Introduction
Emergencies can happen when you least expect them. Whether you’re at home, work, or out in public, knowing how to respond to common emergencies can make all the difference. While professional help should always be sought in serious situations, having a basic understanding of first aid essentials can help stabilize a person’s condition and potentially save a life. In this article, we will explore what to do in some of the most common emergency situations.
Emergencies are unpredictable, and they can strike when you least anticipate them, turning any environment into a potential crisis zone. Whether you’re in the comfort of your home, your workplace, or out in public, possessing the knowledge of how to respond to common emergencies is an invaluable skill that can truly make a difference.
While it’s essential to emphasize that professional medical help should always be summoned in severe situations, being equipped with a fundamental understanding of first aid essentials can serve as a critical bridge between the onset of an emergency and the arrival of medical professionals. This bridge can play a vital role in stabilizing a person’s condition and, in some cases, can even be the decisive factor in saving a life.
In this comprehensive article, we embark on a journey through some of the most prevalent emergency situations one might encounter in everyday life. From minor incidents to potentially life-threatening scenarios, we’ll delve into the actions you can take to provide immediate assistance, alleviate discomfort, and maintain safety until professional help arrives.
Our aim is to empower you with knowledge and confidence, equipping you to respond effectively when the unexpected occurs. Through a better understanding of common emergencies and how to react appropriately, you become a potential lifeline for those in need, ensuring that help is never too far away. So, let’s explore these crucial first aid insights and together, learn how to navigate through the unexpected challenges that life may throw our way.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Shock: First aid – Mayo Clinic
Cuts and Wounds
Small cuts and wounds are everyday occurrences. To provide first aid:
Begin by gently cleaning the wound with mild soap and warm water. This helps remove any dirt or debris that may be present.
After cleaning, pat the area dry with a clean cloth or sterile gauze. Avoid rubbing the wound, as this can introduce more bacteria.
