Introduction
The Energy Transition, known as “Energiewende” in Germany, represents a groundbreaking shift towards sustainable and renewable energy sources. As one of the world’s most ambitious energy transformation initiatives, it has had far-reaching effects, not only within Germany but also on the global stage. In this article, we will explore the lessons learned from Germany’s Energiewende and its profound impact on shaping renewable energy policies worldwide.
Germany’s Energiewende, or Energy Transition, is an exceptional model for transitioning to sustainable and renewable energy sources, offering lessons that resonate globally. This ambitious initiative has not only reshaped Germany’s energy landscape but has also influenced the direction of renewable energy policies on a global scale.
One of the most significant lessons from the Energiewende is the importance of setting clear and ambitious renewable energy targets. Germany’s commitment to phasing out nuclear energy and significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions by transitioning to renewables has served as a beacon for other nations. It underscores the necessity of bold, long-term goals to combat climate change and secure a sustainable energy future.
Additionally, the Energiewende has highlighted the need for comprehensive energy system planning. Germany’s focus on diversifying its energy mix through wind, solar, and biomass sources underscores the importance of a well-balanced energy portfolio. This approach ensures resilience against fluctuations in energy supply and market dynamics, a crucial consideration for countries seeking energy security.
The Energiewende has also underscored the importance of public engagement and support. Germany’s success in implementing the transition owes much to the active involvement of citizens and communities. Encouraging public participation and ensuring a just transition for affected stakeholders are vital components of any renewable energy policy, fostering social acceptance and reducing resistance to change.
Furthermore, the Energiewende has stimulated innovation and technological advancements. Germany’s investments in renewable energy research and development have not only driven down the costs of renewable technologies but have also spurred economic growth through the creation of new industries and job opportunities. This demonstrates that a commitment to innovation can yield both environmental and economic benefits.
On the global stage, Germany’s Energiewende has influenced the adoption of renewable energy policies in numerous countries. Its success has showcased the feasibility of transitioning to green energy sources and has encouraged other nations to follow suit, contributing to a global shift towards sustainable energy solutions.
In conclusion, Germany’s Energiewende is a transformative initiative with profound implications for renewable energy policies worldwide. Its lessons in goal-setting, comprehensive planning, public engagement, innovation, and global influence serve as a valuable blueprint for countries seeking to address the pressing challenges of climate change and shape a more sustainable energy future for all.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Renewable Energy as an Underutilised Resource in Cities …
The Energiewende, initiated in the early 2000s, is characterized by its commitment to reducing carbon emissions, phasing out nuclear energy, and transitioning to renewable sources. Several key aspects of this initiative have made it a model for sustainable energy transition:
The Energiewende, launched in the early 2000s, represents a pioneering effort in sustainable energy transition, setting an example for the world on how to address the pressing challenges of climate change and energy sustainability. Several crucial aspects of this initiative have contributed to its success and made it a model for others to follow:
Commitment to Carbon Reduction: At the core of the Energiewende is a steadfast commitment to reducing carbon emissions. Germany has set ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, aligning its energy policies with the objectives of the Paris Agreement. By prioritizing carbon reduction, the country demonstrates a strong sense of responsibility in mitigating climate change on a global scale.
Phasing Out Nuclear Energy: A distinctive feature of the Energiewende is the decision to phase out nuclear energy. This commitment to nuclear power decommissioning reflects Germany’s dedication to prioritizing safety and reducing long-term nuclear waste concerns. This decision has sparked international discussions on the future of nuclear energy and the feasibility of alternative energy sources.
Transition to Renewable Sources: Perhaps the most remarkable aspect of the Energiewende is its successful transition to renewable energy sources. Germany has invested heavily in wind, solar, hydro, and biomass energy. This transition has not only reduced carbon emissions but also stimulated job creation and innovation in the renewable energy sector. Germany’s success in scaling up renewable energy production serves as a valuable case study for other nations seeking to do the same.
Decentralization and Citizen Participation: The Energiewende places a strong emphasis on decentralization and citizen involvement. Germany’s feed-in tariff system, which allows individuals and communities to generate and sell renewable energy, has encouraged citizen participation and decentralized energy production. This approach has empowered local communities and fostered a sense of ownership in the energy transition.
Investment in Research and Development: Germany’s commitment to research and development (R&D) has played a pivotal role in advancing sustainable technologies. Government incentives and partnerships with industry have fueled innovation in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and grid management. The country’s investments in R&D have yielded technological breakthroughs with global implications.
International Cooperation: Germany actively engages in international cooperation on energy and climate issues. It collaborates with other nations on research, policy development, and capacity building, sharing its experiences and best practices. This spirit of collaboration has strengthened global efforts to combat climate change and achieve a sustainable energy future.
