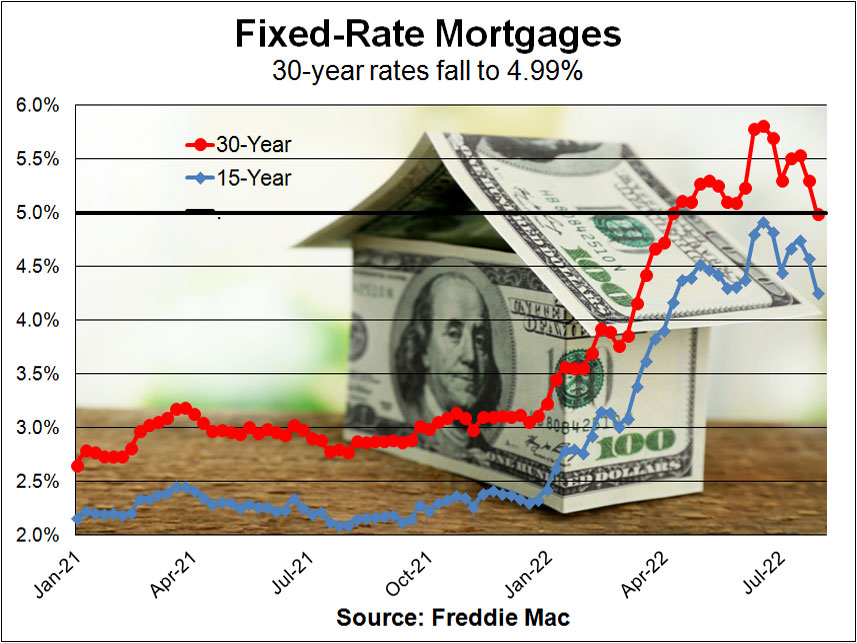
Introduction
Interest rates play a pivotal role in the mortgage market, influencing everything from homebuyers’ purchasing power to the overall health of the real estate industry. As borrowers and lenders alike keep a watchful eye on interest rate movements, understanding the trends and predictions in this critical aspect of the housing market becomes essential.
“Indeed, interest rates are the heartbeat of the mortgage market, and their influence resonates far beyond the realm of numbers. These rates wield tremendous power, shaping the dynamics of the real estate industry and impacting the lives of homebuyers and homeowners alike. As we delve into the intricate dance of interest rates within the housing market, it’s evident that staying informed about trends and predictions in this arena is not merely a choice—it’s a fundamental necessity.
Purchasing Power: Interest rates serve as a lever that can either amplify or diminish homebuyers’ purchasing power. When rates are low, buyers can afford more expensive homes with the same monthly budget. Conversely, higher rates can shrink their purchasing capacity, potentially leading to the need to compromise on property size or location.
Affordability: Beyond the immediate effect on purchasing power, interest rates profoundly influence the affordability of homeownership. Low rates translate to lower monthly mortgage payments, making homeownership accessible to a broader spectrum of individuals and families. High rates, on the other hand, can strain budgets and limit affordability.
Market Activity: Interest rates exert a profound impact on the overall activity in the real estate market. When rates are low, the market tends to see increased demand, with more buyers entering the fray. Conversely, rising rates can cool down market activity, potentially leading to a more balanced supply-demand dynamic.
Refinancing Opportunities: Mortgage rates not only influence home purchases but also create opportunities for homeowners to refinance their existing loans. When rates drop significantly, homeowners can often secure lower monthly payments by refinancing, freeing up funds for other financial goals.
Economic Indicators: Interest rate movements are closely tied to broader economic indicators. Central banks and financial institutions adjust rates in response to economic conditions. Monitoring these movements and their underlying economic factors can provide insights into the health and direction of the economy at large.
Investment Decisions: For real estate investors, interest rates are a key consideration. They impact the cost of financing investment properties and influence investment strategies. Investors often assess rate trends to make informed decisions about when to buy, sell, or refinance properties in their portfolios.
