Table of Contents
The American jail system is profoundly shaped by politics and policy decisions. From sentencing laws to funding allocation, the political landscape plays a pivotal role in determining the structure, function, and outcomes of jails across the United States. This article delves into the multifaceted ways in which politics and policy impact the American jail system, highlighting key areas of influence and their implications.
The American jail system is profoundly shaped by politics and policy decisions. From sentencing laws to funding allocation, the political landscape plays a pivotal role in determining the structure, function, and outcomes of jails across the United States. This article delves into the multifaceted ways in which politics and policy impact the American jail system, highlighting key areas of influence and their implications.
Sentencing Laws and Criminal Justice Policies:
Mandatory Minimum Sentences: Political decisions have led to the establishment of mandatory minimum sentences for certain offenses. These policies limit judicial discretion and contribute to longer jail stays for individuals convicted of those offenses.
Three-Strikes Laws: The implementation of three-strikes laws in some states has resulted in harsh penalties, including life sentences, for individuals with repeat felony convictions. This has had a significant impact on jail populations.
War on Drugs Policies: Past policies, driven by political motivations, led to the mass incarceration of non-violent drug offenders. While some states have since adopted more lenient drug laws, the legacy of these policies still affects many jail systems.
Funding and Resource Allocation:
Budget Decisions: Political leaders make budgetary decisions that directly impact the funding allocated to jails. Adequate funding is necessary for maintaining facilities, providing services, and implementing reforms.
Diversion Programs: Political support for diversion programs, such as drug courts and mental health courts, can lead to reduced jail populations by offering alternative paths to rehabilitation and treatment.
Election of Prosecutors and Sheriffs:
Prosecutor Policies: The election of county prosecutors can influence the prosecution of cases, plea bargains, and sentencing recommendations, all of which have an impact on jail populations.
Sheriff Practices: Elected sheriffs oversee jail operations and can implement policies that affect conditions within the jail, including issues related to overcrowding and inmate treatment.
Bail Reform:
- Bail Policies: Political advocacy and policy changes have brought attention to the inequities of cash bail systems. Some jurisdictions have moved toward bail reform, which reduces pretrial detention rates.
Social and Racial Justice Movements:
- Activism and Reform: Social and racial justice movements have played a role in pushing for criminal justice reforms. This has led to changes in policies related to sentencing, bail, and diversion programs.
Impact on Vulnerable Populations:
- Disproportionate Impact: Political decisions can have a disproportionate impact on vulnerable populations, including communities of color and those with limited economic means. These groups are often disproportionately represented in jails.
Legislation and Advocacy:
- Advocacy Efforts: Political advocacy by organizations and activists can lead to policy changes and legislation aimed at improving jail conditions, addressing overcrowding, and promoting rehabilitation.
Implications:
The intersection of politics and policy with the American jail system has far-reaching implications:
Incarceration Rates: Political decisions can contribute to high incarceration rates, impacting individuals’ lives and communities.
Justice and Fairness: Political decisions can affect the fairness and equity of the criminal justice system, with consequences for marginalized populations.
Costs: Political choices influence the financial burden placed on taxpayers to maintain the jail system.
Reform Opportunities: Political will for reform can lead to positive changes, such as reduced jail populations and improved inmate outcomes.
Public Safety: Policy choices impact public safety, both within jails and in communities affected by reentry.
In conclusion, politics and policy are inextricably linked to the American jail system. Recognizing these connections and their consequences is essential for fostering a criminal justice system that is fair, effective, and aligned with the values and needs of society.
Tough-on-Crime Policies
Over the past few decades, the “tough-on-crime” approach has driven the enactment of stringent sentencing laws. Mandatory minimum sentences, “three strikes” laws, and enhanced penalties for drug offenses have contributed to the rapid growth of the jail population.
The “tough-on-crime” approach, which gained prominence over the past few decades, represents a significant shift in criminal justice policy that has left an indelible mark on the American prison system. While proponents of this approach argue that it was intended to enhance public safety and deter criminal behavior, its consequences have had far-reaching and complex implications.
