Table of Contents
- The Marriage of Marketing and Trade Economics
- Market Access and Expansion
- Competitiveness Enhancement
- Export Diversification
- Risk Mitigation
- Export Promotion as an Engine of Economic Growth
- Revenue Generation
- Job Creation
- Economies of Scale
- Technological Advancement
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
- Enhanced Productivity
- The Role of Government and Trade Promotion Agencies
- Policy Formulation
- Market Access
- Financial Support
- Market Research
- Brand Building
In the globalized world of commerce, the nexus between marketing strategies and trade economics plays a pivotal role in the prosperity of nations. One of the most effective tools in the arsenal of trade economics is export promotion—a multifaceted approach that not only fuels economic growth but also bolsters a country’s standing in the international market. This article explores the symbiotic relationship between marketing and trade economics, with a special focus on the critical role of export promotion in driving economic development.
In the intricate tapestry of the modern global economy, the interplay between marketing strategies and trade economics emerges as a linchpin, influencing the prosperity and growth of nations. At the heart of this dynamic lies the formidable tool of export promotion, a multifaceted strategy that not only fuels economic expansion but also enhances a country’s reputation and influence on the international stage. In this article, we delve deeper into the intricate symbiosis between marketing and trade economics, with a special emphasis on the pivotal role of export promotion in steering nations towards sustainable economic development.
Market Expansion through Export Promotion: Export promotion serves as a potent catalyst for a nation’s economic growth by facilitating market expansion beyond its borders. By strategically marketing their products and services to foreign markets, countries can tap into new customer bases, thereby diversifying their revenue streams and reducing dependence on domestic markets. This diversification acts as a buffer against economic downturns at home, ensuring more stable growth trajectories.
Enhancing Competitiveness: Effective marketing strategies are vital in making a country’s products and services competitive on the global stage. Through export promotion, nations can not only improve the quality and appeal of their offerings but also convey their unique value propositions to international consumers. This drives innovation, efficiency, and productivity improvements across industries, ultimately bolstering a country’s economic competitiveness.
Boosting Foreign Exchange Reserves: Export promotion results in increased foreign exchange earnings, a crucial component of a nation’s economic stability. A robust export sector contributes to a healthier balance of payments by generating more foreign currency than is spent on imports. This, in turn, helps maintain a stable exchange rate and cushions against currency fluctuations.
Job Creation and Skill Development: Export-oriented growth leads to job creation in various sectors, from manufacturing to logistics and marketing. These employment opportunities not only reduce unemployment rates but also foster skill development and knowledge transfer. A skilled workforce is an invaluable asset in today’s knowledge-based global economy.
Diplomatic and Geopolitical Significance: A nation’s ability to engage in international trade and promote its exports often enhances its diplomatic and geopolitical significance. Export promotion can serve as a bridge for diplomacy and cooperation with trading partners, paving the way for stronger diplomatic ties and negotiation power on the global stage.
Sustainable Development Goals: Sustainable economic development is increasingly prioritized by nations worldwide. Export promotion can align with sustainability goals by encouraging the export of environmentally friendly products and promoting responsible business practices. This synergy helps countries address pressing global issues while fostering economic growth.
Reputation and Soft Power: Successful export promotion not only boosts a country’s economic standing but also elevates its global reputation and soft power. The positive image of a nation as a reliable and innovative trade partner can attract foreign investment, tourism, and cultural exchanges, furthering its influence in the global arena.
In conclusion, the synergy between marketing strategies and trade economics is a cornerstone of modern economic prosperity. Export promotion, as a vital tool in this synergy, empowers nations to unlock their economic potential, enhance their global standing, and navigate the complexities of international commerce. It is a force that propels countries toward sustainable economic development while simultaneously strengthening their role in the interconnected world of global trade.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Overview: Development news, research, data | World Bank
The Marriage of Marketing and Trade Economics
At first glance, marketing and trade economics might seem like distant cousins. However, upon closer examination, it becomes evident that they share a profound connection:
At first glance, marketing and trade economics might seem like distant cousins. However, upon closer examination, it becomes evident that they share a profound connection: both are integral components of the intricate web that defines the modern global marketplace.
Marketing is often perceived as the art of promoting products or services to consumers, creating demand, and establishing brand identity. On the other hand, trade economics appears to be more focused on the quantitative aspects of international exchange, including tariffs, trade balances, and exchange rates. Despite these apparent differences, they are inextricably linked in the world of commerce.
One of the most striking connections between marketing and trade economics lies in the concept of international trade itself. Marketing serves as the driving force behind trade, as it shapes consumer preferences, influences purchasing decisions, and ultimately facilitates the flow of goods and services across borders. Effective marketing strategies can create demand for products not only within domestic markets but also in international arenas, stimulating exports and imports.
Furthermore, marketing and trade economics converge in the realm of market research and analysis. Both disciplines rely on data and insights to make informed decisions. Marketers conduct market research to identify target audiences, consumer behavior, and competitive landscapes. Similarly, trade economists analyze data to determine market trends, assess the impact of trade policies, and predict future trade patterns. The synergy between these two fields becomes apparent as they both strive to understand and navigate the complex dynamics of global markets.
Moreover, branding and image play a pivotal role in both marketing and trade economics. A strong and reputable national or corporate brand can significantly impact a country’s export potential. Positive brand associations can enhance consumer trust, making it easier for products to gain access to foreign markets and commanding premium prices. Likewise, trade economists often consider a country’s image and reputation when evaluating trade agreements or assessing the willingness of trading partners to engage in commerce.
The globalization of markets has further intertwined marketing and trade economics. With the advent of digital technology and e-commerce, businesses can reach customers worldwide, blurring the lines between domestic and international marketing efforts. Trade policies and agreements, influenced by economic theories, have a direct impact on a company’s ability to access and compete in foreign markets.
In conclusion, marketing and trade economics, although appearing as separate domains, are interconnected facets of the global economic landscape. Their collaboration is essential for businesses, policymakers, and researchers striving to understand and thrive in today’s complex, interconnected, and ever-evolving world of commerce. Recognizing the profound connection between marketing and trade economics can lead to more informed decisions and strategies that promote sustainable growth and prosperity on a global scale.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: THE ECONOMIC BENEFITS OF US TRADE | Obama White House …

