Table of Contents
In any civilized society, the treatment of individuals within the criminal justice system is a reflection of its values and principles. In the United States, the rights and well-being of inmates have become central to discussions surrounding justice reform. This article delves into the fundamental concept of inmate rights and the vital role advocacy plays in ensuring that incarcerated individuals are treated with dignity and fairness during their time behind bars.
In any civilized society, the treatment of individuals within the criminal justice system serves as a litmus test of its commitment to justice, fairness, and human rights. In the United States, the treatment of inmates and the protection of their rights have emerged as pivotal elements of ongoing conversations about justice reform and the transformation of the prison system. This article delves deeper into the core concept of inmate rights and highlights the crucial role that advocacy plays in safeguarding the dignity and equitable treatment of incarcerated individuals throughout their incarceration.
The Foundations of Inmate Rights:
Constitutional Protections: In the U.S., inmate rights are rooted in the Constitution, ensuring that individuals, even when incarcerated, retain certain fundamental rights. These include protection from cruel and unusual punishment (Eighth Amendment), the right to due process (Fifth and Fourteenth Amendments), and freedom from discrimination (Fourteenth Amendment).
Access to Healthcare: Inmates have the right to receive adequate healthcare while incarcerated. This includes medical, mental health, and dental care. Ensuring access to healthcare is not just a matter of ethical responsibility but also essential for public health within correctional facilities and the broader community.
Protection from Abuse and Harassment: Inmate rights encompass protection from abuse, harassment, and violence, whether inflicted by other inmates or correctional staff. This includes safeguards against sexual assault, excessive use of force, and mistreatment.
Access to Legal Resources: Inmates have the right to access legal resources, including legal representation, to address legal matters such as appeals, grievances, and challenges to their conditions of confinement.
The Role of Advocacy in Safeguarding Inmate Rights:
Legal Advocacy: Legal advocacy groups and organizations play a pivotal role in monitoring and challenging violations of inmate rights. They often provide pro bono legal representation to inmates, ensuring that their grievances are heard in court.
Public Awareness: Advocacy efforts help raise public awareness about issues within the criminal justice system, including the treatment of inmates. This awareness can lead to increased scrutiny, policy changes, and public pressure for reform.
Policy Change: Advocacy can drive policy changes at the local, state, and federal levels. Examples include reforms in solitary confinement practices, efforts to reduce mass incarceration, and initiatives to provide educational and rehabilitative programs for inmates.
Accountability: Advocacy groups hold correctional facilities and government agencies accountable for their actions and adherence to legal standards. They often serve as watchdogs, investigating allegations of abuse and pushing for transparency.
Support for Inmates: Advocacy organizations also provide support and resources to inmates and their families, helping them navigate the complex legal and administrative processes within the criminal justice system.
Moving Forward:
Inmate rights advocacy is an essential component of the broader movement to reform the criminal justice system in the United States. It underscores the principles of justice, compassion, and fairness that should guide the treatment of all individuals, regardless of their circumstances. As society continues to grapple with issues of mass incarceration, racial disparities, and the need for rehabilitation over punishment, the advocacy for inmate rights remains a powerful force for change, striving to ensure that the dignity and humanity of incarcerated individuals are upheld, while promoting a more equitable and just society for all.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here A. THE INTERNATIONAL BILL OF HUMAN RIGHTS
Constitutional Protections
Inmate rights are firmly rooted in the U.S. Constitution, which safeguards certain fundamental rights for all individuals, including those who are incarcerated. These rights include protection against cruel and unusual punishment (Eighth Amendment) and due process (Fifth and Fourteenth Amendments).
In the United States, the concept of inmate rights is deeply entrenched in the country’s legal framework, enshrined in the U.S. Constitution as well as various federal and state laws. These protections are essential to uphold the principles of justice, human dignity, and accountability within the criminal justice system. Let’s delve deeper into the constitutional foundation and broader implications of inmate rights.
