Table of Contents
- American jails have been grappling with two interconnected challenges for years
- Incarceration Rates
- Limited Space
- Impact on Health Services
- Violence and Safety Concerns
- High Turnover Rates
- Recruitment Challenges
- Safety Risks
- Inmate Services
- Sentencing Reform
- Bail Reform
- Investing in Rehabilitation
- Staff Recruitment and Training
- Facility Expansion
American jails have been grappling with two interconnected challenges for years
overcrowding and understaffing. The overreliance on incarceration as a response to crime has led to an influx of inmates, overwhelming correctional facilities and stretching resources thin. Simultaneously, the shortage of qualified personnel has raised concerns about safety, inmate welfare, and the overall effectiveness of the criminal justice system. In this article, we will delve into the issues of overcrowding and understaffing in American jails, their root causes, consequences, and potential solutions.
The challenges of overcrowding and understaffing within American jails have far-reaching implications for both the incarcerated individuals and the broader criminal justice system. These issues have complex roots, multifaceted consequences, and require innovative solutions to alleviate their impact. Let’s explore these dimensions in more detail:
Root Causes:
Tough-on-Crime Policies: Overcrowding can be traced back to the era of tough-on-crime policies, which led to longer sentences, mandatory minimums, and an increased number of individuals entering the correctional system.
Lack of Alternatives: Inadequate investment in alternatives to incarceration, such as diversion programs, drug courts, and mental health treatment options, has contributed to the reliance on jails as the default response to crime.
Pretrial Detention: A significant portion of the jail population consists of individuals awaiting trial who may not pose a flight risk or threat to society. The inability to make bail keeps them in jail, exacerbating overcrowding.
War on Drugs: The war on drugs has resulted in a substantial number of non-violent drug offenders being incarcerated, further straining jail resources.
Mental Health Crisis: Jails have become de facto mental health institutions, as many individuals with mental health issues end up incarcerated due to a lack of appropriate mental health services in the community.
Underinvestment in Rehabilitation: A focus on punishment over rehabilitation has hindered efforts to reduce recidivism, leading to a revolving door of inmates returning to jail.
Consequences:
Safety Concerns: Overcrowding and understaffing pose safety risks for both inmates and correctional staff. Overcrowded conditions can lead to tensions, violence, and a higher likelihood of security breaches.
Inmate Welfare: Overcrowding can lead to inadequate healthcare, mental health services, and basic amenities for inmates, violating their rights and well-being.
Limited Rehabilitation: Understaffing reduces the capacity to provide educational, vocational, and rehabilitation programs, hindering inmates’ chances of successful reentry into society.
Legal Challenges: Overcrowding has led to legal challenges and court-ordered interventions, requiring jurisdictions to address the issue.
Financial Strain: Maintaining overcrowded jails is costly, diverting resources away from more effective crime prevention and rehabilitation efforts.
Community Impact: The high turnover of inmates due to overcrowding can disrupt communities as individuals cycle in and out of jail without addressing the underlying causes of their criminal behavior.
Potential Solutions:
Justice Reform: Implementing criminal justice reform measures, such as reducing mandatory minimum sentences and reevaluating sentencing policies, can reduce the influx of inmates.
Pretrial Reform: Expanding pretrial diversion programs, bail reform, and alternatives to detention can reduce the number of individuals held in jail while awaiting trial.
Mental Health Services: Investing in mental health services and crisis intervention teams can divert individuals with mental health issues away from the criminal justice system.
Community-Based Alternatives: Developing community-based alternatives to incarceration, such as restorative justice programs and drug treatment courts, can address the root causes of criminal behavior.
Staffing and Training: Increasing staffing levels and providing ongoing training for correctional personnel can improve safety and inmate welfare.
Reentry Support: Expanding reentry programs that provide inmates with essential life skills, job training, and support upon release can reduce recidivism.
Data-Driven Approaches: Using data to inform decision-making can help jurisdictions identify and address the drivers of overcrowding more effectively.