One of the key features of the “tough-on-crime” era is the implementation of mandatory minimum sentences. These laws prescribe fixed, often lengthy prison terms for certain offenses, leaving judges with limited discretion in sentencing. While proponents argued that this approach would ensure consistency in punishment and deterrence, it has been criticized for its inflexibility and the potential for unduly harsh sentences, particularly in cases where individual circumstances are not taken into account.
Similarly, “three strikes” laws have had a profound impact on the growth of the jail population. These laws typically mandate life imprisonment for individuals convicted of a third felony, regardless of the nature of the offenses. While these laws were intended to target repeat offenders and violent criminals, they have also resulted in life sentences for non-violent offenses, contributing to the overcrowding of jails.
Enhanced penalties for drug offenses represent another facet of the “tough-on-crime” approach. The War on Drugs, characterized by stringent sentencing guidelines, resulted in lengthy prison terms for drug-related offenses, even for low-level offenders. This approach, rather than addressing the root causes of drug addiction and abuse, has contributed to the overrepresentation of drug offenders in the criminal justice system.
The consequences of the “tough-on-crime” approach extend beyond the sheer growth in the jail population. It has disproportionately affected communities of color, leading to racial disparities in incarceration rates. Additionally, it has strained correctional resources, leading to overcrowded and under-resourced jails, which can compromise safety and rehabilitation efforts.
As the shortcomings of the “tough-on-crime” approach become increasingly evident, there has been a growing momentum for criminal justice reform. Policymakers, activists, and communities are advocating for a more balanced and evidence-based approach to sentencing, one that considers factors like rehabilitation, diversion programs, and the root causes of criminal behavior. Reforms are underway to address the injustices and inefficiencies stemming from the era of punitive sentencing, aiming to create a more equitable and effective criminal justice system that prioritizes rehabilitation, fairness, and public safety.
You can also read more about this here: The 1994 Crime Bill and Beyond: How Federal Funding Shapes the …
War on Drugs
The political declaration of a “war on drugs” in the 1980s and 1990s led to the criminalization of drug offenses and the imprisonment of many non-violent drug offenders, significantly increasing the jail population.
The political declaration of a “war on drugs” in the 1980s and 1990s marked a pivotal moment in the history of criminal justice in the United States. This declared “war” ushered in a set of policies and practices that had profound and far-reaching consequences, particularly in terms of the criminalization of drug offenses and its impact on the soaring jail population.
Under the banner of this “war,” there was a substantial shift in how drug offenses were treated within the criminal justice system. Rather than prioritizing rehabilitation and treatment, the focus shifted towards punitive measures, including mandatory minimum sentences for drug-related offenses. This shift disproportionately affected non-violent drug offenders, many of whom were caught in the web of addiction and substance abuse.
The result was a dramatic increase in the number of individuals incarcerated for drug-related offenses. Prisons and jails became crowded with non-violent offenders, many of whom were low-level drug users or small-time dealers. This surge in the jail population not only strained correctional facilities but also had broader societal impacts. Families were torn apart as parents and siblings were incarcerated, and communities were destabilized by the removal of a significant portion of their residents.
Moreover, the “war on drugs” had a disproportionate impact on minority communities. Racial disparities in drug-related arrests and sentencing became increasingly evident, highlighting systemic injustices within the criminal justice system.
As the years passed, it became clear that the “war on drugs” had not achieved its intended goals of reducing drug use and addiction. Instead, it had contributed to the perpetuation of a cycle of incarceration and failed to address the root causes of substance abuse.
In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the need for reform in drug policy and criminal justice. Many jurisdictions are now shifting towards a more balanced approach that emphasizes diversion programs, treatment, and harm reduction. These reforms aim to address the underlying issues of addiction, reduce incarceration rates, and promote a more equitable and effective approach to drug-related offenses.
In hindsight, the “war on drugs” serves as a sobering lesson about the unintended consequences of well-intentioned policies and the importance of evidence-based, compassionate, and equitable approaches to criminal justice and substance abuse treatment.
