Table of Contents
- The Changing Landscape of Marketing
- Cross-Cultural Consumer Behavior: A Complex Web
- Cultural Norms and Values
- Language and Communication
- Consumer Decision-Making
- Trust and Brand Loyalty
- The Role of Marketing Economics
- Data Analysis
- Market Segmentation
- Pricing Strategies
- Product Localization
- Challenges and Opportunities
- Market Expansion
- Customer Satisfaction
- Competitive Advantage
- Ethical Marketing
In an increasingly interconnected world, businesses are no longer confined by geographical borders. The advent of globalization has opened up vast new markets and opportunities, but it has also brought forth the challenge of understanding and catering to diverse consumer behaviors across cultures. Enter the realm of marketing economics, a discipline that is now focusing more than ever on researching cross-cultural consumer behavior.
In an increasingly interconnected world, businesses are no longer confined by geographical borders. The advent of globalization has opened up vast new markets and opportunities, but it has also brought forth the complex challenge of understanding and catering to diverse consumer behaviors across cultures. Enter the realm of marketing economics, a discipline that is now more vital than ever in researching and deciphering the intricacies of cross-cultural consumer behavior.
1. The Diversity of Global Markets: Globalization has enabled businesses to reach consumers in diverse cultures and regions. Each market comes with its unique set of preferences, values, and consumer behaviors. Understanding and adapting to these differences is essential for success. Marketing economics plays a crucial role in dissecting these nuances, helping businesses tailor their strategies effectively.
2. Cultural Sensitivity and Relevance: Cross-cultural consumer behavior research delves into the cultural and social factors that influence consumer choices. It helps businesses develop culturally sensitive and relevant marketing campaigns that resonate with local audiences. Ignoring these nuances can lead to misunderstandings, insensitivity, or even backlash.
3. Product Localization and Adaptation: Consumer preferences for products and services can vary significantly from one culture to another. Marketing economics guides businesses in product localization and adaptation, ensuring that offerings align with the tastes and needs of specific markets. This not only boosts sales but also enhances brand perception.
4. Communication and Messaging: Effective communication is at the heart of successful marketing. Cross-cultural consumer behavior research helps companies craft messages and branding strategies that are culturally appropriate and resonate with the target audience. It ensures that marketing materials avoid cultural taboos and are received positively.
5. Consumer Trust and Loyalty: Building trust with consumers is crucial in any market, but it takes different forms in various cultures. Understanding the cultural elements that contribute to trust-building helps businesses establish lasting relationships with customers, fostering loyalty and repeat business.
6. Global Competitive Advantage: Companies that invest in understanding cross-cultural consumer behavior gain a competitive advantage in the global marketplace. They can identify unmet needs, anticipate trends, and create innovative solutions that cater to diverse consumer segments effectively.
7. Ethical Considerations: Cross-cultural marketing also involves ethical considerations. Businesses must be aware of and respect local customs, values, and ethical standards. Marketing economics research helps identify potential ethical pitfalls and navigate them with sensitivity.
8. Market Entry and Expansion: For businesses looking to enter new markets or expand their global footprint, cross-cultural consumer behavior insights are invaluable. They inform market entry strategies, including market selection, market positioning, and adaptation of marketing mix elements.
In the globalized business landscape, marketing economics is not just about selling products or services; it’s about building meaningful connections with consumers from different backgrounds. It’s about recognizing that cultural diversity is an asset and an opportunity, and by understanding and embracing it, businesses can thrive in a world where boundaries are increasingly blurred. In essence, marketing economics is the compass that guides companies through the intricate and ever-evolving realm of cross-cultural consumer behavior, helping them navigate the path to global success.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Culture and Consumer Behavior: The Role of Horizontal and …
The Changing Landscape of Marketing
Globalization has reshaped the marketing landscape in profound ways. Businesses that once primarily operated within their domestic markets are now expanding internationally to tap into the growing global consumer base. However, they are quickly realizing that a one-size-fits-all marketing approach is no longer effective.
Globalization has indeed reshaped the marketing landscape in profound ways. It has ushered in a new era of opportunities and challenges for businesses seeking to expand internationally. While the allure of tapping into the vast global consumer base is undeniable, companies are quickly realizing that a one-size-fits-all marketing approach is no longer effective in this dynamic and diverse environment.
Cultural Sensitivity: As businesses venture into new markets, they must navigate a rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and customs. Successful international marketing requires a deep understanding of local cultures and sensitivities. Companies that invest in cultural research and tailor their marketing messages accordingly are more likely to resonate with consumers and avoid cultural missteps.
Language Localization: Language is a potent tool for connecting with consumers. Translating marketing materials is just the first step; it’s equally important to ensure that the messaging is culturally relevant and idiomatic. Localization extends beyond words to encompass visuals, symbols, and even humor.
Market Research: Conducting thorough market research is imperative when entering new territories. Understanding local market dynamics, consumer behavior, and competitive landscapes enables businesses to make informed decisions about product positioning, pricing, and distribution strategies.
Adaptation of Marketing Channels: The effectiveness of marketing channels can vary widely from one region to another. Some markets may rely heavily on social media, while others prefer traditional advertising or local influencers. Businesses must adapt their marketing channel mix to align with the preferences of each target audience.
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating international regulations, such as data privacy laws and advertising standards, can be complex. Companies must ensure compliance with local laws and regulations, which often requires legal expertise and ongoing diligence.
Global Brand Consistency: While adaptation is crucial, maintaining a consistent global brand identity is also essential. Striking the right balance between localized content and a cohesive brand message ensures that consumers recognize and trust the brand, regardless of their location.
