Introduction
Accidents and injuries can happen unexpectedly, and one of the most critical skills you can possess is knowing how to handle severe bleeding and provide effective wound care. Whether you’re at home, at work, or in any situation, having the knowledge to stop bleeding and properly tend to wounds can make a significant difference in someone’s recovery. In this article, we’ll explore the essential steps to take when confronted with severe bleeding and wound care.
Direct Pressure:
Applying direct pressure to the wound is the first and most crucial step in controlling severe bleeding. Use a clean cloth, sterile dressing, or your bare hand to exert firm pressure on the wound. This pressure helps to constrict the blood vessels, slowing down or stopping the bleeding.
Elevation:
If possible, elevate the injured area above the level of the heart. This can further reduce blood flow to the wound and assist in controlling bleeding. However, be cautious not to elevate if it causes discomfort or worsens the injury.
Tourniquet as a Last Resort:
Tourniquets should only be used as a last resort when severe bleeding cannot be controlled by direct pressure or other means. Improper tourniquet use can cause additional harm, so it’s essential to receive proper training on tourniquet application if you plan to use one.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Emergency Wound Care|Natural Disasters and Severe Weather
Ensure Your Safety
Before rushing to assist someone with severe bleeding, it’s vital to ensure your safety and the safety of others. Assess the situation for any potential hazards, such as traffic, fire, or dangerous substances. If the scene is unsafe, call 911 or the appropriate emergency number and wait for professional help. Your safety is the top priority.
Certainly, here’s an extension of the idea:
“Once you’ve assessed the scene and determined it’s safe to approach, your next step is to focus on the injured individual. Keep in mind that in situations involving severe bleeding, time is of the essence. You can make a significant difference by taking swift and appropriate action to control the bleeding and provide essential care until medical professionals arrive.”
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Emergency Wound Care|Natural Disasters and Severe Weather

Call for Help
If the situation is safe, immediately call for professional medical assistance. Severe bleeding can be life-threatening, and it’s crucial to have paramedics or medical personnel on their way as soon as possible.
If the situation is safe, immediately call for professional medical assistance. This swift response is paramount, particularly when dealing with severe bleeding, as it can be unequivocally life-threatening. Here’s why promptly summoning paramedics or medical personnel is absolutely crucial:
Rapid Intervention: Professional medical teams are equipped with the training and resources necessary to provide advanced care. They can assess the extent of the bleeding, determine its cause, and swiftly initiate appropriate treatment, which can be vital in stemming the flow of blood and preventing further harm.
Specialized Equipment: Paramedics and medical personnel have access to specialized equipment, including tourniquets, hemostatic agents, and advanced bandages, which are often required to control severe bleeding effectively. These tools can be the difference between life and death in critical situations.
Monitoring Vital Signs: Medical professionals can continuously monitor the injured person’s vital signs, including blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation. This real-time data is essential for making rapid and informed decisions regarding treatment and intervention.
Administering Medications: In cases of severe bleeding, medical personnel can administer medications to promote clotting or vasoconstriction, further assisting in controlling hemorrhage. They can also provide pain relief and manage any potential shock.
Expertise in Hemorrhage Control: Professionals are trained in various techniques for hemorrhage control, including direct pressure, wound packing, and applying pressure dressings. Their expertise ensures that bleeding is effectively managed, reducing the risk of complications and improving the injured person’s chances of survival.
Ensuring a Safe Transfer: In situations where surgery or specialized interventions are required, medical teams can facilitate the safe transfer of the injured person to an appropriate medical facility. This ensures that they receive the necessary surgical or interventional procedures promptly.
Access to Blood Products: Severe bleeding often leads to a significant loss of blood. Medical personnel have the ability to administer blood products, such as packed red blood cells and plasma, if needed, to restore blood volume and prevent shock.
Documentation and Communication: Medical teams maintain detailed records of the injured person’s condition and the care provided. This documentation is essential for continuity of care and can assist in further medical treatment once the person reaches a hospital or trauma center.
