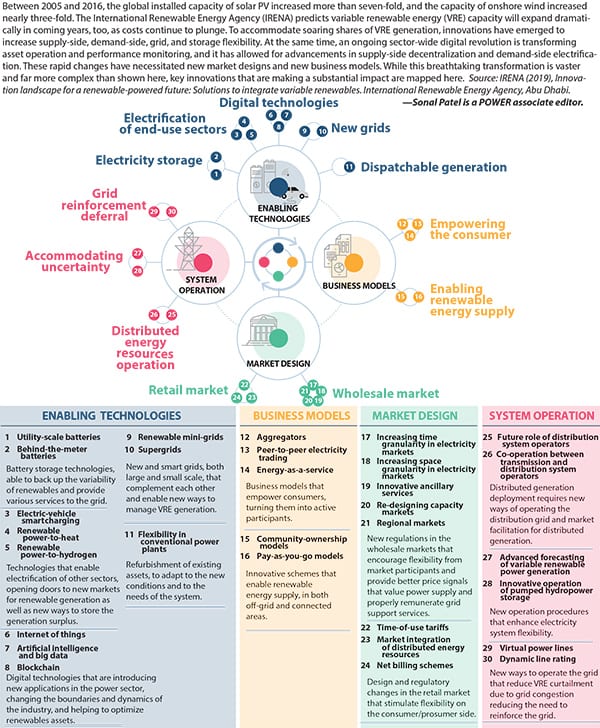
Table of Contents
The landscape of the electricity market is undergoing a revolutionary transformation, driven by advancements in battery technology. Gone are the days when consumers were passive recipients of power from centralized utilities. With the integration of batteries into the grid and the rise of distributed energy resources, consumers are now empowered to take control of their energy consumption, reduce costs and play a pivotal role in creating a more sustainable energy future. In this article, we will explore how battery technology is reshaping the electricity market, putting consumers at the forefront of the energy revolution.
The shift in the electricity market is akin to a seismic change in the way we produce, distribute and consume energy. This transformation, powered by innovative battery technology, signifies not just a change in energy sources but a fundamental shift in power dynamics – from centralized utilities to empowered consumers. Here’s a deeper dive into how this transformation is unfolding:
Energy Democratization: Battery technology is democratizing access to energy. Through residential solar panels and home battery systems, consumers can now generate and store their electricity. This decentralization of energy production empowers individuals and communities to become self-reliant and less dependent on traditional utility companies. It’s a transformation from being mere consumers to energy producers, contributing to a more equitable energy landscape.
Sustainable Energy Choices: With greater control over their energy production and consumption, consumers are making more sustainable choices. They can choose to rely on clean, renewable sources like solar and wind energy, reducing their carbon footprint and supporting a more eco-friendly energy mix. This shift aligns with global efforts to combat climate change.
Grid Resilience: Battery technology enhances grid resilience. During blackouts or emergencies, residential battery systems can kick in, providing homeowners with uninterrupted power. Furthermore, aggregated residential batteries can serve as grid-scale energy storage, stabilizing the grid during peak demand or disruptions, reducing the risk of blackouts.
Financial Savings: Consumers are no longer passive recipients of energy bills. Through smart energy management and load shifting, they can optimize their energy consumption patterns to reduce costs. This financial incentive not only benefits individual consumers but also contributes to more efficient energy usage on a broader scale.
Innovations in Electric Mobility: The integration of battery technology is not limited to stationary applications. Electric vehicles (EVs) have surged in popularity, offering consumers a cleaner and cost-effective alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. EV owners can also contribute to grid stabilization by using their vehicle batteries as storage units.
Investment in Renewable Infrastructure: The growing demand for renewable energy sources and battery storage is driving significant investments in clean energy infrastructure. This, in turn, fosters technological advancements and job creation in the renewable energy sector, stimulating economic growth.
Consumer Education and Engagement: As consumers take on a more active role in managing their energy, there’s a growing need for education and engagement. Understanding how to maximize the benefits of battery technology and renewables is crucial. Consumer engagement can also drive further innovations in energy efficiency and sustainability.
In conclusion, the integration of battery technology is not just a technological advancement; it’s a paradigm shift. Consumers are no longer passive actors in the energy market but active participants shaping the future of energy production and consumption. This transformation holds the promise of a more sustainable, resilient and cost-effective energy future, where consumers are not just beneficiaries but also key agents of change in the global energy revolution.
