, and advocate for resilience is pivotal. By pioneering risk assessment, promoting sustainable practices, and facilitating resilient communities, insurers serve not only as financial protectors but as vital partners in addressing the climate crisis. In doing so, they help forge a more resilient and sustainable future for us all.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Regulators Should Identify and Mitigate Climate Risks in the …
Climate change has amplified the risk associated with insuring properties and assets. Higher temperatures, rising sea levels, and erratic weather patterns make it challenging for insurers to predict and manage risk accurately.
The impact of climate change on the insurance industry is profound and multifaceted. Here are several key points that further elaborate on this complex relationship:
Increasing Frequency and Severity of Extreme Weather Events: Climate change has led to more frequent and severe extreme weather events, including hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and storms. These events result in significant property damage, which, in turn, leads to a surge in insurance claims. Insurers are compelled to reevaluate their risk models and pricing strategies to account for the heightened risk associated with these events.
Rising Costs of Claims: The increase in extreme weather events has translated into higher claims costs for insurers. Repairing or replacing damaged properties and assets is becoming increasingly expensive. This trend puts pressure on insurance companies to adjust premiums to cover these rising costs, potentially making insurance less affordable for consumers.
Property Valuation Challenges: Climate change has implications for property valuations. Properties located in regions vulnerable to climate-related risks, such as coastal areas prone to sea-level rise, may see reduced valuations, impacting the calculation of insurance coverage. This poses challenges for property owners and insurers alike.
Regulatory Changes: Governments and regulatory bodies are responding to climate change by introducing new regulations and requirements for insurers. These changes may include mandates for climate risk disclosures, stress testing of portfolios for climate-related scenarios, and calls for insurers to invest in more sustainable and climate-resilient assets.
Risk Assessment and Underwriting: To adapt to the changing climate landscape, insurers are investing in more advanced risk assessment and underwriting techniques. They are incorporating climate data, predictive modeling, and machine learning to better understand and price climate-related risks. This enables insurers to provide more accurate coverage and manage their own exposure.
Innovation in Insurance Products: Climate change has driven innovation in insurance products. Specialized coverage, such as parametric insurance, has gained prominence. These products offer payouts based on predefined triggers, such as wind speeds or rainfall levels, simplifying the claims process and providing quicker financial relief to policyholders after disasters.
Long-Term Resilience Planning: Insurance companies are increasingly focused on long-term resilience planning. They recognize the need to collaborate with policymakers, scientists, and communities to mitigate the impacts of climate change and build resilience. This may involve supporting climate adaptation projects, incentivizing policyholders to take preventive measures, and encouraging sustainable practices.
Community Engagement: Engaging with local communities is crucial for insurers. By actively participating in community-based initiatives and risk reduction programs, insurers can help communities better prepare for climate-related risks. This proactive engagement can reduce claims and enhance community resilience.
Reinsurance and Risk Transfer: Reinsurance companies play a vital role in spreading risk within the insurance industry. In response to climate change, reinsurers are reassessing their exposure and pricing strategies. This, in turn, influences the cost and availability of insurance coverage for primary insurers and policyholders.
Transparency and Disclosure: Investors are increasingly interested in understanding how insurance companies are managing climate risks within their portfolios. Insurers are responding by enhancing transparency and disclosure practices, providing stakeholders with information on their climate risk exposure and mitigation efforts.
In conclusion, climate change has reshaped the landscape of the insurance industry, necessitating adaptation, innovation, and collaboration. Insurers are navigating a complex terrain, balancing the need to provide coverage to policyholders with the imperative to manage their own exposure to climate-related risks. As climate change continues to evolve, the insurance industry will play a pivotal role in helping individuals, businesses, and communities prepare for and recover from climate-related disasters.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Guidance for New York Domestic Insurers on Managing the …
The surge in weather-related disasters has led to substantial payouts by insurance companies. The financial burden of covering damage from hurricanes, floods, and wildfires strains the industry’s resources.
The insurance industry, often seen as the financial safety net for individuals and businesses, is facing an unprecedented challenge in the form of climate change. The surge in weather-related disasters has led to substantial payouts by insurance companies, creating a significant financial burden. Hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and other extreme weather events have become more frequent and severe, resulting in a growing number of claims.