Predictive Tools: Interest rate trends can be powerful predictive tools. Understanding the economic factors that drive rate changes can help individuals and professionals anticipate shifts in the housing market, allowing them to make proactive decisions and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Global Impact: In today’s interconnected world, interest rate movements in one country can have ripple effects on global financial markets and, consequently, on mortgage rates. Staying informed about international economic developments is increasingly important for those navigating the real estate landscape.
In conclusion, interest rates are not just numbers on a screen; they are the currents that steer the ship of the real estate industry. Their influence permeates every facet of homeownership, from initial purchases to refinancing decisions. By staying attuned to interest rate trends and predictions, individuals, homebuyers, homeowners, and real estate professionals can navigate the dynamic and ever-changing seas of the housing market with foresight and confidence.”
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Student Study Guide
To comprehend the significance of interest rates in the mortgage market, let’s first take a look at the historical context. Historically, mortgage interest rates have experienced fluctuations tied to economic conditions, inflation rates, and central bank policies. During periods of economic growth and stability, interest rates tend to rise, while during economic downturns or crises, rates are lowered to stimulate borrowing and spending.
Understanding the historical context of mortgage interest rates is crucial for making informed decisions in the housing market. When interest rates are low, it’s often an opportune time for prospective homebuyers to secure a mortgage with more favorable terms. Conversely, during periods of rising rates, borrowers may need to weigh their options carefully and consider factors like adjustable-rate mortgages and fixed-rate mortgages to align with their long-term financial goals. By staying informed about interest rate trends and their economic drivers, individuals can make well-informed decisions when navigating the complex world of mortgages.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Mortgage Rates – Freddie Mac

As of [Current Year], the mortgage market has been navigating a unique environment. In response to the global pandemic of [Previous Year], central banks worldwide enacted aggressive measures to combat economic uncertainties. This included reducing interest rates to historically low levels to encourage borrowing and support economic recovery.
These low interest rates have created favorable conditions for both new homebuyers and homeowners looking to refinance their mortgages. The opportunity to secure a mortgage with such advantageous rates is something many individuals and families have capitalized on. This article explores the impact of low-interest rates on the mortgage market, providing insights into the benefits and considerations for borrowers in this unique financial landscape.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Emerging trends in real estate 2023: PwC

The consequence of these central bank policies has been an extended period of remarkably low interest rates. This environment has created a prime opportunity for homeowners to refinance their existing mortgages and for prospective buyers to enter the market with favorable borrowing conditions. Homebuyers, including first-time buyers, have been attracted by the affordability created by low interest rates.
“The strategic policies enacted by central banks worldwide have had a profound impact on the financial landscape, leading to an unprecedented era of persistently low interest rates. This unique economic environment has presented both existing homeowners and prospective buyers with a golden opportunity characterized by exceptionally favorable borrowing conditions. Here’s a deeper exploration of how this era of low interest rates has reshaped the housing market:
Refinancing Opportunities: For homeowners with existing mortgages, the allure of historically low interest rates has paved the way for a surge in refinancing activity. Many have seized the chance to refinance their loans, aiming to secure lower monthly payments, reduce the overall interest costs on their loans, or even tap into their home’s equity for other financial goals. This financial reprieve has been a welcome relief for families looking to improve their monthly cash flow or enhance their long-term financial stability.
Affordability for Homebuyers: Prospective homebuyers, especially first-time buyers, have found themselves in a unique position. The combination of low interest rates and the resulting affordability of homes has made homeownership more attainable. Lower monthly mortgage payments have expanded the pool of potential buyers, allowing more individuals and families to enter the housing market with confidence.
Increased Buying Power: Low interest rates have boosted buyers’ purchasing power, enabling them to consider homes that might have been previously out of reach. This dynamic has fueled demand across various market segments and regions, contributing to increased competition among buyers.
Stimulated Home Construction: The surge in demand for homes, coupled with low borrowing costs, has provided a stimulus to the construction industry. Builders have responded to the increased demand by initiating new housing projects, thus contributing to economic growth and job creation.