Supply Chain and Logistics: Expanding internationally often involves managing complex supply chains and logistics. Businesses need to optimize their operations to meet local demand efficiently and deliver products or services on time, which can impact customer satisfaction and repeat business.
Customer Support and Service: Providing excellent customer support is critical for building trust and loyalty in foreign markets. This includes offering multilingual support, understanding regional preferences, and addressing customer issues promptly and effectively.
Competitive Intelligence: Staying competitive in international markets requires a deep understanding of local and global competitors. Continuous monitoring of competitor strategies and consumer sentiment helps companies adapt and innovate to maintain their edge.
Digital Localization: In the digital age, online presence is vital. Companies must ensure that their websites, apps, and digital marketing campaigns are localized for each market. This includes optimizing for search engines, localizing content, and adhering to regional e-commerce norms.
In summary, globalization has opened doors to immense opportunities for businesses to expand their reach and tap into diverse consumer markets. However, succeeding on the global stage demands a nuanced approach that transcends the limitations of a one-size-fits-all strategy. By embracing cultural sensitivity, conducting thorough market research, and adapting marketing practices to local nuances, businesses can harness the full potential of globalization and thrive in the ever-evolving international marketing landscape.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Global Versus Local Consumer Culture: Theory, Measurement, and …

Cross-Cultural Consumer Behavior: A Complex Web
Cross-cultural consumer behavior is a multifaceted field. It examines how individuals from different cultural backgrounds perceive, evaluate, and respond to marketing stimuli. These stimuli can include advertisements, product packaging, pricing strategies, and even the way products are positioned in the market. Here are some key aspects of cross-cultural consumer behavior:
Cross-cultural consumer behavior is a complex and fascinating area of study that delves deep into the intricate interplay between culture and consumer choices. It goes beyond merely acknowledging the existence of diverse consumer groups; it seeks to unravel the nuanced layers that shape the preferences, decisions, and reactions of individuals from varied cultural backgrounds.
Cultural Values and Norms: At the core of cross-cultural consumer behavior lie cultural values and norms. These fundamental elements influence how individuals perceive products and messages. For instance, a product associated with family values may resonate more with consumers from cultures that prioritize family bonds.
Communication Styles: Language and communication styles play a pivotal role in marketing success. Understanding how different cultures communicate, the nuances of language, and the impact of cultural idioms on messaging can make or break a marketing campaign.
Symbolism and Semiotics: The meaning of symbols, colors, and imagery can vary drastically across cultures. What is considered auspicious in one culture might be seen as ominous in another. Cross-cultural consumer behavior dissects these subtleties to ensure marketing materials are culturally appropriate.
Consumer Decision-Making Processes: The steps consumers take when making purchasing decisions can be influenced by cultural factors. Some cultures may prioritize collective decision-making, while others lean toward individual choices. Understanding these processes is vital for effective marketing.
Brand Perception: How a brand is perceived can differ dramatically across cultures. Cross-cultural consumer behavior examines how brand values and reputation are influenced by cultural contexts and how branding strategies must adapt accordingly.
Consumer Attitudes and Beliefs: Cultural beliefs and attitudes can shape consumer behavior significantly. For instance, religious beliefs, societal roles, and ethical considerations all play roles in influencing purchasing decisions.
Localization vs. Globalization: Striking the right balance between localized marketing strategies and global branding efforts is a key challenge. Cross-cultural consumer behavior helps businesses navigate this delicate equilibrium.
Consumer Response to Advertising Appeals: Different cultures may respond differently to advertising appeals such as humor, fear, or nostalgia. Understanding which appeals resonate with specific audiences is vital for effective campaigns.
Market Entry Strategies: When expanding into new markets, businesses must consider cultural factors. Cross-cultural consumer behavior aids in devising market entry strategies that align with the values and preferences of the target audience.
Ethical Considerations: Ethical standards and expectations can vary between cultures. This field of study explores how ethical practices in marketing and business operations align with cultural values.
In a globalized world where businesses aspire to reach diverse audiences, cross-cultural consumer behavior is not a choice but a necessity. It’s a roadmap that guides marketers toward understanding, respecting, and engaging with consumers from different cultural backgrounds authentically. It transforms marketing from a one-size-fits-all approach into a tailored, culturally sensitive endeavor that fosters trust and lasting relationships with consumers around the world.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Consumer Culture Theory (CCT): Twenty Years of Research …

Cultural Norms and Values
Different cultures have distinct norms and values that shape consumer preferences. What may be considered a luxury item in one culture could be an everyday necessity in another. Understanding these cultural nuances is crucial for effective marketing.
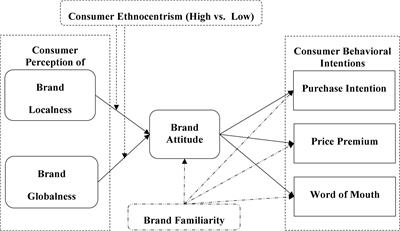
nullDon’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Consumer Perceptions of Brand Localness and … – Frontiers
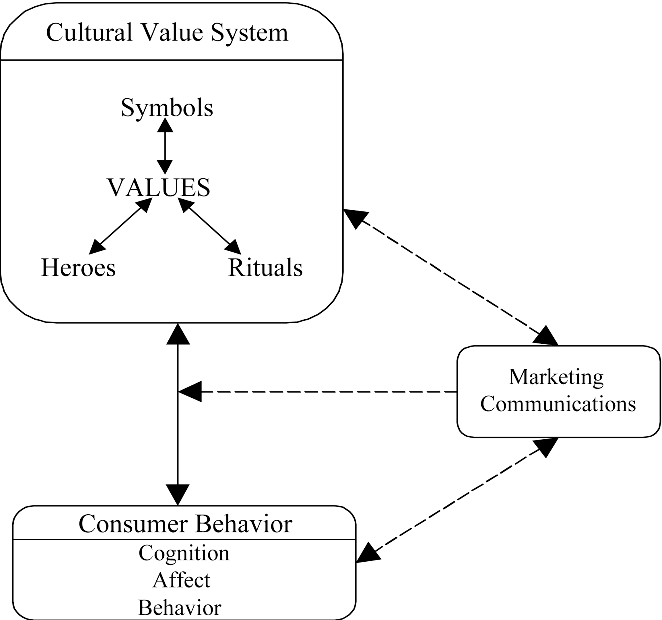
Language and Communication
Language plays a vital role in marketing. The choice of words, slogans, and messaging can vary significantly across cultures. Even colors and symbols can hold different meanings, impacting how a message is received.