In conclusion, the Energiewende serves as a blueprint for sustainable energy transition, emphasizing carbon reduction, the phase-out of nuclear energy, and the adoption of renewables. Germany’s commitment to these principles, coupled with its dedication to research, citizen participation, and international cooperation, demonstrates that a green energy transition is not only feasible but also economically and environmentally advantageous. As the world grapples with the urgent need for sustainable energy solutions, Germany’s Energiewende stands as a shining example of what can be achieved with determination, innovation, and international collaboration.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Lessons Learned from Germany’s Energiewende: The Political …

Germany’s Energiewende has resulted in a significant increase in renewable energy capacity, particularly in wind and solar power. The country’s investment in renewable infrastructure serves as a testament to the feasibility of transitioning to green energy sources.
Germany’s commitment to Energiewende, its ambitious energy transition program, has not only significantly increased the nation’s renewable energy capacity but has also showcased to the world the practicality and potential of embracing green energy sources.
The most striking evidence of this commitment lies in the substantial growth of renewable energy installations, especially in wind and solar power. Wind turbines now gracefully adorn the landscape, harnessing the power of the wind to generate electricity. Solar panels glisten atop rooftops and solar farms, soaking up sunlight to produce clean energy. These visible symbols of change demonstrate Germany’s proactive approach to reducing its carbon footprint and reliance on fossil fuels.
Beyond the visual impact, Germany’s investments in renewable infrastructure underline the economic feasibility of transitioning to green energy sources. The country’s sustained efforts in research and development, as well as incentives for renewable energy projects, have not only created jobs but also bolstered the growth of a robust green energy sector. This success has inspired other nations, prompting them to explore and emulate Germany’s pioneering initiatives.
Germany’s commitment to renewable energy is a testament to its forward-thinking approach. By embracing and expanding renewable energy capacity, Germany not only reduces its greenhouse gas emissions but also positions itself as a leader in the global green energy transition. The lessons learned from its Energiewende serve as a blueprint for other countries looking to reduce their environmental impact, create sustainable jobs, and shape a cleaner, more secure energy future for generations to come.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Renewable Energy as an Underutilised Resource in Cities …

Energiewende encourages decentralized energy generation through small-scale renewable projects and citizen participation. This approach empowers communities and individuals to become active contributors to the energy transition.
The Energiewende, Germany’s groundbreaking energy transition policy, embodies a visionary approach that reaches far beyond simply shifting to renewable energy sources. At its core, this strategy fosters a fundamental transformation of the energy landscape by championing decentralized energy generation through small-scale renewable projects and actively engaging citizens in the process. Here are some key aspects of how this approach empowers communities and individuals to become active contributors to the energy transition:
Local Energy Production: Energiewende prioritizes the development of local energy production, encouraging communities to harness their renewable energy potential. This means small-scale solar panels on rooftops, wind turbines in rural areas, and biomass facilities in agricultural regions. By promoting these decentralized projects, Energiewende reduces reliance on centralized, fossil-fuel-based power plants and encourages self-sufficiency at the community level.
Community Ownership: A significant aspect of this approach involves community ownership of renewable energy projects. Many Energiewende initiatives are community-driven, with local residents actively investing in, owning, and managing renewable energy installations. This not only generates a sense of ownership and pride but also ensures that the economic benefits of clean energy stay within the community, bolstering local economies.
Citizen Participation: Energiewende actively engages citizens in the energy transition process. Through policies such as feed-in tariffs and favorable incentives, individuals are incentivized to invest in renewable energy projects. This participation extends to decision-making processes, where communities have a say in the planning and implementation of local energy initiatives, fostering a sense of democracy and involvement in energy matters.
Energy Education: Energiewende places a strong emphasis on energy education and awareness. Schools, local organizations, and grassroots initiatives often work together to educate citizens about energy efficiency, renewable technologies, and sustainable practices. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed choices about their energy consumption and production.
Environmental Stewardship: The shift toward renewable energy aligns with environmental stewardship and sustainability goals. By engaging communities in the energy transition, Energiewende encourages a deeper understanding of the environmental impact of energy choices. This heightened awareness often leads to broader adoption of energy-efficient practices and a commitment to reducing carbon emissions.
Resilience and Energy Security: Decentralized energy generation enhances energy security and resilience. In the event of disruptions to the centralized grid, communities with distributed renewable energy sources can maintain power locally. This resilience is particularly important in the face of climate-related disasters or other emergencies.