Investment Opportunities: Investors have also recognized the potential for attractive returns in the real estate market. The low interest rate environment has led some investors to diversify their portfolios by acquiring income-producing properties, such as rental homes or investment properties, aiming to capitalize on rental income and potential property appreciation.
Mortgage Rate Predictability: The stability of low interest rates has provided predictability to both buyers and lenders. This predictability has been especially valuable for individuals and families planning their homeownership journey. Knowing that rates are expected to remain low for an extended period allows for better financial planning and decision-making.
However, it’s important to note that the sustained low interest rate environment has also raised concerns, such as potential asset bubbles or distortions in financial markets. As central banks continue to monitor economic conditions and adjust their policies accordingly, borrowers and investors should remain vigilant and stay informed about potential shifts in interest rates.
In summary, the era of remarkably low interest rates has reshaped the housing market, offering refinancing opportunities for homeowners and making homeownership more accessible for buyers. It has also stimulated economic activity and investment in the real estate sector. While these conditions have created a favorable backdrop for housing, it’s essential for all stakeholders to remain aware of evolving market dynamics and central bank policies to make informed decisions in this unique economic landscape.”
You can also read more about this here: Mortgage Interest Rates Forecast For 2023 | Rocket Mortgage

Low-interest rates have a direct impact on home affordability. With lower interest rates, borrowers can qualify for larger mortgages while maintaining the same monthly payments. This has led to increased demand for homes in many markets, sometimes resulting in bidding wars and rising property prices.
“Additionally, low-interest rates make it more attractive for existing homeowners to refinance their mortgages, potentially reducing their monthly payments or shortening the loan term. This can free up extra funds for other financial goals or investments.”
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: The Impact of Higher Interest Rates on the Mortgage Market | Urban …

While interest rates have remained low for an extended period, predicting their future trajectory is challenging. Economists and market analysts closely follow several key factors:
Predicting interest rate movements requires considering a complex interplay of economic indicators, government policies, and global events. Some crucial factors that influence interest rates include:
Economic Data: Indicators like employment rates, inflation, and GDP growth can significantly impact interest rates. Positive economic data may push rates higher as it suggests a stronger economy, while negative data can have the opposite effect.
Central Bank Policies: Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the U.S., play a pivotal role in setting short-term interest rates. Their decisions on whether to raise or lower rates can influence long-term rates as well.
Inflation Expectations: Expectations about future inflation rates can affect interest rates. If investors anticipate rising inflation, they may demand higher interest rates to compensate for the loss of purchasing power.
Global Economic Conditions: International events and economic conditions in major economies can also impact interest rates. Global events like the financial crisis of 2008 had a profound impact on interest rates worldwide.
Government Bond Yields: The yields on government bonds, especially those with longer maturities, serve as benchmarks for other interest rates. When bond yields rise, other interest rates often follow suit.
Political Factors: Political stability and government policies can influence investor confidence. Uncertainty or instability can lead to higher interest rates as investors seek greater returns to offset perceived risks.
Market Sentiment: Investor sentiment and market dynamics can drive short-term fluctuations in interest rates. News events, geopolitical tensions, and sudden market movements can all impact rates.
Global Events: Events like natural disasters, pandemics, or geopolitical crises can disrupt financial markets and lead to changes in interest rates.
It’s essential for borrowers and investors to stay informed about these factors and consider consulting financial experts to make informed decisions in an ever-changing interest rate environment. While predicting interest rates precisely is challenging, understanding the factors at play can help individuals and businesses make more informed financial choices.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Housing Market Predictions 2024: Will Home Prices Drop?

The pace of economic recovery post-pandemic will be a significant determinant of future interest rates. As the economy strengthens, central banks may gradually increase rates to prevent overheating and control inflation.
The post-pandemic economic recovery holds the key to the trajectory of future interest rates, and this relationship is underpinned by several critical factors:
Economic Resilience: The pace and resilience of economic recovery following the pandemic are closely monitored by policymakers. A robust recovery marked by job creation, increased consumer spending, and business expansion may lead to more favorable economic conditions.