1. Constitutional Safeguards: Inmate rights are grounded in the U.S. Constitution, which guarantees certain fundamental rights to all individuals, including those who are incarcerated. These rights are not forfeited upon imprisonment and are essential to preserving the integrity of the justice system.
2. Eighth Amendment Protections: The Eighth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution prohibits “cruel and unusual punishment.” This clause serves as a powerful safeguard against excessive or inhumane treatment of inmates. Courts have interpreted it to include protections against physical abuse, excessive use of force, and degrading conditions of confinement. In essence, it ensures that the punishment meted out during incarceration is proportionate and humane.
3. Due Process Rights: The Fifth and Fourteenth Amendments of the Constitution provide individuals, including inmates, with the right to due process of law. This includes the right to a fair and impartial hearing, the right to be informed of charges, and the right to legal representation. Due process safeguards help prevent arbitrary and unjust treatment within the criminal justice system, ensuring that individuals are treated fairly and justly at all stages of their cases.
4. Access to Healthcare: Inmates also have the right to receive adequate healthcare while incarcerated. This right is derived from the constitutional prohibition against cruel and unusual punishment. It ensures that inmates receive necessary medical attention, medication, and treatment, regardless of their incarceration status.
5. Freedom from Retaliation: Inmate rights include protection from retaliation by prison authorities for exercising their rights or reporting abuse or misconduct. This safeguard ensures that inmates can raise legitimate concerns about their treatment without fear of reprisals.
6. Right to Legal Remedies: Inmates have the right to seek legal remedies when their constitutional rights are violated. They can file lawsuits against prison officials, seek injunctive relief, or request changes in their conditions of confinement. These legal remedies serve as a crucial mechanism for holding those responsible for misconduct accountable.
7. Evolving Interpretations: The interpretation and application of inmate rights continue to evolve through legal precedent and court decisions. Landmark cases have clarified and expanded the scope of these rights, addressing issues such as overcrowding, solitary confinement, and access to mental health care.
8. Advocacy and Reform: In recent years, inmate rights have gained increased attention, leading to advocacy efforts and reforms aimed at improving conditions within the criminal justice system. These efforts strive to align correctional practices with constitutional principles and international human rights standards.
In conclusion, the constitutional foundation of inmate rights underscores the enduring commitment of the United States to safeguard the dignity, humanity, and fairness of all individuals, regardless of their incarceration status. These rights not only protect inmates but also serve as a vital mechanism for upholding the principles of justice and accountability within the criminal justice system. They remind us that the pursuit of justice must extend to all members of society, even those who have been deprived of their liberty.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: National Strategy on Gender Equity and Equality | The White House

Access to Medical Care
Inmates have the right to receive adequate medical care. Deliberate indifference to an inmate’s serious medical needs is a violation of their constitutional rights.
Inmates have the right to receive adequate medical care. Deliberate indifference to an inmate’s serious medical needs is a violation of their constitutional rights. This fundamental principle underscores the importance of upholding the dignity and well-being of incarcerated individuals, regardless of their circumstances. Expanding on this idea, we can explore various facets and implications of this critical issue:
Constitutional Basis: The Eighth Amendment to the United States Constitution prohibits cruel and unusual punishment, and this includes the denial of medical care to inmates. Courts have consistently held that deliberate indifference to an inmate’s serious medical needs constitutes cruel and unusual punishment.
Scope of Medical Needs: Inmates’ medical needs can vary widely, from chronic conditions to acute illnesses and injuries. The right to adequate medical care encompasses not only physical health but also mental health and dental care, ensuring that all aspects of an inmate’s health are addressed.
Challenges of Providing Care: Correctional facilities often face unique challenges in providing medical care, including limited resources, security concerns, and the need for specialized care for certain conditions such as infectious diseases, substance use disorders, and mental illnesses.
Role of Correctional Healthcare Providers: Correctional healthcare providers, including medical staff within prisons and jails, play a crucial role in upholding inmates’ rights. They must assess, diagnose, and treat medical conditions in a manner consistent with accepted medical standards.