In conclusion, addressing the issues of overcrowding and understaffing in American jails requires a comprehensive and multidimensional approach. By addressing the root causes, implementing evidence-based solutions, and prioritizing rehabilitation over punitive measures, we can work toward a criminal justice system that is more effective, fair, and responsive to the needs of both inmates and society as a whole.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: High-quality health systems in the Sustainable Development Goals …

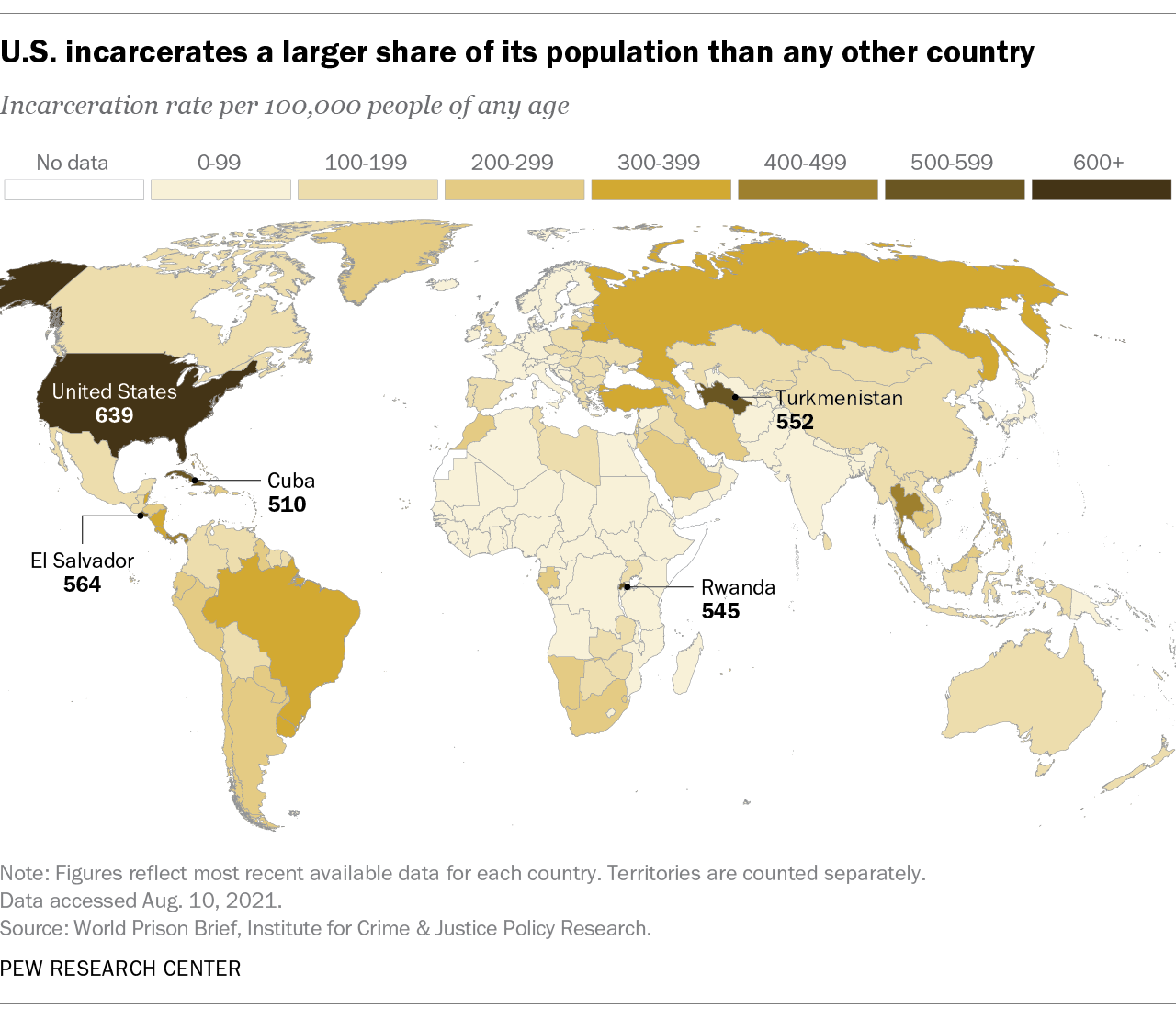
Incarceration Rates
The United States has one of the highest incarceration rates in the world, leading to a significant and sustained increase in the jail population. Factors contributing to this include tough sentencing laws, the war on drugs, and the criminalization of mental illness.
The United States’ exceptionally high incarceration rates have far-reaching consequences that extend beyond just the sheer numbers. This pressing issue is the result of a complex interplay of factors that demand attention and reform:
Tough Sentencing Laws: One key factor behind the surge in incarceration rates is the implementation of tough sentencing laws, such as mandatory minimum sentences and three-strikes laws. While these measures were intended to deter crime, they have led to disproportionately long prison terms for non-violent offenders, often without considering individual circumstances or rehabilitation prospects.