Sentencing Disparities
Politics have also contributed to sentencing disparities, disproportionately affecting minority communities. Policies such as racial profiling and bias in sentencing have fueled concerns of systemic racism within the jail system.
null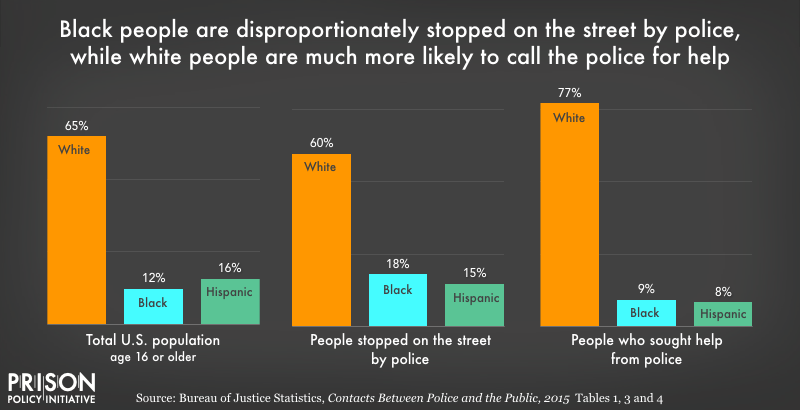
Budgetary Decisions
The allocation of funds to jails is a political process that reflects societal priorities. Politics can influence the amount of funding jails receive for staffing, infrastructure, healthcare, and rehabilitation programs.
The allocation of funds to jails is a dynamic and politically driven process that serves as a reflection of the prevailing societal priorities and attitudes toward criminal justice. In many ways, politics plays a pivotal role in shaping the financial landscape of correctional facilities, impacting critical areas such as staffing, infrastructure, healthcare, and rehabilitation programs.
At the heart of this process is the notion that budget decisions are, to a large extent, a reflection of what society values and prioritizes. The allocation of funds to jails often mirrors public sentiment and political ideologies, which can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another. For instance, some communities may prioritize punitive measures and emphasize a “tough on crime” approach, leading to greater allocations for staffing and security measures within jails.
Conversely, other jurisdictions may adopt a more progressive stance, recognizing the importance of rehabilitation and addressing the root causes of criminal behavior. In such cases, politics can result in increased funding for healthcare services, mental health counseling, and educational programs within correctional facilities. This reflects a broader recognition that rehabilitation efforts can contribute to reduced recidivism rates and the successful reintegration of individuals into society.
Political considerations also extend to issues like infrastructure improvement and modernization of correctional facilities. Decisions related to building or renovating jails often intersect with political debates on criminal justice reform. Some politicians may advocate for the construction of larger facilities to accommodate a growing inmate population, while others may push for more modest investments in rehabilitation-focused infrastructure.
The influence of politics on the allocation of funds to jails underscores the importance of advocacy and public engagement in shaping the criminal justice system. Advocates and activists play a vital role in raising awareness about the consequences of budgetary decisions, pushing for reforms that align with evidence-based practices and a more humane approach to incarceration.
Ultimately, the allocation of funds to jails reflects the broader societal conversation surrounding criminal justice. By engaging in these discussions, promoting transparency, and advocating for the allocation of resources in ways that prioritize rehabilitation, mental health services, and educational opportunities, we can collectively work toward a criminal justice system that aligns with the values and priorities of a just and equitable society.
Impact on Conditions
Inadequate funding can result in overcrowding, understaffing, and limited access to healthcare or rehabilitation services, negatively affecting inmate well-being and public safety.
The consequences of inadequate funding for jails go beyond overcrowding, understaffing, and limited access to essential services. Here’s a more comprehensive look at the implications:
Security Concerns: Inadequate funding can compromise the safety and security of both inmates and correctional staff. Understaffed jails may struggle to maintain order, respond to emergencies, and prevent violence among inmates, putting everyone at risk.
Healthcare Crisis: Limited funding can lead to a healthcare crisis within jails. Insufficient medical staff and resources may result in delayed or subpar medical care for inmates, exacerbating existing health conditions and posing public health risks, especially during disease outbreaks like COVID-19.
Mental Health Neglect: Many inmates have mental health needs that require attention and treatment. Inadequate funding often means insufficient mental health services, leaving inmates with untreated conditions that can lead to deteriorating mental health and increased risk of self-harm.
Overcrowding’s Impact: Overcrowded jails, often a result of insufficient funding for expansion or diversion programs, can lead to a host of problems, including increased violence, reduced access to programming, and compromised living conditions that negatively affect inmate well-being.