Preventive Healthcare: Beyond treating existing conditions, preventive healthcare is essential within correctional facilities. This includes routine check-ups, vaccinations, and health education to reduce the risk of illness and promote overall well-being.
Mental Health Services: Given the high prevalence of mental health issues among inmates, providing adequate mental health services is paramount. Failure to address mental health needs can exacerbate suffering and increase the risk of self-harm or harm to others.
Pregnant Inmates and Vulnerable Populations: Special attention should be given to the healthcare needs of pregnant inmates and other vulnerable populations, such as the elderly and individuals with disabilities. Ensuring their specific needs are met is crucial.
Access to Medications: Inmates who require prescription medications should have timely access to them. Interruptions or delays in medication can have serious health consequences.
Medical Privacy: Inmates have the right to medical privacy, and their healthcare information should be protected in accordance with applicable laws and regulations.
Legal Accountability: Deliberate indifference can take various forms, such as ignoring obvious signs of illness, denying access to medical care, or providing substandard care. Legal accountability for individuals or institutions that violate inmates’ rights is essential to enforce these protections.
Advocacy and Oversight: External oversight, including advocacy groups, watchdog organizations, and governmental bodies, can help ensure that correctional facilities adhere to their obligation to provide adequate medical care to inmates.
Reentry and Continuity of Care: Inmates who receive medical care while incarcerated should have access to continued care upon release, promoting a smoother transition back into society and reducing health disparities.
In conclusion, recognizing and protecting the right of inmates to receive adequate medical care is not just a legal requirement but a moral imperative. It reflects society’s commitment to treating all individuals with dignity and respect, even those who are incarcerated. Upholding this principle is not only a matter of justice but also contributes to safer and more rehabilitative correctional systems.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Human Rights, Stigma, and Substance Use – PMC

Access to Legal Counsel
Inmates have the right to access legal counsel, file grievances, and challenge their convictions or conditions of confinement.
nullAdditionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers | OHCHR

Freedom from Discrimination
Inmates are protected from discrimination based on race, religion, gender, and other factors. Correctional facilities must provide equitable treatment to all inmates.
Ensuring equitable treatment for inmates, regardless of their backgrounds or circumstances, is a fundamental principle that underpins the functioning of a fair and just criminal justice system. While the idea of protecting inmates from discrimination is essential, it extends beyond mere rhetoric and has profound implications for both the incarcerated individuals and society at large.
Upholding Human Dignity: Equitable treatment upholds the inherent dignity of every individual, even those who have committed crimes. It recognizes that inmates, like all people, deserve to be treated with respect, fairness, and humanity. This principle is enshrined in international human rights standards.
Reducing Recidivism: Discrimination within the correctional system can perpetuate cycles of crime and incarceration. By providing equitable treatment and opportunities for rehabilitation, inmates are more likely to reintegrate into society successfully, reducing the likelihood of reoffending.
Fostering a Safer Environment: Equitable treatment within correctional facilities contributes to a safer environment for both inmates and staff. When inmates perceive that they are treated fairly and with respect, conflicts are less likely to escalate, leading to reduced violence and disruptions.
Addressing Disparities: Disparities in the criminal justice system, such as racial or gender-based disparities, have long been a concern. Ensuring equitable treatment is a crucial step in addressing these systemic issues and promoting a more just society.
Access to Rehabilitation Services: Equitable treatment includes equal access to educational, vocational, and rehabilitative programs. These services can play a significant role in an inmate’s ability to reintegrate successfully into society and build a better future.
Mental Health and Medical Care: Equitable treatment extends to mental health and medical care. Inmates should receive the same quality of care as anyone in the community. Addressing mental health issues and medical needs is not only a matter of human rights but also public health.
