Table of Contents
- In the dynamic world of business, pricing strategies are not arbitrary numbers slapped onto products or services. They are, in fact, intricate economic decisions that can make or break a company’s fortunes. This article delves into the fascinating realm of pricing strategies, focusing on three fundamental approaches
- Price Sensitivity
- Economies of Scale
- Rapid Market Entry
- Market Share Expansion
- Brand Recognition
- Early Adopters
- Recouping Development Costs
- Profit Maximization
- Signal Quality
- Profit for Innovation
- Market Dynamics
- Price Wars Mitigation
- Steady Market Presence
- Customer Base Stability
- Market Stability
In the dynamic world of business, pricing strategies are not arbitrary numbers slapped onto products or services. They are, in fact, intricate economic decisions that can make or break a company’s fortunes. This article delves into the fascinating realm of pricing strategies, focusing on three fundamental approaches
penetration pricing, skimming pricing, and competitive pricing. Each strategy carries its unique economic rationale and can profoundly influence a company’s bottom line.
Penetration pricing, skimming pricing, and competitive pricing are three distinct pricing strategies that play a pivotal role in shaping a company’s financial performance. Each of these strategies possesses its own economic rationale and has the potential to significantly impact a business’s bottom line.
1. Penetration Pricing:
Penetration pricing is a strategy where a company sets an initially low price for its products or services in order to quickly capture a significant share of the market. The economic rationale behind this approach is to gain a foothold in the market, attract a large customer base, and establish brand recognition. While this may result in lower initial profit margins, it can lead to long-term profitability through increased market share and customer loyalty. Penetration pricing is especially effective in competitive markets and when a company aims to discourage potential competitors from entering the market.
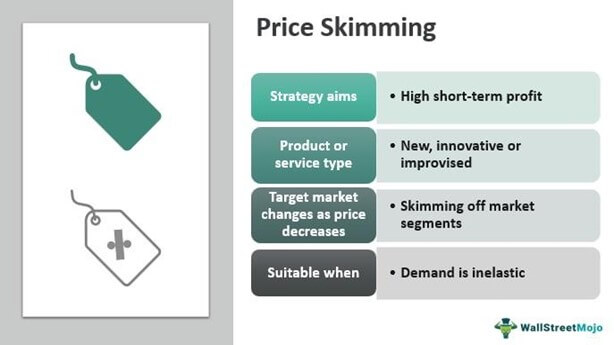
2. Skimming Pricing:
Skimming pricing involves setting a high initial price for a product or service and gradually lowering it over time. This strategy is often used for innovative or high-demand products. The economic rationale is to maximize profit from the early adopters and price-sensitive segments of the market. Skimming pricing takes advantage of consumers willing to pay a premium for a unique product or feature. As competition increases or as the product matures, the price is lowered to attract a broader customer base. While it can generate substantial revenue early on, it may limit market penetration and can be riskier in highly competitive markets.
3. Competitive Pricing:
Competitive pricing is a strategy where a company sets its prices based on the prevailing market rates and the prices of competitors. The economic rationale here is to remain competitive and ensure that customers perceive the product as offering value for money. This strategy is common in industries with many similar products or services. Competitive pricing allows a company to adapt to changes in the market quickly and can help maintain market share. However, it may not always maximize profitability, as it can lead to price wars and pressure on profit margins.
Impact on the Bottom Line:
The choice of pricing strategy can have a profound impact on a company’s financial performance. Penetration pricing may sacrifice short-term profits for long-term market dominance. Skimming pricing can result in higher initial profits but may limit market reach. Competitive pricing aims to balance profitability with market share. A company must carefully evaluate its market position, target audience, and product offering to determine which pricing strategy aligns best with its economic objectives.
Moreover, companies often adapt their pricing strategies over time as market conditions change, new competitors emerge, or consumer preferences shift. Flexibility and a keen understanding of market dynamics are essential for successfully implementing these pricing strategies and achieving financial goals.
