In the realm of dieting, two approaches have long dominated the conversation
low-carb and low-fat diets. Each of these dietary strategies has had its moment in the spotlight, with proponents fervently touting their benefits. But how do they stack up when we compare them head-to-head? In this comprehensive article, we’ll conduct a comparative analysis of low-carb and low-fat diets, exploring their principles, effects on weight loss, impact on health, and sustainability.
As we delve deeper into the realm of low-carb and low-fat diets, it becomes evident that these dietary strategies have each carved out a significant niche in the ever-evolving landscape of nutrition. Each approach boasts its dedicated proponents who passionately extol its virtues. But in the quest for effective weight management and improved health, how do these two dietary giants truly measure up when pitted against each other? In this in-depth exploration, we’re embarking on a comprehensive journey to conduct a head-to-head comparative analysis of low-carb and low-fat diets. Our aim is to uncover the intricate details of their principles, dissect the nuances of their effects on weight loss, scrutinize their impact on health markers, and assess the sustainability of these dietary lifestyles. By the end of this article, you’ll have a well-rounded understanding of these diets, empowering you to make an informed choice that aligns with your health goals and lifestyle preferences.
You can also read more about this here: Dietary and nutritional approaches for prevention and management …

Weight Loss
Low-carb diets often lead to more rapid initial weight loss, which can be motivating. However, long-term weight loss success depends on adherence and individual factors. Low-fat diets may result in slower but sustainable weight loss.
The pace of weight loss on low-carb diets indeed tends to be more rapid during the initial phases, and this quick progress can serve as a powerful motivator. However, it’s essential to recognize that the journey to long-term weight loss success is a multifaceted one, influenced by various factors beyond just the speed of shedding pounds.
Motivation and Momentum: The quick results often observed in the early stages of low-carb diets can boost motivation and create positive momentum. Seeing the scale move downward and experiencing improvements in how clothes fit can encourage individuals to stick with their dietary plan.
Fat Loss vs. Water Weight: The initial rapid weight loss on low-carb diets is often attributed to the loss of water weight, as carbohydrates are stored in the body with water. While this isn’t necessarily indicative of fat loss, it can provide a psychological boost and the motivation to continue.
Adherence and Sustainability: Long-term weight loss success hinges heavily on adherence to the chosen dietary approach. Low-carb diets may be effective for some individuals in the short term but could be challenging to sustain over time. Sustainability is key, and individuals should choose an eating plan they can comfortably maintain for the long haul.
Individual Factors: Weight loss isn’t a one-size-fits-all journey. Individual factors, including genetics, metabolism, hormonal balance, and lifestyle, can all play a significant role in how someone responds to a specific diet. What works well for one person may not yield the same results for another.
Nutrient Balance: While low-carb diets emphasize reduced carbohydrate intake, it’s crucial to maintain a balanced intake of other essential nutrients. Protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals are all essential for overall health and should not be neglected.
Psychological Factors: Sustainable weight loss is not only about the body but also about the mind. Emotional eating patterns, stress management, and a positive relationship with food are crucial aspects of a holistic approach to weight management.
Long-Term Goals: It’s essential to consider long-term health and wellness goals beyond just weight loss. Focusing on overall well-being, improved energy levels, and health markers like blood pressure and cholesterol can be motivating factors.
Support and Accountability: Engaging with a support network, such as a registered dietitian, healthcare provider, or weight loss group, can provide valuable guidance, accountability, and encouragement throughout the weight loss journey.
Maintenance Strategies: Achieving a healthy weight is a significant milestone, but maintaining it is equally important. Low-carb diets may need to evolve into more balanced eating patterns to support long-term weight maintenance.
Slow and Steady Approach: Low-fat diets, while often resulting in slower initial weight loss, can offer a steady and sustainable approach. This may be particularly suitable for individuals seeking consistent progress and who prefer a diet that includes a wider variety of foods.