Apply an over-the-counter antibiotic ointment to the wound to prevent infection. This also helps keep the wound moist for better healing.
Cover the wound with a sterile bandage or dressing to keep it clean and protected. Change the bandage regularly, especially if it becomes wet or dirty.
Keep an eye on the wound for any signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, pus, or worsening pain. If you notice these symptoms, seek medical attention.
If the cut is deep, long, or caused by a dirty or rusty object, or if it won’t stop bleeding, it’s essential to seek professional medical help immediately.
Remember that proper wound care can prevent complications and promote faster healing.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: First aid – Injuries & first aid | NHS inform
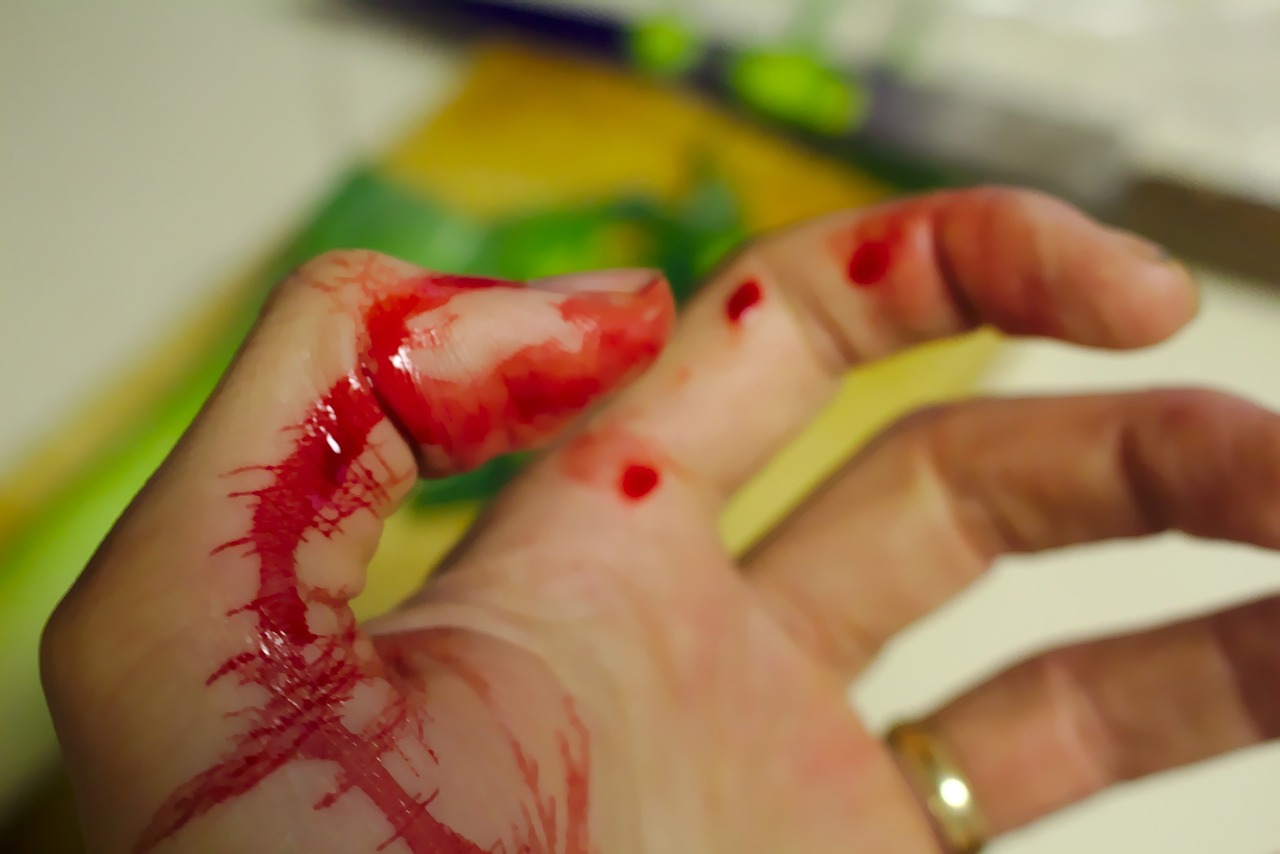

Wash your hands thoroughly.
Clean the wound gently with mild soap and water.
“Cleaning the wound gently with mild soap and water is an essential step in basic first aid. Use a clean cloth or sterile gauze to remove debris and dirt from the injured area. This helps prevent infection and ensures proper wound healing. Remember to rinse the wound thoroughly to ensure all contaminants are removed before applying any antiseptic or dressing.”
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Chemical splash in the eye: First aid – Mayo Clinic
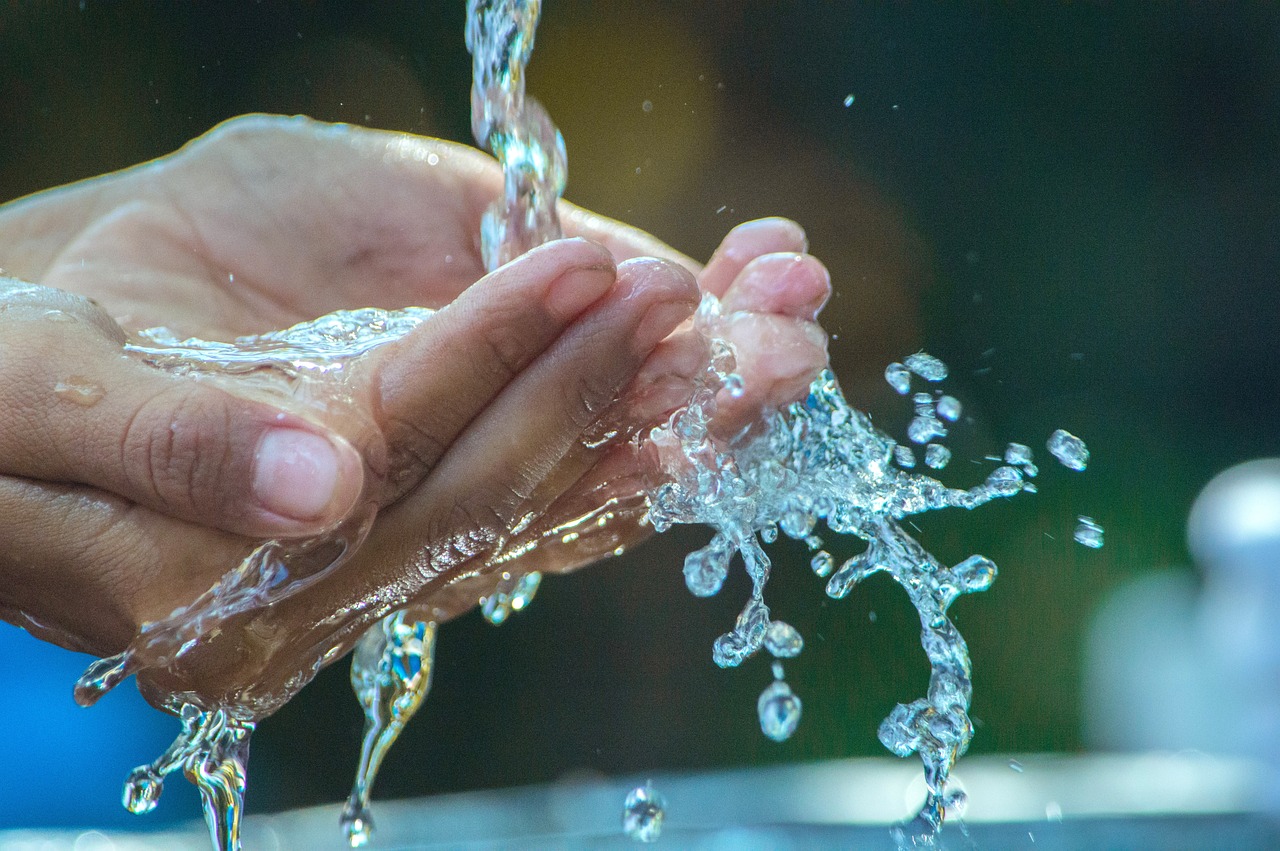

Cover the wound with a sterile bandage.
For deeper or heavily bleeding wounds, apply direct pressure and elevate the injured area. Seek medical attention if needed.
When faced with deeper or heavily bleeding wounds, it’s crucial to act swiftly and decisively to minimize further harm and ensure the best possible outcome:
Assess the Situation: Begin by carefully assessing the extent of the injury. Determine if the wound is deep, whether it involves a major artery, or if there is significant bleeding. Understanding the severity of the situation will guide your response.
Safety First: Ensure your safety and that of the injured person. If the injury occurred in a hazardous environment, move to a safe location before providing aid.
Gloves and Clean Hands: If available, wear disposable gloves or use a clean cloth to cover your hands. Reducing the risk of infection is important.
Apply Direct Pressure: Use a clean cloth, sterile dressing, or your gloved hand to apply direct pressure to the wound. This helps control bleeding by promoting the clotting process. Press down firmly but avoid pressing so hard that it causes additional tissue damage.