In conclusion, pricing strategies are a critical component of a company’s overall business strategy. Selecting the right pricing approach, based on the economic rationale and market conditions, can significantly influence a company’s bottom line, its competitive advantage, and its ability to sustain profitability in the long run.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Organizational Culture and Leadership

Price Sensitivity
Penetration pricing capitalizes on price sensitivity among consumers. Lower prices entice potential customers who may have been hesitant to try a new product or switch from a competitor.
Penetration pricing is a strategic masterstroke that not only capitalizes on price sensitivity but also lays the foundation for long-term market success. Here’s a deeper exploration of how this pricing strategy creates a win-win scenario for both businesses and consumers:
Market Entry and Expansion: Penetration pricing is a potent tool for market entry. Lower prices make it easier for new entrants to gain a foothold in a competitive landscape. It enables businesses to introduce their products or services to a broader audience, fostering market expansion and brand recognition.
Reduced Barriers to Entry: Price sensitivity often translates into a reluctance to try new products or switch from established brands. Penetration pricing dismantles these barriers by reducing the perceived risk associated with trying something new. It encourages consumers to explore alternatives, injecting vitality into the market.
Accelerated Adoption: Lower prices accelerate the adoption curve. Consumers who were previously on the fence are more likely to make the switch, driving faster product adoption rates. This early momentum can lead to a virtuous cycle of positive word-of-mouth and referrals.
Competitive Advantage: In competitive markets, penetration pricing disrupts the status quo. It challenges incumbents to either match the lower prices or differentiate themselves through superior offerings. This competitive pressure often compels businesses to innovate and improve their products or services.
Customer Loyalty: While penetration pricing attracts new customers, it also fosters loyalty. Customers who initially opt for lower-priced options may discover the value in the product or service, leading to long-term relationships. This loyalty can translate into repeat business and higher customer lifetime value.
Data and Insights: The initial phase of penetration pricing provides a wealth of data and insights. Businesses can gather feedback, analyze customer behavior, and fine-tune their offerings based on this feedback. This iterative approach ensures that the product or service aligns better with customer needs.
Economies of Scale: As sales volumes increase due to penetration pricing, businesses often benefit from economies of scale. Larger production runs and increased demand can lead to cost efficiencies, allowing for sustainable profitability even at lower price points.
Brand Recognition: Penetration pricing can be a stepping stone to building brand recognition. Customers who initially engage with a product due to its affordability may later associate the brand with quality and value, setting the stage for premium offerings in the future.
In essence, penetration pricing is not just a short-term tactic; it’s a strategic investment in market share, customer relationships, and brand equity. By strategically using lower prices to break down barriers and entice price-sensitive consumers, businesses set the stage for long-term success and sustainable growth in dynamic and competitive markets.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: The Ultimate Guide to Pricing Strategies & Models

Economies of Scale
As sales volume increases due to lower prices, businesses often achieve economies of scale in production, reducing their cost per unit. This can lead to sustained profitability in the long run.
Certainly! As sales volume increases due to lower prices, businesses often achieve economies of scale in production, reducing their cost per unit. This can lead to sustained profitability in the long run, but the benefits don’t stop there. The concept of economies of scale has far-reaching implications for businesses and the broader economy.
Enhanced Competitiveness: Lowering prices to attract more customers not only increases sales but also helps businesses gain a competitive edge. As a company produces more units, it can invest in better technology, infrastructure, and talent, further improving the quality of its products or services. This, in turn, makes the company more appealing to consumers, allowing it to capture an even larger market share.
Innovation and Research: The increased cash flow resulting from higher sales volumes can be channeled into research and development (R&D) efforts. Companies can allocate more resources to innovate, create new products, and improve existing ones. This innovation cycle can keep a business at the forefront of its industry, ensuring long-term viability.
Global Expansion: Economies of scale not only apply to domestic markets but also facilitate international expansion. Lower per-unit costs make it more feasible for businesses to enter global markets, reach a broader customer base, and potentially diversify their revenue streams. This diversification can act as a buffer against economic downturns in specific regions.
