Table of Contents
- Understanding Price Discrimination
- First-Degree Price Discrimination (Perfect Price Discrimination)
- Second-Degree Price Discrimination
- Third-Degree Price Discrimination
- Maximized Revenue
- Increased Market Share
- Optimized Inventory Management
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
- Ethical Considerations
- Transparency
- Fairness
- Data Privacy
Price discrimination, a pricing strategy widely employed by businesses, involves charging different prices for the same product or service to different customer segments based on their willingness and ability to pay. It’s a powerful tool that allows companies to maximize revenue, cater to diverse consumer preferences, and optimize their market presence. In this article, we will delve into the concept of price discrimination, its various forms, benefits, and ethical considerations.
“Price discrimination, a sophisticated pricing strategy commonly deployed by businesses, revolves around the idea of charging varying prices for the same product or service to different customer segments based on their willingness and capacity to pay. This strategic maneuver is far more than just setting prices; it’s a dynamic tool that empowers companies to not only maximize revenue but also cater to diverse consumer preferences and fine-tune their market presence.
The Art of Segmentation: At the heart of price discrimination lies the art of segmentation. By dissecting the customer base into distinct segments with differing buying behaviors and price sensitivities, businesses can tailor pricing strategies to suit each group’s preferences. This segmentation allows companies to extract the maximum value from each customer category.
Forms of Price Discrimination: Price discrimination takes various forms, from simple tiered pricing for products and services to more intricate methods like personalized pricing and dynamic pricing algorithms. Each form serves a specific purpose, whether it’s capturing consumer surplus, optimizing capacity utilization, or enhancing overall market competitiveness.
Maximizing Revenue: Price discrimination is, fundamentally, about revenue optimization. By setting prices that align with what different customer segments are willing to pay, businesses can boost their overall revenue. This revenue boost isn’t just about increasing the bottom line; it also supports ongoing innovation, expansion, and sustainability.
Consumer Surplus Capture: A key benefit of price discrimination is the capture of consumer surplus. Customers who are willing to pay more for a product or service do so, while those with a lower willingness to pay can still access it at a lower price point. This dynamic ensures that a broader spectrum of consumers can benefit from the offering while the business maximizes its profits.
Ethical Considerations: While price discrimination is a powerful strategy, it also raises ethical considerations. Balancing the pursuit of profit with fairness and transparency is essential. Businesses must navigate the fine line between optimizing prices for revenue and ensuring that pricing practices are not perceived as discriminatory or exploitative.
Market Presence Optimization: Price discrimination allows businesses to optimize their market presence. By catering to various customer segments with tailored pricing, companies can strengthen their competitive position across different market niches. This strategic flexibility enhances market stability and resilience.
In conclusion, price discrimination is a multifaceted strategy that goes beyond mere price setting. It’s a strategic dance that involves segmentation, revenue optimization, and market presence enhancement. When executed thoughtfully and ethically, it can be a potent tool for businesses seeking to thrive in a complex and ever-evolving marketplace.”
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Personalised Pricing in the Digital Era
Understanding Price Discrimination
Price discrimination is not about exploiting customers but rather recognizing the diversity in consumers’ willingness to pay for a product or service. By segmenting the market and charging different prices to various groups of customers, businesses can enhance their profitability while providing value to customers who are willing to pay more.
Price discrimination, often misunderstood as a way to take advantage of consumers, is fundamentally rooted in acknowledging the intricate tapestry of consumer behavior and preferences. It is a strategy that allows businesses to optimize their pricing structure while simultaneously ensuring that customers receive tailored value in line with their preferences and financial capacities.
Equity in Pricing: Price discrimination isn’t just about extracting maximum profit; it’s also about promoting equity in pricing. By offering different price points, businesses can make their products or services accessible to a wider range of consumers. This inclusivity can foster a sense of fairness in the marketplace.
Dynamic Market Response: In a world of rapidly changing economic conditions, consumer behaviors, and market dynamics, price discrimination enables businesses to adapt in real-time. It allows them to respond to shifts in demand and supply, ensuring that they remain competitive and viable in an ever-evolving landscape.
Consumer Choice: Price discrimination empowers consumers by providing them with choices that align with their budget and preferences. This variety allows consumers to select products or services that best suit their individual needs, enhancing overall satisfaction.
