Table of Contents
- Understanding Essential Fatty Acids
- The Importance of Balance
- Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Heart Health
- Brain Function
- Joint Health
- Eye Health
- Sources of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids
- Fatty Fish
- Flaxseeds
- Chia Seeds
- Walnuts
- Vegetable Oils
- Nuts and Seeds
- Poultry
- Balancing Act
- Choose Cooking Oils Wisely
- Eat Fatty Fish Regularly
- Snack on Nuts and Seeds
- Supplement When Necessary
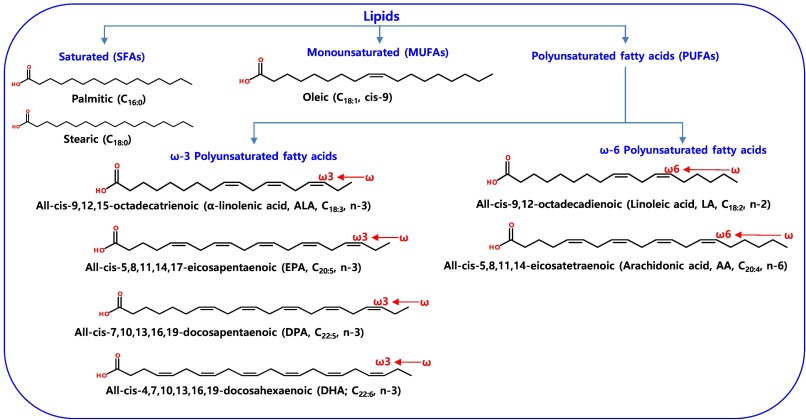
In the world of nutrition, some dietary components are hailed as heroes and among them, essential fatty acids take center stage. Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, often referred to as “essential fats,” are crucial for maintaining overall health. These fats play diverse roles in the body, from supporting brain function to reducing inflammation. In this article, we will explore the significance of these essential fats, their sources and the best ways to incorporate them into your daily diet for optimal well-being.
In the ever-evolving realm of nutrition, essential fatty acids indeed deserve the spotlight as dietary heroes. Among them, Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids stand out as indispensable components crucial for maintaining and enhancing overall health. These essential fats are like the conductors of a symphony within our bodies, orchestrating various processes and harmonizing our well-being. Let’s embark on a deeper exploration of the profound significance of these essential fats, uncovering their sources and unveiling the best strategies for seamlessly integrating them into your daily diet for the betterment of your overall health.
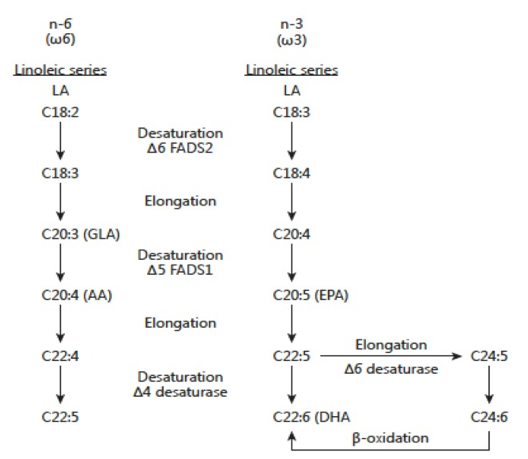
Foundation of Health: Essential fatty acids, as their name suggests, are fundamental to human health. They are labeled “essential” because our bodies cannot produce them on their own. Therefore, we must obtain these crucial nutrients through our diets. Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids serve as the building blocks of cell membranes, playing pivotal roles in maintaining cellular integrity and function.
Brain and Nervous System: Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly the type known as docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), are renowned for their profound impact on brain health. DHA is an integral component of brain cell membranes and is essential for cognitive function, memory and mood regulation. Regular consumption of Omega-3s has been linked to improved cognitive development in infants and a reduced risk of age-related cognitive decline in adults.
Inflammation Management: Both Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids play a critical role in the body’s inflammatory response. Omega-3s, found in fatty fish like salmon and walnuts, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. In contrast, Omega-6s, commonly found in vegetable oils, have a more pro-inflammatory effect. Striking the right balance between these two types of fats is crucial for maintaining a healthy inflammatory response.
Heart Health: Omega-3 fatty acids have been extensively studied for their cardiovascular benefits. They are known to reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering blood pressure, triglyceride levels and the likelihood of abnormal heart rhythms. Incorporating Omega-3-rich foods, such as flaxseeds, chia seeds and fatty fish like mackerel, into your diet can promote a healthier heart.
Skin, Hair and Eye Health: Essential fatty acids contribute to the vitality of your skin, hair and eyes. They help maintain skin’s moisture, suppleness and elasticity, while also supporting the health of hair follicles and the lubrication of the eyes. Omega-3s are particularly known for their role in maintaining eye health.
Balancing the Ratio: Achieving the right balance between Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids is pivotal. In today’s Western diets, Omega-6s are often overconsumed, while Omega-3s are underrepresented. Strive for a balanced ratio to optimize health. Reducing processed foods and vegetable oils rich in Omega-6s and increasing your intake of Omega-3-rich foods can help restore this equilibrium.
Supplementation Consideration: In some cases, individuals may benefit from Omega-3 supplements, especially if they have specific health concerns or dietary restrictions that limit their intake of Omega-3-rich foods. However, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before adding supplements to your regimen.
In conclusion, Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids are unsung heroes in the realm of nutrition, playing multifaceted roles in maintaining and enhancing overall health. From supporting brain function and reducing inflammation to nurturing heart health and promoting radiant skin, these essential fats are truly remarkable. By incorporating a diverse array of sources into your daily diet, you can unlock the full potential of these essential nutrients and embark on a journey toward optimal well-being and vitality.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Omega-3 Fatty Acids – Health Professional Fact Sheet
Understanding Essential Fatty Acids
Before we delve into the specifics, let’s grasp the fundamentals. Essential fatty acids, as the name suggests, are fats that our bodies cannot produce on their own. We must obtain them through our diet, making them truly essential for our health. Two of the most prominent types are Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids.
Before we dive into the intricacies of essential fatty acids, let’s lay down the fundamental groundwork. Essential fatty acids, as their name implies, are fats that our bodies are incapable of producing independently. In essence, we rely entirely on our dietary choices to provide us with these crucial nutrients, hence the term “essential.” Among the vast array of fats found in our diets, two stand out as the stars of the show: Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids.