Environmental Benefits: As businesses produce more efficiently, they can often reduce their environmental footprint. Economies of scale encourage the optimization of resource use, which can lead to lower waste, reduced energy consumption, and decreased emissions. This aligns with sustainability goals and can enhance a company’s reputation.
Job Creation: While there’s a common misconception that lowering prices and increasing efficiency may lead to job losses, the opposite can often be true in the long term. As businesses grow, they usually hire more employees to meet the increased demand, expand operations, and support innovation efforts.
Supplier Relationships: As businesses expand and require larger quantities of inputs, they often develop stronger relationships with suppliers. These relationships can result in better pricing, more reliable supply chains, and collaborative efforts to improve product quality.
Investor Confidence: Consistent profitability due to economies of scale can instill confidence in investors and shareholders. This can lead to greater access to capital, which can be crucial for further expansion, R&D, and strategic initiatives.
Economic Growth: The cumulative effect of multiple businesses achieving economies of scale can contribute significantly to overall economic growth. It can create a virtuous cycle of increased production, job creation, higher consumer spending, and innovation that benefits society as a whole.
In conclusion, economies of scale, driven by increased sales volume and lower prices, have the potential to transform businesses and contribute positively to the broader economy. While the initial price reductions may appear counterintuitive to profitability, the long-term advantages in terms of competitiveness, innovation, sustainability, and economic growth are often well worth the investment.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Penetration Pricing Definition, Examples, and How to Use It

Rapid Market Entry
Penetration pricing accelerates market entry, allowing businesses to swiftly gain a competitive edge.
nullIf you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Price Skimming Definition: How It Works and Its Limitations

Market Share Expansion
Lower prices attract a larger customer base, increasing market share and potential long-term customers.
Lowering prices can be a potent strategy for businesses looking to expand their market reach and cultivate lasting customer relationships. This pricing approach has several far-reaching implications that go beyond merely attracting a larger customer base:
1. Enhanced Market Share: The immediate impact of lower prices is the attraction of more customers. A larger customer base can translate into a more significant market share, positioning the business as a dominant player within its industry. This expanded market presence not only bolsters revenue but also elevates the company’s visibility and influence.
2. Customer Acquisition: Lower prices often act as a powerful customer acquisition tool. They entice consumers who were previously hesitant or budget-conscious to try the product or service. Once these new customers experience the value and quality the business offers, they are more likely to become loyal patrons, contributing to the company’s long-term growth.
3. Competitive Edge: In highly competitive markets, offering lower prices can set a business apart from rivals. It can be a compelling selling point that differentiates the company’s offerings and attracts customers seeking affordability. This competitive edge can be crucial in gaining an edge over competitors and securing a larger slice of the market.
4. Word-of-Mouth Marketing: Satisfied customers often become brand advocates. When they discover a product or service that not only meets their needs but also offers excellent value for the price, they are more likely to spread positive word-of-mouth recommendations. This organic marketing can be a cost-effective way to attract even more customers and build a loyal customer base.
5. Upselling and Cross-Selling Opportunities: Lower-priced products or services can serve as entry points into a broader range of offerings. Once customers are in the door, businesses can capitalize on upselling and cross-selling opportunities by showcasing additional, higher-margin products or services that complement their initial purchase.
6. Pricing Perception: The perception of affordability can be a powerful brand image. Businesses associated with lower prices may be perceived as more accessible and customer-friendly. This perception can resonate with a broad audience and contribute to long-term brand loyalty.
7. Data Insights: Lower prices can also serve as a data collection tool. Businesses can gather valuable information about customer preferences, purchase behavior, and demographic data through increased sales volume. This data can inform future marketing strategies and product development efforts.
However, it’s essential to approach price reductions with a well-thought-out strategy. Businesses should carefully consider their cost structure, profit margins, and the sustainability of lower prices over the long term. Additionally, they should monitor the impact of price changes on customer loyalty and overall profitability to ensure that the strategy aligns with their broader business goals.
