Introduction
Potatoes and sweet potatoes are versatile staples in many cuisines around the world. They both offer a hearty and satisfying addition to meals, whether mashed, baked, roasted, or fried. However, when it comes to nutrition, these two tubers have distinct profiles that make them suitable for different dietary preferences and health goals. In this article, we will compare sweet potatoes and potatoes in terms of their nutritional content, health benefits, and culinary versatility.
Potatoes and sweet potatoes are not only culinary staples but also cultural icons in many regions worldwide. They have earned their place on the global dinner plate, each with its own unique qualities and culinary charm. As we explore their nutritional profiles and health benefits, we’ll uncover the nuanced differences that make them valuable additions to a diverse range of diets and palates.
A Rich Culinary Heritage
Both potatoes and sweet potatoes have found their way into the hearts and stomachs of people across continents. Potatoes, originating in the Andes of South America, have journeyed through history to become the comfort food of choice in many Western countries. Sweet potatoes, on the other hand, have been cultivated for thousands of years in Central and South America, and their vibrant hues grace tables from Asia to Africa.
Texture and Flavor Variations
One of the most intriguing aspects of these tubers is the wide range of textures and flavors they offer. Potatoes exhibit versatility in their creamy, starchy goodness, while sweet potatoes bring a natural sweetness to the table. Whether you prefer the earthy comfort of mashed potatoes or the caramelized sweetness of roasted sweet potatoes, there’s a flavor and texture for every palate.
Nutritional Signatures
While they share commonalities, such as dietary fiber and essential minerals, the nutritional signatures of potatoes and sweet potatoes set them apart:
Sweet Potatoes: With their vibrant orange, purple, or white flesh, sweet potatoes are renowned for their beta-carotene content. This antioxidant, responsible for their striking color, plays a vital role in eye health and immune support. Additionally, sweet potatoes offer a dose of vitamins, particularly vitamin A and vitamin C, elevating their nutritional value.
Potatoes: The nutritional strength of potatoes lies in their vitamin C content, crucial for maintaining healthy skin and boosting the immune system. They are also a good source of potassium, contributing to heart health. However, potatoes are often associated with carbohydrates, making them an energy-rich choice.
Balancing Nutritional Needs
Your choice between sweet potatoes and potatoes can be guided by your nutritional needs and dietary goals. If you seek a nutrient-rich option with lower calorie density, sweet potatoes may be your preference. Their lower glycemic index and higher fiber content can contribute to steady energy and appetite control.
Potatoes, on the other hand, provide a substantial energy source that can be advantageous for active individuals. Their potassium content supports electrolyte balance, particularly important for athletes.
Culinary Versatility Unveiled
Beyond their nutritional merits, both tubers shine in an array of culinary applications. From classic mashed potatoes to sweet potato fries, they offer endless possibilities for creativity in the kitchen. Embrace their versatility, and experiment with flavors, textures, and international recipes that celebrate these beloved tubers.
In conclusion, the world’s love affair with potatoes and sweet potatoes continues to flourish. As you navigate your dietary choices, consider the unique nutritional gifts each tuber brings to your plate. Whether you favor the creamy comfort of potatoes or the sweet and colorful appeal of sweet potatoes, these versatile tubers are sure to remain cherished ingredients in kitchens worldwide.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Sweet potatoes: Health benefits and nutritional information
Sweet potatoes are often celebrated for their vibrant orange flesh, which is a sign of their high beta-carotene content. They belong to the Convolvulaceae family and are known for their natural sweetness. Here’s a closer look at sweet potato nutrition:
Sweet potatoes, with their vibrant orange flesh, not only delight the eye but also offer a nutritional bounty that earns them a place of honor in the world of wholesome foods. These root vegetables, botanically known as members of the Convolvulaceae family, are nature’s way of combining exceptional taste with remarkable health benefits, all in one delicious package.
Beta-Carotene Rich: The striking orange hue of sweet potatoes is a clear indicator of their high beta-carotene content. Beta-carotene, a type of carotenoid, is a potent antioxidant that the body can convert into vitamin A, a crucial nutrient for maintaining healthy vision, skin, and immune function. The abundance of beta-carotene in sweet potatoes not only contributes to their color but also to their status as a nutritional powerhouse.
Complex Carbohydrates: Sweet potatoes are a superb source of complex carbohydrates, which provide a steady and sustained release of energy. This makes them an excellent choice for those looking to maintain balanced blood sugar levels and avoid the energy spikes and crashes associated with simple sugars.
Dietary Fiber: Sweet potatoes are rich in dietary fiber, particularly when consumed with the skin. Fiber is essential for digestive health, promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Additionally, it contributes to a feeling of fullness, which can assist in weight management and appetite control.
Vitamins and Minerals: In addition to beta-carotene, sweet potatoes contain a wealth of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, vitamin B6, potassium, and manganese. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that supports the immune system and collagen production, while vitamin B6 plays a role in brain development and function. Potassium and manganese are essential for maintaining healthy bodily functions, including nerve signaling and bone health.
Natural Sweetness: Sweet potatoes are aptly named for their natural sweetness, which allows them to shine in both savory and sweet dishes. Their inherent sweetness can satisfy sugar cravings in a healthier way, making them a versatile ingredient in a wide range of recipes.