Market Access and Expansion
Effective marketing strategies create demand for products and services, driving businesses to seek new markets. Trade economics comes into play by facilitating access to these markets. Trade agreements, tariff negotiations, and market analysis all form the bridge between marketing initiatives and the global market.
Effective marketing strategies create demand for products and services, driving businesses to seek new markets. Trade economics comes into play by facilitating access to these markets. Trade agreements, tariff negotiations, and market analysis all form the bridge between marketing initiatives and the global market.
Here’s how the intricate dance between marketing and trade economics unfolds to benefit businesses:
Market Expansion: Successful marketing campaigns generate interest and demand for a product or service. As a company’s customer base grows, it naturally seeks expansion beyond its domestic market. Trade economics helps identify and navigate these new opportunities on the global stage.
Market Research: Before venturing into new markets, thorough market research is essential. Trade economics provides valuable insights into the economic conditions, consumer behavior, and regulatory environment of potential target markets. This data helps businesses tailor their marketing strategies to the specific needs and preferences of each market.
Tariff and Regulatory Compliance: When operating in foreign markets, businesses must navigate a complex web of tariffs, trade regulations, and customs procedures. Trade economists assist in understanding these intricacies, ensuring that companies can import and export their products efficiently and in compliance with local laws.
Trade Agreements: Trade agreements play a pivotal role in market access. Businesses benefit from trade agreements that reduce or eliminate trade barriers, such as tariffs or quotas. Understanding the terms and conditions of these agreements is essential for businesses to plan their market entry and expansion strategies effectively.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Expanding into international markets involves certain risks, including currency fluctuations, geopolitical instability, and regulatory changes. Trade economists assess these risks and develop strategies to mitigate them, providing businesses with a clearer picture of potential challenges.
Cost Optimization: Trade economics helps businesses optimize their supply chains and logistics to minimize costs. Efficient supply chains translate into competitive pricing, making products more attractive to consumers and enhancing the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
Competitive Analysis: Trade economics also involves analyzing the competitive landscape in target markets. Understanding local competitors and their strategies is crucial for businesses to position themselves effectively and develop marketing campaigns that stand out.
Cultural Sensitivity: Effective marketing in international markets requires cultural sensitivity. Trade economics experts can provide insights into the cultural nuances of each market, helping businesses craft messages and campaigns that resonate with local audiences.
Government Relations: Establishing positive relations with government entities in foreign markets can be vital. Trade economists can help businesses engage with local authorities, navigate regulatory processes, and build partnerships that facilitate market entry and growth.
Adaptability: The global market is ever-evolving, and trade economics ensures that businesses remain adaptable. By continuously monitoring market conditions and policy changes, companies can adjust their marketing strategies to seize new opportunities or address challenges.
In the modern business landscape, the synergy between marketing and trade economics is essential for global success. While marketing creates the demand, trade economics paves the way for businesses to access and thrive in new markets, ultimately driving growth, expanding brand reach, and increasing profitability on a global scale.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Global Trade Liberalization and the Developing Countries — An IMF …

Competitiveness Enhancement
Marketing promotes the competitiveness of a nation’s goods and services on the international stage. Through branding, quality assurance, and differentiation, marketing can elevate products to a position of superiority in the global marketplace. Trade economics policies ensure that these products can compete fairly with others.
nullDon’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Executive Order on Promoting Competition in the American Economy

Export Diversification
Marketing helps identify untapped markets and consumer preferences. By leveraging these insights, businesses can diversify their export portfolio, reducing dependency on a single market or product. Trade economics incentivizes and facilitates such diversification by easing trade barriers and fostering global partnerships.
Marketing not only plays a pivotal role in identifying untapped markets and understanding consumer preferences but also serves as the gateway to effective diversification strategies in the global marketplace. Here’s an extended exploration of how this process unfolds:
Market Discovery: Marketing research and analysis are instrumental in uncovering new markets with untapped potential. By examining consumer behavior, demographics, and emerging trends, businesses can pinpoint regions or niches that align with their products or services.
Consumer Preferences: Beyond identifying new markets, marketing also delves deep into consumer preferences. It provides insights into what customers value, whether it’s sustainability, convenience, price sensitivity, or other factors. Armed with this knowledge, businesses can tailor their offerings to align with these preferences.
Diversification Strategies: Once untapped markets and consumer preferences are identified, businesses can develop diversification strategies. These strategies may involve adapting existing products, creating new ones, or modifying marketing approaches to resonate with specific target audiences. Diversification mitigates the risk associated with relying solely on a single market or product.
Reducing Dependency: Overdependence on a single market or product can be risky. Economic downturns, political instability, or shifts in consumer behavior can have a detrimental impact. Diversification, as driven by marketing insights, helps businesses reduce this dependency, creating a safety net that can cushion them against adverse market conditions.
Trade Economics Facilitation: Trade economics plays a critical role in incentivizing and facilitating diversification efforts. Government policies, trade agreements, and international partnerships can ease trade barriers, making it more cost-effective and logistically feasible for businesses to enter new markets.
Tariff Reduction: One of the significant ways trade economics promotes diversification is through tariff reduction or elimination. Trade agreements and negotiations strive to create a more level playing field by reducing tariffs on imported and exported goods, making it financially viable for businesses to explore new markets.
Global Partnerships: Trade agreements also foster global partnerships. By engaging in mutually beneficial trade relationships, businesses can gain access to new markets and distribution networks. This paves the way for export portfolio diversification.
Risk Mitigation: Diversification is inherently a risk mitigation strategy. By spreading their operations across multiple markets, businesses decrease their exposure to market-specific risks, such as economic downturns, political instability, or supply chain disruptions.
Competitive Advantage: Companies that effectively leverage marketing insights to diversify their export portfolios often gain a competitive advantage. They can offer a wider range of products or services, making them more attractive to diverse customer bases.
Sustainable Growth: Diversification driven by marketing insights isn’t just about short-term risk mitigation. It also supports sustainable growth. By continually identifying and entering new markets that align with consumer preferences, businesses can maintain a steady growth trajectory over the long term.
In conclusion, marketing’s role in identifying untapped markets and understanding consumer preferences is the first step in a broader strategy of export portfolio diversification. When combined with favorable trade economics, this strategy can help businesses reduce risk, enhance competitiveness, and achieve sustainable global growth. By adapting to changing market dynamics and consumer demands, companies can position themselves for success in an increasingly interconnected world.
You can also read more about this here: Canada’s Indo-Pacific Strategy