As climate change intensifies, so does the frequency and severity of these natural disasters. In the past, insurance companies could rely on historical data to assess risk and set premiums. However, the rapidly changing climate has made it increasingly difficult to predict and price risk accurately. This uncertainty has left insurance companies grappling with how to adapt to a new era of climate-related challenges.
One of the major issues facing the insurance industry is the rising cost of claims. Hurricanes, for example, can cause widespread damage to homes and infrastructure, resulting in billions of dollars in payouts. Floods, another common consequence of extreme weather events, lead to substantial losses for insurers as well. As these events become more frequent, insurance companies must set aside larger reserves to cover potential claims, putting pressure on their financial stability.
Another challenge is the need to reassess risk models. Traditional risk assessment models are based on historical data, which may no longer be reliable in a changing climate. Insurers must invest in advanced climate risk modeling to better understand the evolving landscape of risk. This includes predicting how climate change will impact the frequency and severity of events in specific regions.
Additionally, the insurance industry is facing increased scrutiny from regulators and stakeholders regarding its response to climate change. There is a growing expectation for insurers to incorporate climate risk into their business practices and demonstrate commitment to sustainability and resilience. Failure to do so could result in reputational damage and financial penalties.
To address these challenges, many insurance companies are taking proactive steps. They are investing in climate-resilient infrastructure and adopting innovative risk modeling techniques. Some insurers are even offering incentives for policyholders to implement climate adaptation measures, such as flood-proofing their homes.
Furthermore, there is a growing trend of insurers integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into their investment and underwriting decisions. This not only helps align the industry with sustainability goals but also allows insurers to better assess the risks associated with climate change.
In conclusion, the insurance industry is at a crossroads in the face of climate change. The surge in weather-related disasters is straining resources and challenging traditional risk assessment models. However, it also presents an opportunity for insurers to innovate, adapt, and play a pivotal role in building climate resilience. As climate change continues to unfold, the insurance industry’s response will be closely watched by stakeholders, regulators, and the public.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Billion-Dollar Weather and Climate Disasters | National Centers for …

Reinsurance companies, which help insurers manage large risks, are also grappling with climate change-related losses. The increase in extreme events puts pressure on the entire insurance ecosystem.
The impact of climate change on reinsurance companies and the broader insurance ecosystem is a multifaceted challenge with far-reaching implications. Here’s an extended exploration of this idea:
Escalating Costs and Premiums:
Rising Claims: Reinsurance companies face a surge in claims due to climate-related disasters such as hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and storms. The increasing frequency and severity of these events strain the financial resources of reinsurers.
Premium Adjustments: To cover the growing risks associated with climate change, reinsurers often raise premiums for insurance companies. This, in turn, may lead to higher premiums for policyholders, making insurance less affordable for individuals and businesses.
Reinsurance Market Dynamics:
Limited Capacity: The substantial losses incurred by reinsurance companies can reduce their capacity to underwrite new policies. This limits the availability of insurance coverage, particularly in regions prone to extreme weather events.
Market Consolidation: Climate change-related challenges may drive consolidation within the reinsurance industry, with smaller players struggling to compete in an increasingly risk-laden market.
Reinsurance Strategies:
Risk Assessment: Reinsurers must continually refine their risk assessment models to account for changing climate dynamics. They invest in advanced data analytics and modeling tools to accurately evaluate the potential impact of climate-related events.
Diversification: To mitigate climate-related risks, some reinsurers diversify their portfolios by offering coverage for various types of disasters, including those linked to climate change.
Regulatory Pressures:
Stress Testing: Regulatory authorities are increasingly conducting stress tests to evaluate the resilience of insurance and reinsurance companies in the face of climate change. These tests assess the financial stability of these entities under various climate-related scenarios.
Disclosure Requirements: There is a growing trend toward mandatory climate risk disclosure by financial institutions, including reinsurers. This enhances transparency and accountability regarding climate-related risks.
Investment Strategies:
Evaluating Holdings: Reinsurers are scrutinizing their investment portfolios to ensure they align with climate-conscious strategies. They may divest from industries with high carbon footprints and invest in climate-resilient assets.
Green Investments: Some reinsurers actively invest in green and sustainable projects, contributing to climate mitigation efforts while potentially yielding positive returns.
Collaboration and Innovation:
Data Sharing: Reinsurers collaborate with meteorological agencies, scientific institutions, and climate research organizations to access timely and accurate weather data. This collaboration informs risk assessment and management strategies.