Rehabilitation Roadblocks: Inmates who seek rehabilitation and educational opportunities may face significant barriers when funding is lacking. Educational programs, vocational training, and substance abuse treatment are essential components of successful rehabilitation, but they are often the first to be cut in budget constraints.
Recidivism Rates: Inadequate funding can contribute to higher recidivism rates. When inmates lack access to essential services and rehabilitation programs, they are more likely to return to criminal behavior upon release, perpetuating a cycle of incarceration and reoffending.
Legal Liability: Underfunded jails may face legal liability for failing to provide constitutionally mandated services and protecting the rights of inmates. Lawsuits can result in costly settlements and further strain limited resources.
Community Safety: Ultimately, inadequate funding affects not only inmates but also the communities to which they will return upon release. Insufficient rehabilitation and support services can hinder successful reintegration, potentially endangering public safety.
In conclusion, the consequences of inadequate funding for jails are far-reaching and have profound effects on inmate well-being, staff safety, public health, and community safety. Addressing funding shortfalls within the criminal justice system is essential to ensuring that jails fulfill their mission of maintaining security, rehabilitating inmates, and contributing to a safer and more equitable society.
Bail Policies
Political decisions have a direct impact on bail policies, determining who remains in jail before trial and who is released. Cash bail practices have faced increasing scrutiny for disproportionately affecting low-income individuals.
Political decisions have a direct impact on bail policies, determining who remains in jail before trial and who is released. Cash bail practices have faced increasing scrutiny for disproportionately affecting low-income individuals, perpetuating a cycle of inequality within the criminal justice system.
The link between politics and bail policies is profound, as elected officials, judges, and lawmakers shape the laws and regulations governing pretrial detention. Decisions made at both the local and state levels can influence who gets detained solely because they can’t afford bail and who is allowed to await trial in the community.
One of the significant concerns surrounding cash bail is its inherent bias against those with limited financial means. When individuals are assigned bail amounts they cannot afford, they face the difficult choice of either remaining in jail or accepting a plea deal, often regardless of their guilt or innocence. This not only erodes the principle of presumed innocence until proven guilty but also perpetuates a system where poverty becomes a determining factor in pretrial freedom.
However, political decisions have the power to change this narrative. Reform efforts, driven by advocates, lawmakers, and community organizations, are pushing for alternatives to cash bail. These alternatives focus on risk assessment and individualized determinations, rather than a person’s ability to pay. They seek to ensure that pretrial decisions are based on public safety and flight risk, rather than economic status.
Moreover, political decisions can influence the allocation of resources within the criminal justice system. By investing in community-based support services, mental health programs, and diversion initiatives, policymakers can address the root causes of criminal behavior and reduce the need for pretrial detention. This not only enhances fairness but also promotes rehabilitation and reduces recidivism rates, leading to safer communities.
As political awareness of these issues continues to grow, there is hope for more equitable and just bail policies. Progressive reforms aim to reduce reliance on cash bail, implement risk assessment tools, and provide better support for low-income individuals caught in the criminal justice system. These changes reflect a broader societal commitment to fairness, justice, and the protection of individual rights.
In conclusion, the nexus between political decisions and bail policies is undeniable. As the flaws in cash bail practices become more evident, political will and advocacy are driving a movement toward reform that seeks to level the playing field and ensure that pretrial detention decisions are based on justice and safety, rather than financial status. By addressing these issues, political decisions can contribute to a fairer, more equitable criminal justice system that upholds the principles of justice for all.
Bail Reform Movements
Grassroots movements and political pressure have led to reforms aimed at reducing pretrial detention rates and promoting alternatives to cash bail, such as risk assessment tools and supervised release programs.
nullPolicy Support
The implementation of rehabilitation and reentry programs within jails depends on political support for such initiatives. These programs aim to reduce recidivism rates by providing education, job training, mental health services, and substance abuse treatment.
The successful implementation of rehabilitation and reentry programs within jails hinges on garnering political support for these initiatives. These programs are integral to transforming the criminal justice system and achieving multiple societal benefits. Expanding on this idea:
Political Advocacy for Reform: To establish and sustain rehabilitation and reentry programs, advocates must engage with policymakers and lawmakers. They need to make a compelling case for these initiatives by emphasizing their potential to enhance public safety, reduce the financial burden of incarceration, and promote a more equitable and compassionate approach to justice.
