Table of Contents
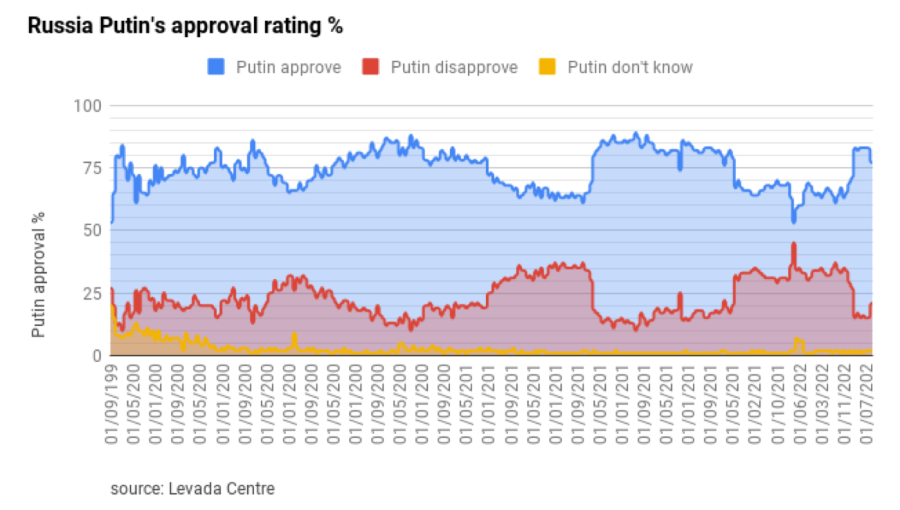
Vladimir Putin, Russia’s enduring political figure, has maintained a remarkable level of popularity for over two decades in power. His approval ratings have consistently been among the highest for world leaders, both domestically and internationally. In this article, we delve into the factors that have contributed to Putin’s enduring popularity, examining the complex web of influences that shape public opinion in Russia.
Vladimir Putin’s enduring political presence in Russia is a phenomenon that has captured the attention of political analysts and observers around the world. His remarkable level of popularity, which has persisted for over two decades in power, is a subject of considerable intrigue. Indeed, his approval ratings consistently rank among the highest for world leaders, a feat that few in the realm of international politics can claim.
To comprehend the factors that have underpinned Putin’s enduring popularity, we must embark on a comprehensive exploration. This article seeks to unravel the intricate tapestry of influences that shape public opinion in Russia. It goes beyond mere charisma or political savvy, delving into the core elements that have solidified Putin’s status as a beloved figure for many Russians.
One crucial aspect to consider is Putin’s image as a strong and assertive leader. In a period marked by economic upheaval and political uncertainty, his decisive actions and strongman persona have resonated with a significant portion of the population. This perception of stability and strength amid turbulent times has garnered him substantial support.
Additionally, Putin’s role in restoring Russia’s international standing cannot be underestimated. His assertive foreign policy, whether viewed positively or negatively, has often been perceived as reasserting Russia’s global influence and pride on the world stage. For many Russians, this has translated into a sense of national pride and a belief in a resurgent Russia.
Furthermore, Putin’s administration has overseen improvements in living standards for many Russians, particularly during the early years of his presidency. Economic stability and a rising middle class have contributed to a sense of well-being among a significant portion of the population.
However, it’s essential to acknowledge that Putin’s enduring popularity is not without controversy. Critics argue that his administration has employed various tactics to stifle political opposition and limit media freedom, raising questions about the true nature of democracy in Russia.
In conclusion, the sustained popularity of Vladimir Putin is a multifaceted phenomenon that defies easy explanation. This article will delve into these complexities, shedding light on the dynamic interplay of factors that have propelled Putin to the forefront of Russian politics for more than two decades. Understanding these influences is crucial not only for comprehending the Russian political landscape but also for gaining insights into the broader dynamics of leadership and public opinion in the contemporary world.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Public opinion on human rights in Putin-era Russia: Continuities …
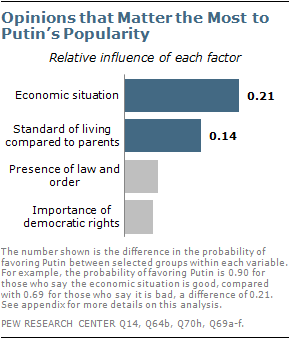
Economic Stability and Growth
One of the key factors contributing to Putin’s popularity is the perception of economic stability and growth under his leadership. When Putin took office in 2000, Russia was grappling with a severe economic crisis. Under his leadership, the country rebounded and the economy experienced steady growth, buoyed by rising oil prices.