Cross-Subsidization: Through price discrimination, companies can subsidize the costs of providing goods or services to price-sensitive customer segments by charging premium prices to those who can afford it. This cross-subsidization can support the sustainability of essential services, such as healthcare or education.
Economic Efficiency: By segmenting the market and pricing accordingly, price discrimination contributes to economic efficiency. It ensures that goods or services are allocated to those who value them the most, reducing waste and maximizing societal welfare.
Market Expansion: Price discrimination can stimulate market expansion. Lower-priced offerings can attract new customers who were previously unable to afford a product, while premium options cater to those seeking added features or exclusivity.
Innovation Incentives: Knowing that they can charge different prices to different segments, businesses are incentivized to invest in innovation and product differentiation. This drive for improvement can ultimately benefit consumers across the board.
In conclusion, price discrimination, when approached ethically and responsibly, serves as a win-win strategy for businesses and consumers alike. It recognizes the complexity of consumer preferences and purchasing power, ultimately fostering an environment of choice, fairness, and economic efficiency in the marketplace. It’s not just about profits; it’s about creating a harmonious ecosystem where businesses thrive, and consumers find value tailored to their needs.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Consumer Welfare and Price Discrimination: A Fine Line

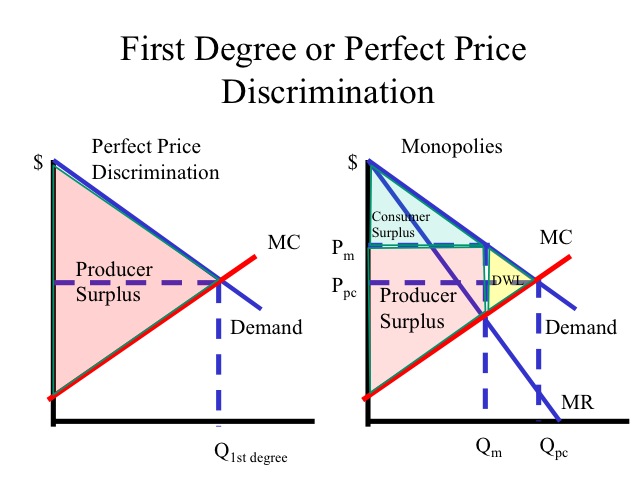
First-Degree Price Discrimination (Perfect Price Discrimination)
In this form, businesses charge each customer the highest price they are willing to pay. It requires detailed knowledge of individual customers’ preferences and price thresholds, making it challenging to implement. However, when successful, it maximizes revenue as no consumer surplus is left on the table.
Implementing a pricing strategy where businesses charge each customer the highest price they are willing to pay, often referred to as personalized or dynamic pricing, represents a pinnacle of pricing sophistication. This approach acknowledges that not all customers have the same willingness to pay, and it tailors pricing to match individual preferences and behaviors.
One of the key challenges in deploying personalized pricing is the need for a wealth of data and advanced analytics. Businesses must gather and analyze vast amounts of information about customers’ purchasing history, browsing behavior, demographics, and more. This data serves as the foundation for predicting how much each customer is willing to pay for a product or service accurately.
To achieve this level of precision, companies often employ machine learning algorithms and predictive modeling. These tools can uncover patterns and trends in customer data, enabling businesses to forecast individual price sensitivities and adjust prices accordingly. This dynamic pricing approach can be particularly advantageous in industries with highly variable demand, such as airlines, hotels, and e-commerce.
However, personalized pricing also raises ethical and transparency concerns. Customers may perceive it as discriminatory or unfair if they suspect they are paying significantly more than others for the same product. Thus, businesses must strike a delicate balance between maximizing revenue and maintaining customer trust.
When executed successfully, personalized pricing has the potential to significantly boost a company’s revenue by capturing the maximum value from each customer. It eliminates consumer surplus, the difference between what a customer is willing to pay and what they actually pay, which is essentially unclaimed profit. This approach aligns with the economic principle of capturing as much of the consumer surplus as possible, as no potential profit is left on the table.
Moreover, personalized pricing can foster customer loyalty when customers perceive that they are receiving offers and prices tailored to their preferences. When customers believe they are getting fair value for their money, they are more likely to return, make repeat purchases, and become brand advocates.