Technological Advancements: Reinsurers are at the forefront of developing innovative technologies such as blockchain-based smart contracts for more efficient claims processing and settlement in the aftermath of climate-related events.
Global Impact:
- International Cooperation: Climate change-related losses transcend borders, necessitating international cooperation among reinsurers, insurers, governments, and global organizations. The sharing of knowledge and resources can help address the global climate risk landscape effectively.
In summary, the challenges posed by climate change-related losses are reshaping the reinsurance industry. Reinsurers are adapting by refining their risk assessment models, diversifying portfolios, and investing in sustainable practices. They are also working alongside regulatory authorities and other stakeholders to navigate the complex landscape of climate-related risks. As climate change continues to exert pressure on the insurance ecosystem, the resilience and adaptability of reinsurance companies play a pivotal role in ensuring financial stability and disaster recovery for individuals, businesses, and communities worldwide.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Global Reinsurers Grapple With Climate Change Risks | S&P Global …

Insurance companies are investing in advanced climate risk modeling tools to better assess and price climate-related risks. These models help insurers make more informed underwriting decisions.
Insurance companies are making substantial investments in cutting-edge climate risk modeling tools, signaling their commitment to navigating the evolving landscape of climate-related challenges. These sophisticated modeling systems are designed to provide insurers with a multidimensional understanding of the intricate web of climate-related risks, ultimately facilitating more accurate risk assessment and pricing strategies. Here’s a closer look at how these advanced tools are reshaping the insurance landscape:
Comprehensive Data Integration: Climate risk models leverage a wealth of data, encompassing historical climate patterns, geological information, and even satellite imagery. By assimilating these diverse datasets, insurers gain a comprehensive view of the potential hazards associated with specific regions and policies.
Scenario Analysis: Insurers employ scenario analysis within these models to explore various climate change scenarios. This forward-looking approach enables them to anticipate potential future risks, such as the increased frequency of extreme weather events, and adjust their risk management strategies accordingly.
Tailored Risk Assessment: Advanced modeling tools allow insurers to customize risk assessments based on the specific needs of individual policyholders or regions. This tailoring ensures that insurance coverage accurately reflects the unique climate-related vulnerabilities of each policyholder.
Underwriting Precision: Climate risk models empower insurers to make more precise underwriting decisions. By factoring in climate-related risks, insurers can adjust policy terms, coverage limits, and premiums to align with the assessed level of exposure.
Risk Mitigation Insights: These tools not only identify risks but also offer insights into risk mitigation measures. Insurers can collaborate with policyholders to implement strategies that reduce their vulnerability to climate-related perils, which can result in more favorable coverage terms.
Stakeholder Transparency: The use of advanced climate risk modeling tools enhances transparency. Insurers can provide policyholders, regulators, and investors with detailed information on how climate risks are assessed and managed, fostering trust and accountability.
Regulatory Compliance: As climate risk disclosure requirements evolve, insurers are better equipped to meet regulatory obligations by utilizing these models. Accurate risk assessments facilitate compliance with emerging reporting standards related to climate-related financial disclosures.
Market Competitiveness: Insurers that leverage advanced climate risk modeling gain a competitive edge. Policyholders increasingly seek insurers that demonstrate a deep understanding of climate risks and offer tailored coverage solutions.
Resilience Planning: Climate risk models also support resilience planning. Insurers can work with communities and businesses to develop strategies that enhance their resilience to climate-related events, ultimately reducing future insurance claims.
Sustainability Initiatives: Insurers are incorporating climate risk modeling into their sustainability initiatives. They leverage their expertise to encourage climate-responsible behaviors and advocate for climate action.
Investment Decisions: Beyond underwriting decisions, climate risk modeling can influence insurers’ investment portfolios. It helps them identify climate-resilient assets and manage exposure to climate-related financial risks.
In essence, advanced climate risk modeling tools represent a critical asset in the insurance industry’s arsenal as it grapples with the complex challenges posed by climate change. By harnessing the power of data-driven insights, insurers not only safeguard their financial stability but also fulfill their role as risk management partners to policyholders, promoting climate resilience and sustainability across the insurance landscape. These tools signify a transformative shift toward a more proactive, informed, and responsible approach to climate-related risk management within the industry.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Climate Change | Department of Financial Services

Some insurers are incentivizing policyholders to take measures that reduce their vulnerability to climate risks. This includes discounts for installing resilient infrastructure and implementing sustainable practices.
