Table of Contents
The American criminal justice system is at a crossroads, with growing recognition that traditional punitive approaches to punishment in jails may not always yield the best outcomes. In this context, restorative justice has emerged as a compelling alternative, offering a more humane and effective way to address the needs of both inmates and society at large. This article explores the principles of restorative justice, its applications in American jails, and the potential for transformative change in the criminal justice landscape.
The American criminal justice system is at a crossroads, with growing recognition that traditional punitive approaches to punishment in jails may not always yield the best outcomes. In this context, restorative justice has emerged as a compelling alternative, offering a more humane and effective way to address the needs of both inmates and society at large.
Restorative justice centers on principles of healing, accountability, and reconciliation. It shifts the focus from punitive measures to repairing harm, facilitating constructive dialogue between offenders, victims, and the community. By fostering empathy and understanding, it can break the cycle of retribution and recidivism.
Within American jails, the application of restorative justice principles presents exciting possibilities. Inmates are provided opportunities for personal growth, rehabilitation, and reintegration into society. Programs like victim-offender dialogues and community service not only hold offenders accountable but also empower them to take responsibility for their actions.
Moreover, restorative justice acknowledges the trauma experienced by victims and seeks to address their needs. It offers victims a voice in the justice process, promoting closure and a sense of justice that conventional punitive approaches often fail to provide.
The potential for transformative change in the criminal justice landscape is significant. Embracing restorative justice can lead to reduced incarceration rates, lower recidivism, and safer communities. However, successful implementation requires collaboration among policymakers, correctional institutions, and community organizations, along with a commitment to evidence-based practices.
As we navigate this crossroads in the American criminal justice system, the adoption of restorative justice principles represents a profound shift toward a more compassionate and equitable approach to justice—one that prioritizes healing, rehabilitation, and the restoration of individuals and communities affected by crime.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Restorative Justice Literature Review
Understanding Restorative Justice
Restorative justice is a paradigm shift in the way society views crime and punishment. It places a greater emphasis on repairing harm and addressing the underlying causes of criminal behavior rather than simply imposing punitive measures. Key principles of restorative justice include:
null
Victim-Centered
Restorative justice places victims at the center of the process, aiming to address their needs, provide closure, and facilitate healing.
Restorative justice represents a profound shift in the way we approach the resolution of crimes and conflicts within our communities. By placing victims at the center of the process, this approach seeks to transform not only the lives of victims but also the broader understanding of justice itself. Here, we delve into the idea of restorative justice and its multifaceted impacts:
Empowering Victims: Restorative justice empowers victims by giving them a voice in the process. Victims have the opportunity to express their feelings, concerns, and needs, which are often overlooked in traditional criminal justice proceedings. This empowerment can be profoundly healing, as it reaffirms their value and agency.
Providing Closure: The process of restorative justice provides a platform for victims to seek closure. Engaging in open and honest dialogue with the offender can help victims gain a better understanding of the motives behind the crime and the steps taken by the offender to make amends. This transparency can contribute to a sense of closure and resolution.
Facilitating Healing: Healing is a central goal of restorative justice. It recognizes that healing is a process that extends beyond physical recovery. Emotional and psychological wounds require attention, and restorative justice provides a supportive environment for victims to heal and move forward with their lives.
Reducing Trauma: Traditional adversarial processes can be retraumatizing for victims, forcing them to relive the crime through testimony and cross-examination. Restorative justice minimizes this trauma by offering an alternative path to justice that prioritizes respectful communication and understanding.
Rebuilding Trust: For some victims, restorative justice can help rebuild trust, not only with the offender but also with the broader community and the criminal justice system itself. This rebuilding of trust is essential for victims to feel safe and supported in their recovery.
Personalized Solutions: Restorative justice allows for personalized solutions that address the unique needs of victims. Compensation, apologies, community service, or other forms of restitution can be tailored to the specific circumstances of the crime and the desires of the victim.
Promoting Accountability: While restorative justice places victims at the center, it also emphasizes the accountability of offenders. Offenders are encouraged to take responsibility for their actions, understand the harm they’ve caused, and actively work toward making amends. This accountability can lead to personal growth and a reduced likelihood of reoffending.
Community Involvement: Restorative justice often involves the broader community, fostering a sense of collective responsibility for addressing crime and harm. Community members can play roles as mediators, supporters, and witnesses, reinforcing the idea that justice is a shared endeavor.