Low in Fat: Sweet potatoes are naturally low in fat, making them a heart-healthy choice. They provide the satisfaction of a rich, creamy texture without the need for excessive amounts of added fats or oils.
Incorporating sweet potatoes into your diet is not only a flavorful choice but also a nutritious one. Whether roasted, mashed, or baked, sweet potatoes offer a delicious and wholesome way to boost your intake of essential nutrients while satisfying your palate. So, the next time you enjoy the vibrant orange goodness of a sweet potato, relish in the fact that you’re nourishing your body with a wide array of health-enhancing benefits.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Potato Nutrition Guide: Which Are the Healthiest Potatoes? | livestrong
Sweet potatoes are one of the best sources of beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A. Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy skin, vision, and immune function.
nullIf you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Review on nutritional composition of orange‐fleshed sweet potato …

Sweet potatoes contain dietary fiber, which supports digestive health and helps maintain steady blood sugar levels.
Sweet potatoes, those vibrant and naturally sweet gems, offer more than just delightful flavor; they bring a host of health benefits to the table. Among their many virtues, sweet potatoes are notable for their dietary fiber content, and the impact this has on both digestive health and blood sugar management.
Digestive Dynamo:
Sweet potatoes are a digestive dynamo thanks to their dietary fiber content. Fiber plays a pivotal role in promoting a healthy digestive system. It adds bulk to the stool, aiding in regular and comfortable bowel movements, which is essential for preventing constipation and other digestive discomforts.
Moreover, the fiber in sweet potatoes acts as a prebiotic, nourishing the beneficial gut bacteria that contribute to gut health. A thriving gut microbiome can enhance nutrient absorption, support immune function, and even influence aspects of mental well-being.
Blood Sugar Harmony:
Sweet potatoes possess a remarkable ability to help maintain steady blood sugar levels. Despite their natural sweetness, their fiber content plays a significant role in this regard. When you consume sweet potatoes, the fiber slows down the digestion and absorption of sugars, preventing rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar.
Additionally, sweet potatoes have a lower glycemic index compared to many other starchy foods. This means that they have a gentler impact on blood sugar levels, making them an excellent choice for individuals looking to manage or prevent conditions like diabetes.
The Fiber Connection:
The dietary fiber in sweet potatoes isn’t just a passive component; it actively contributes to overall health. Beyond its digestive and blood sugar benefits, fiber also imparts a feeling of fullness and satiety. This can help control appetite and potentially support weight management goals.
Incorporating Sweet Potatoes into Your Diet:
To harness the digestive and blood sugar benefits of sweet potatoes, consider incorporating them into your meals regularly. Roasting sweet potato wedges with a sprinkle of cinnamon makes for a satisfying and healthy side dish. You can also mash them as a nutrient-rich alternative to traditional mashed potatoes or add them to soups and stews for extra flavor and nutrition.
A Wholesome Addition:
In essence, sweet potatoes are not only a wholesome addition to your diet but also a culinary delight that supports digestive health and blood sugar management. So, next time you savor the natural sweetness of a roasted sweet potato, remember that you’re also nurturing your well-being, one delicious bite at a time.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Potato or Sweet Potato: Which Is Healthier? – Cleveland Clinic

They are a good source of vitamin C, potassium, and vitamin B6. These nutrients play important roles in immune support, heart health, and overall well-being.
Carrots, often celebrated for their vibrant orange hue and crisp texture, are more than just a crunchy delight. They are a nutritional powerhouse, brimming with essential nutrients that contribute to your overall health and well-being.
First and foremost, carrots are an excellent source of vitamin C, an antioxidant that not only boosts your immune system but also aids in skin health and collagen production. This vitamin’s immune-boosting properties are especially vital in defending your body against common colds and infections, ensuring you stay on top of your game, day in and day out.
Potassium, another standout nutrient found in carrots, plays a pivotal role in maintaining a healthy heart. It helps regulate blood pressure by counteracting the effects of sodium, promoting cardiovascular well-being. This nutrient synergy between vitamin C and potassium creates a dynamic duo, fortifying your body’s defenses against both external threats and internal imbalances.
But the nutritional treasure trove doesn’t end there. Carrots are also rich in vitamin B6, a versatile nutrient with a multitude of functions in the body. This vitamin is essential for brain development, neurotransmitter production, and the metabolism of amino acids, contributing to your mental and physical vitality.
Furthermore, carrots offer a healthy dose of dietary fiber, promoting digestive regularity and aiding in weight management. Their naturally sweet flavor makes them a delightful addition to your diet, whether you’re enjoying them raw as a snack or cooked in a variety of dishes.
So, the next time you crunch into a crisp carrot, savor not only its vibrant taste but also the nutritional gifts it bestows upon you. With their vitamin C for immune support, potassium for heart health, vitamin B6 for overall vitality, and fiber for digestive wellness, carrots are truly a superfood in their own right—a testament to nature’s bounty and its boundless potential to nourish and sustain us.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Review on nutritional composition of orange‐fleshed sweet potato …

Sweet potatoes are relatively low in calories compared to their nutrient density, making them a nutritious option for those aiming to manage their weight.
The humble sweet potato stands as a nutritional superstar, offering a harmonious balance between its delicious taste and its health benefits. What sets sweet potatoes apart is their remarkable nutrient density, which makes them an exceptional choice for individuals seeking to manage their weight without compromising on nutrition.