Incentivizing policyholders to proactively address climate risks and adopt sustainable practices is a proactive and forward-thinking approach that benefits both insurers and insured parties. Here are some key aspects to consider in the context of this strategy:
Premium Discounts for Resilient Infrastructure: Insurers are increasingly offering premium discounts to policyholders who invest in resilient infrastructure. This can include measures such as fortifying homes against hurricanes, installing fire-resistant roofing, elevating properties in flood-prone areas, and reinforcing structures to withstand earthquakes. By encouraging these enhancements, insurers reduce their own exposure to claims, and policyholders gain added protection against climate-related risks. This approach aligns the interests of both parties in mitigating potential losses.
Sustainable Practices and Premium Reductions: Policyholders who adopt sustainable practices can also benefit from premium reductions. For example, homeowners who install solar panels or implement energy-efficient upgrades may receive discounts on their insurance premiums. These practices not only reduce the policyholder’s carbon footprint but also contribute to the resilience of the energy grid during extreme weather events. Insurers see reduced claims associated with energy-related damage, making this a win-win situation.
Wildfire Risk Mitigation: In regions prone to wildfires, insurers are actively promoting measures to mitigate fire risk. This can include creating defensible spaces around properties by clearing vegetation, using fire-resistant building materials, and implementing ember-resistant features. Policyholders who undertake these steps may be eligible for premium discounts. This not only lowers the cost of coverage for homeowners but also reduces the likelihood of catastrophic wildfire-related losses for insurers.
Community Engagement: Insurance companies are engaging with communities to raise awareness about climate risks and the benefits of resilience measures. This can involve workshops, educational campaigns, and partnerships with local organizations. By fostering a culture of preparedness and sustainability within communities, insurers can collectively reduce risk and the associated costs of claims.
Customized Risk Assessments: Some insurers are offering policyholders personalized risk assessments. These assessments provide insights into the specific climate-related risks that a property faces and recommendations for risk reduction measures. Policyholders who implement these recommendations may qualify for premium discounts tailored to their unique circumstances.
Adaptive Insurance Products: Insurers are exploring innovative products that adapt to changing climate conditions. For example, parametric insurance policies provide predetermined payouts when specific climate-related triggers, such as extreme wind speeds or rainfall levels, are met. These policies simplify claims processes and ensure that policyholders receive financial support promptly after a disaster, regardless of the extent of property damage.
Data-Driven Insights: Insurance companies are leveraging climate and weather data to inform policyholders about impending risks. Timely alerts and insights empower individuals and businesses to take protective actions, reducing potential losses and claims. This data-driven approach fosters a sense of shared responsibility between insurers and policyholders.
Long-Term Cost Savings: For policyholders, adopting resilient and sustainable practices not only leads to immediate premium reductions but also offers long-term cost savings. Energy-efficient upgrades, for instance, can result in lower utility bills, making these investments financially advantageous.
Alignment with Corporate Responsibility: Many businesses and individuals are increasingly conscious of their environmental and social responsibilities. Insurers that promote sustainability and resilience align with the values of policyholders and contribute to broader efforts to combat climate change.
In conclusion, the insurance industry’s efforts to incentivize policyholders to address climate risks and adopt sustainable practices reflect a proactive response to the challenges posed by climate change. By fostering a partnership between insurers and insured parties and promoting resilience, these initiatives contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future while simultaneously reducing the financial burden associated with climate-related losses.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: How insurers can promote resilience in the face of climate change

Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are increasingly being integrated into insurance investment strategies. This approach helps insurers align their portfolios with climate-conscious goals.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors have gained significant traction in the insurance industry as insurers recognize the need to address climate change and its associated risks. The integration of ESG principles into insurance investment strategies is not merely a response to regulatory pressures or public sentiment; it represents a strategic shift toward a more sustainable and resilient business model.
Risk Mitigation: ESG integration allows insurers to better understand and manage climate-related risks. By assessing environmental factors, insurers can identify regions prone to extreme weather events and adjust their underwriting and pricing accordingly. This proactive risk management approach helps insurers avoid unexpected financial losses and maintain stability.
