Introduction
Cardiovascular health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, and for men, in particular, it plays a significant role in maintaining a strong heart and a long, fulfilling life. In this article, we will explore the importance of cardiovascular health, risk factors that men should be aware of, and practical steps to promote a healthy heart.
Cardiovascular health is undeniably a cornerstone of well-being, and for men, it carries exceptional importance in ensuring a robust heart and a life filled with vitality and fulfillment. Let’s dive deeper into this vital subject, examining not only the significance of cardiovascular health but also the key risk factors men should be mindful of and actionable strategies to bolster heart health:
The Essence of Cardiovascular Health: The cardiovascular system, comprising the heart and blood vessels, serves as the lifeline of the body. It is responsible for pumping oxygen and nutrients to every cell, tissue, and organ, sustaining their function. Thus, a healthy heart and circulatory system are paramount for overall physical well-being.
- Role in Longevity: A strong heart is often synonymous with a long and fulfilling life. Cardiovascular health is not just about avoiding diseases but also about experiencing vitality and quality of life well into old age.
Recognizing Risk Factors: Men should be well-informed about the risk factors that can undermine cardiovascular health. These include:
High Blood Pressure: Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a leading risk factor for heart disease. Regular blood pressure monitoring and management are essential.
High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol can contribute to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease.
Smoking: Tobacco use is a major contributor to heart disease. Quitting smoking is one of the most impactful steps men can take to protect their heart health.
Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can weaken the heart and increase the risk of heart disease. Regular exercise is a powerful ally in maintaining cardiovascular health.
Unhealthy Diet: Diets rich in saturated fats, salt, and processed foods can contribute to heart disease. Opting for a heart-healthy diet abundant in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is essential.
Excessive Stress: Chronic stress can have detrimental effects on the heart. Stress management techniques, such as meditation and relaxation exercises, can be beneficial.
Family History: A family history of heart disease can increase an individual’s risk. Knowing one’s family medical history can help in taking preventive measures.
Proactive Steps for a Healthy Heart: Fortunately, there are numerous practical steps men can take to promote cardiovascular health:
Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, supports heart health by strengthening the heart muscle and improving circulation.
Healthy Eating Habits: Adopting a heart-healthy diet that prioritizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help control cholesterol and blood pressure.
Regular Checkups: Regular medical checkups are crucial for monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other heart health indicators. These checkups enable early detection and intervention.
Stress Management: Managing stress through relaxation techniques, mindfulness, or hobbies can reduce the strain on the heart.
Quitting Smoking: For smokers, quitting is one of the most impactful decisions for heart health. Numerous resources and support systems are available to help individuals quit smoking.
Medication and Treatment: In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage risk factors like high blood pressure or high cholesterol. Following prescribed treatments is essential.
Community and Support: Encouraging open dialogue about cardiovascular health within communities and among friends and family members can foster a collective commitment to heart health. Men can support each other in making healthier lifestyle choices.
In conclusion, cardiovascular health stands at the core of well-being for men and is a vital determinant of a fulfilling and extended life. By recognizing risk factors, taking proactive measures, and fostering a heart-healthy community, men can embark on a journey toward not only a robust heart but also a rich and vibrant existence filled with vitality and longevity. Prioritizing cardiovascular health is an investment that pays lifelong dividends.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Coronary Artery Disease: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
The Significance of Cardiovascular Health:
The cardiovascular system, comprising the heart and blood vessels, is responsible for pumping oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. A healthy cardiovascular system is vital for sustaining life and overall vitality. Here’s why cardiovascular health is of paramount importance:
A robust and well-functioning cardiovascular system is the cornerstone of good health and longevity. Let’s delve deeper into why cardiovascular health should be considered paramount:
1. Oxygen Delivery: The cardiovascular system’s primary role is to transport oxygen-rich blood to every cell, tissue, and organ in the body. This oxygen is essential for cellular function and energy production. Without a properly functioning cardiovascular system, the body’s cells would starve for oxygen, leading to dysfunction and even cell death.
2. Nutrient Distribution: In addition to oxygen, the cardiovascular system is responsible for delivering vital nutrients, including glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids, to cells throughout the body. These nutrients are the building blocks of life and are necessary for cell growth, repair, and maintenance.
3. Waste Removal: The cardiovascular system also plays a crucial role in removing waste products and carbon dioxide from cells. This process ensures the body remains free of harmful metabolic byproducts and maintains a stable internal environment.
4. Temperature Regulation: Blood circulation helps regulate body temperature. By redistributing heat, the cardiovascular system ensures that the body stays within a narrow temperature range conducive to cellular function. In cold conditions, it directs warm blood to the extremities, while in hot conditions, it aids in dissipating heat through sweat.
5. Immune Response: The bloodstream is a conduit for immune cells and antibodies. A healthy cardiovascular system facilitates the immune response by allowing immune cells to quickly reach sites of infection or injury, aiding in the body’s defense against pathogens.
6. Stamina and Endurance: Cardiovascular health directly impacts an individual’s stamina and endurance. A strong heart and efficient blood vessels enable the body to perform physical activities with less strain, leading to improved fitness and overall vitality.
7. Disease Prevention: A well-maintained cardiovascular system is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, and hypertension. By prioritizing cardiovascular health, individuals can mitigate their risk factors for these potentially life-threatening conditions.
8. Cognitive Function: Research suggests a strong link between cardiovascular health and cognitive function. A healthy cardiovascular system contributes to adequate blood flow to the brain, promoting memory, concentration, and overall cognitive well-being.
9. Emotional Well-Being: Cardiovascular exercise, such as jogging or swimming, releases endorphins—natural mood lifters. These endorphins help reduce stress, anxiety, and depression, contributing to emotional well-being.
10. Longevity: Perhaps most importantly, cardiovascular health is closely tied to longevity. Individuals who take proactive steps to maintain their cardiovascular system are more likely to enjoy a longer, healthier life with a higher quality of life in their later years.
In summary, cardiovascular health is paramount because it underpins nearly every aspect of human vitality and well-being. By nurturing and caring for our cardiovascular system through a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management, we can safeguard our long-term health and enjoy the benefits of a strong, resilient cardiovascular system throughout our lives.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Life’s Essential 8: Updating and Enhancing the American Heart …

Preventing Heart Disease:
Cardiovascular health is a primary defense against heart disease, the leading cause of death for men worldwide. Maintaining a healthy heart significantly reduces the risk of heart-related conditions such as heart attacks and strokes.
Cardiovascular health serves as a robust shield against heart disease, which stands as the foremost global cause of mortality among men. The importance of nurturing a healthy heart extends far beyond simply reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes; it’s a fundamental aspect of overall well-being and longevity.
1. Heart Disease Complexity: Understanding the complexity of heart disease is essential. It encompasses a spectrum of conditions, including coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, arrhythmias, and more. A focus on cardiovascular health is akin to addressing the root causes and risk factors that contribute to these multifaceted heart-related issues.
2. Comprehensive Prevention: Maintaining cardiovascular health goes beyond preventing acute events like heart attacks. It involves comprehensive prevention, tackling risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, and diabetes. By addressing these factors, individuals can significantly reduce their long-term risk of heart disease.
3. Enhancing Quality of Life: A healthy heart translates into a higher quality of life. It enables individuals to remain active, engage in physical activities they enjoy, and maintain vitality as they age. Cardiovascular health is the cornerstone of an active and fulfilling lifestyle.
4. Empowering Longevity: A well-maintained heart is a key to longevity. By prioritizing cardiovascular health through lifestyle choices, individuals can increase their life expectancy and enjoy more years of good health, free from the limitations imposed by heart-related conditions.
5. Reducing Healthcare Costs: Preventing heart disease through cardiovascular health not only benefits individuals but also reduces healthcare costs. Fewer heart-related hospitalizations, surgeries, and treatments mean lower healthcare expenses and a more sustainable healthcare system.
6. Impact on Mental Health: The connection between heart health and mental well-being is significant. Cardiovascular conditions can lead to depression and anxiety, while a healthy heart supports emotional resilience and a positive outlook on life.
7. Lifestyle Choices Matter: The choices individuals make every day, from their diet and exercise routine to their stress management practices, play a pivotal role in maintaining cardiovascular health. By making informed, heart-healthy choices, individuals can take charge of their well-being.
8. Risk Factor Management: Recognizing the importance of cardiovascular health underscores the need to manage risk factors diligently. Regular check-ups, blood pressure monitoring, cholesterol checks, and diabetes management are crucial components of this proactive approach.
9. Family Health Legacy: Cardiovascular health extends its benefits to future generations. By modeling and prioritizing a heart-healthy lifestyle, individuals set positive examples for their families and contribute to the prevention of heart disease in their lineage.
10. Holistic Well-Being: Embracing cardiovascular health is a holistic approach to well-being. It promotes not only physical health but also emotional and social well-being, creating a harmonious and fulfilling life.
In summary, cardiovascular health is the linchpin of a robust defense against heart disease and its multifaceted challenges. Embracing this aspect of well-being isn’t just about preventing heart attacks and strokes; it’s about enhancing the quality and longevity of life, reducing healthcare burdens, and empowering individuals to lead vibrant, active, and fulfilling lives. It’s an investment in well-being that yields rich dividends throughout life’s journey.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Keeping Your Heart Healthy – familydoctor.org