Elevate the Injured Area: If possible, elevate the injured area above the level of the heart. This can further help reduce bleeding. However, be cautious with this step, especially if you suspect a bone fracture, as improper elevation can worsen the injury.
Use Pressure Points: In cases of severe bleeding where direct pressure alone is not sufficient, you can use pressure points. Pressing on certain arterial pressure points can help control bleeding while waiting for medical assistance. However, this should be done with caution and ideally under the guidance of trained personnel.
Bandage and Secure: Once bleeding is under control, cover the wound with a sterile dressing, clean cloth, or bandage. Secure it in place with a bandage or tape. Be mindful not to disturb any clot that has formed.
Monitor and Seek Medical Attention: Keep a close eye on the injured person’s condition. If bleeding continues or worsens, do not remove the initial dressing; instead, apply additional layers. Continue to maintain direct pressure.
Call for Professional Help: Even if you’ve successfully controlled the bleeding, it’s essential to seek professional medical attention for deeper or heavily bleeding wounds. There may be underlying damage that requires further assessment and treatment.
Stay Calm and Offer Comfort: Throughout the process, it’s important to remain as calm as possible. Your reassurance and support can help alleviate anxiety for the injured person, which can be especially beneficial in traumatic situations.
Remember that while providing first aid for bleeding wounds is crucial, it should not substitute professional medical care. Timely and appropriate treatment from healthcare providers is essential to ensure the wound heals properly and to prevent complications.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Make a First Aid Kit | Supplies & Contents | American Red Cross
Burns
Burns can result from various sources, including hot surfaces, flames, or chemicals. For minor burns:
Cool the burn with cold, running water for about 10-20 minutes.
Burns can manifest due to a multitude of sources, each posing unique challenges for treatment and recovery. Whether it’s the searing touch of a hot surface, the relentless bite of flames, or the corrosive effects of chemicals, burns demand our immediate attention and care.