Responsible Investment: Insurers are some of the largest institutional investors globally. Through their investments, they have the power to influence corporate behavior. By incorporating ESG criteria into their investment decisions, insurers can direct capital toward environmentally responsible and socially beneficial projects. This not only aligns with sustainability goals but also helps drive positive change in various industries.
Enhanced Reputation and Attraction: ESG-conscious practices are increasingly expected by consumers, investors, and regulators. Insurers that prioritize ESG principles are likely to enhance their reputation and attract environmentally and socially conscious customers. Additionally, they may find it easier to attract investment and maintain stakeholder trust.
Long-Term Sustainability: Climate change poses long-term risks to the insurance industry. By integrating ESG factors into their strategies, insurers are positioning themselves for long-term sustainability. This includes adapting to changing climate patterns, offering innovative insurance products that incentivize climate-resilient behavior, and participating in climate initiatives that align with their ESG objectives.
Regulatory Compliance: As governments worldwide recognize the urgency of addressing climate change, they are implementing stricter regulations related to ESG and climate risk disclosure. Insurers that have already integrated ESG into their practices will likely find it easier to comply with evolving regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of regulatory penalties or reputational damage.
Investor Expectations: Institutional investors and asset managers increasingly consider ESG factors when allocating capital. Insurance companies that can demonstrate a strong ESG profile are more likely to attract investment and partnerships. This not only bolsters their financial stability but also opens doors to collaborations that promote climate resilience.
Innovation in Insurance Products: ESG integration encourages insurers to develop innovative insurance products tailored to climate-conscious consumers. These products may include coverage for renewable energy projects, green buildings, or emissions reduction initiatives. By aligning their offerings with climate goals, insurers can tap into new markets and revenue streams.
In conclusion, the integration of ESG factors into insurance investment strategies is not a passing trend but a fundamental shift that reflects the industry’s commitment to addressing climate change and sustainability challenges. It’s a proactive response to the evolving risk landscape and an opportunity for insurers to demonstrate leadership in building a more resilient and environmentally responsible future. As ESG considerations continue to shape the insurance landscape, insurers that embrace these principles are better positioned to thrive in an era of climate uncertainty.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Guidance on the integration of ESG risks into insurance underwriting …

Insurers are playing an advocacy role by pushing for climate-conscious policies and supporting climate mitigation efforts. They recognize the importance of addressing climate change at a systemic level.
The advocacy role of insurers in addressing climate change and supporting climate mitigation efforts is a significant and multifaceted endeavor. Here’s an extended exploration of this idea:
Promoting Climate-Conscious Policies:
Engaging with Governments: Insurers actively engage with policymakers and government bodies to advocate for the development and implementation of climate-conscious policies. This includes supporting legislation aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, incentivizing renewable energy adoption, and enhancing disaster resilience.
Risk-Informed Decision-Making: Insurers emphasize the importance of incorporating climate risk assessments into urban planning, infrastructure development, and land-use policies. They provide expertise on assessing vulnerabilities and recommending strategies to mitigate climate-related risks.
Supporting Climate Research and Data Collection:
Funding Research: Many insurance companies allocate resources to fund climate research initiatives. They collaborate with scientific institutions to better understand the evolving climate landscape and its implications for risk assessment.
Data Sharing: Insurers actively contribute to data-sharing initiatives related to climate change. They share valuable insights, such as claims data from weather-related disasters, to improve the accuracy of climate models and support research efforts.
Climate Risk Disclosure:
Transparency Initiatives: Insurers increasingly disclose their climate risk exposure and strategies to manage these risks. This transparency helps investors, policyholders, and stakeholders assess an insurer’s commitment to addressing climate change.
Financial Reporting: Regulatory authorities in some regions require insurers to include climate risk assessments in their financial reporting. This ensures that climate-related risks and opportunities are integrated into an insurer’s financial outlook.
Product Innovation:
Climate-Resilient Products: Insurers are developing innovative insurance products designed to address climate-related risks. These products may include coverage for extreme weather events, crop insurance for farmers, and parametric insurance solutions that trigger payouts based on specific climate triggers.
Green Insurance: Some insurers offer policies that incentivize and reward environmentally responsible practices, such as eco-friendly home upgrades or emissions reduction efforts by businesses.
Climate Leadership Initiatives:
Net-Zero Commitments: Many insurers are making commitments to achieve net-zero carbon emissions within their own operations. This includes reducing emissions from their investment portfolios and underwriting activities.