Optimal Blood Pressure:
Cardiovascular health helps regulate blood pressure. High blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease, so keeping it in check is essential for long-term well-being.
Blood Pressure Management: The Key to Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular health and blood pressure are intertwined aspects of overall well-being, and their close relationship underscores the importance of managing blood pressure effectively. Here, we delve into the significance of blood pressure regulation and its profound impact on long-term health:
**1. ** High Blood Pressure: A Silent Threat:
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, often earns the moniker of a “silent killer” because it frequently goes unnoticed until complications arise. Uncontrolled hypertension places significant stress on the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health issues.
**2. ** Cardiovascular Health and Blood Pressure:
Cardiovascular health plays a pivotal role in regulating blood pressure. A strong and efficient cardiovascular system can effectively pump blood throughout the body, reducing the force exerted on arterial walls. This helps maintain blood pressure within a healthy range.
**3. ** The Importance of Blood Pressure Regulation:
Blood pressure regulation is essential for preventing the development and progression of heart disease. High blood pressure can damage the arteries, lead to the formation of fatty plaques, and increase the risk of blood clots, all of which contribute to cardiovascular problems.
**4. ** Long-Term Consequences:
Uncontrolled high blood pressure can have long-term consequences for cardiovascular health. It can lead to conditions like atherosclerosis (narrowing of the arteries), which restricts blood flow and increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
**5. ** Practical Steps for Blood Pressure Management:
Managing blood pressure effectively is a cornerstone of cardiovascular health. Here are practical steps to help maintain healthy blood pressure:
Dietary Choices: Adopt a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low in sodium and saturated fats.
Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to keep the cardiovascular system strong and support healthy blood pressure levels.
Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation, mindfulness, or yoga to help keep stress-related blood pressure spikes in check.
Weight Management: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight can contribute to elevated blood pressure.
Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking: Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking are risk factors for high blood pressure. Reducing or eliminating these habits is beneficial.
Medication Adherence: If prescribed medication for hypertension, take it as directed and attend regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider.
**6. ** Blood Pressure Monitoring:
Regular monitoring of blood pressure is crucial. Home blood pressure monitors are widely available and can help individuals keep track of their readings between healthcare visits.
**7. ** Consultation with Healthcare Provider:
Individuals should consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance on blood pressure management. They can recommend strategies, prescribe medication if necessary, and monitor progress.
In Conclusion:
Cardiovascular health and blood pressure regulation are intrinsically linked, with blood pressure management serving as a vital component of overall well-being. By understanding the significance of maintaining healthy blood pressure levels, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart disease and related complications. Prioritizing blood pressure regulation is an investment in a healthier, longer, and more vibrant life.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Heart Attack Recovery: How Long It Takes & What to Expect

Enhanced Physical Performance:
A strong cardiovascular system enhances physical performance. Whether you’re engaging in sports, recreational activities, or simply performing daily tasks, good cardiovascular health ensures your body can meet the demands.
A robust cardiovascular system indeed serves as a powerful asset that extends beyond the boundaries of health and longevity. It plays a pivotal role in enhancing physical performance, ensuring that individuals can excel in various aspects of life. Let’s explore this idea further, highlighting the profound impact of cardiovascular health on physical capabilities:
Elevated Athletic Performance: For athletes and sports enthusiasts, a strong cardiovascular system is the bedrock of peak performance. It allows the body to efficiently deliver oxygen-rich blood to muscles, enhancing endurance, speed, and stamina. Athletes with well-conditioned hearts can push their limits, achieve personal bests, and excel in their chosen sports.
Endurance Sports: Long-distance runners, cyclists, and swimmers, among others, heavily rely on their cardiovascular fitness to sustain prolonged efforts. A robust heart ensures they can maintain a high level of performance over extended periods.
Team Sports: Team sports like soccer, basketball, and football require bursts of intense effort interspersed with periods of lower activity. A strong cardiovascular system aids in quick recovery between these bursts, allowing players to maintain their effectiveness throughout the game.
Enhanced Daily Activities: Beyond sports, cardiovascular health greatly influences everyday life. Mundane tasks such as climbing stairs, carrying groceries, or playing with children become more manageable when the heart efficiently pumps oxygen to working muscles. Individuals with good cardiovascular fitness experience less fatigue during these activities.
Increased Productivity: In the workplace, a healthy cardiovascular system can boost productivity. Employees with better cardiovascular fitness are often more energetic, focused, and alert. They can handle demanding workloads with greater ease and efficiency.
Quality of Life: Cardiovascular health directly impacts one’s quality of life. Activities that bring joy and fulfillment, such as hiking, dancing, or traveling, become more accessible and enjoyable when the heart is in excellent condition. Moreover, the emotional and psychological benefits of physical activity contribute to an overall sense of well-being.
Healthy Aging: As individuals age, maintaining cardiovascular health becomes even more critical. A strong heart and circulatory system support independence in older age by ensuring the ability to engage in daily activities without undue fatigue or limitations.
Longevity and Vitality: A well-functioning cardiovascular system contributes to a longer and more vibrant life. Individuals who prioritize heart health not only extend their years but also enhance the quality of those years, enjoying a more active and fulfilling retirement.
Mental Benefits: Physical activity associated with cardiovascular fitness has profound mental benefits. It reduces stress, anxiety, and depression, leading to improved cognitive function and better decision-making abilities.
In essence, a strong cardiovascular system acts as a performance enhancer in every facet of life. It equips individuals to excel in sports, thrive in daily tasks, and lead a life brimming with vitality and achievement. By prioritizing cardiovascular health through regular exercise, a balanced diet, and other heart-healthy practices, individuals can unlock their full physical potential and embrace the myriad opportunities that come their way. A healthy heart is not only the foundation of a longer life but also the key to a life lived to its fullest potential.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Cycling – health benefits – Better Health Channel

Improved Stamina:
Cardiovascular fitness increases stamina, allowing you to engage in activities for longer durations without feeling fatigued.
Cardiovascular fitness, often referred to as aerobic fitness, is a key determinant of endurance and stamina. Here’s a deeper exploration of how cardiovascular fitness enhances stamina and enables individuals to engage in activities for longer durations without succumbing to fatigue:
1. Enhanced Oxygen Delivery: Cardiovascular fitness improves the efficiency of the heart and blood vessels in transporting oxygen-rich blood to working muscles. This increased oxygen supply is essential for sustaining energy production during prolonged physical activities.
2. Efficient Energy Production: Aerobic exercise, which promotes cardiovascular fitness, trains the body to utilize oxygen and available energy sources (such as glucose and fatty acids) more efficiently. This efficient energy utilization helps delay the onset of fatigue.
3. Delayed Lactic Acid Buildup: Lactic acid buildup in muscles is a common contributor to fatigue during intense physical exertion. Cardiovascular fitness helps the body clear lactic acid more effectively, allowing individuals to push their limits and engage in activities for longer periods.
4. Improved Recovery: A well-conditioned cardiovascular system aids in quicker post-exercise recovery. Reduced recovery time means less downtime between activities, allowing individuals to engage in more extended bouts of exercise or physical tasks.
5. Enhanced Endurance Training: Cardiovascular fitness is a foundational element of endurance training. By consistently challenging the cardiovascular system through activities like running, cycling, or swimming, individuals can progressively increase their stamina over time.
6. Mental Stamina: Cardiovascular fitness isn’t limited to physical benefits alone. Engaging in aerobic exercise also enhances mental stamina. Individuals with better cardiovascular fitness often exhibit greater mental resilience, focus, and motivation to sustain physical efforts.
7. Everyday Activities: Improved stamina resulting from cardiovascular fitness isn’t limited to athletic pursuits. It translates into everyday life, making routine activities—such as walking, climbing stairs, or carrying groceries—feel less tiring and more manageable.
8. Weight Management: Cardiovascular fitness plays a crucial role in weight management. By increasing the ability to engage in longer and more intense physical activities, it aids in calorie expenditure, which can be instrumental in weight loss or maintenance efforts.
9. Quality of Life: Having good stamina means individuals can participate more fully in various aspects of life, from recreational sports and hobbies to spending quality time with loved ones. It contributes to an overall improved quality of life.
10. Long-Term Health Benefits: Consistent cardiovascular fitness is associated with reduced risk factors for cardiovascular diseases, obesity, and other chronic health conditions. It supports long-term health and well-being.
In conclusion, cardiovascular fitness is a powerful tool for enhancing stamina and endurance, allowing individuals to engage in activities for extended periods without succumbing to fatigue. It offers physical, mental, and health-related benefits that contribute to an active and fulfilling life. Regular aerobic exercise, tailored to one’s fitness level and preferences, is the key to reaping these stamina-boosting rewards.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Four Types of Exercise Can Improve Your Health and Physical Ability