When dealing with minor burns, the initial response is crucial. Cooling the affected area with cold, running water for a duration of about 10-20 minutes is a crucial first step. This simple yet effective measure helps to achieve several vital goals:
Pain Relief: The immediate cooling action provides instant relief from the intense pain associated with burns. Lowering the temperature of the affected tissue helps to soothe the area and mitigate discomfort.
Reduction of Tissue Damage: Rapid cooling helps to reduce the extent of tissue damage caused by the burn. By dissipating heat, it prevents the burn from deepening and limits the severity of the injury.
Prevention of Further Injury: Prompt cooling also prevents the burn from spreading to nearby healthy tissue. This containment is essential in averting a more extensive injury.
Minimization of Scarring: Proper cooling can contribute to a better overall healing process and may reduce the chances of severe scarring.
Infection Prevention: Cooling helps to cleanse the wound by removing any debris or foreign material that may be present. This cleansing action reduces the risk of infection, a common concern with burns.
However, it’s important to note that this approach is primarily suitable for minor burns, typically classified as first-degree or superficial second-degree burns. For more severe burns, professional medical attention is an absolute necessity. The key takeaway is that swift action and appropriate first aid can significantly improve the outcome for burn victims, highlighting the importance of knowing how to respond effectively to various burn types and their respective causes.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: First Aid Tips: How to Treat Burns, Cuts, and Bites

Avoid using ice.
Apply a sterile, non-stick bandage or a clean cloth.
When applying a sterile, non-stick bandage or a clean cloth to a wound, it’s crucial to follow these steps for effective wound care:
Clean Hands: Before touching the bandage or cloth, make sure your hands are clean. Wash them thoroughly with soap and water to reduce the risk of introducing harmful bacteria to the wound.
Select the Right Size: Choose a bandage or cloth that is appropriately sized to cover the wound without being too tight or too loose. It should provide adequate protection without restricting blood circulation.
Sterility: If you’re using a sterile bandage, open the packaging carefully to maintain its sterility. Avoid touching the inside of the bandage or cloth with your fingers.
Positioning: Gently place the bandage or cloth over the wound, ensuring it covers the entire injured area. Be cautious not to apply excessive pressure that might cause further damage or discomfort.
Secure in Place: Use medical tape or adhesive strips to secure the bandage or cloth in position. Make sure it’s snug but not overly tight, as overly tight bandaging can impede blood flow.
Check for Allergies: If you or the injured person has allergies to adhesives or bandage materials, consider using hypoallergenic options to prevent skin irritation.
Regular Monitoring: Periodically check the bandage or cloth to ensure it remains clean and dry. If it becomes wet, soiled, or dislodged, replace it with a fresh one to maintain wound cleanliness.
Change as Needed: Change the bandage or cloth according to the wound care instructions provided by a healthcare professional or as necessary based on the type and severity of the wound.
Seek Medical Attention: If the wound is deep, shows signs of infection (increased redness, swelling, discharge), or if there are any concerns about the wound’s healing progress, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Remember that proper bandaging helps protect the wound from external contaminants, promotes a moist healing environment, and supports the body’s natural healing process. It’s an essential part of wound care, whether it’s a minor scrape or a more significant injury.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Sprain: First aid – Mayo Clinic

Never pop blisters.
For severe burns or burns involving the face, hands, feet, or genitals, call 911 immediately.
“When faced with severe burns or burns affecting sensitive areas like the face, hands, feet, or genitals, it’s crucial to act swiftly. Dial 911 immediately to summon professional medical help. Severe burns can have lasting consequences, and prompt intervention by healthcare experts is vital to minimize damage, manage pain, and ensure the best possible outcome for the victim. While waiting for help to arrive, gently cool the burn with running cold water if it’s a chemical burn or with a clean, cold, damp cloth if it’s a thermal burn, but avoid any home remedies that could worsen the injury.”
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: How to Respond: Injury and Illness at School

Choking
Choking can occur when a person’s airway is blocked. If someone is choking:
Choking is a distressing and potentially life-threatening situation that can happen suddenly and without warning. Knowing how to respond effectively can make all the difference in ensuring the person’s safety. If someone is choking, follow these steps promptly:
Assess the Situation: First, assess the severity of the choking. Ask the person if they can speak or cough. If they are coughing forcefully, it’s a sign that they may be able to clear the obstruction themselves. Encourage them to keep coughing.