At the heart of the appeal of sweet potatoes is their relatively low calorie content. They provide a satisfying, hearty meal without burdening you with excessive calories. This characteristic makes them a valuable ally for those aiming to achieve or maintain a healthy weight.
But it’s not just about the calorie count. Sweet potatoes bring much more to the table in terms of nutrition. They are rich in dietary fiber, particularly when consumed with their skin intact. This fiber contributes to a feeling of fullness and satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating or snacking on less nutritious options throughout the day.
Additionally, sweet potatoes are abundant in essential vitamins and minerals. They are an excellent source of vitamin A in the form of beta-carotene, a powerful antioxidant that supports eye health and immune function. Sweet potatoes also provide a significant dose of vitamin C, which plays a role in collagen production and aids in the body’s absorption of iron.
Potassium, another vital mineral found in sweet potatoes, helps regulate blood pressure and maintain proper muscle and nerve function. The presence of manganese contributes to the body’s ability to metabolize carbohydrates and supports bone health.
Furthermore, the complex carbohydrates in sweet potatoes release energy gradually, preventing rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. This stable energy supply can help control cravings and maintain steady energy levels throughout the day, making it easier to adhere to a balanced diet.
As part of a well-rounded diet, sweet potatoes can play a pivotal role in weight management. Their nutrient density, combined with their satiating fiber content and balanced carbohydrate profile, makes them a valuable addition to meals. Whether roasted, mashed, or baked, sweet potatoes offer a delicious way to savor nutritious, satisfying flavors while supporting your weight management goals.
So, next time you savor a delightful dish featuring sweet potatoes, relish not only in their flavor but also in the knowledge that you’re making a wise choice for your health and well-being. Sweet potatoes are a testament to the idea that nutritious foods can be both delicious and supportive of your weight management journey.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Sweet Potato vs. Regular Potato: How do they compare?

Potatoes, a member of the Solanaceae family, come in various types and colors, including russet, red, yellow, and purple. They are valued for their versatility and are a staple in many households. Here’s an overview of potato nutrition:
nullIf you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Sweet Potato vs. French Fries: Nutrition, Calories, and More

Potatoes are a good source of vitamin C, which is important for collagen production, immune function, and skin health.
Potatoes, often regarded as a staple in many diets, offer more than just comforting flavors and versatility in the kitchen. They are also a valuable source of vitamin C, and here’s how this nutrient contributes to your overall health:
Collagen Production: Vitamin C plays a pivotal role in collagen synthesis, a structural protein that supports the health of your skin, connective tissues, and blood vessels. Adequate vitamin C intake can help maintain the strength and elasticity of your skin, contributing to a youthful complexion. Collagen is also vital for wound healing and tissue repair.
Immune Function: Vitamin C is renowned for its immune-boosting properties. It enhances the production and function of immune cells, helping your body defend against infections and illnesses. During periods of increased stress or exposure to germs, a sufficient intake of vitamin C can be especially beneficial in supporting your immune system.
Antioxidant Protection: As an antioxidant, vitamin C helps neutralize harmful free radicals in your body. These unstable molecules can damage cells and DNA, potentially leading to chronic diseases and premature aging. A diet rich in vitamin C can assist in reducing oxidative stress and its associated health risks.
Wound Healing: In addition to collagen synthesis, vitamin C aids in wound healing by supporting the formation of new blood vessels and connective tissue. Whether you have a minor cut or are recovering from surgery, maintaining an adequate intake of vitamin C can promote efficient healing.
Skin Health: Beyond collagen production, vitamin C contributes to overall skin health. It can help reduce the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots, making your skin look healthier and more vibrant. Some skincare products even incorporate vitamin C for its potential benefits.
Cardiovascular Health: Emerging research suggests that vitamin C may have a role in promoting cardiovascular health. It may help improve blood vessel function, reduce blood pressure, and lower the risk of heart disease.
Stress Management: Vitamin C is known to support the adrenal glands, which produce stress hormones. During times of stress, your body’s vitamin C requirements may increase. Ensuring an adequate intake can help your body better manage stress.
Potatoes, as a source of vitamin C, provide a tasty and nutritious way to incorporate this essential nutrient into your diet. Whether you enjoy them mashed, roasted, or in a hearty potato salad, you’re not only savoring their comforting flavors but also benefiting from their contribution to collagen production, immune defense, and overall well-being. So, relish your potatoes knowing that they’re more than just a delicious side dish—they’re a source of essential nutrition.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Sweet Potato vs. Regular Potato: How do they compare?

They contain potassium, a mineral that plays a key role in maintaining blood pressure and heart health.
Bananas, often enjoyed for their sweet and creamy flavor, offer more than just delightful taste; they are a nutritional powerhouse, primarily due to their high potassium content. Here’s an extended idea about how bananas, rich in potassium, contribute significantly to maintaining optimal blood pressure and heart health:
Potassium for Blood Pressure Regulation: Bananas are renowned for their potassium content, and this mineral plays a pivotal role in our body’s intricate system for regulating blood pressure. Potassium acts as a counterbalance to sodium, which is commonly found in salt. Sodium has the effect of increasing blood pressure, while potassium helps counteract this rise by relaxing blood vessels and reducing the overall strain on the cardiovascular system.
