Introduction
As urban areas continue to expand and encroach upon natural habitats, human-wildlife conflicts have become increasingly common. The clash between human development and wildlife survival poses challenges that demand innovative solutions. Fortunately, successful initiatives from around the world provide valuable lessons on how to effectively manage these conflicts and create harmonious coexistence in urban environments.
As urban areas continue to expand and encroach upon natural habitats, human-wildlife conflicts have become increasingly common. The clash between human development and wildlife survival poses challenges that demand innovative solutions. Fortunately, successful initiatives from around the world provide valuable lessons on how to effectively manage these conflicts and create harmonious coexistence in urban environments.
One key lesson is the importance of proactive urban planning and wildlife management. Cities that consider wildlife in their development strategies are better equipped to prevent conflicts from arising in the first place. This can involve preserving green spaces, creating wildlife corridors, and setting aside areas specifically designed to support local fauna. The incorporation of wildlife-friendly infrastructure, such as wildlife bridges and tunnels, can also minimize potential hazards for animals and humans alike.
Education plays a pivotal role in fostering coexistence. Communities that understand the importance of local wildlife are more likely to support conservation efforts. Public awareness campaigns, school programs, and community engagement initiatives can raise awareness about the value of urban biodiversity and the necessity of responsible interactions with wildlife.
Additionally, successful urban wildlife management often includes non-lethal approaches. Relocation and humane deterrents can be effective in minimizing conflicts without resorting to harm or extermination. These approaches are not only more ethical but can also be more sustainable in the long term.
Collaboration between local governments, conservation organizations, and the community is essential. By working together, these stakeholders can develop comprehensive strategies that take into account the needs of both humans and wildlife. In some cases, citizen science projects can engage residents in monitoring urban wildlife populations, contributing valuable data for research and conservation efforts.
It’s also crucial to recognize that urban wildlife can offer tangible benefits to cities. Many species provide ecosystem services like pollination and pest control, which can enhance the quality of life for urban residents. By valuing and protecting these services, cities can foster a greater appreciation for the wildlife that shares their environment.
In conclusion, the challenges of human-wildlife conflicts in urban areas are real and complex, but they are not insurmountable. By drawing on successful initiatives and best practices from around the world, we can learn how to manage these conflicts effectively and create urban environments where humans and wildlife can coexist in harmony. As cities continue to grow and evolve, the lessons learned from these initiatives are more critical than ever to ensure a sustainable and thriving future for all.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Strategy for preventing and managing human wildlife conflicts in …
The city of Chicago, nestled along Lake Michigan, is home to a thriving population of urban coyotes. These adaptable canids have found a way to share the city with millions of residents. Chicago’s success in coexisting with coyotes is attributed to a multifaceted approach:
The city of Chicago, nestled along Lake Michigan, is home to a thriving population of urban coyotes. These adaptable canids have found a way to share the city with millions of residents. Chicago’s success in coexisting with coyotes is attributed to a multifaceted approach that serves as a model for harmonious human-wildlife cohabitation in urban environments.
1. Public Awareness and Education: Chicago has invested in public awareness and education programs to inform residents about coyotes and their behavior. These initiatives have helped dispel myths and misconceptions while fostering a greater understanding of coyotes’ role in urban ecosystems. By providing residents with information on how to peacefully coexist with these animals, the city has contributed to minimizing conflicts.
2. Responsible Garbage Management: Chicago has implemented stringent garbage management practices, such as secured trash bins, which deter coyotes from scavenging in neighborhoods. By reducing easily accessible food sources, the city has helped discourage coyotes from becoming too habituated to human-provided food.
3. Green Spaces and Habitat Preservation: Chicago has actively preserved green spaces and natural habitats within the city, offering critical areas for coyotes to forage and establish dens. This proactive conservation approach ensures that these adaptable canids have access to suitable environments while maintaining ecological balance.
4. Wildlife Monitoring and Research: The city has invested in wildlife monitoring and research efforts to better understand coyote behavior, population dynamics, and movements within the urban landscape. This data-driven approach helps inform urban planning and management strategies, contributing to successful coexistence.
5. Humane Coexistence Policies: Chicago has adopted a humane coexistence policy, emphasizing non-lethal methods for managing conflicts with coyotes. This includes techniques like hazing, which involves making coyotes uncomfortable around humans, and relocation when necessary.
6. Collaboration with Experts: The city collaborates with wildlife experts and organizations to develop and implement effective coyote management strategies. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that decisions are based on scientific knowledge and ethical considerations.