In conclusion, personalized pricing, while challenging to implement, can be a powerful revenue optimization strategy when applied correctly. It requires a deep understanding of individual customer behavior and preferences, advanced analytics, and careful consideration of ethical implications. When successfully executed, it maximizes revenue, eliminates consumer surplus, and can enhance customer loyalty, making it a valuable tool in a competitive business landscape.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Personalised Pricing in the Digital Era

Second-Degree Price Discrimination
This method involves tiered pricing, where customers self-select into different pricing categories based on their consumption habits. Common examples include quantity discounts, such as “buy one, get one free,” or subscription-based services with different price tiers.
nullFor a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Dynamic Pricing: From Price Discrimination Theory to Modern …
Third-Degree Price Discrimination
The most prevalent form of price discrimination, this strategy categorizes customers into distinct groups based on observable characteristics, such as age, location, or income level. Different prices are then offered to each group. Airlines, for instance, charge different fares to business and leisure travelers.
Certainly, let’s delve deeper into the concept of price discrimination and how businesses employ this strategy to cater to different customer segments based on observable characteristics:
“One of the most prevalent and widely utilized forms of price discrimination is segmentation-based pricing. This strategic approach involves categorizing customers into distinct groups, or segments, based on readily observable characteristics that influence their purchasing behavior. These characteristics can encompass a wide range of factors, including age, location, income level, and even past buying history. Once these customer segments are identified, businesses set different prices for each group. This strategy is employed across various industries, but let’s explore it further with a common example in the airline industry:
Airlines and Segment-Based Pricing:
The airline industry is a prime example of how segmentation-based pricing is put into practice. Airlines recognize that different travelers have distinct needs, preferences, and willingness to pay for their services. Therefore, they segment their customer base into several categories, including:
Business Travelers: These customers often require flexibility in travel plans, such as the ability to change flights or make last-minute bookings. They are typically less price-sensitive because their travel decisions are driven by business commitments.
Leisure Travelers: Leisure travelers, on the other hand, are often more budget-conscious. They plan vacations and trips well in advance and seek cost-effective options. They are willing to forgo flexibility for lower fares.
Frequent Flyers: Airlines also identify and reward loyal customers with frequent flyer programs. These programs offer perks like discounted fares, priority boarding, and lounge access, recognizing the value these customers bring over the long term.
Geographical Segmentation: Airlines may adjust prices based on the departure and destination locations. Popular routes with high demand often command higher fares, while less-traveled routes may offer lower prices to attract passengers.
Key Implications of Segmentation-Based Pricing:
Maximizing Revenue: The primary goal of segmentation-based pricing is to maximize revenue by charging each customer segment the highest price they are willing to pay. This tailored approach optimizes the airline’s revenue potential, as opposed to a one-size-fits-all pricing strategy.
Enhancing Customer Experience: By offering pricing options that align with different customer needs, airlines can enhance the overall customer experience. Business travelers appreciate the flexibility and convenience of higher-priced tickets, while budget-conscious leisure travelers benefit from cost-effective fares.
Optimizing Capacity: Pricing strategies can also help airlines manage seat availability. Higher fares for business travelers can ensure that seats are available when needed, while lower fares for leisure travelers help fill remaining capacity.
Competitive Advantage: Airlines that effectively implement segmentation-based pricing gain a competitive advantage. They can tailor their offerings to match the needs of various customer segments, potentially luring customers away from competitors with less flexible pricing structures.
Data Utilization: Airlines rely on extensive data analysis to segment their customers accurately. This data-driven approach enables airlines to fine-tune pricing strategies, identify emerging trends, and adapt to changes in market dynamics.
In essence, segmentation-based pricing is a dynamic and strategic approach to catering to diverse customer segments. It acknowledges that customers have varying preferences and willingness to pay, allowing businesses to extract the maximum value from each segment while providing customers with options that align with their specific needs. By understanding and effectively implementing this pricing strategy, businesses across industries can unlock revenue potential and offer tailored experiences to their customers.”
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here AI-enabled price discrimination as an abuse of dominance: a law …

Maximized Revenue
Price discrimination allows businesses to capture the maximum possible revenue by tailoring prices to the willingness to pay of different customer segments.
Price discrimination, a strategic pricing approach rooted in economics, encompasses a range of tactics that empower businesses to optimize revenue while accommodating diverse customer behaviors and preferences. Let’s explore this concept further to appreciate its nuances and significance:
Segmentation Precision: Price discrimination hinges on segmenting customers effectively. Businesses delve into demographic, psychographic, and behavioral data to categorize customers based on their willingness to pay. This precision in segmentation allows companies to target each group with pricing strategies tailored to their unique characteristics.