Recidivism Reduction: The primary objective of rehabilitation and reentry programs is to lower recidivism rates. By offering education, vocational training, mental health support, and substance abuse treatment, these programs address the root causes of criminal behavior. This not only benefits individual inmates but also contributes to a safer society by preventing reoffending.
Education as a Key Pillar: Education programs in jails equip inmates with valuable skills and knowledge, making them more employable upon release. Politicians who support education initiatives within correctional facilities recognize that providing inmates with the means to secure stable employment reduces their likelihood of returning to a life of crime.
Job Training and Employment Opportunities: Vocational training programs align with economic and workforce development goals. Political backing for these programs acknowledges the importance of equipping inmates with practical skills that enhance their employability, reduce unemployment rates among the formerly incarcerated, and promote self-sufficiency.
Mental Health and Substance Abuse Services: Politicians who advocate for mental health and substance abuse treatment within jails acknowledge the critical role these services play in addressing the underlying issues that contribute to criminal behavior. These programs prioritize the well-being and rehabilitation of inmates while supporting broader public health objectives.
Community Reintegration: Political support for reentry programs demonstrates an understanding of the importance of a smooth transition from incarceration back into the community. These programs help released individuals access housing, employment, and social services, reducing the likelihood of reoffending and contributing to community stability.
Cost Savings and Fiscal Responsibility: Rehabilitation and reentry programs are often seen as fiscally responsible investments. Politicians who champion these initiatives recognize that they can lead to long-term cost savings by reducing the strain on correctional budgets, lowering recidivism-related expenses, and contributing to overall economic productivity.
Addressing Racial Disparities: Rehabilitation and reentry programs can help address racial disparities within the criminal justice system. Politicians who support these initiatives acknowledge the importance of equity and inclusivity in the pursuit of justice reform.
Public Safety: Politicians who endorse rehabilitation and reentry programs emphasize their commitment to public safety. By reducing the chances of released individuals returning to criminal activity, these programs contribute to safer communities.
Evidence-Based Decision-Making: Political support for these programs is often rooted in evidence-based practices. Policymakers recognize the value of data-driven decisions and program evaluation to ensure that taxpayer dollars are being spent effectively and that outcomes align with program objectives.
In conclusion, garnering political support for rehabilitation and reentry programs within jails is pivotal for achieving lasting criminal justice reform. These programs address the multifaceted challenges facing incarcerated individuals and contribute to a safer and more just society. Politicians who champion these initiatives demonstrate a commitment to evidence-based, compassionate, and cost-effective solutions that benefit both inmates and the broader community. Their support plays a crucial role in reshaping the criminal justice landscape and fostering positive change within the system.

Political Will
The extent to which these programs are offered and funded can vary widely based on the political climate and priorities of a particular jurisdiction.
The availability and funding of rehabilitation programs within the American criminal justice system exhibit a remarkable degree of variability, often reflecting the prevailing political climate and the specific priorities of a given jurisdiction. This dynamic landscape underscores the significant impact that policy decisions and budget allocations can have on the success of rehabilitation initiatives. Here, we delve into the factors that influence the scope of these programs and why they are intrinsically linked to the prevailing political climate.
**1. Political Ideology: The political ideology of a jurisdiction’s leadership plays a pivotal role in shaping the availability of rehabilitation programs. Administrations with a strong focus on tough-on-crime policies may prioritize punitive measures over rehabilitation, leading to reduced funding for such programs. Conversely, leadership that emphasizes evidence-based and progressive approaches tends to be more supportive of rehabilitation initiatives.
**2. Budget Priorities: The allocation of financial resources is a central factor. The extent to which a jurisdiction prioritizes criminal justice reform and rehabilitation programs within its budget can determine the scope and effectiveness of these initiatives. Budget constraints or competing priorities may limit the funding available for rehabilitation efforts.
**3. Public Opinion: Public opinion and perception of crime and punishment can influence political decisions. Jurisdictions may respond to the desires of their constituents, which can lead to shifts in policy and funding for rehabilitation programs. Public support for rehabilitation often correlates with an increased focus on these initiatives.
