Table of Contents
In today’s fiercely competitive business landscape, companies must leverage every available advantage to succeed. One often-overlooked strategy that can significantly impact a brand’s profitability and market share is optimal product positioning. By utilizing economic analysis, businesses can fine-tune their product placement strategies, ensuring they resonate with target audiences and outperform competitors. In this article, we’ll explore the concept of optimal product positioning and how economic analysis can be a game-changer in achieving a competitive edge.
In today’s fiercely competitive business landscape, where every advantage can make a difference, companies must be agile and strategic in their pursuit of success. One often-overlooked but highly impactful strategy that can significantly boost a brand’s profitability and market share is optimal product positioning. By employing economic analysis, businesses can master the art of fine-tuning their product placement strategies to resonate with their target audiences and outshine competitors. In this article, we’ll embark on a journey to explore the concept of optimal product positioning and unveil how economic analysis can serve as the ultimate game-changer in achieving a competitive edge.
Precise Targeting: Optimal product positioning starts with a deep understanding of the target audience. Economic analysis allows businesses to not only identify their most profitable customer segments but also discern the nuanced preferences, behaviors, and purchasing patterns within those segments. Armed with this knowledge, companies can position their products to meet the specific needs and desires of each customer group.
Price Optimization: Economic analysis empowers businesses to set prices strategically. It goes beyond mere cost-plus pricing and delves into factors like price elasticity of demand, competitive pricing dynamics, and consumer willingness to pay. This insight enables companies to position their products at price points that maximize profitability while remaining attractive to customers.
Product Differentiation: Effective product positioning relies on product differentiation—highlighting what sets a product apart from the competition. Economic analysis can guide businesses in identifying unique selling points (USPs) that resonate with customers and justify premium pricing, thereby creating a competitive advantage.
Market Entry and Expansion: When entering new markets or expanding product lines, economic analysis can inform the selection of positioning strategies. It helps evaluate market conditions, assess competition, and determine the optimal positioning that aligns with the market’s economic dynamics.
Promotion and Messaging: Crafting compelling marketing messages and promotional campaigns is pivotal in product positioning. Economic analysis informs the messaging strategy by emphasizing the economic value and benefits that products bring to customers. This ensures that promotional efforts resonate with the target audience.
Dynamic Adaptation: Markets are dynamic, and consumer preferences evolve. Economic analysis equips businesses with the tools to adapt their product positioning strategies in real-time. By monitoring economic indicators and market trends, companies can stay ahead of the curve and make proactive adjustments.
Resource Allocation: Efficient resource allocation is a fundamental component of optimal product positioning. Economic analysis guides the allocation of marketing budgets, sales efforts, and research and development investments to maximize the return on investment for each product.
Competitive Resilience: In a competitive landscape, companies must anticipate and respond to competitors’ moves. Economic analysis helps businesses assess their competitive position and identify opportunities to differentiate themselves effectively, ensuring they remain resilient in the face of market challenges.
Risk Mitigation: Every business venture carries risks. Economic analysis aids in risk assessment by evaluating the economic impact of various positioning strategies. This allows companies to make informed decisions and develop contingency plans to mitigate potential risks.
Sustainability and Ethics: Economic analysis extends beyond profit considerations. It can encompass ethical and sustainability dimensions, helping companies align their product positioning with social and environmental values that resonate with customers and contribute to long-term brand loyalty.
In conclusion, optimal product positioning is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor; it’s a dynamic and data-driven process that requires a keen understanding of economic principles and consumer behavior. By harnessing the power of economic analysis, businesses can unlock a competitive edge that goes beyond intuition and gut feeling. It’s a strategic imperative in today’s complex and ever-evolving business environment.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here A Complete Guide to Successful Brand Positioning
Understanding Product Positioning
Product positioning is the art and science of creating a distinct image and identity for a product or service in the minds of consumers. It involves crafting a value proposition that differentiates a brand from its competitors and aligns with the needs and desires of the target audience. Effective product positioning lays the foundation for a brand’s marketing and communication strategies, influencing everything from pricing to messaging.
nullIf you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Market research and competitive analysis | U.S. Small Business …

The Role of Economic Analysis
Economic analysis is a systematic approach to understanding the financial implications of various decisions. When applied to product positioning, economic analysis helps businesses evaluate the costs, benefits, and potential risks associated with different positioning strategies. It provides data-driven insights into how a brand can optimize its market presence, pricing structure, and competitive positioning.
