Table of Contents
In the ever-evolving landscape of commerce, businesses grapple with a crucial challenge
determining the optimal price for their products or services. Price plays a pivotal role in market dynamics, influencing consumer behavior, competition, and a company’s bottom line. To navigate this complex terrain, economic analysis, particularly the concept of market equilibrium, plays a central role in guiding price determination and shaping effective marketing strategies. In this article, we will explore the profound significance of economic analysis in the realm of marketing.
Determining the optimal price for products or services is a fundamental challenge for businesses across industries. Price is not just a number on a tag; it’s a strategic lever that profoundly influences market dynamics, consumer behavior, competition, and ultimately, a company’s bottom line. In this ever-evolving marketplace, economic analysis, and particularly the concept of market equilibrium, emerges as a guiding compass for price determination and the formulation of effective marketing strategies. Let’s delve deeper into the profound significance of economic analysis in the realm of marketing:
Market Dynamics and Competitive Edge: The dynamics of a market are inextricably linked to pricing strategies. Economic analysis helps companies grasp the intricacies of supply and demand, identifying equilibrium points where the quantity of goods or services supplied equals the quantity demanded. By understanding these dynamics, businesses can identify market gaps, anticipate shifts in demand, and adjust prices to gain a competitive edge.
Consumer Behavior and Perceived Value: Consumers are sensitive to price changes, and their purchasing decisions are often driven by perceived value. Economic analysis, through concepts like consumer surplus and elasticity, allows companies to comprehend how price adjustments influence consumer behavior. It empowers businesses to strike the right balance between pricing their offerings competitively and ensuring that consumers perceive value in their purchases.
Profit Maximization and Revenue Strategies: At its core, every business aims to maximize profits. Economic analysis guides this pursuit by helping companies optimize pricing to achieve the highest revenue while factoring in production costs, competition, and consumer demand. Differentiation in pricing strategies, such as dynamic pricing or price discrimination, can be fine-tuned with economic insights to meet profit objectives.
Market Segmentation and Personalization: Not all consumers are alike, and economic analysis plays a pivotal role in segmenting the customer base based on price sensitivity. By understanding the elasticity of demand within different segments, companies can tailor pricing and marketing strategies to resonate with specific customer groups. Personalization is key to capturing the diverse preferences and behaviors of consumers.
Strategic Decision-Making: Economic analysis is an essential tool for making strategic decisions. It guides decisions regarding product positioning, entry into new markets, and expansion strategies. By modeling various scenarios and analyzing market conditions, companies can make informed choices that align with their overarching goals.
Ethical Pricing Practices: Ethical considerations are integral to pricing decisions. Economic analysis ensures that prices remain fair and transparent. Companies must strike a balance between profit motives and ethical pricing practices to maintain trust with consumers and uphold their brand reputation.
Market Research and Data Analysis: Economic analysis often requires a thorough examination of market data, from historical pricing trends to consumer surveys. This data-driven approach allows businesses to refine pricing strategies continually and adapt to evolving market conditions.
Navigating External Factors: The economic landscape is subject to external factors, such as economic recessions, inflation, and regulatory changes. Economic analysis provides businesses with the tools to navigate these challenges, make proactive adjustments, and maintain profitability in turbulent times.
In conclusion, economic analysis serves as a cornerstone in the world of marketing, shaping how companies determine prices and formulate their strategies. It empowers businesses to not only respond to market dynamics but also proactively influence them. As the marketplace evolves, the significance of economic analysis in guiding pricing decisions and marketing strategies remains undeniably profound, enabling businesses to thrive in an ever-changing and competitive landscape.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: How retailers can keep up with consumers | McKinsey

Understanding Market Equilibrium
At the heart of economic analysis is the concept of market equilibrium. Market equilibrium represents the point at which the quantity of a product or service demanded by consumers matches the quantity supplied by producers. In simpler terms, it’s the sweet spot where supply meets demand.
At the heart of economic analysis is the concept of market equilibrium. Market equilibrium represents the point at which the quantity of a product or service demanded by consumers matches the quantity supplied by producers. In simpler terms, it’s the sweet spot where supply meets demand. Understanding the dynamics and implications of market equilibrium is fundamental for both businesses and policymakers, and it holds several key insights:
Price Stability: Market equilibrium typically results in price stability. When supply and demand are in balance, there is no significant pressure for prices to rise or fall. This predictability is beneficial for both consumers and producers, as it allows for better planning and decision-making.
Efficient Allocation: Market equilibrium ensures that resources are allocated efficiently. Goods and services are distributed to those who value them the most. Inefficiencies arise when there is an excess supply (surplus) or excess demand (shortage) because resources are not being used optimally.
Consumer Welfare: Market equilibrium is often associated with consumer welfare because it signifies that consumers can obtain the goods and services they desire at reasonable prices. This enhances consumer satisfaction and purchasing power.
Producer Profitability: For producers, market equilibrium is a desirable state because it implies that they can sell their products at a price that covers their costs and generates profit. This encourages businesses to continue producing and investing in their operations.
Dynamic Nature: It’s essential to recognize that market equilibrium is not a static state. Markets are dynamic and subject to constant changes in supply and demand. Economic events, technological advancements, consumer preferences, and external factors can all shift the equilibrium point.
Role of Prices: Prices play a critical role in the market equilibrium process. They act as signals that convey information about supply and demand conditions. When demand exceeds supply, prices tend to rise, signaling producers to increase production. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, prices tend to fall, signaling producers to reduce output.
Government Intervention: Governments may intervene in markets to influence or stabilize market equilibrium. For example, they can implement price controls, subsidies, or tariffs to address market imbalances or achieve specific policy objectives.