Putin’s government implemented economic reforms, paid off foreign debts and established a sovereign wealth fund, which helped stabilize the economy and improved the standard of living for many Russians. These economic achievements have bolstered Putin’s image as a leader who can deliver prosperity, a sentiment that resonates with a significant portion of the population.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here What Could Come Next? Assessing the Putin Regime’s Stability and …

National Pride and Sovereignty
Putin’s assertive foreign policy, which seeks to protect and project Russian interests on the global stage, has also garnered him support among the Russian populace. His actions in Crimea, for example, were framed as efforts to protect ethnic Russians and assert Russian sovereignty, drawing widespread support at home.
This brand of patriotism and assertion of national sovereignty has resonated with many Russians who value a strong, assertive Russia on the international stage. Putin’s image as a defender of Russian interests has played a crucial role in shaping public opinion in his favor.
Putin’s assertive foreign policy, characterized by his unwavering commitment to protecting and projecting Russian interests worldwide, has not only had an impact on global politics but has also cultivated significant domestic support. His approach, particularly evident in the annexation of Crimea, was strategically framed as safeguarding ethnic Russians and asserting Russian sovereignty over a historically significant region. This narrative resonated deeply within Russia, garnering widespread support from the Russian populace.
One of the key elements behind this domestic support is the perception of Putin as a defender of Russian interests on the global stage. This image has played a pivotal role in shaping public opinion in his favor. Many Russians view Putin’s assertiveness as a means of reasserting Russia’s status as a major global power, which had waned in the tumultuous years following the dissolution of the Soviet Union. This desire for a strong and assertive Russia has historical roots, as Russians have a long-standing tradition of valuing a powerful state that can protect their interests and project strength internationally.
Furthermore, Putin’s foreign policy successes or at least the perception of them, have contributed to his popularity at home. Whether it’s the restoration of Russia’s presence in Crimea or his efforts to maintain Russia’s influence in other post-Soviet states, these actions have been portrayed as victories for Russia on the international stage. These perceived successes have bolstered Putin’s image as a shrewd and effective leader, capable of advancing Russian interests in a complex and competitive global arena.
It’s worth noting that while Putin’s assertive foreign policy has garnered him significant domestic support, it has also sparked tensions with Western powers and raised concerns about Russia’s intentions on the global stage. As a result, his leadership remains a subject of ongoing debate and scrutiny both within Russia and on the international stage. Nevertheless, there is no denying the impact of his brand of patriotism and his role as a defender of Russian interests in shaping the political landscape in Russia and beyond.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: What do ordinary Russians really think about the war in Ukraine …

Media Control and Propaganda
The Russian media landscape has been carefully managed under Putin’s rule, with state-controlled or state-influenced outlets dominating the information space. This control over the media has allowed Putin to craft a positive image and shape the narrative surrounding his leadership.
State-controlled media often portrays Putin as a strong and capable leader who has restored Russia’s standing in the world and has effectively countered perceived Western encroachments. The suppression or marginalization of dissenting voices in the media landscape has limited the exposure of alternative viewpoints, reinforcing Putin’s image as a popular and unifying figure.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: PUTIN’S ASYMMETRIC ASSAULT ON DEMOCRACY IN RUSSIA …
Suppression of Political Opposition
Putin’s government has been criticized for its suppression of political opposition, including the arrest and prosecution of prominent figures like Alexei Navalny. While these actions have drawn condemnation from Western countries, they have also resonated with many Russians who prioritize stability and the preservation of the status quo.
For some segments of the population, the suppression of political opposition is seen as a necessary measure to maintain order and prevent the chaos that characterized the 1990s. Putin’s tough stance on dissent is often framed as a way to safeguard Russia’s interests and maintain political stability.