In summary, lower prices can indeed attract a larger customer base, but their impact extends beyond immediate sales growth. This pricing strategy can lead to increased market share, customer acquisition, a competitive advantage, word-of-mouth marketing, and opportunities for upselling and cross-selling. When executed wisely, lower prices can be a catalyst for long-term success and sustained profitability.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: The 5 most common pricing strategies | BDC.ca

Brand Recognition
A strong market presence from the outset can foster brand recognition and customer loyalty.
Establishing a strong market presence from the very beginning of a business venture is akin to planting the seeds for long-term success. It’s a strategic move that sets the stage for brand recognition and customer loyalty to flourish.
Here’s how a robust initial market presence contributes to these crucial aspects:
Brand Recognition: When a new business enters the market with a strong presence, it leaves an indelible mark on the minds of consumers. This is the first step towards brand recognition. Memorable branding, a compelling story, and a unique value proposition can help a brand stand out in a crowded marketplace.
Trust and Credibility: An early strong presence signals to consumers that the business is serious, reliable, and committed to delivering value. This instills trust and credibility, two vital elements for building a loyal customer base.
Consistent Messaging: An established market presence allows a business to consistently communicate its message and values. This repetition reinforces the brand’s identity in the minds of consumers, making it more likely that they will remember and choose the brand when making purchasing decisions.
Customer Engagement: Early engagement with customers is an opportunity to listen, learn, and adapt. Businesses can use their strong market presence to gather feedback, understand customer needs, and refine their offerings accordingly. This customer-centric approach fosters loyalty as consumers feel heard and valued.
Competitive Advantage: A strong market presence can give a business an edge over competitors. It positions the brand as a leader in the industry and can deter potential competitors from entering the same market space.
Consistency Builds Loyalty: When consumers consistently encounter a brand they trust and recognize, they are more likely to become repeat customers. Over time, this leads to customer loyalty, where individuals not only choose the brand repeatedly but also become advocates, spreading positive word-of-mouth.
Long-Term Growth: A strong market presence isn’t just about the present; it’s an investment in the future. It lays the foundation for sustained growth, as the brand becomes a familiar and respected name in the market.
In essence, building a strong market presence from the outset is like building a solid foundation for a skyscraper. It provides stability, visibility, and a platform for growth. It’s a strategic move that pays dividends in the form of brand recognition, customer loyalty, and long-term success.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Penetration Pricing Definition, Examples, and How to Use It

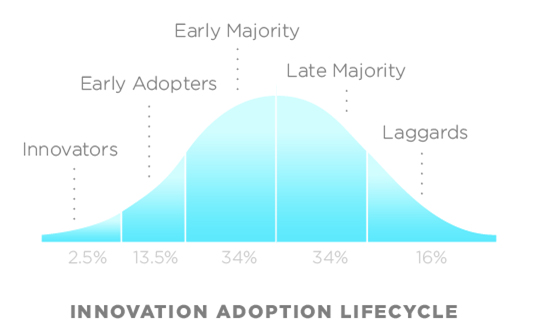
Early Adopters
Skimming pricing targets early adopters and customers who are willing to pay a premium for the latest innovations or distinctive qualities.
Skimming pricing is a strategic approach that specifically targets early adopters and customers who are not just willing but eager to pay a premium for the latest innovations or distinctive qualities in a product or service. This pricing strategy acknowledges the unique dynamics of the market, particularly in industries where rapid technological advancements and novelty play a significant role.
The primary advantage of skimming pricing is the ability to capture maximum value from a product or service during its initial launch phase. Early adopters, often characterized by their enthusiasm for cutting-edge features and a willingness to embrace change, are more likely to accept higher price points. By setting an initial high price, businesses can generate substantial revenue and even recoup development and marketing costs quickly, which is particularly important in industries with short product life cycles.