Economic analysis, when applied to product positioning, serves as a compass guiding businesses through the intricate landscape of strategic decision-making. This systematic approach illuminates the financial dimensions of product positioning strategies, offering a roadmap to navigate the complexities of the market. Let’s delve deeper into how economic analysis plays a pivotal role in shaping a brand’s market presence, pricing strategies, and competitive positioning:
1. Cost-Benefit Assessment: Economic analysis involves a rigorous evaluation of the costs and benefits associated with various product positioning strategies. Businesses can quantify the financial investments required to implement different approaches and weigh them against the potential returns. This assessment allows for a clear understanding of the financial feasibility and potential profitability of each strategy.
2. Risk Mitigation: Beyond costs and benefits, economic analysis also factors in potential risks. It helps businesses identify and assess the financial implications of risks associated with product positioning, such as market volatility, competitive responses, or shifts in consumer preferences. Armed with this knowledge, companies can develop risk mitigation strategies and contingency plans.
3. Pricing Structure Optimization: Economic analysis provides insights into how pricing structures impact revenue and profitability. It helps businesses determine optimal pricing strategies based on factors like production costs, competitor pricing, and consumer willingness to pay. This optimization ensures that pricing aligns with the market’s economic realities.
4. Market Presence Enhancement: Economic analysis guides decisions related to a brand’s market presence. It assists in assessing the financial viability of expanding into new markets, launching new product lines, or diversifying existing offerings. By quantifying the potential returns and associated costs, businesses can make informed decisions about market expansion strategies.
5. Competitive Positioning: Understanding the economic landscape of competitors is crucial. Economic analysis allows businesses to assess how their pricing, value proposition, and positioning compare to rivals. This insight enables companies to fine-tune their competitive strategies, whether it involves undercutting competitors on price or differentiating through added value.
6. Data-Driven Decision-Making: Economic analysis is rooted in data and empirical evidence. It encourages data-driven decision-making, ensuring that strategic choices are based on quantifiable insights rather than intuition. This approach enhances the accuracy and reliability of decision outcomes.
7. Long-Term Sustainability: Businesses can employ economic analysis to evaluate the long-term sustainability of their positioning strategies. It helps assess whether a chosen approach is viable over an extended period, taking into account factors like changing market conditions and evolving consumer behaviors.
8. Resource Allocation: Economic analysis is instrumental in resource allocation. It ensures that budget allocations for marketing, research, and development align with the selected product positioning strategy. This efficient resource utilization is critical for maintaining financial health and competitiveness.
In conclusion, economic analysis serves as a compass for businesses navigating the complex terrain of product positioning. It empowers companies to make well-informed, data-driven decisions that optimize market presence, pricing strategies, and competitive positioning. In an era of rapid market evolution and heightened competition, embracing economic analysis as an integral part of the decision-making process is key to achieving financial sustainability and market success.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Competitive Advantage Definition With Types and Examples

Cost Optimization
Economic analysis enables businesses to assess the cost-effectiveness of different positioning strategies. By evaluating the expenses associated with reaching specific target markets or altering product features, companies can make informed decisions that minimize costs while maximizing returns.
Economic analysis stands as a cornerstone of strategic decision-making for businesses seeking to optimize their positioning strategies. This analytical approach empowers companies to dissect the intricate web of costs and benefits associated with various strategies aimed at capturing the attention and loyalty of specific target markets. Expanding on this idea, let’s delve deeper into how economic analysis enhances cost-effectiveness and informs strategic choices:
Resource Allocation: Economic analysis begins with a thorough evaluation of resource allocation. Businesses assess how efficiently their resources, including marketing budgets, personnel, and production capacity, are utilized to achieve specific positioning goals. This step ensures that resources are channeled toward strategies that offer the highest potential returns.
Market Segmentation: Understanding the economic viability of market segmentation is critical. By dividing the market into distinct segments based on demographics, psychographics, or behavior, companies can tailor their messaging and offerings more effectively. Economic analysis quantifies the costs and potential revenue gains associated with each segment, helping businesses identify the most lucrative opportunities.
Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA): CBA is an essential tool within economic analysis. It quantifies the costs of implementing various positioning strategies and juxtaposes them against the anticipated benefits. This systematic approach ensures that strategies are selected based on their potential to deliver a positive return on investment.