Maximizing Revenue: At its core, price discrimination is about maximizing revenue. By charging each customer segment the highest price they are willing to pay, businesses tap into the full revenue potential of their product or service. This approach ensures that the company captures as much value as possible from the market.
Consumer Surplus Capture: One of the key advantages of price discrimination is its ability to capture consumer surplus. Consumer surplus represents the difference between what a customer is willing to pay for a product or service and what they actually pay. Price discrimination aims to reduce this surplus by aligning prices more closely with individual preferences.
Flexible Pricing Structures: Price discrimination offers flexibility in setting prices. Businesses can implement various pricing structures, such as tiered pricing, personalized offers, or dynamic pricing, to cater to different customer segments. This adaptability allows for quick responses to market changes and competitive pressures.
Product Bundling: A common price discrimination tactic is product bundling. By offering packages that include multiple products or services at a discounted price, businesses encourage customers to spend more while feeling they are getting a better deal. This can boost overall revenue and cross-selling opportunities.
Timing Strategies: Timing is crucial in price discrimination. Businesses often adjust prices based on the timing of the purchase. For instance, early bird discounts, last-minute deals, and seasonal promotions are all strategies that leverage timing to influence purchasing decisions.
Ethical Considerations: While price discrimination can be a powerful revenue optimization tool, it must be employed ethically. Overly aggressive or discriminatory pricing practices can lead to customer backlash and damage a brand’s reputation. Striking a balance between revenue goals and fair pricing is essential.
Market Segmentation Refinement: Price discrimination encourages businesses to refine their market segmentation continually. As they gain insights into customer behavior and preferences, they can adjust their pricing strategies to better align with changing market dynamics.
Competitive Advantage: Businesses that effectively implement price discrimination gain a competitive advantage. They can offer customized pricing that competitors may struggle to match. This uniqueness can attract and retain customers who value tailored pricing.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations: Price discrimination is subject to legal and regulatory scrutiny in some jurisdictions. Antitrust laws and consumer protection regulations aim to prevent discriminatory practices that harm consumers or stifle competition. Businesses must navigate these legal considerations carefully.
In summary, price discrimination is a multifaceted pricing strategy that optimizes revenue by tailoring prices to the diverse preferences and behaviors of customer segments. When executed thoughtfully and ethically, it allows businesses to capture the full value of their offerings while providing customers with pricing options that align with their perceived value. Price discrimination is a dynamic tool that keeps businesses responsive to market dynamics and competitive forces.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Ultimate FAQ:Price Profiling, What, How, Why, When – FasterCapital
Increased Market Share
By accommodating various customer groups with different price points, companies can expand their market reach and attract a broader customer base.
By accommodating various customer groups with different price points, companies can not only expand their market reach and attract a broader customer base but also unlock several strategic advantages:
Market Segmentation: Offering different price points allows companies to segment their market effectively. They can cater to customers with varying budgets, needs, and preferences. This segmentation enables more targeted marketing and product development.
Competitive Edge: Price differentiation can give companies a competitive edge. By offering a range of price options, they can outmaneuver competitors that rely on a one-size-fits-all pricing strategy, appealing to a wider audience and capturing market share.
Maximized Revenue: Different price points enable revenue maximization. Companies can capture value from both price-sensitive and price-insensitive customers. While some customers may opt for lower-cost options, others may choose premium offerings, leading to increased overall revenue.
Customer Retention: Price flexibility fosters customer loyalty. When companies provide options that align with customers’ evolving needs and budgets, they are more likely to retain their patronage over the long term.
Cross-Selling and Upselling: Offering different price points creates opportunities for cross-selling and upselling. Customers initially attracted by lower-priced products may eventually upgrade to higher-priced versions as their needs grow or budgets allow.
Brand Perception: A diversified pricing strategy can positively impact brand perception. Customers may perceive a company as customer-centric and responsive to their financial constraints, enhancing brand loyalty and advocacy.
Risk Mitigation: Relying solely on premium pricing can be risky, as economic downturns or competitive pressures may erode customer demand. Having lower-priced options provides a buffer during such periods, ensuring a more stable revenue stream.
Innovation Catalyst: Price differentiation encourages innovation. Companies are motivated to develop new products or features for premium offerings, driving creativity and differentiation in the market.