Preventing Recidivism: By addressing the root causes of criminal behavior and promoting personal growth and accountability, restorative justice can contribute to a reduction in recidivism rates. It offers a path for offenders to reintegrate into society as law-abiding citizens.
Transforming Justice Culture: Restorative justice challenges the punitive aspects of the traditional justice system and promotes a culture of empathy, dialogue, and reconciliation. It encourages a shift away from punitive measures and toward healing and rehabilitation as central principles of justice.
In conclusion, restorative justice is a transformative approach that recognizes the profound impacts of crime on victims and seeks to address their needs while holding offenders accountable. By placing victims at the center of the process and emphasizing healing, closure, and understanding, restorative justice offers a powerful alternative to the adversarial model, paving the way for a more compassionate and effective system of justice.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: What is “Restorative Justice” and How Does it Impact Individuals …

Accountability
Offenders are encouraged to take responsibility for their actions, acknowledge the harm they’ve caused, and actively participate in making amends.
Encouraging offenders to take responsibility for their actions and actively participate in the process of making amends is a fundamental aspect of restorative justice and rehabilitation. This approach goes beyond punitive measures and focuses on holistic personal growth and community healing:
Accountability and Self-Reflection: By accepting responsibility for their actions, offenders are prompted to engage in critical self-reflection. They must confront the consequences of their behavior, which often leads to a deeper understanding of the harm they’ve caused to victims, families, and communities. This self-awareness can be a powerful catalyst for change.
Victim-Centered Justice: Restorative justice places victims at the center of the process. Offenders are encouraged to listen to the perspectives and experiences of those they have harmed, fostering empathy and understanding. This dialogue allows victims to express their feelings, seek answers, and, in some cases, find closure or satisfaction.
Making Amends and Restitution: Beyond words, restorative justice emphasizes concrete actions. Offenders are encouraged to actively engage in making amends, which may involve restitution to victims, community service, or other forms of restitution. These actions demonstrate a commitment to repairing the harm caused.
Community Reintegration: Encouraging offenders to take responsibility and make amends is not just about addressing the immediate consequences of their actions; it also paves the way for successful reintegration into the community. When individuals recognize the harm they’ve caused and actively work to make amends, they are better equipped to rebuild their lives and relationships.
Conflict Resolution Skills: Participation in restorative justice processes can equip offenders with valuable conflict resolution skills. They learn to communicate, empathize, and find mutually acceptable solutions to complex interpersonal conflicts, skills that can benefit them in various aspects of life.
Reducing Recidivism: Research has shown that restorative justice approaches are associated with lower rates of recidivism. When offenders take responsibility for their actions and actively engage in the process of making amends, they are less likely to reoffend, contributing to safer communities.
Promoting a Safer Society: Ultimately, the goal of restorative justice is not only to rehabilitate offenders but also to create safer, more cohesive societies. By addressing the root causes of criminal behavior and repairing the harm done, this approach helps prevent future crime and builds trust within communities.
In conclusion, encouraging offenders to take responsibility for their actions and actively participate in making amends is a compassionate and effective approach to justice. It promotes accountability, healing, and personal growth while fostering safer and more resilient communities. By emphasizing restitution and reintegration, restorative justice aims to break the cycle of crime and contribute to a more just and compassionate society.
Community Involvement
Restorative justice involves the broader community in the resolution process, fostering a sense of responsibility and connection among all stakeholders.
Restorative justice is a transformative approach to conflict resolution that transcends traditional punitive measures. It recognizes that when a harm or offense occurs, it affects not just the victim and the offender but the entire community. This unique paradigm shifts the focus from punishment to healing and reconciliation, involving the broader community in the process.
At its core, restorative justice encourages open and honest communication among all parties involved. This dialogue allows victims to express their pain and suffering, offenders to take responsibility for their actions, and the community to voice its concerns and expectations. Such conversations often take place in carefully moderated circles, providing a safe and supportive space for everyone to participate.
One of the profound benefits of restorative justice is that it restores a sense of agency and empowerment to victims. Instead of being passive observers in the criminal justice process, victims become active participants in determining the outcome. They have the opportunity to ask questions, seek restitution, and, most importantly, find closure. This process can be incredibly empowering, helping victims regain a sense of control over their lives.