Product Features and Customization: Tailoring product features to meet the specific needs and preferences of target markets is a common positioning strategy. Economic analysis evaluates the costs of product customization or adaptation and weighs them against the increased sales and market share that result from meeting customer demands.
Competitive Benchmarking: Economic analysis extends to competitive benchmarking, where businesses assess the financial implications of positioning themselves relative to competitors. Analyzing the costs and benefits of being a price leader, a value leader, or a niche player informs strategic positioning decisions.
Market Entry and Expansion: When businesses contemplate entering new markets or expanding their presence, economic analysis guides their choices. It helps in assessing the costs associated with market research, market entry strategies, and potential returns from tapping into new customer bases.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Gains: Economic analysis assists in evaluating the balance between short-term gains and long-term sustainability. Companies weigh the immediate costs of certain positioning strategies against the potential for enduring customer loyalty, repeat business, and brand strength.
Adaptability and Flexibility: The economic analysis is not static; it’s an ongoing process. Businesses continuously monitor the costs and benefits of their positioning strategies and adapt them as market dynamics evolve. This adaptability ensures that strategies remain cost-effective and aligned with changing customer preferences.
Ethical and Social Considerations: Beyond financial factors, economic analysis can incorporate ethical and social considerations. It helps businesses assess the potential social impact of their positioning strategies, ensuring alignment with their values and corporate responsibility objectives.
Risk Mitigation: Economic analysis considers risk factors associated with positioning strategies. Businesses evaluate the potential downside risks and develop contingency plans to mitigate them while maximizing cost-effectiveness.
In summary, economic analysis is a compass that guides businesses through the complex terrain of positioning strategies. It empowers them to make data-driven decisions that optimize resource allocation, minimize costs, and maximize returns. By applying rigorous economic scrutiny to their strategic choices, companies can navigate competitive landscapes with confidence, ultimately achieving sustainable growth and profitability while delivering value to their target markets.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Pareto Efficiency Examples and Production Possibility Frontier

Pricing Strategies
Pricing is a critical aspect of product positioning. Economic analysis allows businesses to determine the optimal price point that maximizes profitability while remaining competitive. This can involve price elasticity assessments, competitive pricing analysis, and dynamic pricing strategies.
Pricing is not just a number on a tag; it’s a strategic tool that plays a pivotal role in defining a product’s place in the market. The art of pricing, informed by economic analysis, allows businesses to finely tune their product positioning for maximum impact on profitability and competitiveness.
Understanding Price Elasticity: Economic analysis begins with an exploration of price elasticity. This crucial concept helps businesses grasp how sensitive consumer demand is to changes in price. Products with inelastic demand, for example, can tolerate price increases without significant drops in sales, potentially leading to increased profitability. Conversely, products with elastic demand require careful pricing to maintain competitiveness.
Competitive Pricing Analysis: To remain competitive, companies need to have a finger on the pulse of the market. Competitive pricing analysis involves evaluating the prices of similar products offered by competitors. This insight helps businesses set their prices in a way that attracts customers while considering factors like quality, brand reputation, and unique selling propositions.
Value-Based Pricing: Beyond competition, economic analysis supports value-based pricing. By assessing how much value their product or service provides to customers, businesses can set prices that align with the perceived benefits. This strategy allows for premium pricing if the product offers superior features or cost-effective pricing if it fulfills essential needs.
Dynamic Pricing Strategies: In today’s fast-paced marketplaces, static pricing may not suffice. Dynamic pricing strategies, informed by economic models and real-time data, enable businesses to adjust prices based on factors like demand fluctuations, competitor pricing changes, and inventory levels. This agility can optimize revenue and profitability.
Psychological Pricing: Economic analysis delves into the psychology of pricing. It explores how pricing strategies, like charm pricing (ending prices with .99) or bundling, can influence consumer behavior and perceptions of value. Leveraging these psychological triggers can be a powerful tool for positioning products effectively.
Price Discrimination: For businesses with diverse customer segments, price discrimination strategies can be beneficial. This involves offering different prices to different groups based on factors like location, age, or loyalty. Careful economic analysis ensures that these strategies are profitable and compliant with legal and ethical standards.
Optimizing Profit Margins: Ultimately, economic analysis guides businesses in optimizing profit margins. By factoring in production costs, distribution expenses, and marketing investments, companies can strike a balance between profitability and affordability. This balance ensures that they generate adequate revenue while maintaining competitiveness.