Economic Benefits: Energiewende has the potential to stimulate economic growth at the local level. It creates jobs in the renewable energy sector, supports local manufacturing of clean energy technologies, and reduces energy costs for citizens. These economic benefits can rejuvenate communities and improve overall quality of life.
In essence, Energiewende’s focus on decentralized energy generation and citizen participation is a paradigm shift in how we approach energy production and consumption. It transforms communities and individuals from passive consumers to active contributors to the energy transition, fostering a sense of responsibility, ownership, and shared commitment to a sustainable energy future. This model serves as an inspiring example for other regions seeking to transition to clean and decentralized energy systems.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Renewable Energy as an Underutilised Resource in Cities …
A strong emphasis on energy efficiency measures, such as building retrofitting and industrial optimization, has been a cornerstone of the Energiewende. These efforts demonstrate that reducing energy consumption is as vital as increasing renewable energy production.
A strong emphasis on energy efficiency measures, such as building retrofitting and industrial optimization, has been a cornerstone of the Energiewende, Germany’s ambitious transition to renewable energy sources. These efforts go beyond simply adopting clean energy; they highlight a fundamental principle that reducing energy consumption is as vital as increasing renewable energy production in achieving sustainability and combating climate change.
One key aspect of this commitment to energy efficiency is the retrofitting of buildings. Germany has embarked on a comprehensive program to enhance the energy performance of existing structures. This involves upgrading insulation, improving windows and doors, and implementing efficient heating and cooling systems. Such measures not only reduce energy consumption but also make homes and commercial buildings more comfortable while cutting heating and cooling costs for occupants.
In the industrial sector, the optimization of processes and machinery has been instrumental in achieving energy efficiency targets. German industries have embraced cutting-edge technologies, such as Industry 4.0, to streamline operations and minimize energy waste. These efforts not only reduce carbon emissions but also enhance the competitiveness of German industries in global markets by lowering production costs.
Furthermore, the commitment to energy efficiency has a cascading effect across various sectors of the economy. It fosters the growth of green technology companies specializing in energy-efficient solutions, creating jobs and economic opportunities. It also reduces dependence on energy imports, enhancing energy security.
Importantly, these energy efficiency measures are not confined to Germany alone. They serve as a model for other nations looking to reduce their carbon footprint and enhance energy sustainability. Germany’s success in this regard showcases that sustainable practices can go hand in hand with economic growth and competitiveness.
In conclusion, Germany’s emphasis on energy efficiency within the Energiewende is a pivotal element of its commitment to sustainability and climate action. It underscores the importance of reducing energy consumption alongside increasing the use of renewable energy sources. Through building retrofitting, industrial optimization, and broader adoption of energy-efficient practices, Germany demonstrates that a holistic approach to energy sustainability is not only achievable but also economically beneficial, serving as an inspiration for nations worldwide seeking to tackle the challenges of a changing climate.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: How expensive is an energy transition? A lesson from the German …
Germany’s commitment to research and development has led to technological advancements in renewable energy technologies. These innovations have a ripple effect, influencing the global renewable energy market and driving down costs.
Germany’s unwavering commitment to research and development in the field of renewable energy technologies has positioned it as a trailblazer in the global transition toward sustainable energy sources. The impact of its innovations transcends national borders, creating a profound ripple effect that continues to shape the global renewable energy market while driving down costs. Here are some key aspects that further illuminate this transformative influence:
Pioneering Renewable Energy Policies: Germany’s ambitious renewable energy policies, notably the Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG), have provided a strong foundation for the growth of clean energy technologies. These policies have set clear targets, established feed-in tariffs, and incentivized renewable energy production, spurring investment in the sector.
Technological Advancements: The commitment of German institutions and companies to research and development has led to significant technological advancements in solar, wind, and biomass energy. Breakthroughs in efficiency, storage, and grid integration have made renewable energy sources more reliable and accessible.
Market Expansion: Germany’s leadership in renewable energy has expanded the global market for clean technologies. Its success has encouraged other nations to invest in renewable energy, fostering a competitive marketplace that drives innovation and cost reduction.
Cost Reduction: Germany’s early adoption and investment in renewables have played a pivotal role in driving down the costs of renewable energy technologies. Economies of scale, coupled with technological improvements, have made solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems more affordable worldwide.
Export of Expertise: German companies, with their wealth of knowledge and experience, have become global leaders in renewable energy solutions. They export their expertise and technologies, contributing to the global dissemination of clean energy practices and know-how.
Climate Change Mitigation: Germany’s commitment to renewable energy aligns with global efforts to mitigate climate change. By reducing carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels, Germany’s contributions have a direct impact on global climate goals.