Cognitive Health:
Research suggests a link between cardiovascular health and cognitive function. A healthy heart supports optimal brain function and may reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
The intriguing connection between cardiovascular health and cognitive function unveils a profound interplay between the heart and the brain. Delving deeper into this relationship reveals how a healthy heart serves as a guardian of cognitive well-being and may offer protection against cognitive decline:
1. Blood Flow and Oxygen: The heart’s primary role is to pump oxygen-rich blood throughout the body, including the brain. Adequate blood flow and oxygen supply are crucial for optimal cognitive function. A healthy heart ensures that the brain receives the nutrients and oxygen it needs to operate at its best.
2. Reduced Risk of Cognitive Decline: Studies have shown that individuals with better cardiovascular health are less likely to experience cognitive decline as they age. A strong heart contributes to better brain health, reducing the risk of conditions such as dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
3. Vascular Health: Cardiovascular health is closely tied to vascular health. The brain’s blood vessels play a vital role in cognitive function. Conditions like high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, and diabetes, which can result from poor cardiovascular health, may damage these vessels and impair cognitive abilities.
4. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress, common in cardiovascular conditions, can also affect the brain. These processes have been linked to cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases. A healthy heart can mitigate these risks.
5. Shared Risk Factors: Cardiovascular risk factors, such as high cholesterol, obesity, and diabetes, are often shared with cognitive decline risk factors. By addressing heart health, individuals can simultaneously reduce their risk of cognitive problems.
6. Lifestyle Choices: Many lifestyle choices that support cardiovascular health also benefit the brain. Regular exercise, a heart-healthy diet, and stress management practices have a positive impact on both cardiovascular and cognitive well-being.
7. Cognitive Reserve: A healthy heart may contribute to cognitive reserve—a concept suggesting that individuals with robust brain health can better withstand cognitive decline or brain injuries before noticeable symptoms appear.
8. Emotional Well-Being: Cardiovascular health and cognitive function are intertwined with emotional well-being. Individuals with healthy hearts may experience lower rates of depression and anxiety, which can negatively affect cognitive abilities.
9. Long-Term Well-Being: Recognizing the link between heart and brain health underscores the importance of long-term well-being. Cardiovascular health isn’t just about preventing heart attacks; it’s about preserving cognitive vitality and maintaining a high quality of life as individuals age.
10. Holistic Health: Embracing the connection between cardiovascular and cognitive health promotes a holistic approach to well-being. It encourages individuals to prioritize a heart-healthy lifestyle that not only extends life but also enriches it with mental clarity, resilience, and cognitive vitality.
In summary, the intriguing link between cardiovascular health and cognitive function emphasizes the importance of a healthy heart in safeguarding brain health. A heart that thrives supports optimal cognitive function, reduces the risk of cognitive decline, and contributes to overall well-being. By nurturing cardiovascular health, individuals not only protect their hearts but also invest in a future of cognitive vitality and mental well-being.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Life’s Essential 8: Updating and Enhancing the American Heart …

Longevity:
Cardiovascular health contributes to a longer, more active life. By taking care of your heart, you increase your chances of enjoying a fulfilling and extended lifespan.
The Fountain of Youth: Cardiovascular Health and Longevity
It’s often said that the key to a longer, more fulfilling life lies within our hearts. Cardiovascular health is not just a shield against diseases; it’s a passport to an extended and vibrant journey through life. Here, we explore how nurturing your cardiovascular well-being can contribute to a fulfilling and extended lifespan:
**1. ** Vitality Through the Ages:
Cardiovascular health is a timeless companion throughout life’s various stages. Whether you’re in your 30s, 50s, or beyond, a strong heart ensures that you can continue to embrace new experiences and maintain your zest for life.
**2. ** Reduced Risk of Heart Disease:
A well-maintained cardiovascular system significantly reduces the risk of heart disease, the leading cause of premature death. By taking care of your heart, you are actively working to prevent life-threatening conditions such as heart attacks and strokes.
**3. ** Enhanced Physical Activity:
A robust cardiovascular system equates to improved physical endurance and stamina. This means you can engage in a wide range of activities and hobbies, from hiking and dancing to playing sports and chasing after grandchildren.
**4. ** Mental and Emotional Well-Being:
Cardiovascular health isn’t limited to the physical domain; it also impacts mental and emotional well-being. A healthy heart supports cognitive function, reduces the risk of cognitive decline, and contributes to emotional resilience.
**5. ** Reduced Dependency:
A strong cardiovascular system can help maintain independence in later years. By reducing the risk of debilitating health issues, it enables individuals to enjoy self-sufficiency and autonomy.
**6. ** Fulfillment in Golden Years:
Cardiovascular health extends its benefits into retirement and the golden years. It empowers individuals to make the most of their retirement years, travel, pursue hobbies, and savor the joys of life without the encumbrance of chronic health problems.
**7. ** Positive Impact on Relationships:
Good heart health fosters the ability to engage in meaningful relationships. Whether it’s spending time with family, forming new friendships, or nurturing romantic connections, a vibrant heart contributes to the quality of these relationships.
**8. ** Inspirational Legacy:
When individuals prioritize their cardiovascular health, they become inspirations to others. Their commitment to well-being serves as a testament that age is just a number, and a fulfilling life is attainable at any stage.
**9. ** Global Perspective on Longevity:
On a global scale, societies that prioritize cardiovascular health tend to have higher life expectancies. Access to quality healthcare, heart-healthy diets, and active lifestyles contribute to extended lifespans.
**10. ** Community Impact:
Individuals who maintain cardiovascular health can actively engage in their communities, volunteering, mentoring, and contributing to the collective well-being.
In Conclusion:
Cardiovascular health isn’t just about preventing diseases; it’s about savoring the precious moments that life has to offer. By taking care of your heart, you’re not just adding years to your life; you’re adding life to your years. It’s a journey of vitality, fulfillment, and the enduring pursuit of a life well-lived. So, nurture your cardiovascular well-being, and embrace the promise of an extended and vibrant lifespan.
You can also read more about this here: Getting Good Sleep Could Add Years to Your Life – American …

Key Risk Factors for Men:
While cardiovascular health is essential for everyone, men face specific risk factors that make heart health a particular concern:
Indeed, cardiovascular health is a universal concern, but it’s important to recognize that men may face specific risk factors that warrant special attention and tailored preventive measures. Let’s delve into these unique risk factors that make heart health a particular concern for men:
Higher Incidence of Heart Disease: Statistically, men have a higher incidence of heart disease compared to women. This elevated risk begins to manifest in midlife and continues into older age. Understanding this gender-based difference is crucial in addressing men’s heart health.
Hormonal Differences: Hormonal differences between men and women can influence heart health. Estrogen, which is more prevalent in women, has cardio-protective effects. Menopause in women marks a time of increased heart disease risk, and the absence of these protective effects can be a contributing factor.
Risk Factors Unique to Men:
- Low Testosterone: Low testosterone levels in men, often associated with aging, obesity, or certain medical conditions, can increase the risk of heart disease. Monitoring and addressing hormonal imbalances is important for heart health.
- Increased Belly Fat: Men tend to carry excess weight around the abdomen, which is linked to a higher risk of heart disease. This visceral fat can contribute to insulin resistance and other metabolic issues.
Occupational and Lifestyle Factors: Men are often more engaged in physically demanding or high-stress occupations, which can impact heart health. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a reluctance to seek medical help can contribute to higher cardiovascular risk.
Greater Likelihood of Risky Behaviors: Men are statistically more likely to engage in risky behaviors that can harm their hearts. This includes a higher prevalence of smoking, which is a significant contributor to heart disease, as well as a tendency to delay seeking medical attention for symptoms.
Delayed Awareness: Men sometimes delay seeking medical help when experiencing symptoms of heart disease, possibly due to a perception of invincibility or a reluctance to admit vulnerability. Early intervention is crucial in managing heart conditions effectively.
Less Focus on Preventive Care: Men may not prioritize preventive healthcare as much as women do. Regular checkups, screenings, and risk assessments can help identify heart disease risk factors early and initiate timely interventions.
Given these unique risk factors, it’s imperative for men to take a proactive approach to heart health:
Regular Health Checkups: Men should schedule regular checkups with their healthcare providers to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other heart health indicators. These visits provide an opportunity to discuss risk factors and prevention strategies.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is paramount. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and quitting smoking or avoiding tobacco use.
Awareness and Education: Men should educate themselves about the signs and symptoms of heart disease and the importance of seeking timely medical attention. Knowledge empowers individuals to take control of their heart health.
Hormonal Health: For those experiencing hormonal imbalances or conditions affecting testosterone levels, consultation with a healthcare provider is essential to address these issues and mitigate associated heart disease risk.
In conclusion, while cardiovascular health is a universal concern, men may face specific risk factors that necessitate tailored attention to heart health. By acknowledging these unique risks, seeking regular medical care, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, and being proactive in addressing potential issues, men can take control of their cardiovascular well-being and enjoy long, healthy lives.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: Have all risk factors …
Age:
Men are more likely to develop heart disease as they age. It’s crucial to monitor heart health, especially after the age of 45.
The risk of heart disease indeed increases with age, particularly in men. Let’s explore why this trend occurs and why diligent heart health monitoring, especially after the age of 45, is imperative:
1. Age-Related Changes: As men age, several physiological changes occur in the cardiovascular system. The heart muscle may thicken, blood vessels can become less flexible, and cholesterol levels may rise. These age-related changes can collectively increase the risk of heart disease.
2. Accumulation of Risk Factors: Over time, individuals may accumulate risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, and obesity. These factors can compound the likelihood of developing cardiovascular issues as men grow older.
3. Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as a sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary habits, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption, can contribute to the development of heart disease over the years. These habits often become more ingrained as people age.
4. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes in men, particularly a decline in testosterone levels with age, may affect cardiovascular health. While the relationship between hormonal changes and heart disease is complex, it underscores the importance of monitoring heart health as men age.
5. Family History: Genetic factors play a significant role in heart disease risk. Men with a family history of heart disease may be at higher risk themselves, and this risk tends to become more pronounced as they age.
6. Early Detection: Monitoring heart health through regular check-ups, screenings, and lifestyle assessments becomes crucial as men reach and surpass the age of 45. Detecting risk factors or the early signs of heart disease allows for timely interventions and lifestyle modifications.
7. Preventive Measures: Taking proactive steps to address risk factors and adopt heart-healthy habits can substantially mitigate the risk of heart disease. Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and smoking cessation, can have a profound impact on cardiovascular health.
8. Medical Management: In some cases, medication or medical interventions may be necessary to manage risk factors or treat heart conditions. Regular monitoring helps healthcare professionals identify the need for such interventions promptly.
9. Quality of Life: Maintaining good heart health in midlife and beyond is not only about preventing heart disease but also about preserving a high quality of life. It enables men to enjoy their later years with vitality, independence, and the ability to engage in activities they love.
10. Family and Community Impact: Heart health isn’t solely an individual concern. It has a ripple effect on families and communities. By prioritizing heart health, men can serve as role models for their loved ones and contribute to the well-being of their communities.
In summary, as men age, the risk of heart disease tends to increase due to a combination of age-related changes, lifestyle factors, and genetic predispositions. Monitoring heart health becomes essential, especially after the age of 45, to detect and address risk factors or early signs of heart disease. Proactive measures, including lifestyle modifications and medical interventions when necessary, can significantly reduce the risk and promote a healthier and more fulfilling life in the later years.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Cardiovascular Risks Associated with Gender and Aging – PMC