Chicago’s experience with urban coyotes serves as a testament to the potential for wildlife and humans to peacefully coexist in urban environments. By combining public education, responsible management practices, habitat preservation, and a commitment to humane coexistence, the city has created a harmonious balance that allows both residents and coyotes to thrive together. This model can inspire other urban areas worldwide to adopt similar approaches and embrace the unique wildlife that shares our urban landscapes, ultimately fostering a more sustainable and compassionate coexistence.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Coyote Management & Coexistence Plan | City of Chicago

Peregrine falcons, once on the brink of extinction due to the effects of the pesticide DDT, have made a remarkable comeback in cities worldwide, including New York City. These raptors have adapted to skyscraper living, nesting on building ledges high above the streets. The city’s initiative to protect these birds provides several key takeaways:
Peregrine falcons, once on the brink of extinction due to the effects of the pesticide DDT, have made a remarkable comeback in cities worldwide, including New York City. These raptors have adapted to skyscraper living, nesting on building ledges high above the streets. The city’s initiative to protect these birds provides several key takeaways:
1. Resilience of Wildlife: The recovery of peregrine falcons in urban environments demonstrates the remarkable resilience of wildlife in the face of adversity. Despite facing near-extinction, these birds have not only survived but thrived in the midst of one of the world’s busiest urban landscapes.
2. Urban Biodiversity: Peregrine falcons are just one example of the diverse range of wildlife that can coexist with humans in urban areas. Their presence highlights the importance of preserving and promoting urban biodiversity, as cities can play a vital role in the conservation of species threatened elsewhere.
3. Adaptive Behavior: The peregrine falcons’ adaptation to skyscraper living showcases the incredible adaptability of wildlife when presented with new opportunities. By nesting on high-rise buildings, they’ve found a safe haven amidst the urban hustle and bustle, revealing how nature can find innovative solutions to challenges.
4. Community Engagement: The city’s efforts to protect these raptors have fostered community engagement and education about wildlife conservation. Local residents, schools, and organizations often come together to support peregrine falcon protection initiatives, fostering a sense of shared responsibility for urban nature.
5. Ecological Balance: Peregrine falcons play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance by controlling populations of pigeons and other urban birds. Their presence helps manage potential urban pests in a natural and sustainable manner.
6. Environmental Recovery: The recovery of peregrine falcons is a testament to the positive impact of environmental regulations and policies. The ban on DDT and other harmful pesticides allowed these birds to rebound, underscoring the importance of sound environmental management.
7. Global Inspiration: The success of peregrine falcon conservation in cities like New York serves as an inspiration for other urban areas around the world. It demonstrates that with proper protection and support, even endangered species can find a home in the urban jungle.
In conclusion, the resurgence of peregrine falcons in New York City symbolizes the potential for harmonious coexistence between humans and wildlife in urban environments. It reminds us of the critical role cities can play in conservation efforts and highlights the importance of protecting and celebrating the natural world in the heart of our urban landscapes.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Public perceptions and attitudes toward urban wildlife encounters …

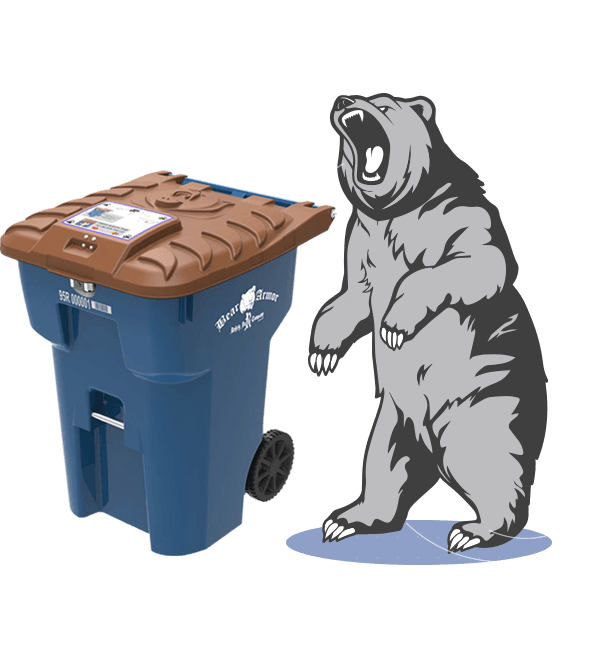
In Lake Tahoe, a popular destination for both tourists and black bears, human-bear conflicts were on the rise due to bears accessing unsecured garbage bins. To address this issue, the community implemented a simple yet effective solution:
In Lake Tahoe, a renowned destination cherished by both tourists and its resident black bear population, a growing concern was the escalating human-bear conflicts, primarily stemming from bears accessing unsecured garbage bins. The community recognized the need for innovative solutions to mitigate these conflicts and maintain the delicate balance between human activities and the natural environment. In response to this challenge, they implemented a straightforward yet highly effective solution that has not only reduced conflicts but also served as an inspiring model for other regions facing similar issues.