Job Creation: The growth of the renewable energy sector in Germany has led to the creation of numerous jobs. This serves as an example for other countries seeking to stimulate economic growth while transitioning to cleaner energy sources.
International Collaborations: Germany actively engages in international collaborations, sharing knowledge and resources to address global energy challenges. Initiatives such as the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) promote cooperation among nations in advancing renewable energy technologies.
Energy Security: Germany’s investments in renewables enhance energy security by diversifying its energy mix and reducing reliance on fossil fuel imports. This model inspires other nations to pursue similar strategies to strengthen their energy independence.
Sustainable Development: Germany’s commitment to renewables aligns with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly Goal 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and Goal 13 (Climate Action). Its influence advances global progress toward achieving these vital objectives.
In summary, Germany’s dedication to research and development in renewable energy technologies has been a catalyst for transformation in the global energy landscape. Its innovations have not only driven down costs but also spurred international collaboration, created jobs, and contributed to a more sustainable and resilient global energy sector. As the world continues its pursuit of clean energy solutions, Germany’s leadership remains a beacon of inspiration and an engine of progress.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here How Turkey Can Ensure a Successful Energy Transition – Center for …
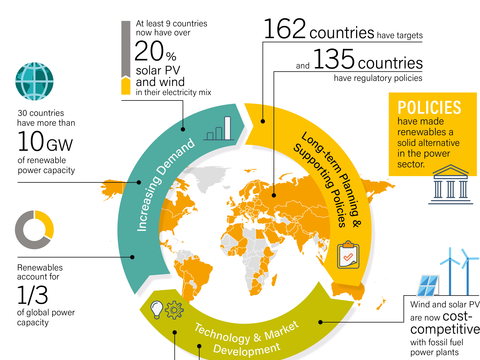
The lessons and impacts of Germany’s Energiewende on global renewable energy policies are profound and far-reaching:
The lessons and impacts of Germany’s Energiewende on global renewable energy policies are profound and far-reaching, resonating with nations around the world as they grapple with the urgent need to transition to sustainable energy sources.
Pioneering Sustainability: Germany’s Energiewende serves as a pioneering model for sustainability and environmental responsibility. It highlights the feasibility of reducing reliance on fossil fuels, which has inspired countries to adopt similar clean energy initiatives.
Policy Innovation: Germany’s policy framework for the Energiewende, including feed-in tariffs and incentives for renewable energy adoption, has been emulated by many countries. These policy innovations have accelerated the growth of renewable energy industries globally.
Renewable Energy Capacity: The rapid expansion of Germany’s renewable energy capacity, particularly in wind and solar, underscores the potential for a clean energy transition. Other nations have taken note of Germany’s successes and strive to replicate its achievements.
Decentralized Energy: The Energiewende promotes decentralized energy generation through rooftop solar panels and community-owned wind farms. This approach has spurred interest in distributed energy solutions worldwide, reducing reliance on centralized power grids.
Market Transformation: Germany’s commitment to renewables has transformed its energy market. The focus on green technologies has become a catalyst for innovation, job creation, and economic growth. Other countries seek to replicate this transformation to reap similar benefits.
Technological Advancements: Germany’s investment in renewable energy technologies has driven technological advancements in the sector. This benefits not only Germany but also contributes to global progress in renewable energy innovations.
Energy Security: Germany’s pursuit of energy independence and reduced reliance on energy imports has been a strategic lesson for other nations concerned about energy security. Diversifying energy sources can enhance resilience in the face of supply disruptions.
Climate Leadership: The Energiewende aligns with global efforts to combat climate change. Germany’s leadership in this regard has encouraged international collaboration and collective action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Global Energy Transition: Germany’s journey serves as a case study for the global energy transition. Its experiences, both successes and challenges, offer valuable insights for other nations embarking on similar paths.
Global Collaboration: The impacts of the Energiewende extend beyond Germany’s borders through international cooperation. Germany actively collaborates with other nations on renewable energy projects and shares its experiences, fostering a sense of collective responsibility for a sustainable future.
In conclusion, the lessons and impacts of Germany’s Energiewende are profound, inspiring countries worldwide to embrace renewable energy and sustainable practices. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and energy transition, Germany’s pioneering efforts continue to shape global renewable energy policies and set a course toward a more sustainable and environmentally responsible future for all.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: How Turkey Can Ensure a Successful Energy Transition – Center for …
Germany’s commitment to renewable energy has inspired nations worldwide to enact similar policies. Countries like Denmark, Sweden, and the Netherlands have adopted Energiewende-inspired models, setting ambitious renewable energy targets and promoting sustainable practices.