Emissions Reduction Targets: Insurers set specific emissions reduction targets and develop comprehensive sustainability strategies aligned with global climate goals, such as the Paris Agreement.
Community and Stakeholder Engagement:
Education and Awareness: Insurers engage with their customers and communities to raise awareness about climate risks and the importance of preparedness. They provide resources and information on how individuals and businesses can reduce their climate-related vulnerabilities.
Collaboration with NGOs: Insurers collaborate with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and climate advocacy groups to amplify their climate advocacy efforts. Joint initiatives may focus on climate resilience, disaster response, or environmental conservation.
Global Partnerships:
- International Collaboration: Insurers often participate in global climate initiatives and partnerships, working alongside organizations like the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the United Nations Principles for Sustainable Insurance (PSI). These collaborations aim to drive climate action on a global scale.
In conclusion, insurers play a vital role in advocating for climate-conscious policies and supporting climate mitigation efforts. Their influence extends beyond risk assessment and coverage; they actively engage with governments, fund research, and promote climate-resilient practices. Insurers understand that addressing climate change is not only essential for the sustainability of their industry but also for the well-being of communities, economies, and the planet as a whole. Their advocacy efforts are crucial in building a more climate-resilient and sustainable future.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Building Alliances for Climate Action | FEMA
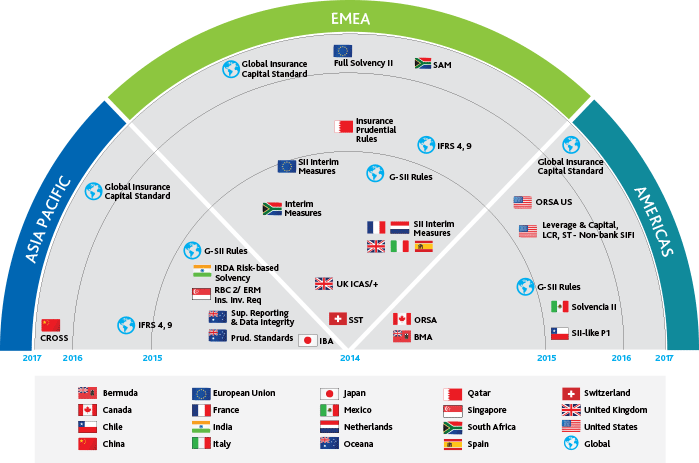
Government regulations are evolving to address the challenges posed by climate change in the insurance sector. Regulatory bodies are considering measures to ensure insurers are adequately prepared for climate risks, including stress tests and disclosure requirements.
As the specter of climate change looms larger, government regulations in the insurance sector are undergoing significant evolution to meet the growing challenges head-on. Regulatory bodies around the world recognize the urgency of ensuring that insurers are well-prepared to navigate the complex and evolving landscape of climate-related risks. To this end, they are introducing a range of measures designed to enhance resilience, transparency, and accountability within the industry. Here’s a closer look at how government regulations are adapting to address these challenges:
Climate Stress Tests: Regulatory bodies are increasingly implementing climate stress tests for insurers. These tests simulate a variety of climate-related scenarios, assessing the potential impacts on an insurer’s financial stability. By subjecting insurers to such stress tests, regulators ensure they have the financial resilience to weather the climate-related challenges of the future.
Disclosure Requirements: There is a growing trend toward enhanced climate risk disclosure requirements. Regulators are mandating that insurers disclose detailed information about their exposure to climate risks, their risk management strategies, and their plans for climate-related contingencies. This transparency fosters informed decision-making by both regulators and consumers.
Climate Risk Assessment Guidelines: Regulatory authorities are publishing guidelines and frameworks to assist insurers in conducting comprehensive climate risk assessments. These guidelines often outline best practices, risk assessment methodologies, and the incorporation of climate risks into decision-making processes.
Capital Adequacy Standards: In some cases, regulators are considering revisions to capital adequacy standards to account for climate-related risks. This ensures that insurers maintain sufficient capital reserves to cover potential losses resulting from extreme weather events and other climate-related perils.
Climate Liability: Some jurisdictions are exploring the concept of climate liability for insurers. This means that insurers may be held financially responsible for failing to adequately consider and prepare for climate risks in their underwriting and risk management practices.