Family History:
A family history of heart disease increases a man’s risk. Be aware of any familial predispositions and discuss them with a healthcare provider.
Understanding the influence of family history on heart disease risk is paramount in making informed decisions about heart health. Here’s a more comprehensive exploration of how a family history of heart disease can significantly impact an individual’s risk and the importance of discussing it with a healthcare provider:
1. Genetic Predisposition: Family history can reveal a genetic predisposition to heart disease. If close relatives, such as parents or siblings, have experienced heart conditions, it suggests a genetic link that may increase an individual’s susceptibility.
2. Risk Assessment: Healthcare providers use family history as a vital component of risk assessment. Knowing the extent and severity of heart disease within the family helps healthcare professionals tailor preventive strategies and screenings to address specific risks.
3. Early Warning: A family history of heart disease can serve as an early warning. It prompts individuals to be more vigilant about their heart health, motivating them to adopt heart-healthy lifestyle choices and seek regular check-ups and screenings.
4. Shared Lifestyle Factors: Beyond genetics, family history can highlight shared lifestyle factors that contribute to heart disease risk. Families often have similar dietary habits, physical activity levels, and exposure to environmental factors—all of which can influence heart health.
5. Potential for Early Intervention: Recognizing a family history of heart disease provides an opportunity for early intervention. Healthcare providers may recommend more frequent check-ups, cholesterol screenings, blood pressure monitoring, and other preventive measures to detect issues at an early stage.
6. Lifestyle Modification: Armed with knowledge of a family history of heart disease, individuals can take proactive steps to modify their lifestyle. This may involve adopting a heart-healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and quitting smoking.
7. Medication Consideration: In some cases, healthcare providers may consider medication as a preventive measure for individuals with a strong family history of heart disease. These medications can help manage risk factors like high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
8. Importance of Open Dialogue: Discussing family history with a healthcare provider is crucial. It allows for a comprehensive assessment of individual risk and informs personalized preventive strategies. Open dialogue also fosters a trusting patient-provider relationship.
9. Emotional Support: Coping with a family history of heart disease can be emotionally challenging. It’s essential to recognize the emotional impact and seek support, whether through counseling, support groups, or discussions with healthcare providers.
10. Empowerment: Knowing one’s family history empowers individuals to take control of their heart health. It shifts the focus from a sense of vulnerability to one of empowerment, enabling them to make informed decisions that can positively impact their future well-being.
In conclusion, a family history of heart disease is a critical piece of the heart health puzzle. It signifies genetic and lifestyle factors that can influence an individual’s risk. By discussing this history with a healthcare provider, individuals can access personalized guidance and support to mitigate their risk, adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle, and make informed choices that promote long-term cardiovascular well-being. It’s a proactive step towards a heart-healthy future.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Keeping Your Heart Healthy – familydoctor.org

Unhealthy Lifestyle:
Factors like smoking, poor dietary choices, excessive alcohol consumption, and physical inactivity can significantly elevate the risk of heart disease in men.
Navigating the Hazards: Mitigating Heart Disease Risk Factors for Men
Understanding the risk factors that can elevate the likelihood of heart disease in men is a crucial step towards preventing cardiovascular problems. Let’s delve deeper into these risk factors and explore how they can be managed and mitigated:
**1. ** Smoking: The Silent Arsonist:
Smoking is a leading contributor to heart disease. The toxic chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the heart and blood vessels, leading to the formation of fatty deposits in the arteries (atherosclerosis) and increasing the risk of blood clots.
Mitigation Strategy: Quitting smoking is the most effective way to reduce this risk. Seek support from smoking cessation programs and healthcare providers for a successful smoke-free journey.
**2. ** Dietary Choices: Fueling or Sabotaging Heart Health:
Poor dietary choices, such as consuming foods high in saturated and trans fats, excessive salt, and added sugars, can lead to high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and obesity – all risk factors for heart disease.
Mitigation Strategy: Adopt a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats like those found in nuts and olive oil. Limit processed foods and sugary beverages.
**3. ** Excessive Alcohol Consumption: A Risky Habit:
While moderate alcohol consumption may have some heart benefits, excessive drinking can increase blood pressure and lead to heart muscle damage, arrhythmias, and cardiomyopathy.
Mitigation Strategy: If you choose to consume alcohol, do so in moderation. For men, this generally means up to one drink per day.
**4. ** Physical Inactivity: A Sedentary Lifestyle’s Toll:
Lack of regular physical activity weakens the cardiovascular system, contributing to obesity, high blood pressure, and unhealthy cholesterol levels. Inactivity can also increase the risk of diabetes, another heart disease risk factor.
Mitigation Strategy: Engage in regular physical activity, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. Incorporate activities you enjoy into your routine, whether it’s walking, jogging, swimming, or dancing.
**5. ** Stress and Mental Health: Silent Contributors:
Chronic stress, anxiety, and depression can take a toll on heart health. They can lead to behaviors that increase heart disease risk, such as overeating, smoking, or excessive alcohol consumption.
Mitigation Strategy: Implement stress-reduction techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and yoga to manage stress effectively. Seek professional help when dealing with mental health concerns.
**6. ** High Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: Silent Predators:
Elevated blood pressure and cholesterol levels are direct risk factors for heart disease. They can lead to atherosclerosis, heart attacks, and strokes if left unmanaged.
Mitigation Strategy: Regularly monitor blood pressure and cholesterol levels. If they are high, work with healthcare providers to develop a management plan that may include medication and lifestyle changes.
**7. ** Diabetes: A Sneaky Co-Conspirator:
Diabetes significantly increases the risk of heart disease. Elevated blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and contribute to atherosclerosis.
Mitigation Strategy: If you have diabetes, carefully manage your blood sugar levels through medication, dietary choices, and regular monitoring.
In Conclusion:
Understanding the risk factors associated with heart disease in men is the first step in its prevention. By addressing and mitigating these factors through lifestyle changes, regular healthcare check-ups, and effective management strategies, men can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease and enjoy a heart-healthy life. It’s a journey towards a stronger, more vibrant heart and a future brimming with vitality.
You can also read more about this here: 7 powerful ways you can strengthen your heart | UCI Health …