The significance of language in marketing transcends mere communication—it becomes a powerful instrument that can either harmonize with diverse cultures or, if mishandled, lead to misunderstandings and even alienation. This multifaceted role of language and its impact on marketing strategies are worth exploring further:
1. Cultural Sensitivity: Language is deeply intertwined with culture. Marketing content that is culturally sensitive demonstrates respect for local customs, beliefs, and values. It acknowledges the unique identities of diverse communities and establishes a genuine connection with potential customers. A well-crafted message in the local language resonates more profoundly and fosters a sense of inclusivity.
2. Nuanced Messaging: Language allows for nuance and subtlety in messaging. The choice of words can evoke specific emotions, trigger associations, or convey a brand’s personality. In some cultures, direct and concise language may be preferred, while in others, poetic and metaphorical expressions may be more effective. Understanding these nuances is crucial for crafting messages that resonate.
3. Brand Identity: The language used in marketing materials can shape a brand’s identity. Whether a brand aims to be perceived as formal, friendly, authoritative, or innovative, the words and tone employed play a pivotal role. Consistency in language across all touchpoints reinforces brand identity and builds trust with consumers.
4. Color and Symbolism: Beyond words, color and symbolism are integral to marketing across cultures. Colors can hold various cultural associations—red symbolizes luck and prosperity in some cultures but signifies danger in others. Similarly, symbols may have different meanings or connotations. Understanding these cultural nuances is vital to avoid unintentional misinterpretation.
5. Adaptation vs. Translation: Effective cross-cultural marketing goes beyond mere translation. It involves adaptation—tailoring the message to align with local cultural norms and preferences. This may entail modifying slogans, imagery, and even product offerings to better suit the target audience while maintaining brand consistency.
6. Building Trust: Language proficiency fosters trust. Consumers are more likely to engage with brands that communicate clearly and authentically in their language. Language barriers can create skepticism, hindering the development of trustful relationships between brands and consumers.
7. Global Campaigns with Local Flavor: Successful global marketing campaigns strike a delicate balance between global consistency and local relevance. While maintaining a core message, they incorporate elements that resonate with each specific culture or market. This approach ensures that the campaign is relatable and appealing to diverse audiences.
8. Avoiding Cultural Insensitivity: Missteps in language or cultural symbolism can have severe consequences, including backlash and reputational damage. Sensitivity training and thorough research into cultural norms are essential to avoid inadvertent cultural insensitivity or stereotypes.
In essence, language is a bridge between brands and consumers, and its role in marketing is far-reaching. It’s not merely a tool for conveying information but a means of fostering connections, understanding cultural intricacies, and shaping brand perception. Savvy marketers recognize that effective communication transcends linguistic borders and cultural divides, acknowledging that the art of language can truly make or break a marketing campaign in an increasingly globalized world.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: The Impact of Globalization on Cross-Cultural Communication …

Consumer Decision-Making
The decision-making process can differ among cultures. Some societies prioritize individual needs and desires, while others emphasize group consensus and family opinions. These variations influence the factors consumers consider when making purchasing decisions.
Indeed, the decision-making process is a deeply cultural phenomenon, reflecting the values and norms that shape societies around the world. Understanding these cultural differences is crucial for businesses and marketers aiming to connect with diverse consumer bases. Let’s delve into how these cultural distinctions influence consumers’ considerations during purchasing decisions:
Individualism vs. Collectivism: In individualistic societies, such as those found in many Western cultures, individual needs, desires, and personal preferences play a central role in decision-making. Consumers in these cultures often prioritize self-expression and the fulfillment of personal goals. In contrast, collectivist societies, such as many Asian cultures, emphasize group harmony and consensus. Here, family and community opinions carry significant weight in purchasing decisions. Marketers need to tailor their messaging accordingly, focusing on individual empowerment in individualistic cultures and emphasizing familial benefits in collectivist ones.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Orientation: The concept of time orientation greatly affects consumer behavior. Cultures with a long-term orientation, like many in East Asia, prioritize thrift, perseverance, and the building of long-lasting relationships. In such societies, consumers may be more inclined to invest in products and services that promise enduring quality and benefits. In contrast, cultures with a short-term orientation, such as some Western cultures, often seek immediate gratification and may prioritize products that offer instant rewards. Businesses must align their offerings with these time orientation preferences.
Power Distance: The extent to which a culture accepts hierarchical authority and power distances can influence decision-making. In cultures with a high power distance, individuals may defer to authority figures or experts when making decisions. Marketers should consider building trust through endorsements or expert recommendations. In low power distance cultures, consumers may be more independent in their decision-making, seeking information and making choices autonomously.
