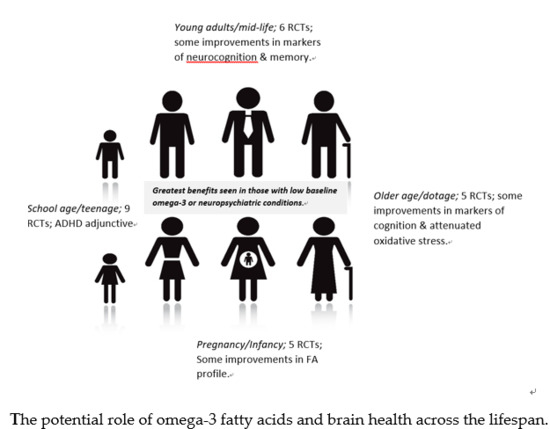
Introduction
In the world of nutrition and overall well-being, few dietary components have garnered as much attention as omega-3 fatty acids. These essential fats, particularly prevalent in fatty fish, have been linked to numerous health benefits, with a significant focus on their role in brain health. In this article, we dive into the fascinating connection between fatty fish, omega-3s, and the well-being of one of our most vital organs—the brain.
In the realm of nutrition and holistic well-being, few dietary components have captured the spotlight quite like omega-3 fatty acids. These essential fats, predominantly found in fatty fish, have emerged as potent allies in promoting overall health, with particular emphasis on their remarkable influence on brain health. In the following discourse, we embark on a captivating exploration of the intricate relationship between fatty fish, omega-3s, and the well-being of one of our most essential organs—the brain.
Omega-3 fatty acids, a category that includes alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), have risen to prominence due to their multifaceted benefits. While ALA is present in plant-based sources like flaxseeds and walnuts, EPA and DHA are most abundant in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout.
The connection between omega-3 fatty acids and brain health has become a captivating focal point in scientific research. Numerous studies have revealed that DHA, in particular, is an integral component of brain cell membranes, where it contributes to the structure and fluidity of these vital membranes. This structural role is pivotal, as it facilitates efficient signaling between brain cells, which is essential for cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and problem-solving.
Beyond structural support, omega-3s also display their cognitive prowess by exerting anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects within the brain. This dual action can help shield brain cells from oxidative stress and chronic inflammation, both of which are implicated in neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
Moreover, omega-3s have been linked to mood regulation and mental health. Research suggests that these fatty acids may play a role in reducing the risk of depression and anxiety disorders. They also appear to support the production of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which are crucial for maintaining a balanced mood.
The benefits of omega-3s extend further into the realm of neurological development. DHA, in particular, is vital during pregnancy and early childhood, as it contributes to the growth and development of the fetal brain and visual system. Consequently, it is often recommended that pregnant and nursing mothers incorporate omega-3-rich foods into their diets.
To harness the brain-boosting potential of omega-3 fatty acids, it’s advisable to make fatty fish a regular part of your diet. Aim for at least two servings of fish per week, with an emphasis on cold-water varieties known for their high omega-3 content. For those who prefer a plant-based approach, consider incorporating flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts into your meals.
In conclusion, the profound impact of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly when sourced from fatty fish, on the well-being of our brains is a captivating journey into the realms of nutrition and neuroscience. These essential fats, with their roles in cognitive function, mood regulation, and brain development, underscore the importance of mindful dietary choices for the maintenance of optimal mental and emotional health throughout the lifespan. By embracing the wisdom of including omega-3-rich foods in our diets, we can empower ourselves to nurture and support one of our most vital organs—the extraordinary human brain.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Omega-3 Fatty Acids – Health Professional Fact Sheet
Omega-3 fatty acids are a group of polyunsaturated fats that our bodies cannot produce on their own. Therefore, they must be obtained through our diet. The three primary types of omega-3s are alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). It’s DHA, in particular, that takes center stage in the realm of brain health.
Omega-3 fatty acids, a crucial group of polyunsaturated fats, are a topic of significant interest in the world of nutrition and health. Their importance stems from the fact that our bodies cannot synthesize them internally, making it imperative to obtain them through our diet. These fats come in various forms, with the three primary types being alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). However, when it comes to brain health, it’s DHA that truly shines, taking center stage for several compelling reasons:
1. Brain Structure and Function: DHA is a fundamental component of brain cell membranes. It contributes to the fluidity and flexibility of these membranes, allowing for efficient signaling between brain cells. This structural role is essential for optimal cognitive function, memory retention, and overall mental sharpness.