Risk Mitigation
International marketing strategies expose businesses to currency fluctuations, geopolitical risks, and market volatilities. Trade economics, through mechanisms like export credit insurance and risk assessment, helps mitigate these uncertainties, providing a safety net for exporters.
International marketing strategies expose businesses to currency fluctuations, geopolitical risks, and market volatilities. Trade economics, through mechanisms like export credit insurance and risk assessment, helps mitigate these uncertainties, providing a safety net for exporters. Here’s how trade economics plays a crucial role:
Currency Risk Management: Trade economics involves strategies to manage currency risk. By utilizing financial instruments such as forward contracts or options, businesses can hedge against adverse currency movements. This safeguard ensures that fluctuations in exchange rates don’t erode their profits when conducting international transactions.
Market Research and Entry Strategies: Trade economists conduct in-depth market research to identify opportunities and risks in foreign markets. They help businesses formulate entry strategies that align with the economic and regulatory conditions of the target market, reducing the likelihood of costly missteps.
Supply Chain Optimization: Efficient supply chain management is fundamental to international trade. Trade economists analyze supply chain costs, lead times, and risks, helping businesses optimize their logistics to minimize disruptions and lower operational expenses.
Geopolitical Risk Assessment: Understanding geopolitical dynamics is essential when expanding internationally. Trade economists assess the political stability and regulatory environment of target countries, allowing businesses to make informed decisions about market entry and risk mitigation.
Export Credit Insurance: Trade economics facilitates the use of export credit insurance, which protects exporters against the risk of non-payment by foreign buyers. This insurance provides financial security and confidence for businesses exploring new markets.
Tariff and Trade Barrier Analysis: Trade economists help businesses navigate complex international trade regulations, tariffs, and trade barriers. They identify potential obstacles and assist in developing strategies to minimize the impact of these barriers on trade flows.
Market Diversification: Trade economics encourages market diversification, reducing dependency on a single market. This strategy spreads risk and makes businesses less vulnerable to economic downturns in specific regions.
Risk Mitigation Strategies: Beyond insurance, trade economists help companies develop comprehensive risk mitigation strategies. These strategies may include diversifying suppliers, setting up contingency plans, and staying adaptable in response to changing market conditions.
Financial Planning and Budgeting: Trade economics assists in financial planning and budgeting for international expansion. It helps businesses allocate resources effectively and manage cash flow, reducing the financial strain associated with global trade.
Trade Policy Advocacy: Trade economists often advocate for businesses’ interests in the development of trade policies. Their insights help shape favorable trade agreements and regulations that benefit exporters.
Monitoring and Adaptation: Trade economists continuously monitor market conditions and adjust strategies as needed. This agility ensures that businesses can respond quickly to unforeseen challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
In summary, trade economics is an invaluable tool for businesses venturing into international markets. It provides the knowledge and strategies necessary to navigate the complexities of global trade, manage risks, and seize opportunities for growth, ultimately fostering a more secure and prosperous international business environment.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Overview: Development news, research, data | World Bank

Export Promotion as an Engine of Economic Growth
Export promotion encompasses a wide array of strategies and policies designed to stimulate and support a nation’s export activities. Here’s how export promotion fuels economic growth:
Export promotion encompasses a wide array of strategies and policies designed to stimulate and support a nation’s export activities. These initiatives are not just about selling products or services across borders; they play a pivotal role in shaping a nation’s economic landscape and fostering sustainable growth. Here’s how export promotion fuels economic growth:
Boosting Domestic Industries: Export promotion encourages the growth and competitiveness of domestic industries. When local businesses expand their presence in international markets, they often invest in upgrading their products and processes to meet international standards. This, in turn, enhances their competitiveness at home and abroad.
Creating Jobs: Expanding export activities typically leads to an increase in job opportunities. As businesses grow and cater to international demand, they need a larger workforce to meet production and distribution requirements. This not only reduces unemployment rates but also enhances the standard of living for citizens.
Generating Revenue: Exporting goods and services generates foreign exchange earnings for a nation. This influx of foreign currency can be used to pay for imports, service foreign debt, or bolster foreign exchange reserves, all of which contribute to economic stability.
Economies of Scale: Serving international markets often requires companies to scale up their operations. This can lead to economies of scale, driving down production costs and making products more affordable for both domestic and international consumers. Lower costs can also lead to higher profit margins for businesses.
Encouraging Innovation: To remain competitive in global markets, companies must innovate. Export-oriented businesses are more likely to invest in research and development, leading to technological advancements and a culture of innovation within the country.
Attracting Foreign Investment: A thriving export sector can attract foreign investors looking to tap into a dynamic market. Foreign direct investment (FDI) can further stimulate economic growth by bringing in capital, expertise, and technology.
Diversifying Risk: Relying solely on the domestic market can expose a nation’s economy to fluctuations and downturns. Exporting allows for diversification of risk, as economic shocks in one market may be offset by stability in others.
Enhancing Global Reputation: Successful exports build a nation’s reputation for quality and reliability. This can extend beyond the specific industries involved and positively impact the perception of a nation’s products and services on the global stage.
In conclusion, export promotion is not just about selling products abroad; it’s a multifaceted approach that drives economic growth, strengthens domestic industries, and positions a nation competitively in the global marketplace. By fostering innovation, creating jobs, and increasing revenue, export promotion is a vital component of a nation’s economic development strategy.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Global Trade Liberalization and the Developing Countries — An IMF …