Adapting to Market Changes: Markets are dynamic, and economic analysis helps businesses adapt to evolving conditions. By continuously monitoring economic indicators, customer preferences, and market trends, companies can proactively adjust their pricing strategies to remain relevant and competitive.
In essence, pricing is a multifaceted endeavor that extends far beyond setting arbitrary numbers. Economic analysis acts as a compass, allowing businesses to navigate the intricate terrain of pricing with precision. When done right, it not only maximizes profitability but also positions products in a way that resonates with consumers, fostering long-term success and brand loyalty in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Market research and competitive analysis | U.S. Small Business …

Market Segmentation
Economic analysis helps identify the most profitable market segments for a product. By understanding the spending behaviors and preferences of different customer groups, companies can tailor their positioning to attract and retain high-value customers.
nullYou can also read more about this here: A Complete Guide to Successful Brand Positioning

Resource Allocation
Businesses often have limited resources, and economic analysis assists in allocating these resources effectively. It helps prioritize marketing efforts, advertising budgets, and product development initiatives based on their potential return on investment (ROI).
In the challenging landscape of business operations, where resources are finite and competition is fierce, economic analysis emerges as a guiding light, offering a data-driven path toward resource allocation that maximizes returns. The allocation of limited resources, whether financial, human, or time-related, is a critical decision for any business. Here’s an expanded perspective on how economic analysis plays a pivotal role in this resource allocation process, spanning various facets of business operations:
1. Marketing Strategy: Economic analysis empowers businesses to make strategic decisions regarding their marketing efforts. By quantifying the potential return on investment for different marketing channels, strategies, and campaigns, companies can allocate their marketing budgets effectively. This ensures that every dollar spent contributes to revenue growth, customer acquisition, or brand visibility in a manner that aligns with overarching business goals.
2. Advertising Budgets: Advertising can be a substantial expense for businesses, and economic analysis provides a systematic approach to optimizing advertising budgets. It enables companies to identify the most cost-effective channels and campaigns, ensuring that advertising spend generates a positive ROI. This data-driven approach minimizes wasteful spending and maximizes the impact of advertising efforts.
3. Product Development: Economic analysis extends its influence to product development initiatives. It guides businesses in identifying and prioritizing product features or innovations that are most likely to yield significant returns. By evaluating potential development costs against expected revenue or market demand, economic analysis helps streamline product development efforts and ensures that resources are invested wisely.
4. Resource Allocation: Beyond marketing and product development, economic analysis assists in the broader allocation of resources across various departments and functions. It aids in determining staffing levels, technology investments, and infrastructure upgrades based on their potential economic benefits. This systematic approach ensures that resources are channeled where they can generate the most value.
5. Risk Assessment: Economic analysis also factors in risk assessment. Businesses often face uncertainty in their decisions, and economic models can incorporate risk factors and probabilities. This enables companies to make informed resource allocation decisions that consider potential risks and rewards, fostering a balanced approach to resource management.
6. Opportunity Cost Evaluation: Resource allocation decisions come with opportunity costs. When a resource is allocated to one initiative, it may come at the expense of another potentially lucrative opportunity. Economic analysis helps quantify these opportunity costs, allowing businesses to make trade-offs that align with their strategic priorities.
7. Performance Measurement: Economic analysis doesn’t stop at resource allocation; it extends to performance measurement. After resources are deployed, businesses can use economic metrics to evaluate the actual return on investment. This feedback loop informs future resource allocation decisions, enabling continuous improvement and optimization.
8. Strategic Decision-Making: Ultimately, economic analysis is a cornerstone of strategic decision-making. It provides the analytical rigor needed to make informed choices that align with long-term business objectives. In a rapidly evolving business environment, it equips businesses with the agility to adapt and allocate resources optimally in response to changing market dynamics.
In summary, economic analysis is the compass that guides businesses through the resource allocation maze. It empowers companies to prioritize marketing efforts, advertising budgets, product development initiatives, and broader resource allocation decisions based on their potential return on investment. This systematic and data-driven approach is essential in an era where efficient resource utilization is a linchpin of sustainable business success. It is the key to ensuring that limited resources are leveraged to their maximum potential, driving economic efficiency and profitability.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Market research and competitive analysis | U.S. Small Business …

Risk Mitigation
Economic analysis assesses the potential risks associated with different positioning strategies. By identifying and quantifying risks, businesses can develop contingency plans and mitigate potential negative outcomes.