You can also read more about this here: Electric vehicles – IEA
From Passive Consumption to Active Participation
Traditionally, consumers received electricity from centralized power plants without much control or choice. However, the emergence of advanced battery technology is transforming consumers into active participants in the electricity market. With residential battery systems and smart grid solutions, consumers can generate, store and manage their own electricity, becoming “prosumers” who both consume and produce energy.
Traditionally, the flow of electricity from centralized power plants to our homes was a one-way street, with consumers having little agency or choice in how they received and utilized this vital resource. However, the landscape of energy is rapidly evolving, thanks to the relentless progress of advanced battery technology. This evolution is turning passive consumers into active participants in the electricity market, ushering in an era of unprecedented energy empowerment.
At the forefront of this transformation are residential battery systems, which have emerged as game-changers in the way we interact with electricity. These systems allow homeowners to not only draw power from the grid but also to generate and store their own electricity. Imagine capturing excess energy from your rooftop solar panels during the day and using it to power your home during the evening or in times of high demand. This level of control was once a distant dream but is now a tangible reality for many.
Furthermore, the integration of smart grid solutions adds another layer of sophistication to the equation. With the aid of advanced technologies such as real-time data analytics and artificial intelligence, consumers can optimize their energy consumption patterns, making informed decisions about when to draw power from the grid, when to tap into their stored energy reserves and even when to sell excess electricity back to the grid. This not only reduces energy bills but also contributes to grid stability and resilience.
The term “prosumer” aptly describes this new breed of energy consumer. Prosumers are individuals who not only consume electricity but also produce it and they are at the forefront of a paradigm shift in the energy landscape. They are empowered to make choices that align with their energy preferences, financial goals and environmental values. This transition from passive consumers to prosumers not only democratizes energy but also encourages a more sustainable and resilient energy ecosystem.
As we continue to witness advancements in battery technology and the proliferation of renewable energy sources, the energy market will evolve even further. The power to shape our energy future is increasingly in the hands of individuals and communities, paving the way for a more decentralized, sustainable and customer-centric energy landscape. In this new era, the consumer is no longer just a recipient of electricity but a co-creator of the energy ecosystem, driving positive change for our planet and our wallets.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: DIRECTIVE (EU) 2019/ 944 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT …
Energy Independence and Resilience
Battery technology enables energy independence and resilience for consumers. By installing solar panels and battery storage systems, homeowners can generate and store their own electricity from renewable sources like the sun. This reduces their reliance on grid-supplied power and provides a reliable energy source, even during grid outages, enhancing energy resilience.
Battery technology is revolutionizing the way consumers interact with energy, offering not only independence but also resilience in an ever-changing energy landscape. The marriage of solar panels and battery storage systems has unlocked a new era of energy self-sufficiency and reliability for homeowners. Here’s a deeper dive into how battery technology enables both energy independence and resilience:
Energy Independence: Homeowners who invest in solar panels and battery storage systems become architects of their own energy destiny. Solar panels harness the power of the sun, converting it into electricity that can be used to power homes or stored for later use. This independence from the grid means that homeowners have greater control over their energy production and consumption. They can choose when and how to use the electricity they generate, reducing their reliance on grid-supplied power.
Energy Cost Control: Solar panels and batteries provide homeowners with the ability to manage their energy costs more effectively. Excess energy generated during sunny days can be stored in batteries and used during the evenings or cloudy periods, reducing the need to purchase electricity from the grid at peak rates. This cost-saving potential empowers homeowners to make more efficient use of their energy resources.
Resilience During Grid Outages: One of the most significant advantages of battery technology is its ability to provide a reliable source of electricity during grid outages. When a power outage occurs, solar panels can continue to generate electricity and the battery storage system can supply power to essential appliances and devices. This not only enhances comfort during outages but also ensures the functionality of critical equipment such as medical devices, refrigeration and communication tools.
Environmental Sustainability: Solar panels and battery storage systems align with environmental sustainability goals. By generating and storing electricity from renewable sources like the sun, homeowners reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner, more sustainable energy future. This environmentally friendly approach benefits not only individual households but also the broader community and planet.
Grid Support: Beyond personal benefits, homes equipped with solar panels and batteries can play a role in supporting the broader power grid. During periods of excess energy generation, homeowners can contribute surplus electricity back to the grid, reducing strain during peak demand hours. This supports grid stability and resilience, benefiting the entire community.
Technological Advancements: Ongoing advancements in battery technology, such as increased energy density and longer lifespans, continue to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of energy storage systems. These innovations make energy independence and resilience more accessible and affordable for a wider range of homeowners.