Uncertainty Avoidance: Cultures vary in their tolerance for uncertainty and ambiguity. High uncertainty avoidance cultures prefer clear rules, established procedures, and familiar brands that reduce perceived risks. In these cultures, consumers may rely on well-known brands and established product categories. Low uncertainty avoidance cultures are more open to novelty and experimentation, making them more receptive to new and innovative products.
Communication Styles: The way information is communicated also varies across cultures. Some cultures are more indirect in their communication, relying on nuanced, implicit messages. In contrast, others are more direct and explicit in their communication. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective advertising and marketing campaigns, as misinterpretations can lead to misunderstandings and missed opportunities.
Symbols and Symbolism: Symbols and symbolism hold cultural significance. Certain colors, gestures, and symbols may convey different meanings in different cultures. It’s essential for marketers to be aware of these cultural nuances to avoid inadvertently sending the wrong message or causing offense.
Cultural Celebrations and Traditions: Cultural celebrations and traditions often influence consumer behavior, driving specific purchasing decisions. For example, holidays and festivals can lead to increased spending on gifts and traditional foods, creating unique marketing opportunities.
In conclusion, cultural variations profoundly influence consumers’ considerations during purchasing decisions. Recognizing and respecting these differences is essential for businesses seeking to engage with diverse markets. Successful marketers adapt their strategies to align with the cultural values, preferences, and decision-making processes of their target audiences, fostering trust and building meaningful connections in the global marketplace.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Research: How Cultural Differences Can Impact Global Teams

Trust and Brand Loyalty
Trust is a critical factor in consumer behavior. Cultures with a high level of trust may rely on word-of-mouth recommendations, while others may require extensive marketing efforts to build trust in a brand.
Trust is a critical factor in consumer behavior, and its influence on purchasing decisions can vary significantly across different cultures and regions. Understanding the role of trust in consumer behavior is essential for businesses operating in diverse markets. Here are some extended insights into the dynamics of trust and its impact on consumer behavior:
Cultural Variations: Trust is deeply rooted in cultural norms and values. In cultures with a high level of trust, such as some Scandinavian countries, word-of-mouth recommendations and personal referrals play a central role in consumer decision-making. People trust the opinions and experiences of their close-knit communities. In contrast, in cultures with lower inherent trust, consumers may be more skeptical and require extensive marketing efforts to build confidence in a brand.
Brand Reputation: Trust is often closely tied to a brand’s reputation. Companies that consistently deliver high-quality products and services, maintain transparency, and uphold ethical standards tend to earn and retain consumer trust more easily. Building a positive brand reputation takes time and effort but can pay off in the form of loyal customers who rely on the brand’s consistency.
Social Proof: Trust can be influenced by social proof, where consumers look to the behavior of others as a guide. Positive online reviews, testimonials, and user-generated content can significantly impact trust levels. In today’s digital age, consumers often seek validation from the experiences of their peers before making purchasing decisions.
Trust in E-commerce: E-commerce platforms rely heavily on trust. Consumers must trust that their personal and financial information is secure when making online purchases. Establishing trust through secure payment gateways, data encryption, and clear privacy policies is essential for e-commerce businesses to thrive.
Building Trust Through Transparency: Transparency is a key factor in building trust. Businesses that openly communicate their practices, pricing, and product information are more likely to gain the trust of consumers. Transparency extends to addressing issues or mistakes honestly, which can actually enhance trust when handled well.
Local vs. Global Brands: Trust can vary in consumers’ perceptions of local versus global brands. In some regions, local brands may enjoy higher trust levels due to their familiarity and perceived connection to the community. Global brands often need to work harder to gain the trust of consumers in new markets, especially if there’s a perception of cultural insensitivity or lack of local understanding.
Building Trust Over Time: Trust is not something that can be established overnight. It often requires consistent efforts over time to build and maintain. Businesses that invest in long-term customer relationships, quality assurance, and ethical practices are more likely to earn and sustain consumer trust.
Crisis Management: How a business handles crises can significantly impact trust. Swift and transparent responses to issues or product recalls can help rebuild trust and even enhance a brand’s reputation if handled effectively.
In conclusion, trust is a complex and culturally influenced factor that profoundly shapes consumer behavior. Businesses must adapt their marketing and customer engagement strategies to align with the trust dynamics of the specific markets they serve. Whether relying on word-of-mouth in high-trust cultures or implementing comprehensive marketing campaigns in lower-trust environments, understanding and nurturing trust is a fundamental aspect of successful consumer engagement.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Culture and the Consumer Journey – ScienceDirect
The Role of Marketing Economics
Marketing economics, as a discipline, focuses on applying economic principles to the field of marketing. It plays a pivotal role in researching cross-cultural consumer behavior by:
nullAdditionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Culture and Consumer Behavior: The Role of Horizontal and …

Data Analysis
Marketing economists analyze data from various sources, including surveys, market research, and consumer feedback, to identify cultural trends and consumer preferences.
“Marketing economists serve as data detectives, meticulously mining information from an array of sources such as surveys, extensive market research, and insightful consumer feedback. Their mission is to uncover the intricate tapestry of cultural trends and consumer preferences, bringing a nuanced understanding to the forefront.
Surveys as Cultural Snapshots: Surveys are like snapshots of cultural shifts. Marketing economists design and conduct surveys that capture not only what consumers purchase but also why they do so. These surveys unveil evolving tastes, values, and preferences, painting a detailed picture of cultural dynamics over time.
Market Research: A Treasure Trove of Insights: Market research, a cornerstone of their toolkit, provides a treasure trove of insights. It involves exhaustive investigations into consumer behavior, market size, and competitive landscapes. Marketing economists meticulously sift through this data to extract patterns, helping businesses adapt their strategies to changing consumer demands.