Moreover, skimming pricing can help create a sense of exclusivity and prestige around a product. When a new offering is priced at a premium, it can enhance the perceived value and quality of the product. This premium positioning can attract not only early adopters but also brand-conscious consumers who associate higher prices with superior quality and status.
However, it’s essential to recognize that skimming pricing is not without its challenges. As time progresses, the market often becomes more competitive, and competitors may introduce similar or superior alternatives at lower prices. This can lead to a loss of market share and necessitate price reductions to maintain sales volumes. Therefore, businesses employing skimming pricing must have a clear plan for transitioning to more sustainable pricing strategies as the product matures and faces increased competition.
Additionally, businesses must carefully manage customer expectations. Early adopters who pay a premium for a product may expect ongoing value and continuous innovation. Consistency in delivering on promises is critical to retaining these customers and maintaining brand loyalty.
In conclusion, skimming pricing is a valuable strategy that caters to early adopters and customers seeking the latest innovations. It can maximize initial profits, enhance brand image, and create a sense of exclusivity. However, businesses must be prepared to adapt their pricing strategies as market dynamics evolve and competition intensifies to ensure long-term success in the ever-changing business landscape.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: What Is Skim Pricing? And Is It Right for Your Business? | Coursera
Recouping Development Costs
High initial prices help businesses recoup the substantial costs associated with research, development, and marketing.
nullFor a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Understanding Pricing Strategies, Price Points And Maximizing …

Profit Maximization
Skimming pricing aims to extract the maximum profit from each sale, making it an effective strategy for niche or luxury markets.
“Skimming pricing, a deliberate pricing strategy, is designed to extract the utmost profit from every sale. It proves highly effective, particularly in niche or luxury markets, where the emphasis lies in capturing a select and discerning customer base. By setting initial prices at a premium, businesses can capitalize on the exclusivity and perceived value of their offerings. As demand stabilizes or the market evolves, they can gradually adjust pricing to accommodate a broader audience while still maintaining a premium position. This approach not only boosts profitability but also reinforces the aura of prestige and desirability associated with their products or services, further solidifying their foothold in their respective markets.”
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: The Ultimate Guide to Pricing Strategies & Models
Signal Quality
High prices can signal quality and exclusivity, attracting a particular segment of the market.
The concept that high prices can signal quality and exclusivity is deeply ingrained in consumer psychology and economics. It taps into several fascinating economic principles and behavioral tendencies that underpin the success of the skimming pricing strategy:
1. Veblen Effect:
The idea that higher prices can make a product more desirable is known as the Veblen effect. Named after the economist Thorstein Veblen, this phenomenon suggests that some consumers associate high prices with prestige and status. When a product is priced at a premium, it can attract a specific segment of consumers who are willing to pay more precisely because of its elevated price tag. Luxury brands often leverage the Veblen effect to enhance their appeal to affluent customers.
2. Perceived Value:
High prices can create a perception of greater value. Consumers often equate cost with quality, assuming that a more expensive product is superior in terms of materials, craftsmanship, or features. This perception can drive purchasing decisions, especially when consumers are seeking assurance that they are making a wise investment.
3. Scarcity and Exclusivity:
Premium pricing can create an aura of scarcity and exclusivity. When a product is priced at a premium, it implies that it is not readily available to everyone. This scarcity can foster a sense of exclusivity, attracting consumers who want to be part of an exclusive group that can afford such products.
4. Aspirational Purchases:
High prices can turn products into aspirational purchases. Consumers may aspire to own luxury or high-end items as a symbol of success, achievement, or social status. They are willing to pay a premium for the emotional and psychological benefits associated with these purchases.
5. Brand Building:
For businesses, employing high prices strategically can contribute to brand building. Premium pricing can reinforce a brand’s image as a leader in its industry, further enhancing its perceived value and credibility. This, in turn, can attract a loyal customer base that identifies with the brand’s ethos and values.