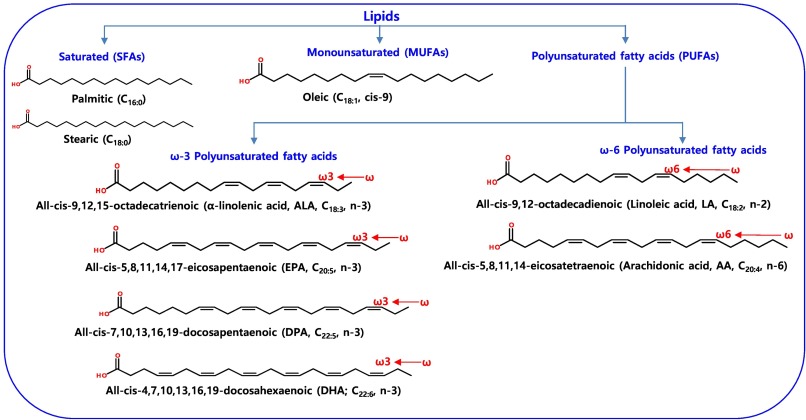
Omega-3 fatty acids are celebrated for their remarkable health benefits. These unsung heroes are prominently found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel and sardines, as well as in flaxseeds, chia seeds and walnuts. What makes Omega-3s so special is their role in reducing inflammation throughout the body. They are like the calming force amidst the storms of inflammation, helping to mitigate chronic diseases and conditions like heart disease, arthritis and even certain neurological disorders. Omega-3s also support brain health and have been linked to improved cognitive function and mood regulation.
On the other side of the essential fatty acid spectrum are Omega-6 fatty acids, which are found in abundance in vegetable oils, nuts and seeds. While Omega-6s are also essential for our health, it’s the balance between Omega-3s and Omega-6s that’s crucial. In today’s modern Western diet, there’s often an overabundance of Omega-6s compared to Omega-3s, which can lead to an unhealthy imbalance. This imbalance has been associated with increased inflammation and a higher risk of chronic diseases. Therefore, achieving a harmonious Omega-3 to Omega-6 ratio is essential for maintaining optimal health.
These essential fatty acids play multifaceted roles in our bodies. They serve as structural components of cell membranes, ensuring proper cellular function. They also play a pivotal role in hormone production and regulation, including hormones that control inflammation, blood clotting and the contraction and relaxation of artery walls.
In addition to their physiological functions, essential fatty acids offer the tantalizing promise of radiant skin and lustrous hair. They help maintain the integrity of the skin’s lipid barrier, keeping it hydrated and protected against external aggressors. This can result in a complexion that’s not only healthier but also more youthful and glowing.
As we journey deeper into the world of essential fatty acids, we’ll uncover their profound impact on our health and well-being. We’ll explore how to strike the right balance between Omega-3s and Omega-6s in our diets, ensuring that these truly essential nutrients work harmoniously to support our overall health, from reducing inflammation to nourishing our skin. So, join us in this exploration of the fats that matter most, as we discover how essential fatty acids are the unsung heroes of a healthy, vibrant life.
You can also read more about this here: Omega-3 Fatty Acids – Health Professional Fact Sheet
The Importance of Balance
Maintaining the right balance between Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids is crucial. In the typical Western diet, there is often an overabundance of Omega-6 fatty acids, primarily due to the prevalence of vegetable oils in processed foods. This imbalance can lead to chronic inflammation and increase the risk of various health issues, including heart disease, arthritis and obesity.
Maintaining the delicate equilibrium between Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids in your diet is paramount for overall health and well-being. In today’s modern world, the typical Western diet frequently tips the scales in favor of Omega-6 fatty acids, primarily due to the widespread use of vegetable oils in processed and convenience foods. Understanding and addressing this imbalance is essential because it can have far-reaching consequences for your health.
Omega-6 fatty acids, found abundantly in soybean oil, corn oil and sunflower oil, are not inherently harmful; in fact, they play crucial roles in the body’s inflammatory response and cell signaling. However, it’s the disproportionate ratio of Omega-6 to Omega-3 fatty acids that raises concern. Ideally, the Omega-6 to Omega-3 ratio should be roughly 1:1 to 4:1 for optimal health benefits.
When this balance is disrupted, as it often is in Western diets with ratios ranging from 10:1 to 20:1 or even higher, it can lead to chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation is at the root of numerous health issues and is linked to conditions such as heart disease, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, obesity and even certain cancers.
The excess of Omega-6 fatty acids can promote inflammation, while Omega-3 fatty acids, typically found in fatty fish like salmon, flaxseeds and walnuts, have anti-inflammatory properties. These two types of fatty acids often compete for the same enzymes in the body. When there’s an overabundance of Omega-6s, they can overpower the anti-inflammatory effects of Omega-3s, creating a pro-inflammatory environment.
To restore this balance and mitigate the risks associated with an Omega-6 dominance, consider the following dietary adjustments:
Choose Cooking Oils Wisely: Opt for cooking oils with a more favorable Omega-6 to Omega-3 ratio, such as olive oil or canola oil and limit the use of oils high in Omega-6s.
Increase Omega-3 Intake: Incorporate more sources of Omega-3 fatty acids into your diet, such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds and walnuts.
Minimize Processed Foods: Processed and fast foods are often laden with Omega-6-rich oils. Reducing their consumption can significantly impact the balance of fatty acids in your diet.
Read Food Labels: Be diligent in reading food labels to identify products with healthier fat profiles, opting for those with lower Omega-6 content.
Consider Supplements: In some cases, Omega-3 supplements, like fish oil capsules, may be recommended to help restore the balance. Consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
Embrace Whole Foods: Whole, unprocessed foods naturally contain more balanced ratios of fatty acids. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help restore equilibrium.
In conclusion, striking the right balance between Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids is a pivotal step towards maintaining optimal health and preventing chronic inflammation-related diseases. By being mindful of your dietary choices and making adjustments to prioritize Omega-3 sources, you can regain control over this essential balance and pave the way for a healthier, inflammation-resistant future.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Omega-3 Fatty Acids – Health Professional Fact Sheet

Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids offer a wide range of health benefits, including:
Omega-3 fatty acids offer a wide range of health benefits, making them a valuable addition to your diet. Here are some of the key advantages they provide:
Heart Health: Omega-3s are renowned for their heart-protective properties. They can help lower triglyceride levels, reduce blood pressure and improve overall cardiovascular health. Regular consumption of omega-3-rich foods or supplements may reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Brain Function: Omega-3s play a vital role in brain development and function. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a type of omega-3, is a major structural component of the brain and is essential for cognitive function. Consuming sufficient omega-3s may support memory, concentration and mental clarity.
Inflammation Reduction: Omega-3s have natural anti-inflammatory properties. They can help reduce chronic inflammation in the body, which is associated with various health conditions, including arthritis, asthma and inflammatory bowel disease. By incorporating omega-3-rich foods, you may alleviate symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Joint Health: Omega-3s may provide relief for joint pain and stiffness, particularly in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. They can help reduce inflammation in the joints, potentially leading to increased mobility and reduced discomfort.
Eye Health: DHA, one of the omega-3 fatty acids, is also present in high concentrations in the retina. Consuming omega-3s may help protect against age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and maintain overall eye health.
Healthy Skin: Omega-3s contribute to skin health by maintaining its moisture and elasticity. They may help alleviate dry skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis and promote a youthful complexion.
