Table of Contents
Moving Beyond the Basics
The landscape of healthcare is continually evolving, driven by groundbreaking innovations that revolutionize patient care and medical practices. At the forefront of this transformation are medical workers who pioneer new roles and embrace cutting-edge technologies. In this article, we explore how medical workers are shaping the future of healthcare through their pioneering roles and contributions to innovative advancements.
The healthcare industry stands at a fascinating crossroads where groundbreaking innovations are reshaping the way we approach patient care and medical practices. Central to this transformative journey are the medical workers who not only adapt to change but also actively drive it forward. These professionals are the unsung heroes, forging new roles and harnessing cutting-edge technologies to pioneer advancements that will define the future of healthcare. In this article, we embark on a journey to explore how these remarkable medical workers are shaping the healthcare landscape through their pioneering roles and invaluable contributions to innovative advancements.
Telemedicine and Remote Care: Medical workers, particularly in the fields of telemedicine and telehealth, have been at the forefront of transforming the delivery of healthcare. They’ve embraced digital platforms and telecommunication technologies to provide remote care, expanding access to medical services for patients in even the most remote areas. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, and these pioneers continue to refine and expand this mode of care delivery.
AI and Data-Driven Insights: Medical professionals are harnessing the power of artificial intelligence and data analytics to revolutionize diagnostics and treatment plans. Through machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics, they are extracting valuable insights from vast datasets, leading to more precise diagnoses, personalized treatments, and improved patient outcomes.
Genomic Medicine: Genomic medicine is another frontier where medical workers are making significant strides. They are integrating genetic information into patient care, offering tailored treatment plans and preventative strategies based on an individual’s unique genetic makeup. These pioneers are unlocking the potential of precision medicine, which holds the promise of more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
Robotics and Minimally Invasive Surgery: Surgeons and medical workers are embracing robotic-assisted surgery and minimally invasive techniques to enhance precision and reduce the invasiveness of procedures. These technologies are leading to quicker recovery times, less pain, and improved patient satisfaction.
Virtual Reality and Simulation: In the realm of medical training and education, professionals are using virtual reality and simulation technologies to provide hands-on experience and enhance the skills of medical students and practicing clinicians. These pioneers are shaping the next generation of healthcare providers.
Patient-Centered Care: The shift toward patient-centered care is being championed by medical workers who prioritize the individual needs and preferences of patients. They are promoting shared decision-making, active patient engagement, and a holistic approach to healthcare that considers not just physical health but also mental and social well-being.
Global Health and Telemedicine Outreach: Beyond their local communities, medical workers are using telemedicine and telehealth platforms to extend their expertise to underserved regions around the world. They’re addressing global health disparities by providing consultations, training local healthcare providers, and delivering life-saving interventions.
Ethical and Regulatory Advocacy: Pioneers in the field are actively engaged in ethical and regulatory discussions surrounding emerging healthcare technologies. They’re advocating for responsible AI usage, data privacy, and equitable access to innovations, ensuring that the benefits of healthcare advancements are widely accessible and ethically sound.
In essence, medical workers are not merely adapting to change; they are architects of change, actively shaping the future of healthcare. Through their innovative roles and tireless dedication, they’re bringing us closer to a healthcare system that is more accessible, personalized, and effective. As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, their pioneering spirit and contributions serve as guiding lights, illuminating a path toward better health and well-being for all.
You can also read more about this here: Education Innovation and Research – Innovating Education and …

Telemedicine and Virtual Care
One of the most transformative innovations in healthcare has been the widespread adoption of telemedicine and virtual care. Medical workers, including doctors, nurses, and allied health professionals, have played pioneering roles in implementing these technologies. They provide remote consultations, monitor patients’ conditions through telehealth platforms, and ensure that healthcare services remain accessible, even in remote or underserved areas.
The rapid expansion of telemedicine and virtual care represents a remarkable leap forward in the realm of healthcare, fundamentally altering the way medical services are delivered and accessed. The tireless efforts of medical workers, including doctors, nurses, and allied health professionals, have been pivotal in bringing about this transformation. Here’s a deeper exploration of their pioneering roles and the far-reaching impact of telemedicine:
Accessibility: Telemedicine has revolutionized healthcare accessibility, particularly for individuals in remote or underserved areas. Medical professionals, through virtual consultations, bridge geographical gaps, making it possible for patients to receive timely care without the need for extensive travel.