Economic analysis is an invaluable tool that goes beyond assessing current market conditions; it also delves into the realm of strategic planning, helping businesses anticipate and manage risks effectively. This forward-looking perspective, rooted in quantitative assessments, empowers companies to make informed decisions and safeguard their interests. Let’s explore how economic analysis aids in risk assessment and mitigation:
Risk Identification: Economic analysis begins by identifying potential risks associated with different positioning strategies. These risks can range from market volatility and competitive pressures to regulatory changes and economic downturns. By systematically identifying and categorizing risks, businesses create a comprehensive risk profile.
Quantification of Risks: Once risks are identified, economic analysis quantifies them. This involves assigning probabilities and potential impact levels to each risk scenario. Quantification transforms abstract threats into measurable variables, enabling businesses to prioritize risks based on their likelihood and potential severity.
Scenario Modeling: Economic analysis often employs scenario modeling, where various risk scenarios are simulated. These simulations provide a clearer picture of how different factors may interact and impact the business. By exploring a range of scenarios, companies can better understand the potential outcomes of their positioning strategies.
Contingency Planning: Armed with a quantified understanding of risks and their potential consequences, businesses can develop contingency plans. These plans outline specific actions to be taken in response to each risk scenario. Contingency planning helps companies respond swiftly and effectively should a risk materialize, reducing its impact.
Resource Allocation: Economic analysis also guides resource allocation to address risks. By evaluating the potential costs associated with risk mitigation measures, businesses can allocate budgets and resources strategically. This ensures that resources are available when needed to implement contingency plans.
Diversification Strategies: Economic analysis encourages diversification as a risk mitigation strategy. Diversifying product lines, customer segments, or geographic markets can reduce the reliance on a single source of revenue and spread risk across different areas. Diversification is a proactive approach to risk management.
Monitoring and Early Warning Systems: Economic analysis emphasizes continuous monitoring of key indicators and early warning systems. By tracking relevant economic, market, and industry metrics, businesses can detect warning signs of impending risks. Timely detection allows for proactive risk mitigation measures.
Regulatory Compliance: Economic analysis includes assessing the impact of regulatory changes. Businesses must stay informed about evolving regulations that could affect their operations. Compliance with existing and anticipated regulations is an essential aspect of risk management.
Competitive Intelligence: Economic analysis extends to monitoring competitors’ activities. Understanding competitive dynamics and market trends helps businesses anticipate competitive risks and respond with agility. A proactive stance can help avert potential threats.
Stakeholder Communication: Effective communication with stakeholders is vital in risk management. Businesses must transparently communicate their risk assessment, mitigation strategies, and contingency plans to shareholders, employees, customers, and partners. Open communication builds trust and confidence.
In summary, economic analysis serves as the compass guiding businesses through the complex terrain of risk assessment and mitigation. By systematically identifying, quantifying, and modeling risks, companies are better equipped to make informed decisions, allocate resources judiciously, and develop proactive strategies that protect their interests. In an ever-changing business landscape, economic analysis is a valuable ally in achieving resilience and sustained success.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Market research and competitive analysis | U.S. Small Business …
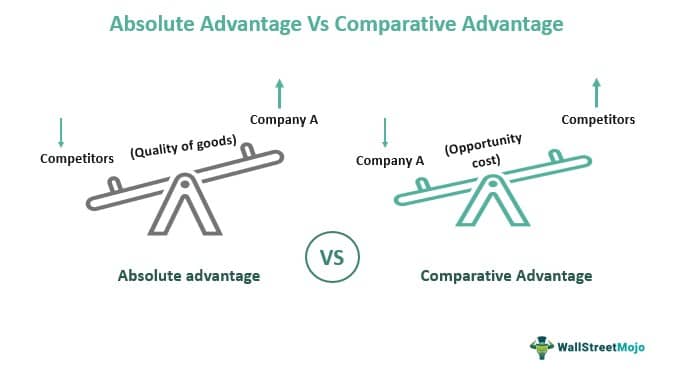
Competitive Advantage
Effective economic analysis allows companies to position their products in a way that sets them apart from competitors. It helps identify unique selling points and value propositions that resonate with customers and create a competitive edge.
Effective economic analysis is not just about positioning products differently but also about gaining a deeper understanding of how businesses can thrive in a competitive landscape. Here are some expanded insights into the role of economic analysis in creating a competitive edge:
Market Dynamics: Economic analysis delves into the dynamics of supply and demand, consumer behavior, and market trends. By comprehending these factors, companies can identify emerging opportunities and challenges, enabling them to adapt their strategies proactively.