Germany’s commitment to renewable energy, often referred to as the Energiewende, has not only been a domestic success story but also a global inspiration. The impact of Germany’s renewable energy transition has reverberated worldwide, leading to a growing number of countries looking to emulate its achievements and adopt similar policies.
Nordic and European Trailblazers: Nations like Denmark, Sweden, and the Netherlands have taken cues from Germany’s pioneering efforts. They have embarked on their own renewable energy journeys, setting ambitious targets for increasing the share of renewables in their energy mix. Denmark, for instance, is renowned for its wind energy sector, while Sweden is making significant strides in hydropower and biomass.
Global Renewable Energy Expansion: Germany’s commitment to renewable energy has sparked a global expansion of clean energy initiatives. Countries across Europe and beyond are now setting aggressive renewable energy targets, committing to reducing carbon emissions, and investing in green technologies. This collective action contributes to mitigating climate change and transitioning to a more sustainable energy landscape.
Technological Advancements: Germany’s leadership has driven innovation in renewable energy technologies. This, in turn, has accelerated the global development and deployment of renewable energy solutions. As Germany continues to invest in research and development, it contributes to the growth of a vibrant global green tech sector, benefiting economies and the environment.
Economic Opportunities: The Energiewende has created economic opportunities not only in Germany but also in countries adopting similar models. The renewable energy sector has become a source of job growth, attracting investments and fostering a competitive edge in the global market for clean energy technologies and services.
Environmental Benefits: The adoption of renewable energy policies inspired by Germany results in significant environmental benefits. Reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, improved air quality, and decreased dependence on fossil fuels are common outcomes, contributing to a healthier and more sustainable planet.
Global Cooperation: Germany’s leadership in renewable energy has spurred international cooperation on climate and energy-related issues. It has played an active role in global climate negotiations, fostering collaboration among nations to combat climate change collectively.
In conclusion, Germany’s commitment to renewable energy through the Energiewende has had far-reaching effects, inspiring nations worldwide to pursue cleaner, more sustainable energy solutions. This global shift towards renewable energy not only mitigates the impacts of climate change but also fosters economic growth, technological innovation, and international cooperation. Germany’s influence on the clean energy transition continues to shape a greener and more sustainable future for nations across the globe.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: The role of renewable energy in the global energy transformation …

Germany’s support for renewable energy technologies has driven innovation and cost reduction. Solar and wind technologies, once considered expensive, have become increasingly affordable and accessible, encouraging their global adoption.
Germany’s steadfast commitment to supporting renewable energy technologies has not only revolutionized its own energy landscape but has also catalyzed a worldwide shift towards sustainability. The impact of this dedication extends far beyond the borders of Germany:
Technological Advancements: Germany’s investments in renewable energy R&D have led to significant technological advancements. These innovations include more efficient solar panels, larger and more productive wind turbines, and improved energy storage solutions. These technological strides have set new benchmarks for renewable energy globally.
Cost Reduction: The pioneering efforts of Germany in the renewable energy sector have driven down the costs of solar and wind technologies. Through economies of scale, innovation, and competition, the once-expensive renewable energy sources have become some of the most cost-competitive options for electricity generation worldwide. This cost reduction has made clean energy more accessible to a broader range of nations and industries.
Global Transition to Renewable Energy: Germany’s successful energy transition, known as the Energiewende, has become a model for countries seeking to decarbonize their energy systems. Its experience demonstrates the feasibility of transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable sources while maintaining energy security and economic growth.
Investment in Infrastructure: Germany’s investments in renewable energy infrastructure, such as wind farms and solar installations, have created jobs and economic opportunities. These projects have not only bolstered Germany’s economy but have also served as a blueprint for job creation and infrastructure development in other nations.
Carbon Emission Reduction: By prioritizing renewables, Germany has significantly reduced its carbon emissions, contributing to global efforts to combat climate change. Its success in reducing emissions while maintaining a robust economy underscores the feasibility of achieving ambitious environmental goals.
Global Renewable Energy Market: Germany’s leadership has fostered a global market for renewable energy technologies. German companies specializing in solar panels, wind turbines, and related components have expanded their reach internationally, exporting clean energy solutions and expertise.
Influence on EU Policy: Germany’s commitment to renewable energy has influenced European Union policies and targets. Its leadership in this area has played a pivotal role in shaping the EU’s renewable energy goals and strategies.
Energy Security: The diversification of Germany’s energy mix, including a substantial contribution from renewables, enhances energy security by reducing dependence on fossil fuel imports. This approach has inspired other nations to prioritize energy independence through clean energy sources.
Energy Exporter: Germany’s surplus renewable energy production has enabled it to become a net energy exporter. This economic benefit has led to cross-border energy trade and cooperation with neighboring countries, fostering regional stability and cooperation.