Improved Mood: There is evidence to suggest that omega-3s may have a positive impact on mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety. While more research is needed, incorporating omega-3-rich foods may be a valuable component of a holistic approach to mental well-being.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: Omega-3s may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases, including certain cancers. Their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties can protect cells from damage and support overall health.
Pregnancy and Infant Development: Omega-3s are crucial during pregnancy for fetal brain and eye development. They are also beneficial for breastfeeding mothers, as they can enhance the quality of breast milk. Ensuring an adequate intake of omega-3s is essential for the health and development of both mother and child.
Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into your diet, whether through fatty fish like salmon and trout, flaxseeds, chia seeds or supplements, can offer a host of health benefits that contribute to your overall well-being. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the best approach for including omega-3s in your dietary regimen and ensuring you meet your specific health goals.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Mechanisms and innovations: The science behind dietary omega-3 …

Heart Health
Omega-3s can lower triglycerides, reduce blood pressure and prevent the formation of blood clots, all of which contribute to cardiovascular well-being.
The cardiovascular benefits of omega-3 fatty acids extend far beyond their ability to lower triglycerides, reduce blood pressure and prevent blood clot formation. Here’s a more comprehensive look at how these essential fats support heart health:
Anti-Inflammatory Action: Omega-3s have potent anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation is a key driver of heart disease and by reducing inflammation, omega-3s can help protect the delicate lining of blood vessels and decrease the risk of atherosclerosis, the hardening and narrowing of arteries.
Improved Cholesterol Profile: In addition to lowering triglycerides, omega-3s can increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “good” cholesterol. This HDL boost can further reduce the risk of plaque buildup in arteries.
Blood Pressure Regulation: Omega-3s help regulate blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels and improving blood flow. This effect can lead to lower overall blood pressure levels and reduced strain on the heart.
Arrhythmia Prevention: Omega-3s have been shown to reduce the risk of arrhythmias, irregular heart rhythms that can be life-threatening. By stabilizing electrical activity in the heart, omega-3s contribute to a more regular heartbeat.
Enhanced Endothelial Function: The endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels, plays a crucial role in maintaining vascular health. Omega-3s support endothelial function, ensuring that blood vessels remain flexible and responsive.
Reduced Risk of Heart Attacks: Omega-3s may reduce the risk of heart attacks by preventing the formation of blood clots that can block coronary arteries. This protective effect can be particularly valuable for individuals at high risk of heart disease.
Heart Disease Prevention: Regular consumption of omega-3-rich foods or supplements has been associated with a lower overall risk of heart disease. This comprehensive protection stems from their ability to address multiple cardiovascular risk factors.
Brain Health Benefits: Omega-3s also offer cognitive benefits, which indirectly contribute to heart health. A healthy brain can help regulate stress, manage lifestyle factors like diet and exercise and make informed decisions that support cardiovascular well-being.
Dietary Sources: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3s. Plant-based options, such as flaxseeds, chia seeds and walnuts, provide a vegetarian or vegan alternative. Omega-3 supplements, when recommended by a healthcare professional, can also be a valuable addition to a heart-healthy regimen.
In summary, omega-3 fatty acids are a versatile and essential component of heart health. Their multifaceted benefits, ranging from inflammation reduction to blood pressure regulation and arrhythmia prevention, make them a cornerstone of cardiovascular well-being. Incorporating omega-3-rich foods or supplements into your diet can significantly enhance your heart’s resilience and support a longer, healthier life.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Omega-3 Fatty Acids – Health Professional Fact Sheet

Brain Function
DHA, a type of Omega-3, is a major component of brain cell membranes and is essential for cognitive function. Consuming Omega-3s may support memory and mental clarity.
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), a specific type of Omega-3 fatty acid, holds a prominent role in the intricate workings of our brain. As a major component of brain cell membranes, it’s indispensable for cognitive function and overall brain health. Let’s explore how this remarkable fatty acid, found predominantly in fatty fish like salmon and in fish oil supplements, goes beyond its structural role to become a crucial factor in supporting memory and mental clarity.
Enhanced Cognitive Function: DHA is instrumental in promoting optimal brain function. It contributes to the fluidity and flexibility of brain cell membranes, which is essential for efficient signal transmission between neurons. This improved neuronal communication can result in sharper cognitive abilities, enhancing your capacity for tasks that require quick thinking and problem-solving.
Memory Mastery: DHA has been closely associated with memory enhancement. It plays a role in facilitating the creation and retention of memories, making it particularly valuable for students, professionals and individuals looking to preserve their cognitive abilities as they age. Adequate DHA levels have been linked to better memory recall and improved learning capabilities.
Brain Health Across the Lifespan: Maintaining optimal DHA levels throughout life is essential for preserving cognitive function as we age. Research suggests that DHA may help reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. By supporting the health of brain cells and protecting against oxidative stress, DHA contributes to long-term brain vitality.
Mood and Mental Clarity: Beyond memory, DHA is associated with emotional well-being and mental clarity. Some studies have indicated that DHA supplementation may help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety, potentially leading to a brighter and more focused outlook on life.
Early Brain Development: DHA is crucial during pregnancy and infancy when the brain undergoes rapid development. It’s a key component of breast milk, underscoring its importance for infants. Expectant mothers are often advised to ensure an adequate intake of DHA to support their baby’s brain development.
To harness the cognitive benefits of DHA, incorporating DHA-rich foods or supplements into your diet can be a smart choice. Fatty fish, algae-based supplements and fortified foods are excellent sources. However, it’s essential to maintain a balanced diet that includes various nutrients and to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements. By nourishing your brain with DHA, you’re not only investing in sharper memory and mental clarity but also in long-term brain health that can help you age gracefully and maintain cognitive vitality.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Mechanisms and innovations: The science behind dietary omega-3 …
Joint Health
Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties that can alleviate symptoms of conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Omega-3s have emerged as a beacon of hope for individuals grappling with chronic inflammatory conditions and one such ailment where they have shown remarkable promise is rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This autoimmune disease, characterized by painful joint inflammation, stiffness and swelling, can significantly impact one’s quality of life. However, the incorporation of Omega-3 fatty acids into the diet has opened up a new avenue for managing its symptoms and improving the overall well-being of those affected.
The anti-inflammatory properties of Omega-3s, particularly the types found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel and sardines, have been the subject of extensive research. These fatty acids, namely eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), have demonstrated their ability to mitigate the inflammatory response within the body. In the context of rheumatoid arthritis, this means relief from the relentless pain and discomfort that often accompany the condition.
One of the primary mechanisms through which Omega-3s exert their anti-inflammatory effects is by competing with Omega-6 fatty acids for space in the body’s cell membranes. Omega-6 fatty acids, while essential, have a pro-inflammatory tendency when consumed in excess. By increasing the intake of Omega-3s, you create a healthier balance, reducing the overall inflammatory load.