Global Expansion: Different price points can facilitate entry into international markets. Companies can adapt their pricing strategies to local economic conditions and consumer behaviors, making their products more accessible and competitive.
Sustainability: Offering lower-priced options can align with sustainability goals. Companies can make eco-friendly or socially responsible products accessible to a broader audience, contributing to positive environmental and societal impact.
Data Collection: Varied price points provide opportunities to collect valuable data on customer preferences and willingness to pay. This data can inform pricing adjustments and product development strategies.
Market Resilience: Diversified pricing strategies make companies more resilient in the face of economic fluctuations. They can pivot between price points as market conditions change, ensuring continued customer engagement.
In conclusion, accommodating diverse customer groups with different price points is a multifaceted strategy that extends beyond revenue generation. It influences market segmentation, customer loyalty, brand perception, and innovation. By embracing price differentiation, companies can navigate dynamic market landscapes more effectively and build lasting relationships with a broad and varied customer base.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: CEIS Tor Vergata The value of personal information in markets with …

Optimized Inventory Management
Businesses can reduce excess inventory by adjusting prices to stimulate demand during off-peak periods.
nullTo expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: The Ultimate Guide to Amazon Dynamic Pricing Strategy in 2023

Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Consumers who are price-sensitive benefit from lower prices, while those willing to pay more enjoy premium offerings, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
The concept of tailoring pricing strategies to cater to both price-sensitive and value-conscious consumers represents a win-win scenario for businesses and their diverse customer base. This approach goes beyond mere pricing; it fosters customer satisfaction by aligning products and services with individual preferences and budgets, creating a more harmonious customer experience. Here’s an extended perspective on how catering to different customer segments through varied pricing strategies can elevate satisfaction levels:
1. Inclusivity and Accessibility: By offering lower-priced options, businesses ensure that their products or services are accessible to a broader range of consumers. Price-sensitive customers, who may have previously been unable to engage with the brand, now find an entry point. This inclusivity not only broadens the customer base but also fosters a sense of equity and affordability, enhancing overall customer satisfaction.
2. Value and Affordability: Price-sensitive consumers value affordability and are more likely to perceive the brand positively when they can access products or services that meet their budget constraints. These customers often become loyal patrons because they recognize the brand’s commitment to delivering value at an accessible price point.
3. Premium Offerings for Discerning Customers: On the flip side, catering to consumers willing to pay more enables businesses to offer premium products or services. This appeals to customers seeking enhanced features, superior quality, or a more exclusive experience. These premium offerings cater to their specific needs, resulting in increased customer satisfaction due to the alignment between expectations and delivery.
4. Personalization and Customization: Offering a range of pricing options allows businesses to personalize and customize their offerings to suit different segments of their customer base. Customers appreciate when a brand understands their unique preferences and needs, leading to higher satisfaction levels and stronger brand loyalty.
5. Competitive Advantage: By offering a spectrum of pricing choices, businesses gain a competitive edge. They can adapt to changing market conditions and consumer preferences more effectively than competitors with rigid pricing structures. This adaptability enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring that the brand remains relevant and responsive to evolving needs.
6. Perceived Value: Customers often associate pricing with value. When businesses offer tiered pricing, it can enhance the perceived value of their products or services. Price-sensitive consumers perceive affordability as value, while premium customers view higher prices as indicative of superior quality or exclusivity.
7. Loyalty and Advocacy: Satisfied customers are more likely to become brand advocates and loyal supporters. Price-sensitive customers who appreciate accessible pricing share their positive experiences, while premium customers become brand advocates when they receive exceptional value and service commensurate with their investment.
8. Customer-Centric Approach: The flexibility to cater to diverse customer segments reflects a customer-centric approach. Customers appreciate when businesses prioritize their needs and preferences, leading to higher satisfaction and a stronger emotional connection to the brand.