Advocacy for International Collaboration: Germany actively engages in international climate negotiations and partnerships. Its commitment to collaborative efforts underscores the importance of global cooperation in addressing climate change and promoting renewable energy adoption.
In summary, Germany’s pioneering efforts in renewable energy have had a profound and far-reaching impact on the world. By driving innovation, reducing costs, and demonstrating the feasibility of transitioning to clean energy, Germany has set a high bar for sustainability and has inspired nations across the globe to follow suit. This legacy of leadership in renewable energy serves as a beacon of hope in the collective effort to combat climate change and build a sustainable future.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Global Energy Transformation: A Roadmap to 2050
The Energiewende showcases the benefits of diversifying energy sources. Nations are now more inclined to invest in a mix of renewables, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and enhancing energy security.
The Energiewende’s emphasis on diversifying energy sources not only showcases its benefits but also offers valuable insights for nations worldwide. This approach has far-reaching implications and has spurred a series of positive developments:
Reduced Environmental Impact: By transitioning away from fossil fuels and embracing a mix of renewables, nations can significantly reduce their carbon footprint. This reduction in greenhouse gas emissions contributes to mitigating climate change and protecting the environment, which is crucial for the well-being of current and future generations.
Enhanced Energy Security: Relying on a single energy source, especially one subject to price volatility or geopolitical tensions, can pose significant risks to a nation’s energy security. Diversification ensures a more stable and resilient energy supply, reducing vulnerability to supply disruptions.
Economic Resilience: A diverse energy portfolio can insulate a nation’s economy from the shocks of energy price fluctuations. Renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, often have fixed or predictable costs, providing greater economic stability over the long term.
Job Creation: The renewable energy sector is a significant source of job creation. Investments in various renewable technologies, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and bioenergy, foster employment opportunities in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research and development.
Technological Advancements: Diversification encourages innovation across a range of renewable technologies. As nations invest in a mix of energy sources, they stimulate competition and technological advancements, resulting in more efficient and cost-effective renewable solutions.
Energy Access: Diversifying energy sources can improve energy access for underserved populations. Smaller-scale renewable projects, such as off-grid solar installations and microgrids, provide energy access to remote and marginalized communities, addressing energy poverty.
Local Economic Development: Distributed renewable energy systems, like rooftop solar panels and community wind farms, promote local economic development. They empower communities to generate their own energy, reducing dependency on centralized power plants and stimulating local economies.
Resilience to Energy Crises: A diverse energy mix enhances a nation’s resilience in the face of energy crises, whether due to natural disasters or geopolitical conflicts. Localized and decentralized renewable systems can continue to provide power even when traditional infrastructure is disrupted.
Global Energy Transition: As more nations diversify their energy sources, the global energy landscape shifts toward sustainability. This collective effort contributes to a more stable and secure global energy environment, fostering international cooperation on climate and energy issues.
Renewable Energy Diplomacy: Diversifying energy sources can also enhance a nation’s diplomatic standing. It can lead to collaboration with other countries on renewable energy projects, promoting international partnerships and fostering goodwill.
In conclusion, the Energiewende’s lessons on diversifying energy sources offer a blueprint for nations seeking a sustainable and secure energy future. By embracing a mix of renewables, countries can simultaneously reduce their environmental impact, enhance energy security, and promote economic growth. This diversified approach is not only beneficial for individual nations but also contributes to the global transition toward cleaner and more resilient energy systems.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Global Energy Transformation: A Roadmap to 2050
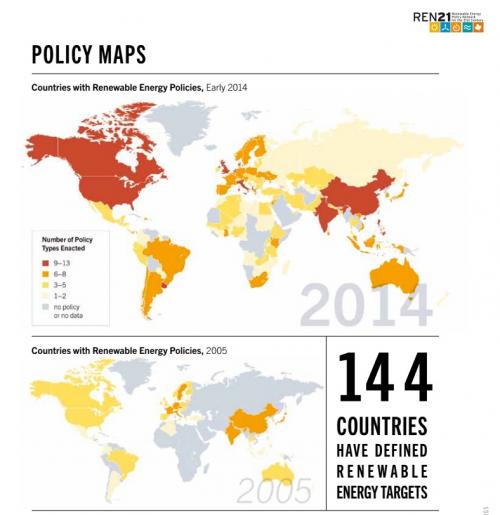
Germany’s leadership in renewable energy has contributed to international climate agreements like the Paris Agreement. By demonstrating its commitment to reducing carbon emissions, Germany encourages global cooperation in addressing climate change.