For offenders, restorative justice offers a chance for personal growth and rehabilitation. By facing the consequences of their actions and engaging in meaningful dialogue with their victims, offenders gain a deeper understanding of the harm they’ve caused. This increased awareness can be a catalyst for change, motivating them to make amends and take steps towards reintegration into the community as responsible and productive members.
Furthermore, restorative justice promotes accountability. It encourages offenders to acknowledge their wrongdoing and take concrete steps to make things right. This could involve making reparations, performing community service, or undergoing counseling and rehabilitation. These actions not only benefit the victim but also demonstrate a commitment to personal growth and change.
Restorative justice also has a ripple effect on the broader community. It fosters a sense of collective responsibility and connection among community members. When individuals come together to support victims and offenders on their paths to healing and reintegration, it builds a stronger and more empathetic community fabric. This communal involvement can serve as a powerful deterrent to future offenses, as individuals become more invested in preventing harm and fostering a safer environment.
In conclusion, restorative justice represents a profound departure from punitive approaches, emphasizing healing, reconciliation, and community involvement. By involving all stakeholders in the resolution process, it not only addresses the immediate issues at hand but also contributes to the long-term well-being of individuals and the communities they are part of. It is a testament to the power of empathy, communication, and collective responsibility in building a more just and harmonious society.
You can also read more about this here: Restorative Justice Literature Review

Reparation
The focus is on repairing the harm caused by the offense, which may involve restitution, community service, or other measures.
null
Inmate Accountability Circles
Inmate accountability circles bring together offenders, victims, and trained facilitators to discuss the harm caused by the offense. These circles provide a platform for inmates to take responsibility for their actions and work toward making amends.
Inmate accountability circles bring together offenders, victims, and trained facilitators to discuss the harm caused by the offense. These circles provide a transformative platform for inmates to take responsibility for their actions and work toward making amends, with a range of positive impacts and outcomes:
Restorative Justice: Inmate accountability circles are a cornerstone of the restorative justice approach. They shift the focus from punishment to repairing harm and promoting healing for all parties involved. Victims have the opportunity to express the impact of the offense, while offenders can genuinely understand the consequences of their actions.
Personal Responsibility: These circles encourage inmates to confront their actions and accept personal responsibility for the harm caused. This acknowledgment is a critical step toward rehabilitation and personal growth, as it promotes self-awareness and empathy.
Empowerment: Inmate participation in accountability circles can empower them to take control of their behavior and make positive changes. By actively engaging in the process of restitution and reconciliation, inmates regain a sense of agency over their lives and choices.
Victim Healing: Victims often find closure and healing through these circles. Having the opportunity to communicate their feelings, ask questions, and receive sincere apologies from offenders can contribute to their emotional recovery and sense of justice.
Community Reintegration: The transformative nature of accountability circles can positively impact an inmate’s readiness for reintegration into society. When individuals genuinely address the harm they’ve caused and take steps to make amends, it fosters a sense of responsibility and commitment to leading a law-abiding life upon release.
Reducing Recidivism: Research indicates that restorative justice practices, including accountability circles, are associated with lower recidivism rates. Inmates who actively engage in the process and work toward making amends are less likely to reoffend, contributing to overall community safety.
Conflict Resolution Skills: Participation in these circles equips inmates with valuable conflict resolution skills. Learning to communicate openly, listen actively, and negotiate amicable solutions can benefit them in various aspects of life, including personal relationships and future employment.
Rebuilding Trust: In some cases, these circles help rebuild trust between offenders and their communities. When inmates genuinely commit to making amends and actively contribute to restitution, it can foster a sense of trust that they are genuinely committed to change.
Community Support: Accountability circles often involve community members as facilitators or observers. This not only helps connect inmates with external resources and support networks but also emphasizes the importance of community involvement in the rehabilitation process.
Cultural Sensitivity: These circles can be adapted to be culturally sensitive, addressing the unique needs and perspectives of diverse inmate populations. This inclusivity ensures that the benefits of restorative justice are accessible to all.
In conclusion, inmate accountability circles are powerful tools for promoting accountability, empathy, and healing within the criminal justice system. By offering a platform for open and sincere dialogue, they support personal growth and reconciliation, ultimately contributing to a more compassionate and effective approach to addressing the harm caused by criminal offenses.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Restorative Justice Literature Review

Victim-Offender Dialogues
Victim-offender dialogues facilitate direct communication between victims and offenders, allowing victims to express their feelings and expectations and giving offenders an opportunity to apologize and make restitution.