Competitive Benchmarking: Economic analysis involves studying competitors’ pricing, cost structures, and strategies. This benchmarking process helps businesses identify gaps or weaknesses in the market that they can exploit to stand out.
Cost Optimization: A significant aspect of economic analysis is cost optimization. Companies can use cost analysis to identify areas where they can reduce expenses without compromising product quality. This cost efficiency can lead to competitive pricing or higher profit margins.
Resource Allocation: Economic analysis guides resource allocation decisions. Companies can determine where to invest resources, whether it’s in research and development, marketing, or expanding production capacity, based on a clear understanding of market dynamics and potential returns.
Innovation and Product Development: Through economic analysis, businesses can gauge the demand for innovative products or services. This insight can drive research and development efforts to create products that address unmet consumer needs and preferences.
Pricing Strategies: Economic analysis informs pricing strategies beyond mere differentiation. It helps companies identify the price elasticity of their products, allowing for data-driven decisions on pricing levels and potential discounting strategies.
Customer Segmentation: Companies can use economic analysis to segment their customer base effectively. Understanding which customer segments offer the most value allows businesses to tailor their marketing efforts and product offerings accordingly.
Risk Management: Economic analysis also involves risk assessment. Companies can identify potential risks and develop contingency plans to mitigate them. This proactive approach ensures business continuity even in uncertain economic conditions.
Sustainability Considerations: Economic analysis is increasingly considering sustainability factors. Companies can assess the economic viability of sustainable practices and products, which can not only attract environmentally conscious customers but also enhance long-term profitability.
Global Expansion: For companies looking to expand internationally, economic analysis helps in understanding the economic conditions, regulations, and consumer behaviors in different markets. This knowledge is essential for successful global expansion.
Long-Term Strategy: Beyond immediate gains, economic analysis supports the development of long-term strategies. It enables companies to make decisions that align with their overarching business goals and sustainability, fostering growth and competitiveness over time.
In conclusion, effective economic analysis is a multifaceted process that equips companies with the knowledge and insights needed to excel in competitive markets. It goes beyond differentiation and positioning to encompass cost optimization, resource allocation, innovation, and risk management. By embracing economic analysis as a core strategic tool, businesses can not only set themselves apart but also thrive and evolve in dynamic and competitive business environments.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Competitive Advantage Definition With Types and Examples
Performance Measurement
Economic analysis provides the framework for measuring the success of product positioning strategies. Key performance indicators (KPIs) can be established and tracked to ensure that the chosen positioning strategy is delivering the expected results.
nullLooking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Competitive Advantage Definition With Types and Examples

Case in Point: The Smartphone Industry
The smartphone industry is a prime example of the importance of optimal product positioning. Companies like Apple and Samsung have used economic analysis to determine the right balance between features, quality, and price. By targeting specific customer segments with tailored product offerings, they have achieved sustained competitive advantage and market leadership.
“The smartphone industry stands as a compelling testament to the paramount importance of optimal product positioning. Giants like Apple and Samsung have masterfully wielded economic analysis as a compass to navigate the intricate landscape of consumer preferences. Their journey has illuminated the path to striking the perfect equilibrium between features, quality, and price—a pursuit that has yielded remarkable results.
Understanding Consumer Preferences: Economic analysis in the smartphone arena delves deep into understanding the nuanced preferences of diverse customer segments. It’s not merely about packing a device with features; it’s about discerning which features matter most to different types of users. This knowledge forms the foundation for product differentiation.
Tailored Product Offerings: Armed with insights from economic analysis, companies craft tailored product offerings that cater to specific customer segments. For example, they may offer premium devices with cutting-edge features for tech enthusiasts while simultaneously providing more budget-friendly alternatives for price-conscious consumers. This segmentation allows them to capture a broader market share.
Striking the Right Price-Quality Balance: Economics plays a pivotal role in helping companies strike the right balance between price and quality. It’s a delicate dance. Premium devices come with premium price tags, but they must justify their cost with superior quality and features. Economic analysis helps optimize pricing strategies to maximize value perception.
Long-Term Competitive Advantage: The true measure of success lies in achieving and sustaining a competitive advantage. By employing economic analysis to tailor their product positioning, companies like Apple and Samsung have not only secured a competitive edge but have also maintained it over the years. This long-term advantage is built on a deep understanding of consumer behavior and preferences.