6. Sustainable Profit Margins:
From an economic standpoint, skimming pricing with higher initial prices can generate substantial profit margins, which are crucial for funding ongoing research, development, and innovation. This financial strength enables companies to continue delivering high-quality products and maintaining their reputation for excellence.
In essence, the idea that high prices signal quality and exclusivity is not merely a marketing ploy but a deeply rooted economic and psychological phenomenon. It plays on consumers’ perceptions, aspirations, and desires, often leading them to make purchasing decisions that align with their self-image and lifestyle. For businesses, understanding and effectively harnessing this phenomenon can be a powerful tool for achieving sustainable profitability and brand recognition.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Beyond the Many Faces of Price: An Integration of Pricing Strategies
Profit for Innovation
Businesses can generate revenue to reinvest in research and development for future innovations.
Businesses can generate revenue to reinvest in research and development for future innovations, and this strategic allocation of resources serves as a cornerstone for sustained growth and competitiveness. Here, we explore how this cyclical process of revenue generation and reinvestment contributes to a company’s long-term success:
Driving Innovation: The revenue generated by a business provides the financial fuel needed to fund research and development (R&D) initiatives. These initiatives can encompass a wide range of activities, from product development and process optimization to exploring emerging technologies. By allocating resources to R&D, companies can continuously explore new ideas and push the boundaries of what’s possible within their industry.
Staying Ahead of Competitors: In today’s fast-paced business environment, innovation is often the key differentiator between market leaders and followers. By consistently reinvesting in R&D, companies can stay ahead of their competitors, introducing new and improved products or services that capture market share and customer loyalty.
Adapting to Market Changes: Markets evolve, and consumer preferences shift over time. Businesses that reinvest in R&D can better adapt to these changes by developing products or services that align with current trends and customer demands. This adaptability enhances their resilience in the face of economic fluctuations or industry disruptions.
Improving Efficiency and Productivity: Reinvestment in R&D doesn’t just lead to new products; it can also lead to process improvements and increased efficiency. Streamlining operations and optimizing supply chains can result in cost savings, which can be redirected into further innovation efforts or used to offer competitive pricing to customers.
Building Intellectual Property: R&D investments often yield valuable intellectual property, such as patents, trademarks, and proprietary technology. These assets not only protect a company’s innovations but can also be monetized through licensing or used as bargaining chips in strategic partnerships.
Attracting Talent: Companies that are committed to innovation tend to attract top talent in their respective industries. Skilled professionals are more likely to join and remain with organizations that prioritize R&D, providing a continuous pool of expertise to drive innovation initiatives.
Meeting Regulatory Requirements: In certain industries, complying with ever-changing regulations is a necessity. Reinvestment in R&D allows companies to proactively address regulatory challenges and develop solutions that not only ensure compliance but also create competitive advantages.
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction: Innovations driven by R&D can lead to improved products and services that better meet customer needs and expectations. This, in turn, fosters customer loyalty, positive word-of-mouth, and a strong brand reputation.
Global Expansion: For companies looking to expand into new markets, investing in R&D can help tailor offerings to meet the specific demands and cultural nuances of different regions, facilitating successful market penetration.
In conclusion, the cycle of generating revenue and reinvesting it in research and development is a dynamic and essential process for businesses. It propels them forward, helping them adapt to change, outpace competitors, and ultimately thrive in an ever-evolving economic landscape. By recognizing the value of innovation and consistently allocating resources to foster it, businesses can secure their future relevance and success.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Skimming vs. Penetration Pricing: What’s the Difference? | Indeed.com
Market Dynamics
Competitive pricing is a response to the existing market conditions and the pricing strategies of competitors.
nullShould you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Penetration Pricing Definition, Examples, and How to Use It
Price Wars Mitigation
By aligning with competitors’ prices, businesses aim to avoid destructive price wars that can erode profitability.
Certainly, let’s explore the concept of aligning with competitors’ prices further:
“Strategically aligning with competitors’ prices is a prudent move that businesses undertake to navigate the complex terrain of pricing dynamics. This approach goes beyond mere price matching; it encompasses a multifaceted strategy aimed at achieving several key objectives while minimizing the risks associated with destructive price wars.