Victim-offender dialogues represent a significant departure from the conventional modes of justice, as they prioritize healing, accountability, and reconciliation over punitive measures. These dialogues are powerful tools in the realm of restorative justice, enabling a profound transformation in the lives of both victims and offenders.
For victims, the opportunity to engage in direct communication with the individuals who harmed them can be a profoundly cathartic and empowering experience. It allows them to voice their pain, anger, and expectations in a safe and structured environment. This process can be instrumental in their journey towards emotional healing and closure, as they no longer feel like passive bystanders in their own recovery.
Conversely, offenders also stand to gain significantly from participating in these dialogues. It provides them with a chance to confront the consequences of their actions and take genuine responsibility for the harm they’ve caused. Apologizing directly to their victims can be a deeply humbling and transformative experience, fostering a sense of empathy and remorse that can drive personal growth and rehabilitation.
Beyond the emotional aspects, victim-offender dialogues often involve discussions about restitution. Offenders may have the opportunity to make amends by compensating victims for their losses, whether financial or otherwise. This not only provides concrete assistance to victims but also underscores the tangible consequences of criminal behavior for offenders.
Furthermore, these dialogues can help break the cycle of recidivism by addressing the root causes of criminal behavior. By allowing offenders to gain insight into the impact of their actions on victims and society at large, they are more likely to commit to positive change and rehabilitation, reducing the likelihood of reoffending.
In a broader societal context, victim-offender dialogues contribute to a sense of justice that extends beyond punishment. They promote a vision of justice that seeks to repair the harm done, strengthen community bonds, and ultimately build safer and more empathetic communities. As we continue to explore and embrace restorative justice practices, victim-offender dialogues serve as a compelling testament to the transformative power of human connection, empathy, and genuine accountability.

Conflict Resolution Programs
Jails can implement conflict resolution programs that equip inmates with skills to manage conflicts nonviolently. These programs contribute to a more peaceful and harmonious jail environment.
The implementation of conflict resolution programs within jails represents a proactive approach to addressing the inherent challenges of confinement while fostering a more harmonious and secure environment for both inmates and staff.
These programs go beyond traditional punitive measures and instead empower inmates with valuable skills for managing conflicts in a nonviolent manner. By providing inmates with tools to resolve disputes peacefully, jails aim to reduce the incidence of violent altercations, which can lead to injuries, psychological trauma, and overall unrest within the facility.
One key aspect of these programs is education on communication and problem-solving techniques. Inmates learn how to express their concerns, grievances, and needs in a constructive way, promoting dialogue and understanding among inmates and between inmates and correctional staff. This not only helps to de-escalate conflicts but also enhances inmates’ ability to navigate interpersonal challenges upon release, which can contribute to successful reintegration into society.
Furthermore, conflict resolution programs often include anger management and emotional regulation components. These components assist inmates in recognizing and managing their emotions effectively, reducing impulsive and aggressive behaviors. Such skills are not only beneficial within the jail environment but also have long-term implications for an individual’s ability to make healthier choices post-release.
By fostering a more peaceful jail environment through these programs, correctional facilities can create a safer atmosphere for both inmates and staff. This, in turn, can lead to increased morale among staff, improved mental well-being among inmates, and better overall outcomes for rehabilitation and reentry efforts. Ultimately, the goal is not only to manage conflicts within the walls of the jail but also to equip individuals with the tools they need to lead more constructive, violence-free lives upon their return to the community.
Reentry Support
Restorative justice principles can be applied to reentry programs, where inmates work on rehabilitation, skill-building, and community reintegration with the aim of reducing recidivism.
nullDon’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Rehabilitation, Reentry, and Reaffirming Trust

Reduced Recidivism
Studies show that restorative justice programs in jails are associated with lower rates of reoffending, as they address the root causes of criminal behavior and provide inmates with a path to rehabilitation.
Numerous studies and empirical evidence highlight the effectiveness of restorative justice programs within jail settings. These programs stand out as a transformative approach that not only reduces rates of reoffending but also fundamentally reshapes the way we view and address criminal behavior.