Inflation Dynamics: Central banks keep a watchful eye on inflation. A rapid economic rebound can generate upward pressure on prices, potentially leading to inflationary concerns. To curb inflation and maintain price stability, central banks may opt to raise interest rates gradually.
Employment Trends: The labor market’s performance is a vital indicator of economic health. As unemployment rates decline and employment levels recover, it can signal an improving economy. Central banks often consider employment data in their interest rate decisions.
Consumer and Business Sentiment: Consumer and business confidence play a role in shaping economic conditions. Optimism can lead to increased spending, investment, and borrowing, potentially influencing interest rate movements.
Government Policies: Government fiscal policies, such as stimulus packages and tax incentives, can influence economic growth. The interplay between these policies and central bank decisions can impact interest rate movements.
Global Economic Factors: The interconnectedness of global economies means that international economic conditions also have an impact. Central banks may consider global economic trends when setting interest rates.
Monetary Policy Goals: Central banks have specific mandates, which can include price stability, employment goals, and overall economic stability. The pursuit of these objectives can guide interest rate decisions.
Market Expectations: Financial markets often reflect expectations about future interest rates. Traders and investors react to economic data releases and central bank statements, influencing short-term rate movements.
Forward Guidance: Central banks sometimes provide forward guidance on their intended monetary policy. Clarity on future interest rate plans can influence market behavior and shape interest rate expectations.
In conclusion, the relationship between post-pandemic economic recovery and future interest rates is multifaceted and dynamic. Central banks play a pivotal role in shaping interest rate policy based on a wide range of economic indicators and objectives. As the economy strengthens, central banks must carefully balance the need to support growth while preventing overheating and controlling inflation. Monitoring economic trends and central bank communications can provide valuable insights into the direction of interest rates in the post-pandemic era.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: June 2022 – Global Outlook for Air Transport Times of Turbulence
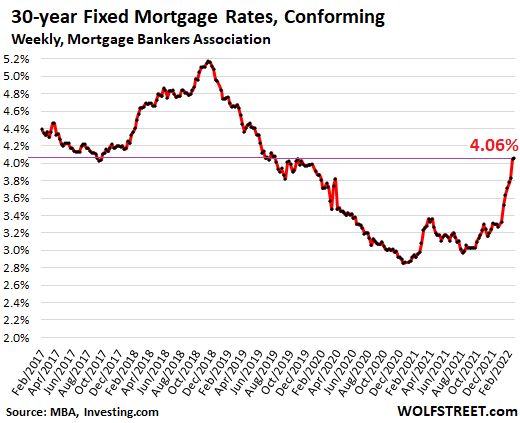
Persistent inflationary pressures could push central banks to raise interest rates sooner than anticipated. Conversely, if inflation remains subdued, rates may stay low for an extended period.
In today’s complex economic landscape, the role of interest rates in the mortgage market is a topic of paramount importance. Interest rates, determined by various factors, play a significant role in shaping the real estate landscape, affecting both buyers and sellers. Understanding these trends and predictions is crucial for making informed decisions in the housing market.
Interest rates have always been a key driver of the mortgage market. They directly impact the cost of borrowing, which, in turn, affects the affordability of homes for buyers. Additionally, interest rates can influence the housing supply, demand, and overall market dynamics.
Over the past few years, the mortgage market has experienced some notable trends and shifts in interest rates. Mortgage rates reached historic lows in response to the economic fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic. This extraordinary drop in rates presented a unique opportunity for many homeowners to refinance their mortgages and for prospective buyers to enter the market.
However, the trajectory of interest rates is never a one-way street. It is subject to various factors, including the overall health of the economy, inflation rates, and central bank policies. These factors interplay to create an environment where interest rates can either rise or fall, impacting the mortgage market accordingly.