Germany’s leadership in renewable energy represents a beacon of hope in the battle against climate change. Through its unwavering dedication to sustainability and reduced carbon emissions, Germany has not only set an example but also actively contributed to international climate agreements like the Paris Agreement.
One of the standout achievements of Germany in this regard is its ambitious Energiewende, or energy transition, program. This initiative envisions a future where the majority of energy comes from renewable sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Germany’s investments in wind, solar, and bioenergy have not only significantly reduced its carbon footprint but also accelerated the development and adoption of green technologies globally.
By showcasing its commitment to environmental responsibility, Germany inspires other nations to follow suit. Its success in transitioning to renewable energy sources has demonstrated that a sustainable future is both achievable and economically viable. This demonstration of feasibility has encouraged global cooperation in addressing climate change, as other nations recognize the benefits of adopting similar measures.
Furthermore, Germany’s commitment extends beyond its borders. It actively participates in climate negotiations, providing diplomatic leadership and financial support to developing countries seeking to reduce their own emissions and adapt to the effects of climate change. This cooperative spirit reinforces the idea that tackling climate change is a global endeavor that requires the collaboration of all nations.
Germany’s leadership in renewable energy not only contributes to international climate agreements but also fosters innovation and job creation within its borders. Its thriving green technology sector serves as a model for sustainable economic development, highlighting the potential for green investments to drive economic growth while safeguarding the environment.
In summary, Germany’s leadership in renewable energy is a testament to its commitment to combat climate change. By showcasing the feasibility of sustainable energy practices and actively participating in international climate agreements, Germany catalyzes global cooperation in addressing one of the most pressing challenges of our time. Its leadership not only benefits the environment but also sets the stage for a more sustainable and prosperous future for all.
You can also read more about this here: U.S. Energy Policy Should Take A Lesson From Germany’s …

The renewable energy sector has become a significant driver of economic growth. Many countries now see renewable energy as a source of job creation and economic development, leading to increased investment in green technologies.
The renewable energy sector has emerged as a transformative force, not only in the global energy landscape but also as a potent driver of economic growth. Its impact extends far beyond environmental benefits, as many countries now view renewable energy as a catalyst for job creation and economic development on a substantial scale.
One of the most striking aspects of the renewable energy sector is its ability to generate employment opportunities. From the construction and maintenance of solar and wind farms to the production and installation of clean energy technologies, the sector provides a diverse range of jobs that span various skill levels. This is especially significant in regions where unemployment rates are high or traditional industries are declining, as renewable energy presents a viable pathway to revitalize local economies.
Moreover, the renewable energy sector has spurred innovation and technological advancement. Investments in green technologies have not only made energy production more sustainable but have also given rise to a new wave of research and development. This commitment to innovation has not only created jobs in research and engineering but has also led to the development of cutting-edge technologies that can be exported and utilized worldwide, further boosting economic growth.
In addition to job creation and technological advancement, the renewable energy sector has a ripple effect on related industries. For example, as the demand for renewable energy grows, so does the demand for energy storage solutions, electric vehicles, and smart grid technologies. These industries, in turn, foster economic development and employment opportunities.
Furthermore, the transition to renewable energy aligns with global efforts to combat climate change, making it an attractive sector for international investments and collaborations. Countries that prioritize clean energy not only reduce their carbon footprint but also position themselves as leaders in the global shift toward sustainability. This leadership status can attract foreign investments and open doors to international trade partnerships, further fueling economic growth.
In conclusion, the renewable energy sector’s role in economic growth is multifaceted. It not only creates jobs, fosters innovation, and stimulates related industries but also positions countries as champions of sustainability on the global stage. As more nations recognize the economic potential of renewable energy, the sector is poised to play an even more prominent role in driving economic development, while simultaneously contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally responsible future.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: The role of renewable energy in the global energy transformation …

Germany’s Energiewende has also highlighted the challenges associated with energy transition, such as grid integration, energy storage, and system reliability. These challenges provide valuable insights for other nations undergoing similar transformations.
Germany’s Energiewende, while undeniably groundbreaking, has not been without its share of challenges. These hurdles encountered along the path to a renewable energy-driven future have served as invaluable learning opportunities, not only for Germany but for other nations embarking on similar transformative journeys.
One of the most significant challenges illuminated by the Energiewende is the issue of grid integration. As Germany expanded its renewable energy capacity, the need to efficiently integrate intermittent energy sources like wind and solar into the grid became apparent. This challenge has prompted a deeper understanding of grid management and the development of smart grid technologies, offering crucial insights for other countries looking to incorporate renewables into their energy systems seamlessly.