Promoting Fair Legal Proceedings: Equitable treatment extends to the legal process itself. Inmates have the right to a fair trial, legal representation, and protection from discrimination during court proceedings. This ensures that justice is served justly.
Training and Sensitization: Correctional staff should undergo training to recognize and eliminate bias, discrimination, and stereotypes that may impact their interactions with inmates. Sensitization programs can help create a culture of equity within correctional facilities.
Accountability: Mechanisms for accountability must be in place to address instances of discrimination or inequitable treatment. Inmates should have a way to report violations of their rights, and corrective action should be taken when needed.
Community Reintegration: Ultimately, equitable treatment within correctional facilities plays a pivotal role in preparing inmates for successful community reintegration. When they are treated fairly and given the tools for personal growth, they are more likely to become law-abiding, productive members of society.
In conclusion, the principle of equitable treatment for inmates is not just a legal requirement; it is a cornerstone of a just and humane criminal justice system. By upholding this principle, society can work towards breaking the cycles of crime and incarceration while affirming the universal value of every individual, regardless of their past actions.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Human Rights, Stigma, and Substance Use – PMC

Access to Education and Rehabilitation
Inmates have the right to access educational and rehabilitative programs that can help them prepare for reintegration into society.
Inmates have the right to access educational and rehabilitative programs that can help them prepare for reintegration into society. This fundamental principle recognizes that while individuals may have made mistakes and face the consequences of their actions, society benefits when they have the opportunity to reform and contribute positively upon release. Providing inmates with access to education, vocational training, and rehabilitation services serves several crucial purposes:
Reducing Recidivism: When inmates are equipped with skills and knowledge, they are better positioned to secure employment and become self-sufficient after release. This reduces the likelihood of them returning to criminal activities, ultimately lowering recidivism rates and enhancing public safety.
Promoting Personal Growth: Incarceration should not only be punitive but also an opportunity for personal growth and development. Educational programs can empower inmates to address the root causes of their criminal behavior, such as addiction or lack of education, helping them build a foundation for a more constructive and law-abiding life.
Fostering Accountability: Rehabilitation programs often incorporate elements of restorative justice, where inmates confront the harm they’ve caused to victims and communities. This process encourages accountability and encourages individuals to make amends, promoting healing and reconciliation.
Supporting Reintegration: Preparing inmates for reintegration into society involves more than just providing them with skills. It also includes addressing mental health and substance abuse issues, as well as offering social services that can help them navigate challenges they may face upon release, such as finding housing or re-establishing family relationships.
Respecting Human Dignity: Recognizing the right of inmates to access education and rehabilitation programs is a testament to the belief in the inherent worth and dignity of every individual. It upholds the principle that even those who have committed crimes are entitled to opportunities for self-improvement and transformation.
In conclusion, ensuring inmates have access to educational and rehabilitative programs is not just a matter of providing basic rights; it’s a strategy that benefits both inmates and society as a whole by reducing crime, promoting personal growth, fostering accountability, supporting reintegration, and upholding the fundamental principles of human dignity and justice.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Basic Principles for the Treatment of Prisoners | OHCHR

Legal Representation
Advocacy often begins with legal representation. Public defenders, legal aid organizations, and pro bono attorneys play a crucial role in ensuring that inmates’ legal rights are upheld.
Advocacy often begins with legal representation, as it serves as the cornerstone of justice within our legal system. Public defenders, legal aid organizations, and pro bono attorneys play a crucial role in ensuring that inmates’ legal rights are upheld, but their impact extends far beyond the confines of the courtroom.
First and foremost, these dedicated professionals are the voice of those who might otherwise go unheard. Public defenders, often overworked and under-resourced, tirelessly advocate for individuals who are unable to afford private legal counsel. They become champions of justice for the marginalized, the vulnerable, and the disadvantaged, embodying the principles of fairness and equality.
Moreover, their work transcends individual cases; it has a ripple effect throughout the criminal justice system. By working diligently to protect the rights of inmates prior to trial, these legal advocates help maintain the integrity of the entire legal process. They serve as a critical check on the power of law enforcement, ensuring that the accused are treated with dignity and respect, and that evidence is gathered and presented within the bounds of the law.