Legal Protections: Calling for professional medical assistance is not only the right thing to do but is also often legally required in cases of severe injury or life-threatening situations. It ensures that the injured person receives the care they need while also providing legal protections for those providing assistance.
In summary, when faced with severe bleeding, every second counts. Professional medical assistance is a lifeline, offering advanced skills, specialized equipment, and rapid response that can be the decisive factor in saving a life. Always remember that your immediate action in calling for help can significantly impact the outcome of an emergency, and it is a critical part of being prepared and responsible in accident and injury situations.
You can also read more about this here: Severe bleeding: First aid – Mayo Clinic

Apply Direct Pressure
If you have access to gloves or any form of barrier protection, use it to avoid contact with the person’s blood. Apply direct and firm pressure to the bleeding wound using a clean cloth, bandage, or your hand if necessary. Maintain this pressure until the bleeding stops or professional help arrives. Elevate the bleeding limb, if possible, to help control the bleeding.
Maintain Reassurance:
While providing first aid for severe bleeding, it’s crucial to keep the injured person as calm and reassured as possible. Anxiety and stress can exacerbate bleeding, so offer verbal support and let them know that help is on the way.
Monitor for Shock:
Severe bleeding can lead to shock, a condition where the body’s vital organs don’t receive enough blood and oxygen. Watch for signs of shock, such as rapid breathing, weakness, confusion, or bluish skin. If you suspect shock, keep the person lying down with their legs elevated slightly (unless they have a head, neck, back, or leg injury) and cover them with a blanket to maintain body warmth.
Stay Updated:
Keep the injured person’s condition in mind while waiting for professional medical help. If the bleeding continues despite your efforts, continue applying pressure and do not remove any soaked dressings. Instead, add more layers if necessary.
Be Prepared for Professionals:
When professional help arrives, be ready to provide them with information about what you’ve done so far and any specific details about the injury and the person’s condition. Your actions can help ensure a seamless transition of care from first aid to medical treatment.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Emergency Wound Care|Natural Disasters and Severe Weather
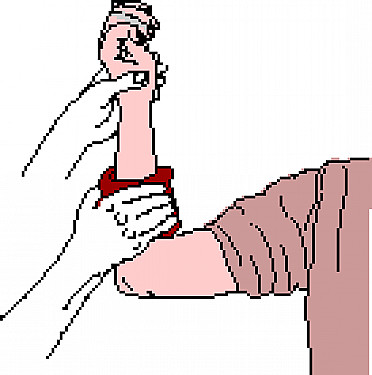
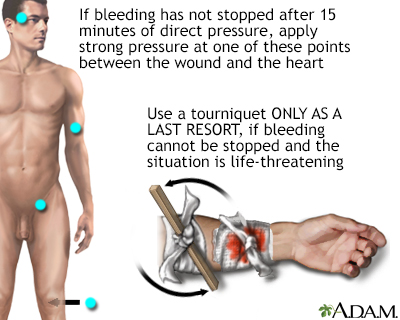
Use a Tourniquet (As a Last Resort)
In cases of severe, life-threatening bleeding that cannot be controlled with direct pressure, you may need to use a tourniquet. Apply it above the wound, but always use a tourniquet as a last resort and for a limited time to avoid causing further complications. Make a note of the time you applied the tourniquet, as it should not be left on for an extended period.
Here’s an extension of the idea:
“While tourniquets can be a lifesaver in situations with uncontrollable bleeding, it’s essential to use them cautiously and as a last resort. Apply the tourniquet proximal to the wound, ensuring it’s tight enough to stop the bleeding. Always remember, though, that prolonged use of a tourniquet can lead to tissue damage, so it’s crucial to note the time it was applied. Your goal is to control the bleeding temporarily while waiting for professional medical assistance to arrive.”
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Stop the Bleed-Tourniquet | Homeland Security
Keep the Injured Person Calm
Pain and anxiety can exacerbate bleeding. While providing care, try to keep the injured person as calm and still as possible. Encourage slow, deep breaths to help reduce anxiety and lower heart rate.