Continuity of Care: Medical workers ensure the continuity of care through telehealth platforms. Patients with chronic conditions, for instance, can benefit from regular check-ins and remote monitoring, ensuring that their health status is consistently tracked and managed.
Emergency Response: In critical situations, telemedicine allows medical professionals to provide timely guidance and expertise. Paramedics and first responders can consult with specialists in real-time, leading to more informed decisions and potentially life-saving interventions.
Specialized Care: Telemedicine enables patients to access specialized care that may not be readily available in their local healthcare facilities. Medical workers can connect with experts across the globe to seek advice, collaborate on complex cases, or provide specialized consultations.
Mental Health Support: The field of mental health has seen significant benefits from virtual care. Mental health professionals offer therapy, counseling, and support through telehealth platforms, enhancing access to vital mental health services, which are especially crucial during times of crisis.
Reducing Healthcare Disparities: Telemedicine holds promise in reducing healthcare disparities, as it can bridge gaps in access to care for vulnerable populations, including those with limited mobility, elderly individuals, and individuals with disabilities.
Public Health Initiatives: Medical workers use telemedicine to support public health initiatives such as remote monitoring of infectious diseases, contact tracing, and vaccination campaigns. These efforts have been instrumental in managing and responding to public health emergencies.
Education and Training: Medical professionals have embraced telemedicine as a tool for education and training. It facilitates medical conferences, workshops, and continuing education programs, fostering knowledge exchange and skill development among healthcare providers.
Research and Data Collection: Telemedicine generates vast amounts of health data that can be valuable for research and population health studies. Medical workers are at the forefront of using this data to advance medical research, improve patient outcomes, and shape healthcare policies.
Patient Empowerment: Telemedicine empowers patients to take a more active role in managing their health. Medical workers provide guidance, answer questions, and offer resources through virtual channels, enabling patients to make informed decisions about their care.
In essence, medical workers have been instrumental in the widespread adoption of telemedicine and virtual care, leveraging technology to enhance healthcare accessibility, improve patient outcomes, and transform the healthcare landscape. Their pioneering spirit, adaptability, and dedication have not only shaped the present but are also paving the way for a future where healthcare is more accessible, efficient, and patient-centered than ever before.
You can also read more about this here: Global strategy on digital health 2020-2025

Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Medical workers are harnessing the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to enhance diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient care. Radiologists use AI algorithms to detect anomalies in medical images, while healthcare providers leverage predictive analytics to identify patients at risk of developing chronic diseases. This innovative use of technology enhances efficiency and accuracy in healthcare delivery.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning into the healthcare landscape represents a remarkable leap forward in the quest for more efficient, accurate, and patient-centric medical practices. This transformative adoption of technology not only enhances healthcare delivery but also opens up new horizons for medical professionals and patients alike.
Advanced Medical Imaging: AI algorithms have revolutionized medical imaging, assisting radiologists in the early detection of abnormalities and diseases. From identifying subtle changes in X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to automating the interpretation of mammograms, AI-powered tools reduce the potential for oversight, leading to more timely and accurate diagnoses.
Personalized Treatment Plans: Machine learning enables healthcare providers to analyze vast datasets, from genetic profiles to patient histories, to create tailored treatment plans. This individualized approach ensures that patients receive treatments that are most likely to be effective for their specific conditions, optimizing outcomes and reducing adverse effects.
Predictive Analytics: Healthcare systems are increasingly using predictive analytics to forecast disease trends and identify individuals at high risk of developing chronic conditions. This proactive approach allows medical professionals to intervene early, potentially preventing the onset of illnesses through lifestyle changes or preventative measures.
Clinical Decision Support: AI-driven clinical decision support systems assist healthcare providers by offering evidence-based recommendations at the point of care. These tools help improve diagnosis accuracy, reduce medical errors, and ensure that clinicians stay updated on the latest research and guidelines.
Efficient Administrative Tasks: AI streamlines administrative tasks, such as billing, scheduling, and record-keeping. This automation allows healthcare staff to redirect their time and energy toward patient care, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing administrative burdens.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring: AI plays a pivotal role in the expansion of telemedicine and remote monitoring. AI-driven chatbots, for instance, can assist patients with non-urgent medical inquiries, while wearable devices collect real-time data on vital signs, enabling remote patient monitoring for chronic conditions.