2. Neurotransmitter Production: DHA supports the production and functioning of neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers that facilitate communication between brain cells. These neurotransmitters play a pivotal role in regulating mood, memory, and various cognitive processes.
3. Neuroprotection: DHA exhibits neuroprotective properties, helping to shield brain cells from oxidative stress and inflammation. These factors are linked to neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. A diet rich in DHA may contribute to a lower risk of these debilitating disorders.
4. Cognitive Development: DHA is particularly critical during periods of rapid brain growth and development, such as in infancy and early childhood. Adequate intake of DHA during pregnancy and breastfeeding is essential for the proper formation of a child’s nervous system, visual acuity, and cognitive abilities.
5. Mood and Mental Health: Emerging research suggests that DHA may have a role in mood regulation and mental health. Some studies have indicated that higher DHA levels are associated with a reduced risk of depression and anxiety, although more research is needed to establish these connections definitively.
6. Lifelong Cognitive Maintenance: Maintaining a consistent intake of DHA throughout adulthood and into old age is valuable for preserving cognitive function and reducing the risk of age-related cognitive decline and dementia. Including sources of DHA in your diet may contribute to a sharper mind as you age.
7. Dietary Sources: Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are among the richest natural sources of DHA. Additionally, DHA supplements derived from microalgae are available for individuals who follow vegetarian or vegan diets or those who prefer an alternative to fish.
In summary, while all omega-3 fatty acids are essential for health, DHA stands out as a superstar in the realm of brain health. Its pivotal roles in brain structure, neurotransmitter function, neuroprotection, cognitive development, mood regulation, and lifelong cognitive maintenance make it a nutrient worth prioritizing in your diet for overall mental well-being and cognitive vitality.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and the brain: a review of the …

The human brain is a complex organ with a substantial fat content. DHA is a key structural component of brain cell membranes, playing a crucial role in maintaining their integrity and fluidity. It’s also involved in the formation and maintenance of synapses, the connections between brain cells that facilitate communication. These functions are vital for various aspects of brain health, including:
The human brain is indeed a marvel of complexity, and the role of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) within it cannot be overstated. This omega-3 fatty acid is not just a passive component; it actively contributes to the brain’s intricate functions and overall health. Here’s a deeper look into how DHA is essential for various aspects of brain health:
Cognitive Function: DHA is a key player in maintaining optimal cognitive function. It supports memory, problem-solving, and decision-making abilities. An adequate supply of DHA is especially crucial during periods of rapid brain development, such as infancy and early childhood, but it continues to be vital throughout life for maintaining cognitive sharpness.
Mood Regulation: DHA has been linked to mood regulation and emotional well-being. Research suggests that individuals with higher levels of DHA may experience a reduced risk of depression and anxiety disorders. Its role in maintaining the fluidity of cell membranes allows for efficient neurotransmitter communication, which can have a positive impact on mood stability.
Neuroprotection: DHA’s presence helps protect the brain from oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are implicated in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Its ability to maintain cell membrane integrity and flexibility contributes to the overall resilience of brain cells.
Neuroplasticity: DHA supports neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and change throughout life. This is vital for learning new skills, recovering from injuries, and adapting to changing environments. DHA facilitates the formation of new neural connections and strengthens existing ones, enhancing the brain’s capacity to learn and grow.
Visual Health: While often associated with the brain, DHA is also essential for eye health, specifically in the retina. It plays a role in maintaining visual acuity, particularly in low-light conditions. Ensuring an adequate intake of DHA can support both brain and visual health.
Aging and Longevity: Some studies suggest that higher DHA levels may be associated with a reduced risk of cognitive decline in older adults. While more research is needed in this area, it’s clear that DHA plays a role in promoting brain health as we age.
Incorporating sources of DHA, such as fatty fish or DHA-fortified foods, into your diet is one way to support these critical brain functions. Additionally, DHA supplements are available for those who may not consume enough through dietary sources. Ensuring an ample supply of DHA is a proactive step in maintaining and enhancing brain health throughout the lifespan.