In conclusion, tailoring pricing strategies to accommodate both price-sensitive and premium-conscious customers fosters a balanced and customer-centric approach. It’s a strategy that acknowledges the diverse needs and budgets of the customer base, resulting in increased satisfaction levels across the board. By providing accessible options and premium offerings, businesses can create a positive and harmonious customer experience that not only drives loyalty but also positions the brand for sustainable growth and success in today’s competitive marketplace.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Understanding Customer Experience Throughout the Customer …

Ethical Considerations
While price discrimination can be a powerful revenue optimization strategy, businesses must be cautious and ethical in its implementation:
While price discrimination undoubtedly offers businesses a potent tool for revenue optimization, it comes with a set of considerations that necessitate a cautious and ethical approach to implementation. Striking the right balance between profit maximization and fairness to customers is paramount. Let’s explore these considerations in depth:
Fairness and Transparency: Price discrimination should be conducted with fairness and transparency in mind. Customers should have a clear understanding of why prices vary, such as based on the timing of their purchase, their location, or their membership status. Ensuring that customers perceive the practice as equitable is essential for maintaining trust.
Avoiding Discrimination Bias: Businesses must avoid any form of discrimination that is unethical, illegal, or discriminatory against certain groups. Discriminating based on factors like race, gender, religion, or disability is not only unethical but also illegal in many jurisdictions. It’s essential to implement price discrimination strategies that are free from bias.
Data Privacy: Collecting and using customer data for price discrimination requires stringent data privacy practices. Businesses must adhere to relevant data protection regulations like GDPR or CCPA and be transparent with customers about how their data is used in pricing decisions.
Communication and Consent: Informing customers about price variations and obtaining their consent, when necessary, is crucial. Customers should be aware of how their actions, such as signing up for loyalty programs or sharing information, can influence pricing. Consent-based pricing ensures customers are willingly participating in the arrangement.
Balancing Long-Term Relationships: Overzealous price discrimination can harm long-term customer relationships. Businesses should consider the potential repercussions of excessively high prices on customer loyalty and satisfaction. Maintaining a balance between short-term profit gains and long-term customer relationships is key.
Competitive Considerations: Price discrimination should be implemented carefully in competitive markets. Drastic price differences that are perceived as unfair can lead to negative public perception and backlash, potentially damaging a brand’s reputation.
Economic Efficiency: Price discrimination is most effective when it enhances overall economic efficiency. It can result in more efficient resource allocation, benefiting both businesses and consumers. However, businesses must ensure that price discrimination does not lead to market inefficiencies or anti-competitive behavior.
Regular Review and Monitoring: Price discrimination strategies should be subject to regular review and monitoring. Businesses should assess the impact of these strategies on their customer base, competitive positioning, and profitability. Adjustments may be necessary to align with changing market dynamics.
Customer Experience: Customer experience remains paramount. Price discrimination should not compromise the quality of products or services provided to customers. Customers paying different prices should still receive a consistent and satisfactory experience.
Legal Compliance: Staying compliant with local, national, and international laws is non-negotiable. Businesses must understand the legal landscape regarding price discrimination in their operating regions and adhere to relevant regulations.
In conclusion, while price discrimination can be a valuable revenue optimization strategy, it demands a delicate balance between maximizing profits and ethical considerations. Businesses should prioritize fairness, transparency, and customer trust in their pricing practices. By doing so, they can harness the potential benefits of price discrimination while mitigating the risks associated with its implementation, ultimately fostering a stronger and more enduring relationship with their customer base.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Consumer Welfare and Price Discrimination: A Fine Line

Transparency
Companies should be transparent about their pricing policies and avoid hidden fees or discriminatory practices that may alienate customers.
Transparency in pricing is not just a business practice; it’s a fundamental cornerstone of building trust and credibility with customers. To achieve this, companies should adopt a commitment to honesty and clarity in their pricing policies while actively avoiding practices that can alienate their valued customers.
Clear and Honest Communication: Transparency starts with clear and honest communication. Companies should provide customers with all the information they need to make informed decisions about their purchases. This includes presenting prices, taxes, and fees in a straightforward manner, leaving no room for ambiguity.
No Hidden Fees: Hidden fees are one of the quickest ways to erode trust. Companies should strive to eliminate hidden or unexpected charges in their pricing structures. Customers appreciate knowing the full cost upfront, and surprise fees can lead to frustration and dissatisfaction.
Consistency: Consistency in pricing is vital. Companies should ensure that their pricing remains consistent across different channels and customer segments. Offering special deals or discounts to certain customers, while charging others more for the same product or service, can lead to a perception of unfairness and discrimination.
Accessibility of Information: Make pricing information easily accessible. This includes having a comprehensive pricing page on your website, providing detailed breakdowns of costs, and being responsive to customer inquiries about pricing. Customers should feel that the information they need is readily available.