Pain and anxiety are not only distressing experiences for the injured person but can also have a direct impact on the severity of bleeding and overall well-being. In the context of providing care in traumatic situations, here’s why it’s crucial to prioritize the injured person’s comfort and emotional state while managing bleeding:
Pain-Induced Stress Response: Pain triggers a physiological stress response, leading to the release of stress hormones like adrenaline. This can further increase heart rate and blood pressure, potentially exacerbating bleeding. By alleviating pain or providing pain management, you can help mitigate this stress response and reduce the risk of increased bleeding.
Anxiety and Hemorrhage: Anxiety can intensify bleeding due to the release of stress hormones, which can impair the body’s natural ability to form blood clots. Therefore, keeping the injured person as calm as possible is essential for promoting clotting and minimizing blood loss.
Minimizing Movement: Encouraging the injured person to stay still helps prevent exacerbation of injuries and reduces the likelihood of reopening wounds. Unnecessary movement can lead to additional bleeding and complications.
Deep Breathing: Deep, slow breaths not only help calm anxiety but also have a direct impact on heart rate and blood pressure. By encouraging the injured person to take slow, deep breaths, you can help lower their heart rate, reducing the risk of further blood loss.
Communication: Effective communication is key to keeping the injured person calm. Explain the steps you are taking and reassure them that professional help is on the way. Knowing that they are in capable hands and that their needs are being attended to can provide a sense of security and comfort.
Pain Management: If resources and training allow, consider providing pain relief measures. However, always ensure that any pain management interventions are appropriate for the specific situation and do not compromise the injured person’s safety or wellbeing.
Distraction Techniques: Engaging the injured person in conversation or offering distractions like storytelling or reminiscing about positive experiences can divert their attention from pain and anxiety, helping to keep them calm and focused.
Monitoring: Continuously monitor the injured person’s mental and emotional state as well as their physical condition. Be prepared to adapt your approach based on their needs and responses.
Empathy and Reassurance: Offering emotional support, empathy, and reassurance can go a long way in easing anxiety. Let the injured person know that they are not alone and that you are there to help them through the situation.
In conclusion, addressing pain and anxiety while managing bleeding is an integral part of providing holistic care during traumatic situations. By keeping the injured person calm, comfortable, and focused, you not only alleviate their distress but also contribute to a more favorable outcome in terms of bleeding control and overall recovery. Remember that your compassion and efforts to promote emotional well-being are as valuable as any physical interventions you provide.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: First aid – NHS

Clean and Dress the Wound
Once the bleeding is under control, you can proceed to clean and dress the wound. Use sterile dressings or a clean cloth to cover the wound, applying gentle pressure to maintain control over bleeding. If possible, clean the wound with mild soap and water, but avoid scrubbing to prevent further damage.
Apply Antibiotic Ointment:
After cleaning the wound, applying a thin layer of antibiotic ointment can help prevent infection. Be cautious not to overdo it; a little goes a long way. Use a sterile cotton swab or clean hands to apply the ointment.
Cover with a Bandage:
Choose an appropriate bandage or dressing size to adequately cover the wound. Ensure that the bandage is sterile, and use medical tape or adhesive strips to secure it in place. Be careful not to wrap it too tightly, as this could impede blood flow.
Change Dressings as Needed:
Monitor the wound for any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge. If you notice any concerning changes or if the dressing becomes soaked with blood or other fluids, replace it with a fresh, sterile one. Proper wound care involves keeping the wound clean and dry.
Consider Tetanus Vaccination:
Depending on the cause of the wound and the person’s vaccination history, a tetanus shot may be necessary. Tetanus can occur from contaminated wounds or objects. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine if a tetanus booster is required.
Seek Medical Evaluation:
While initial first aid is essential, any significant wound should be evaluated by a medical professional. They can assess the wound’s depth, the potential for damage to underlying structures, and the need for stitches or other interventions. Timely medical care is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring proper healing.
