Introduction
Sustainable investing, often referred to as socially responsible investing (SRI) or environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investing, is a financial strategy that has gained significant traction in recent years. It represents a fundamental shift in how individuals and institutions approach investment decisions, placing a premium on not only financial returns but also environmental and social impact. In this article, we will explore the concept of sustainable investing, its principles, and the crucial role it plays in balancing profit and purpose.
Sustainable investing has emerged as a powerful force reshaping the investment landscape, and its ascent shows no signs of slowing down. This approach to investment is more than just a trend; it reflects a broader shift in societal values and the recognition that traditional financial metrics alone are insufficient for measuring the true worth of an investment.
A Response to Global Challenges: The growing popularity of sustainable investing can be attributed, in part, to our heightened awareness of pressing global challenges. Climate change, social inequality, and corporate misconduct have spurred a collective call to action. Sustainable investing is an individual response to these challenges, enabling investors to channel their capital toward solutions and positive change.
Mainstream Acceptance: What was once considered a niche investment strategy has now entered the mainstream. Institutional investors, such as pension funds and asset management firms, have incorporated ESG criteria into their decision-making processes. This institutional adoption has not only legitimized sustainable investing but has also propelled it into the financial mainstream.
Financial Performance: Initially, there was skepticism about whether sustainable investments could deliver competitive financial returns. However, a growing body of research suggests that companies with strong ESG practices are often better equipped to navigate complex challenges, leading to long-term value creation. As a result, investors are increasingly recognizing that sustainable investments can be financially rewarding.
Global Standards and Reporting: Efforts are underway to standardize ESG reporting and metrics, which will enhance transparency and comparability among companies. Initiatives like the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) are playing a pivotal role in establishing consistent reporting standards.
Inclusive and Diverse Investing: Sustainable investing has also opened doors to more inclusive and diverse investment opportunities. It fosters support for businesses and initiatives that promote diversity, equity, and inclusion, aligning with the values of an increasingly diverse investor base.
A Tool for Change: Beyond financial returns, sustainable investing is seen as a tool for driving change. By allocating capital to companies with strong sustainability practices, investors can exert influence and encourage responsible behavior within the corporate world. This influence extends to pressing issues such as climate action, gender equality, and ethical governance.
Beyond Divestment to Engagement: While some investors choose to divest from industries or companies that conflict with their values, others take an engagement approach. Shareholder engagement involves actively participating in dialogues with companies to influence their ESG practices. This form of investor activism has led to meaningful corporate reforms.
The Future of Finance: As sustainable investing continues to gain momentum, it is poised to redefine the future of finance. It offers a path to align individual and institutional wealth with global sustainability goals. This shift is indicative of a broader societal transformation where profit and purpose converge, demonstrating that financial success and positive impact can indeed go hand in hand.
In conclusion, sustainable investing is no longer on the periphery of the financial world; it is at the forefront of an investment revolution. Its principles and practices are shaping how investors and institutions evaluate opportunities, emphasizing the importance of considering environmental, social, and governance factors alongside financial metrics. As the global community grapples with multifaceted challenges, sustainable investing stands as a beacon of hope, offering a way to invest in a more equitable, sustainable, and responsible future.
The Principles of Sustainable Investing
Sustainable investing goes beyond traditional financial metrics. It seeks to align investment choices with a broader set of values and objectives, often encompassing environmental, social, and ethical considerations. The core principles of sustainable investing include:
Environmental Responsibility: Sustainable investors assess a company’s impact on the environment, considering factors such as carbon emissions, water usage, and resource conservation. They favor companies with strong environmental stewardship and sustainability practices.
Social Impact: Social considerations are central to sustainable investing. Investors look at a company’s commitment to fair labor practices, diversity and inclusion, and community engagement. Investments are directed toward businesses that prioritize social responsibility.
Governance: Strong corporate governance is a hallmark of sustainable investing. Investors evaluate a company’s leadership, ethics, and transparency. They favor firms with robust governance structures and practices that align with long-term shareholder interests.
Positive Screening: Sustainable investors actively seek out companies that excel in ESG criteria. These may include renewable energy companies, organizations with fair labor policies, or those that promote gender equality and diversity.
Negative Screening: Conversely, investors may exclude certain industries or companies that engage in activities deemed socially or environmentally harmful, such as tobacco, weapons manufacturing, or fossil fuels.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Shareholders Are Getting Serious About Sustainability

Balancing Profit and Purpose
Enhanced Risk Management: Sustainable investing considers a broader range of risks, including those related to ESG factors. Companies with strong sustainability practices often exhibit better risk management and resilience in the face of environmental and social challenges.
Long-Term Value Creation: Sustainable investing takes a long-term perspective. By focusing on ESG factors, investors aim to identify companies that are well-positioned for sustainable growth, as they are more likely to anticipate and adapt to changing market conditions.
Market Performance: Research suggests that sustainable investments can deliver competitive financial returns. Companies that address ESG issues effectively may enjoy a stronger reputation, reduced operational risks, and enhanced competitiveness in the market.
Alignment with Values: Sustainable investing allows individuals and organizations to align their investment choices with their personal or corporate values. It provides a tangible way to support causes and issues that matter deeply to them.
Impact on Corporate Behavior: By directing investments toward companies with strong ESG practices, sustainable investors can influence corporate behavior. This pressure encourages firms to adopt more responsible practices, creating a positive ripple effect throughout the business world.