Restorative justice programs excel because they adopt a holistic perspective, aiming to delve into the underlying causes of criminal actions. Instead of simply punishing inmates, these programs encourage open dialogue and interaction between offenders and their victims or affected parties. By doing so, they facilitate a deep understanding of the harm caused and the consequences of criminal behavior, fostering empathy and accountability in the process.
This emphasis on understanding and accountability sets the stage for rehabilitation. Restorative justice programs provide inmates with opportunities to actively participate in their own personal growth and healing. This can include educational programs, counseling, and skill-building exercises tailored to address the specific needs of the individual. By addressing the root causes of their actions and providing them with essential tools, these programs empower inmates to make positive changes in their lives.
Moreover, the sense of responsibility and accountability instilled through restorative justice programs often leads to a profound transformation in the mindset of offenders. It encourages them to take ownership of their actions and actively seek ways to make amends and contribute positively to society. In turn, this shift in perspective not only reduces the likelihood of reoffending but also promotes the reintegration of individuals into their communities as law-abiding citizens.
The success of restorative justice programs is a testament to the power of empathy, understanding, and rehabilitation in the criminal justice system. By prioritizing these principles and offering inmates a path toward personal growth and reintegration, we not only reduce the cycle of recidivism but also foster a more compassionate and equitable approach to justice. These programs offer hope, healing, and the opportunity for lasting change, ultimately benefiting both inmates and society as a whole.
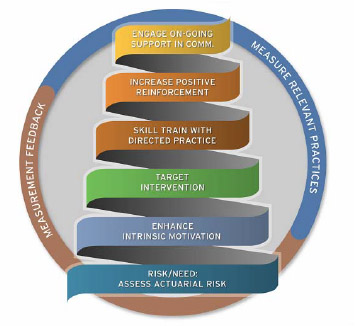
Improved Jail Environment
Restorative justice fosters a more positive and cooperative atmosphere within jails, reducing violence and tensions among inmates.
Restorative justice’s positive impact on the atmosphere within jails goes beyond reducing violence and tensions among inmates. It has the potential to transform the entire correctional environment in several significant ways:
Conflict Resolution Skills: Restorative justice programs often equip inmates with valuable conflict resolution and communication skills. Inmates learn to address issues constructively, leading to fewer confrontations and a more peaceful atmosphere within the jail.
Increased Accountability: In a restorative justice framework, inmates are encouraged to take responsibility for their actions and the harm they’ve caused. This accountability fosters a culture of personal growth and maturity, reducing the likelihood of aggressive or antagonistic behavior.
Empathy and Understanding: Restorative justice processes, such as victim-offender dialogues, promote empathy and understanding between inmates. When individuals gain insight into the consequences of their actions on others, they are more likely to show empathy and restraint.
Conflict Prevention: By addressing underlying issues and conflicts directly, restorative justice programs can help prevent disputes and rivalries from escalating into violence. Inmates become more adept at resolving conflicts peacefully, contributing to a safer environment.
Positive Peer Influence: Inmates who participate in restorative justice programs often become advocates for nonviolent conflict resolution within the jail community. Their positive influence can ripple through the population, encouraging others to adopt more cooperative attitudes.
Strengthening Inmate Bonds: Restorative justice processes can help build trust and connections among inmates, reducing the need for self-protective behaviors that may lead to conflicts. Inmates who perceive a supportive community are less likely to engage in disruptive or violent conduct.
Improved Staff-Inmate Relations: A more cooperative and peaceful atmosphere benefits not only inmates but also correctional staff. It can lead to improved relationships between staff and inmates, contributing to a safer and more efficient working environment.
Preparation for Reentry: Restorative justice programs often emphasize personal growth, responsibility, and rehabilitation. Inmates who participate in these programs are better prepared for reentry into society as more socially and emotionally adept individuals.
In conclusion, the positive and cooperative atmosphere fostered by restorative justice within jails transcends immediate conflict reduction. It cultivates an environment that prioritizes personal growth, accountability, and empathy, ultimately contributing to safer and more rehabilitative correctional settings. As restorative justice principles continue to gain recognition and adoption within the criminal justice system, they hold the potential to transform the culture of incarceration, making jails more humane and conducive to rehabilitation.
Victim Satisfaction
Victims often report higher levels of satisfaction with restorative justice processes, as they have a direct say in the resolution and can find closure.