Market Disequilibrium: Market equilibrium is not always achieved, and markets can experience periods of disequilibrium, characterized by surpluses or shortages. These imbalances can create opportunities for arbitrage, speculation, and market corrections.
Elasticity and Equilibrium: The concept of elasticity, which measures the responsiveness of supply and demand to price changes, is closely linked to market equilibrium. Highly elastic goods may experience frequent shifts in equilibrium, while inelastic goods may have more stable equilibriums.
Global Impact: Market equilibrium is not limited to local markets; it also applies to international trade. Understanding the equilibrium price of goods in global markets is crucial for international trade negotiations and the flow of goods across borders.
In summary, market equilibrium is a central concept in economics that has far-reaching implications for the functioning of markets and the allocation of resources. It reflects the delicate balance between supply and demand and serves as a foundation for decision-making in both the business world and public policy. Recognizing the dynamic nature of market equilibrium is essential for adapting to changing economic conditions and maintaining a healthy and efficient marketplace.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: 9. The labour market: Wages, profits, and unemployment – The …
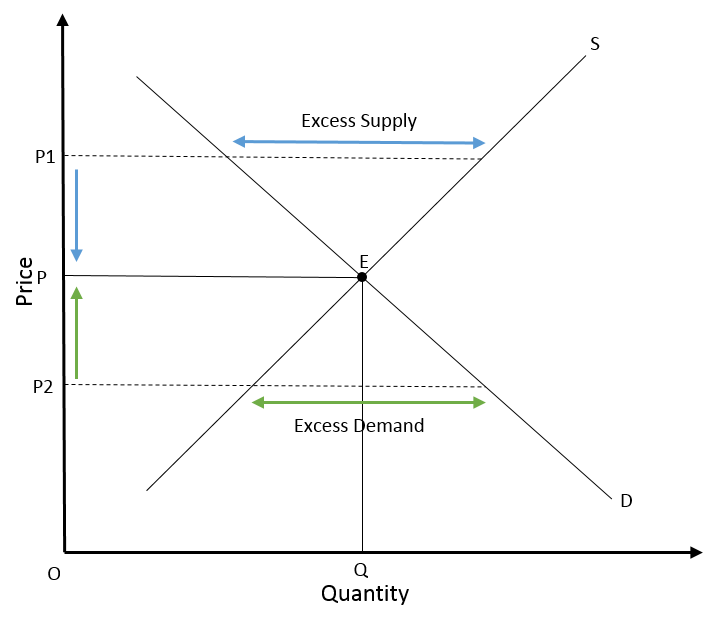
Role of Economic Analysis in Price Determination
Economic analysis, through the lens of market equilibrium, significantly influences price determination in marketing:
nullIf you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Equilibrium Price: Definition, Types, Example, and How to Calculate
Economics as the Compass in Marketing
In the dynamic world of marketing, economic analysis serves as the compass guiding businesses through the intricacies of price determination and market equilibrium. It empowers companies to navigate competitive landscapes, allocate resources efficiently, and craft value propositions that resonate with consumers. As businesses strive to achieve their objectives in a constantly evolving marketplace, the role of economics in marketing remains indispensable, offering valuable insights that drive strategic decision-making and ultimately lead to success.
“In the dynamic world of marketing, economic analysis serves as the compass guiding businesses through the intricacies of price determination and market equilibrium. It empowers companies to navigate competitive landscapes, allocate resources efficiently, and craft value propositions that resonate with consumers.
Efficient Resource Allocation: Economic analysis helps businesses allocate their resources wisely. By understanding the cost structures and profit margins associated with various products and services, companies can make informed decisions about where to invest their marketing budgets. This optimization ensures that resources are channeled into strategies that yield the highest returns.
Pricing Strategies: Price is a critical element of marketing, and economic analysis provides the tools to determine optimal pricing strategies. It considers factors like demand elasticity, competitor pricing, and production costs to strike a balance between maximizing profits and appealing to consumers. Effective pricing strategies are crucial for achieving both short-term revenue goals and long-term sustainability.
Consumer Behavior Insights: Economics delves into consumer behavior, unraveling the complex motivations behind purchasing decisions. This insight is invaluable for tailoring marketing messages and product offerings to meet the needs and preferences of target audiences. By understanding the psychology of buyers, businesses can create more compelling and resonant marketing campaigns.
Market Dynamics: The ever-changing marketplace requires businesses to adapt swiftly. Economic analysis equips them with the ability to monitor market trends, anticipate shifts in demand, and identify emerging opportunities. This proactive stance helps companies stay ahead of the competition and seize favorable market conditions.
Strategic Decision-Making: In a data-driven era, strategic decision-making is paramount. Economics provides the analytical framework for evaluating the potential outcomes of various marketing strategies. Through scenario analysis and forecasting, businesses can make choices that align with their overarching objectives and respond effectively to market challenges.
Continuous Improvement: The role of economics in marketing extends to fostering a culture of continuous improvement. By regularly assessing the performance of marketing initiatives, businesses can refine their strategies, adapt to changing consumer preferences, and remain innovative in their approaches.
Global Market Expansion: In an era of globalization, economics plays a crucial role in helping businesses expand into international markets. It provides insights into the economic conditions, regulatory environments, and consumer behaviors of diverse regions, aiding in successful market entry and growth.
In summary, the role of economics in marketing is multifaceted and ever-relevant. It offers a strategic foundation for businesses to navigate the complexities of the modern marketplace, make data-driven decisions, and ultimately achieve success in a dynamic and competitive environment.”
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: The Future of Jobs Report 2020 | World Economic Forum
More links
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Supply and demand | Definition, Example, & Graph | Britannica Money