“Putin’s government’s approach to handling political opposition remains a topic of intense debate, both within Russia and on the international stage. It represents a complex interplay of factors, including the preservation of political stability, national security concerns and the suppression of dissent. To better understand the nuances of this contentious issue, let’s delve into the various perspectives and considerations at play:
1. Political Opposition and Its Suppression: Critics argue that Putin’s government has been heavy-handed in dealing with political opposition, citing the arrest and prosecution of figures like Alexei Navalny as evidence of stifling dissent. Such actions have drawn widespread condemnation from Western countries, who advocate for democratic norms and respect for human rights.
2. Public Opinion in Russia: However, it’s important to recognize that Putin’s stance on political opposition resonates with a substantial segment of the Russian population. For many Russians, particularly those who experienced the tumultuous 1990s, stability and order are paramount. The memory of economic hardship, political chaos and societal upheaval during that era has led some to view strong measures against political opposition as necessary to prevent a return to those turbulent times.
3. Framing of Putin’s Policies: Putin’s government has framed its tough stance on dissent as a means to safeguard Russia’s interests, both domestically and internationally. They argue that political stability and a unified front are essential for the country’s development and security, especially in the face of perceived external threats.
4. National Security Concerns: Russia faces unique security challenges, including territorial disputes, regional conflicts and counterterrorism efforts. The government maintains that suppressing political opposition helps maintain a cohesive and controlled response to these challenges.
5. Debate on Democratic Values: The tension between political stability and democratic values is a central theme in this debate. While Western countries emphasize the importance of open political competition and the protection of individual freedoms, Russia’s leadership contends that the pursuit of these values can lead to instability and division.
6. International Relations: The suppression of political opposition has also had implications for Russia’s relations with other countries. It has led to tensions and sanctions from Western nations, impacting diplomatic ties and economic interactions.
7. Evolving Political Landscape: Russia’s political landscape is evolving. The government has taken steps to strengthen its control over the media and civil society, making it increasingly challenging for opposition voices to gain traction. However, opposition movements have adapted by using social media and other platforms to reach a global audience, putting pressure on the government to respond.
In summary, the suppression of political opposition in Russia remains a contentious and multifaceted issue. It reflects a delicate balance between the government’s goal of maintaining political stability, national security concerns and the democratic values and human rights principles upheld by many in the international community. The ongoing debate underscores the complex challenges of governance in a rapidly changing world and raises important questions about the relationship between political order, individual freedoms and the preservation of societal stability.”
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Russia’s Road to Autocracy | Journal of Democracy

Nostalgia for Soviet Era
Putin’s rule has coincided with a period of nostalgia for the Soviet era among certain segments of the Russian population. Many Russians associate the Soviet period with a sense of order and national pride and Putin has strategically tapped into this sentiment to bolster his popularity.
By promoting Soviet symbols, celebrating Soviet achievements and highlighting Russia’s role in the victory over Nazi Germany in World War II, Putin has tapped into the nostalgia for the Soviet past. This appeal to historical pride and a shared sense of identity has contributed to his enduring popularity.
Putin’s skillful utilization of Soviet nostalgia goes beyond merely tapping into sentiment; it represents a carefully crafted political strategy that has allowed him to connect with a broad swath of the Russian population.
Promotion of Soviet Symbols: Putin’s government has actively promoted Soviet symbols and imagery as a means of fostering a connection with the past. This includes the revival of Soviet-era holidays and celebrations. For instance, Victory Day, commemorating the Soviet Union’s triumph in World War II, has become a massive nationwide event under Putin’s rule. The annual military parade on Red Square in Moscow, featuring tanks, troops and veterans, serves as a powerful reminder of Russia’s historical role in defeating Nazi Germany. By embracing these symbols, Putin aligns himself with Russia’s proudest moments, reinforcing his image as a defender of the nation’s legacy.