Fair Pricing Practices: Companies should avoid discriminatory pricing practices that alienate certain customer groups. Discriminatory practices, such as price gouging during crises or price discrimination based on demographic factors, can harm a company’s reputation and customer loyalty.
Value Proposition: Demonstrating the value of your product or service is essential in pricing transparency. Customers are more likely to accept a higher price if they see the value it brings. Clearly communicate the benefits and features that justify the price, helping customers understand what they’re getting in return.
Feedback and Improvement: Solicit feedback from customers regarding pricing. This can help identify any pain points or areas where transparency can be improved. Act on this feedback to continuously refine pricing policies and practices.
Educate Customers: Educate your customers about your pricing structure. Help them understand why certain costs exist, such as taxes or service fees. When customers are informed about the rationale behind pricing, they are more likely to accept it.
Ethical Considerations: Consider the ethical implications of your pricing decisions. Avoid tactics that may exploit vulnerabilities or unfairly disadvantage certain customer groups. Ethical pricing not only fosters trust but also contributes to long-term brand reputation.
Legal Compliance: Ensure that your pricing practices are in compliance with local and national laws and regulations. Violating pricing laws can lead to legal troubles and severe damage to your brand’s reputation.
In a world where consumers have access to extensive information and options, transparent pricing practices are a competitive advantage. Companies that prioritize transparency not only build trust but also cultivate long-lasting relationships with their customers, fostering loyalty and positive word-of-mouth recommendations.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: No 117 – Fintech and the digital transformation of financial services …

Fairness
Discrimination should not lead to unfair treatment or exploitation of vulnerable customer groups. Prices should reflect actual differences in costs or value.
nullFor a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Personalised Pricing in the Digital Era

Data Privacy
Collecting and using customer data for price discrimination should adhere to data privacy regulations and customer consent.
In today’s data-driven landscape, the ethical and legal considerations surrounding the collection and utilization of customer data for price discrimination are of paramount importance. While optimizing pricing strategies is a legitimate business goal, it must be pursued in a manner that respects the rights and privacy of consumers. Here’s an extended perspective on why adhering to data privacy regulations and obtaining customer consent are crucial in the context of price discrimination:
1. Ethical Responsibility: Businesses have an ethical responsibility to treat their customers with fairness and transparency. Engaging in price discrimination without proper consent or in violation of privacy regulations can erode trust and damage brand reputation. Upholding ethical standards in pricing practices is vital for long-term customer loyalty.
2. Legal Compliance: The regulatory landscape surrounding data privacy is evolving rapidly. Governments and authorities worldwide are enacting stringent data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Violating these regulations can result in severe penalties and legal consequences. Adhering to data privacy laws is not just a choice but a legal obligation.
3. Customer Trust: Price discrimination practices that lack transparency can undermine customer trust. When customers discover that they have been subjected to differential pricing without their knowledge or consent, it can lead to frustration and disillusionment. Trust is hard-earned and easily lost in today’s hyperconnected world.
4. Consent-Based Personalization: Customers appreciate personalized experiences when they have opted in and provided their consent. By obtaining explicit consent for data collection and personalized pricing, businesses can create a win-win scenario. Customers receive tailored offers that genuinely resonate with their preferences, while businesses benefit from increased customer satisfaction and potentially higher sales.
5. Reputation Management: Reputation is a priceless asset in the digital age. Public perception matters, and instances of unethical or non-compliant price discrimination can quickly become public knowledge through social media and news outlets. Managing reputation risks should be a top priority for businesses.
6. Long-Term Customer Relationships: Sustainable customer relationships are built on trust and mutual respect. Businesses should view customer data as a valuable resource that needs to be protected and handled responsibly. Customers are more likely to maintain long-term relationships with companies that prioritize their privacy and data security.
7. Competitive Advantage: Adhering to data privacy regulations and obtaining customer consent can be a source of competitive advantage. It sets businesses apart as responsible and customer-centric organizations that prioritize data ethics. This can attract customers who value transparency and data protection.
8. Mitigating Legal Risks: The consequences of non-compliance with data privacy regulations can be financially burdensome. Fines, legal battles, and damage control efforts can drain resources and disrupt business operations. Adhering to regulations and obtaining consent proactively mitigates these legal risks.
9. Customer Education: An essential aspect of obtaining consent is ensuring that customers understand how their data will be used, including for pricing purposes. Transparent communication and education about data practices can foster a sense of empowerment and informed decision-making among customers.