The War on Drugs: The “War on Drugs” policies of the past few decades have played a significant role in the over-incarceration crisis. The focus on punitive measures rather than addressing the root causes of drug addiction has led to the imprisonment of countless individuals, particularly from marginalized communities, for drug-related offenses.
Criminalization of Mental Illness: The criminal justice system has become an unintended repository for those with mental health issues. Instead of providing proper mental health treatment and support, individuals in crisis are often funneled into the criminal justice system, leading to a cycle of incarceration that exacerbates their conditions rather than addressing them.
Racial Disparities: It’s essential to recognize the stark racial disparities within the U.S. incarceration system. Black Americans, in particular, are disproportionately represented in the prison population, revealing systemic biases in policing, sentencing, and access to legal representation. Addressing racial disparities is a crucial aspect of any comprehensive reform effort.
Economic Costs: The financial burden of maintaining such a vast incarcerated population is substantial. These costs not only strain state budgets but also divert resources from more constructive investments in education, healthcare, and community programs that can address the root causes of crime.
Social Reintegration Challenges: High incarceration rates make reintegration into society after release even more challenging. Former inmates often face stigma, limited job opportunities, and a lack of support systems, which can increase the risk of recidivism.
International Comparisons: When compared to other developed nations, the United States’ approach to incarceration stands out as exceptionally punitive. Examining successful models of criminal justice from around the world can provide valuable insights into alternative methods of reducing crime and rehabilitating offenders.
In addressing the issue of high incarceration rates, it is essential to consider a holistic approach that encompasses sentencing reform, drug policy reform, mental health support, and efforts to tackle systemic biases. This multifaceted approach can lead to a more just and effective criminal justice system that prioritizes rehabilitation, reduces recidivism, and addresses the root causes of crime, ultimately benefiting both individuals and society as a whole.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Handbook on strategies to reduce overcrowding in prisons | UNODC
Limited Space
Many jails are operating above their intended capacity, with inmates often housed in conditions that are crowded and substandard. Overcrowding compromises the safety, well-being, and rehabilitation prospects of inmates.
The issue of overcrowding in many jails across the country is a pressing concern that warrants immediate attention. These facilities, originally designed to accommodate a specific number of inmates, are now strained beyond their intended capacity. This overcrowding has dire consequences that ripple throughout the criminal justice system and society at large.
First and foremost, the safety of both inmates and staff is compromised in overcrowded jails. The close quarters increase tensions and create a volatile atmosphere, leading to an elevated risk of violence and conflicts. Overworked correctional officers may find it challenging to maintain order and ensure the well-being of all inmates when they are stretched thin due to the sheer volume of people to oversee. This not only endangers lives but also exacerbates the cycle of criminality, as individuals are exposed to a toxic environment that fosters aggression rather than rehabilitation.
In addition to safety concerns, the well-being of inmates is severely impacted by overcrowding. Living in cramped conditions with limited access to resources, such as medical care and mental health services, can lead to deteriorating physical and mental health. Inmates may suffer from stress-related illnesses, infectious diseases, and inadequate nutrition. Moreover, the lack of privacy and personal space can erode an individual’s sense of dignity and self-worth, hindering their prospects for successful reintegration into society upon release.
Furthermore, overcrowding hampers the effectiveness of rehabilitation efforts within the correctional system. Programs designed to address underlying issues like substance abuse, anger management, and education may be under-resourced and oversubscribed. This means that inmates do not receive the necessary support and interventions to address the root causes of their criminal behavior, making it more likely that they will reoffend upon release.
The fiscal impact of overcrowding cannot be overlooked either. Operating jails above capacity strains resources, leading to higher operational costs, including increased staffing, healthcare expenses, and facility maintenance. These costs burden taxpayers and divert funds from more constructive initiatives, such as community-based rehabilitation programs and alternatives to incarceration that have been shown to reduce recidivism.
In conclusion, the issue of overcrowding in jails is a multi-faceted problem that compromises safety, well-being, and rehabilitation prospects for inmates. Addressing this issue requires a holistic approach that includes criminal justice reform, investment in community-based programs, and a commitment to finding alternatives to incarceration for non-violent offenders. By alleviating overcrowding, we can promote a safer, more humane, and more effective criminal justice system that ultimately benefits society as a whole.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Emerging Issues on Privatized Prisons
Impact on Health Services
Overcrowding strains healthcare services within correctional facilities, making it challenging to provide adequate medical and mental health care to inmates. This can lead to deteriorating health conditions and a risk to public health when individuals are released.
nullExplore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Handbook on strategies to reduce overcrowding in prisons | UNODC
Violence and Safety Concerns
Overcrowding can lead to heightened tensions among inmates, escalating violence, and security risks for both inmates and staff.