Encouragement of Green Insurance Products: Regulatory bodies are encouraging the development and promotion of green insurance products. These products incentivize policyholders to adopt sustainable practices and reduce their carbon footprint, aligning insurance with broader climate goals.
International Coordination: Many climate-related risks transcend national borders. Regulatory bodies are increasingly engaging in international coordination and collaboration to address these challenges collectively. This includes sharing best practices, harmonizing reporting standards, and cooperating on stress tests.
Scenario Analysis: Regulators are encouraging insurers to incorporate scenario analysis into their risk management practices. This involves assessing the potential impacts of different climate scenarios on investment portfolios, underwriting practices, and claims exposure.
Consumer Protection: Regulatory authorities are taking steps to ensure that consumers are adequately protected in the face of climate risks. This may involve requirements for clear and transparent policy language regarding climate-related coverage or disclosure of potential climate-related exclusions.
Climate Education: Some regulators are focusing on climate education within the industry. They provide resources and guidance to insurers to help them better understand and manage climate risks, fostering a more resilient insurance sector.
Sustainable Investment Guidelines: Regulatory bodies are encouraging insurers to align their investment portfolios with sustainability goals. This includes guidelines for incorporating climate considerations into investment decisions.
The evolving regulatory landscape underscores the critical role of government oversight in addressing climate risks within the insurance sector. By implementing these measures, regulators aim to ensure that insurers not only withstand the challenges of climate change but also contribute to a more sustainable and resilient global economy. The collaborative efforts of regulators, insurers, and other stakeholders are pivotal in the ongoing fight against climate-related risks and their far-reaching consequences.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Assessing insurance regulation and supervision of climate-related …
Conclusion
The insurance industry stands at a crossroads in the face of climate change. While it faces growing challenges from more frequent and severe weather events, it also has the opportunity to lead in climate risk management and mitigation. As the world continues to grapple with the impacts of a changing climate, the insurance industry’s response will play a critical role in building resilience and ensuring financial protection for communities and businesses.
The insurance industry’s response to the challenges of climate change holds significant implications for both its own sustainability and its role in broader climate risk management and mitigation. Here are some key points to extend the idea:
Assessing and Quantifying Climate Risk: To effectively address climate change, insurers must continually refine their methods for assessing and quantifying climate-related risks. This includes analyzing historical weather data, climate models, and other sources of information to accurately estimate the likelihood and severity of climate-related events. Advanced risk modeling techniques and technologies are becoming essential tools in this process.
Resilience-Building Partnerships: Insurance companies can partner with governments, municipalities, and organizations to promote resilience-building initiatives. These partnerships may involve the development of resilient infrastructure, early warning systems, and community-level climate adaptation plans. By actively participating in and supporting these efforts, insurers can contribute to the reduction of climate risks and, in turn, potential losses.
Innovative Insurance Products: Insurers can develop innovative insurance products that address emerging climate risks. For example, parametric insurance policies can provide rapid payouts based on predetermined triggers, allowing policyholders to receive financial support quickly in the aftermath of a climate-related disaster. These products help bridge the financial gap during recovery and reduce policyholder uncertainty.
Promoting Sustainable Practices: Beyond offering premium discounts, insurers can actively promote sustainable practices among their policyholders. This can include encouraging energy-efficient upgrades, incentivizing the use of renewable energy sources, and providing guidance on climate-friendly measures. These efforts align with broader sustainability goals and contribute to climate mitigation.
Data and Technology Investments: The insurance industry can invest in advanced data analytics and technology solutions to enhance its risk assessment capabilities. This includes leveraging artificial intelligence, machine learning, and predictive modeling to better understand and predict climate-related risks. Real-time weather data and remote sensing technologies can also play a crucial role in monitoring and responding to emerging climate threats.
Global Cooperation and Advocacy: Insurers can participate in international efforts to address climate change. This includes supporting global climate agreements, advocating for stronger climate policies, and engaging in industry forums dedicated to climate risk management. By working together on a global scale, the insurance industry can influence climate action and foster collective resilience.
Customer Education: Insurers have a role in educating their policyholders about climate risks and the importance of mitigation and adaptation measures. Providing resources, guidance, and risk communication can empower individuals and businesses to make informed decisions and take proactive steps to protect themselves.
Financial Resilience: Just as insurers promote resilience among policyholders, they must also ensure their own financial resilience. This involves stress-testing their portfolios against climate-related scenarios and building sufficient reserves to cover potential increased claims resulting from extreme weather events.