Drug Discovery: AI expedites drug discovery by analyzing vast datasets and simulating drug interactions. This accelerates the development of new medications and treatments, potentially addressing unmet medical needs more rapidly.
Healthcare Access: AI-powered tools, like language translation and speech recognition, help overcome language barriers and improve healthcare access for diverse populations. This inclusivity ensures that healthcare services are available and comprehensible to all.
Continuous Learning and Research: AI-driven systems have the capacity to analyze medical literature and research papers at an unprecedented scale. This aids medical professionals in staying current with the latest medical advancements and fosters continuous learning.
Ethical Considerations: The integration of AI in healthcare also necessitates careful consideration of ethical and privacy concerns. Ensuring that patient data is secure, and AI systems make unbiased and ethical decisions is an ongoing challenge.
Cost Efficiency: While there may be initial investments in AI technology, over time, it has the potential to reduce healthcare costs by optimizing resource allocation, reducing unnecessary tests, and improving treatment outcomes.
In conclusion, the utilization of artificial intelligence and machine learning in healthcare is ushering in a new era of medical practice. From enhancing diagnostic accuracy to personalized treatment plans and more efficient administrative processes, the innovative use of technology benefits both medical professionals and patients. As AI continues to evolve, it promises to further refine healthcare delivery, ultimately contributing to improved patient outcomes, increased accessibility, and the continued advancement of medical science.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: National Library of Medicine (NLM) | National Institutes of Health (NIH)

Robotics and Minimally Invasive Surgery
Surgeons and surgical teams are pioneering the use of robotic-assisted surgery for complex procedures. These robots offer greater precision and control, resulting in smaller incisions, reduced recovery times, and improved patient outcomes. Medical workers are at the forefront of adopting and mastering these cutting-edge technologies.
Expanding on the topic of robotic-assisted surgery and the pioneering roles of medical workers in this field, it’s worth exploring the broader implications and advancements in this innovative technology:
Expanding Range of Procedures:
Initially used for a limited range of procedures, robotic-assisted surgery is continually expanding its scope. Surgeons and medical teams are pioneering the application of robotics in various specialties, including gynecology, urology, cardiothoracic surgery, and orthopedics. As the technology matures, it enables the performance of increasingly complex surgeries with minimal invasiveness.
Training and Certification:
Pioneering the use of robotic-assisted surgery also involves developing comprehensive training programs for medical professionals. Surgeons must undergo specialized training to become proficient in robotic surgery techniques. Medical institutions are at the forefront of creating these training programs and ensuring that surgeons are certified to operate robotic surgical systems safely and effectively.
Telesurgery and Remote Expertise:
Robotic-assisted surgery has opened the door to telesurgery, where surgeons can perform procedures on patients located miles away. This advancement is particularly crucial in rural or underserved areas where access to specialized surgical expertise is limited. Pioneering medical workers are exploring the possibilities of remote surgery, further expanding the reach of healthcare.
Improving Patient Outcomes:
As medical workers continue to refine their skills in robotic-assisted surgery, patient outcomes are consistently improving. Smaller incisions result in reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recoveries. Patients benefit from less scarring, minimized risk of infection, and improved overall surgical experiences.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning:
Robotic-assisted surgery is increasingly integrated with AI and machine learning algorithms. Surgeons can access real-time data and predictive analytics during surgery, enhancing decision-making and precision. Pioneering medical workers are at the forefront of developing and refining these AI-driven surgical tools.
Reducing Healthcare Costs:
The efficiency and precision of robotic-assisted surgery can lead to cost savings in healthcare. Shorter hospital stays and fewer post-operative complications translate into reduced healthcare expenditures. Medical workers are pioneering efforts to make this advanced technology more accessible and cost-effective.
Patient Education and Informed Consent:
Pioneering medical workers also play a crucial role in patient education and informed consent. They are at the forefront of explaining the benefits and potential risks of robotic-assisted surgery to patients, ensuring that individuals are well-informed and can make decisions aligned with their healthcare preferences.