Blood Pressure Management: Consuming potassium-rich foods like bananas can aid in blood pressure management. When your diet contains an adequate amount of potassium, it helps your body maintain a delicate balance between sodium and potassium levels. This balance contributes to a reduction in high blood pressure, a condition that can strain the heart and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Reducing the Risk of Stroke: High blood pressure is a leading risk factor for stroke. By including bananas in your diet, you are taking a proactive step in reducing your risk of stroke. The potassium in bananas not only helps lower blood pressure but also supports the health of blood vessels, making them less susceptible to damage that can lead to stroke.
Heart Health Benefits: Optimal blood pressure management is integral to overall heart health. A diet rich in potassium, with the inclusion of bananas, supports cardiovascular well-being. It aids in keeping arteries flexible, reducing the risk of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), and promoting proper blood flow. Additionally, potassium helps maintain a steady heart rhythm, reducing the risk of arrhythmias.
Preventing Muscle Cramps: Potassium is also vital for muscle function. Low potassium levels can lead to muscle weakness and cramps. Including bananas in your diet can help prevent these issues and promote healthy muscle function, including the heart, which is a specialized muscle.
Nutrient-Rich Package: Bananas offer potassium within a nutrient-rich package. They contain other essential nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin B6, and dietary fiber. This combination of nutrients not only supports heart health but also contributes to your overall well-being.
Incorporating bananas into your daily diet can be a simple and delicious way to support your heart health and maintain optimal blood pressure. Whether enjoyed as a snack, sliced onto cereal, blended into smoothies, or added to your favorite baked goods, these versatile fruits provide a natural and nutritious source of potassium, benefiting your cardiovascular system and overall vitality.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Sweet Potato vs. Regular Potato: How do they compare?
Potatoes are a carbohydrate-rich food, providing a quick source of energy. However, this also means they can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels.
Potatoes, often celebrated for their versatility and comforting taste, are indeed a carbohydrate powerhouse. They are an excellent source of complex carbohydrates, which the body readily converts into glucose—a primary energy source. While this makes potatoes a valuable addition to your diet for a quick boost of energy, it’s essential to understand the dynamics of their impact on blood sugar levels.
Carbohydrate Composition Matters:
The impact of potatoes on blood sugar levels can vary based on their carbohydrate composition. Potatoes primarily consist of starch, a complex carbohydrate made up of long chains of glucose molecules. This starch is digested and broken down into glucose during the digestive process. The speed at which this breakdown occurs depends on the type of potato and how it’s prepared.
Glycemic Index (GI):
The concept of the Glycemic Index (GI) helps classify foods based on their effect on blood sugar levels. High-GI foods are rapidly digested and cause a quick spike in blood sugar, while low-GI foods are digested more slowly and lead to a gradual rise in blood sugar levels.
Potatoes, particularly when boiled or mashed, tend to have a high GI, causing a more rapid increase in blood glucose levels when compared to foods with lower GI values. However, not all potatoes are created equal in this regard. Waxy potatoes, like red potatoes, generally have a lower GI than starchy varieties like russet potatoes.
Balancing Act:
The key to enjoying potatoes while managing blood sugar levels is balance. Here are some strategies to consider:
Portion Control: Pay attention to portion sizes. Smaller servings can help mitigate the impact on blood sugar levels.
Cooking Methods: Opt for healthier cooking methods like roasting, steaming, or baking with minimal added fats. These methods can have a lower impact on the GI compared to frying or boiling.
Pair with Fiber: Combining potatoes with fiber-rich foods like vegetables, beans, or whole grains can slow down the absorption of glucose, moderating the rise in blood sugar.
Monitor Timing: Consider when you consume potatoes. Eating them as part of a balanced meal can help distribute the impact on blood sugar more evenly.
Varietal Choices: Experiment with different types of potatoes to find those with a lower GI that may have a milder effect on your blood sugar levels.
Individual Responses Vary:
It’s important to recognize that individual responses to potatoes can vary. Factors like metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and overall diet play a role in how potatoes affect blood sugar levels. If you have specific concerns about managing your blood sugar, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian who can provide personalized guidance.
In conclusion, while potatoes can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels due to their carbohydrate content, they can still be enjoyed as part of a balanced diet. By making informed choices about the type of potato, portion sizes, and meal composition, you can savor the goodness of potatoes while managing their effect on your blood sugar.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Sweet Potato vs. Regular Potato: How do they compare?

Potatoes contain dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and provides a feeling of fullness.
nullFor a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Sweet Potato vs. Regular Potato: How do they compare?

Let’s break down the nutritional differences between sweet potatoes and potatoes:
Certainly, let’s embark on a journey of culinary exploration to uncover the intriguing nutritional distinctions that set sweet potatoes and regular potatoes apart. While they share the same family name, they have unique characteristics that make each a standout in its own right.
Starting with sweet potatoes, these vibrant tubers are celebrated not only for their sweet, earthy flavor but also for their exceptional nutritional value. One of their most notable attributes is their status as a nutritional powerhouse. Sweet potatoes are rich in complex carbohydrates, fiber, and an array of essential vitamins and minerals. They are a superb source of beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, which plays a vital role in eye health and immune function. This orange-hued gem also boasts high levels of vitamin C, manganese, and potassium, contributing to overall well-being and antioxidant support.