Furthermore, the efforts of public defenders and pro bono attorneys contribute to a broader conversation about reforming the criminal justice system. They witness firsthand the flaws and inequities within the system and use this knowledge to advocate for change. Their experiences shed light on issues such as bail reform, over-criminalization, and the need for alternatives to incarceration.
In essence, the work of public defenders, legal aid organizations, and pro bono attorneys is not just about legal representation; it is a tireless pursuit of justice, equity, and a more humane society. It is a commitment to upholding the values upon which our legal system was built, ensuring that every individual, regardless of their circumstances, is afforded their fundamental rights. In doing so, they not only advocate for their clients but also for a more just and compassionate society for all.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Basic Principles on the Role of Lawyers | OHCHR

Access to Information
Advocacy groups and individuals work to provide inmates with information about their rights, grievances, and avenues for redress. This empowers inmates to advocate for themselves.
nullTo delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: National Strategy on Gender Equity and Equality | The White House

Policy Reform
Advocacy efforts extend to policy reform. Activists and organizations work to change laws and regulations that perpetuate unfair treatment or inhumane conditions within correctional facilities.
Advocacy efforts extend to policy reform. Activists and organizations work tirelessly to change laws and regulations that perpetuate unfair treatment or inhumane conditions within correctional facilities. This critical aspect of criminal justice reform is essential for addressing systemic issues and ensuring that the principles of justice, rehabilitation, and human rights are upheld:
Sentencing Reform: Advocates often push for sentencing reform to address the problem of excessively long and mandatory sentences. They argue that many non-violent offenses result in disproportionately harsh punishments, contributing to prison overcrowding and the perpetuation of a cycle of incarceration. By advocating for changes in sentencing laws, they seek to create a more balanced and just system.
Bail and Pretrial Detention Reform: The bail system in many jurisdictions has come under scrutiny for perpetuating inequalities, as individuals with financial means can secure their release while those without funds remain incarcerated. Advocates work to reform bail practices, aiming to replace cash bail with more equitable alternatives based on risk assessment. This ensures that pretrial detention is used sparingly and only when necessary for public safety.
Solitary Confinement Restrictions: The use of solitary confinement has been widely criticized for its adverse effects on inmates’ mental health. Advocacy efforts have led to changes in policies that limit the use of prolonged isolation, especially for vulnerable populations such as juveniles and those with mental illnesses.
Prison Conditions: Activists focus on improving prison conditions, addressing issues such as overcrowding, access to healthcare, and the quality of food and sanitation. Through litigation, lobbying, and public awareness campaigns, they advocate for changes that uphold basic human rights standards for incarcerated individuals.
Reentry Programs: To reduce recidivism rates, advocacy efforts often revolve around improving reentry programs that help individuals transition back into society. This includes access to education, job training, housing, and mental health services. Policy reform is crucial in allocating resources and support for these programs.
Racial and Social Justice: Many advocacy initiatives are rooted in the fight for racial and social justice within the criminal justice system. Activists work to eliminate racial profiling, bias in policing, and discriminatory sentencing practices. Policy reform in these areas is seen as essential for dismantling systemic racism.
Juvenile Justice Reform: Advocates for juvenile justice reform aim to change policies that treat young offenders as adults and push for more rehabilitative and age-appropriate approaches. This includes diversion programs, counseling, and educational opportunities within the juvenile justice system.
Transparency and Accountability: Advocacy efforts often seek greater transparency and accountability in the criminal justice system. This includes pushing for body-worn cameras for law enforcement, access to records, and oversight of correctional facilities to prevent abuse and misconduct.
Restorative Justice: Advocates champion restorative justice practices that focus on repairing harm done to victims and communities while rehabilitating offenders. Policy changes are necessary to implement these alternative approaches effectively.
