Table of Contents
Climate change is one of the most pressing challenges of our time, with far-reaching consequences for the environment and human society. The urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition to clean, sustainable energy sources has become paramount. Batteries, often seen as unassuming energy storage devices, are emerging as powerful tools in the fight against climate change. In this article, we will explore how batteries are playing a pivotal role in mitigating climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions across various sectors.
Climate change stands as one of the defining challenges of the 21st century, with its profound implications spanning the realms of the environment, economy and society at large. The imperative to confront this global crisis has never been more urgent, as the consequences of unchecked climate change become increasingly apparent. Fortunately, one of the unsung heroes in our battle against climate change is the unassuming battery, which is quietly and effectively catalyzing transformation across various sectors.
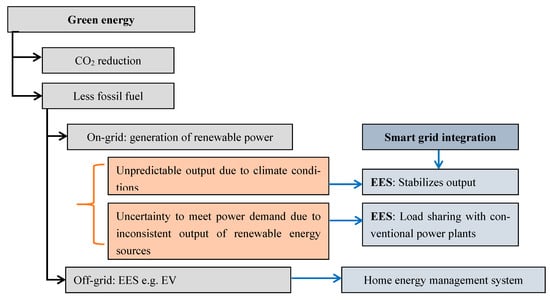
Clean Energy Integration: Batteries are indispensable in the integration of clean energy sources like solar and wind into our grids. They store excess energy generated during peak production periods and release it when demand is high or renewable energy generation is low. This mitigates the need for fossil fuel backup power and reduces carbon emissions.
Electric Vehicles (EVs): The transition from internal combustion engines to electric vehicles is a linchpin in reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector. Batteries power EVs, offering a sustainable alternative that contributes to cleaner air and reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
Energy Efficiency: Batteries enhance energy efficiency by capturing surplus energy and releasing it when needed. This optimizes energy use, reducing the overall demand for power and the associated emissions from energy production.
Grid Resilience: Energy storage systems equipped with batteries fortify grid resilience, helping communities weather the impacts of extreme weather events associated with climate change. These systems ensure a stable power supply, even when central grids are compromised.
Decentralized Energy: Battery technology facilitates decentralized energy production. Communities and individual consumers can harness renewable energy sources like rooftop solar panels and store excess energy for later use, reducing their reliance on centralized power plants.
Carbon Reduction in Industry: Batteries play a role in reducing carbon emissions in industrial applications. They enable efficient energy storage for industrial processes, helping factories optimize their operations and lower their carbon footprint.
Grid Decarbonization: By enabling the integration of intermittent renewables, batteries facilitate the transition to a low-carbon grid. They smooth out energy supply and demand fluctuations, ensuring a reliable power supply while reducing the need for fossil fuel backup.
Climate Adaptation: Batteries are essential in climate adaptation efforts. They provide backup power during extreme weather events, helping communities maintain critical services and reducing the risks associated with power outages during emergencies.
Supporting Renewable Growth: As the renewable energy sector expands, batteries become crucial for stabilizing energy supply and reducing curtailment, where excess renewable energy goes to waste due to lack of demand.
Carbon Accounting: Batteries are a key component in carbon accounting strategies, helping organizations and governments track and manage their emissions by optimizing energy use and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
In summary, batteries are silent champions in the global fight against climate change, working tirelessly behind the scenes to reduce greenhouse gas emissions across a spectrum of sectors. Their versatility and adaptability are unlocking new possibilities for a sustainable future, where clean energy and resilience to climate impacts become the cornerstones of our society. By recognizing and harnessing the power of batteries, we take significant strides towards mitigating climate change and preserving the planet for future generations.
You can also read more about this here: Frontier Technology Issues: Lithium-ion batteries: a pillar for a fossil …
Renewable Energy Integration
One of the primary sources of greenhouse gas emissions is the burning of fossil fuels for electricity generation. Batteries are instrumental in integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind into the grid. These sources are intermittent, producing energy only when the sun shines or the wind blows. Battery storage allows excess energy to be captured and used when these sources are inactive, ensuring a continuous and reliable energy supply without relying on fossil fuels.
The burning of fossil fuels for electricity generation has long been a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change and environmental degradation. As the world grapples with the urgent need to transition to cleaner energy sources, batteries have emerged as indispensable tools in the fight against climate change.
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, offer a promising solution to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. They harness the Earth’s natural resources to generate electricity without producing harmful greenhouse gases. However, one of their inherent challenges is their intermittency. Solar panels generate electricity only when the sun is shining and wind turbines produce energy when the wind is blowing. This variability creates a reliability gap in the energy supply, as it doesn’t always align with energy demand.