The Power of Consumer Feedback: Consumer feedback is a goldmine of information. Marketing economists tap into this valuable resource, examining customer reviews, comments, and social media interactions. By analyzing the sentiment and content of feedback, they gain real-time insights into consumer perceptions and emerging trends.
Identifying Cultural Influencers: Beyond data analysis, marketing economists keep an eye on cultural influencers. They track celebrities, social media personalities, and thought leaders whose actions and opinions sway consumer behavior. By understanding these influencers, businesses can strategically align their marketing efforts to leverage their impact.
Adapting to Multicultural Markets: In our globalized world, multicultural markets are the norm. Marketing economists are keenly aware of the diverse consumer landscapes they navigate. They help businesses navigate the intricacies of multicultural marketing by identifying cultural nuances and tailoring strategies accordingly.
Data-Driven Strategy Formulation: The ultimate goal of this data-driven pursuit is to inform strategic decision-making. Armed with a deep understanding of cultural trends and consumer preferences, marketing economists assist businesses in formulating strategies that resonate with target audiences. These strategies can encompass everything from product development and branding to advertising and pricing.
In a rapidly changing world, marketing economists are at the forefront of deciphering cultural shifts and consumer behavior. Their work not only guides businesses but also enriches our understanding of the ever-evolving tapestry of human preferences and cultural dynamics.”
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Research: How Cultural Differences Can Impact Global Teams

Market Segmentation
They use economic models to segment markets based on cultural factors. This segmentation allows businesses to tailor their marketing strategies to specific cultural groups.
Segmenting markets based on cultural factors is a dynamic process that empowers businesses to engage with diverse consumer groups more effectively. Here’s an extended idea of how this segmentation contributes to tailored marketing strategies and successful cross-cultural marketing:
1. Cultural Sensitivity and Relevance:
By employing economic models to segment markets along cultural lines, businesses gain a deeper understanding of the unique values, beliefs, and behaviors of different consumer groups. This knowledge allows them to develop marketing campaigns that resonate with the cultural nuances of each segment. For instance, a campaign targeting a conservative and family-centric culture would emphasize different themes and values compared to one targeting an individualistic and adventurous culture. Cultural sensitivity and relevance are crucial in capturing the attention and trust of consumers.
2. Language and Communication:
Segmentation based on cultural factors goes beyond just language translation; it involves understanding the nuances of communication styles, idioms, and metaphors specific to each culture. Businesses can use economic models to identify which language variants or dialects are most effective in reaching specific cultural groups. This approach ensures that marketing messages are not only comprehensible but also relatable, fostering a stronger emotional connection with the audience.
3. Product Localization:
Cultural segmentation guides businesses in customizing their products and services to meet the unique preferences and needs of different cultural groups. For example, dietary preferences, packaging designs, product features, and even product names may need to be adapted to align with cultural norms and tastes. This localization enhances the perceived value of the products and increases the likelihood of acceptance in the market.
4. Targeted Advertising and Content Creation:
Economic models used for cultural segmentation provide valuable insights into the media consumption habits and preferences of specific cultural groups. Armed with this knowledge, businesses can select the most appropriate advertising channels and platforms to reach their target audience effectively. Furthermore, content creation becomes more strategic, allowing businesses to craft messages, visuals, and stories that resonate deeply with the cultural identity of the consumers.
5. Building Trust and Brand Loyalty:
Trust is the cornerstone of successful marketing, especially in cross-cultural contexts. Cultural segmentation helps businesses build trust by aligning marketing efforts with the values and expectations of the target audience. When consumers perceive that a brand understands and respects their culture, they are more likely to develop brand loyalty and become long-term customers. This trust-building process is essential for sustainable success in diverse markets.
6. Adaptation and Evolution:
Cultural segmentation is not static; it requires continuous adaptation and evolution. As cultures evolve and change, businesses must stay attuned to these shifts. Economic models enable ongoing monitoring and adjustment of marketing strategies to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
7. Ethical Marketing Practices:
Lastly, cultural segmentation promotes ethical marketing practices by preventing cultural insensitivity or appropriation. It encourages businesses to consider the broader social and ethical implications of their marketing strategies, fostering positive brand perception and avoiding controversies that can damage a brand’s reputation.
In essence, cultural segmentation guided by economic models is a strategic imperative in today’s globalized marketplace. It enables businesses to tailor their marketing efforts to diverse cultural groups, fostering deeper connections, trust, and brand loyalty. By understanding and respecting the cultural factors that influence consumer behavior, businesses can position themselves as inclusive, culturally aware, and socially responsible, ultimately enhancing their competitiveness and growth in the global market.
You can also read more about this here: Fragmentation And Segmentation: Marketing Global Benefits

Pricing Strategies
Economists examine the elasticity of demand in different cultural contexts to determine the optimal pricing strategy. Cultural factors often influence how consumers perceive price and value.
Economists delve into the elasticity of demand within various cultural contexts to determine the optimal pricing strategy. The elasticity of demand, which measures how consumer behavior responds to price changes, is a critical concept in economics. However, this elasticity is not universal; it can vary significantly based on cultural factors, which profoundly influence how consumers perceive price and value.
One crucial aspect of pricing strategy in different cultural contexts is understanding the concept of price sensitivity. In some cultures, consumers may be highly price-sensitive, seeking bargains and discounts as a primary motivator for purchasing decisions. In contrast, in other cultures, consumers may place a higher emphasis on brand prestige, quality, or exclusivity, and price may be a less critical factor.
Cultural factors can also shape the perception of value. What represents good value in one culture may not hold the same meaning in another. Economists need to consider how cultural norms, expectations, and social influences affect consumers’ assessments of value. This understanding is essential for pricing products or services competitively while maintaining profitability.