You can also read more about this here: How Omega-3 Fish Oil Affects Your Brain and Mental Health

Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout, are abundant sources of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA and EPA. These fish consume algae, which is rich in omega-3s, and store these beneficial fats in their tissues. When we include fatty fish in our diet, we harness the brain-boosting power of these essential fats.
nullLooking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Omega-3 Fatty Acids & the Important Role They Play

Incorporating more fatty fish into your diet doesn’t have to be complicated. Here are some simple tips to get you started:
Incorporating more fatty fish into your diet doesn’t need to be a daunting task. In fact, it can be an enjoyable and straightforward endeavor that brings numerous health benefits to your plate. Here are some practical and easy-to-follow tips to help you get started on your journey to enjoying the goodness of fatty fish:
Start with Familiar Favorites: Begin by incorporating fatty fish varieties that you already enjoy. Salmon, for example, is a popular choice due to its mild, versatile flavor and wide availability. You can try different preparations, such as grilled, baked, or pan-seared salmon fillets.
Explore Canned and Smoked Options: Canned fish, like tuna and sardines, as well as smoked fish like mackerel and trout, are convenient choices that can be easily added to salads, sandwiches, or pasta dishes. They provide all the health benefits of fresh fatty fish without the need for extensive cooking.
Include Fish in Weekly Meal Plans: To make fatty fish a regular part of your diet, consider planning a weekly fish night. This can create a routine that ensures you consistently enjoy the benefits of omega-3s.
Experiment with Seafood Recipes: Challenge your culinary skills by experimenting with different seafood recipes. Explore online resources, cookbooks, or cooking shows for inspiration. You’ll find an abundance of delicious recipes for fish tacos, seafood stir-fries, and fish curry, among many others.
Fish for Breakfast: Don’t limit fish consumption to lunch or dinner. Try incorporating smoked salmon or sardines into your breakfast routine. They pair wonderfully with scrambled eggs, whole-grain toast, or atop a bagel with cream cheese.
Frozen Fish Can Be a Lifesaver: Keep a supply of frozen fish in your freezer. It’s convenient for those days when you need a quick and healthy meal. Frozen fish often retains its quality and nutritional value, making it a reliable choice.
Dine Out Mindfully: When dining at restaurants, take advantage of seafood options on the menu. Many eateries offer dishes featuring fatty fish, allowing you to enjoy them without any extra effort in the kitchen.
Learn to Love Fishy Flavors: Fatty fish like mackerel and sardines have a stronger taste than some other seafood. If you’re not accustomed to these flavors, consider acquiring a taste gradually. Start with small servings and explore different cooking methods and seasonings until you find a preparation that suits your palate.
Pair with Complementary Foods: Enhance the flavors and nutritional value of your fatty fish dishes by pairing them with complementary foods. Vegetables, whole grains, and legumes make fantastic companions, creating a balanced and satisfying meal.
Consult with a Dietitian: If you have specific dietary goals or health concerns, consider consulting a registered dietitian. They can provide personalized guidance on incorporating fatty fish into your diet while addressing your individual needs.
Incorporating more fatty fish into your diet can be a rewarding journey towards better health. These simple tips can help you make this transition smoothly, ensuring that you reap the numerous benefits of omega-3 fatty acids while savoring delicious seafood creations.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Omega-3 Fatty Acids – Health Professional Fact Sheet
Prepare salmon or trout by grilling or baking with herbs and spices for a delicious and healthy main course.
Preparing salmon or trout for a delightful and nourishing main course can be a culinary adventure that pleases both the palate and the body. These fatty fish are not only sumptuously flavorful but also brimming with health benefits, making them a wonderful addition to your regular menu.
Grilling or baking these fish is an excellent choice, as it retains their natural flavors and ensures a tender, moist texture. Here’s why it’s such a fantastic option:
1. Omega-3 Richness: Salmon and trout are exceptional sources of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA. These essential fatty acids are renowned for their heart-healthy properties, contributing to reduced inflammation, improved cholesterol levels, and enhanced brain function. Regular consumption of omega-3s is associated with a lower risk of heart disease, making these fish a fantastic choice for cardiovascular well-being.
2. Protein Powerhouse: Both salmon and trout are excellent sources of high-quality protein. Protein is essential for muscle maintenance, immune support, and overall growth and repair in the body. A serving of grilled or baked salmon or trout can provide a substantial portion of your daily protein needs.
3. Rich in Nutrients: These fish are packed with essential nutrients such as B vitamins (including B12 and niacin), selenium, and phosphorus. B vitamins are vital for energy production and neurological health, while selenium is an antioxidant that supports the immune system, and phosphorus is crucial for bone health.