Overcrowding can lead to heightened tensions among inmates, escalating violence, and security risks for both inmates and staff. The ramifications of overcrowded correctional facilities go beyond the physical constraints of space and have far-reaching consequences that impact various aspects of the criminal justice system:
Increased Violence: Overcrowding fosters an environment where conflicts are more likely to arise. Inmates, forced to share limited resources and space, may become territorial or engage in disputes over personal boundaries, possessions, or privileges. These disputes can escalate into violence, putting both inmates and staff at risk.
Diminished Rehabilitation Opportunities: Overcrowding often strains the resources available for rehabilitation and educational programs. With limited access to these opportunities, inmates may miss out on crucial skill-building and counseling that could contribute to their successful reentry into society. This lack of rehabilitation can perpetuate a cycle of incarceration.
Mental Health Implications: The stress and anxiety of overcrowded conditions can exacerbate mental health issues among inmates. It can lead to increased incidents of depression, anxiety, and even self-harm. Addressing the mental health needs of inmates becomes even more challenging in crowded environments.
Staff Safety: Overcrowding not only jeopardizes inmate safety but also poses risks to correctional staff. Increased tensions and violence make it more challenging for staff to maintain order and security within the facility, potentially putting their own well-being at risk.
Legal and Ethical Concerns: Overcrowding may raise legal and ethical concerns related to inmates’ constitutional rights. Courts have, in some cases, ruled that overcrowded conditions amount to cruel and unusual punishment, violating the Eighth Amendment. Such rulings can result in costly litigation and mandated changes in prison operations.
Resource Strain: Overcrowding can strain correctional facilities’ resources, including personnel, medical services, and infrastructure. These strains can lead to budgetary challenges as agencies struggle to meet the increasing demands of a growing inmate population.
Inefficiencies: Overcrowding often leads to inefficiencies in day-to-day operations. For instance, meal distribution, medical care, and transportation become more complex and time-consuming, potentially diverting resources from essential programs and services.
Inmate Degradation: Overcrowded conditions can lead to the degradation of inmates’ physical and mental well-being. Living in cramped quarters with limited access to hygiene facilities can result in deteriorating health and a dehumanizing experience that erodes an individual’s sense of dignity.
Recidivism Risks: Overcrowding can undermine efforts to reduce recidivism rates. Inadequate access to education, vocational training, and counseling makes it more challenging for inmates to develop the skills and mindset needed for a successful reentry into society.
Community Safety: Ultimately, the consequences of overcrowding extend to community safety. Inmates released without adequate preparation due to overcrowding-related challenges may struggle to reintegrate into society, increasing the risk of reoffending and negatively impacting public safety.
Efforts to address overcrowding involve a combination of strategies, including sentencing reform, diversion programs, and improved reentry support. By alleviating overcrowded conditions, correctional facilities can provide a safer and more rehabilitative environment, benefiting both inmates and the communities they will eventually rejoin.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Why So Many Jails Are in a ‘State of Complete Meltdown’ | The …

High Turnover Rates
Jails often experience high turnover rates among correctional officers due to the demanding and stressful nature of the job. This can result in a lack of experienced personnel.
The high turnover rates among correctional officers in jails are emblematic of the unique challenges they face on a daily basis. The demanding and often emotionally taxing nature of the job places immense pressure on these dedicated professionals, contributing to a revolving door of personnel that, unfortunately, has far-reaching consequences for both the staff and the incarcerated individuals.
One of the immediate repercussions of this turnover is the loss of experienced officers. Seasoned correctional staff bring a wealth of knowledge and expertise to the table, honed through years of working in the complex and dynamic environment of a jail. They have a deep understanding of the facility’s operations, security protocols, and inmate dynamics, which is invaluable in maintaining order and safety.
When experienced officers depart, it disrupts the continuity of institutional knowledge and can lead to gaps in security and operational efficiency. New recruits, while well-trained, often require time to acclimate to the unique challenges of a correctional setting. This transition period can leave facilities vulnerable to incidents that could have been prevented with the presence of seasoned personnel.
Furthermore, high turnover rates have a cascading effect on morale among correctional officers. When colleagues frequently come and go, it can erode the sense of camaraderie and teamwork that is crucial for maintaining a positive work environment. Lower morale can contribute to burnout and further exacerbate the stressors of the job, potentially leading to more departures.