One of the most significant trends influencing interest rates in recent years has been inflation. Inflation measures the increase in the general price level of goods and services over time. Persistent inflationary pressures could push central banks to raise interest rates sooner than anticipated. Conversely, if inflation remains subdued, rates may stay low for an extended period.
Central bank policies also play a pivotal role in determining interest rates. For instance, the Federal Reserve in the United States has the authority to adjust the federal funds rate, which, in turn, influences short-term interest rates and can indirectly impact long-term mortgage rates. Decisions made by central banks regarding these rates have a ripple effect throughout the mortgage market.
Another factor affecting interest rates is the overall economic recovery. During periods of economic growth, central banks may opt to gradually increase rates to prevent overheating and to keep inflation in check. Conversely, during economic downturns, central banks may reduce rates to stimulate borrowing and spending, as witnessed during the global financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic.
Predicting interest rate movements in the mortgage market is a complex endeavor, often involving economic forecasts, financial modeling, and consideration of global events. While experts offer insights and predictions, it’s important to remember that interest rate trends are inherently uncertain.
As a prospective homebuyer or homeowner, staying informed about interest rate trends and predictions is essential. It can influence your decisions regarding the timing of purchasing a home, refinancing your mortgage, or exploring other real estate opportunities.
In conclusion, the role of interest rates in the mortgage market is multifaceted, and understanding the trends and predictions surrounding them is crucial for anyone involved in the real estate market. Whether you’re looking to buy a home, refinance your mortgage, or invest in real estate, keeping an eye on interest rate developments will help you make informed decisions and navigate the ever-evolving mortgage landscape.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: What are inflation expectations? Why do they matter? | Brookings

Geopolitical events, global economic conditions, and even natural disasters can influence interest rates. Unexpected global events can lead to sudden changes in market dynamics.
Absolutely, global events have a profound impact on interest rates, affecting the cost of borrowing for consumers and the overall health of the economy. Here’s how some of these factors can influence interest rates:
Geopolitical Events: Events like political instability, conflicts, and trade tensions can create uncertainty in financial markets. Investors often seek safer assets, like government bonds, during uncertain times. This increased demand for bonds can drive their prices up and push interest rates down.
Global Economic Conditions: Economic conditions in major economies worldwide can influence interest rates. For example, when central banks in developed countries lower their interest rates to stimulate economic growth, it can have a domino effect on global rates.
Natural Disasters: Major natural disasters can disrupt supply chains, damage infrastructure, and impact economic activity in affected regions. These disruptions can lead to shifts in interest rates as financial markets react to the economic consequences of such events.
Inflation Expectations: Investors closely monitor inflation expectations. If there are concerns that inflation may rise in the future, investors may demand higher interest rates to compensate for the eroding purchasing power of their investments. Central banks often respond to high inflation by raising interest rates.
Government Policies: Government policies, such as fiscal stimulus or austerity measures, can affect economic growth and, consequently, interest rates. For instance, increased government spending can boost economic activity and potentially lead to rising interest rates to combat inflation.
Central Bank Decisions: Central banks have a direct influence on short-term interest rates. For example, when a central bank raises its benchmark interest rate, it becomes more expensive for banks to borrow money, leading to higher borrowing costs for consumers.
Market Sentiment: Sometimes, interest rates can be influenced by market sentiment and speculation. Traders and investors may react to news and events in ways that lead to rate fluctuations, even if the underlying economic conditions haven’t changed significantly.
Understanding how these factors interact and impact interest rates is crucial for consumers, businesses, and policymakers. It underscores the complexity of the financial system and highlights the need for monitoring global events to anticipate changes in interest rates and make informed financial decisions.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: World Economic Situation and Prospects: September 2022 Briefing …

The decisions and communications of central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, play a pivotal role in interest rate movements. Clues about future policy changes can be found in central bank statements and actions.