Community Education and Engagement: The first step in this initiative involved a robust community education and engagement effort. Local authorities, environmental organizations, and community leaders collaborated to educate residents and tourists about the importance of secure garbage disposal practices. They emphasized that the responsibility for minimizing human-bear conflicts rested on everyone’s shoulders, and they encouraged active participation.
Bear-Resistant Trash Bins: One of the cornerstones of this solution was the widespread adoption of bear-resistant trash bins. The community made it easy for residents and businesses to acquire these specialized containers by offering incentives and subsidies. Bear-resistant bins are designed to withstand the strength and ingenuity of bears, making it significantly more challenging for them to access the contents inside. This innovation not only protected bears but also maintained the cleanliness of the area, enhancing the overall visitor experience.
Stricter Enforcement and Fines: To further discourage improper garbage disposal, the community implemented stricter enforcement measures and imposed fines for those who did not comply with the bear-resistant bin requirements. This created a powerful incentive for individuals to take the issue seriously and ensure they were part of the solution rather than the problem.
Community Collaboration and Monitoring: A vital aspect of the success of this solution was the ongoing collaboration among residents, local authorities, and wildlife experts. Regular monitoring of bear activity and garbage disposal practices allowed the community to adapt and refine their strategies as needed. The shared commitment to coexisting with bears in a respectful and responsible manner created a strong sense of unity within the community.
Measurable Success: Over time, the impact of these efforts became evident. The number of bear-related conflicts, including property damage and human-bear encounters, significantly decreased. Bear populations remained healthy, and the community continued to enjoy the presence of these magnificent creatures while ensuring the safety and well-being of both residents and tourists.
In conclusion, Lake Tahoe’s approach to mitigating human-bear conflicts serves as a shining example of how proactive community engagement, education, and the implementation of practical solutions can lead to harmonious coexistence between humans and wildlife. By fostering a shared sense of responsibility and working together to protect their unique natural environment, the community of Lake Tahoe not only reduced conflicts but also demonstrated the power of collective action in preserving the delicate balance of urban and natural spaces. This success story serves as an inspiration for other regions grappling with similar challenges, highlighting the potential for positive change when communities come together to protect their shared natural heritage.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here THIS IS A COURTESY COPY OF THIS EMERGENCY ADOPTION …
Martinez, California, faced a unique challenge when beavers began damming the Alhambra Creek, leading to localized flooding. The city’s approach demonstrates how creativity and cooperation can resolve such issues:
Martinez, California, faced a unique challenge when beavers began damming the Alhambra Creek, leading to localized flooding. The city’s approach demonstrates how creativity and cooperation can resolve such issues while preserving the delicate balance between urban development and nature.
Collaborative Problem Solving: Rather than resorting to traditional methods that might have harmed the beavers or disrupted their ecosystem, Martinez chose a collaborative path. City officials, environmentalists, and concerned citizens came together to brainstorm solutions that would address the flooding issue without harming the resident beavers.
Flow Devices as a Solution: The installation of flow devices in the beaver dams emerged as a brilliant solution. These devices allowed water to pass through the dams, mitigating the flooding risk while maintaining the structural integrity of the dams. This approach addressed the immediate problem while respecting the beavers’ natural behaviors and habitat.
Educational Outreach: Beyond the technical aspects, the city embarked on a comprehensive educational outreach program. Martinez residents were informed about the benefits of having beavers in the ecosystem, including improved water quality and increased biodiversity. This approach helped foster understanding and appreciation among the community members.
Tourism and Economic Opportunities: The beavers in Alhambra Creek became a unique local attraction. Tourists and wildlife enthusiasts flocked to Martinez to catch a glimpse of these industrious creatures. Recognizing the potential for tourism, the city leveraged this newfound interest to boost its local economy and promote further awareness about urban wildlife.
Sustainable Coexistence: The success of Martinez’s approach showcases how creative problem-solving, collaboration, and community engagement can lead to sustainable coexistence with urban wildlife. It is a shining example of how cities can adapt to the challenges posed by expanding urbanization while respecting the natural world and its inhabitants.