This is where battery storage systems step in as game-changers. They are the linchpin in the seamless integration of renewable energy into the grid. When renewable sources like solar and wind produce more energy than is currently needed, excess electricity can be stored in batteries. This surplus energy doesn’t go to waste but is rather captured and preserved for future use.
The importance of this cannot be overstated. Batteries essentially act as energy reservoirs, allowing us to bank clean energy when it’s abundant and use it when it’s needed, even when the sun has set and the winds have calmed. This transformative capability bridges the gap between energy generation and consumption, ensuring a continuous and reliable energy supply. As a result, grid stability is enhanced and the need for backup power from fossil fuel-based plants is greatly reduced.
By enabling the grid to rely less on fossil fuels for backup power, batteries play a pivotal role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. They help break the fossil fuel dependency cycle that has contributed to climate change for decades. As the world transitions to a cleaner and more sustainable energy mix, batteries are at the forefront, accelerating the adoption of renewable energy sources and significantly mitigating the environmental impact of electricity generation.
Moreover, the advancement of battery technology is making renewable energy systems even more efficient. Smarter energy management systems can optimize the use of stored energy, ensuring it’s dispatched precisely when and where it’s needed most. This not only enhances grid reliability but also maximizes the environmental benefits of renewable energy.
In conclusion, batteries are pivotal in the battle against climate change by facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid. Their ability to capture, store and deliver clean energy when it’s needed ensures a reliable and continuous energy supply without relying on fossil fuels. As we continue to innovate in battery technology and expand their deployment, we move closer to a sustainable energy future, where greenhouse gas emissions from electricity generation become a relic of the past and clean, renewable energy powers our world.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: The Long-Term Strategy of the United States, Pathways to Net-Zero …
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The transportation sector is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. Electric vehicles, powered by batteries, are a promising solution to reduce emissions from cars and trucks. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions and as the electricity grid becomes greener, the overall carbon footprint of EVs continues to decrease.
The transportation sector has long stood as a prominent contributor to the mounting challenge of greenhouse gas emissions, but within this challenge, there lies an equally potent solution—Electric Vehicles (EVs) powered by advanced batteries. These innovative vehicles represent a beacon of hope in the quest to dramatically curtail emissions from cars and trucks, heralding a cleaner, more sustainable future.
One of the most compelling aspects of EVs is their capacity to produce zero tailpipe emissions. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine vehicles that release harmful pollutants and greenhouse gases directly into the atmosphere, EVs operate with unparalleled efficiency and environmental friendliness. When you hit the accelerator of an EV, you’re not just experiencing a smooth, quiet ride; you’re also contributing to a reduction in air pollution and a healthier planet.
As a profound testament to their eco-friendliness, EVs become even greener as the electricity grid evolves. The ongoing transition toward renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind and hydroelectric power, is transforming the electricity grid into a cleaner and more sustainable energy source. When EVs are charged using electricity generated from these renewables, their overall carbon footprint shrinks dramatically. This symbiotic relationship between clean energy generation and clean transportation underscores the potential for EVs to be a driving force behind a carbon-neutral future.
Furthermore, the efficiency of electric motors in EVs is unparalleled, making them inherently more energy-efficient than their gasoline counterparts. This efficiency not only conserves energy but also reduces the overall demand for fossil fuels. When combined with regenerative braking technology that captures and stores energy during deceleration, EVs showcase a remarkable ability to maximize every kilowatt-hour of electricity they consume.
In essence, EVs powered by advanced batteries are more than just a mode of transportation; they are a compelling solution to a global challenge. They represent a pivotal step toward reducing emissions from the transportation sector, combating climate change and fostering cleaner air for all. As the world continues to embrace this transformation, the road ahead becomes not only cleaner but also more sustainable, offering a promising vision of a greener and healthier tomorrow.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: A Vision for a Sustainable Battery Value Chain in 2030 Unlocking …
Grid Stabilization
Batteries provide grid stability by smoothing out fluctuations in energy supply and demand. Traditional power grids often rely on fossil fuel-based peaker plants to meet peak demand. By reducing the need for these plants and ensuring a steady energy supply, batteries decrease emissions associated with peaker plant operations.
Batteries are the unsung heroes of modern energy systems, operating behind the scenes to provide a seamless and sustainable energy experience. One of their most critical roles is to ensure grid stability by addressing the inherent fluctuations in energy supply and demand, a task that has traditionally fallen on the shoulders of fossil fuel-based peaker plants.