Stay Calm and Encourage Calmness: If the person is unable to speak or is struggling to breathe, it’s crucial to stay calm yourself. Panic can escalate the situation. Encourage the choking individual to stay calm as well.
Call for Help: If the person is unable to cough or breathe, call 911 or your local emergency number immediately. Time is of the essence in a choking emergency, and professional medical assistance may be required.
Perform the Heimlich Maneuver (Abdominal Thrusts): If the choking person cannot breathe or cough, stand behind them and place your arms around their waist. Make a fist with one hand and place it just above their navel, thumb side in. Grasp your fist with your other hand and give quick, upward thrusts into the person’s abdomen, aiming to force the object out. Continue these thrusts until the object is dislodged or until professional help arrives.
Encourage Self-Help: If the choking person is conscious and able to cough forcefully, encourage them to continue coughing and avoid any interventions that might worsen the situation.
Alternate Between Back Blows and Abdominal Thrusts for Infants: If the choking victim is an infant, the Heimlich maneuver is not recommended. Instead, support the infant’s head and neck and give gentle back blows followed by chest or abdominal thrusts until the obstruction is cleared.
Provide Support: Be reassuring and offer support throughout the ordeal. Reassure the person that help is on the way if you’ve called for it. Stay with them until the situation is resolved or until professional medical assistance arrives.
Avoid Forceful Finger-Sweeping: It’s crucial to avoid attempting to remove the object with your fingers, as this can push it deeper into the airway and worsen the situation.
Be Prepared: Knowing how to respond to choking emergencies in advance can be invaluable. Consider taking a CPR and first aid course to learn proper techniques and build confidence in handling such situations.
Choking incidents can be terrifying, but remaining calm and taking swift, appropriate action can save lives. Always prioritize safety and seek professional medical help when needed.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Travel First Aid Essentials For Horses

Encourage them to cough forcefully.
Perform the Heimlich maneuver by standing behind the person, placing your fist above their navel, and applying quick, upward pressure.
If the person loses consciousness, start CPR and call 911.
Performing the Heimlich maneuver is a crucial skill that can be a lifesaver in cases of choking emergencies. It’s important to act swiftly and confidently when someone is in distress. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the steps involved:
Assess the Situation: Quickly assess the person’s condition. If they are unable to cough, speak, or breathe, and they are clutching their throat or making the universal choking sign (hands around the neck), immediate action is necessary.
Position Yourself: Stand behind the person and make sure both of you are on stable footing. Ensure the person is aware that you are going to assist them.
Fist Above Navel: Form a fist with one hand and place the thumb side just above the person’s navel but below the ribcage.
Grasp with Other Hand: With your other hand, grasp your fist and press it inward and upward with quick, forceful movements. The goal is to create an upward flow of air to dislodge the obstructing object from the person’s airway.
Repeat if Necessary: If the first attempt doesn’t clear the obstruction, repeat the process until the object is expelled or the person becomes unconscious.
Now, if the person does lose consciousness during these efforts:
Lower to the Ground: Gently lower the person to the ground, ensuring their head is supported.
Call 911: While someone is attending to the person, call 911 or your local emergency number immediately. If you are alone, perform the Heimlich maneuver and then call for help as soon as possible.
Begin CPR: If the person remains unresponsive and you are trained in CPR, start cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) immediately. Follow the recommended chest compression and rescue breaths ratio until professional medical help arrives.
Remember, choking emergencies can happen suddenly and without warning. Knowing how to respond with the Heimlich maneuver and, if necessary, transitioning to CPR, can be the difference between a life-threatening situation and a successful rescue. Immediate action is the key to ensuring the best possible outcome for someone in distress.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: What should I do if someone is choking? – NHS

Heart Attacks
Heart attacks are medical emergencies that require immediate attention:
Heart attacks are medical emergencies that require immediate attention due to their life-threatening nature. Here are key steps to take when a heart attack is suspected:
Recognize the Signs: Understanding the signs and symptoms of a heart attack is crucial. Common signs include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, nausea, and pain radiating to the arms, neck, jaw, shoulder blades, or back.
Call 911: As soon as you suspect a heart attack, dial 911 or your local emergency number. Emergency medical services (EMS) can provide rapid response and necessary medical assistance.