Narrative of Great Patriotic War: Putin’s emphasis on Russia’s role in the Great Patriotic War (as World War II is known in Russia) resonates deeply with the Russian population. He has consistently highlighted the sacrifices made by Soviet citizens and the resilience displayed during the war. This narrative fosters a sense of shared history and pride, casting Putin as the steward of a legacy that must be preserved and protected. It also indirectly portrays Russia as a victim of external aggression, reinforcing the idea that the nation must remain vigilant and strong in the face of perceived threats.
Education and Media: Putin’s influence extends into the education system and media, where the narrative of Soviet heroism is reinforced. History textbooks often highlight Soviet achievements and portray Russia as a historical victor. State-controlled media plays a significant role in shaping the historical narrative, ensuring that the positive aspects of the Soviet era are highlighted while downplaying the more complex or negative aspects. This control over information reinforces the nostalgia-driven image Putin seeks to cultivate.
Contemporary Benefits: In addition to appealing to nostalgia, Putin has linked Russia’s past achievements to present-day benefits. He suggests that by preserving and honoring the Soviet legacy, Russia can continue to be a strong and respected global player. This narrative ties historical pride to contemporary goals, fostering a sense of continuity and purpose.
While Putin’s use of Soviet nostalgia has bolstered his popularity, it’s important to note that not all Russians view the Soviet era through a rose-tinted lens. Some segments of the population, particularly younger generations, may have a more critical view of that period, including its authoritarianism and human rights abuses. Nevertheless, for a significant portion of the Russian electorate, Putin’s skillful manipulation of Soviet nostalgia has been a powerful tool in maintaining his political dominance and shaping the national identity.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Civil Society in Russia: Its Role under an Authoritarian Regime, Part …

Vladimir Putin’s popularity in Russia is the result of a complex interplay of factors, including economic stability, assertive foreign policy, control over the media, suppression of political opposition and nostalgia for the Soviet era. While these factors have contributed to his enduring appeal, it’s essential to recognize that public opinion in Russia is diverse and not all segments of the population support him unquestioningly. Putin’s popularity remains a subject of debate and analysis, reflecting the complexities of contemporary Russian politics and society.
Vladimir Putin’s enduring popularity in Russia is indeed a multifaceted phenomenon that defies simple explanations. It is the product of a complex interplay of factors that have shaped public perception and support over the years.
1. Economic Stability: Putin’s early years in power were marked by efforts to stabilize Russia’s economy after the turmoil of the 1990s. His administration’s focus on economic stability and moderate growth was well-received by many Russians, especially those who had experienced the economic hardships of the post-Soviet era.
2. Assertive Foreign Policy: Putin’s assertive foreign policy stance, particularly on issues like Crimea and Ukraine, has resonated with segments of the population who perceive it as defending Russian interests and national pride on the global stage.
3. Media Control: The government’s influence and control over media outlets have allowed it to shape narratives and control the dissemination of information. This has played a significant role in shaping public opinion and maintaining Putin’s image as a strong and capable leader.
4. Suppression of Political Opposition: Measures taken to suppress political opposition and dissent have limited the presence of viable alternatives to Putin’s leadership. This, in turn, has contributed to his political longevity.
5. Nostalgia for the Soviet Era: Nostalgia for the stability and superpower status of the Soviet era has led some Russians to view Putin as a leader who has restored a sense of pride and influence on the world stage.
However, it’s important to emphasize that Putin’s popularity is not universal in Russia. Public opinion in the country is diverse, reflecting a wide range of views and perspectives. There are segments of the population that are critical of Putin’s leadership, particularly on issues related to political freedoms, human rights and corruption.
Putin’s popularity is also influenced by generational differences. Younger generations, who have grown up in a more connected and globalized world, may have different priorities and expectations than older generations who remember the Soviet era more vividly.
In conclusion, Putin’s enduring popularity in Russia is a complex phenomenon influenced by a combination of factors, from economic stability and foreign policy assertiveness to media control and nostalgia for the past. However, it’s crucial to recognize that public opinion in Russia is far from monolithic and debates and discussions about Putin’s leadership are an integral part of contemporary Russian politics and society. Understanding the nuances of this popularity is essential for comprehending the dynamics of Russia’s political landscape.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Endogenous Popularity: How Perceptions of Support Affect the …
More links
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: My Country, Right or Wrong: Russian Public Opinion on Ukraine …