In traditional power grids, peaker plants are called into action during periods of peak energy demand. These plants, often powered by fossil fuels like natural gas, are designed to rapidly generate electricity to meet the surging requirements of homes, businesses and industries. While they serve a crucial purpose, their operation comes at a significant environmental cost.
Firing up peaker plants is akin to unleashing the energy industry’s “firefighters.” They provide quick and reliable bursts of power, but this often involves burning fossil fuels, releasing carbon emissions and contributing to air pollution. These emissions not only exacerbate climate change but also impact local air quality, posing health risks to nearby communities.
Batteries, with their ability to store and release electricity rapidly, offer an eco-friendly alternative to peaker plants. During times of low demand or when renewable energy sources are generating surplus electricity, batteries store excess energy efficiently. When demand peaks, batteries discharge this stored energy, smoothing out the fluctuations and providing the required power instantaneously.
This transition from peaker plants to battery storage systems has a two-fold benefit for the environment. Firstly, it reduces the need for peaker plants, thereby decreasing the carbon emissions and air pollutants associated with their operation. This translates into a tangible reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
Secondly, the use of batteries encourages the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid. Batteries are a crucial enabler of renewables, as they can store excess energy generated from sources like solar panels and wind turbines and release it when needed, regardless of weather conditions or time of day. This synergy reduces reliance on fossil fuels for meeting peak demand, further reducing emissions and promoting cleaner energy generation.
Additionally, batteries contribute to grid stability by providing rapid response capabilities. They can react within milliseconds to fluctuations in supply and demand, helping to maintain a consistent voltage and frequency. This enhances the reliability and resilience of the grid, reducing the risk of power outages and disruptions.
In conclusion, batteries are instrumental in modernizing and greening our energy systems. By replacing the need for fossil fuel-based peaker plants during peak demand periods, they significantly reduce emissions and contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy landscape. Their role in supporting renewable energy integration and ensuring grid stability places them at the forefront of the transition to a cleaner and more resilient energy future.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: A Vision for a Sustainable Battery Value Chain in 2030 Unlocking …
Energy Efficiency
Batteries play a vital role in improving the overall efficiency of energy systems. They store excess energy during periods of low demand and release it during high-demand hours. This load balancing reduces the need for inefficient and carbon-intensive power plants, ultimately lowering emissions.
The significance of batteries in the realm of energy efficiency cannot be overstated. These unassuming devices serve as linchpins in the transformation of our energy landscape, ushering in a new era of sustainability and environmental responsibility. Delving deeper into their pivotal role, we uncover a tapestry of benefits and implications that reverberate across the energy sector and beyond:
Efficient Energy Storage: Batteries represent a breakthrough in energy storage technology. They excel in capturing surplus energy when it’s abundant and releasing it precisely when it’s needed most. This efficiency minimizes energy wastage and optimizes the utilization of renewable resources like solar and wind, which can be intermittent in nature.
Load Balancing: One of the primary functions of batteries is load balancing. They bridge the gap between energy supply and demand by storing excess energy during off-peak hours and discharging it during peak demand periods. This helps stabilize the grid, preventing overloads and reducing the reliance on peaker power plants, which are often fossil-fuel-based and carbon-intensive.
Reducing Carbon Emissions: By facilitating load balancing and reducing the need for inefficient, carbon-intensive power plants, batteries play a pivotal role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. They contribute to the decarbonization of the energy sector, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
Grid Resilience: Batteries enhance the resilience of power grids. They provide rapid response capabilities to address sudden fluctuations in energy supply or unforeseen disruptions. This resilience is crucial in the face of extreme weather events, natural disasters or cyberattacks, ensuring that electricity supply remains stable and uninterrupted.
Energy Independence: On an individual and community level, battery storage systems promote energy independence. Homeowners and businesses can generate, store and manage their energy locally, reducing their reliance on centralized power grids. This newfound autonomy provides peace of mind during grid outages.
Grid Deferral: In densely populated areas, batteries can defer the need for costly grid upgrades and infrastructure expansion. Instead of building additional transmission lines or substations, utilities can strategically deploy batteries to alleviate grid congestion and ensure a reliable power supply.
Market Flexibility: Batteries are versatile assets in energy markets. They can participate in various markets, including frequency regulation, demand response and ancillary services. This flexibility allows them to adapt to changing market conditions and contribute to grid stability.
Promoting Renewable Integration: As renewable energy sources like solar and wind become increasingly prevalent, batteries play a critical role in integrating these resources into the grid. They store excess renewable energy and release it when generation is low, ensuring a consistent energy supply.