In conclusion, the pioneering roles of medical workers in advancing robotic-assisted surgery are reshaping the landscape of healthcare. As the technology continues to evolve, it holds the promise of even more precise, minimally invasive, and patient-centered surgical interventions. Medical professionals are not just users of these technologies; they are actively shaping the future of surgery and contributing to better healthcare outcomes for patients worldwide. Their dedication to innovation and continuous learning is driving progress in the field of surgical medicine.
You can also read more about this here: Origins of Robotic Surgery: From Skepticism to Standard of Care …
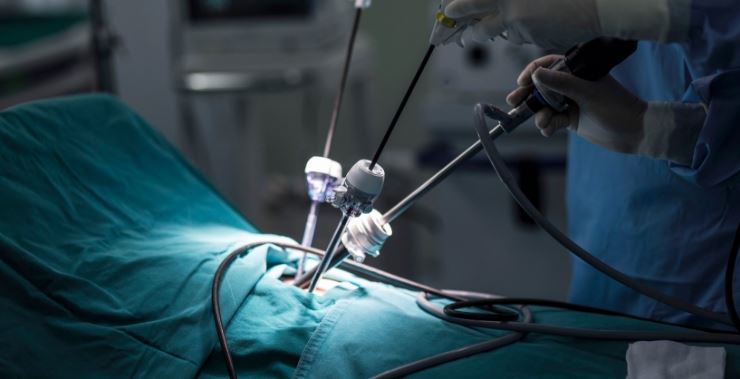
Genomic Medicine
Genomic medicine is revolutionizing how medical workers approach diagnosis and treatment. Genetic counselors and researchers are pioneering the use of genomics to identify genetic factors associated with diseases, allowing for personalized treatment plans and targeted therapies. This innovative field has the potential to transform the future of medicine.
Genomic medicine represents a groundbreaking paradigm shift in the world of healthcare, one that promises to redefine the way medical workers understand, diagnose, and treat diseases. Expanding on this idea, let’s delve into the various aspects of how genomic medicine is revolutionizing the field:
Precision Diagnostics: Genomic medicine enables medical professionals to delve deep into an individual’s genetic makeup, unveiling potential disease risks and genetic predispositions. This level of precision in diagnostics is unparalleled, allowing for earlier and more accurate disease detection.
Personalized Treatment Plans: The ability to identify specific genetic factors associated with diseases empowers medical workers to craft highly personalized treatment plans. Patients are no longer treated with a one-size-fits-all approach; instead, therapies are tailored to their unique genetic profiles, maximizing treatment efficacy.
Targeted Therapies: Genomic insights have paved the way for targeted therapies, a significant advancement in medicine. These therapies are designed to pinpoint the root cause of diseases at the genetic level, leading to more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
Risk Prediction and Prevention: Genomic medicine allows for the prediction of disease risk based on an individual’s genetic markers. Medical workers can proactively intervene to prevent diseases in high-risk individuals through lifestyle changes, surveillance, or preventive measures.
Rare Disease Diagnosis: For patients with rare and undiagnosed diseases, genomics offers newfound hope. Genetic counselors and researchers can identify the genetic mutations responsible for these conditions, potentially leading to more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment strategies.
Pharmacogenomics: Genomic medicine plays a pivotal role in pharmacogenomics, which focuses on how a person’s genetic makeup influences their response to drugs. This knowledge helps avoid adverse drug reactions and ensures medications are both safe and effective.
Cancer Genomics: The field of cancer genomics has been particularly transformative. Genetic profiling of tumors allows for precise cancer diagnoses, prognosis predictions, and the development of targeted therapies that specifically attack cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue.
Genomic Counseling: Genetic counselors play a crucial role in helping patients understand the implications of their genetic information. They provide support, education, and guidance on making informed decisions regarding genetic testing and treatment options.
Big Data and AI Integration: The sheer volume of genomic data generated requires sophisticated analysis, and artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming increasingly integrated into genomic medicine. AI-driven algorithms help interpret vast datasets, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and treatment recommendations.
Ethical Considerations: As genomic medicine advances, ethical considerations surrounding privacy, consent, and genetic discrimination become paramount. Medical workers are actively engaged in discussions and policies that safeguard patient rights and data security.
Research and Discovery: Genomic research continues to uncover new genetic links to diseases, leading to ongoing breakthroughs in understanding and treatment. Medical workers at the forefront of genomics are pioneers in discovering novel insights that shape the future of medicine.