On the other side of the spectrum, we have regular potatoes, which come in various types, with Russet, Yukon Gold, and red potatoes being some of the most common. These starch-laden spuds are a comforting staple in many diets and offer their unique set of nutrients. Potatoes are a good source of vitamin C, particularly when consumed with their skins, as well as vitamin B6, potassium, and dietary fiber. While their carbohydrate content is substantial, they provide a readily available source of energy.
However, it’s crucial to be aware of the distinction in calorie content between sweet potatoes and regular potatoes. Sweet potatoes tend to be lower in calories due to their lower carbohydrate content compared to regular potatoes. This makes them an attractive option for those who are mindful of calorie intake.
Another significant difference lies in their glycemic index (GI). Sweet potatoes generally have a lower GI than regular potatoes, meaning they have a gentler impact on blood sugar levels. This makes sweet potatoes a preferred choice for individuals aiming to manage their blood sugar.
Finally, it’s worth noting the versatility of these two tubers in the kitchen. Sweet potatoes shine in both savory and sweet dishes, from mashed sweet potatoes with a hint of cinnamon to crispy sweet potato fries. Regular potatoes, on the other hand, are celebrated for their creaminess when mashed and their ability to form the perfect golden crust when roasted or fried.
In summary, sweet potatoes and regular potatoes may share a family name, but they bring distinct nutritional profiles and culinary attributes to the table. Sweet potatoes dazzle with their vibrant color, rich flavor, and nutritional density, making them a nutritional powerhouse. Regular potatoes, meanwhile, offer comfort and versatility, providing an excellent source of energy and essential nutrients.
In your culinary endeavors, consider these nutritional nuances and culinary characteristics to make informed choices and savor the unique qualities of both sweet and regular potatoes. Whether you’re crafting a wholesome salad, a comforting casserole, or a delightful side dish, these tubers stand ready to elevate your culinary creations.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Sweet Potato vs. Regular Potato: How do they compare?

Generally lower in calories and carbohydrates compared to potatoes.
When comparing potatoes to other food options, particularly in the context of calories and carbohydrates, it becomes evident that potatoes have distinct nutritional advantages.
1. Nutrient Density: Potatoes are nutrient-dense, offering essential vitamins and minerals such as vitamin C, potassium, vitamin B6, and dietary fiber. These nutrients are vital for overall health, supporting immune function, heart health, and digestion. While they contain carbohydrates, these are predominantly complex carbohydrates that provide a steady source of energy and are more satiating than simple carbohydrates found in some other foods.
2. Fiber Content: Potatoes are a good source of dietary fiber, particularly when consumed with their skin. Fiber is beneficial for digestive health, promoting regular bowel movements and aiding in the prevention of constipation. It also contributes to a feeling of fullness, which can be helpful for weight management and portion control.
3. Versatility: Potatoes are incredibly versatile in the kitchen. They can be prepared in numerous ways, from baking and boiling to mashing and roasting. Their adaptability makes them a staple in various cuisines worldwide and allows for diverse and delicious meal options.
4. Satiety: Potatoes have a high satiety index, meaning they help keep you feeling full and satisfied. This quality can be beneficial for those looking to manage their calorie intake and potentially aid in weight management by reducing overall food consumption.
5. Low in Fat: Potatoes are naturally low in fat and cholesterol, making them a heart-healthy choice when prepared in a health-conscious manner. They can be enjoyed without the need for excessive fats or oils.
6. Micronutrients: In addition to the nutrients mentioned earlier, potatoes also contain smaller amounts of various vitamins and minerals, such as folate, magnesium, and iron. These micronutrients play important roles in various bodily functions.
It’s important to note that the calorie and carbohydrate content of potatoes can vary depending on their preparation. For instance, deep-frying or loading potatoes with high-calorie toppings like butter and sour cream can significantly increase their calorie count. However, when prepared in a healthful manner, such as baking or boiling, and paired with lean protein and vegetables, potatoes can be a nutritious and satisfying component of a balanced meal.
In summary, while potatoes may contain calories and carbohydrates, they offer a range of valuable nutrients and health benefits when incorporated into a balanced diet. The key lies in mindful preparation methods and portion control to fully enjoy the advantages of this versatile and nourishing food.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Sweet Potato vs Regular Potato: How Do They Compare? | Nutritics

Higher in calories and carbohydrates, particularly when consumed in larger quantities or prepared with added fats.
When considering the nutritional aspects of foods, it’s essential to acknowledge that their calorie and carbohydrate content can vary significantly, especially when consumed in substantial quantities or prepared with additional fats. This understanding is crucial for making informed dietary choices and managing overall calorie and macronutrient intake effectively.
Caloric Density: Foods that are higher in calories often possess a denser energy content, which means they provide more calories per gram or serving. This can be both a blessing and a potential pitfall, depending on individual dietary goals. While calorie-dense foods can provide concentrated energy, making them suitable for individuals with higher energy needs or athletes, they can also pose a challenge for those looking to manage their weight.
Portion Awareness: When consuming calorie-dense foods or dishes prepared with added fats, portion control becomes paramount. Larger quantities can easily contribute to calorie excess, potentially leading to weight gain over time. Therefore, being mindful of portion sizes is essential for those seeking to manage their caloric intake while enjoying these foods.
Carbohydrate Considerations: Carbohydrates, especially refined carbs like sugar and white flour, can quickly elevate the carbohydrate content of a meal or dish. These carbs are rapidly digested and absorbed, leading to spikes in blood sugar levels. For individuals who need to monitor their blood sugar, such as those with diabetes, or those following low-carb diets, an awareness of carbohydrate content is vital.