Addressing the issue of turnover among correctional officers necessitates a multi-faceted approach. It involves improving working conditions, providing mental health support, and offering opportunities for career advancement and development. Additionally, comprehensive training programs can help new recruits adapt more quickly to the rigors of the job, although retaining experienced personnel remains a top priority.
In the long term, recognizing the value of correctional officers and providing them with the support they need can not only reduce turnover but also enhance the overall safety and effectiveness of correctional facilities. It’s essential to view correctional officers not just as employees but as crucial partners in the rehabilitation and reformation of inmates, and to invest in their well-being accordingly. By doing so, we can work towards creating a more stable and secure environment within our jails.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Workforce Issues in Corrections | National Institute of Justice

Recruitment Challenges
Recruiting qualified correctional staff can be challenging, as the job requires specialized training and carries significant responsibilities. A shortage of qualified candidates exacerbates the problem.
Recruiting and retaining qualified correctional staff presents an ongoing challenge within the criminal justice system, and the difficulties associated with this process have far-reaching consequences.
The role of correctional staff is multifaceted and demanding. It encompasses responsibilities such as ensuring the safety and security of inmates, implementing rehabilitation programs, and maintaining order within correctional facilities. To effectively fulfill these duties, correctional staff members need specialized training in areas like conflict resolution, crisis management, and behavioral psychology. Finding individuals with the right skill set and a strong commitment to upholding justice can be a daunting task.
The shortage of qualified candidates compounds the issue. As the demand for correctional staff continues to grow due to rising incarceration rates or staff turnover, correctional facilities often struggle to fill open positions with adequately trained and experienced individuals. This staffing shortage can result in overworked and stressed employees, which can, in turn, lead to burnout, reduced morale, and decreased job satisfaction. Ultimately, these factors can jeopardize the safety and well-being of both staff and inmates.
Moreover, the difficulty in recruiting qualified correctional staff can have a direct impact on the effectiveness of rehabilitation and reentry programs. These programs rely on the expertise and dedication of staff members to provide inmates with the support and guidance needed for successful reintegration into society. When facilities are understaffed or staffed by individuals who lack the necessary qualifications, the quality and availability of these programs may suffer, hindering the rehabilitation process and increasing the risk of recidivism.
Addressing the challenge of recruiting qualified correctional staff requires a multifaceted approach. It involves offering competitive salaries and benefits to attract and retain talent, investing in ongoing training and professional development, and creating a positive work environment that fosters job satisfaction and long-term commitment. By tackling this issue head-on, the criminal justice system can improve safety within correctional facilities, enhance the effectiveness of rehabilitation efforts, and ultimately contribute to more successful reintegration and reduced rates of recidivism.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Understanding and Addressing Staff Shortages in Corrections …

Safety Risks
Understaffing compromises the safety of correctional officers, who are often outnumbered by inmates. It also hampers their ability to respond effectively to incidents and emergencies.
nullTo delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Understanding and Addressing Staff Shortages in Corrections …

Inmate Services
A shortage of staff impacts the ability to provide essential services to inmates, including educational programs, mental health counseling, and rehabilitation initiatives.
The shortage of staff within correctional facilities has far-reaching consequences that ripple throughout the entire system, significantly impeding the ability to deliver critical services to inmates. This staffing deficit is not merely a matter of numbers; it directly affects the well-being of incarcerated individuals and the overall success of rehabilitation efforts.
One of the most immediate and noticeable impacts of staff shortages is the strain it places on the delivery of essential services. Educational programs that are instrumental in helping inmates acquire valuable skills for reintegration into society often suffer from limited staffing. As a result, the access to educational opportunities becomes inconsistent, hindering the prospects of inmates seeking to improve themselves during their incarceration.
Mental health counseling, another vital service within correctional facilities, is also adversely affected. The shortage of mental health professionals can lead to delays in diagnosing and treating mental health conditions among inmates, exacerbating the already challenging issue of mental illness within the incarcerated population. Timely intervention and counseling are critical for preventing the escalation of mental health issues and promoting overall well-being.
Rehabilitation initiatives, which play a pivotal role in reducing recidivism and facilitating successful reentry into society, are similarly compromised. Inadequate staffing levels can result in limited access to rehabilitation programs, including substance abuse treatment, vocational training, and cognitive-behavioral therapy. These programs are essential for addressing the root causes of criminal behavior and preparing individuals for a law-abiding life upon release.
The consequences of staff shortages extend beyond the immediate impact on inmates. They also place immense strain on the correctional staff themselves, leading to burnout, fatigue, and increased stress levels. Overworked and understaffed correctional officers may struggle to maintain safety and security within the facility, which can escalate tensions and potentially compromise the overall environment.