In conclusion, while price discrimination can be a legitimate strategy for optimizing revenues, it must be conducted ethically and in compliance with data privacy regulations. Upholding customer trust, legal compliance, and a commitment to transparent, consent-based practices are essential principles that should guide any business seeking to engage in price discrimination or personalized pricing. By doing so, businesses can strike the delicate balance between optimizing pricing strategies and maintaining ethical and legal integrity in the digital age.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Consumer Welfare and Price Discrimination: A Fine Line

Price discrimination is a dynamic pricing strategy that, when executed thoughtfully, can lead to optimal revenue generation for businesses. By recognizing the diversity in customer preferences and willingness to pay, companies can offer tailored pricing solutions that benefit both their bottom line and customer satisfaction. However, ethical considerations should always guide the implementation of price discrimination to ensure fairness and transparency in the marketplace.
Price discrimination, as a dynamic pricing strategy, holds the potential to be a win-win for both businesses and customers when approached with careful consideration. The practice acknowledges the inherent diversity in consumer preferences, affording companies the opportunity to fine-tune pricing solutions for maximum revenue. Let’s delve deeper into how price discrimination can be optimized, while keeping ethical principles at the forefront:
Segmentation Precision: Effective price discrimination begins with precise customer segmentation. Businesses should analyze data and consider various factors, such as demographics, purchase history, and behavior, to create distinct customer segments. This segmentation allows for tailored pricing strategies that align with the unique preferences and willingness to pay of each group.
Customized Offerings: Beyond pricing, companies can tailor product or service offerings to cater to different customer segments. This customization might involve bundling or unbundling features, creating subscription tiers, or offering exclusive access. Such customization not only maximizes revenue but also enhances customer satisfaction by delivering value-aligned solutions.
Dynamic Pricing Algorithms: Advanced algorithms and data analytics play a pivotal role in price discrimination success. By continuously analyzing real-time data, companies can adjust prices dynamically to respond to shifts in demand, inventory levels, or market conditions. This ensures that prices remain competitive and maximize revenue without alienating customers.
Transparency and Communication: Transparency is paramount in price discrimination to maintain customer trust. Businesses should clearly communicate the reasons behind pricing variations, emphasizing that they are based on factors like demand fluctuations or loyalty program benefits. Customers are more likely to accept varying prices when they understand the rationale.
Ethical Considerations: Ethical guidelines should underpin the entire process of price discrimination. Companies must avoid discriminatory practices that unfairly disadvantage certain customer groups or perpetuate biases. Ethical oversight is essential to ensure that price discrimination is used as a revenue optimization tool rather than a means of exploitation.
Customer Feedback Loop: Establishing a feedback loop with customers can provide valuable insights into the perceived fairness of pricing strategies. By actively seeking and listening to customer feedback, businesses can adapt their pricing practices to align more closely with customer expectations and ethical standards.
Regular Audits and Assessments: Price discrimination strategies should undergo regular audits and assessments to evaluate their impact on customer satisfaction and overall business performance. This ongoing evaluation ensures that pricing practices remain in harmony with ethical guidelines and yield positive results.
Competitive Intelligence: Businesses should also consider the competitive landscape when implementing price discrimination. Understanding how competitors price their products or services can help companies strike a balance between revenue optimization and remaining competitive in the market.
Value-Added Services: To mitigate potential negative reactions to price discrimination, companies can complement it with value-added services or benefits. For instance, offering personalized recommendations, excellent customer service, or loyalty rewards can offset any concerns customers may have about pricing disparities.
Long-Term Customer Relationships: Price discrimination should be viewed as a means to enhance long-term customer relationships. Businesses that focus on customer satisfaction and loyalty through fair and well-communicated pricing practices are more likely to build lasting connections with their clientele.
In conclusion, price discrimination, when executed thoughtfully and ethically, can be a powerful strategy for revenue optimization. It acknowledges the diversity in customer preferences and willingness to pay, allowing businesses to offer tailored pricing solutions that benefit both their bottom line and customer satisfaction. By incorporating customer segmentation, transparency, ethical considerations, and continuous evaluation into their pricing strategies, companies can strike the right balance, ensuring fairness and transparency in the marketplace while maximizing revenue.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: The Root Causes of Health Inequity – Communities in Action – NCBI …
More links
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Consumer Welfare and Price Discrimination: A Fine Line