Transparency and Disclosure: Increasing transparency in the industry regarding climate risk exposure and mitigation efforts is essential. This transparency can help investors, regulators, and customers assess an insurer’s commitment to addressing climate challenges and complying with emerging disclosure requirements.
Adaptive Strategies: Insurers should adopt adaptive strategies that allow for flexibility in responding to changing climate conditions. This includes regularly reviewing and updating risk assessment methodologies and adjusting pricing and coverage terms to reflect evolving risks.
In summary, the insurance industry’s pivotal role in managing climate risk extends beyond providing financial protection; it encompasses active participation in resilience-building, innovation, advocacy, and sustainability efforts. By embracing these responsibilities and collaborating with various stakeholders, insurers can not only navigate the challenges of climate change but also lead the way in building a more resilient and climate-resilient world.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: COP27 Reaches Breakthrough Agreement on New “Loss and …
By embracing innovative solutions, advocating for climate action, and adapting to evolving regulations, the insurance industry can navigate the complex terrain of climate change and continue to provide vital coverage to those in need.
By embracing innovative solutions, advocating for climate action, and adapting to evolving regulations, the insurance industry can navigate the complex terrain of climate change and continue to provide vital coverage to those in need. Here’s how these strategies can bolster the industry’s resilience in the face of climate challenges:
Innovative Risk Modeling: Insurers can invest in advanced data analytics and modeling tools to better assess climate-related risks. By harnessing the power of big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, insurers can improve their risk modeling accuracy. This enables them to offer more precise pricing for policies and identify emerging climate risks in real-time.
Climate-Resilient Products: Developing insurance products that encourage climate-resilient practices can be a win-win for insurers and policyholders. For example, insurers can offer reduced premiums to homeowners who invest in climate-adaptive home improvements, such as flood-resistant infrastructure or fire-resistant landscaping. Such products incentivize risk reduction while maintaining affordability.
Green Investment Portfolios: Insurance companies can allocate a portion of their investment portfolios to green and sustainable projects. This not only aligns with ESG principles but also helps diversify risk. Investments in renewable energy, clean technology, and sustainable infrastructure can yield financial returns while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Climate Advocacy: Insurers have significant influence, and they can use it to advocate for climate action at local, national, and international levels. By supporting policies that mitigate climate change and promote resilience, insurers can help create a more stable operating environment. This advocacy also aligns with public sentiment, potentially enhancing the industry’s reputation.
Collaborative Partnerships: Insurance companies can collaborate with other stakeholders, including governments, environmental organizations, and research institutions. By working together, these entities can share data, insights, and resources to develop innovative solutions for climate-related challenges. Collaborations can lead to more effective risk mitigation strategies.
Climate Disclosure and Transparency: Increasing transparency regarding climate-related risks and actions is crucial. Insurers can voluntarily disclose their exposure to climate risks, their sustainability goals, and their progress in achieving them. Transparent reporting not only builds trust with stakeholders but also helps identify areas for improvement.
Regulatory Compliance: Keeping abreast of evolving regulations related to climate risk and ESG is essential. Insurers should proactively adapt their practices to comply with these regulations. Being ahead of the curve in terms of compliance can help insurers avoid penalties and reputational damage.
Investment in Climate Research: Supporting climate research and data collection initiatives can provide insurers with valuable insights into emerging risks. This knowledge can inform underwriting decisions and help insurers better prepare for future climate-related events.
Customer Education: Educating policyholders about climate risks and the benefits of climate-resilient practices can empower individuals and businesses to make informed decisions. Insurers can play a role in raising awareness and providing resources for risk reduction.
Scenario Planning: Insurers can develop scenario planning frameworks that simulate the impact of various climate-related events on their portfolios. This proactive approach allows insurers to stress-test their operations and financial resilience under different climate scenarios.
In summary, the insurance industry faces a complex landscape of climate-related challenges, but it also has the tools and resources to adapt and thrive. By embracing innovation, advocating for climate action, and aligning with evolving regulations and customer expectations, insurers can not only manage climate risks but also contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future. Climate change presents both risks and opportunities, and the insurance industry is poised to play a crucial role in addressing this global challenge.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Opportunity and threats of climate change on insurance | McKinsey
More links
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Regulators Should Identify and Mitigate Climate Risks in the …