Maintaining Profitability: One of the primary goals of aligning with competitors’ prices is to protect and maintain profitability. Engaging in price wars often results in a race to the bottom, where businesses continually lower prices to gain a competitive edge. This can lead to diminishing profit margins and financial instability. By mirroring competitors’ prices, businesses can avoid this downward spiral and preserve their profitability.
Market Stability: Destructive price wars can disrupt market stability and create uncertainty for both businesses and consumers. When prices fluctuate wildly, it can erode trust in the market, making customers hesitant to make purchases. Aligning with competitors’ prices contributes to a more stable pricing environment, fostering confidence among consumers and businesses alike.
Competitive Positioning: While aligning prices, businesses can strategically position themselves within the market. They can choose to be price leaders, offering competitive prices that attract budget-conscious customers. Alternatively, they may opt for a premium pricing strategy, emphasizing quality, unique features, or superior customer service. This flexibility allows businesses to cater to different customer segments effectively.
Risk Mitigation: Price wars come with inherent risks, including reduced profitability, strained supplier relationships, and potential long-term damage to a brand’s image. By avoiding these conflicts, businesses can minimize these risks and maintain healthier relationships with suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders.
Focus on Value-Added Services: Instead of competing solely on price, businesses can allocate resources to provide additional value-added services or features that differentiate them from competitors. This can include superior product quality, faster shipping, extended warranties, or exceptional customer support. These value propositions can attract customers even when prices align with competitors.
Customer Loyalty: Consistently matching competitors’ prices can build trust and loyalty among price-sensitive customers. When customers perceive that they consistently get good deals, they are more likely to return for repeat purchases and recommend the business to others.
Data-Driven Insights: Aligning with competitors’ prices often requires monitoring and analyzing market data in real-time. This data-driven approach provides valuable insights into market trends, consumer behavior, and competitors’ strategies. Businesses can use this information to make informed decisions and adapt their pricing strategies proactively.
Long-Term Sustainability: A strategy based on alignment with competitors’ prices contributes to long-term business sustainability. It helps businesses navigate the competitive landscape while maintaining healthy profit margins and market stability, positioning them for continued success in the market.
In summary, strategic alignment with competitors’ prices is a well-considered approach that allows businesses to safeguard profitability, maintain market stability, and differentiate themselves within a competitive landscape. By focusing on value, customer loyalty, risk mitigation, and long-term sustainability, businesses can thrive while avoiding the pitfalls of destructive price wars.”
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Pricing Strategies for Small Business

Steady Market Presence
Competitive pricing helps businesses maintain a steady market presence without engaging in aggressive price fluctuations.
Competitive pricing is a strategic approach that offers businesses a multitude of advantages beyond maintaining market presence. Let’s explore how competitive pricing contributes to business success while avoiding the pitfalls of erratic price fluctuations:
Market Stability: Competitive pricing fosters market stability. By avoiding extreme price hikes or deep discounts, businesses contribute to a more predictable market environment. This stability benefits both consumers and competitors, promoting trust and confidence in the market.
Customer Loyalty: Consistent and competitive pricing engenders customer loyalty. When customers know they can rely on fair and stable prices, they are more likely to return for repeat purchases. This loyalty translates into long-term revenue streams and reduces the need for constant customer acquisition efforts.
Brand Image: Maintaining competitive pricing is crucial for brand image. Customers perceive businesses with consistent pricing as reliable and trustworthy. This positive image not only attracts new customers but also reinforces existing customer relationships.
Reduced Price Wars: Competitive pricing reduces the likelihood of price wars with competitors. By adhering to reasonable pricing strategies, businesses can often deter competitors from initiating aggressive pricing battles that can erode profit margins for all parties involved.
Profit Margin Maintenance: While competitive pricing may involve narrower profit margins, it helps businesses maintain a consistent and predictable cash flow. This stability allows for more sustainable growth and investment in product development, customer service, and marketing.