In conclusion, genomic medicine represents an exciting frontier in healthcare, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve patient outcomes and transform the way medical workers approach diseases. With its potential to revolutionize diagnostics, treatment, and disease prevention, genomic medicine is undoubtedly reshaping the landscape of modern healthcare, driving it toward a more personalized, precise, and effective future.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Celebrating 10 Hispanic pioneers in medicine | AAMC

Nursing Informatics
In the digital age, nurses are taking on pioneering roles in nursing informatics. They integrate technology into patient care, manage electronic health records, and optimize healthcare workflows. Nursing informaticists ensure that healthcare data is used efficiently to improve patient outcomes and streamline healthcare processes.
In the ever-evolving digital landscape of healthcare, nurses are emerging as pioneers in the field of nursing informatics. Their roles have expanded to encompass a wide range of responsibilities that leverage technology to enhance patient care, streamline healthcare processes, and drive improvements in the quality of care delivery. Here’s a closer look at how nurses are shaping the landscape of nursing informatics in the digital age:
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Management: Nursing informaticists are at the forefront of managing electronic health records (EHRs). They ensure that these digital repositories of patient information are accurate, up-to-date, and readily accessible to healthcare providers. This allows for quicker and more informed decision-making, reduces the risk of errors, and enhances patient safety.
Integration of Technology: Nursing informaticists integrate cutting-edge technology solutions into patient care processes. This includes the use of wearable devices, mobile applications, telemedicine platforms, and remote monitoring tools. These technologies enable real-time data collection, providing clinicians with valuable insights into patients’ health statuses and allowing for timely interventions.
Data Analysis and Decision Support: With access to vast amounts of healthcare data, nursing informaticists play a vital role in data analysis. They employ data analytics tools to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies in patient data. This data-driven approach assists healthcare providers in making evidence-based decisions, improving treatment plans, and predicting potential health risks.
Interoperability: Ensuring that different healthcare systems and technologies can communicate and share data seamlessly is a significant challenge. Nursing informaticists work to establish interoperability standards and protocols, facilitating the exchange of information between EHRs, diagnostic equipment, and other healthcare technologies.
Patient Engagement: Nursing informaticists promote patient engagement through technology. They develop patient portals, mobile apps, and educational resources that empower patients to actively participate in their healthcare. This can include accessing their health records, scheduling appointments, and receiving personalized health recommendations.
Telehealth and Telemedicine: The recent surge in telehealth and telemedicine services has been facilitated by nursing informaticists. They help design, implement, and manage these remote healthcare delivery systems, enabling patients to receive care from the comfort of their homes and reducing the need for in-person visits.
Quality Improvement: Nursing informaticists contribute to quality improvement initiatives by tracking key performance indicators, benchmarking healthcare outcomes, and implementing best practices based on data-driven insights. This ensures that healthcare organizations continuously enhance the quality of care they provide.
Patient Safety: Leveraging technology, nursing informaticists implement strategies to enhance patient safety. This includes medication management systems that reduce medication errors, alert systems for critical events, and automated documentation to ensure accurate and timely recording of patient information.
Education and Training: Recognizing the importance of digital literacy in modern healthcare, nursing informaticists also contribute to the education and training of healthcare professionals. They develop training programs, conduct workshops, and provide ongoing support to ensure that nurses and other staff are proficient in using digital tools effectively.
Ethical and Legal Considerations: With the increasing reliance on healthcare technology, nursing informaticists are involved in addressing ethical and legal considerations related to patient privacy, data security, and compliance with healthcare regulations and standards.
In essence, nursing informaticists are catalysts for positive change in healthcare delivery. They are at the forefront of embracing and harnessing technology to enhance patient care, improve healthcare outcomes, and drive efficiency in healthcare processes. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the roles and responsibilities of nursing informaticists, making them indispensable members of the healthcare team in the digital age.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Celebrating 10 Hispanic pioneers in medicine | AAMC

Public Health Innovations
Public health professionals, including epidemiologists and health educators, are at the forefront of innovative efforts to prevent and manage disease outbreaks. They use data analytics, contact tracing apps, and community engagement strategies to respond to public health crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
Public health professionals, including epidemiologists and health educators, have emerged as the unsung heroes in the ongoing battle against infectious diseases and public health crises. Their work encompasses a wide range of innovative strategies and tools to prevent, manage, and ultimately overcome such challenges. Beyond the immediate response to crises like the COVID-19 pandemic, these professionals play a pivotal role in safeguarding the health of communities worldwide. Here are some additional aspects of their crucial work:
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Epidemiologists are masters of data analytics. They collect, analyze, and interpret vast amounts of data to track the spread of diseases, identify hotspots, and make informed decisions. Data-driven insights are instrumental in shaping public health policies and interventions.