Addressing the staffing shortage within correctional facilities is imperative for the well-being of both inmates and staff, as well as the broader goals of rehabilitation and public safety. This may involve investing in recruitment and retention efforts, improving working conditions, and exploring innovative approaches to service delivery. By adequately staffing correctional facilities, we can enhance the chances of successful rehabilitation, reduce recidivism rates, and create safer environments for both inmates and those tasked with overseeing them.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Understaffed and Overcrowded: State Prisons Crippled by Budget …

Sentencing Reform
Reevaluating sentencing laws and promoting alternatives to incarceration can reduce the flow of inmates into jails, alleviating overcrowding.
Reevaluating sentencing laws and promoting alternatives to incarceration represents a multifaceted approach to addressing jail overcrowding, and it carries several important benefits:
Reducing Nonviolent Offenders: Many individuals in jails are nonviolent offenders who do not pose a significant risk to public safety. Reevaluating sentencing laws to favor alternatives such as probation, community service, or drug rehabilitation programs can divert these individuals away from incarceration, freeing up valuable jail space for more serious offenders.
Cost Savings: Alternatives to incarceration are often more cost-effective than housing inmates in jails. Resources that would otherwise be spent on maintaining overcrowded facilities can be redirected toward rehabilitation and support programs that address the underlying causes of criminal behavior.
Rehabilitation Focus: Alternative sentencing options provide an opportunity to focus on rehabilitation and addressing the root causes of criminal conduct. This approach can reduce recidivism rates and improve long-term public safety outcomes.
Pretrial Detention: Reevaluating bail practices and promoting alternatives like electronic monitoring or community supervision for low-risk pretrial detainees can alleviate overcrowding in jails. This approach ensures that individuals who pose minimal flight or safety risks are not needlessly incarcerated while awaiting trial.
Diversion Programs: Specialized diversion programs for individuals with mental health or substance abuse issues can be more effective at addressing their needs than incarceration. By providing treatment and support, these programs can help individuals reintegrate into society successfully, reducing the likelihood of future arrests.
Community Reintegration: Emphasizing alternatives to incarceration aligns with the broader goal of successful community reintegration. It encourages individuals to remain connected with their communities, maintain employment, and support their families, which ultimately benefits society as a whole.
Reserving Jail Space: By reserving jail space for individuals who pose a genuine threat to public safety, the criminal justice system can prioritize the protection of communities while also addressing the needs of lower-risk individuals through alternative sentencing.
In conclusion, reevaluating sentencing laws and promoting alternatives to incarceration is a forward-thinking approach that offers numerous advantages. It reduces overcrowding, saves costs, prioritizes rehabilitation, and contributes to more effective and humane criminal justice practices. By shifting the focus from punitive measures to restorative and rehabilitative ones, the criminal justice system can work toward better outcomes for both individuals and society as a whole.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Prison overcrowding – Penal Reform International
Bail Reform
Implementing bail reform measures can help reduce pretrial detention rates, easing the burden on jails.
Implementing bail reform measures can help reduce pretrial detention rates, easing the burden on jails. This not only addresses the issue of overcrowding but also has broader societal and economic implications that contribute to a more equitable and efficient criminal justice system.
One of the significant benefits of bail reform is its potential to promote fairness in the legal process. Under traditional bail systems, individuals with limited financial resources often find themselves stuck in pretrial detention simply because they cannot afford to pay bail. This wealth-based inequality can result in innocent individuals pleading guilty to avoid prolonged detention, undermining the principles of justice and due process.
Bail reform, which aims to replace cash bail with risk assessments, helps level the playing field. By assessing an individual’s flight risk and danger to the community, courts can make more informed decisions about whether to detain or release a defendant. This approach ensures that pretrial detention is based on objective criteria rather than financial status, reducing the likelihood of unjust imprisonment and promoting the presumption of innocence until proven guilty.
Additionally, bail reform can have a positive economic impact. Maintaining a large pretrial detainee population is costly, as it requires resources for housing, food, medical care, and security. By reducing pretrial detention rates, jurisdictions can allocate these funds to other pressing needs, such as education, healthcare, and community-based programs that address the root causes of crime. This reallocation of resources can contribute to economic growth and improve the overall well-being of communities.
Moreover, bail reform can help reduce recidivism rates. When individuals are detained pretrial, they often lose their jobs, housing, and support networks. These destabilizing factors can increase the likelihood of reoffending upon release. In contrast, bail reform measures that prioritize community supervision and support services help individuals maintain their ties to the community and access necessary resources, reducing their risk of returning to the criminal justice system.