Revenue Generation
Exports generate substantial revenue for a country. The influx of foreign exchange strengthens a nation’s currency, stabilizes its financial markets, and provides resources for infrastructure development, education, and healthcare.
nullFor additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Global Trade Liberalization and the Developing Countries — An IMF …

Job Creation
Export-driven industries often require a larger workforce, leading to increased employment opportunities. This not only reduces unemployment rates but also enhances the overall standard of living.
Export-driven industries often have a significant impact on the labor market, creating a ripple effect that extends far beyond the confines of the industry itself. The need for a larger workforce in these sectors not only bolsters employment opportunities but also plays a pivotal role in elevating the overall standard of living in several ways.
Job Creation: Export-oriented industries tend to generate a multitude of job openings across various skill levels. From factory workers to logistics experts and marketing professionals, these sectors provide diverse employment opportunities. This inclusivity in hiring can help address unemployment issues and reduce dependency on government welfare programs.
Skills Development: As export-driven industries expand, they often invest in training and skill development programs for their employees. This not only enhances the employability of the workforce but also fosters a culture of continuous learning and professional growth, equipping individuals with valuable skills that can be applied in various contexts.
Higher Incomes: A thriving export-oriented industry can lead to higher wages and better compensation packages for employees. Increased demand for labor can push employers to offer competitive salaries and benefits, ultimately improving the economic well-being of workers and their families.
Economic Diversification: A robust export sector contributes to economic diversification, reducing reliance on a single industry or revenue source. This diversification makes the economy more resilient to external shocks and fluctuations, ultimately creating a more stable and prosperous environment for citizens.
Infrastructure Development: To support export activities, governments often invest in infrastructure development, including transportation networks, ports, and communication systems. These investments not only facilitate trade but also improve the overall quality of life by enhancing connectivity and accessibility.
Increased Tax Revenue: Export-driven industries contribute significantly to government revenues through taxes, tariffs, and export-related fees. These funds can be reinvested in public services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure, further elevating the standard of living for citizens.
Innovation and Technology Transfer: To remain competitive in the global market, export-focused companies frequently invest in research and development. This drive for innovation can lead to the development and adoption of advanced technologies, which can subsequently spill over into other industries, driving overall economic progress.
Global Trade Relationships: Export-oriented industries foster international trade relationships and collaborations. These connections can open doors for other businesses and industries, creating a network of global opportunities and partnerships.
Sustainable Growth: By focusing on global markets and adhering to international standards, export-driven industries often adopt sustainable practices. This commitment to sustainability not only benefits the environment but also positions the nation as a responsible global player.
In conclusion, the expansion of export-driven industries can be a catalyst for positive economic and social change. Beyond merely increasing job opportunities, these industries contribute to broader economic development, skills enhancement, and improved living standards for the population, making them a crucial driver of prosperity and progress in many regions.
You can also read more about this here: Economic Growth – United Nations Sustainable Development

Economies of Scale
Exporting on a global scale allows companies to exploit economies of scale, leading to cost efficiencies. As production levels increase, per-unit costs decrease, making products more competitive in international markets.
Expanding business operations to a global scale and tapping into international markets offer a multitude of advantages, with economies of scale being a significant driver. This approach not only enhances cost efficiencies but also unlocks a host of strategic benefits. Here’s an extended exploration of the idea:
Economies of Scale and Cost Efficiencies: Operating on a global scale allows businesses to take full advantage of economies of scale. As production levels increase, the average cost per unit decreases due to the spreading of fixed costs over a larger output. This reduction in per-unit costs directly contributes to cost efficiencies, enabling companies to offer competitive prices in international markets.
Global Market Access: Expanding internationally provides access to a vast and diverse customer base. It allows businesses to tap into emerging markets with growing consumer demand, reducing dependence on a single domestic market and mitigating the risks associated with economic downturns in specific regions.
Increased Sales Volume: Access to a global customer pool translates into higher sales volumes. Larger sales volumes can lead to enhanced revenue streams, improved cash flow, and greater profitability, all of which contribute to the financial strength of the business.
Risk Diversification: Operating in multiple markets diversifies business risks. Economic, geopolitical, or regulatory changes that may negatively impact one market can be offset by positive developments in others. This diversification strategy enhances resilience in the face of market-specific challenges.
Brand Recognition and Reputation: Expanding globally often enhances brand recognition and reputation. A global presence can lend credibility to a brand and reinforce the perception of stability and trustworthiness. This, in turn, attracts consumers and partners alike.
Access to Talent and Innovation: Operating in diverse geographic locations opens doors to a broader talent pool and diverse perspectives. Companies can tap into local expertise, foster innovation, and adapt products or services to suit regional preferences effectively.
Supply Chain Optimization: A global presence enables supply chain optimization. Companies can source materials and components from regions with cost advantages or proximity to suppliers, reducing logistics costs and improving supply chain resilience.
Competitive Advantage: By leveraging economies of scale, companies can gain a competitive advantage in international markets. Lower production costs allow for competitive pricing, product differentiation, or reinvestment in research and development, strengthening market positioning.
Global Partnerships and Alliances: International expansion fosters opportunities for global partnerships and alliances. Collaborating with local businesses or forming strategic alliances can enhance market penetration, distribution networks, and access to specialized knowledge.
Regulatory and Tax Benefits: Different countries offer various regulatory and tax incentives to attract foreign businesses. Companies can strategically choose locations that provide favorable regulatory environments, tax benefits, or financial incentives, further optimizing their operations.
Enhanced Innovation: Operating in a global context exposes businesses to diverse markets and consumer needs. This exposure can stimulate innovation, encouraging companies to adapt and refine their products or services to meet the demands of different cultures and regions.
Sustainability Initiatives: Global operations also open doors to sustainability initiatives. Businesses can adopt environmentally responsible practices, such as sustainable sourcing, reduced carbon emissions, and ethical labor practices, which resonate with eco-conscious consumers worldwide.
In conclusion, expanding operations on a global scale is not merely about extending market reach; it’s a strategic move that can significantly impact a company’s efficiency, profitability, and long-term sustainability. By exploiting economies of scale and reaping the associated benefits, businesses can position themselves for success in a competitive global landscape, while simultaneously contributing to economic growth and development in various regions across the world.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Overview: Development news, research, data | World Bank