Advanced Modeling: Epidemiologists employ sophisticated modeling techniques to predict disease trajectories, assess the impact of interventions, and make projections for resource allocation. Models help health authorities make timely decisions that can save lives.
Contact Tracing Technology: The advent of contact tracing apps and digital tools has revolutionized disease control efforts. Public health professionals leverage these technologies to rapidly identify and notify individuals who may have been exposed to a contagious disease. This technology has been especially vital during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Vaccination Campaigns: Health educators play a pivotal role in promoting vaccination as a primary preventive measure. They design and implement public awareness campaigns, dispelling misinformation, addressing vaccine hesitancy, and ensuring that individuals have access to immunization services.
Community Engagement: Building trust within communities is essential for the success of public health interventions. Health educators work tirelessly to engage with diverse communities, understand their unique needs and concerns, and tailor public health messaging and strategies accordingly.
Public Health Preparedness: Beyond immediate crises, public health professionals are dedicated to preparing for future outbreaks. They develop and refine response plans, stockpile essential supplies, and conduct drills and simulations to ensure readiness.
Global Collaboration: Disease knows no borders, and public health professionals actively collaborate on an international scale. They share information, research findings, and best practices with their counterparts worldwide, contributing to a collective effort to combat global health threats.
Health Equity: Public health professionals advocate for health equity, recognizing that marginalized communities often bear the brunt of disease outbreaks. They work to address disparities in healthcare access, social determinants of health, and systemic inequalities that exacerbate health crises.
Mental Health Support: Pandemics and outbreaks take a toll on mental health. Public health professionals incorporate mental health support into their response efforts, ensuring that individuals and communities have access to the necessary resources and counseling services.
Continuous Learning: The field of public health is dynamic, with new challenges and pathogens constantly emerging. Public health professionals engage in continuous learning, staying up-to-date with the latest research, technologies, and best practices to adapt to evolving threats.
In conclusion, public health professionals are the linchpin in our collective response to disease outbreaks. Their work extends far beyond crisis management and encompasses data-driven decision-making, community engagement, and advocacy for health equity. As they tirelessly work to protect our well-being, we owe them our gratitude and support for their unwavering commitment to safeguarding public health.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Meet 10 Nurses Pioneering Innovative COVID-19 Solutions

Patient Advocacy and Education
Patient advocates and educators play a crucial role in empowering patients to take control of their health. They pioneer new approaches to health education, leveraging digital tools, social media, and community outreach to promote health literacy and patient engagement.
Patient advocates and educators serve as the unsung heroes of modern healthcare, and their role in empowering individuals to take control of their health cannot be overstated. In an increasingly complex healthcare landscape, their dedication to pioneering innovative approaches to health education has become paramount, ultimately leading to improved health literacy and increased patient engagement.
One of the most remarkable aspects of patient advocates and educators is their ability to adapt to the evolving digital age. They recognize that information is now at our fingertips, and they leverage this accessibility by harnessing digital tools and platforms to disseminate crucial health information. Social media, for instance, provides a powerful medium for reaching a wide audience quickly and effectively. Patient advocates create informative content, host live Q&A sessions, and engage with patients and caregivers in real-time, making health information more accessible and relatable.
Furthermore, these advocates often use storytelling as a compelling educational tool. By sharing personal journeys, struggles, and triumphs, they humanize healthcare experiences and connect with individuals on a deeply emotional level. This approach goes beyond mere facts and figures; it instills a sense of empathy and understanding, encouraging patients to actively participate in their healthcare decisions.
Community outreach is another cornerstone of the work carried out by patient advocates and educators. They understand that healthcare doesn’t exist in a vacuum but is deeply intertwined with social determinants and community factors. They collaborate with local organizations, schools, and grassroots initiatives to bring health education directly to the communities that need it most. By meeting individuals where they are, they break down barriers to access and create a more inclusive healthcare environment.