Lastly, bail reform fosters trust in the criminal justice system. When the public sees that decisions regarding pretrial detention are based on risk assessments rather than financial considerations, it enhances perceptions of fairness and transparency. This trust can lead to increased cooperation with law enforcement, better community engagement, and improved overall public safety.
In conclusion, bail reform not only eases the burden on jails but also promotes fairness, efficiency, and economic growth within the criminal justice system. By reducing pretrial detention rates, jurisdictions can create a more just and equitable legal process that aligns with the principles of justice and the preservation of individual rights while contributing to the betterment of society as a whole.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Prison Conditions

Investing in Rehabilitation
Redirecting resources towards rehabilitation and reentry programs can help reduce recidivism and lower the overall jail population.
nullFor a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Prison overcrowding – Penal Reform International

Staff Recruitment and Training
Improving recruitment strategies, offering competitive salaries, and investing in ongoing training can attract and retain qualified correctional officers.
Elevating the standards and professionalism of correctional officers is essential for the effective operation of correctional facilities and the well-being of both staff and inmates. Expanding on the idea of improving the recruitment, retention, and training of correctional officers:
Comprehensive Recruitment Strategies: Effective recruitment begins with identifying individuals who possess the right qualities for the job. Correctional facilities should develop comprehensive recruitment strategies that not only attract candidates but also assess their suitability for the demanding role. This might include comprehensive background checks, psychological evaluations, and interviews to gauge their temperament, ethical standards, and communication skills.
Competitive Salaries and Benefits: Offering competitive salaries and benefits is crucial for attracting and retaining qualified correctional officers. Adequate compensation not only acknowledges the challenging nature of the job but also reduces turnover rates. Competitive benefits packages that include healthcare, retirement plans, and professional development opportunities can further enhance job satisfaction.
Specialized Training Programs: Ongoing training is vital for the professional development of correctional officers. Implementing specialized training programs that focus on crisis intervention, de-escalation techniques, cultural competency, and mental health awareness equips officers with the skills necessary to handle complex situations effectively. Regular refresher courses ensure that they stay up-to-date with the latest best practices.
Mental Health Support: Working in a correctional environment can be mentally taxing. Offering mental health support services, such as counseling and stress management programs, can help officers cope with the unique stressors of their profession. Ensuring that they have access to these resources can contribute to their overall well-being and job satisfaction.
Career Advancement Opportunities: Establishing clear pathways for career advancement within the correctional field is essential for retaining skilled officers. Providing opportunities for promotions, leadership training, and specialized roles within the facility not only recognizes their dedication but also motivates them to excel in their careers.
Safe Working Conditions: Ensuring safe working conditions is fundamental. Correctional officers must have access to protective equipment and training to manage security risks effectively. Facilities should also take measures to minimize the risk of violence within the institution, such as implementing effective inmate classification systems and conflict resolution programs.
Community Engagement and Support: Engaging with the local community and building positive relationships can enhance the image of the correctional facility and foster support for the officers. Community partnerships can also provide resources and programs that benefit both inmates and staff.
Ethical Leadership and Accountability: Effective leadership within the correctional system is critical. Leaders should set an example of professionalism, ethical conduct, and accountability. This not only fosters a positive organizational culture but also helps retain officers who value integrity and ethical standards.
Diversity and Inclusion Initiatives: Embracing diversity and inclusion initiatives can create a more welcoming and inclusive work environment. Encouraging diversity among correctional officers ensures a broader range of perspectives and experiences, which can contribute to better decision-making and more effective interactions with a diverse inmate population.
Feedback Mechanisms: Providing correctional officers with a voice through feedback mechanisms can empower them to share concerns, suggest improvements, and contribute to decision-making processes. This involvement can increase job satisfaction and create a sense of ownership within the organization.
In summary, investing in recruitment, retention, and ongoing training is pivotal for maintaining a professional and skilled correctional workforce. By implementing these strategies, correctional facilities can attract and retain officers who are not only well-prepared for the challenges of the job but also committed to upholding ethical standards and promoting a safe and rehabilitative environment within the correctional system.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: 5 of the biggest challenges facing corrections in 2019

Facility Expansion
In some cases, expanding jail facilities or building new ones may be necessary to address overcrowding, provided it is accompanied by comprehensive criminal justice reform efforts.