Technological Advancement
To compete globally, businesses invest in research and development, leading to technological innovation. This innovation, often spurred by the necessity to meet international standards and consumer preferences, benefits the entire economy.
The pursuit of global competitiveness propels businesses into a realm of continual innovation and technological advancement. This endeavor to remain at the forefront of global markets goes beyond the mere quest for profits; it becomes a driving force that fosters innovation at a macroeconomic level, benefiting not only individual companies but the entire economy:
Technological Advancements: To compete effectively on a global scale, businesses engage in relentless research and development efforts. These investments yield technological advancements that have far-reaching implications. New technologies often find applications beyond their initial industries, resulting in a broader societal impact.
Job Creation: The drive for global competitiveness necessitates a skilled workforce. This requirement leads to the creation of high-quality jobs, which, in turn, enhances the economic well-being of individuals and families. The demand for skilled workers drives education and training initiatives, preparing the workforce for evolving industries.
Economic Growth: Businesses that invest in research and development contribute significantly to economic growth. Technological innovation drives productivity gains, which, in turn, boost GDP. As businesses expand globally, they stimulate economic activity in multiple sectors, leading to a stronger overall economy.
Export Opportunities: Global competitiveness often requires businesses to export their products and services. This expansion into international markets opens up new revenue streams, reduces dependence on domestic markets, and supports economic stability.
Knowledge Transfer: Businesses engaged in global competition often collaborate with academic institutions, research centers, and other companies. This knowledge-sharing ecosystem accelerates innovation by facilitating the transfer of expertise, ideas, and best practices, benefitting a wide range of industries.
Infrastructure Development: The need to meet international standards and consumer preferences drives infrastructure development. This includes improvements in logistics, transportation, telecommunications, and energy systems. Enhanced infrastructure benefits not only businesses but also society at large.
Environmental Sustainability: The pursuit of global competitiveness often leads to innovations in environmental sustainability. Businesses invest in eco-friendly technologies, reduce their carbon footprints, and adopt sustainable practices to meet international regulations and consumer demands, contributing to a greener future.
Healthcare and Medicine: Innovations driven by global competition extend to healthcare and medicine. Businesses invest in cutting-edge medical research, drug development, and healthcare technologies, leading to advancements that improve public health and quality of life.
Competitive Consumer Markets: Global competition fosters diverse and competitive consumer markets. Consumers benefit from a wide range of choices, improved product quality, and competitive pricing, resulting in enhanced overall satisfaction.
Resilience and Adaptability: Businesses engaged in global competition are more resilient and adaptable to change. They continuously evolve to meet evolving market dynamics and consumer preferences, fostering an economy that can weather economic fluctuations and disruptions.
In conclusion, the pursuit of global competitiveness acts as a catalyst for technological innovation and economic growth. The innovations generated by businesses striving to excel on the global stage have far-reaching effects, benefiting not only individual companies but also the broader economy. This cycle of innovation, job creation, and economic expansion drives progress, enhances quality of life, and positions nations at the forefront of the global marketplace. It underscores the significance of fostering an environment that encourages and supports businesses in their pursuit of global competitiveness.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Export Promotion as a Development Strategy: Evidence from …

Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
A robust export sector can attract FDI from foreign companies seeking access to a growing market. FDI brings in capital, expertise, and technology, which can have a transformative impact on the domestic economy.
nullFor additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Trade and Investment | Secretaría de Economía | Gobierno | gob.mx
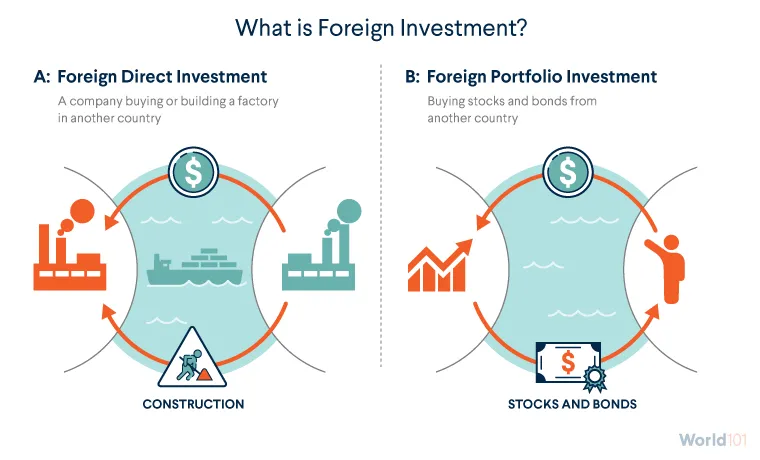
Enhanced Productivity
Export-oriented businesses are driven to improve efficiency, quality, and competitiveness. This focus on continuous improvement permeates the entire economy, leading to enhanced productivity and higher overall economic performance.
Export-oriented businesses play a pivotal role in driving not only their own success but also that of the broader economy. Their relentless pursuit of efficiency, quality, and competitiveness creates a ripple effect that permeates every facet of economic activity, resulting in a range of far-reaching benefits.
Efficiency is at the heart of export-oriented businesses’ success. To meet international standards and compete in global markets, these companies must continually find ways to optimize their processes, reduce waste, and streamline operations. This commitment to efficiency breeds innovation and fosters the adoption of advanced technologies, automation, and best practices. As a result, not only do these businesses become more profitable, but they also set benchmarks for efficiency that others in the economy strive to emulate.
Quality is another hallmark of export-oriented businesses. To gain and maintain a competitive edge in international markets, these companies must produce goods and services of the highest caliber. This pursuit of quality excellence instills a culture of precision, accountability, and attention to detail. The focus on quality cascades into other sectors, raising the overall standard of goods and services within the economy. Consumers benefit from improved products, and businesses can more confidently compete on a global scale.
Competitiveness is the driving force behind export-oriented businesses. To succeed internationally, they must continuously assess and adapt to changing market conditions, emerging technologies, and shifting consumer preferences. This relentless pursuit of competitiveness fosters a dynamic business environment that encourages innovation and adaptation. In this environment, businesses are more likely to invest in research and development, explore new markets, and engage in strategic collaborations, all of which contribute to a more vibrant and resilient economy.
The impact of export-oriented businesses extends well beyond their individual success. Their commitment to efficiency, quality, and competitiveness serves as a catalyst for enhanced productivity and economic growth at the national level. This, in turn, leads to higher overall economic performance, with increased GDP, more job opportunities, and improved living standards for the population.
In conclusion, export-oriented businesses are not just key players in international trade; they are also powerful engines of economic growth and development. Their unwavering commitment to efficiency, quality, and competitiveness sets the stage for a more productive and prosperous economy, benefiting both businesses and society as a whole.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Economic Growth – United Nations Sustainable Development