Studies have indicated that regular consumption of Omega-3-rich foods or supplements can lead to a reduction in the number of tender and swollen joints, decreased morning stiffness and an overall improvement in the quality of life for RA patients. Additionally, Omega-3s may enable some individuals to reduce their reliance on anti-inflammatory medications, which can have side effects and long-term consequences.
It’s important to note that while Omega-3s offer considerable promise, they are not a standalone solution for rheumatoid arthritis. Rather, they should be integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan developed in consultation with a healthcare professional. This plan may include medications, physical therapy and lifestyle modifications alongside dietary changes.
Incorporating Omega-3-rich foods into one’s diet is a proactive step that can contribute to managing rheumatoid arthritis effectively. However, individuals with RA should consult their healthcare providers before making significant dietary adjustments or adding supplements to their regimen. This collaborative approach ensures that the incorporation of Omega-3s aligns with individual health needs and maximizes the potential benefits, providing a more comfortable and active life for those living with rheumatoid arthritis.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Omega-3 Fatty Acids: An Essential Contribution | The Nutrition Source
Eye Health
DHA is also present in the retina, making Omega-3s beneficial for maintaining good vision, particularly in later years.
DHA or docosahexaenoic acid, is a type of omega-3 fatty acid that serves as a guardian of your vision, especially as you age. Its presence in the retina and various aspects of eye health highlight the significance of omega-3s in maintaining good vision throughout your life:
Retina Support: DHA is a crucial structural component of the retina, the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. It plays a pivotal role in the development and maintenance of the retina’s photoreceptor cells, which are responsible for capturing and processing visual information.
Preventing Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): Age-related macular degeneration is a leading cause of vision loss in older adults. Studies suggest that a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA, may help reduce the risk of AMD. DHA’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties can protect the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision.
Dry Eye Relief: Omega-3s, including DHA, can alleviate symptoms of dry eye syndrome. Dry eyes can cause discomfort, irritation and blurred vision. Consuming omega-3-rich foods or supplements can help improve tear quality and reduce dry eye symptoms.
Cataract Prevention: While more research is needed, some studies suggest that omega-3s may help prevent the development of cataracts, a clouding of the eye’s lens that can impair vision. DHA’s anti-inflammatory properties may play a role in maintaining the clarity of the lens.
Visual Acuity: DHA supports visual acuity, which is essential for tasks like reading, recognizing faces and driving. Maintaining optimal levels of DHA can help ensure that your vision remains sharp and clear, even as you age.
Overall Eye Health: Omega-3s contribute to overall eye health by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the eye tissues. This not only benefits the retina but also supports the health of other structures in the eye.
Dietary Sources: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel and trout are excellent dietary sources of DHA. Including these fish in your diet, along with other omega-3-rich foods like flaxseeds and walnuts, can help ensure you’re getting an adequate supply of DHA.
Supplements: In cases where it’s challenging to obtain sufficient DHA from dietary sources, omega-3 supplements can be a convenient option. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen.
Incorporating DHA-rich foods into your diet and maintaining a healthy intake of omega-3 fatty acids can be a proactive step in safeguarding your vision, particularly as you age. By nourishing your eyes with these essential nutrients, you support their structure and function, promoting good vision and visual comfort well into your later years.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Mechanisms and innovations: The science behind dietary omega-3 …

Sources of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Now, let’s explore the sources of these essential fats:
Certainly, let’s delve into the abundant sources of these essential fats, which are vital for overall health and well-being:
Fatty Fish: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, trout, sardines and herring are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids. These fats not only support heart health but also play a crucial role in brain function and reducing inflammation.
Flaxseeds: Flaxseeds are a plant-based powerhouse of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid. Ground flaxseeds can be easily added to cereals, smoothies or used as an egg substitute in baking.
Chia Seeds: Chia seeds are another plant-based source of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly ALA. They are versatile and can be used in puddings, yogurt or sprinkled on top of salads and oatmeal.
Walnuts: Walnuts are unique among nuts because they are rich in ALA omega-3 fatty acids. A small handful of walnuts makes for a convenient and heart-healthy snack.
Hemp Seeds: Hemp seeds are a nutrient-dense option packed with omega-3 fatty acids, particularly ALA. They can be added to smoothies, salads or baked goods.
Canola Oil: Canola oil contains a moderate amount of ALA omega-3 fatty acids. It’s a versatile cooking oil suitable for various culinary applications.
Soybeans and Tofu: Soybeans and tofu are plant-based sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Incorporating these into your diet can provide essential fats while offering a source of plant-based protein.
Avocado: Avocado is rich in monounsaturated fats, which are heart-healthy fats. While not a direct source of omega-3s, avocados contribute to overall healthy fat intake and can be enjoyed in salads, sandwiches or as a creamy spread.
Olive Oil: Olive oil is another monounsaturated fat source that is a staple in the Mediterranean diet. Its use is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease and may contribute to a longer, healthier life.
Algal Oil Supplements: For those who prefer a plant-based alternative to fish oil supplements, algal oil supplements are available. They are derived from algae and provide a source of omega-3 fatty acids, including DHA and EPA.
Eggs: Eggs enriched with omega-3s are available and provide a convenient way to increase your intake of these essential fats. These eggs are laid by hens fed a diet high in omega-3-rich foods.
Krill Oil: Krill oil supplements offer an alternative source of omega-3 fatty acids. Krill are tiny crustaceans found in the ocean and krill oil is a source of EPA and DHA.
Incorporating these sources of essential fats into your diet can help you achieve a well-rounded and balanced intake of omega-3 and other beneficial fats. These fats are not only essential for your health but also add depth and flavor to your culinary creations, making healthy eating a delicious and enjoyable journey.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Omega-3 Fatty Acids: An Essential Contribution | The Nutrition Source

Fatty Fish
Salmon, mackerel, trout and sardines are rich sources of EPA and DHA.
Certainly, let’s expand on the significance of salmon, mackerel, trout and sardines as rich sources of EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), two essential omega-3 fatty acids and how their consumption can benefit overall health:
Essential Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Salmon, mackerel, trout and sardines are prized for their high content of EPA and DHA, which are types of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids. These fatty acids are considered essential because the human body cannot produce them on its own, making dietary intake crucial.
Heart Health: EPA and DHA are well-known for their positive impact on cardiovascular health. Regular consumption of fatty fish has been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease. These omega-3s help lower triglyceride levels, reduce blood pressure and improve the function of blood vessels. They also have anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce the risk of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
Brain Function and Development: DHA, in particular, plays a critical role in brain function and development. It is a major component of brain cell membranes and is essential for cognitive functions, memory and mood regulation. Consuming these fatty fish, especially during pregnancy and early childhood, can support healthy brain development.
Reducing Inflammation: EPA and DHA have potent anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation is a contributing factor to various health issues, including autoimmune diseases, arthritis and even cancer. Including fatty fish in your diet can help modulate inflammation and reduce the risk of chronic inflammatory conditions.