In conclusion, battery technology, when integrated with solar panels, empowers homeowners to achieve energy independence and resilience. It provides greater control over energy production and consumption, reduces costs and ensures a reliable power source during grid outages. As the world continues its transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, the role of battery technology in reshaping the way we access and use energy cannot be overstated. It represents a future where consumers have more agency and sustainability in their energy choices.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Eight Office of Electricity Projects Selected for the 2021 Technology …

Load Shifting and Cost Savings
Battery technology empowers consumers to shift their electricity consumption to times when energy is cheaper or more readily available. By storing excess energy during off-peak hours and using it during peak demand times, consumers can reduce their energy bills significantly. This load shifting not only benefits consumers but also optimizes grid efficiency.
Battery technology represents a groundbreaking leap forward in how we manage and consume electricity, ushering in a new era of energy efficiency and sustainability. Beyond its immediate benefits to consumers, the widespread adoption of energy storage systems has the potential to revolutionize the entire energy landscape.
One of the most significant advantages of battery technology is its ability to enable consumers to shift their electricity consumption strategically. With smart grid integration and real-time monitoring, consumers can store excess energy during off-peak hours when electricity is abundant and cheap. They can then tap into this stored energy during peak demand periods when electricity prices soar. This not only leads to substantial cost savings for consumers but also helps alleviate the strain on the grid during peak hours.
Reducing energy bills is a compelling incentive for individuals and businesses alike. By making the most of inexpensive electricity during off-peak periods, consumers can effectively lower their monthly expenses. This economic benefit extends to electric vehicle owners, who can charge their vehicles during off-peak times, making electric transportation more affordable and sustainable.
Furthermore, the practice of load shifting contributes significantly to grid optimization and stability. Electricity demand is not constant; it fluctuates throughout the day. By strategically deploying stored energy during peak hours, consumers can reduce the stress on the grid, preventing potential blackouts and brownouts. This, in turn, leads to more reliable and resilient electricity infrastructure, benefiting entire communities and regions.
The synergy between battery technology and renewable energy sources like solar and wind power further enhances the advantages of load shifting. Solar panels, for instance, generate the most electricity during daylight hours, which may not always align with peak consumption times. Batteries offer a solution by storing excess solar energy generated during the day for use in the evening when demand typically surges. This maximizes the utilization of clean, renewable energy and reduces reliance on fossil fuels during peak periods, contributing to a greener and more sustainable energy ecosystem.
In conclusion, battery technology’s ability to facilitate load shifting represents a significant stride toward a more efficient, cost-effective and environmentally friendly energy future. Beyond the immediate financial benefits to consumers, this innovation plays a pivotal role in optimizing grid performance, enhancing energy resilience and advancing the integration of renewable energy sources. As energy storage solutions continue to evolve and proliferate, they hold the potential to reshape the way we produce, consume and think about electricity on a global scale.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Load Shifting: What Is It and How Does It Work?
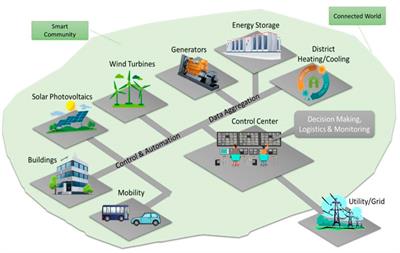
Grid Stabilization and Decentralization
Batteries play a vital role in stabilizing the grid by absorbing excess energy during periods of low demand and releasing it when demand is high. Grid-scale battery installations, combined with distributed energy resources, contribute to grid decentralization and reduce the need for expensive and polluting peaker plants.
Batteries play a vital role in stabilizing the grid by absorbing excess energy during periods of low demand and releasing it when demand is high, but their significance goes well beyond this fundamental function. In the age of renewable energy integration and growing concerns about climate change, batteries have emerged as crucial tools in the pursuit of a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure.
One of the remarkable aspects of grid-scale battery installations is their capacity to seamlessly integrate with renewable energy sources like wind and solar. These sources are inherently intermittent and their energy generation depends on weather conditions. Batteries act as a bridge, capturing surplus energy when the sun is shining or the wind is blowing and making it available when these resources are less active or even offline. This buffering effect ensures a consistent and reliable energy supply, mitigating the variability challenges associated with renewables and enhancing the grid’s overall stability.
Moreover, the synergy between grid-scale batteries and distributed energy resources (DERs) is transforming the energy landscape. DERs, including rooftop solar panels and small-scale wind turbines, empower consumers to generate their own electricity. When coupled with batteries, these localized power sources can operate independently from the central grid during outages or peak demand periods, enhancing grid decentralization. This decentralization not only makes the grid more resilient to disruptions but also empowers communities and individuals to take control of their energy production and consumption, reducing their reliance on traditional utilities.