The Role of Government and Trade Promotion Agencies
Successful export promotion requires the active involvement of governments and trade promotion agencies. These entities play several crucial roles:
Achieving successful export promotion necessitates the proactive engagement of governments and trade promotion agencies, as their involvement is pivotal to unlocking a nation’s international trade potential. Let’s explore the multifaceted roles they play in this critical endeavor:
Policy Formulation: Governments shape the regulatory environment for international trade. They formulate policies that govern tariffs, customs procedures, trade agreements, and export incentives. A conducive policy framework is essential for creating a favorable trade environment that encourages businesses to explore foreign markets.
Market Research and Analysis: Trade promotion agencies conduct in-depth market research and analysis to identify export opportunities. They help businesses understand the demand and competition in target markets, enabling informed decision-making and market entry strategies.
Export Strategy Development: Governments and trade promotion agencies assist businesses in crafting export strategies. This includes market selection, pricing strategies, product adaptation, and supply chain optimization. These strategies are tailored to align with a company’s capabilities and the characteristics of the target market.
Access to Funding: Export promotion agencies often provide financial support to businesses looking to expand internationally. This may include grants, subsidies, or low-interest loans to help companies cover the initial costs associated with export activities, such as market research or product modification.
Trade Missions and Exhibitions: Governments and trade promotion agencies organize trade missions and participate in international exhibitions and fairs. These events facilitate networking, market entry, and business partnerships. They also provide a platform for showcasing a nation’s products and services to a global audience.
Trade Agreements and Negotiations: Governments are responsible for negotiating trade agreements and resolving trade-related disputes. Trade promotion agencies support these efforts by providing data and analysis that inform negotiation strategies. Successful agreements can lead to preferential access to foreign markets, reducing trade barriers.
Export Training and Capacity Building: To succeed in international markets, businesses need to develop export capabilities. Governments and trade promotion agencies offer training programs and capacity-building initiatives. These programs equip companies with the skills and knowledge required for global trade.
Trade Compliance and Standards: Exporting involves adhering to various international trade regulations and quality standards. Trade promotion agencies guide businesses in complying with these requirements, ensuring that products meet the necessary standards for entry into foreign markets.
Export Promotion Campaigns: Governments and agencies run marketing and promotional campaigns to raise awareness of a nation’s products and services abroad. These campaigns highlight the unique selling points of domestic goods and help create brand recognition in foreign markets.
Risk Mitigation: International trade involves financial and operational risks. Governments may provide export credit insurance or guarantees to mitigate risks associated with non-payment by foreign buyers or political instability in target markets.
Diplomatic Support: In cases where trade issues intersect with diplomatic matters, governments can use their diplomatic channels to address challenges and facilitate trade relationships. Diplomatic support can be crucial in resolving disputes and fostering trade partnerships.
Data and Information Sharing: Trade promotion agencies collect and disseminate valuable market information, trade statistics, and trade-related data. This information helps businesses stay informed about market trends, consumer preferences, and trade regulations.
In conclusion, the active involvement of governments and trade promotion agencies is essential for successful export promotion. Their multifaceted roles encompass policy formulation, market research, strategy development, funding access, and trade negotiation support. By collaborating with businesses, these entities pave the way for nations to capitalize on international trade opportunities, driving economic growth and prosperity on a global scale.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here U.S. Trade Policy: Background and Current Issues