Eye Health: DHA is also found in high concentrations in the retina of the eye. Adequate DHA intake may support eye health and reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and other vision problems.
Joint Health: Omega-3 fatty acids have been associated with improved joint health and reduced symptoms of conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. They can help reduce joint pain and stiffness and may even slow down the progression of joint diseases.
Mood and Mental Health: There is growing evidence that EPA and DHA can have a positive impact on mood and mental health. They may help reduce the symptoms of depression and anxiety, possibly by influencing neurotransmitter function and brain structure.
Skin Health: Omega-3s can promote healthy skin by supporting the skin barrier, reducing inflammation and keeping skin hydrated. This can lead to a more youthful and radiant complexion.
Weight Management: Including fatty fish in a balanced diet may aid in weight management. Omega-3s can help regulate appetite, promote a feeling of fullness and improve insulin sensitivity, potentially assisting in weight loss or maintenance.
In summary, salmon, mackerel, trout and sardines are nutritional powerhouses packed with EPA and DHA, essential for numerous aspects of health. Regularly incorporating these fish into your diet can provide a wide range of benefits, from protecting your heart and brain to reducing inflammation and supporting overall well-being.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Mechanisms and innovations: The science behind dietary omega-3 …

Flaxseeds
These tiny seeds are packed with ALA, a plant-based Omega-3.
Within these minuscule seeds lies a powerhouse of nutrition. They are densely packed with ALA, a plant-based Omega-3 fatty acid that holds immense health benefits. ALA is known for its anti-inflammatory properties, aiding in reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease. Additionally, this plant-based Omega-3 contributes to optimal brain function and supports overall well-being. The incorporation of these small yet mighty seeds into your diet can significantly enhance your nutritional profile and pave the way for a healthier, happier life.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Omega-3 Fatty Acids – Consumer

Chia Seeds
Like flaxseeds, chia seeds are an excellent source of ALA.
Much like their nutritional counterpart, flaxseeds, chia seeds are a nutritional powerhouse rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an omega-3 fatty acid that holds a pivotal role in supporting our well-being.
Chia seeds, with their tiny but mighty presence, boast a considerable ALA content, making them a fantastic addition to your diet for various reasons:
Heart Health: The ALA in chia seeds is known for its heart-protective properties. It can help lower the risk of heart disease by reducing levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglycerides while promoting the health of blood vessels. Incorporating chia seeds into your meals may contribute to a healthier cardiovascular system.
Brain Function: Omega-3 fatty acids, including ALA, play a crucial role in maintaining optimal brain function. They support cognitive health, memory and may even help protect against age-related cognitive decline. Including chia seeds in your diet can be a flavorful way to give your brain a nutritional boost.
Inflammation Reduction: ALA’s anti-inflammatory properties make it valuable in mitigating chronic inflammation, which is linked to various health issues, including arthritis and heart disease. By incorporating chia seeds, you’re helping your body in its fight against inflammation, promoting overall wellness.
Skin and Hair Health: Omega-3 fatty acids, including ALA, contribute to the health of your skin and hair. They help maintain the skin’s moisture and elasticity, potentially reducing the appearance of fine lines. Additionally, these essential fats support a healthy scalp and hair follicles, promoting lustrous locks.
Digestive Regularity: Chia seeds are rich in soluble fiber, which can absorb water and form a gel-like consistency in your digestive tract. This can help promote regular bowel movements and alleviate digestive discomfort, contributing to your overall well-being.
Incorporating chia seeds into your daily meals can be a versatile and flavorful way to reap the benefits of ALA. Sprinkle them over yogurt, blend them into smoothies, stir them into oatmeal or use them as an egg substitute in baking. These small seeds offer big rewards for your health, ensuring that you’re nourishing your body with the essential nutrients it needs to thrive.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: The 7 Best Plant Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids

Walnuts
Walnuts provide a convenient way to incorporate Omega-3s into your diet.
Walnuts are nature’s nutritional gems, offering a convenient and delicious means of boosting your omega-3 fatty acid intake—a crucial component for maintaining optimal health. Here’s why they’re an excellent choice and how they can effortlessly become a staple in your diet:
Omega-3 Powerhouse: Omega-3 fatty acids are celebrated for their numerous health benefits, from supporting heart health to reducing inflammation and enhancing brain function. Walnuts stand out among nuts as one of the best sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3. Incorporating walnuts into your meals can help you meet your daily omega-3 requirements without the need for supplements or fatty fish.
Heart Health: Omega-3s are renowned for their ability to promote cardiovascular well-being. They help reduce levels of unhealthy LDL cholesterol and triglycerides while increasing good HDL cholesterol. This combination can lead to a healthier heart, lower blood pressure and a reduced risk of heart disease.
Brain Boost: The omega-3s in walnuts are not just good for your heart; they’re also brain-boosting nutrients. These fatty acids support cognitive function and may help prevent age-related cognitive decline. Regular consumption of walnuts has been linked to improved memory and mental clarity.
Inflammation Reduction: Chronic inflammation is a risk factor for numerous chronic diseases. Omega-3s have potent anti-inflammatory properties and incorporating walnuts into your diet can help dampen inflammation, potentially reducing the risk of conditions like arthritis and diabetes.
Weight Management: Despite their calorie density, walnuts can be a valuable asset for weight management. Their combination of protein, healthy fats and fiber creates a sense of fullness and satiety, which can help curb overeating and promote weight loss when consumed in moderation.
Versatility: Walnuts are incredibly versatile and can be effortlessly integrated into your daily meals. Add them to your morning oatmeal or yogurt for a satisfying crunch, toss them into a salad for added texture and flavor or blend them into a creamy walnut butter to spread on whole-grain toast.
Snacking with Purpose: As a convenient snack, walnuts require no preparation and can be enjoyed on the go. A small handful can provide a satisfying and nutritious pick-me-up during busy days.
By making walnuts a regular part of your diet, you’re not only elevating your nutritional intake but also embracing a tasty and effortless way to safeguard your health. They’re a versatile, heart-healthy and brain-boosting addition to your meals that can help you meet your omega-3 needs while delighting your taste buds. So, reach for a handful of walnuts and savor the benefits they bring to your overall well-being.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Omega-3 Fatty Acids: An Essential Contribution | The Nutrition Source

Vegetable Oils
Sunflower, safflower, corn and soybean oils are common sources of Omega-6 fatty acids.
Sunflower, safflower, corn and soybean oils are household staples, frequently found in our kitchens. Beyond their culinary versatility, they serve as common sources of Omega-6 fatty acids, an essential component of a balanced diet.
Omega-6 fatty acids play a crucial role in our overall health, even though they often share the spotlight with their Omega-3 counterparts. These fatty acids are pivotal in maintaining cell structure, supporting brain function and regulating metabolism. While Omega-3s are celebrated for their anti-inflammatory properties, Omega-6s complement this by contributing to a well-rounded immune response.