Community Policing: Some advocacy groups promote community policing models that emphasize building positive relationships between law enforcement and the communities they serve. Policy changes support the adoption of community-oriented strategies that prioritize prevention over punitive measures.
In conclusion, advocacy for policy reform plays a crucial role in reshaping the criminal justice system to be fairer, more humane, and focused on rehabilitation rather than punishment. These efforts are instrumental in addressing the root causes of systemic issues and creating a more just and equitable society for all.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: The Nelson Mandela Rules: Protecting the Rights of Persons …

Awareness and Accountability
Advocacy brings attention to issues within the criminal justice system, from overcrowding to the use of solitary confinement. By raising awareness and holding authorities accountable, advocates help shed light on problems that require solutions.
Advocacy plays a pivotal role in shedding light on critical issues within the criminal justice system, addressing a range of concerns from overcrowding to the use of solitary confinement. It serves as a powerful catalyst for change, acting as a beacon that illuminates the darkest corners of our legal and correctional systems.
Through diligent efforts and unwavering commitment, advocates not only raise awareness but also demand accountability from those in authority. Their tireless work serves as a reminder that the criminal justice system is a reflection of society’s values, and it must evolve to uphold principles of fairness, justice, and compassion.
By relentlessly championing the cause, advocates compel society to confront uncomfortable truths and acknowledge systemic flaws. They challenge the status quo, pushing for reforms that address root causes and provide humane alternatives. In doing so, they not only advocate for the rights and dignity of incarcerated individuals but also contribute to the broader goal of creating a more just and equitable society.
Advocacy is the driving force that calls upon policymakers, legislators, and citizens to engage in critical conversations and seek innovative solutions. It fosters a sense of responsibility among all stakeholders to actively participate in shaping a criminal justice system that aligns with our shared values and aspirations for a fair and compassionate society. Ultimately, advocacy is the beacon of hope that guides us toward a future where justice is blind to privilege and disparities, and where the inherent dignity of every individual is upheld, regardless of their circumstances.
You can also read more about this here: National Strategy on Gender Equity and Equality | The White House

Support Services
Many advocacy groups offer support services to inmates upon their release, including housing assistance, job training, and mental health services. These services aim to reduce recidivism rates and promote successful reintegration.
Many advocacy groups recognize the critical importance of providing comprehensive support services to inmates upon their release. Beyond the confines of prison walls, these organizations extend a helping hand to individuals who are embarking on their journey toward reintegration into society.
One of the key facets of this support is housing assistance. Advocacy groups understand that stable housing is a fundamental building block for a successful reentry into the community. By offering guidance and resources for finding suitable housing, they help former inmates establish a stable and secure environment from which they can rebuild their lives.
In addition to housing assistance, these organizations also prioritize job training. Employment plays a pivotal role in reducing recidivism rates, as gainful employment provides financial stability and a sense of purpose. Advocacy groups collaborate with various vocational training programs and job placement services to equip ex-inmates with the skills and knowledge needed to secure meaningful employment opportunities.
Recognizing the intricate relationship between mental health and successful reintegration, advocacy groups also make mental health services readily available. Many individuals leaving the prison system face psychological challenges, such as trauma or addiction, which can hinder their ability to reintegrate effectively. By offering counseling, therapy, and addiction recovery programs, these groups address the root causes of criminal behavior and support individuals in building healthier, more stable lives.
In essence, the array of support services provided by advocacy groups serves as a multifaceted safety net for formerly incarcerated individuals. The ultimate goal is not only to reduce recidivism rates but also to empower these individuals to become productive, law-abiding members of society. Through housing assistance, job training, and mental health services, these organizations pave the way for successful reintegration and, in doing so, contribute to safer and more resilient communities.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities | OHCHR

Overcrowding
Overcrowded prisons and jails present a significant challenge to ensuring inmates’ rights. Advocates continue to push for reforms that address this issue.
nullFor a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Handbook on strategies to reduce overcrowding in prisons | UNODC

Mental Health Care
The lack of adequate mental health care within correctional facilities is a pressing concern. Advocacy efforts seek to improve mental health services and divert individuals with mental illnesses away from incarceration.