Furthermore, the way pricing information is communicated can vary significantly across cultures. In some cultures, haggling and negotiation are common practices, while in others, fixed pricing is the norm. The presentation of price, including the use of currency symbols, decimal points, and rounding practices, can also influence how consumers perceive pricing information.
Economists often use cross-cultural studies and market research to gain insights into these nuances. By analyzing consumer behavior and preferences in different cultural contexts, economists can tailor pricing strategies to resonate with local audiences effectively. This might involve adapting pricing structures, promotional tactics, or even product features to align with cultural norms and values.
For multinational businesses, understanding cultural influences on pricing is crucial for successful market entry and expansion. A pricing strategy that works well in one cultural context may need significant adjustments to thrive in another. Failure to account for these cultural factors can result in pricing strategies that miss the mark, leading to lost sales or damaged brand reputation.
In conclusion, economists recognize that cultural factors play a pivotal role in shaping consumer perceptions of price and value. By conducting in-depth analyses of price elasticity and considering cultural nuances, businesses can develop pricing strategies that resonate with consumers in different cultural contexts. This adaptability is essential for achieving success in today’s global marketplace and tailoring pricing strategies that are sensitive to local preferences and expectations.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Culture and the Consumer Journey – ScienceDirect
Product Localization
Understanding cross-cultural consumer behavior informs decisions regarding product localization. This involves adapting products to meet the preferences and needs of specific cultural markets.
nullLooking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Digital Globalization: the new era of global flows – McKinsey …

Challenges and Opportunities
While researching cross-cultural consumer behavior is crucial for global businesses, it comes with challenges. These challenges include navigating language barriers, respecting cultural sensitivities, and adapting marketing strategies effectively. However, the rewards are substantial:
Certainly, let’s explore the idea of researching cross-cultural consumer behavior, its challenges, and the substantial rewards for global businesses in more detail:
“Conducting research on cross-cultural consumer behavior is a vital undertaking for global businesses aiming to thrive in diverse markets worldwide. However, this endeavor is not without its unique challenges, which include navigating language barriers, respecting cultural sensitivities, and adapting marketing strategies effectively. Nonetheless, the potential rewards are substantial and transformative:
Challenges in Researching Cross-Cultural Consumer Behavior:
Language Barriers: One of the primary challenges is overcoming language barriers. Effective research often requires surveys, interviews, and data collection in multiple languages. Translating research instruments accurately while maintaining cultural nuances can be complex and time-consuming.
Cultural Sensitivities: Cultural sensitivities and taboos vary significantly across regions. Researchers must tread carefully to ensure they do not inadvertently offend or alienate potential participants. Understanding local customs, norms, and etiquette is paramount to conducting respectful and ethical research.
Data Quality: Data quality can be a concern when conducting cross-cultural research. Respondents from different cultures may interpret questions differently or provide socially desirable responses. Researchers must implement rigorous data validation techniques to ensure data accuracy and reliability.
Sampling Challenges: Obtaining a representative sample from diverse cultural backgrounds can be challenging. Sampling bias can occur if certain groups are overrepresented or underrepresented in the study. Researchers must use stratified sampling methods and work with local partners to address these challenges.
Cultural Bias: Research instruments and methodologies developed in one culture may not be suitable for another. Cultural bias can skew results, leading to misinterpretation. Researchers need to use culturally adapted research tools to minimize bias and ensure validity.
Dynamic Cultural Shifts: Cultures are not static; they evolve over time. Keeping pace with cultural shifts and changes in consumer behavior is essential for accurate and up-to-date research. This requires ongoing monitoring and adaptation of research strategies.
Substantial Rewards for Global Businesses:
Market Expansion: Understanding cross-cultural consumer behavior opens doors to new markets. Businesses can identify untapped opportunities in regions with different cultural norms, preferences, and purchasing behaviors.
Tailored Marketing Strategies: Armed with insights into cross-cultural behavior, businesses can tailor their marketing strategies effectively. They can craft messages, branding, and product offerings that resonate with specific cultural values and preferences.
Increased Sales and Market Share: Adapting to local consumer behavior can lead to increased sales and market share. Businesses that connect with consumers on a cultural level often outperform competitors that apply a one-size-fits-all approach.
Brand Loyalty: Demonstrating cultural sensitivity and an understanding of local customs can build brand loyalty. Consumers appreciate brands that make an effort to connect authentically with their culture and values.
Risk Mitigation: Cross-cultural research helps businesses anticipate potential risks and pitfalls. It allows them to avoid cultural missteps that can lead to reputational damage and financial losses.
Innovation and Product Development: Insights from cross-cultural research can drive innovation and product development. Businesses can identify unmet needs and preferences in different markets, leading to the creation of products tailored to specific cultural contexts.
Global Brand Image: Successfully navigating cross-cultural consumer behavior enhances a global brand’s image. It positions the brand as culturally aware and inclusive, appealing to a broader and more diverse customer base.
In conclusion, while researching cross-cultural consumer behavior presents its share of challenges, the rewards for global businesses are substantial. By investing in culturally sensitive research, businesses can expand their market reach, tailor their strategies effectively, and build lasting relationships with diverse consumer segments, ultimately achieving sustainable growth and success in the global marketplace.”
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Methodological issues in cross-cultural research: An overview and …

Market Expansion
Businesses that successfully understand and cater to cross-cultural consumer behavior can expand into new markets with confidence.