Balanced Preparation: Preparing foods with added fats, whether it’s butter, oils, or creams, can elevate their caloric density and carbohydrate content. However, fats also provide satiety and flavor, enhancing the overall enjoyment of a meal. Balancing added fats with nutrient-rich ingredients, such as vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, allows for a more well-rounded and satisfying dining experience without excessive calorie or carb intake.
Context Matters: It’s essential to consider the broader context of one’s diet when evaluating the impact of calorie and carbohydrate content. Occasional indulgences in calorie-dense or carbohydrate-rich foods are not inherently problematic. In fact, they can be part of a balanced diet. What matters most is overall dietary patterns and the frequency of such indulgences.
In summary, understanding the implications of higher calorie and carbohydrate content, particularly in larger quantities or when prepared with added fats, empowers individuals to make informed dietary choices that align with their health and wellness goals. Whether it’s managing weight, blood sugar, or simply enjoying the pleasures of diverse foods, awareness and moderation are key principles for achieving a balanced and fulfilling approach to nutrition.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Sweet Potato vs. Regular Potato: How do they compare?

Contain more fiber, which can promote feelings of fullness and support digestive health.
nullLooking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Sweet Potato vs. Potato: What’s the Difference?
Also contain fiber but may have less fiber content than sweet potatoes, depending on the variety.
Sweet potatoes and their starchy cousins, regular potatoes, both offer valuable dietary fiber, although the quantity can vary depending on the specific variety. While both are excellent sources of fiber, it’s important to recognize that there can be differences in fiber content between them.
In the sweet potato corner, you’ll find a range of varieties, each with its unique characteristics. Some sweet potato varieties are indeed high in fiber, boasting a substantial amount of this digestive-friendly nutrient. However, it’s worth noting that not all sweet potatoes are created equal in this regard. Some varieties may have slightly lower fiber content, although they still contribute to your daily fiber intake.
On the other side, we have regular potatoes, which also contain fiber but are often associated with having slightly less fiber compared to sweet potatoes. However, like their sweet counterparts, the exact fiber content can vary depending on the potato variety and how it’s prepared. For instance, leaving the skin on potatoes significantly increases their fiber content.
The bottom line is that whether you opt for sweet potatoes or regular potatoes, you’re still benefiting from a good dose of fiber, which is essential for digestive health and overall well-being. The key lies in enjoying a diverse range of vegetables and incorporating them into your meals to ensure a well-rounded intake of essential nutrients and dietary fiber. So, whether you prefer the sweetness of sweet potatoes or the comforting familiarity of regular potatoes, rest assured that both can be valuable additions to your balanced and nutritious diet.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Sweet Potato vs. Regular Potato: How do they compare?
Rich in vitamin A (beta-carotene) and vitamin C.
Delving deeper into the nutritional treasure trove of sweet potatoes, their richness in vitamin A (in the form of beta-carotene) and vitamin C unveils a multitude of health benefits that go beyond the surface.
1. Vision and Eye Health: The beta-carotene in sweet potatoes plays a pivotal role in maintaining good vision and overall eye health. Once consumed, the body converts beta-carotene into vitamin A, which is essential for the proper functioning of the retina and the prevention of conditions like night blindness. Adequate vitamin A intake can also help reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a common cause of vision loss in older adults.
2. Immune System Support: Vitamin C is well-known for its immune-boosting properties. In sweet potatoes, this vitamin works in synergy with the beta-carotene, creating a powerful combination. Vitamin C enhances the production and function of white blood cells, crucial for immune defense. Regular consumption of vitamin C-rich foods, like sweet potatoes, can help the body ward off infections and recover faster when illness strikes.
3. Antioxidant Power: Beta-carotene and vitamin C are both potent antioxidants. They help combat the damaging effects of free radicals in the body, which can contribute to chronic diseases and aging. Antioxidants like beta-carotene and vitamin C neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and the risk of chronic conditions such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes.
4. Skin Health: The benefits of sweet potatoes extend to your skin. Vitamin A supports skin health by promoting cell turnover and preventing dryness and flakiness. It’s no surprise that beta-carotene-rich foods are often associated with a healthy, glowing complexion. Additionally, vitamin C plays a role in collagen synthesis, contributing to skin elasticity and youthful appearance.
5. Respiratory Health: Vitamin C is known to boost the immune system’s response to respiratory infections. This can be especially valuable during cold and flu seasons. Regular intake of vitamin C from sweet potatoes and other sources can help reduce the severity and duration of respiratory illnesses.
6. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Both beta-carotene and vitamin C have anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation is linked to a wide range of health issues, including arthritis and heart disease. Consuming sweet potatoes as part of an anti-inflammatory diet may help mitigate the risk of these conditions.
7. Fertility and Reproduction: Vitamin A is essential for healthy reproduction, and its deficiency can lead to infertility in both men and women. By providing a reliable source of vitamin A, sweet potatoes can support reproductive health and fertility.
Incorporating sweet potatoes into your diet can be a flavorful way to reap these health benefits. Whether roasted, mashed, or as a side dish, sweet potatoes offer a delectable and nutritious addition to your meals. So, the next time you savor the vibrant orange goodness of sweet potatoes, know that you’re nourishing your body with a host of vitamins and antioxidants that promote well-being from the inside out.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Potato or Sweet Potato: Which Is Healthier? – Cleveland Clinic
Good source of vitamin C, but lower in vitamin A.