**4. Criminal Justice Trends: Broader trends in criminal justice, such as the movement toward decarceration and the recognition of the ineffectiveness of mass incarceration, can shape political priorities. As society evolves, there is a growing acknowledgment of the need for more balanced and rehabilitative approaches within the criminal justice system.
**5. Advocacy and Awareness: The advocacy efforts of organizations and individuals within a jurisdiction can impact political decision-making. Awareness campaigns, lobbying, and grassroots movements can raise the profile of rehabilitation programs and influence policymakers to allocate resources accordingly.
**6. Research and Evidence: The availability of research and evidence demonstrating the effectiveness of rehabilitation programs is a key factor. Jurisdictions with access to compelling data on reduced recidivism rates and improved outcomes for participants are more likely to prioritize funding for these initiatives.
**7. Legislative Changes: Legislative action, including the passage of criminal justice reform bills, can mandate the expansion or improvement of rehabilitation programs. These legal mandates can drive changes in funding and program availability.
**8. Collaborative Efforts: Collaboration between government agencies, nonprofit organizations, and community stakeholders can help secure funding and support for rehabilitation programs. These partnerships can leverage resources and expertise to enhance the reach and impact of initiatives.
In conclusion, the political climate and priorities of a jurisdiction significantly influence the extent to which rehabilitation programs are offered and funded. Recognizing the intricate relationship between policy decisions, public sentiment, and budget allocations is essential for advocates and policymakers seeking to expand and strengthen rehabilitation efforts. As the landscape of criminal justice continues to evolve, the role of rehabilitation in reducing recidivism and fostering positive reintegration will remain a topic of critical importance.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: The History of Mass Incarceration | Brennan Center for Justice

Sheriff Elections
Local sheriff elections can impact jail policies, as sheriffs hold significant authority over jail operations. Their campaign promises and policy positions can shape the direction of the jail system.
Local sheriff elections can impact jail policies, as sheriffs hold significant authority over jail operations. Their campaign promises and policy positions can shape the direction of the jail system, influencing not only how it’s run but also its impact on the community. Expanding on this concept, we can explore the broader implications and considerations:
Transparency and Accountability: Sheriff elections bring issues related to jail policies into the public spotlight. Candidates often campaign on platforms that emphasize transparency, accountability, and responsible management of correctional facilities. This can lead to increased public scrutiny and engagement in matters of criminal justice.
Criminal Justice Reform: In recent years, many sheriff candidates have run on platforms of criminal justice reform. They advocate for alternatives to incarceration, mental health and addiction treatment, and reducing the jail population. Elected sheriffs who prioritize reform can work to implement evidence-based practices within the jail system.
Collaboration with Communities: Sheriffs play a pivotal role in fostering collaboration between law enforcement agencies, community organizations, and local government. This collaboration can lead to innovative approaches to inmate rehabilitation, diversion programs, and addressing the root causes of crime.
Inmate Treatment and Conditions: Sheriff elections can influence policies related to inmate treatment and conditions of confinement. Elected sheriffs may advocate for better access to healthcare, mental health services, and educational programs within jails to improve rehabilitation outcomes.
Reducing Overcrowding: Addressing jail overcrowding is a critical issue, and sheriffs have the authority to implement policies that aim to reduce it. This includes using alternatives to incarceration, bail reform, and diversion programs to ensure that the jail population is manageable and humane.
Inclusivity and Equity: Sheriff elections can also bring attention to issues of inclusivity and equity within the criminal justice system. Candidates may focus on reducing racial and socioeconomic disparities in arrests and sentencing, ultimately leading to more equitable jail policies.
Budget Allocation: Elected sheriffs have a say in how the budget is allocated within their jurisdiction, including funding for correctional facilities. Their priorities can influence resource allocation for inmate rehabilitation, staff training, and safety measures.
Staff Training and Oversight: Sheriff elections can impact staff training and oversight within jails. Candidates may emphasize the importance of ensuring that correctional officers are well-trained in handling inmates with respect and professionalism.
Recidivism Reduction: Elected sheriffs committed to reducing recidivism can implement programs and initiatives aimed at preparing inmates for successful reentry into society. This may involve job training, addiction treatment, and access to support services.