Additionally, patient advocates and educators foster a sense of partnership between patients and healthcare providers. They emphasize the importance of informed consent, shared decision-making, and open communication. This not only empowers patients to ask questions and seek clarification but also encourages a more patient-centered approach within healthcare settings.
Ultimately, the impact of patient advocates and educators goes beyond individual patients; it extends to the entire healthcare system. By promoting health literacy and patient engagement, they contribute to more informed healthcare decisions, better treatment adherence, and ultimately, improved health outcomes. Their tireless efforts in pioneering new approaches to health education are reshaping the way we approach healthcare, making it more accessible, inclusive, and patient-centric. In an era where information is abundant, they serve as the guiding lights, helping individuals navigate the complex world of healthcare with confidence and empowerment.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: 2024 Mission Statement

Healthcare Policy and Administration
Healthcare administrators and policy experts are pioneers in shaping the regulatory and organizational frameworks that govern healthcare delivery. They work on innovative policies that aim to improve access, affordability, and quality of care for patients.
Healthcare administrators and policy experts are at the forefront of a dynamic and ever-evolving landscape, where they play pivotal roles in shaping the regulatory and organizational structures that define healthcare delivery. Their dedication and expertise extend far beyond the confines of traditional healthcare settings, as they continuously strive to pioneer innovative policies aimed at achieving a higher standard of care in terms of access, affordability, and quality for patients.
Expanding Access: One of the most pressing challenges in healthcare is ensuring that everyone has access to essential medical services. Healthcare administrators and policy experts are instrumental in crafting policies that expand access to care, whether through the expansion of Medicaid, the establishment of community health clinics in underserved areas, or the promotion of telemedicine services. Their work directly impacts the lives of millions, breaking down barriers to healthcare access.
Affordability: The cost of healthcare is a significant concern for individuals and families. Healthcare administrators and policy experts work diligently to find solutions that make healthcare more affordable. This may involve initiatives to control drug prices, promote price transparency, or implement health insurance reforms that protect patients from high out-of-pocket costs. Their efforts aim to ensure that financial burdens do not deter people from seeking the care they need.
Quality Improvement: Quality of care is paramount in healthcare, and these professionals are at the forefront of initiatives to enhance healthcare quality and patient safety. They develop and implement policies that incentivize healthcare providers to adhere to evidence-based practices, reduce medical errors, and improve patient outcomes. These efforts result in a higher standard of care and better health outcomes for patients.
Innovation and Technology: Healthcare administrators and policy experts recognize the transformative potential of innovation and technology in healthcare. They advocate for policies that promote the adoption of electronic health records, telemedicine, and other technological advancements that improve the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery. This not only enhances patient care but also ensures that healthcare remains adaptable and responsive to evolving needs.
Health Equity: Achieving health equity is a fundamental goal of healthcare policy. These professionals champion policies that address health disparities among different population groups. They advocate for culturally competent care, targeted interventions for underserved communities, and the collection of data to identify and eliminate disparities. Their work drives progress toward a more equitable healthcare system.
Patient-Centered Care: The shift towards patient-centered care is a hallmark of modern healthcare. Healthcare administrators and policy experts promote policies that prioritize the preferences and needs of patients. This may involve shared decision-making, patient engagement initiatives, and efforts to enhance the patient experience within healthcare settings.
In conclusion, healthcare administrators and policy experts are instrumental in driving positive change within the healthcare system. Their pioneering efforts shape policies and regulations that directly impact the lives of patients, making healthcare more accessible, affordable, and of higher quality. Their dedication to innovation and improvement ensures that healthcare continues to evolve to meet the evolving needs of society.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: An Innovative Approach to Health Care Delivery for Patients with …
Added Perspective
Innovations in healthcare are driven by the dedication and pioneering spirit of medical workers across diverse roles and specialties. These healthcare professionals are not just adapting to change; they are actively leading the way in adopting and shaping innovative technologies and practices that redefine patient care. As healthcare continues to evolve, the contributions of medical workers in pioneering roles will be instrumental in delivering better, more accessible, and more efficient healthcare for individuals and communities worldwide. Their commitment to innovation ensures that the future of healthcare is brighter and more patient-centric than ever before.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: AbleTo | Pioneering High-Quality Virtual Behavioral Health Care

More links
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: New Roles for Medical Assistants in Innovative Primary Care …