Energy storage has emerged as another critical challenge. Balancing the variable nature of renewable energy sources with consistent energy supply demands innovative storage solutions. Germany’s experience has driven advancements in energy storage technologies, such as battery systems and pumped hydro storage, offering a blueprint for overcoming this challenge in other regions.
System reliability is paramount in any energy transition. Germany’s journey has underscored the importance of maintaining a reliable energy supply during the shift from conventional to renewable sources. This has led to greater investments in grid infrastructure and the development of backup solutions, ensuring that energy systems remain dependable even in times of transition.
The Energiewende’s emphasis on energy efficiency has also yielded valuable lessons. Germany’s pursuit of energy efficiency has not only reduced consumption but has also minimized environmental impacts. This focus on efficiency serves as a reminder to other nations that optimizing energy use is a crucial component of any successful energy transition strategy.
Moreover, the Energiewende has highlighted the need for robust policy frameworks and long-term planning. Germany’s success in renewable energy adoption has been underpinned by a stable regulatory environment and a clear vision for the future. These elements provide a blueprint for other countries to create the necessary conditions for a successful energy transition.
In summary, while Germany’s Energiewende has brought forth challenges, it has equally generated a wealth of knowledge and experience that can benefit nations worldwide. By addressing grid integration, energy storage, system reliability, energy efficiency, and policy stability, Germany’s journey offers a roadmap for others, helping them navigate the complexities of transitioning to a sustainable energy future. These challenges are not obstacles but stepping stones toward a greener and more sustainable global energy landscape.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Global Energy Transformation: A Roadmap to 2050
Conclusion
Germany’s Energiewende serves as a remarkable case study of a nation’s commitment to transitioning to sustainable and renewable energy sources. Its impact on global renewable energy policies cannot be overstated, as it has inspired nations to follow suit, fostered technological advancements, and contributed to international climate goals. The lessons learned from the Energiewende are guiding the world toward a more sustainable energy future, where renewable sources play a pivotal role in addressing the pressing challenges of climate change and energy security.
Germany’s Energiewende, often hailed as a flagship model for sustainable energy transition, continues to influence and inspire nations worldwide in their pursuit of cleaner, more sustainable energy systems. Its significance reaches beyond Germany’s borders, serving as a catalyst for global change in several key ways:
Pioneer of Renewable Energy Integration: Germany’s pioneering efforts in integrating renewable energy sources into its grid have provided valuable insights for other countries. By overcoming technical and logistical challenges, Germany has demonstrated the feasibility of incorporating renewables at scale, thus inspiring nations to adopt similar strategies. Its experiences have helped others navigate the complexities of grid integration and energy market reforms.
Policy Innovation: The Energiewende has prompted nations to revisit and reform their energy policies. Germany’s feed-in tariff system, which incentivizes renewable energy production, has been emulated in various forms worldwide. This innovative policy approach has accelerated the deployment of renewables and facilitated citizen participation in energy production.
Technological Advancements: Germany’s commitment to research and development has fostered technological advancements with global implications. Innovations in solar panel efficiency, wind turbine design, and energy storage technologies have been driven by Germany’s investment in green technology. These advancements benefit not only Germany but also the wider world by making renewable energy more accessible and cost-effective.
Global Climate Leadership: The Energiewende aligns with Germany’s broader commitment to addressing climate change. As a signatory to international climate agreements, Germany’s progress in reducing carbon emissions through its energy transition has bolstered global climate leadership. Its actions and achievements serve as a reminder that nations can take meaningful steps toward achieving international climate goals.
International Collaboration: Germany actively engages in international partnerships and initiatives related to renewable energy and climate change. By sharing experiences, expertise, and financial resources, it contributes to global efforts to combat climate change and enhance energy security. This spirit of collaboration reinforces the importance of multilateral approaches to solving global challenges.
Economic Opportunities: The Energiewende has not only reduced Germany’s carbon footprint but also stimulated economic growth. By investing in green technologies and renewable energy infrastructure, Germany has created jobs and positioned itself as a leader in sustainable industries. This economic success story has inspired other countries to view sustainability as a driver of economic prosperity.
In conclusion, Germany’s Energiewende continues to serve as a beacon of hope and a practical model for nations seeking to transition to cleaner, more sustainable energy sources. Its impact extends far beyond Germany’s borders, shaping global renewable energy policies, fostering technological advancements, and contributing to international climate objectives. As the world confronts the urgency of climate change and the need for sustainable energy solutions, the lessons and inspiration drawn from the Energiewende are guiding the planet toward a more sustainable and environmentally secure future.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: How Turkey Can Ensure a Successful Energy Transition – Center for …
More links
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: How expensive is an energy transition? A lesson from the German …