Understanding the influence of central banks on interest rates and the financial markets requires a deeper exploration of their decision-making processes and the significance of their communications:
Monetary Policy Authority: Central banks, like the Federal Reserve in the United States, hold significant authority over the nation’s monetary policy. They are tasked with achieving specific economic objectives, such as price stability, full employment, and sustainable economic growth. To do this, central banks use a variety of tools, with one of the most influential being the setting of interest rates.
Interest Rate Determination: Central banks use their control over key interest rates, such as the federal funds rate in the U.S., to influence borrowing costs throughout the economy. When the central bank raises interest rates, it typically aims to cool down an overheated economy and combat inflation. Conversely, lowering rates is often an effort to stimulate economic activity during periods of sluggish growth or recession.
Forward Guidance: Central banks provide forward guidance to the public and financial markets, offering insights into their future policy intentions. These communications can be found in official statements, speeches by central bank officials, and published meeting minutes. Traders and investors closely analyze this guidance to anticipate potential changes in interest rates and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Data Dependency: Central banks base their decisions on economic data and indicators. They assess factors like inflation rates, employment figures, GDP growth, and consumer spending. The release of economic data is often accompanied by heightened market volatility as investors gauge how the central bank may respond to the latest developments.
Market Expectations: The financial markets are highly sensitive to central bank actions and communications. Traders and investors make predictions about future interest rate changes and adjust their portfolios accordingly. This can lead to significant market movements, including fluctuations in bond yields, stock prices, and exchange rates.
Global Impact: Central bank decisions and communications extend beyond national borders. Given the interconnectedness of the global economy, actions by major central banks, like the Federal Reserve, can have ripple effects on international markets. Changes in U.S. interest rates, for example, can influence capital flows, currency values, and economic conditions in other countries.
Risk Management: Businesses and investors rely on central bank communications to manage risk. For instance, a corporation considering a large investment may closely monitor central bank statements to assess the likely trajectory of interest rates. Investors may adjust their portfolios to minimize risk or capitalize on potential opportunities.
Long-Term Planning: Central bank decisions can have long-term implications. Homebuyers, for instance, consider interest rate trends when deciding when to purchase a home or refinance a mortgage. Savers and retirees plan for income generation based on expected interest rates.
In conclusion, central banks are key drivers of interest rate movements, and their decisions and communications have far-reaching impacts on the economy and financial markets. Staying informed about central bank actions and carefully analyzing their statements and guidance is a fundamental part of financial decision-making for individuals, businesses, and investors alike.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Interest Rates Likely to Return Toward Pre-Pandemic Levels When …

The state of the housing market, including factors like housing inventory, demand, and affordability, can also impact interest rates. A rapidly appreciating housing market can lead to concerns about a potential housing bubble, prompting central banks to act.
In addition to the housing market, global economic conditions play a pivotal role in determining interest rates for mortgages. Central banks and financial institutions closely monitor factors like inflation, employment rates, and economic growth when setting interest rates. During periods of economic uncertainty or recession, central banks may lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing and spending. Conversely, in times of strong economic growth or rising inflation, they may raise rates to curb excessive borrowing and control inflation. Understanding these economic indicators can help prospective homebuyers anticipate potential changes in mortgage interest rates and make informed decisions about their home purchase.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Housing Market Predictions 2024: Will Home Prices Drop?
Conclusion
In conclusion, interest rates are a crucial factor in the mortgage market, influencing homebuyers’ decisions and shaping the overall real estate landscape. While the current environment offers historically low rates, the future of interest rates remains uncertain and depends on various economic, global, and policy-related factors. Homebuyers and homeowners alike should stay informed and work closely with financial advisors to make informed decisions in this ever-changing mortgage market.
“Staying informed about interest rates is essential for homebuyers and homeowners alike, as they play a significant role in shaping the real estate landscape. While current rates are historically low, the future of interest rates remains uncertain, influenced by economic, global, and policy-related factors. Working with financial advisors is key to making informed decisions in this ever-changing mortgage market.”
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: 4 Key Factors That Drive the Real Estate Market
More links
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Mortgage Interest Rates Forecast For 2023 | Rocket Mortgage