Victims often report higher levels of satisfaction with restorative justice processes, as they have a direct say in the resolution and can find closure. This victim-centered approach to justice not only empowers those who have been harmed but also offers several additional benefits for both individuals and society as a whole.
Firstly, restorative justice places the victim at the center of the process, acknowledging their needs, emotions, and desire for healing. Traditional adversarial justice systems often leave victims feeling like passive bystanders, whereas restorative justice allows them to actively participate in shaping the outcome. This empowerment can be profoundly therapeutic, providing victims with a sense of agency and control over their own recovery.
Moreover, restorative justice fosters a sense of accountability in the offender. By engaging in face-to-face dialogues or meetings with the victim, offenders are confronted with the real impact of their actions. This humanizing experience can lead to genuine remorse and a greater willingness to make amends, which can be essential for both the victim’s healing and the offender’s rehabilitation.
Restorative justice processes also have the potential to reduce recidivism rates. Studies have shown that offenders who participate in restorative justice programs are less likely to reoffend than those who go through traditional punitive measures. This is because the focus shifts from punishment to addressing the underlying causes of criminal behavior and repairing harm. When offenders take responsibility for their actions and actively work to make amends, they are more likely to reintegrate successfully into society as law-abiding citizens.
Furthermore, restorative justice can contribute to the overall well-being of communities. By promoting dialogue, empathy, and understanding, it helps build social bonds and trust. When individuals and communities see that conflicts can be resolved in a way that restores harmony and addresses harm, it can lead to greater social cohesion and a reduction in community violence.
In conclusion, the victim-centered approach of restorative justice processes not only provides satisfaction and closure to those who have been harmed but also offers a range of broader benefits. It empowers victims, holds offenders accountable, reduces recidivism, and promotes community healing. By embracing these principles, the criminal justice system can move closer to achieving both justice and the restoration of individuals and communities affected by crime.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice Module 8 Key Issues: 2 …
Resource Efficiency
Restorative justice can be more cost-effective than traditional punitive approaches, as it reduces the strain on jail resources and lowers recidivism rates.
nullTo expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: What is “Restorative Justice” and How Does it Impact Individuals …
Community Healing
Restorative justice contributes to community healing by fostering understanding and empathy among all parties involved.
Restorative justice is a profound paradigm shift in the field of criminal justice, and its impact on community healing cannot be overstated. Expanding on this idea:
Victim-Centered Healing: Restorative justice places victims at the center of the process, giving them a voice and allowing them to express their feelings, concerns, and needs. This not only empowers victims but also fosters a sense of validation, as their experiences are acknowledged and respected.
Offender Accountability: One of the fundamental principles of restorative justice is offender accountability. It encourages offenders to take responsibility for their actions and acknowledge the harm they have caused. This acknowledgment is a crucial step in the healing process for both victims and offenders.
Community Involvement: Restorative justice often involves the broader community in the healing process. Community members have the opportunity to participate in dialogues and support the rehabilitation and reintegration of offenders. This promotes a sense of collective responsibility for preventing future harm.
Healing Through Dialogue: Restorative justice practices facilitate open and honest dialogue between all parties involved. These conversations, conducted in a safe and structured environment, allow for the expression of emotions, concerns, and the seeking of answers. Through dialogue, misunderstandings can be clarified, and empathy can emerge.
Emphasis on Understanding: Restorative justice encourages participants to understand each other’s perspectives and experiences. This focus on empathy and understanding helps bridge the gap between victims and offenders, often resulting in a deeper sense of connection and closure.
Reducing Recidivism: Research has shown that restorative justice practices can lead to lower rates of recidivism compared to traditional punitive approaches. When offenders actively engage in making amends and rebuilding relationships, they are less likely to reoffend.
Healing Beyond the Individual: The healing achieved through restorative justice extends beyond individual victims and offenders. It ripples out to families, communities, and even society at large. When harm is addressed and resolved, it contributes to a sense of collective well-being and cohesion.
Conflict Transformation: Restorative justice is not limited to addressing criminal offenses. It can be applied to various conflicts and disputes within communities, workplaces, and schools. By transforming conflicts into opportunities for understanding and growth, it promotes healthier relationships and environments.
Cultural Sensitivity: Restorative justice can be adapted to be culturally sensitive, recognizing that different communities may have unique perspectives on justice and healing. This adaptability allows for a more inclusive and equitable approach to addressing harm.