Stay Calm: While waiting for help to arrive, try to stay as calm as possible. Anxiety can exacerbate symptoms. If you are with someone experiencing a heart attack, reassure them and encourage them to remain calm.
Chew Aspirin: If the person experiencing a heart attack is conscious and not allergic to aspirin, they can chew and swallow an aspirin (usually 325 mg). Aspirin can help prevent further blood clot formation.
Rest: If possible, have the person sit down or lie down in a comfortable position. It’s important to minimize physical exertion, as it can strain the heart.
Perform CPR: If the person becomes unresponsive and stops breathing, initiate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) if you are trained to do so. CPR can help maintain blood circulation until professional help arrives.
Use an Automated External Defibrillator (AED): If an AED is available and you are trained to use it, follow the device’s instructions for administering an electric shock to restore the heart’s normal rhythm.
Follow Medical Advice: Once EMS arrives, follow their instructions and provide them with any relevant medical history or information about the person’s condition.
Go to the Hospital: Even if the symptoms seem to subside, it’s crucial to go to the hospital for further evaluation. Heart attacks can have varying degrees of severity, and prompt medical assessment is essential to determine the extent of damage and appropriate treatment.
Support and Recovery: After receiving medical treatment for a heart attack, individuals often require a period of recovery and may need ongoing cardiac care and lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of future heart issues.
Remember that early intervention is critical in improving the chances of survival and minimizing heart damage during a heart attack. Recognizing the signs and taking swift action can save lives.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: First-aid kits: Stock supplies that can save lives – Mayo Clinic

Have the person sit down and rest.
If available, provide aspirin (if not allergic) to chew slowly.
“Offering aspirin, as long as there are no allergies, can be a crucial step in certain emergency situations. When someone is experiencing the signs of a heart attack, giving them an aspirin to chew slowly can potentially save their life. Aspirin works by helping to prevent further blood clot formation, which is often a key factor in heart attacks. Remember that time is of the essence during a heart attack, so if you or someone you’re assisting has aspirin on hand, providing it promptly can significantly improve the chances of a positive outcome. However, always ensure the person isn’t allergic to aspirin before administering it.”
You can also read more about this here: First aid basics and DRSABCD – Better Health Channel
During a seizure
Keep the person safe by removing any nearby objects.
Ensuring the safety of the person in distress is the first and foremost priority when responding to any emergency situation. In cases where someone is injured or experiencing a medical crisis, like a fall or a sudden illness, taking steps to create a safe environment can prevent further harm. Here’s why and how to keep the person safe by removing any nearby objects:
Preventing Additional Injuries: Accidents or medical emergencies can happen anywhere, and the scene of the incident may be cluttered or contain hazards that could lead to additional injuries. By removing nearby objects, you reduce the risk of the person or others tripping, falling, or colliding with obstacles.
Facilitating Access: Medical professionals may need to access the person quickly. Removing nearby objects creates a clear path for first responders or medical personnel to reach the individual and provide necessary assistance.
Enhancing Safety: In some cases, the person may be disoriented, confused, or agitated due to their condition. Removing objects that could pose a threat, such as sharp or heavy items, helps protect both the individual and those providing care.
Reducing Stress: A clutter-free environment can contribute to a calmer and less stressful atmosphere, which can be beneficial for the person’s well-being and can aid in their recovery or stabilization.
To remove nearby objects and ensure the person’s safety:
Assess the Area: Quickly scan the immediate vicinity to identify any potential hazards or objects that could pose a danger.
Secure Hazardous Items: If you identify items that could be hazardous, such as sharp objects, chemicals, or heavy furniture, take measures to secure or remove them from the area.
Create Space: If possible, create some space around the person to allow them room to breathe and receive assistance comfortably.
Maintain Communication: If the person is conscious and alert, inform them of your actions and reassure them that you’re taking steps to keep them safe.
Use Caution: While it’s essential to act quickly, do so with caution to avoid causing further harm to the person or yourself. If an object is heavy or requires specialized tools to move safely, consider waiting for professional help.
Remember that in emergencies, your safety and the safety of the person in need should be the top priority. Once you’ve taken steps to ensure safety, focus on providing appropriate care or seeking professional medical assistance as necessary.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Using Epilepsy Rescue Treatments | Epilepsy Foundation

Do not put anything in their mouth.