Policy Formulation
Governments create trade policies that facilitate exports. These policies can include tariff reductions, export subsidies, trade agreements, and trade finance programs.
Governments play a pivotal role in shaping the international trade landscape by creating trade policies that not only facilitate exports but also drive economic growth and foster diplomatic relations. Here’s an extended exploration of this idea:
Boosting Export Competitiveness: Trade policies are designed to enhance the competitiveness of a nation’s exports in the global market. Governments may strategically reduce tariffs or provide export subsidies to make their products more attractive to international buyers. By doing so, they create an environment in which domestic industries can thrive on the global stage.
Supporting Diverse Industries: Trade policies are not one-size-fits-all; they cater to a country’s diverse range of industries. Governments craft policies that align with the strengths and potential of various sectors, whether it’s agriculture, technology, manufacturing, or services. This tailored approach maximizes the export potential of each industry.
Promoting International Relations: Trade agreements are a key component of trade policies. They facilitate diplomatic relations and cooperation between countries. By entering into bilateral or multilateral agreements, governments can strengthen political and economic ties, opening doors for smoother trade relations and collaborative initiatives beyond commerce.
Attracting Foreign Investment: A conducive trade policy environment can attract foreign direct investment (FDI). Investors are more likely to commit capital to countries with favorable trade policies that ensure a stable and profitable business climate. FDI can lead to job creation, technology transfer, and economic growth.
Facilitating Trade Finance: Governments often establish trade finance programs to provide exporters with access to working capital and credit insurance. These programs mitigate the financial risks associated with exporting and encourage smaller businesses to engage in international trade.
Ensuring Compliance: Trade policies include regulatory frameworks that govern international trade. They set standards for product quality, safety, and labeling. By ensuring compliance with these standards, governments protect consumers and maintain the integrity of their exports in global markets.
Balancing Trade Deficits: Trade policies are instrumental in addressing trade imbalances. Governments may employ measures such as import restrictions or currency interventions to rectify trade deficits. These policies aim to create a more equitable trade relationship with trading partners.
Supporting Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs): Trade policies can be tailored to support the growth of SMEs in international trade. Simplified export procedures, reduced bureaucratic barriers, and export promotion programs make it easier for smaller businesses to access global markets.
Environmental and Social Responsibility: Increasingly, trade policies incorporate environmental and social responsibility considerations. Governments may incentivize sustainable practices, fair labor standards, and responsible sourcing to meet global expectations for ethical trade.
Economic Diversification: Trade policies often align with broader economic diversification goals. Governments seek to reduce dependency on a single industry or trading partner by expanding export opportunities across various sectors and geographic regions.
Adaptation to Global Trends: Trade policies must evolve to address emerging global trends. In today’s digital economy, governments consider e-commerce, data privacy, and intellectual property rights in their policies to reflect the changing nature of trade.
Global Response to Crises: Trade policies can also be used as a global response to crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Governments may temporarily adjust trade policies to ensure the flow of essential goods and medical supplies, demonstrating the flexibility and adaptability of trade frameworks.
In summary, governments’ role in shaping trade policies extends beyond boosting exports; it encompasses economic development, diplomatic relations, and responsible global engagement. A well-crafted and flexible trade policy framework not only strengthens a nation’s economic competitiveness but also contributes to its broader geopolitical standing and its ability to address global challenges collaboratively.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Executive Order on Promoting Competition in the American Economy

Market Access
Trade promotion agencies identify and provide access to potential export markets. They assist businesses in navigating regulatory requirements, market entry strategies, and trade missions.
nullTo expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Executive Order on Promoting Competition in the American Economy

Financial Support
Governments often provide financial support to exporters through grants, subsidies, and low-interest loans. These incentives help businesses enter new markets and expand their export activities.
Governments’ financial support to exporters plays a pivotal role in fostering economic growth, promoting international trade, and enhancing a country’s global competitiveness. Let’s explore the extended idea in greater depth:
Market Diversification and Expansion: Government grants, subsidies, and low-interest loans offer businesses the financial means to diversify their markets and expand their export activities. By providing this support, governments enable companies to explore new horizons, tap into uncharted territories, and reduce their reliance on domestic markets. This strategic approach not only increases the resilience of individual businesses but also contributes to the overall economic stability of a nation.
Boosting Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs): Export support programs are particularly beneficial for SMEs, which often lack the financial resources and experience to enter international markets independently. Government assistance levels the playing field, allowing these smaller enterprises to compete on a global scale. This inclusivity fosters entrepreneurship and innovation, fueling economic growth from the grassroots level.
Job Creation and Skill Enhancement: Financial incentives for exporters lead to the creation of jobs, spanning from manufacturing and logistics to marketing and sales. A thriving export sector not only reduces unemployment rates but also serves as a conduit for skill development and knowledge transfer. As employees gain expertise in international trade, they contribute to a more competent and competitive workforce.
Economic Resilience: Export support programs contribute to economic resilience by diversifying revenue streams. In times of economic uncertainty or domestic market fluctuations, businesses with a strong export focus are less vulnerable. Governments can thereby shield their economies from the negative impacts of global economic crises.
Market Penetration and Competitiveness: With financial backing, businesses can invest in market research, product adaptation, and marketing campaigns tailored to specific international audiences. This level of preparation enhances their competitiveness in foreign markets, ensuring that products and services meet the unique demands and preferences of customers worldwide.
Promoting Sustainable Practices: Governments can use export incentives to encourage businesses to adopt sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. Incentives can be tied to meeting specific sustainability criteria, leading to responsible production and reducing the environmental impact of exports. This aligns with global efforts to address climate change and environmental degradation.
Enhancing Diplomatic Relations: Export support programs can serve as diplomatic tools, strengthening relations between exporting and importing countries. Trade agreements and collaborations often emerge from these economic ties, contributing to a more stable and cooperative global community.
Attracting Foreign Investment: A robust export sector can attract foreign investment, as investors see a country with export potential as a promising destination for capital. This influx of foreign investment can further stimulate economic growth, creating a positive feedback loop.
Global Competitiveness: Nations that actively support their exporters increase their global competitiveness. By nurturing a thriving export sector, governments position their countries as attractive hubs for international business, fostering a positive image and attracting foreign investors, partners, and multinational corporations.
In summary, government financial support for exporters transcends mere economic policy; it shapes the destiny of nations on the global stage. By providing the necessary resources and incentives, governments empower businesses to venture into new markets, creating jobs, enhancing competitiveness, and driving sustainable economic growth. This support is a testament to the symbiotic relationship between government policy and the success of businesses in the global marketplace.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Market Development | USDA Foreign Agricultural Service