Martinez’s experience with the beavers in Alhambra Creek offers valuable insights for other urban areas grappling with similar human-wildlife conflicts. It underscores the importance of innovative, environmentally friendly solutions and the potential for these challenges to become opportunities for enhancing the quality of life in our cities. By embracing creativity and cooperation, we can achieve a harmonious balance where humans and wildlife thrive together in urban environments, preserving the wonders of the natural world even within the confines of our cities.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Coyote Management Plan

Toronto, a major city in Canada, has taken innovative steps to reduce bird collisions with buildings. The city’s Bird-Friendly Development Guidelines offer valuable insights:
Toronto, a major city in Canada, has emerged as a pioneer in addressing the critical issue of bird collisions with buildings. The metropolis, known for its iconic skyline and bustling urban life, has recognized the importance of preserving its avian inhabitants and has taken innovative steps to create a more bird-friendly urban environment. One of the cornerstones of these efforts is the city’s Bird-Friendly Development Guidelines, which serve as a beacon of hope and inspiration for urban planners and conservationists worldwide.
The Bird-Friendly Development Guidelines in Toronto represent a proactive approach to urban planning that places a strong emphasis on the preservation of avian life. These guidelines provide a comprehensive framework for architects, developers, and city officials to consider when designing and constructing buildings. They offer valuable insights into how to minimize the hazards that urban structures pose to birds while maximizing the city’s sustainability and aesthetics.
Some key aspects of these guidelines include:
Glass Design: Recommendations for the use of bird-friendly glass, which may include patterns, films, or fritting, to make windows more visible to birds. This simple yet effective measure helps prevent collisions by breaking up the reflection of the sky and surrounding vegetation, making it easier for birds to perceive the presence of the glass.
Lighting: Suggestions for minimizing light pollution during migration seasons, which can disorient and attract birds. The guidelines encourage the use of motion sensors and timers to reduce unnecessary illumination at night, promoting a safer environment for nocturnal migrants.
Landscaping: Promoting bird-friendly landscaping practices around buildings, including the use of native plants and green roofs that provide habitat and food sources for birds. This creates pockets of green space within the urban jungle, offering respite and sustenance to avian visitors.
Education and Advocacy: The guidelines emphasize the importance of public awareness and advocacy to engage residents, businesses, and institutions in bird conservation efforts. Education campaigns help spread the word about the importance of bird-friendly practices and how individuals can contribute to safeguarding avian life in the city.
By implementing these guidelines, Toronto has not only become a model for other urban centers but has also demonstrated its commitment to creating a harmonious coexistence between the city’s residents and its feathered inhabitants. As more cities worldwide grapple with the challenges of urbanization and its impact on wildlife, Toronto’s innovative approach provides a beacon of hope and a roadmap for fostering a more sustainable and bird-friendly urban future.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Environmental Impact: Concept, Consequences, Measurement – PMC

These initiatives from cities worldwide showcase the power of proactive measures, community involvement, and innovative solutions in managing human-wildlife conflicts in urban areas. By learning from these success stories and applying similar strategies, other cities can create more harmonious environments where humans and wildlife coexist, ensuring the sustainability of both urban development and the natural world.
These remarkable initiatives from cities around the world serve as inspiring examples of how proactive measures, community engagement, and innovative solutions can effectively address the complex challenges posed by human-wildlife conflicts within urban areas. They demonstrate that it’s possible to find common ground between human progress and the preservation of our natural heritage.
One key takeaway from these success stories is the power of collaboration and community involvement. In many cases, residents, local organizations, and government agencies have come together to develop and implement strategies that benefit both humans and wildlife. This sense of shared responsibility not only strengthens the bonds within communities but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the biodiversity that thrives alongside us.
Moreover, these initiatives underscore the value of innovative solutions. From wildlife corridors and green infrastructure to educational programs and responsible waste management, cities have embraced creative approaches to mitigate conflicts and enhance coexistence. These solutions often provide win-win scenarios, enhancing the quality of urban life while safeguarding the habitats and well-being of urban wildlife.
By sharing and disseminating the lessons learned from these successful endeavors, other cities can draw inspiration and guidance. They can adapt similar strategies to their unique urban environments, ultimately fostering more harmonious and sustainable coexistence between humans and wildlife. It’s a collective effort that not only contributes to the well-being of our urban ecosystems but also ensures the long-term viability of our cities.
In an era of rapid urbanization and environmental challenges, these initiatives provide a beacon of hope. They demonstrate that, with dedication, creativity, and a shared vision, we can build cities where the vibrant pulse of urban life harmoniously coexists with the rustle of leaves, the songs of birds, and the presence of wildlife. In doing so, we create urban environments that are not only centers of human innovation and culture but also sanctuaries for nature’s beauty and resilience.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Chapter 7 : Risk management and decision making in relation to …

More links
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: What is human-wildlife conflict and why is it more than just a …