High Blood Pressure and Cholesterol:
Elevated blood pressure and cholesterol levels are major risk factors for heart disease. Regular screenings and management are essential.
Elevated blood pressure and high cholesterol levels represent two of the most significant risk factors for heart disease, making their regular screening and management absolutely crucial for maintaining heart health. Let’s delve deeper into the importance of monitoring and controlling these vital cardiovascular indicators:
Blood Pressure Management:
The Silent Threat: High blood pressure, or hypertension, is often referred to as the “silent killer” because it typically presents no symptoms until it has caused significant damage to the heart and blood vessels. Regular blood pressure screenings are the primary means of detection.
A Risk Multiplier: Hypertension significantly amplifies the risk of heart disease. It puts extra strain on the heart, causing it to work harder to pump blood. Over time, this can lead to heart muscle thickening, weakened arteries, and an increased risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular issues.
Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet low in sodium, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress, can help lower blood pressure. For some individuals, medication may also be necessary.
Regular Monitoring: Regular blood pressure checks are essential, especially for those with a family history of hypertension or other risk factors. Monitoring blood pressure at home can provide valuable insights and early warnings.
Cholesterol Control:
The Cholesterol Connection: High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, are associated with the buildup of plaque in the arteries. This can narrow the arteries and restrict blood flow, increasing the risk of heart disease.
Screening and Assessment: Cholesterol levels should be regularly screened, and a lipid profile conducted to assess the levels of LDL cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, and triglycerides. Based on the results, healthcare providers can recommend appropriate interventions.
Dietary Choices: Adopting a heart-healthy diet that includes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins while limiting saturated and trans fats is vital for cholesterol management. Some individuals may also benefit from cholesterol-lowering medications prescribed by their healthcare provider.
Lifestyle Modifications: Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking are all effective ways to improve cholesterol levels and reduce heart disease risk.
Individualized Approach: Cholesterol management is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor. It requires an individualized approach based on a person’s specific risk factors and health profile.
In conclusion, elevated blood pressure and high cholesterol levels are formidable adversaries when it comes to heart health. They quietly undermine cardiovascular well-being and significantly increase the risk of heart disease. However, with regular screenings, early detection, and appropriate management strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to control these risk factors and protect their hearts.
The key takeaway is that heart health is within reach through preventive measures, lifestyle adjustments, and, when necessary, medical interventions. By prioritizing regular checkups, adhering to heart-healthy behaviors, and seeking guidance from healthcare providers, individuals can keep blood pressure and cholesterol levels in check, ultimately reducing their risk of heart disease and enjoying a longer and healthier life.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Heart Attack Recovery: How Long It Takes & What to Expect

Diabetes:
Men with diabetes are at a higher risk of heart disease. Managing blood sugar levels and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle are critical.
The connection between diabetes and an increased risk of heart disease is a critical health concern for men. Let’s delve into why this relationship exists and the vital importance of managing blood sugar levels and embracing a heart-healthy lifestyle:
1. Insulin Resistance: In type 2 diabetes, which is the most common form of diabetes in adults, the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance often leads to elevated blood sugar levels, which can damage blood vessels and the heart.
2. Impact on Blood Vessels: High blood sugar levels can cause inflammation and damage to the lining of blood vessels, a condition known as endothelial dysfunction. This damage makes blood vessels more susceptible to the formation of fatty deposits (atherosclerosis), narrowing them and reducing blood flow to the heart.
3. Increased Risk Factors: Diabetes is often accompanied by other risk factors for heart disease, such as obesity, high blood pressure, and abnormal lipid profiles (elevated triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol). The presence of these risk factors further escalates the risk of heart disease.
4. Blood Clot Formation: Diabetes can increase the likelihood of blood clot formation, especially when blood vessels are already compromised. Blood clots can block arteries, leading to heart attacks and strokes.
5. Autonomic Nervous System Dysfunction: Diabetes can affect the autonomic nervous system, which controls heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital functions. Dysfunction in this system can contribute to irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) and increase the risk of heart complications.
6. Silent Heart Disease: Diabetic individuals may develop heart disease without experiencing typical symptoms like chest pain (angina). This phenomenon is known as “silent heart disease,” making regular monitoring and preventive measures even more critical.
7. Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle plays a significant role in both diabetes management and heart health. Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and smoking cessation, can help manage diabetes and reduce the risk of heart disease.
8. Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining strict control over blood sugar levels is paramount for individuals with diabetes. This can be achieved through medication, insulin therapy, dietary choices, and regular monitoring.
9. Medication Management: Some medications used to manage diabetes may also have benefits for heart health, such as reducing the risk of heart attacks. It’s essential to work closely with healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
10. Early Detection: Routine medical check-ups and screenings are essential for early detection of heart disease in individuals with diabetes. Detecting problems early allows for timely intervention and management.
In conclusion, men with diabetes face a heightened risk of heart disease due to the complex interplay of factors related to blood sugar control, vascular health, and other associated risk factors. Managing blood sugar levels through medical guidance, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, and prioritizing regular check-ups are essential steps to reduce this risk and maintain overall well-being. By addressing both diabetes and heart health comprehensively, individuals can work towards a healthier and more heart-protected future.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: Have all risk factors …

Promoting Cardiovascular Health:
Now that we understand the significance and risk factors, let’s explore practical steps men can take to promote cardiovascular health:
Certainly, let’s delve into practical steps that men can take to promote and prioritize their cardiovascular health. These steps encompass a holistic approach to well-being, addressing various aspects of lifestyle and healthcare:
1. Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet:
- Embrace a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Limit saturated and trans fats, high-sodium foods, sugary beverages, and processed snacks.
- Control portion sizes to maintain a healthy weight.
2. Stay Physically Active:
- Engage in regular aerobic exercises like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling for at least 150 minutes per week.
- Incorporate strength training exercises to build muscle and boost metabolism.
- Aim for a balanced fitness routine that combines cardio, strength, and flexibility exercises.
3. Manage Weight Effectively:
- Maintain a healthy weight through a combination of a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Monitor calorie intake and consider consulting a registered dietitian or healthcare provider for personalized weight management guidance.
4. Quit Smoking:
- Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease. Seek smoking cessation support and resources to quit.
- Avoid exposure to secondhand smoke, which can also harm cardiovascular health.
5. Control Blood Pressure:
- Monitor blood pressure regularly, and work with a healthcare provider to manage it within a healthy range.
- Lifestyle modifications, including a low-sodium diet, exercise, and stress reduction techniques, can help control blood pressure.
6. Manage Cholesterol Levels:
- Understand your cholesterol levels and work with a healthcare provider to maintain healthy levels.
- Diet, exercise, and, if necessary, medication can help manage cholesterol.
7. Manage Diabetes:
- If you have diabetes or prediabetes, work closely with a healthcare team to control blood sugar levels.
- Monitor blood glucose regularly and adhere to a diabetes management plan.
8. Prioritize Mental Health:
- Chronic stress and mental health issues can impact cardiovascular health. Engage in stress-reduction activities like meditation, yoga, or hobbies.
- Seek support from mental health professionals if needed.
9. Get Regular Check-Ups:
- Schedule regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor heart health.
- Follow recommended screenings for blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes, and other risk factors.
10. Stay Hydrated and Limit Alcohol: – Stay properly hydrated by drinking plenty of water. – Limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels, as excessive drinking can harm the heart.
11. Prioritize Sleep: – Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. – Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a sleep-friendly environment.
12. Foster Social Connections: – Maintain healthy relationships and social connections, as social isolation can negatively impact heart health. – Engage in activities that promote emotional well-being.
13. Avoid Excessive Caffeine and Energy Drinks: – Limit caffeine intake, especially from energy drinks, as excessive caffeine consumption can affect heart rhythm.
14. Practice Safe Driving Habits: – Follow safe driving practices, wear seatbelts, and avoid aggressive driving behaviors that can lead to accidents and heart-related injuries.
15. Take Medications as Prescribed: – If prescribed medications for conditions like high blood pressure or cholesterol, take them as directed by a healthcare provider.
16. Stay Informed: – Stay up-to-date on the latest developments in cardiovascular health and research. – Be proactive in seeking information about heart-healthy living.
Remember that cardiovascular health is a lifelong journey, and small, sustainable changes can yield significant benefits over time. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance and to track progress in maintaining a healthy heart. By embracing these practical steps, men can take proactive control of their cardiovascular well-being and enjoy a life filled with vitality and longevity.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Walking – the first steps in cardiovascular disease prevention – PMC

Regular Checkups:
Schedule regular checkups with a healthcare provider to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall heart health.
Guardians of Your Heart: The Importance of Regular Heart Checkups
Regular heart checkups are the foundation of proactive cardiovascular health management. These checkups serve as a vital link between you and your healthcare provider, ensuring that potential heart issues are detected and addressed promptly. Let’s delve deeper into the significance of these checkups and what they encompass:
**1. ** Blood Pressure Monitoring: A Silent Indicator:
High blood pressure often lurks without symptoms, earning its reputation as the “silent killer.” Regular checkups allow healthcare providers to monitor your blood pressure, ensuring it stays within a healthy range. Early detection and intervention can prevent long-term complications.
**2. ** Cholesterol Levels: Unmasking Hidden Threats:
Elevated cholesterol levels can lead to the buildup of plaque in your arteries, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease. Regular checkups include assessing your cholesterol levels, enabling healthcare providers to identify potential issues and recommend appropriate interventions.
**3. ** Overall Heart Health Assessment: A Comprehensive Approach:
Beyond blood pressure and cholesterol, regular heart checkups encompass a comprehensive assessment of your cardiovascular health. Healthcare providers evaluate your risk factors, family history, and lifestyle to create a personalized heart health plan.
**4. ** Discussion of Symptoms and Concerns:
These checkups provide an opportunity to discuss any symptoms or concerns you may have, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or palpitations. Open communication helps healthcare providers pinpoint potential issues.
**5. ** Lifestyle and Risk Factor Evaluation:
Healthcare providers assess your lifestyle habits, including diet, physical activity, and smoking status. They also review your family history to identify any genetic predispositions to heart disease.
**6. ** Medication Management:
If you’re taking medications for conditions like high blood pressure or cholesterol, regular checkups include medication management. Healthcare providers ensure your medications are effective and adjust them as needed.
**7. ** Preventive Recommendations:
Based on the assessment, healthcare providers offer preventive recommendations tailored to your specific needs. These may include dietary changes, exercise routines, stress management techniques, and smoking cessation support.
**8. ** Tracking Progress:
Regular checkups allow for the tracking of your heart health progress over time. Improvements or potential concerns can be identified and addressed through ongoing assessments.
**9. ** Risk Reduction:
Perhaps most importantly, these checkups are a proactive step in reducing your risk of heart disease. By monitoring and managing your cardiovascular health, you’re taking control of your well-being and working towards a heart-healthy future.
**10. ** Peace of Mind:
Regular heart checkups provide peace of mind. Knowing that you’re actively monitoring your heart health and addressing any concerns as they arise can alleviate anxiety and empower you to make informed decisions about your well-being.
In Conclusion:
Regular heart checkups are more than just medical appointments; they are your bridge to a healthier, longer life. By scheduling these checkups and maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider, you’re taking proactive steps to safeguard your cardiovascular health. Remember, a strong and healthy heart is your most valuable asset, and regular checkups are your armor against potential heart-related challenges.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Diabetes and Your Heart | CDC