The inadequacy of mental health care within correctional facilities is a critical and urgent issue that demands immediate attention and reform. It is widely acknowledged that many individuals within the criminal justice system have significant mental health needs that often go unaddressed, leading to detrimental outcomes for both the individuals and society at large.
Advocacy efforts are crucial in this context, aiming to bring about meaningful change in the provision of mental health services within correctional facilities. One fundamental goal of these efforts is to shift the paradigm from punitive measures toward rehabilitation and treatment for individuals with mental illnesses. This involves diverting individuals away from incarceration whenever possible and connecting them with appropriate mental health care and support services.
By improving mental health services within correctional facilities, advocacy initiatives seek to ensure that individuals in custody receive the care and treatment they require. This can involve comprehensive mental health assessments, access to counseling and therapy, medication management, and specialized programs tailored to address the unique needs of individuals with mental illnesses.
Additionally, diversion programs are a key component of these advocacy efforts. These programs aim to identify individuals with mental illnesses at the pretrial stage and provide them with alternative options, such as mental health treatment, community-based support, or specialized courts like mental health courts. Diversion not only addresses the root causes of criminal behavior but also helps reduce the burden on an already overburdened criminal justice system.
Ultimately, the goal of these advocacy efforts is to break the cycle of incarceration for individuals with mental illnesses, reduce recidivism rates, and promote better mental health outcomes. By addressing the mental health needs of incarcerated individuals in a compassionate and effective manner, we can move toward a more just and humane criminal justice system that prioritizes treatment, recovery, and community reintegration over punishment.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Executive Order on Advancing Effective, Accountable Policing and …
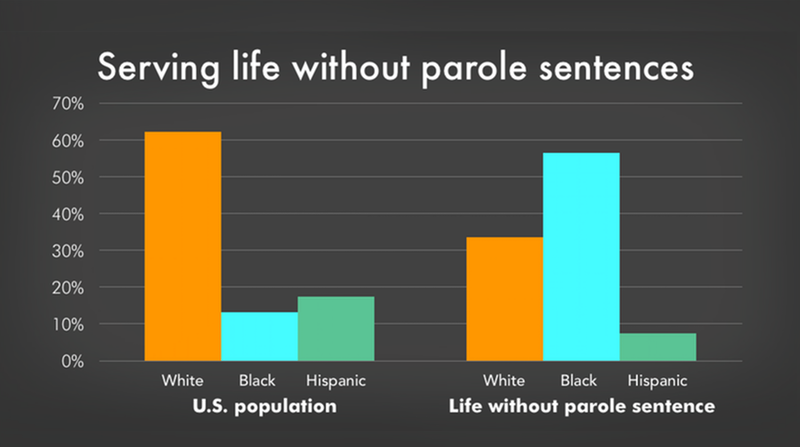
Racial Disparities
Advocates are at the forefront of addressing racial disparities in the criminal justice system, advocating for equitable treatment and an end to systemic racism.
Advocates dedicated to addressing racial disparities in the criminal justice system are engaging in a critical and multifaceted effort to bring about systemic change. Their work extends well beyond acknowledging the existence of disparities; it involves comprehensive strategies aimed at dismantling the structures that perpetuate racial inequality. Here are some key aspects of their mission:
Data Collection and Analysis: Advocates tirelessly collect and analyze data on arrest rates, sentencing disparities, and the impact of policies such as racial profiling and mandatory minimum sentences. These efforts help quantify the extent of racial disparities and serve as the foundation for evidence-based advocacy.
Policy Reform: Advocates collaborate with lawmakers and policymakers to push for reforms that address racial disparities. This includes advocating for changes in sentencing guidelines, bail practices, and drug policies that disproportionately affect communities of color.