Remember, if at any point you are unsure about how to handle a wound or if there are concerns about infection or complications, seeking medical advice is always a safe course of action.
You can also read more about this here: What are the treatment options for chronic wounds …
Monitor for Signs of Shock
Severe bleeding can lead to shock, a life-threatening condition. Keep an eye out for signs of shock, including rapid breathing, rapid pulse, confusion, and pale, cool, or clammy skin. If you suspect shock, keep the person lying down with their legs elevated (unless there are fractures) and cover them with a blanket to maintain body heat.
Here’s an extension of the idea:
“Recognizing the signs of shock in someone with severe bleeding is critical for their well-being. Along with the physical symptoms, they may also appear anxious or disoriented. To help prevent shock, it’s essential to keep the injured person lying down and elevate their legs slightly, unless you suspect fractures. Providing reassurance and covering them with a blanket can help maintain their body heat and reduce the risk of shock, but remember, professional medical help is still required to address the underlying cause of the severe bleeding.”
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Bleeding – Better Health Channel
Conclusion
Knowing how to handle severe bleeding and provide proper wound care is a valuable skill that can save lives. Always prioritize safety, call for professional help, and use the appropriate techniques to control bleeding and care for wounds. Being prepared and acting swiftly can make a significant difference in the outcome of accident and injury situations.
Knowing how to handle severe bleeding and provide proper wound care is not just a valuable skill; it’s an essential life skill that can have a profound impact on the well-being of those in need. It is, in essence, the ability to be a first responder in times of crisis, and here’s why it is a skill worth acquiring and honing:
Immediate Response: Accidents and injuries can occur unexpectedly and in any setting, from home to the workplace or out in the community. Being prepared with the knowledge of how to respond immediately can be the difference between life and death.
Empowerment: Acquiring first aid and wound care skills empowers you to take control of an emergency situation. It transforms you from a bystander into an effective responder, capable of providing life-saving assistance.
Minimizing Harm: Quick and appropriate action can minimize the extent of injuries and prevent them from worsening. This is particularly important when dealing with severe bleeding, where every moment counts in controlling hemorrhage.
Professional Help Bridge: While professional medical help is essential, it may take some time to arrive, especially in remote or challenging environments. Your immediate actions can bridge the gap between the injury and the arrival of paramedics or medical personnel.
Enhancing Survival Rates: Immediate care, including bleeding control and wound management, significantly enhances the chances of survival, especially in situations like cardiac arrest, severe allergic reactions, or traumatic injuries.
Continuity of Care: The care you provide in the immediate aftermath of an injury can significantly impact subsequent medical treatment. Properly managed wounds are less likely to become infected, and controlled bleeding reduces the risk of complications.
Preparedness: Being prepared to respond to accidents and injuries is not just about acquiring knowledge; it’s about having the right tools and resources readily available, such as first aid kits and basic medical supplies.
Community Contribution: Your ability to provide assistance in an emergency extends beyond personal preparedness. It can benefit your community by creating a network of individuals who are capable of responding effectively in times of crisis.
Personal and Professional Growth: Learning first aid and wound care is an opportunity for personal and professional growth. It can boost your confidence, improve your problem-solving skills, and enhance your ability to handle stressful situations.
Legal and Ethical Responsibility: In many places, there is a legal and ethical responsibility to provide assistance to those in need when it is safe to do so. Acquiring these skills ensures that you are prepared to fulfill this duty.
In conclusion, knowing how to handle severe bleeding and provide proper wound care is not just about acquiring a skill; it’s about becoming a responsible and compassionate member of society. Whether you’re a parent, a teacher, a coworker, or simply a concerned citizen, being prepared and acting swiftly in accidents and injury situations can make a profound and positive difference in the lives of those you help. Your willingness to be a first responder can be a beacon of hope and support during someone’s darkest hour.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: The Effect of Aloe Vera Clinical Trials on Prevention and Healing of …
More links
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Bleeding Cuts & Wounds: How To Stop Bleeding & First Aid Treatment