A Path to Reconciliation: In some cases, restorative justice can lead to genuine reconciliation between victims and offenders. While not always achievable or desired, this outcome represents a powerful form of community healing, demonstrating the transformative potential of restorative practices.
In a world where traditional punitive approaches have often left victims feeling unheard and offenders without a path to rehabilitation, restorative justice offers a profound alternative. It promotes a deeper understanding of the complexities of crime, emphasizes healing and accountability, and ultimately seeks to create a more just and harmonious society where the scars of harm can be mended, and communities can move forward together.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: What is “Restorative Justice” and How Does it Impact Individuals …
Restorative justice offers a promising path forward for American jails, aligning with the values of accountability, rehabilitation, and community engagement. By shifting the focus from punitive measures to healing and reconciliation, it has the potential to reduce recidivism, improve the jail environment, and provide more satisfying outcomes for victims. As restorative justice programs continue to gain momentum, they represent a transformative force in the effort to create a more just and compassionate criminal justice system in the United States.
Restorative justice stands as a beacon of hope and transformation within the realm of American jails, offering a profound departure from the traditional punitive approach. It embodies core values of accountability, rehabilitation, and community engagement, ushering in a new era where healing and reconciliation are at the forefront of the criminal justice discourse. This paradigm shift holds tremendous promise in reshaping the landscape of American jails, and its potential reaches far beyond the confines of correctional facilities. Here, we will explore the multifaceted benefits and impacts of restorative justice programs within the context of American jails.
**1. Reducing Recidivism: One of the primary virtues of restorative justice is its capacity to reduce recidivism rates. By addressing the root causes of criminal behavior and fostering a sense of responsibility and empathy in offenders, these programs empower individuals to reintegrate into society as law-abiding citizens. The focus on healing and personal growth rather than punishment can break the cycle of reoffending.
**2. Improving the Jail Environment: Restorative justice initiatives inherently promote a more positive and humane jail environment. When inmates are actively engaged in processes that encourage personal reflection, accountability, and empathy, the atmosphere within correctional facilities can become less hostile and more conducive to rehabilitation. This, in turn, benefits both inmates and staff by fostering a safer and more constructive environment.
**3. Empowering Victims: Victims of crimes often find a measure of closure and healing through restorative justice processes. These programs offer victims the opportunity to voice their experiences, have their questions answered, and participate in the resolution of the harm done to them. By empowering victims and acknowledging their needs, restorative justice helps restore a sense of justice and dignity.
**4. Community Reintegration: Restorative justice extends its impact well beyond the walls of correctional facilities. It emphasizes the importance of reintegrating offenders into their communities successfully. Through restitution, community service, and victim-offender dialogue, these programs encourage individuals to take responsibility for their actions and contribute positively to their communities.
**5. Enhanced Accountability: Accountability takes on a more profound meaning in restorative justice. It involves acknowledging the harm caused to victims and society, making amends, and actively working toward personal growth and rehabilitation. This heightened sense of accountability can lead to more enduring and meaningful behavioral change.
**6. Resource Efficiency: Restorative justice programs often make more efficient use of resources. They prioritize interventions that address the root causes of criminal behavior, potentially reducing the need for long-term incarceration. This can result in cost savings for the criminal justice system while promoting better outcomes.
**7. Victim Satisfaction: Restorative justice processes consistently yield high levels of victim satisfaction. Victims who participate in these programs report greater closure and a sense that justice has been served. This satisfaction contributes to a sense of healing and closure for both victims and offenders.
**8. Cultural Competency: Restorative justice can be adapted to accommodate various cultural norms and values, making it a flexible approach that can resonate with diverse populations. This adaptability ensures that the principles of healing and reconciliation are accessible to a wide range of individuals.
In conclusion, restorative justice programs are a transformative force within American jails, offering a vision of a more just and compassionate criminal justice system. By emphasizing accountability, rehabilitation, and community engagement, they address the root causes of criminal behavior while promoting healing and reconciliation. As these programs continue to gain momentum, they hold the potential to reshape the future of American jails, foster safer communities, and usher in an era of justice that truly serves the needs of all stakeholders.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Literature Review: Restorative Justice for Juveniles | Office of …
More links
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Incorporating Restorative and Community Justice Into American …