Understanding and catering to cross-cultural consumer behavior is not just a key to expanding into new markets; it’s a strategic imperative that can unlock a world of opportunities for businesses. Let’s explore how this approach goes beyond market expansion and leads to sustainable global success:
Cultural Sensitivity: Cross-cultural consumer understanding requires a deep appreciation of cultural nuances, values, and norms. Businesses that prioritize cultural sensitivity in their marketing and product offerings are more likely to resonate with diverse audiences. This sensitivity fosters goodwill and positive brand perception.
Global Market Entry: Armed with insights into cross-cultural behavior, businesses can confidently enter new global markets. They can tailor their marketing messages and adapt their products or services to align with the preferences and needs of local consumers. This localization strategy increases the likelihood of acceptance and success in foreign markets.
Brand Trust and Loyalty: Building trust is essential in cross-cultural marketing. When businesses demonstrate an understanding of and respect for different cultures, consumers are more likely to trust their brand. Trust leads to customer loyalty, which, in turn, translates into long-term success and repeat business.
Inclusivity and Diversity: Embracing cross-cultural consumer behavior goes hand in hand with inclusivity and diversity. Businesses that celebrate diversity not only appeal to a broader customer base but also attract a diverse talent pool. This diversity can lead to a more creative and innovative work environment.
Customer Insights: Cross-cultural consumer research provides businesses with invaluable customer insights. They can uncover unique pain points, preferences, and trends that may not be apparent in their home market. These insights can inform product development and marketing strategies both locally and internationally.
Mitigating Risks: Entering new markets can be risky, but an understanding of cross-cultural behavior helps mitigate those risks. By being aware of potential cultural missteps or misunderstandings, businesses can proactively address and navigate challenges, reducing the likelihood of costly missteps.
Competitive Advantage: In today’s interconnected world, businesses that excel in cross-cultural marketing gain a competitive edge. They can tap into emerging markets, connect with diverse customer segments, and outperform competitors that are less culturally attuned.
Word-of-Mouth Marketing: Satisfied customers from diverse backgrounds can become powerful advocates for a business. Positive word-of-mouth marketing, facilitated by cross-cultural understanding, can drive organic growth and lead to a broader customer base.
Adaptation to Change: Consumer behavior evolves, and cultural dynamics shift. Businesses that understand cross-cultural behavior are better positioned to adapt to these changes. They can modify their strategies to stay relevant and aligned with shifting consumer preferences.
Ethical Considerations: Cross-cultural understanding encourages ethical marketing practices. Businesses can avoid cultural insensitivity or offensive messaging, ensuring that their marketing efforts are not only effective but also responsible and respectful.
In conclusion, businesses that embrace cross-cultural consumer behavior are not only poised for successful market expansion but also for sustained global growth. By respecting and connecting with diverse audiences, these businesses foster trust, loyalty, and innovation, all of which contribute to long-term competitiveness and success in an increasingly diverse and interconnected world.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Market Sustainability: A Globalization and Consumer Culture …
Customer Satisfaction
Tailored marketing strategies lead to higher customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
Tailored marketing strategies, customized to meet the unique needs and preferences of individual customers, are the cornerstone of building lasting relationships and driving business success. Here’s why they are so essential:
Enhanced Relevance: Tailored strategies ensure that marketing messages, product recommendations, and offers resonate with each customer on a personal level. When customers receive content that aligns with their interests and past behaviors, they are more likely to engage and convert.
Improved Customer Experience: Personalized experiences make customers feel valued and understood. Whether it’s addressing them by name or suggesting products based on their browsing history, tailored marketing demonstrates a commitment to providing exceptional customer experiences.
Higher Conversion Rates: When marketing efforts align closely with customer preferences, conversion rates tend to soar. Tailored strategies reduce the chances of customers dismissing marketing messages as irrelevant noise and increase the likelihood of them taking desired actions.
Reduced Abandonment: Customers are less likely to abandon shopping carts or browse away from a website when they encounter personalized offers or recommendations. Tailored marketing can gently guide them toward completing their purchase.
Brand Loyalty: Customers who consistently receive personalized experiences are more likely to become loyal advocates for a brand. They feel a stronger emotional connection and are more likely to stick around for the long term.
Cross-Selling and Up-Selling: Tailored strategies can identify opportunities for cross-selling related products or services or up-selling to higher-value options. This not only increases revenue but also enhances the customer’s overall satisfaction by offering them relevant choices.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Tailored marketing relies on data analysis and insights. Businesses that invest in these strategies gain a deeper understanding of their customer base, allowing them to make data-driven decisions that benefit both the customer and the business.
Competitive Edge: In a competitive marketplace, personalized marketing can be a key differentiator. Brands that deliver relevant content and offers consistently outshine competitors in the eyes of consumers.
Retention and Churn Reduction: Personalized retention strategies can identify and engage at-risk customers before they churn. By offering tailored incentives or solutions, businesses can retain valuable customers and reduce churn rates.
Adaptability: Tailored marketing is adaptable to changing customer preferences and market dynamics. It allows businesses to respond quickly to shifts in consumer behavior and market trends, ensuring continued relevance and competitiveness.
Measurable Results: Personalization strategies are often highly trackable and measurable. This enables businesses to assess the effectiveness of their efforts and make refinements based on real-time data.
In conclusion, tailored marketing strategies are not just a trend but a fundamental requirement for businesses looking to thrive in today’s customer-centric landscape. By investing in personalization, companies can forge deeper connections with their audience, drive higher satisfaction and loyalty, and ultimately achieve sustainable growth and success.
You can also read more about this here: Cross-Cultural Variations in Consumer Behavior: A Literature …

Competitive Advantage
A deep understanding of cross-cultural consumer behavior provides a competitive advantage in a globalized marketplace.
nullDon’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: (PDF) The Influence of Culture on Global Marketing Strategies: A …

Ethical Marketing
Ethical considerations, including cultural sensitivities, are essential. Researching cross-cultural behavior helps businesses avoid cultural misunderstandings or offensive marketing practices.