Market Research
Trade promotion agencies conduct market research to identify export opportunities and consumer trends. This information is invaluable for businesses in tailoring their marketing strategies.
Trade promotion agencies conduct market research to identify export opportunities and consumer trends. This information is invaluable for businesses in tailoring their marketing strategies. In this age of globalization and rapidly changing consumer preferences, the synergy between these agencies and businesses has never been more critical.
Identifying Emerging Markets: Trade promotion agencies continuously scan global markets to identify emerging opportunities for exports. They delve deep into market research, analyzing factors such as economic growth, political stability, and consumer demographics. Armed with this data, businesses can strategically target markets with untapped potential, avoiding the pitfalls of entering saturated markets.
Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding the cultural nuances and consumer behaviors of a target market is essential for marketing success. Trade promotion agencies often provide insights into local customs, preferences, and taboos. This cultural intelligence enables businesses to create marketing campaigns that resonate with the local population, fostering a deeper connection with consumers.
Compliance and Regulations: International trade comes with a complex web of regulations and compliance requirements. Trade promotion agencies keep abreast of the latest trade policies, tariffs, and standards. This knowledge is indispensable for businesses to ensure their marketing strategies and product offerings align with legal and regulatory frameworks, avoiding costly mistakes and potential legal issues.
Competitive Analysis: Market research conducted by trade promotion agencies also includes an analysis of competitors in the target market. This information helps businesses to assess the competitive landscape, identify gaps in the market, and refine their marketing strategies to gain a competitive edge. It can inform decisions about pricing, product differentiation, and market positioning.
Consumer Trends: Consumer preferences are constantly evolving. Trade promotion agencies monitor these trends closely, providing businesses with insights into what products or services are in demand and how consumers prefer to engage with brands. Armed with this information, companies can adapt their marketing strategies to align with current consumer preferences and stay ahead of the curve.
Risk Mitigation: International business inherently carries risks, such as currency fluctuations, political instability, and supply chain disruptions. By leveraging the research conducted by trade promotion agencies, businesses can make informed decisions to mitigate these risks. This might involve diversifying into multiple markets, currency hedging, or contingency planning to ensure marketing strategies remain robust even in challenging circumstances.
Market Entry Strategies: Trade promotion agencies often offer guidance on market entry strategies, including recommendations on distribution channels, partnerships, and marketing tactics. Businesses can use this guidance to tailor their marketing plans to suit the specific challenges and opportunities presented by each market.
Resource Allocation: Budget constraints are a reality for most businesses. Market research conducted by trade promotion agencies helps companies allocate their marketing resources more efficiently. By focusing efforts on markets with the greatest potential and aligning strategies with local conditions, businesses can maximize the impact of their marketing initiatives.
In summary, the relationship between trade promotion agencies and businesses is symbiotic. Agencies provide businesses with a wealth of data and insights that empower them to craft effective and tailored marketing strategies for international markets. This collaboration is a cornerstone of successful global trade, allowing businesses to navigate the complexities of international commerce with confidence and precision.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Economic Issues 1 — Growth in East Asia

Brand Building
Governments can assist in the branding and promotion of national products abroad. This branding enhances the image and reputation of a country’s products in international markets.
Governments can play a crucial role in the branding and promotion of national products abroad, and their involvement extends far beyond just marketing. This active support can have a profound impact on a country’s economic growth and global standing. Here are several ways in which governments can assist in enhancing the image and reputation of their nation’s products in international markets:
Investment in Market Research: Governments can allocate resources to conduct comprehensive market research, identifying target markets and consumer preferences. This data-driven approach enables businesses to tailor their products and marketing strategies more effectively.
Trade Missions and Delegations: Organizing trade missions and delegations to foreign countries can create valuable opportunities for businesses to establish relationships with potential buyers, distributors, and partners. Government-sponsored events and trade shows can provide a platform for showcasing national products.
Export Assistance Programs: Governments can develop export assistance programs that offer financial incentives, export credit guarantees, and grants to businesses looking to expand internationally. These incentives can offset some of the risks and costs associated with entering foreign markets.
Brand Building and Protection: Governments can support the branding and protection of national products by registering trademarks and geographical indications. This safeguards the authenticity and reputation of products associated with a specific region or country.
Quality Standards and Certification: Setting and enforcing quality standards ensures that products maintain a consistent level of quality, which is essential for building a positive reputation in international markets. Governments can work with industry associations to establish and maintain these standards.
Promotion and Marketing Campaigns: Governments can collaborate with industry associations and businesses to launch promotional and marketing campaigns in target markets. These campaigns can highlight the unique qualities of national products and build awareness among consumers.
Diplomatic Efforts: Diplomatic channels can be leveraged to negotiate trade agreements that reduce or eliminate trade barriers and tariffs, making it easier for national products to access international markets.
Education and Training: Providing training and educational resources to businesses on export strategies, international marketing, and compliance with foreign regulations can empower them to navigate the complexities of global markets more effectively.
Crisis Management: In the event of trade disputes, product recalls, or other crises that may harm a nation’s reputation, governments can step in to provide support, guidance, and crisis management strategies to protect the integrity of national products.
Sustainability Initiatives: Promoting sustainability and responsible production practices can enhance a country’s image as a responsible global player. Governments can encourage businesses to adopt environmentally friendly practices and certifications.
Cultural Exchange and Tourism: Encouraging cultural exchange and tourism can also indirectly promote national products. Visitors to a country often become brand ambassadors when they return home, sharing their positive experiences with local products and culture.
Research and Development: Investment in research and development can lead to product innovations that make national products more competitive and appealing in international markets.
By actively supporting the branding and promotion of national products abroad, governments not only boost the economic prospects of their country but also contribute to the development of a positive global image. This not only benefits businesses but also bolsters the overall reputation and influence of the nation in the global arena.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: The Development of China’s Export Performance, Presentation by …

The intricate dance between marketing and trade economics is a testament to the interdependence of national economies in today’s globalized world. Export promotion emerges as a linchpin in this relationship, serving as a catalyst for economic growth, job creation, and technological advancement. Governments and trade promotion agencies, as stewards of this process, play a pivotal role in guiding businesses toward international success. In essence, the fusion of marketing and trade economics paves the way for nations to not only thrive but also to excel in the global arena, fostering economic growth and prosperity for their citizens.
nullTo expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Economic Issues 8 — Why Is China Growing So Fast?
More links
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Economy & Trade | United States Trade Representative