In conclusion, while the speed of weight loss can be motivating, it’s only one aspect of the broader journey to long-term success. Weight loss sustainability, individual factors, psychological well-being, and overall health should all be considered when choosing and adhering to a dietary plan. Ultimately, the most effective diet is one that aligns with an individual’s preferences, lifestyle, and goals and is sustainable in the long term.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: A Comparative Study Evaluating the Effectiveness Between …

Health Impact
Both diets have demonstrated positive effects on health markers, but the choice between them should consider individual health needs. Low-carb diets may benefit those with blood sugar issues, while low-fat diets may be preferable for heart health.
Both diets have demonstrated positive effects on health markers, but the choice between them should consider individual health needs and lifestyle factors. Low-carb diets, like the Atkins Diet, may benefit those with blood sugar issues by stabilizing glucose levels and promoting weight loss. On the other hand, low-fat diets are often recommended for heart health as they can help reduce cholesterol levels and lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases. However, it’s crucial to note that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to dieting, and consulting with a healthcare professional or nutritionist can provide personalized guidance to determine the most suitable dietary plan based on specific health goals and concerns. Ultimately, a balanced and sustainable diet that aligns with individual preferences and needs is key to long-term success and overall well-being.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Low Carb vs. Low Fat Diets — Which Is Best for Weight Loss?

Sustainability
Sustainability varies widely among individuals and depends on personal preferences. Finding a diet that aligns with one’s lifestyle and food choices is key to long-term success.
Indeed, sustainability in the context of diets is a highly individualized concept that hinges on personal preferences and lifestyle considerations. Here’s an extended exploration of why finding a diet that aligns with one’s unique circumstances is crucial for long-term success:
Tailored to Lifestyle: The sustainability of a diet is closely linked to how seamlessly it can be integrated into one’s daily life. A diet that complements an individual’s lifestyle, work schedule, and social commitments is more likely to be maintained over time. For example, a busy professional may prefer a meal prep-friendly diet, while someone with a more flexible schedule might opt for a different approach.
Resonating with Food Choices: Sustainability is also about enjoying what you eat. A diet that resonates with an individual’s taste preferences and cultural background is more likely to be embraced and adhered to. Restrictive diets that eliminate beloved foods or entire food groups may lead to dissatisfaction and decreased adherence.
Flexible and Adaptable: A sustainable diet should offer flexibility and adaptability. Life is dynamic, and dietary needs may change over time due to factors like age, physical activity level, or health conditions. A diet that can be adjusted to accommodate these changes is more likely to stand the test of time.
Health and Nutritional Balance: A sustainable diet should prioritize health and nutritional balance. It should provide essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals necessary for overall well-being. Diets that severely restrict or exclude entire food groups may pose long-term health risks if not carefully managed.
Realistic Goal Setting: Setting realistic and achievable goals is an integral part of sustainability. Rapid weight loss or extreme dietary changes may yield short-term results but can be challenging to maintain over time. A sustainable approach involves gradual and manageable changes that can be maintained for the long haul.
Psychological Well-being: Mental health and emotional well-being play a significant role in diet sustainability. Extreme diets or those driven solely by weight loss goals can lead to stress, anxiety, and an unhealthy relationship with food. A sustainable diet should promote a positive and balanced mindset around eating.
Social and Cultural Considerations: Social and cultural factors can greatly impact the sustainability of a diet. Considerations like family meals, cultural traditions, and social gatherings should be factored into one’s dietary choices. A diet that accommodates these aspects is more likely to be sustainable within a social context.
Holistic Approach: Sustainability should encompass a holistic approach to health and well-being. Beyond weight management, a diet should address other aspects of health, including energy levels, digestion, sleep quality, and overall vitality. This comprehensive view encourages long-term commitment to a healthy lifestyle.
Professional Guidance: Consulting with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians can provide valuable guidance in finding a sustainable diet. These experts can assess individual health needs, provide personalized recommendations, and monitor progress to ensure that dietary choices align with long-term health goals.
Continuous Self-Assessment: Finally, sustainability involves continuous self-assessment and adjustment. Individuals should periodically evaluate the suitability of their chosen diet, making tweaks and modifications as needed to maintain motivation and achieve sustained success.