Healthy Diet:
Adopt a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low in saturated and trans fats. Limit salt and sugar intake.
Adopting a heart-healthy diet is one of the most impactful steps individuals can take to safeguard their cardiovascular well-being. A diet that promotes heart health not only reduces the risk of heart disease but also supports overall health and vitality. Let’s explore this concept further and emphasize the key components of a heart-healthy diet:
Embrace Nutrient-Rich Foods:
Fruits and Vegetables: These are nutritional powerhouses rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and dietary fiber. Aim to fill half your plate with a colorful variety of fruits and vegetables. They help reduce the risk of heart disease by improving blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat bread over refined grains. Whole grains are packed with fiber, which aids in controlling cholesterol levels and maintaining steady blood sugar.
Lean Proteins: Incorporate lean protein sources such as skinless poultry, fish, legumes, tofu, and lean cuts of meat. Fish, particularly fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, is rich in heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids, which can reduce the risk of irregular heartbeats and lower triglycerides.
Mindful Fat Choices:
Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats in your diet, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats are monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats that can help lower bad LDL cholesterol when used in place of saturated and trans fats.
Limit Saturated and Trans Fats: Minimize saturated fats found in red meat, full-fat dairy products, and some oils like coconut and palm oil. Avoid trans fats found in many processed and fried foods. These fats can raise bad cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
Watch Sodium Intake:
- Reduce Salt: High sodium intake can lead to high blood pressure, a major risk factor for heart disease. Limit the use of salt in cooking and avoid high-sodium processed foods. Opt for herbs, spices, and salt-free seasonings to flavor your dishes.
Moderate Sugar Consumption:
- Limit Added Sugars: Excessive sugar intake can contribute to obesity and increase the risk of heart disease. Be mindful of sugary beverages, desserts, and processed snacks. Opt for natural sweeteners like honey or fresh fruit to satisfy your sweet tooth.
Portion Control:
- Be Mindful of Portions: Watch portion sizes to avoid overeating. Eating in moderation helps maintain a healthy weight, which is crucial for heart health.
Stay Hydrated:
- Drink Water: Staying well-hydrated is essential for overall health. Limit sugary beverages and choose water, herbal teas, or unsweetened beverages as your primary sources of hydration.
Balanced Eating Patterns:
- Consistency Matters: Consistency in your eating patterns is important. Regular meals and snacks spaced throughout the day can help stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent overeating.
Meal Planning:
- Plan Ahead: Planning meals in advance and grocery shopping with a list can help you make healthier choices and reduce the temptation to buy unhealthy options.
Remember that adopting a heart-healthy diet is not a restrictive or joyless endeavor. It’s about making informed choices that prioritize your long-term well-being while still enjoying delicious and satisfying meals. Gradual changes in dietary habits can lead to lasting improvements in heart health. By fueling your body with wholesome, nutrient-rich foods and minimizing the intake of harmful fats, sodium, and sugars, you can take proactive steps to protect your heart and embrace a life filled with vitality and vitality.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: 7 powerful ways you can strengthen your heart | UCI Health …
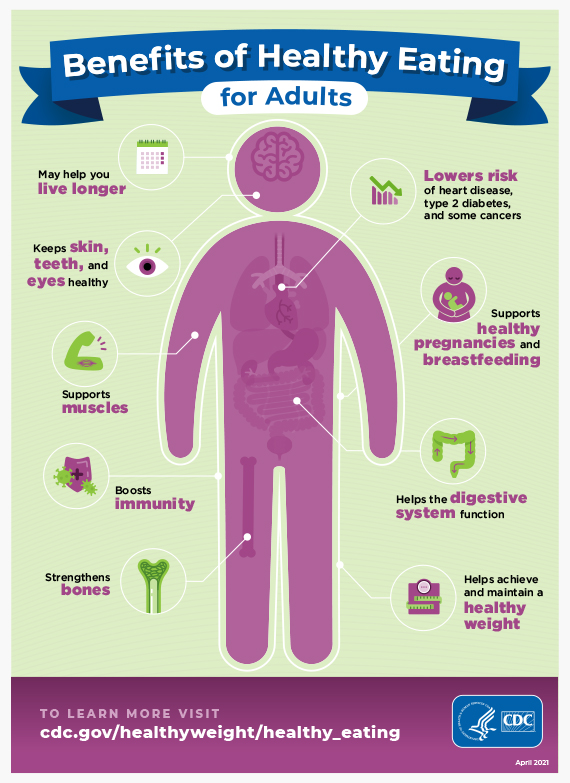
Regular Exercise:
Engage in regular physical activity, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. Cardiovascular workouts like brisk walking, jogging, or swimming are excellent choices.
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle, and it plays a pivotal role in promoting heart health. Expanding on the idea of engaging in regular exercise, especially cardiovascular workouts, provides a more comprehensive view of its benefits:
1. Cardiovascular Health: Cardiovascular exercises, such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, and cycling, are aptly named for their profound impact on heart health. These activities increase your heart rate, strengthen your heart muscle, and enhance its ability to pump blood efficiently. This improved cardiovascular fitness reduces the risk of heart disease, lowers blood pressure, and helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
2. Weight Management: Regular physical activity is a powerful tool for managing body weight. It helps burn calories, build lean muscle, and increase metabolic rate. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for heart health, as excess body fat can contribute to risk factors like high blood pressure and diabetes.
3. Blood Sugar Control: Exercise enhances the body’s sensitivity to insulin, allowing cells to better utilize glucose from the bloodstream. This improved insulin sensitivity is particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition, as it helps stabilize blood sugar levels.
4. Stress Reduction: Physical activity has a natural stress-relieving effect. It triggers the release of endorphins, which are mood-elevating chemicals in the brain. Reduced stress levels can have a positive impact on heart health by lowering the risk of stress-induced hypertension and promoting overall well-being.
5. Improved Blood Circulation: Cardiovascular workouts improve blood circulation throughout the body. This means that oxygen and nutrients are delivered more efficiently to tissues, while waste products are removed more effectively. Enhanced circulation benefits the heart and other vital organs.
6. Lowered Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a known risk factor for heart disease. Regular exercise can help reduce systemic inflammation by modulating the body’s immune response. This anti-inflammatory effect contributes to overall heart health.
7. Mental Health Benefits: Physical activity isn’t just beneficial for the body; it also has positive effects on mental health. Engaging in regular exercise can alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression, which are linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
8. Increased Energy Levels: Regular physical activity improves endurance and energy levels. With enhanced stamina, everyday tasks become more manageable, and individuals can engage in a broader range of activities without feeling fatigued.
9. Social Interaction: Many cardiovascular exercises can be enjoyed with others, such as group fitness classes or team sports. Social interaction and support can further boost mental and emotional well-being, which indirectly contributes to heart health.
10. Long-Term Heart Protection: Consistency is key. Regular physical activity is not just about immediate benefits; it’s an investment in long-term heart protection. It helps build a strong foundation for a healthy, vibrant life as you age.
Incorporating cardiovascular workouts into your weekly routine, with the goal of achieving at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, is a proactive step toward a healthier heart. Remember to consult with a healthcare provider before starting a new exercise regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or concerns. By making physical activity a regular part of your life, you’re taking a significant stride toward promoting heart health and overall well-being.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Lack of exercise is a major cause of chronic diseases – PMC

Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Achieve and maintain a healthy weight to reduce the strain on your heart and lower the risk of heart disease.
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is a fundamental pillar of heart health that not only reduces the strain on your heart but also significantly lowers the risk of heart disease. Here’s a closer look at how weight management impacts cardiovascular well-being:
1. Reducing Excess Strain: Carrying excess body weight places a significant burden on the heart. The heart has to work harder to pump blood throughout the body, which can lead to increased blood pressure and strain on the cardiovascular system. Achieving a healthy weight alleviates this extra load, allowing the heart to function more efficiently.
2. Lowering Blood Pressure: High blood pressure (hypertension) is a leading risk factor for heart disease. Excess weight is closely linked to hypertension. Losing weight through a combination of diet and exercise can lead to lower blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart-related complications.
3. Improving Cholesterol Levels: Obesity and excess body fat can contribute to unfavorable changes in cholesterol levels, including higher levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and lower levels of HDL (good) cholesterol. Weight loss can improve these lipid profiles, promoting heart health.
4. Managing Diabetes Risk: Excess weight is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes, which, in turn, increases the risk of heart disease. Maintaining a healthy weight can help prevent or manage diabetes and its cardiovascular consequences.
5. Enhancing Blood Sugar Control: Even without diabetes, carrying extra weight can lead to insulin resistance, making it harder for the body to control blood sugar levels. Weight loss can improve insulin sensitivity and contribute to better blood sugar control.
6. Reducing Inflammation: Obesity is associated with chronic inflammation, which plays a role in the development of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and heart disease. Losing weight can reduce inflammation and lower cardiovascular risk.
7. Decreasing Fat Deposits: Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, is linked to the accumulation of harmful fat deposits in and around the heart and blood vessels. Weight loss can help reduce these fat deposits and improve heart health.
8. Promoting Better Sleep: Obesity is a common contributor to sleep apnea, a condition that can disrupt sleep patterns and contribute to heart problems. Weight loss often leads to improved sleep quality, benefiting cardiovascular well-being.
9. Enhancing Physical Fitness: Shedding excess pounds can enhance physical fitness and endurance, making it easier to engage in regular exercise. Improved fitness levels further support heart health.
10. Boosting Confidence and Motivation: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can boost confidence and motivation. Feeling better physically and emotionally can inspire individuals to make sustained lifestyle changes that benefit their hearts.
11. Long-Term Heart Health: Weight management isn’t just about short-term results; it’s about long-term heart health. Sustainable weight loss and maintenance provide lasting benefits, reducing the risk of heart disease over a lifetime.
12. Holistic Well-Being: Weight management is a holistic approach to health that encompasses not only physical but also emotional well-being. It promotes a sense of accomplishment and overall vitality.
In conclusion, achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is a pivotal step in safeguarding heart health and reducing the risk of heart disease. It alleviates strain on the heart, improves cardiovascular risk factors, and fosters overall well-being. It’s an investment in long-term health and longevity, empowering individuals to enjoy a life filled with vitality and a reduced risk of heart-related complications.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: 7 powerful ways you can strengthen your heart | UCI Health …

Manage Stress:
Practice stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga to help manage stress, which can contribute to heart disease.
Calm Hearts, Strong Defenses: The Role of Stress Reduction in Heart Health
The link between stress and heart health is a well-established one, and it underscores the importance of incorporating stress-reduction techniques into your daily life. Here, we explore the profound impact of stress on heart disease and the effective strategies to keep your heart resilient:
**1. ** Understanding the Stress-Heart Connection:
Stress, particularly chronic stress, can have a detrimental effect on the cardiovascular system. It can lead to elevated blood pressure, increased heart rate, and the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. Over time, these responses can contribute to the development of heart disease.
**2. ** Mindfulness: A Present-Moment Sanctuary:
Mindfulness is the practice of being fully present in the moment, free from judgment and excessive worry about the past or future. It promotes a state of relaxation, reducing the body’s stress response. Regular mindfulness practice can help lower blood pressure and improve heart health.
**3. ** Meditation: A Tranquil Journey Inward:
Meditation offers a similar respite from the demands of daily life. By focusing your attention and quieting the mind, meditation can lower stress levels, reduce anxiety, and enhance emotional well-being—all of which have a positive impact on heart health.
**4. ** Yoga: A Mind-Body Harmony:
Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation. It promotes relaxation, flexibility, and stress reduction. Regular yoga practice can help lower blood pressure, improve circulation, and strengthen the heart.
**5. ** The Power of Stress Reduction:
By incorporating stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine, you’re essentially fortifying your heart’s defenses. Stress reduction helps prevent the detrimental effects of chronic stress on the cardiovascular system.
**6. ** Restorative Sleep: A Stress-Busting Ally:
Quality sleep is another crucial component of heart health. Stress-reduction techniques can improve sleep quality, further enhancing the heart’s ability to recover and repair during the night.
**7. ** Healthy Coping Mechanisms:
Stress can lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as overeating, smoking, or excessive alcohol consumption. By reducing stress through mindfulness, meditation, or yoga, you can mitigate these behaviors that contribute to heart disease.
**8. ** Consistency Matters:
The key to reaping the benefits of stress-reduction techniques is consistency. Regular practice, even if just a few minutes a day, can have a lasting impact on your heart health.
**9. ** Personalized Approach:
Find the stress-reduction technique that resonates with you the most. Whether it’s mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or a combination of these practices, choose what aligns with your preferences and lifestyle.
**10. ** Holistic Heart Care:
Stress reduction is an integral part of holistic heart care. Combining it with a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and regular checkups with a healthcare provider creates a comprehensive strategy to protect your cardiovascular health.
In Conclusion:
Managing stress is not just about maintaining mental and emotional well-being; it’s a vital aspect of heart health. By incorporating mindfulness, meditation, or yoga into your daily routine, you’re nurturing your heart, bolstering its resilience, and reducing the risk of heart disease. Remember, a calm mind is a kind gift to your heart, ensuring it beats strong and steady for a long and healthy life.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Lifestyle Changes for Heart Attack Prevention | American Heart …

Quit Smoking:
If you smoke, quit. Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease, and quitting is one of the most significant steps you can take for your cardiovascular health.
Addressing smoking habits is undeniably one of the most impactful actions individuals can take to enhance their cardiovascular health and overall well-being. Smoking is a potent risk factor for heart disease, and quitting smoking represents a profound positive change. Let’s delve deeper into why quitting smoking is such a critical step for heart health:
Reducing Heart Disease Risk:
Direct Link to Heart Disease: Smoking damages the heart and blood vessels in multiple ways. It leads to the accumulation of fatty deposits in the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis, which narrows the arteries and restricts blood flow. This process significantly raises the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Increased Blood Pressure: Smoking causes a temporary increase in blood pressure, putting additional strain on the heart. Over time, this sustained pressure can lead to hypertension, a leading cause of heart disease.
Harmful Effects on Cholesterol: Smoking lowers high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels, the “good” cholesterol that helps remove bad cholesterol from the bloodstream. This imbalance can result in higher levels of bad LDL cholesterol, increasing the risk of heart disease.
Rapid Benefits of Quitting:
Immediate Improvements: The positive effects of quitting smoking begin almost immediately. Within just a few hours, blood pressure and heart rate start to drop. Within days, carbon monoxide levels in the blood decrease, allowing oxygen levels to return to normal.
Long-Term Benefits: Over time, the risk of heart disease steadily decreases the longer a person remains smoke-free. Within a year of quitting, the risk of heart attack drops significantly, and after several years, it approaches that of a non-smoker.
Improvement in Blood Vessel Function:
- Enhanced Blood Flow: Smoking impairs the function of the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels, reducing their ability to relax and expand. Quitting smoking allows blood vessels to regain their normal function, improving blood flow throughout the body, including the heart.
Lowering Risk of Blood Clots:
- Reduced Clot Formation: Smoking promotes the formation of blood clots, which can block arteries and lead to heart attacks. Quitting smoking reduces the risk of these dangerous clots.
Quality of Life and Overall Health:
Improved Physical Fitness: Smoking hampers physical endurance and lung capacity. Quitting smoking enhances physical fitness, making it easier to engage in regular exercise, which is vital for heart health.
Reduced Risk of Secondary Health Issues: Smoking is associated with a range of health issues, including lung disease and cancer. Quitting smoking not only improves heart health but also lowers the risk of these other debilitating conditions.
Support and Resources:
- Seek Help: Quitting smoking can be challenging, but numerous resources and support systems are available. Consider consulting with a healthcare provider, joining smoking cessation programs, or using smoking cessation aids like nicotine replacement therapy or prescription medications.
In conclusion, quitting smoking is an extraordinary gift to your heart and overall health. It’s a direct and tangible way to reduce the risk of heart disease, improve cardiovascular function, and enhance the quality of life. The decision to quit smoking may be one of the most significant and life-transforming choices you can make for your well-being. While it may be challenging, the benefits far outweigh the challenges, offering a longer, healthier, and more fulfilling life.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Keep Your Heart Healthy – MyHealthfinder | health.gov