Addressing overcrowding within the corrections system often necessitates the expansion of existing jail facilities or the construction of new ones. However, it’s crucial to recognize that expanding jail capacity should be viewed as just one facet of a more comprehensive approach to criminal justice reform. Let’s explore how such expansion can be part of a broader strategy aimed at fostering positive change within the system.
**1. Assessment of Needs: Before embarking on jail expansion projects, a thorough assessment of needs should be conducted. This includes analyzing current population trends, reviewing the reasons for overcrowding, and considering alternative approaches to address root causes of incarceration, such as substance abuse or mental health issues.
**2. Modern Facilities: If expansion is deemed necessary, it provides an opportunity to build modern, efficient, and more humane facilities. Such facilities can incorporate design principles that prioritize inmate safety, rehabilitation, and access to support services. Additionally, they can be designed with environmental sustainability in mind.
**3. Alternatives to Incarceration: Simultaneously, criminal justice reform efforts should focus on reducing the need for incarceration through alternatives such as diversion programs, mental health courts, drug courts, and community supervision. By diverting individuals away from jail and into treatment or support programs, the demand for expanded facilities can be mitigated.
**4. Pretrial Justice Reform: A significant portion of jail populations consists of individuals awaiting trial, many of whom are detained simply because they cannot afford bail. Pretrial justice reform, including bail reform and speedy trial initiatives, can reduce the pressure on jail capacities by ensuring that pretrial detention is reserved for those who pose a genuine flight risk or threat to public safety.
**5. Reentry and Rehabilitation Programs: To further alleviate overcrowding, emphasis should be placed on reentry and rehabilitation programs that reduce recidivism. Investing in education, job training, and support services for inmates can increase their chances of successful reintegration into society, reducing the need for re-incarceration.
**6. Data-Driven Decision-Making: Utilizing data to inform expansion decisions is crucial. Understanding the demographics and needs of the incarcerated population allows for targeted interventions and efficient resource allocation. Data can also help measure the impact of reforms and assess the ongoing need for expanded jail capacity.
**7. Community Involvement: Engaging the community in discussions about criminal justice reform and jail expansion is essential. Input from community members, stakeholders, and advocacy groups can lead to more balanced and informed decisions, ensuring that expansion efforts align with community values and needs.
**8. Oversight and Accountability: Effective oversight and accountability mechanisms must be in place to ensure that jail expansion efforts adhere to best practices, respect inmates’ rights, and deliver on their intended outcomes. Transparency and public reporting can help maintain trust and accountability.
In conclusion, expanding jail facilities can be a necessary response to overcrowding, but it should be embedded within a broader context of criminal justice reform. Comprehensive efforts should seek to reduce the overall reliance on incarceration, improve conditions for inmates, and prioritize rehabilitation and reintegration. Expansion, when coupled with these reform strategies, can contribute to a more effective and just criminal justice system that promotes both public safety and individual well-being.
You can also read more about this here: Handbook on strategies to reduce overcrowding in prisons | UNODC

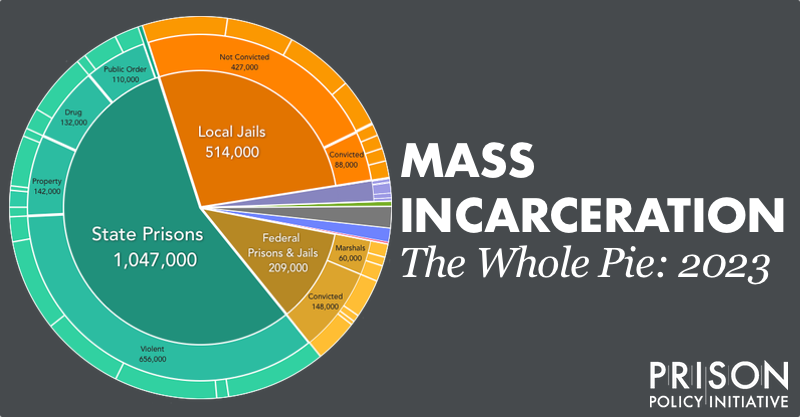
Overcrowding and understaffing are pressing issues that American jails face daily. These challenges not only impact the safety and well-being of inmates and staff but also raise fundamental questions about the efficacy of the criminal justice system. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach that includes criminal justice reform, sentencing reform, investment in rehabilitation, and comprehensive strategies to attract and retain qualified correctional personnel. By tackling overcrowding and understaffing, the United States can move toward a more just and effective criminal justice system that prioritizes safety, rehabilitation, and the welfare of all its citizens.
More links
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Understanding and Addressing Staff Shortages in Corrections …