In conclusion, sustainability in dieting is not a one-size-fits-all concept. It’s a highly personalized journey that considers lifestyle, food preferences, health goals, and cultural factors. Finding a diet that aligns with these individual aspects is paramount for long-term success and overall well-being. It’s an ongoing process of self-discovery and adaptation that can lead to a healthier and more fulfilling lifestyle.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Advantages and Disadvantages of the Ketogenic Diet: A Review …
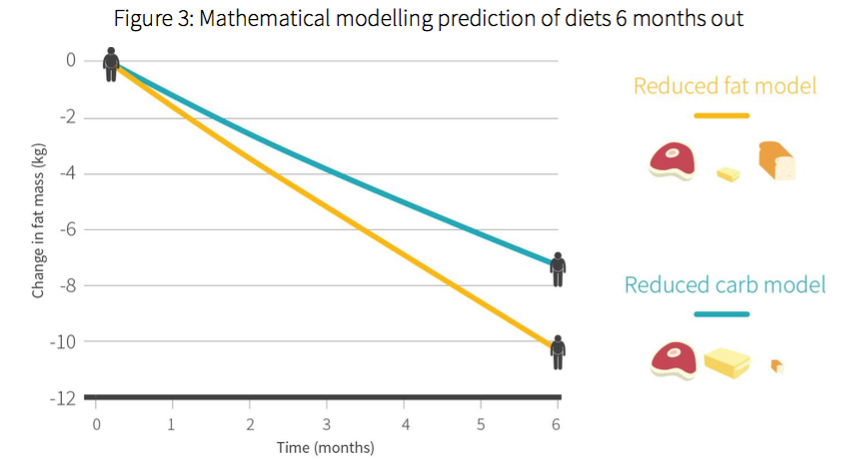
Conclusion
The choice between a low-carb and low-fat diet ultimately depends on individual goals, preferences, and health considerations. Both approaches have their merits, and neither is universally superior. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian when choosing a diet plan, as they can offer personalized guidance based on your unique needs. In the end, the most effective diet is one that you can maintain consistently and that supports your overall health and well-being.
Indeed, the choice between a low-carb and low-fat diet is not a one-size-fits-all decision; rather, it’s a deeply personal one that should take into account a multitude of factors. Here’s an extended look at why individualization and expert guidance are pivotal in this dietary choice:
Personalized Goals: Your dietary choice should align with your specific health and fitness objectives. If rapid initial weight loss is your primary aim, a low-carb diet might provide the jumpstart you need. Conversely, if you’re looking for a heart-healthy approach with gradual but sustainable weight loss, a low-fat diet could be more suitable. Your diet should be a means to achieve your unique goals.
Food Preferences: Personal taste preferences play a substantial role in dietary adherence. Some individuals thrive on low-carb diets, relishing in the consumption of proteins and healthy fats. Others find satisfaction in low-fat diets with a focus on fruits, vegetables, and grains. Your diet should be enjoyable and satisfying to ensure long-term commitment.
Health Considerations: Underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or high cholesterol, can significantly influence the ideal dietary choice. Consultation with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian is crucial here. They can provide tailored recommendations based on your medical history and health goals, ensuring your diet supports your well-being.
Cultural and Lifestyle Factors: Cultural background, social gatherings, and daily routines all influence dietary choices. A diet that seamlessly integrates with your lifestyle is more likely to be maintained. Flexibility in choosing a diet that accommodates your cultural practices and social interactions is key to long-term success.
Expert Guidance: Healthcare providers and registered dietitians possess specialized knowledge to guide you through the dietary decision-making process. Their expertise ensures that your chosen diet is not only effective but also safe and sustainable. They can help you navigate potential pitfalls and provide ongoing support and adjustments as needed.
In the end, the most effective diet is not one dictated by trends or general recommendations; it’s the one that aligns with your unique circumstances and allows you to maintain it consistently. Sustainability is the linchpin of dietary success. Remember that both low-carb and low-fat diets have their merits and can be effective when personalized. Seek expert guidance to craft a dietary plan that’s not just about shedding pounds but about enhancing your overall health and well-being, now and for the long term.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: 23 Studies on Low Carb and Low Fat Diets — Time to Retire the Fad
More links
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Effects of Low-Carbohydrate Diets Versus Low-Fat Diets on …