Technological Advancements: Ongoing research and development in battery technology are driving efficiency improvements and cost reductions. Advanced batteries, such as lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, making energy storage more accessible and impactful.
Economic Benefits: The adoption of battery storage systems creates economic opportunities, including job creation in the manufacturing, installation and maintenance of batteries and associated infrastructure. These benefits stimulate local economies and support a skilled workforce.
In conclusion, batteries are catalysts for a more efficient, resilient and sustainable energy future. Their multifaceted role in load balancing, emissions reduction, grid stability and energy independence represents a transformative force in the global transition toward cleaner and more reliable energy systems. As battery technology continues to evolve, the potential for even greater energy efficiency and environmental impact grows, reinforcing their status as critical enablers of a sustainable energy landscape.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Inflation Reduction Act Summary: Energy and Climate Provisions …

Off-Grid and Remote Areas
In remote areas without access to centralized power grids, batteries combined with renewable energy sources provide a clean and reliable energy supply. This eliminates the need for diesel generators, which are both carbon-intensive and expensive to operate in remote locations.
In remote areas around the world, access to a reliable and sustainable energy supply has often been a significant challenge. These regions, far from centralized power grids, have historically relied on diesel generators to meet their energy needs. However, this dependence on diesel generators has come at a considerable environmental and economic cost.
Environmental Benefits: The shift from diesel generators to batteries combined with renewable energy sources represents a profound transformation. Diesel generators are notorious for their carbon emissions, air pollutants and noise pollution. In contrast, renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines produce electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or pollutants. When paired with advanced battery systems, these sources provide a quiet, clean and sustainable energy solution that significantly reduces the carbon footprint of remote communities.
Reduced Air Pollution: Diesel generators not only emit carbon dioxide but also release harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter. These pollutants pose health risks to the local population and can have far-reaching environmental consequences. By transitioning to renewable energy and batteries, remote areas can enjoy improved air quality and better respiratory health for their residents.
Economic Advantages: Diesel fuel is expensive and often needs to be transported long distances to remote locations, adding to the cost of energy production. Furthermore, the maintenance and repair of diesel generators can be costly and challenging in these areas. The adoption of renewable energy systems with batteries reduces the reliance on imported fuel and lowers operational costs. Over time, this shift can result in significant cost savings for remote communities, allowing them to invest in other essential services and infrastructure.
Energy Independence: By generating their own clean energy locally, remote communities gain energy independence and resilience. They are no longer at the mercy of volatile fuel prices or supply chain disruptions. This newfound energy autonomy fosters self-reliance and reduces vulnerability to external factors that can impact energy supply.
Sustainable Development: Access to clean and reliable energy is a fundamental driver of sustainable development. It enables education, healthcare, economic growth and improved living standards in remote areas. By embracing renewable energy and battery solutions, these communities can leapfrog the fossil fuel era, setting a sustainable course for their future development.
In conclusion, the transition from diesel generators to renewable energy sources paired with advanced battery technology in remote areas represents a win-win scenario. It not only reduces carbon emissions, air pollution and operating costs but also fosters economic development and energy independence. This transformation demonstrates the potential of renewable energy and batteries to address some of the world’s most pressing challenges, from climate change mitigation to sustainable development, even in the most remote and off-grid locations.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Social, environmental, and economic consequences of integrating …

Challenges and Innovations
While batteries are a valuable tool in mitigating climate change, challenges exist. Battery production, especially for lithium-ion batteries, requires mining and processing of raw materials, which can have environmental and social impacts. Moreover, recycling and sustainable disposal of batteries are essential to minimize their environmental footprint.
Innovations in battery technology, such as solid-state batteries and alternative chemistries, aim to improve energy density, cycle life and sustainability. Additionally, advancements in recycling and repurposing used batteries are crucial to reducing the environmental impact of battery production and disposal.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: A Vision for a Sustainable Battery Value Chain in 2030 Unlocking …
Batteries have transcended their role as mere energy storage devices; they have become catalysts for change in the fight against climate change. By enabling the integration of renewable energy sources, powering electric vehicles, stabilizing the grid, improving energy efficiency and providing clean energy in off-grid areas, batteries are instrumental in reducing greenhouse gas emissions across various sectors. As the world collectively works towards a more sustainable and carbon-neutral future, the role of batteries in climate change mitigation will continue to grow in significance, offering a ray of hope for a greener and more sustainable world.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Considering Well-to-Wheels Analysis in Control Design …
More links
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here FACT SHEET: President Biden to Catalyze Global Climate Action …