However, the balance between Omega-3s and Omega-6s is essential. An overabundance of Omega-6s, particularly from processed and refined oils, can lead to an imbalance and promote inflammation. It’s all about achieving harmony between the two types of fatty acids to ensure optimal health.
Incorporating oils like sunflower, safflower, corn and soybean into your diet can be part of a balanced approach to nutrition. But it’s equally important to diversify your fat sources. Consider incorporating foods rich in Omega-3s, such as fatty fish, flaxseeds and walnuts, to create a harmonious blend of essential fatty acids.
By understanding the role of Omega-6 fatty acids and making informed dietary choices, you can ensure that your body benefits from their contributions while maintaining a balanced and inflammation-free state. So, let these common oils be a part of your culinary repertoire, but remember to embrace variety and balance for the sake of your overall well-being.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Mechanisms and innovations: The science behind dietary omega-3 …

Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, sunflower seeds and pine nuts contain Omega-6 fats.
Nuts and seeds like almonds, sunflower seeds and pine nuts indeed contain Omega-6 fats, which are an essential component of a balanced diet. Here’s why incorporating these nutrient-packed morsels into your daily eating habits can be a wise choice:
Essential Fatty Acids: Omega-6 fatty acids are part of a group of essential fatty acids that your body needs but can’t produce on its own. These fatty acids play a crucial role in various bodily functions, including cell growth, brain development and maintaining the health of your skin, hair and bones.
Energy Source: Omega-6 fats are a dense source of energy. When consumed, they provide a readily available source of fuel for your body, helping you stay energized throughout the day.
Healthy Skin and Hair: Omega-6 fatty acids contribute to the health and appearance of your skin and hair. They help maintain the integrity of your skin’s outermost layer, preventing moisture loss and promoting a healthy complexion. For your hair, Omega-6 fats contribute to its strength and luster.
Inflammatory Response: While Omega-6 fats are essential, maintaining a proper balance of Omega-3 to Omega-6 fatty acids is key. An imbalance can potentially contribute to excessive inflammation in the body. However, when Omega-6s are consumed as part of a balanced diet that includes Omega-3s (found in fatty fish, flaxseeds and walnuts, for example), they can support a healthy inflammatory response.
Nutrient Variety: Almonds, sunflower seeds and pine nuts provide a tasty and nutrient-rich way to incorporate Omega-6 fats into your diet. Beyond their Omega-6 content, they offer a wide array of vitamins, minerals and antioxidants that contribute to overall health.
Versatile Ingredients: These nuts and seeds are incredibly versatile and can be easily incorporated into various dishes. Sprinkle them over salads, add them to yogurt, blend them into smoothies or simply enjoy them as a satisfying snack.
Dietary Diversity: Including a diverse range of fats in your diet is essential for overall health. Omega-6 fats are just one component of a well-rounded dietary profile that includes healthy fats like monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
Portion Control: While Omega-6 fats are beneficial, it’s important to consume them in moderation. Nuts and seeds, including almonds, sunflower seeds and pine nuts, are calorie-dense foods. A small handful as a snack or a sprinkle as a topping can provide the desired nutritional benefits without excessive calorie intake.
Incorporating almonds, sunflower seeds and pine nuts into your diet can be a flavorful and nutritious way to ensure you’re getting the essential Omega-6 fatty acids your body needs. By doing so in moderation and as part of a well-balanced diet, you’re not only supporting your overall health but also delighting in the delicious flavors and textures they bring to your meals and snacks.
You can also read more about this here: Essential Fatty Acids | Linus Pauling Institute | Oregon State University

Poultry
Chicken and turkey also provide Omega-6 fatty acids.
When we think of Omega-6 fatty acids, chicken and turkey might not be the first foods that come to mind, but they are indeed valuable sources of these essential nutrients. Omega-6 fatty acids, while often overshadowed by their Omega-3 counterparts, play a vital role in maintaining our health.
Chicken and turkey, in addition to being excellent sources of lean protein, contribute to your Omega-6 intake. These poultry options provide a balance of both Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, making them a versatile choice for those looking to incorporate healthy fats into their diet.
Omega-6 fatty acids are not inherently harmful; in fact, they are essential for various bodily functions. They are a component of cell membranes, playing a role in cell structure and function. Omega-6s are also involved in processes related to inflammation and blood clotting. However, the key to reaping the benefits of these fatty acids lies in achieving the right balance between Omega-3 and Omega-6 intake.
An imbalance, where Omega-6 intake significantly exceeds Omega-3 intake, can contribute to chronic inflammation, which is associated with various health issues. Therefore, it’s essential to maintain a balanced ratio of these two types of fatty acids to support overall health.
Chicken and turkey can be part of a balanced diet that provides a combination of both Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids. Pairing them with Omega-3-rich foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds or walnuts can help strike that equilibrium. This approach not only ensures that you receive the benefits of Omega-6s for cell structure and function but also minimizes the risk of excessive inflammation.
So, when you enjoy a grilled chicken breast or savor a slice of roasted turkey, you’re not only relishing a delicious meal but also contributing to the essential balance of fatty acids that support your overall well-being. These lean poultry options provide a versatile canvas for culinary creativity while offering valuable nutrients for your body’s cellular health and beyond.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Omega-3 Fatty Acids: An Essential Contribution | The Nutrition Source
Balancing Act
Tips for a Healthy Omega-3 to Omega-6 Ratio
Tips for maintaining a healthy omega-3 to omega-6 ratio in your diet are essential for overall well-being and are often a cornerstone of a balanced and heart-healthy eating plan. Here are some practical and meaningful tips to help you achieve and maintain this vital nutritional balance:
Prioritize Fatty Fish: Incorporate fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines and trout into your diet regularly. These cold-water fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), which are known for their numerous health benefits, including reducing inflammation and supporting heart health.
Choose Lean Meats: When selecting meats, opt for lean cuts like skinless poultry, turkey and lean beef. These meats contain fewer omega-6 fatty acids compared to their higher-fat counterparts. Removing the skin from poultry can further reduce the omega-6 content.
Select Cooking Oils Wisely: Pay attention to the cooking oils you use. Opt for oils with a healthier omega-3 to omega-6 ratio, such as olive oil and avocado oil, while reducing the use of oils like soybean, corn and sunflower oils, which are high in omega-6 fatty acids.
Incorporate Nuts and Seeds: Include a variety of nuts and seeds in your diet, such as walnuts, flaxseeds and chia seeds. These are excellent sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid. Adding them to yogurt, oatmeal or smoothies is an easy way to increase your omega-3 intake.
Read Food Labels: Be an informed consumer by reading food labels. Many processed foods contain oils high in omega-6 fatty acids, so checking labels can help you make healthier choices and avoid excessive omega-6 consumption.
Limit Processed Foods: Processed and fast foods often contain unhealthy oils and high levels of omega-6 fatty acids. Reducing your intake of these foods can have a positive impact on your omega-3 to omega-6 ratio.