Sweet potatoes, while celebrated for their nutritional benefits, present an interesting contrast when it comes to vitamins. They are notably a good source of vitamin C, contributing to your daily dose of this essential antioxidant vitamin. Vitamin C, as we know, plays a pivotal role in bolstering the immune system, promoting healthy skin, and assisting in wound healing. Sweet potatoes provide a tasty and natural way to enhance your vitamin C intake.
However, sweet potatoes have a relatively lower vitamin A content compared to their close relatives, carrots, and pumpkin, which are renowned for their exceptional vitamin A levels. While sweet potatoes boast beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, this conversion occurs more efficiently in some vegetables than in sweet potatoes. Nevertheless, sweet potatoes still offer a modest amount of vitamin A, contributing to maintaining good vision and supporting healthy skin.
The key takeaway here is that while sweet potatoes may not be the absolute heavyweight champions in the vitamin A department, they bring a unique set of nutrients to the table. Their vitamin C content and other essential nutrients make them a valuable addition to a balanced diet. By incorporating a variety of colorful vegetables into your meals, including sweet potatoes, you can ensure that you’re reaping a broad spectrum of vitamins and minerals, each playing its part in promoting your overall health and well-being.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Sweet Potatoes vs White Potatoes Nutrition Profile Comparison
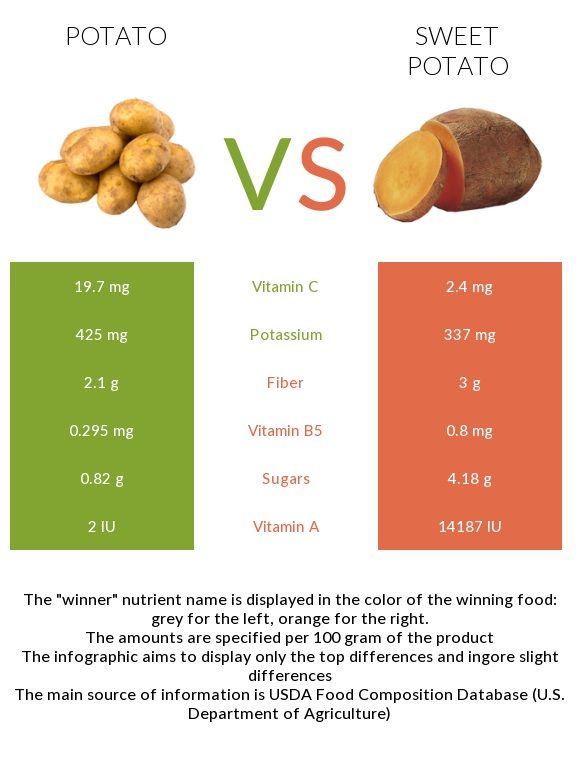
Provide potassium, an essential mineral for heart health.
nullFor additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Potato or Sweet Potato: Which Is Healthier? – Cleveland Clinic
Tend to have a lower glycemic index (GI), which means they have a milder impact on blood sugar levels.
The concept of the glycemic index (GI) is a valuable tool in understanding how different foods affect our blood sugar levels. When it comes to sweet potatoes, they have a distinct advantage in the GI department, which can have significant implications for your overall health and well-being.
The Low-GI Advantage:
Sweet potatoes are often celebrated for their lower glycemic index, a quality that sets them apart from many other carbohydrate-rich foods. The glycemic index measures how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels when compared to a reference food, typically pure glucose.
Sweet potatoes have a relatively low GI compared to other starchy foods, which means they release glucose into the bloodstream at a slower and steadier rate. This gradual release of energy helps prevent the rapid spikes and subsequent crashes in blood sugar levels that can be associated with high-GI foods.
Blood Sugar Stability:
The low-GI nature of sweet potatoes can be particularly beneficial for individuals concerned about blood sugar stability. By choosing foods with a lower GI, you can help maintain more consistent energy levels throughout the day. This is especially important for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
Satiety and Weight Management:
The slower digestion and absorption of carbohydrates due to the low GI of sweet potatoes can also play a role in promoting a feeling of fullness and satiety. When you feel satisfied after a meal, you’re less likely to experience intense hunger cravings and, subsequently, less inclined to snack on less healthy options. This aspect of sweet potatoes can support weight management and healthy eating patterns.
Nutrient-Rich Choice:
What makes sweet potatoes even more appealing is that their low GI status doesn’t mean sacrificing nutrition. Quite the opposite; sweet potatoes are nutrient powerhouses. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber, which contribute to overall health and well-being.
Incorporating Sweet Potatoes Wisely:
To make the most of sweet potatoes’ low GI advantage, consider incorporating them into your meals regularly. They make an excellent side dish, whether roasted, mashed, or used in salads. Sweet potatoes also lend themselves to a variety of culinary creations, from soups to casseroles, adding both flavor and nutritional value.
The Balanced Plate:
In the quest for a balanced and healthful diet, understanding the glycemic index of foods like sweet potatoes can be a valuable tool. Their low GI, combined with their rich nutrient profile, makes them a wise and satisfying choice for those looking to manage blood sugar levels, support weight goals, and savor the goodness of a naturally sweet and nutritious food.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Sweet Potato vs. Regular Potato: How do they compare?