4. Versatile Flavor: Salmon and trout have a rich, slightly nutty flavor that pairs beautifully with various herbs and spices. The versatility of their taste profile allows you to experiment with a wide range of seasonings, from zesty lemon and dill to smoky paprika and garlic.
5. Easy Preparation: Grilling or baking salmon or trout is a straightforward process that requires minimal effort. You can marinate the fish for extra flavor or simply season it with your favorite herbs and spices, then let the heat do the rest. This simplicity makes it a perfect choice for both novice and seasoned home chefs.
6. Variety of Options: Salmon and trout come in various forms, including fillets, steaks, and whole fish. This variety allows you to choose the preparation method that suits your preferences and kitchen equipment best.
In conclusion, grilling or baking salmon or trout isn’t just about creating a delicious main course; it’s about embracing a heart-healthy, nutrient-rich, and protein-packed meal that supports overall well-being. So, whether you’re hosting a dinner party or preparing a weeknight family meal, consider incorporating these delectable fish into your menu. With a little creativity and your favorite herbs and spices, you can elevate your dining experience while nurturing your health at the same time.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Omega-3 in fish: How eating fish helps your heart – Mayo Clinic

Canned sardines or mackerel can be convenient options for salads, sandwiches, or quick protein-packed snacks.
Canned sardines or mackerel, often overlooked in favor of fresh seafood, offer not only convenience but also a plethora of nutritional benefits that make them a fantastic addition to your culinary repertoire. Here, we’ll explore why these canned fish are more than just a convenient option:
Nutrient Density: Canned sardines and mackerel are densely packed with essential nutrients. They’re excellent sources of high-quality protein, offering all the amino acids your body needs for muscle repair, immune support, and overall growth. Additionally, they’re rich in vitamins and minerals, such as calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin B12, which are essential for bone health, immune function, and neurological well-being.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These small fish are among the most abundant sources of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Omega-3s are renowned for their anti-inflammatory properties and their role in promoting heart and brain health. Regular consumption of canned sardines or mackerel can contribute significantly to reducing the risk of heart disease, improving cognitive function, and even easing symptoms of conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Convenience Without Sacrificing Nutrition: Canned fish provide the convenience of a long shelf life and no need for refrigeration until opened. This makes them an excellent choice for quick, protein-packed meals. Whether you’re crafting a salad, a sandwich, or a wholesome snack, canned sardines or mackerel can be a versatile and readily available source of nutrition.
Sustainability: Opting for canned sardines or mackerel often aligns with sustainable seafood choices. These species tend to be lower on the food chain, which means they reproduce more quickly and are less likely to be overfished. When you choose canned options from responsible producers, you can enjoy your meal with the satisfaction of knowing you’re making an eco-conscious choice.
Economical: Canned fish is often more affordable than fresh seafood, making it an economical choice for those on a budget. This accessibility means that you can enjoy the nutritional benefits of fish regularly without breaking the bank.
Incorporating canned sardines or mackerel into your diet not only adds convenience to your meals but also introduces a powerhouse of nutrients and health benefits. Whether you’re pursuing a balanced diet, focusing on heart and brain health, or simply looking for a quick and nutritious meal option, these canned fish deserve a place in your pantry and on your plate.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Brain foods: the effects of nutrients on brain function – PMC
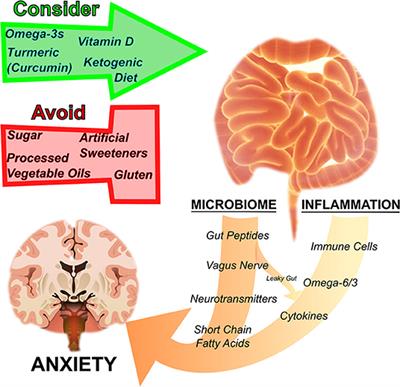
If you have dietary restrictions or limited access to fatty fish, omega-3 supplements derived from fish oil or algae can provide a concentrated source of these essential fatty acids.
nullFor additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Brain Functions …

Remember that a balanced diet, rich in a variety of nutrients, supports overall brain health. Incorporate a range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins alongside your fatty fish consumption.
Certainly, prioritizing a balanced diet goes beyond individual food components; it’s a holistic approach to nourishing your body and, importantly, supporting your brain health. Here’s a more comprehensive look at how a well-rounded diet can benefit your cognitive well-being, in addition to the inclusion of fatty fish:
Diverse Nutrient Intake: A balanced diet provides a broad spectrum of essential nutrients that are crucial for brain function. Vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and other micronutrients from a variety of foods contribute to optimal cognitive health.