Ethical considerations, especially those rooted in cultural sensitivities, are paramount in today’s interconnected global marketplace. In this context, researching cross-cultural behavior becomes not just an option but a critical imperative for businesses. It serves as a compass that guides ethical decision-making and helps companies steer clear of cultural misunderstandings or offensive marketing practices.
1. Respecting Cultural Values: Each culture has its own set of deeply ingrained values, beliefs, and norms. What might be perfectly acceptable in one culture could be considered offensive or disrespectful in another. Cross-cultural behavior research enables businesses to navigate these cultural intricacies and tailor their marketing strategies accordingly. By doing so, they demonstrate respect for local values and customs.
2. Avoiding Cultural Stereotypes: Stereotyping can lead to harmful and offensive marketing practices. Effective cross-cultural research helps companies avoid relying on stereotypes that oversimplify or misrepresent cultures. Instead, it encourages a nuanced and accurate understanding of cultural diversity, leading to more respectful and inclusive marketing campaigns.
3. Preventing Cultural Insensitivity: Cultural insensitivity in marketing can have severe consequences, including backlash, damage to brand reputation, and loss of customers. Researching cross-cultural behavior helps businesses identify potential pitfalls and blind spots that may lead to insensitivity, allowing them to proactively mitigate these risks.
4. Building Trust and Credibility: Consumers are more likely to trust and engage with brands that demonstrate cultural sensitivity and ethical awareness. Cross-cultural behavior research contributes to building trust by ensuring that marketing materials align with local customs and values. This trust, in turn, fosters stronger customer relationships and brand loyalty.
5. Ethical Marketing in the Digital Age: The digital age has amplified the reach and impact of marketing campaigns. With social media and the internet connecting people worldwide, ethical considerations in cross-cultural marketing are more crucial than ever. One misstep can go viral and have far-reaching consequences.
6. Compliance with Regulations: Many countries have regulations governing advertising and marketing practices to protect consumers from offensive or misleading content. Cross-cultural research helps businesses stay in compliance with these regulations by ensuring that their marketing materials meet local standards and expectations.
7. Ethical Supply Chains: Ethical considerations extend beyond marketing to supply chains and sourcing practices. Companies that demonstrate ethical behavior throughout their operations, from production to marketing, build a stronger reputation and are more attractive to socially conscious consumers.
In conclusion, ethical considerations and cultural sensitivity are non-negotiable elements of successful cross-cultural marketing. Businesses that invest in researching cross-cultural behavior not only avoid potential pitfalls but also demonstrate a commitment to responsible and respectful engagement with diverse audiences. In an age where consumers prioritize ethical and socially responsible brands, these considerations are not just an ethical imperative but a strategic advantage that can lead to long-term success and positive brand impact.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here A cross-cultural investigation of the effect of cosmopolitan consumer …

In conclusion, the globalization of marketing economics has highlighted the importance of researching cross-cultural consumer behavior. It’s no longer enough for businesses to offer standardized marketing messages; they must adapt to diverse cultural contexts. Through data analysis, segmentation, and strategic adaptation, marketing economists are helping businesses bridge the cultural divide and thrive in an interconnected world. Ultimately, the successful understanding and incorporation of cross-cultural consumer behavior are key factors in a business’s global success.
In conclusion, the globalization of marketing economics has not only underscored the significance of researching cross-cultural consumer behavior but has also illuminated the path toward thriving in this interconnected world. Offering standardized marketing messages is no longer sufficient; businesses must actively embrace and adapt to the rich tapestry of diverse cultural contexts that shape consumer preferences and behaviors.
One pivotal tool in this pursuit is data analysis. In today’s digital age, businesses have access to a wealth of data that can provide insights into how different cultural groups engage with their products and services. Marketing economists, armed with advanced analytics and machine learning, can dissect this data to uncover hidden patterns, preferences, and trends among various cultural segments. These insights become the foundation for crafting tailored marketing strategies that resonate with specific audiences.
Segmentation is another key strategy. Rather than treating the global market as a monolith, businesses can use segmentation to divide it into manageable and meaningful subgroups. This allows for the creation of niche marketing campaigns that speak directly to the unique needs and desires of each segment. From demographic and psychographic data to geographic and behavioral characteristics, segmentation ensures that no cultural nuance is overlooked.
Strategic adaptation is the linchpin of success in cross-cultural marketing. It’s about more than just translating content; it’s about contextualizing it. Marketing economists help businesses refine their messaging, visuals, and campaigns to align with the values, norms, and aspirations of each target culture. This can involve tailoring product features, packaging, and branding to better suit local preferences.
Moreover, the role of marketing economists extends beyond just understanding cultural nuances. They also help businesses stay attuned to the dynamic nature of cultural shifts. Cultural trends evolve, and what resonates with a particular group today may change tomorrow. Continual analysis and adaptation ensure that marketing efforts remain effective in the face of cultural evolution.
In this ever-shrinking global village, the successful understanding and incorporation of cross-cultural consumer behavior are not just nice-to-haves but critical factors in a business’s global success. Businesses that embrace diversity, invest in robust research, and commit to thoughtful adaptation will not only bridge the cultural divide but also build lasting connections with consumers around the world. The future of marketing economics lies in recognizing that our world is a mosaic of cultures, and true success lies in celebrating and responding to this beautiful diversity.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Global Versus Local Consumer Culture: Theory, Measurement, and …
More links
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Culture and Consumer Behavior: The Role of Horizontal and …