May have a higher GI, potentially causing more significant fluctuations in blood sugar when consumed in large quantities or in processed forms.
The glycemic index (GI) is a crucial concept in understanding how different foods can affect our blood sugar levels. When it comes to some foods, like carrots, it’s essential to delve into the nuances of their GI, especially in relation to how they’re prepared and consumed.
Carrots, known for their natural sweetness and crisp texture, are generally considered a low-GI food when consumed in their raw, unprocessed form. This means that their carbohydrates are digested and absorbed slowly, resulting in gradual and manageable increases in blood sugar levels. This quality makes raw carrots a suitable choice for individuals concerned about blood sugar control.
However, it’s worth noting that the GI of carrots can vary depending on factors such as cooking method and processing. When carrots are cooked or processed into forms like carrot juice or carrot cake, their GI can increase. Cooking breaks down the cellular structure of the carrots, making the carbohydrates more accessible for digestion, which can lead to a faster spike in blood sugar when consumed in large quantities.
So, while raw carrots are an excellent choice for maintaining stable blood sugar levels, it’s essential to be mindful of their GI when they are part of cooked or processed dishes. For those with concerns about blood sugar control, it’s advisable to consume cooked or processed carrots in moderation and alongside other foods that can help mitigate their potential impact on blood sugar.
In summary, the glycemic index of carrots can indeed vary, potentially leading to more significant fluctuations in blood sugar when consumed in large quantities or in processed forms. Being aware of these variations allows you to make informed choices about how to incorporate this nutritious vegetable into your diet while keeping your blood sugar levels in check.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Sweet Potato vs. Regular Potato: How do they compare?

Both sweet potatoes and potatoes can be prepared in countless ways, from mashed to roasted to fried. They are versatile ingredients that lend themselves to a wide range of dishes, including soups, salads, casseroles, and more.
Sweet potatoes and regular potatoes, each with their distinct flavors and textures, are like culinary canvases waiting to be transformed into delectable creations. Their versatility knows no bounds, offering a plethora of preparation methods that cater to a diverse array of tastes and preferences. Whether you’re seeking comfort food, a healthy side, or a flavorful centerpiece, these tubers rise to the occasion, ready to take on any culinary challenge.
Let’s explore the boundless possibilities that sweet potatoes and regular potatoes bring to your kitchen:
Mashed Marvels: Both varieties can be transformed into silky-smooth mashed delights. Sweet potatoes offer a hint of sweetness, perfect for pairing with savory dishes. Traditional mashed potatoes, on the other hand, provide a creamy, buttery canvas that welcomes various seasonings and herbs.
Roasted Perfection: Few things rival the simple pleasure of roasted potatoes. Sweet potatoes develop a caramelized sweetness when roasted, while regular potatoes achieve a crispy exterior and fluffy interior. Combine them in a medley for a harmonious blend of flavors and textures.
Fries and Chips: Transform sweet potatoes into sweet potato fries or chips for a healthier twist on the classic snack. Regular potatoes excel in this department, delivering the quintessential golden, crispy fry.
Stews and Soups: Both sweet potatoes and regular potatoes shine in hearty stews and comforting soups. Their natural creaminess thickens broths, while their earthy flavors contribute depth to every spoonful.
Salad Stars: Add a satisfying element to salads with either roasted sweet potato cubes or boiled new potatoes. They offer a delightful contrast to crisp greens and fresh ingredients.
Casseroles and Gratins: Layered casseroles and gratins become sumptuous feasts with the addition of these tubers. Sweet potatoes add a sweet and colorful twist, while regular potatoes create creamy, savory layers.
Frittatas and Quiches: Slice them thinly and include them in frittatas or quiches for an extra layer of heartiness and flavor. Their earthy tones complement a variety of fillings.
Stuffed Delights: Scoop out the flesh and fill sweet potato or regular potato skins with a range of delectable fillings, from cheese and bacon to veggies and herbs.
Pancakes and Waffles: Grate sweet potatoes or potatoes into your pancake or waffle batter for a unique breakfast twist. Their natural sweetness or starchiness adds texture and flavor to your morning meal.
Curries and Stir-Fries: Cubed sweet potatoes or regular potatoes absorb the flavors of spices and sauces in curries and stir-fries, delivering a hearty and satisfying element to these dishes.
Incorporating sweet potatoes and regular potatoes into your culinary repertoire opens the door to a world of taste sensations. Whether you prefer the subtle sweetness of sweet potatoes or the comforting familiarity of regular potatoes, both offer endless possibilities for creating delicious, nutritious, and comforting meals. So, embrace their versatility, experiment with flavors and techniques, and let these tubers elevate your culinary adventures to new heights.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Sweet Potato vs Yam: A Comprehensive Comparison

Conclusion
When choosing between sweet potatoes and potatoes, consider your nutritional needs and personal preferences. Sweet potatoes are rich in vitamins, lower in calories, and have a lower glycemic index, making them an excellent choice for those seeking a nutritious and satisfying option. Potatoes, on the other hand, offer versatility, an array of varieties, and a source of vitamin C and potassium. Enjoy both in moderation as part of a balanced diet to reap their unique nutritional benefits and flavors.
nullIf you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Utilization of ensiled sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam …
More links
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Potato or Sweet Potato: Which Is Healthier? – Cleveland Clinic