In the broader context of environmental sustainability, grid-scale batteries play a pivotal role in reducing the need for expensive and polluting peaker plants. Peaker plants are typically fired up during periods of high electricity demand, such as hot summer days, to meet the surge in consumption. However, these plants are often powered by fossil fuels and emit significant greenhouse gases. By storing excess energy during off-peak times and releasing it during peak demand, batteries can offset the need for these environmentally harmful facilities, contributing to a cleaner and greener energy mix.
In conclusion, batteries are not just grid stabilizers; they are linchpins in the transition to a more sustainable, resilient and decentralized energy system. Their ability to integrate renewable energy, empower consumers and reduce the reliance on peaker plants makes them essential components of a modern, environmentally conscious grid. As technology continues to advance and battery storage becomes more widespread, their impact on the energy landscape will only continue to grow, ushering in a brighter, cleaner and more reliable energy future.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: World Energy Trilemma 2017
Electric Vehicles as Energy Assets
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is closely tied to battery technology. EV owners can use their vehicle batteries as mobile energy storage units. They can charge their vehicles during periods of low demand and return excess energy to the grid during peak hours, effectively turning EVs into energy assets that enhance grid stability.
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of transportation and it is intimately linked with the advancements in battery technology. Beyond the evident environmental benefits of reducing emissions and dependence on fossil fuels, the widespread adoption of EVs is bringing about a profound transformation in how we think about energy, mobility and the power grid.
At the heart of this transformation lies the concept of bidirectional charging, which turns EVs into dynamic and adaptable components of the energy ecosystem. With bidirectional charging capabilities, EV owners gain not only the convenience of charging their vehicles at home but also the power to harness their EV batteries as mobile energy storage units.
This innovation opens up a realm of possibilities. Imagine a world where EV owners are not just consumers of electricity but active participants in a distributed energy network. During periods of low electricity demand, such as late at night or when renewable energy sources are generating surplus power, EVs can act as reservoirs, soaking up excess electricity. This surplus energy can then be utilized to charge the vehicle’s battery, essentially “filling the tank” when electricity is abundant and cheap.
However, the true magic happens during peak demand hours when the grid is under stress. EV owners can choose to sell some of the stored energy in their vehicle’s battery back to the grid, effectively becoming small-scale power providers. This process, known as vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, not only helps balance the grid during peak times but also provides an additional income stream for EV owners.
Moreover, the strategic deployment of EVs in regions susceptible to power outages or natural disasters can serve as mobile emergency power sources, ensuring critical infrastructure and homes remain powered during crises.
As we continue to integrate EVs into our daily lives, this symbiotic relationship between electric vehicles and the grid is poised to become a cornerstone of the modern energy landscape. It enhances grid stability, promotes renewable energy integration and empowers consumers to actively engage with their energy consumption and generation. In essence, the transition to electric vehicles represents a significant step toward a more sustainable, resilient and democratized energy future.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: FACT SHEET: Biden-Harris Administration Announces New Private …
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The adoption of battery-powered EVs and the integration of renewable energy sources with battery storage contribute to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. By reducing the dependence on fossil fuels, battery technology plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change.
The widespread adoption of battery-powered electric vehicles (EVs) and the seamless integration of renewable energy sources with advanced battery storage systems mark a momentous shift in our approach to combating climate change. This holistic approach brings forth substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, offering a glimmer of hope in our collective fight against the looming environmental crisis.
Battery-powered EVs have emerged as a beacon of sustainability in the transportation sector. They offer a clean and efficient alternative to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles, dramatically cutting down on tailpipe emissions. These eco-friendly vehicles are a testament to the transformative power of battery technology, enabling us to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels, the primary drivers of greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector.
Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind with cutting-edge battery storage systems presents a game-changing synergy. These systems capture the intermittent energy generated by renewables, storing it for use during periods of high demand or when the sun isn’t shining and the wind isn’t blowing. This eliminates one of the main challenges associated with renewables—their variability—and allows for a more reliable and consistent energy supply.
By reducing the reliance on fossil fuels for electricity generation, battery technology acts as a linchpin in the fight against climate change. It not only curtails emissions but also drives a paradigm shift towards cleaner, more sustainable energy sources. This shift is not confined to a single sector; it ripples through our entire energy ecosystem, from transportation to residential and industrial use.