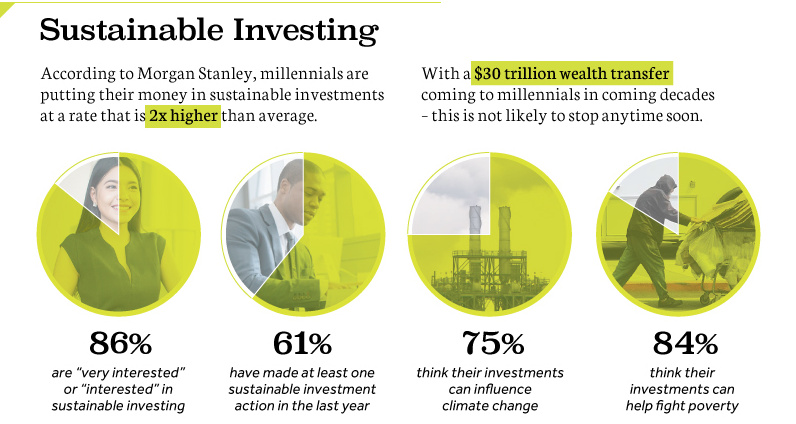
Challenges and Considerations
While sustainable investing offers numerous benefits, it is not without challenges:
Lack of Standardization: The absence of universal ESG standards and metrics can make it difficult for investors to compare companies and assess their sustainability performance.
Greenwashing: Some companies may exaggerate their sustainability efforts to attract investors. Discerning genuine commitment from greenwashing requires due diligence.
Risk of Underperformance: There is a perception that sustainable investing may lead to lower returns, although evidence increasingly suggests that this is not the case.
Complexity: Sustainable investing demands a deeper level of research and analysis, which can be more time-consuming than traditional investment strategies.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Shareholders Are Getting Serious About Sustainability

Conclusion
Sustainable investing represents a paradigm shift in the world of finance, where profit and purpose are no longer mutually exclusive. Investors are increasingly recognizing that aligning their portfolios with ESG principles can lead to competitive financial returns while addressing pressing global challenges. As sustainable investing continues to gain momentum, it is likely to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of finance, promoting responsible business practices, and driving positive change on a global scale. Balancing profit and purpose has never been more accessible or more important.
Indeed, the paradigm shift brought about by sustainable investing is not only reshaping finance but also redefining the role of businesses and investors in society. This transformation goes beyond the simple juxtaposition of profit and purpose; it signifies a profound evolution in our approach to capitalism and wealth creation.
A New Definition of Success: Sustainable investing challenges the conventional notion of success in the financial world. It acknowledges that financial returns are just one dimension of success, and true prosperity encompasses environmental stewardship, social equity, and ethical governance. This broader perspective on success is resonating with a new generation of investors who prioritize values and impact alongside financial gains.
Risk Mitigation: Beyond competitive financial returns, sustainable investing has emerged as a risk mitigation strategy. Companies that prioritize ESG factors are often better prepared to navigate an increasingly complex and interconnected world. As a result, investments guided by sustainability principles can offer a buffer against unforeseen economic, environmental, or social shocks.
Innovation and Opportunity: The pursuit of sustainability has ignited a wave of innovation and opportunity. Entrepreneurs and businesses are developing innovative solutions to address global challenges, from renewable energy technologies to sustainable agriculture practices. Sustainable investing not only supports these endeavors but also offers opportunities for investors to participate in the growth of transformative industries.
Transparency and Accountability: The demand for transparency and accountability is driving companies to adopt responsible practices. ESG reporting and disclosure are becoming standard practices for many businesses, enabling investors to make informed decisions and hold companies accountable for their actions. This transparency fosters trust and aligns corporate behavior with societal expectations.
Global Collaborations: Sustainable investing is fostering global collaborations and partnerships. Initiatives like the United Nations Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI) are uniting investors worldwide to address shared challenges. This collective effort amplifies the impact of sustainable investing on a global scale.
Redefining Corporate Purpose: Businesses are redefining their purpose beyond profit maximization. They are recognizing their roles as stewards of the environment, champions of social progress, and ethical leaders in their respective industries. This shift in corporate purpose aligns with the values of sustainable investors and contributes to a more responsible and inclusive business environment.
The Role of Governments: Sustainable investing is prompting governments to enact policies that support responsible finance. Regulations and incentives are emerging to encourage ESG integration and sustainability practices. Governments are recognizing that a sustainable financial system is not only good for investors but also essential for addressing critical global challenges.
Reshaping Investment Strategies: Traditional investment strategies are evolving to incorporate sustainable principles. Asset managers are offering a wide range of sustainable investment options, from ESG-themed funds to impact investing portfolios. This diversity allows investors to tailor their strategies to align with their values and objectives.
In essence, sustainable investing represents a fundamental shift toward a more holistic and responsible approach to finance. It is not a fleeting trend but a movement that is gaining momentum and reshaping the future of investing. As more investors and businesses embrace sustainability principles, the lines between profit and purpose will continue to blur, ultimately fostering a more sustainable, equitable, and prosperous world. Balancing profit and purpose is not only accessible but also imperative for the future of finance and our planet.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: The Rise of Sustainable Business Practices: Strategies for …