Supplement Wisely: If it’s challenging to get enough omega-3s through your diet alone, consider omega-3 supplements. High-quality fish oil or algae oil supplements can provide a convenient way to balance your omega-3 to omega-6 ratio.
Consult a Dietitian: If you have specific dietary concerns or health conditions, it’s advisable to consult a registered dietitian or healthcare professional. They can provide personalized guidance on achieving and maintaining a healthy omega-3 to omega-6 ratio based on your unique needs.
Maintaining a balanced omega-3 to omega-6 ratio is a proactive step towards supporting heart health, reducing inflammation and promoting overall well-being. By making thoughtful choices about the foods you consume and the oils you cook with, you can ensure that your dietary choices align with these health goals and set the foundation for a healthier future.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Omega-3 Fatty Acids: An Essential Contribution | The Nutrition Source

Choose Cooking Oils Wisely
Opt for oils with a more balanced Omega-3 to Omega-6 ratio, such as olive oil or canola oil, for cooking and salad dressings.
When it comes to choosing cooking oils, the type you select can significantly impact your health. Opting for oils with a more balanced Omega-3 to Omega-6 ratio, such as olive oil or canola oil, is a smart choice that can benefit your well-being in multiple ways.
Heart Health: Olive oil, in particular, is renowned for its heart-healthy properties. It is rich in monounsaturated fats, which have been associated with reduced risk factors for heart disease. Consuming olive oil regularly can help lower levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol while preserving the levels of HDL (good) cholesterol in your blood. This, in turn, supports cardiovascular health and reduces the risk of heart disease.
Inflammation Control: An excessive intake of Omega-6 fatty acids, often found in oils like corn or soybean oil, can contribute to chronic inflammation, which is linked to various health issues, including heart disease, arthritis and certain cancers. Choosing oils with a balanced ratio helps mitigate this inflammation by promoting a healthier balance between Omega-3s and Omega-6s.
Cognitive Benefits: Omega-3 fatty acids, such as those found in canola oil, have been linked to cognitive health and improved brain function. These essential fats are crucial for brain development and maintenance and incorporating them into your diet may help support memory and cognitive function as you age.
Stable Cooking: Oils like olive and canola have higher smoke points compared to some other oils, making them suitable for various cooking methods, from sautéing to baking. This means they are less likely to break down and release harmful compounds when exposed to high temperatures, ensuring the integrity of your dishes.
Versatility: Both olive oil and canola oil are incredibly versatile in the kitchen. Olive oil adds a rich, fruity flavor to salad dressings, marinades and Mediterranean-inspired dishes. Canola oil, with its neutral taste, works well in a wide range of recipes, from stir-fries to baking.
When incorporating these oils into your diet, remember that moderation is key. Oils are calorie-dense, so be mindful of portion sizes to maintain a balanced diet. Additionally, consider the specific cooking needs of your dishes; olive oil may be better suited for drizzling over salads or dipping bread, while canola oil’s neutral flavor makes it an ideal choice for frying and baking.
By making a simple switch to oils with a more balanced Omega-3 to Omega-6 ratio, you can enhance the nutritional value of your meals and promote overall well-being. Your heart, brain and taste buds will thank you for choosing these health-conscious options in your culinary adventures.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Feeding Oil to Horses: Choose Wisely – Kentucky Equine Research
Eat Fatty Fish Regularly
Include fatty fish in your diet at least twice a week to increase Omega-3 intake.
Incorporating fatty fish into your diet is a simple yet powerful dietary choice that can have profound effects on your health. Omega-3 fatty acids, abundant in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel and sardines, offer a wide array of benefits that extend beyond their reputation as “heart-healthy” nutrients. Here’s why you should aim to include these marine marvels in your meals at least twice a week:
1. Heart Health Champion: Omega-3 fatty acids are renowned for their role in supporting cardiovascular health. They can reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering blood pressure, triglyceride levels and the risk of abnormal heart rhythms. Regular consumption of fatty fish can help maintain a healthy heart and reduce the chances of cardiac events.
2. Brain Boost: Your brain is composed largely of fat and Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), are critical for its structure and function. They support cognitive function, memory and mood stability. Consuming fatty fish can be a tasty way to nourish your brain and potentially reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline.
3. Joint and Inflammatory Support: Omega-3s possess anti-inflammatory properties that can help alleviate symptoms of conditions like arthritis and joint pain. They can reduce inflammation throughout the body, providing relief and improved joint mobility for those dealing with these issues.
4. Eye Health: DHA, one of the Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, is a major structural component of the retina. Consuming Omega-3s can support good vision and reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration, a leading cause of blindness in older adults.
5. Skin and Hair Benefits: Omega-3s contribute to healthy skin by maintaining its moisture and elasticity. They can also help manage conditions like eczema and psoriasis. Additionally, these fatty acids promote hair health, making it shiny and strong.
6. Mood and Emotional Well-being: Emerging research suggests that Omega-3s may play a role in mood regulation and mental health. They may help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety and promote emotional well-being.
By making fatty fish a regular part of your diet, you can harness the potent benefits of Omega-3 fatty acids, enhancing your overall health and vitality. Whether you grill salmon, bake mackerel or enjoy sardines in a salad, these culinary choices not only tantalize your taste buds but also offer a bounty of health advantages. So, for the sake of your heart, brain, joints and well-being, consider scheduling those delicious seafood feasts at least twice a week. Your body and mind will thank you for it.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: An Increase in the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio Increases the …

Snack on Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, walnuts and flaxseeds make for healthy snacks that boost your Omega-3 and Omega-6 levels.
When it comes to wholesome snacking that elevates your Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acid levels, almonds, walnuts and flaxseeds stand out as nutritional powerhouses:
1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These essential fats are renowned for their heart-healthy properties. Almonds, walnuts and flaxseeds are rich sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of Omega-3 that supports cardiovascular health. Omega-3s are known to reduce inflammation, lower the risk of heart disease and contribute to overall well-being.
2. Heart-Healthy Benefits: Incorporating these nuts and seeds into your snacks can have a profound impact on your heart health. Almonds, for instance, are packed with monounsaturated fats, which can help lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease.
3. Brain Boost: Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in cognitive function. Regular consumption of almonds, walnuts and flaxseeds can support memory, concentration and overall brain health. These nutrients are especially vital for maintaining mental clarity as you age.
4. Omega-6 Fatty Acids: While Omega-3s often steal the spotlight, Omega-6 fatty acids are equally important for health. Almonds and walnuts contain a balanced ratio of Omega-3s to Omega-6s, promoting a healthy balance of these essential fats. Omega-6s play a role in immune function, skin health and inflammation regulation.
5. Nutrient Density: In addition to healthy fats, these snacks provide a wealth of essential nutrients. Almonds offer vitamin E and magnesium, both of which are beneficial for heart health and overall well-being. Walnuts provide a generous dose of antioxidants, particularly polyphenols, which combat oxidative stress and inflammation. Flaxseeds are a rich source of fiber, promoting digestive health and a feeling of fullness.