Time the seizure and call 911 if it lasts longer than five minutes.
When witnessing someone having a seizure, it’s essential to be vigilant and responsive. Timing the duration of the seizure is a crucial step, as it can help guide your actions and ensure the person’s safety. Here’s why timing is so important and what to do in the event of a prolonged seizure:
Assess the Situation: Begin by assessing the person’s safety. If they are at risk of injury due to the surroundings (such as sharp objects, stairs, or traffic), try to move them to a safer area, but do so carefully to avoid causing harm during the seizure.
Start Timing: As soon as the seizure begins, start timing it. Use a watch or your phone to track the duration. Most seizures are brief and last only a matter of seconds to a couple of minutes. However, if a seizure continues for more than five minutes, it is considered a prolonged seizure, or status epilepticus.
Call 911: If the seizure extends beyond the five-minute mark, it’s critical to call 911 or your local emergency number immediately. Prolonged seizures can be a medical emergency, and professional medical attention is essential.
Stay Calm and Supportive: While waiting for help to arrive, stay with the person and offer reassurance. Clear the area around them to prevent injury, and place them on their side if possible to help keep their airway clear.
Do Not Restrain: Avoid restraining the person or putting anything in their mouth during the seizure. Contrary to common misconceptions, it’s not possible to swallow the tongue during a seizure, and attempting to hold down or restrict movements can cause harm.
Monitor Breathing: Pay close attention to the person’s breathing. If they stop breathing or have difficulty breathing after the seizure ends, be prepared to perform CPR if you are trained to do so.
Remember that every seizure is unique, and the person may require different levels of care. While most seizures are not life-threatening and resolve on their own, knowing when to seek medical assistance for a prolonged seizure is vital. Timing the seizure is a simple yet essential step in ensuring the person’s well-being and getting them the help they may need.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: First aid – NHS

Conclusion
Being prepared to respond to common emergencies with first aid essentials can make a significant difference in the outcomes of these situations. However, it’s important to remember that professional medical assistance should always be sought when an emergency occurs. In the meantime, knowing what to do can help stabilize the situation and provide crucial support until help arrives.
Being prepared to respond to common emergencies with first aid essentials can make a significant difference in the outcomes of these situations. However, it’s important to remember that professional medical assistance should always be sought when an emergency occurs. In the meantime, knowing what to do can help stabilize the situation and provide crucial support until help arrives.
Here are some key reasons why having first aid knowledge and supplies is important:
Immediate Response: In many emergencies, time is of the essence. Knowing how to administer basic first aid can prevent a situation from worsening while waiting for professional medical help to arrive.
Reduced Severity: Quick and appropriate first aid measures can often reduce the severity of injuries or medical conditions. For example, applying pressure to a bleeding wound can minimize blood loss.
Increased Survival Rates: In cases like cardiac arrest or severe allergic reactions, performing CPR or using an epinephrine auto-injector can mean the difference between life and death.
Comfort and Reassurance: Providing first aid can offer comfort and reassurance to the injured or ill person. It shows that someone cares and is taking action to help.
Preventing Complications: Some injuries, if not treated promptly, can lead to complications. For instance, an infected wound can result in a more serious infection if not cleaned and dressed appropriately.
Promoting Recovery: Properly immobilizing a broken bone or splinting an injury can aid in the healing process and potentially shorten the recovery time.
Supporting Others: Knowing first aid allows you to assist family members, friends, or even strangers in distress. Your actions can make a significant impact on their well-being.
Safety in Remote Areas: If you enjoy outdoor activities or frequently travel to remote locations, having first aid knowledge and supplies can be crucial, as it may take longer for professional medical help to reach you.
Community Resilience: Communities benefit from individuals who are trained in first aid. In the event of a disaster or large-scale emergency, having a network of people with first aid skills can help save lives.
Remember that while first aid knowledge is valuable, it is not a substitute for professional medical care. In any emergency, the primary goal is to stabilize the situation and ensure the person receives the necessary medical attention. Whether it’s performing CPR, stopping severe bleeding, or assisting someone experiencing a heart attack, your readiness to respond can make a positive impact and potentially save lives.
You can also read more about this here: Guidelines for Bystander First Aid 2016 – PMC
More links
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Make a First Aid Kit | Supplies & Contents | American Red Cross