Innovation and Evolution: The smartphone industry is marked by relentless innovation. Economic analysis keeps these companies nimble. It guides them in identifying emerging trends, predicting shifts in consumer demand, and adapting their product portfolios accordingly. This continuous evolution ensures that they remain at the forefront of technology and market leadership.
Global Market Penetration: Beyond domestic markets, economic analysis also aids in global market penetration. It helps companies adapt their product offerings to suit the economic conditions, cultural nuances, and consumer behaviors of diverse regions, thus facilitating international expansion.
In conclusion, the smartphone industry serves as a prominent showcase of how economic analysis, when wielded effectively, can be a game-changer. It’s not just about making phones; it’s about crafting a strategy that resonates with consumers, maximizes value, and ensures sustained leadership in a fiercely competitive landscape. As technology continues to advance, the smartphone industry’s reliance on economic analysis will remain a cornerstone of its success.”
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Product Differentiation: What It Is, How Businesses Do It, and the 3 …
Optimal product positioning is a strategic imperative for businesses looking to thrive in competitive markets. Leveraging economic analysis as a foundational tool in this process can lead to cost optimization, improved pricing strategies, targeted market segmentation, resource allocation efficiency, risk mitigation, and ultimately, a significant competitive advantage. By integrating economic insights into their decision-making processes, companies can position their products effectively, attract loyal customers, and secure a strong foothold in their respective industries.
Expanding on the concept of optimal product positioning and the strategic significance of leveraging economic analysis, let’s delve deeper into each of the key benefits it offers:
Cost Optimization: Economic analysis empowers businesses to identify and eliminate unnecessary costs in their product positioning strategies. By conducting a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis, companies can refine their approach, ensuring that every dollar spent contributes to enhancing their market presence and profitability. This disciplined cost management not only bolsters the bottom line but also enables businesses to offer competitive pricing without compromising quality.
Improved Pricing Strategies: The pricing of a product is a critical element of its positioning. Economic analysis enables companies to determine the sweet spot in pricing—finding the balance between maximizing revenue and meeting consumer expectations. Whether it involves dynamic pricing models, bundling strategies, or value-based pricing, this insight-driven approach allows businesses to set prices that attract customers and boost profitability.
Targeted Market Segmentation: In an era of increasingly diverse consumer preferences, successful product positioning demands a keen understanding of different market segments. Economic analysis provides the data and insights necessary to identify and prioritize these segments effectively. By tailoring marketing efforts and product features to specific customer groups, businesses can optimize their appeal and foster deeper connections with their audience.
Resource Allocation Efficiency: Scarce resources, such as time, manpower, and marketing budgets, must be allocated efficiently to maximize their impact. Economic analysis helps companies make informed decisions regarding where and how to allocate these resources for the greatest return on investment. Whether it’s focusing on high-potential markets or optimizing advertising spend, resource allocation becomes a strategic asset.
Risk Mitigation: Every product positioning strategy carries inherent risks, from market saturation to unexpected economic downturns. By employing economic analysis, businesses can anticipate and quantify these risks, developing contingency plans and risk mitigation strategies. This proactive approach ensures resilience in the face of challenges, safeguarding the brand’s reputation and market position.
Competitive Advantage and Innovation: In the relentless competition of the marketplace, staying ahead requires innovation. Economic analysis not only uncovers opportunities for differentiation but also encourages continuous improvement. Businesses that embrace economic insights are better positioned to innovate their products, services, and strategies to meet evolving consumer demands and preferences.
Performance Measurement and Adaptation: Setting clear key performance indicators (KPIs) based on economic analysis allows companies to measure the success of their product positioning strategies accurately. Regular performance evaluations provide opportunities for course correction and adaptation, ensuring that the chosen positioning remains aligned with market dynamics and consumer expectations.
In a nutshell, optimal product positioning guided by economic analysis is not merely a strategic choice; it’s a business imperative. It empowers companies to navigate the complexities of competitive markets with precision and confidence. By leveraging economic insights, businesses can fine-tune their strategies, allocate resources wisely, mitigate risks effectively, and ultimately secure a distinctive competitive advantage that drives sustained success in their respective industries.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Analysis of Toyota Motor Corporation | Thembani Nkomo
More links
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: The Importance of Competition for the American Economy | CEA …