Community Engagement: Advocates understand the importance of engaging directly with affected communities. They work to build trust, raise awareness, and empower individuals and families impacted by the criminal justice system.
Implicit Bias Training: Advocates advocate for the implementation of implicit bias training for law enforcement, judges, and other criminal justice professionals. This training helps reduce the influence of unconscious biases that can lead to racial disparities.
Reentry Support: Recognizing that the impact of racial disparities extends beyond incarceration, advocates support programs and policies that assist formerly incarcerated individuals in successfully reentering society. This includes access to housing, education, and job opportunities.
Legislation and Litigation: Advocacy groups often play a crucial role in initiating or supporting legislation and litigation that challenge discriminatory practices and policies in the criminal justice system. Landmark cases and new laws can set precedents for more equitable treatment.
Public Awareness and Accountability: Advocates use media campaigns, public demonstrations, and community forums to raise awareness about racial disparities and hold institutions accountable for addressing them. They amplify the voices of those directly affected by these disparities.
Collaboration: Advocates recognize that addressing racial disparities requires collaboration across various sectors, including education, healthcare, and employment. They work with other advocacy groups and institutions to create a comprehensive approach to systemic change.
Long-Term Commitment: Advocates understand that dismantling systemic racism within the criminal justice system is a long-term endeavor. They remain committed to their mission, advocating tirelessly for reform and equity.
In conclusion, advocates addressing racial disparities in the criminal justice system are instrumental in pushing for equitable treatment and an end to systemic racism. Their multifaceted efforts encompass data analysis, policy reform, community engagement, training, litigation, and collaboration across sectors. Their dedication to this vital cause represents a significant step towards achieving a more just and equitable society for all.
You can also read more about this here: Executive Order on Advancing Effective, Accountable Policing and …
Inmate rights and advocacy are integral components of a just and humane criminal justice system. Upholding the rights of incarcerated individuals not only reflects society’s commitment to justice but also contributes to safer communities and successful reintegration. As advocacy efforts continue to evolve, there is hope for a future where inmate rights are consistently respected, and the dignity of every individual within the criminal justice system is upheld.
Inmate rights and advocacy are integral components of a just and humane criminal justice system. Upholding the rights of incarcerated individuals not only reflects society’s commitment to justice but also contributes to safer communities and successful reintegration.
One critical aspect of inmate rights is ensuring that individuals in custody are treated with dignity and respect. Advocacy efforts have shed light on the importance of humane conditions of confinement, access to healthcare, and protection from abuse and mistreatment. These rights are not only enshrined in the law but also align with our shared values of fairness and compassion.
Moreover, advocating for inmate rights goes beyond the prison walls. It involves addressing systemic issues such as over-policing, racial disparities in sentencing, and the impact of poverty on incarceration rates. By advocating for reforms in these areas, we can help prevent unjust incarcerations in the first place, reducing the overall burden on the criminal justice system and fostering a more equitable society.
Advocacy also plays a vital role in promoting rehabilitation and reintegration. When inmates have access to education, job training, and mental health services, they are more likely to leave prison better equipped to lead law-abiding lives. Advocacy efforts have led to the development of innovative reentry programs that provide support and resources to individuals returning to their communities, reducing recidivism and enhancing public safety.
As advocacy efforts continue to evolve, there is hope for a future where inmate rights are consistently respected, and the dignity of every individual within the criminal justice system is upheld. This future envisions a system that prioritizes rehabilitation over retribution, prevention over punishment, and fairness over bias.
In conclusion, inmate rights and advocacy are cornerstones of a just and compassionate criminal justice system. By championing these principles, we can work towards a society where justice is truly blind, where the rights and dignity of all individuals are upheld, and where the cycle of incarceration is broken, leading to safer communities and a more equitable future for all.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Human Rights, Stigma, and Substance Use – PMC
More links
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Executive Order on Advancing Effective, Accountable Policing and …