Fruits and Vegetables: Colorful fruits and vegetables are packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and phytochemicals that protect your brain from oxidative stress and inflammation. They promote cognitive longevity and reduce the risk of cognitive decline as you age.
Whole Grains: Complex carbohydrates from whole grains are a steady source of glucose, the brain’s primary energy fuel. They help maintain consistent energy levels, enhancing concentration and mental clarity throughout the day.
Lean Proteins: Lean proteins provide amino acids necessary for neurotransmitter synthesis. These neurotransmitters, like dopamine and serotonin, play a vital role in mood regulation, focus, and overall mental well-being.
Healthy Fats: While fatty fish is an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, incorporating other sources like nuts, seeds, and olive oil further enriches your diet with these essential fats, promoting healthy brain structure and function.
Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential for optimal brain function. Dehydration can lead to cognitive deficits, so including water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables is key to maintaining proper hydration.
Moderation and Variety: A balanced diet also means enjoying foods in moderation and varying your choices. This approach ensures you obtain a broad spectrum of nutrients and minimizes the risk of overconsumption of any one nutrient.
Mindful Eating: Practicing mindful eating by savoring and fully experiencing your meals can enhance your connection between food and brain. It encourages healthy eating habits and may reduce stress-related overeating.
Customized Nutrition: Tailoring your diet to meet your specific needs is essential. Consider factors like age, activity level, and any underlying health conditions when planning your meals to optimize brain health.
Long-Term Brain Resilience: A balanced diet is not just about immediate benefits but also about building long-term brain resilience. It can reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and support cognitive performance throughout your life.
In conclusion, while fatty fish plays a crucial role in brain health due to its omega-3 content, it should be part of a larger dietary strategy. A balanced diet, rich in a diverse range of nutrients from various food groups, provides the foundation for optimal cognitive function, mental clarity, and long-term brain health.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: How Omega-3 Fish Oil Affects Your Brain and Mental Health
Conclusion
Fatty fish and the omega-3 fatty acids they contain, particularly DHA, are not just a dietary choice; they are a choice for the health and vitality of your brain. By including these brain-boosting foods in your diet, you can support cognitive function, emotional well-being, and long-term brain health. Whether you enjoy a succulent salmon fillet or a can of sardines, your brain will thank you for the omega-3 nourishment that fatty fish provides.
Fatty fish and the omega-3 fatty acids they contain, particularly DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are not just a dietary choice; they are a powerful ally in promoting the health and vitality of your brain. The brain, often referred to as the body’s command center, relies on a consistent supply of nutrients to function optimally, and omega-3s are among the most crucial.
Enhanced Cognitive Function: DHA is a superstar when it comes to cognitive function. It’s a primary structural component of brain cell membranes, essential for nerve signal transmission and the formation of synaptic connections. Regular consumption of fatty fish can support memory, focus, and overall cognitive performance, which is beneficial for people of all ages, from children developing their brains to adults looking to maintain mental acuity.
Emotional Well-Being: The link between omega-3s and emotional health is fascinating. Research suggests that these fatty acids may help regulate mood and reduce the risk of mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. The brain’s composition significantly influences how we feel, and nourishing it with DHA can contribute to a positive outlook on life.
Long-Term Brain Health: As we age, concerns about cognitive decline become more prevalent. Omega-3s have been associated with a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and dementia. By incorporating fatty fish into your diet throughout your life, you’re potentially providing your brain with the protective support it needs to stay sharp and resilient as you age.
Versatile Options: The beauty of including brain-boosting fatty fish in your diet is that there’s something for everyone. Whether you enjoy a succulent salmon fillet, mackerel, trout, or even a can of sardines, there are diverse options to suit various palates and culinary preferences. You can grill, bake, pan-sear, or even enjoy them in sushi form, making it easy to incorporate these brain-boosting foods into your regular meals.
In conclusion, opting for fatty fish as a source of omega-3 fatty acids, especially DHA, is a wise choice for your brain’s health and vitality. It’s not just about immediate benefits but also long-term well-being. By nourishing your brain with these essential nutrients, you’re investing in a brighter, more focused, and emotionally resilient future. So, whether it’s a delightful seafood dinner or a quick sardine sandwich, know that your brain is thanking you for the omega-3 nourishment that fatty fish provides.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: The Psychoneuroimmunological Role of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated …
More links
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Brain Functions …