Battery technology also plays a pivotal role in grid resilience, ensuring that renewable energy can be harnessed effectively and distributed efficiently. This resilience minimizes the need for backup fossil fuel power plants, further reducing emissions and paving the way for a cleaner and more sustainable future.
In sum, the adoption of battery-powered EVs and the seamless integration of renewables with advanced battery storage systems herald a transformative era. It’s an era where we’re reducing our reliance on fossil fuels, mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and steering our world towards a greener and more sustainable future. Battery technology is not just a technological marvel; it’s a beacon of hope in the battle against climate change, demonstrating that we have the tools to make a significant difference in preserving our planet for future generations.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: The Long-Term Strategy of the United States, Pathways to Net-Zero …

Economic Opportunities and Job Creation
The growth of battery technology creates economic opportunities and jobs. It spurs innovation in manufacturing, research and development, while also creating jobs in battery production, installation and maintenance. As the industry expands, it fosters economic growth and technological advancement.
The growth of battery technology creates economic opportunities and jobs on a scale that reaches far beyond what meets the eye. It not only spurs innovation in manufacturing, research and development but also creates jobs in battery production, installation and maintenance. However, its impact on the economy goes even deeper, fostering economic growth and technological advancement in various interconnected ways.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain: The battery industry’s expansion leads to increased demand for battery components and materials like lithium, cobalt and nickel. This demand, in turn, generates economic opportunities for mining and processing these materials. Moreover, the manufacturing of battery cells and packs requires a skilled workforce, contributing to job creation in manufacturing hubs worldwide. These manufacturing facilities often require ancillary services, such as logistics and transportation, further boosting job creation.
Research and Development: As battery technology evolves, there’s a continuous need for research and development. This involves scientists, engineers and technicians working on improving battery efficiency, safety and environmental impact. The innovation in battery chemistry and design has broader applications beyond energy storage, including electric vehicles, renewable energy systems and portable electronics. This research generates high-value jobs and attracts talent to the field.
Energy Sector Growth: The integration of batteries into renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind farms, enhances their reliability and stability. This not only accelerates the adoption of clean energy but also stimulates growth in the energy sector. Battery installation, operation and maintenance require skilled technicians and engineers, creating a new workforce specialized in energy storage systems.
Transportation and Electric Vehicles: The electric vehicle (EV) market is closely tied to battery technology. As EV adoption surges, it drives job creation in vehicle manufacturing, charging infrastructure development and battery recycling. Governments and private industries are investing heavily in electric mobility, further fueling the demand for EV-related jobs.
Energy Independence and Security: The development of advanced battery technology enhances a nation’s energy independence and security. By relying on domestically produced batteries, countries reduce their dependence on foreign oil and energy sources. This, in turn, strengthens national economies and reduces vulnerability to energy supply disruptions.
Environmental and Sustainability Initiatives: Battery technology plays a crucial role in achieving environmental and sustainability goals. Governments and businesses are increasingly investing in clean energy technologies to combat climate change. The battery industry aligns with these efforts by creating green jobs that contribute to a more sustainable future.
Entrepreneurship and Start-ups: The rapid evolution of battery technology presents entrepreneurial opportunities. Innovators and start-ups are developing new battery-related technologies, applications and services. These ventures contribute to economic diversification, driving job creation in emerging markets.
Global Collaboration: The battery industry often involves international collaboration. Companies and research institutions from different countries work together on projects and share knowledge, leading to a global exchange of ideas and expertise. This collaboration strengthens diplomatic and trade relations, opening up new markets and opportunities for international businesses.
In conclusion, the growth of battery technology is a multifaceted catalyst for economic expansion and technological progress. It creates a ripple effect that extends from raw material extraction to advanced research and development, manufacturing and everyday applications. By fostering innovation and providing a diverse array of job opportunities, the battery industry serves as a cornerstone for economic growth and sustainable development in an increasingly electrified and interconnected world.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: FACT SHEET: Biden-Harris Administration Announces New Private …

Battery technology is reshaping the electricity market, enabling consumers to become active participants and advocates for a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. Through energy independence, cost savings, grid stabilization and reduced greenhouse gas emissions, batteries are empowering consumers to make informed energy choices. As battery technology continues to advance and become more accessible, consumers are positioned to lead the way in creating a resilient, decentralized and environmentally responsible energy landscape. The electricity market transformation is not just about delivering power; it’s about empowering consumers to shape their energy destiny and drive a sustainable energy revolution.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: A new Circular Economy Action Plan, 2020
More links
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Committing to an All-Electric Future | General Motors