Public Opinion and Accountability: Ultimately, sheriffs are accountable to the electorate. If they fail to deliver on their campaign promises or if their policies lead to negative outcomes, they can face electoral consequences. This dynamic promotes responsiveness to public concerns.
In conclusion, sheriff elections are a critical component of the democratic process, shaping the direction of local jail policies and the broader criminal justice system. Engaged citizens and advocacy groups often play a pivotal role in holding elected sheriffs accountable for their promises and actions, ensuring that jail operations align with the evolving values and needs of the community.
County Commission Decisions
County commissioners often make funding decisions for jails, and their political affiliations and priorities can influence resource allocation.
null
The influence of politics on the American jail system is undeniable. Policy decisions related to sentencing, funding, bail, rehabilitation, and local governance have far-reaching consequences for inmates, communities, and society as a whole. Understanding the political dynamics that shape the jail system is crucial for promoting reform, addressing issues of fairness and equity, and ultimately working toward a more just and effective criminal justice system in the United States.
The interplay between politics and the American jail system is a complex and influential factor that extends well beyond the confines of correctional facilities. This relationship holds significant implications for the direction and impact of the criminal justice system. Here, we’ll delve deeper into the multifaceted influence of politics on the jail system and its broader consequences:
Sentencing Policies: Political decisions play a pivotal role in shaping sentencing policies, including the implementation of mandatory minimums and three-strikes laws. These policies directly affect the length of time individuals spend in jail, contributing to issues of overcrowding and the cost of incarceration.
Funding Allocation: Budget decisions made by policymakers determine the allocation of resources to the jail system. Adequate funding can support programs for rehabilitation, mental health services, and educational initiatives, while inadequate funding can lead to understaffing and limited access to essential services.
Bail Reform: Political debates surrounding bail reform influence whether individuals are detained pretrial or released. Decisions regarding cash bail and alternative pretrial release options have a direct impact on jail populations and can exacerbate issues of inequity for low-income individuals.
Rehabilitation Programs: The availability and quality of rehabilitation programs within jails often hinge on political priorities and funding. Progressive policies can promote the development of effective programs that address the underlying causes of criminal behavior and reduce recidivism.
Local Governance: The structure and management of jails can vary widely based on local governance and political leadership. Some jurisdictions emphasize diversion programs and community-based alternatives to incarceration, while others maintain a punitive approach.
Influence of Interest Groups: Political influence from interest groups, such as those representing law enforcement, private prison companies, or advocacy organizations, can shape policies related to the jail system. These groups may lobby for policies that align with their interests.
Impact on Communities: Political decisions regarding the jail system have a direct impact on communities, particularly marginalized and disadvantaged populations. Overly punitive policies can perpetuate cycles of poverty and incarceration, affecting not only individuals but entire neighborhoods.
Fairness and Equity: Political discourse surrounding criminal justice often centers on issues of fairness and equity. Policymakers have the opportunity to address disparities in sentencing, incarceration rates, and access to resources within the jail system.
Public Opinion and Accountability: The jail system is influenced by public opinion and electoral politics. Elected officials are accountable to their constituents, and shifts in public sentiment can drive changes in criminal justice policies.
Promoting Reform: Recognizing the political dimensions of the jail system is crucial for promoting reform efforts. Advocacy, activism, and grassroots movements often shape political will and lead to changes in policies and practices.
International Comparisons: Understanding how politics influence the jail system allows for comparisons with international models of criminal justice. It enables policymakers to draw insights from other countries’ approaches to incarceration and rehabilitation.
Balancing Punishment and Rehabilitation: Political decisions ultimately determine the balance between punitive measures and rehabilitation within the jail system. Striking the right balance is essential for achieving the goals of justice, public safety, and individual rehabilitation.
In conclusion, the influence of politics on the American jail system is undeniable and far-reaching. Recognizing and critically assessing this influence is essential for addressing issues of fairness, equity, and the cost-effectiveness of the criminal justice system. By engaging in informed debates, advocating for evidence-based policies, and promoting transparency and accountability, we can work toward a more just, equitable, and effective jail system that aligns with the values of society as a whole.