6. Versatile Snacking: Almonds, walnuts and flaxseeds are incredibly versatile and can be enjoyed in various ways. Sprinkle them on yogurt or oatmeal, add them to smoothies or simply enjoy them as a quick and nutritious snack on their own.
7. Satiety and Weight Management: The combination of healthy fats, fiber and protein in these snacks contributes to feelings of fullness and satisfaction. This can help control appetite and reduce overall calorie intake, supporting your weight management goals.
8. Nutritional Synergy: Combining almonds, walnuts and flaxseeds in your diet creates a synergy of nutrients. The diversity of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and healthy fats in these foods enhances their collective health benefits, making your snacking choice even more impactful.
Incorporating almonds, walnuts and flaxseeds into your daily snacks is a simple yet powerful way to support your heart health, boost brain function and embrace a more nutrient-rich diet. These delicious and versatile snacks are a tasty addition to your eating plan, helping you achieve a healthier and more balanced lifestyle.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Choosing Healthy Fats – HelpGuide.org

Supplement When Necessary
If it’s challenging to obtain enough Omega-3s from food sources, consider Omega-3 supplements.
When it comes to ensuring an adequate intake of Omega-3 fatty acids, sometimes dietary choices alone may not suffice and this is where Omega-3 supplements can be a valuable addition to your health regimen. Let’s explore the considerations and potential benefits associated with Omega-3 supplementation:
Dietary Challenges: For many individuals, especially those with dietary restrictions or specific health concerns, obtaining sufficient Omega-3s solely from food sources can be challenging. Factors such as dietary preferences, allergies or medical conditions may limit access to Omega-3-rich foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds or walnuts. In such cases, supplements can bridge the gap and help meet your nutritional needs.
Variety of Options: Omega-3 supplements come in various forms, with the most common being fish oil, krill oil and algae-based supplements. Each type has its unique composition and potential benefits. Fish oil, derived from cold-water fish like salmon and mackerel, is rich in both eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Krill oil, sourced from tiny shrimp-like crustaceans called krill, contains a mix of EPA and DHA, along with phospholipids and antioxidants. Algae-based supplements are an excellent choice for vegetarians and vegans, as they provide a direct source of EPA and DHA without relying on fish.
Heart Health: Omega-3 supplements, particularly fish oil, are renowned for their cardiovascular benefits. They can help lower blood pressure, reduce triglyceride levels and promote overall heart health. Individuals with a family history of heart disease or those at risk may find Omega-3 supplementation to be a proactive measure in safeguarding their cardiovascular well-being.
Brain Function: Omega-3s, especially DHA, are crucial for brain health and cognitive function. Supplementation may be beneficial for individuals looking to support their memory, concentration and overall cognitive vitality. Studies have suggested that Omega-3 supplements may play a role in reducing the risk of age-related cognitive decline.
Inflammation Management: Omega-3s have well-established anti-inflammatory properties. Supplementing with Omega-3s can help regulate the body’s inflammatory response, potentially alleviating symptoms in conditions characterized by chronic inflammation, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Pregnancy and Child Development: Omega-3 supplements, particularly those rich in DHA, are often recommended for pregnant and breastfeeding women. DHA is essential for fetal brain and eye development. Additionally, Omega-3 supplementation during pregnancy may reduce the risk of preterm birth and support the baby’s cognitive development.
Quality Matters: When considering Omega-3 supplements, it’s essential to choose high-quality products from reputable manufacturers. Look for supplements that undergo third-party testing for purity and potency to ensure you’re getting a safe and effective product.
Consultation with a Healthcare Professional: Before starting any supplementation regimen, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a physician or registered dietitian. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific health goals, dietary habits and any underlying medical conditions.
In conclusion, Omega-3 supplements can be a valuable resource for individuals seeking to enhance their health and well-being, especially when dietary challenges make it difficult to obtain these essential fatty acids from food sources alone. When used judiciously and under professional guidance, Omega-3 supplements can play a supportive role in promoting heart health, brain function and overall vitality, helping you achieve your health and wellness goals.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: An Increase in the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio Increases the …
Essential fats, particularly Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, are fundamental building blocks of good health. By understanding their significance, sources and the importance of balance, you can make informed dietary choices to promote overall well-being. Whether you’re looking to support your heart, brain or joints, incorporating these essential fats into your diet is a delicious and rewarding investment in your long-term health.
Essential fats, with a particular emphasis on Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, serve as the foundational building blocks of good health, influencing various aspects of our well-being. It’s essential to delve deeper into their significance, sources and the delicate art of balance to make informed dietary choices that pave the way for lasting vitality.
Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids are like the two halves of a harmonious equation, each with its unique role in maintaining our health. Omega-3s, often found in fatty fish, flaxseeds and walnuts, are renowned for their heart-healthy properties. They have the remarkable ability to reduce triglycerides, lower blood pressure and decrease the risk of abnormal heart rhythms, ultimately promoting cardiovascular well-being.
On the other hand, Omega-6 fatty acids, abundant in vegetable oils, nuts and seeds, are vital for maintaining healthy skin and hair. They are essential for the production of prostaglandins, hormone-like substances that regulate inflammation, blood clotting and blood vessel constriction. When balanced correctly with Omega-3s, Omega-6s contribute to overall health and vitality.
However, the key to unlocking the full potential of these essential fats lies in achieving a delicate equilibrium between them. In our modern diets, Omega-6s often overshadow Omega-3s, tipping the balance towards excess inflammation. This imbalance can contribute to chronic inflammation, a root cause of many diseases, including heart disease, diabetes and arthritis.
Therefore, the importance of balance cannot be overstated. Striving to achieve a healthy ratio of Omega-3 to Omega-6 fatty acids in your diet is a proactive step towards long-term well-being. Incorporating Omega-3-rich foods and reducing excessive intake of Omega-6 sources can help restore this equilibrium.
The beauty of essential fats is that they offer a diverse range of health benefits. Omega-3s are brain boosters, supporting cognitive function and potentially reducing the risk of neurological conditions. They are also joint-friendly, alleviating symptoms of conditions like arthritis. Omega-6s, when consumed in moderation, maintain the integrity of your skin’s lipid barrier, promoting a youthful complexion.
Incorporating these essential fats into your diet is not just a health-conscious choice; it’s a delicious and rewarding investment in your long-term vitality. From a succulent piece of salmon to a handful of crunchy walnuts or a drizzle of flaxseed oil on your salad, there are myriad ways to savor the benefits of essential fats while savoring delectable flavors.
So, embrace the power of Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids as your allies in the journey towards robust health. With a clear understanding of their significance and the art of balance, you can make informed dietary choices that support your heart, brain, joints and overall well-being, enriching your life with both delicious and nourishing moments.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Brain foods: the effects of nutrients on brain function – PMC
More links
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Mechanisms and innovations: The science behind dietary omega-3 …