Market Expansion: Competitive pricing can facilitate market expansion. When businesses offer reasonably priced products or services, they can tap into new customer segments or geographical markets that may have been previously untapped due to pricing barriers.
Cost Efficiency: Stable pricing supports cost efficiency. Businesses can plan their procurement, production, and distribution more effectively when pricing remains relatively consistent. This leads to reduced operational costs and optimized supply chain management.
Pricing Strategy Longevity: Competitive pricing often aligns with long-term pricing strategies. This stability enables businesses to establish and pursue strategic goals over an extended period, fostering sustainable growth and market dominance.
Customer Retention: Consistent pricing strategies contribute to higher customer retention rates. Customers who feel they are treated fairly and consistently in terms of pricing are less likely to explore alternatives, reducing churn and fostering long-term relationships.
Ethical Considerations: Maintaining competitive pricing also aligns with ethical considerations. Businesses are perceived as more responsible and considerate when they avoid exploiting customers with erratic pricing tactics.
Data-Driven Adjustments: Competitive pricing does not mean inflexibility. Businesses can still adjust prices in response to changing market conditions or competitive pressures, but these adjustments are typically well-considered and data-driven, avoiding abrupt and disruptive changes.
In conclusion, competitive pricing is not solely about survival; it’s about thriving in the market by creating a stable and customer-centric environment. By adhering to competitive yet consistent pricing strategies, businesses can build trust, retain customers, and achieve sustainable growth, all while contributing to the overall stability and health of the market.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Skimming vs. Penetration Pricing: What’s the Difference? | Indeed.com

Customer Base Stability
Customers are less likely to switch brands due to price changes, fostering loyalty.
Customers are less likely to switch brands due to price changes, fostering loyalty. This loyalty is the result of a delicate balance between competitive pricing and the perceived value that a brand offers. When a customer believes that a brand consistently delivers high-quality products, exceptional customer service, or unique features, they are more willing to absorb minor price fluctuations. This phenomenon underscores the importance of building a strong brand identity that transcends price considerations.
In addition, customer loyalty also thrives on the emotional connection between a brand and its patrons. Brands that cultivate trust, engage in transparent communication, and actively listen to customer feedback can weather pricing changes more effectively. Loyalty is not solely dependent on the cost; it’s nurtured through meaningful experiences, personalized interactions, and a sense of belonging to a community that a brand represents.
Moreover, fostering loyalty through price stability doesn’t mean businesses can take pricing for granted. Customers are still price-sensitive to a certain extent, and consistent, fair pricing practices are essential. Brands that provide clarity in their pricing structures and offer value-added incentives, such as loyalty programs or discounts for long-term customers, can reinforce loyalty even in the face of competitive pricing pressures.
In today’s competitive marketplace, businesses must recognize that loyalty is a multi-faceted concept, influenced by factors beyond just price. While price stability is a valuable tool for retaining customers, it should be complemented by a broader strategy that focuses on delivering exceptional value, building trust, and creating a memorable customer experience to ensure enduring brand loyalty.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: The Ultimate Guide to Pricing Strategies & Models

Market Stability
By preventing price wars, competitive pricing contributes to overall market stability.
nullDon’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: The Basics of Penetration Pricing Strategy

Pricing strategies are not one-size-fits-all; they are tailored to a company’s objectives, market conditions, and target audiences. Understanding the economics behind these strategies is pivotal for businesses seeking to make sound pricing decisions. Whether it’s penetrating the market with aggressive pricing, skimming profits from niche segments, or navigating market equilibrium, each strategy has its place in the complex world of economics and business. Successful companies are those that leverage these strategies strategically, adapting them as market dynamics evolve, ultimately achieving a harmonious balance between revenue generation and market sustainability.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Difference Between Penetration Pricing and Skimming Pricing (with …
More links
You can also read more about this here: The Ultimate Guide to Pricing Strategies & Models