Limit Alcohol Intake:
If you consume alcohol, do so in moderation. Excessive alcohol can contribute to high blood pressure and other heart-related issues.
Moderation in alcohol consumption is a prudent approach to safeguarding heart health, and it’s essential to understand the reasons behind this recommendation. Expanding on the idea of moderate alcohol consumption and its impact on heart-related issues provides a comprehensive perspective:
1. Blood Pressure Management: Excessive alcohol intake is associated with high blood pressure, a significant risk factor for heart disease. Alcohol can disrupt the balance of the sympathetic nervous system, which regulates blood pressure, leading to hypertension over time. Moderation helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
2. Heart Rhythm Disturbances: Heavy drinking can lead to irregular heart rhythms, known as arrhythmias. These abnormal heart rhythms can increase the risk of heart-related complications, including strokes and heart attacks. Moderation minimizes the likelihood of these disturbances.
3. Cardiomyopathy: Chronic and excessive alcohol consumption can cause cardiomyopathy, a condition where the heart muscle weakens and cannot pump blood effectively. This condition can result in heart failure, a severe and potentially life-threatening condition.
4. Cholesterol Levels: Alcohol can affect blood lipid profiles, potentially leading to unfavorable changes. While moderate alcohol consumption may have a mild beneficial impact on certain cholesterol markers, excessive drinking can negate these benefits and lead to unhealthy lipid profiles.
5. Weight Management: Alcoholic beverages are calorie-dense, and excessive consumption can contribute to weight gain and obesity. Obesity is a known risk factor for heart disease, making moderation an important aspect of weight management for heart health.
6. Interactions with Medications: Alcohol can interact negatively with various medications, including those prescribed for heart conditions. It may reduce the effectiveness of certain medications or lead to adverse effects. Moderation minimizes the risk of medication-alcohol interactions.
7. Liver Health: Chronic alcohol abuse can damage the liver, affecting its ability to metabolize and process nutrients, including those important for heart health. A healthy liver is essential for overall well-being, including cardiovascular health.
8. Mental Health: Excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety, which are also linked to heart disease risk. Moderation supports both mental and heart health.
9. Social and Behavioral Aspects: Practicing moderation in alcohol consumption can promote responsible and mindful drinking habits. It can help individuals make healthier choices and avoid situations that may lead to excessive drinking.
10. Quality of Life: Ultimately, moderation in alcohol consumption contributes to a higher quality of life. It allows individuals to enjoy occasional drinks while minimizing the potential negative health consequences associated with excessive alcohol intake.
In summary, moderation in alcohol consumption is a practical and evidence-based approach to protect heart health and reduce the risk of heart-related issues. It allows individuals to enjoy the social and cultural aspects of alcohol in a responsible and health-conscious manner. If you choose to consume alcohol, doing so in moderation is a wise choice for both short-term and long-term cardiovascular well-being. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying health conditions or concerns regarding alcohol consumption.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: A Heart-Healthy Diet for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: Where …
Medication Adherence:
If prescribed medication for conditions like high blood pressure or cholesterol, take it as directed and attend regular follow-up appointments.
Taking prescribed medication for conditions such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol and attending regular follow-up appointments are essential aspects of managing cardiovascular health effectively. Here’s an extended perspective on the importance of medication adherence and medical monitoring:
1. Medication Adherence:
- Medications prescribed for conditions like high blood pressure and high cholesterol are typically designed to manage these conditions effectively. Adherence to medication regimens is crucial to achieving the desired therapeutic effects.
- Skipping doses or discontinuing medications without medical guidance can lead to uncontrolled risk factors, increasing the likelihood of heart-related complications.
2. Blood Pressure Control:
- High blood pressure (hypertension) is often referred to as the “silent killer” because it may not have noticeable symptoms. Regularly taking prescribed blood pressure medication can help maintain optimal blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
- Consistent medication use complements lifestyle changes like diet and exercise in managing blood pressure effectively.
3. Cholesterol Management:
- Medications prescribed to lower cholesterol levels, such as statins, play a vital role in reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease. Adhering to the prescribed regimen helps control lipid profiles and prevent plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Cholesterol-lowering medications are often a long-term commitment, and continuous use is essential for sustained benefits.
4. Preventing Complications:
- Cardiovascular conditions, especially high blood pressure and high cholesterol, can lead to serious complications like heart attacks and strokes if left uncontrolled. Medication adherence is a key preventive measure to avoid such complications.
- Regular use of prescribed medications is part of a comprehensive strategy to manage heart health and prevent adverse events.
5. Customized Treatment Plans:
- Healthcare providers tailor medication regimens to individual needs. Medications are selected based on the severity of the condition, potential side effects, and the patient’s overall health profile.
- Follow-up appointments allow providers to assess the effectiveness of the chosen treatment plan and make adjustments as needed.
6. Monitoring and Adjustments:
- Regular follow-up appointments provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments. They can assess medication efficacy, identify potential side effects, and modify treatment plans accordingly.
- These appointments are valuable for optimizing treatment outcomes and ensuring that medications remain appropriate for the individual’s current health status.
7. Empowering Self-Care:
- Medication adherence empowers individuals to actively participate in their own care. Taking medications as directed is a proactive step in managing one’s health and reducing cardiovascular risk.
- It complements other heart-healthy behaviors, such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress.
8. Open Communication:
- Effective communication with healthcare providers is essential. Patients should report any concerns or side effects promptly to their providers, who can address these issues and make necessary adjustments to medications or dosages.
9. Improved Quality of Life:
- Properly managed cardiovascular conditions contribute to an improved quality of life. Adhering to prescribed medications and attending follow-up appointments can help individuals lead active, fulfilling lives free from the limitations imposed by uncontrolled heart conditions.
In summary, medication adherence and regular follow-up appointments are integral components of cardiovascular health management. They help control risk factors, prevent complications, and optimize treatment outcomes. By actively participating in their care and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can enhance their heart health and reduce the impact of cardiovascular conditions on their lives. It’s a partnership that fosters long-term well-being and heart-healthy living.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Self‐Care for the Prevention and Management of Cardiovascular …
In Conclusion:
Cardiovascular health is a cornerstone of men’s well-being. By understanding the significance of heart health, recognizing the risk factors, and taking proactive steps to promote cardiovascular well-being, men can pave the way for a strong heart and a longer, healthier life. Prioritizing cardiovascular health is an investment in both the present and the future, ensuring that you can enjoy all that life has to offer with vitality and vigor.
Heart Health: The Beacon of Men’s Well-Being
Cardiovascular health is not just a cornerstone; it’s the very foundation of men’s overall well-being. By embracing the profound importance of heart health, acknowledging the risk factors, and proactively championing cardiovascular well-being, men can script a narrative of robust hearts and extended, thriving lives. Prioritizing heart health is an investment that reaps rewards both in the present and the distant future, promising a life brimming with vitality and enduring vigor.
**1. ** The Heart: Your Loyal Ally:
Your heart is more than a muscular organ—it’s your unwavering ally throughout life’s journey. By nurturing it, you’re ensuring that it continues to beat with resilience, supplying your body with the vital oxygen and nutrients it needs.
**2. ** The Risk Factors:
Acknowledging the risk factors is the first step toward safeguarding your heart. From smoking and poor dietary choices to stress and inactivity, these factors can chip away at your heart’s health over time. Awareness empowers you to make informed choices.
**3. ** Proactive Measures: The Heart’s Safeguard:
Proactivity is your strongest defense. Engage in regular physical activity, adopt a heart-healthy diet, and prioritize stress reduction through mindfulness, meditation, or yoga. Quit smoking, moderate alcohol consumption, and aim for restorative sleep.
**4. ** Regular Heart Checkups: The Navigator:
Regular checkups with a healthcare provider are your navigational compass in the journey to heart health. They monitor your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall heart health, providing insights and recommendations tailored to your specific needs.
**5. ** The Mind-Heart Connection:
Embrace the mind-heart connection. Stress reduction isn’t just about a calmer mind; it’s about a healthier heart. Mindfulness, meditation, or yoga are your tools to achieve this balance.
**6. ** Positive Lifestyle Choices:
Your lifestyle choices ripple through your heart’s health. Opt for a balanced diet filled with fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Engage in regular exercise and maintain a healthy weight. Nurture your emotional well-being and seek professional help when needed.
**7. ** Heart-Healthy Aging:
The investment in heart health pays dividends as you age. It ensures that you’re not just adding years to your life but quality years filled with meaningful experiences, cherished moments, and vibrant well-being.
**8. ** Inspiration and Legacy:
By prioritizing heart health, you become an inspiration to others. Your commitment serves as a beacon, illuminating the path to a heart-healthy life for those around you.
**9. ** A Future of Possibilities:
When you take charge of your heart health, you’re crafting a future of boundless possibilities. It’s a life without the shackles of chronic illness, where you’re free to explore, learn, grow, and savor every moment.
**10. ** A Lifetime of Vitality:
The journey to heart health is a commitment to a lifetime of vitality. It’s a promise to your heart that you’ll cherish and protect it, ensuring that it continues to beat with strength and endurance, accompanying you on every adventure life unfolds.
In Conclusion:
Heart health is the compass that guides your life’s journey. By recognizing its paramount importance, understanding the risk factors, and taking proactive measures, you’re not just caring for your heart—you’re investing in a future that’s rich with vitality, well-being, and the limitless possibilities that life has to offer. It’s a tribute to your heart’s unwavering loyalty, ensuring that it remains your steadfast ally through every chapter of your extraordinary life.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Cardiovascular Disease and the Female Disadvantage – PMC
More links
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: 7 powerful ways you can strengthen your heart | UCI Health …
