Introduction
Heart disease remains a leading cause of mortality worldwide, making it crucial to explore effective strategies for prevention and management. Statins, a class of medications designed to lower cholesterol levels, have played a significant role in reducing the risk of heart disease. In this article, we will delve into the latest research and guidelines surrounding statins and their impact on heart health.
Heart disease stands as an enduring global health challenge, continuing to be a leading cause of mortality. Given its profound impact, it becomes increasingly crucial to delve into effective strategies for both prevention and management. In this pursuit, statins, a class of medications meticulously designed to lower cholesterol levels, have emerged as formidable allies in the battle against heart disease. These medications have played a significant role in reducing the risk of heart-related ailments, making them subjects of extensive research and ongoing exploration within the medical community. In this article, we embark on a journey into the latest research findings and clinical guidelines that revolve around statins, aiming to uncover the profound impact they wield on heart health.
As we traverse the landscape of cardiovascular health, it becomes evident that heart disease is a complex and multifaceted adversary. It takes its toll through a multitude of factors, including elevated cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, obesity, and lifestyle choices. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to combating heart disease, statins have undeniably emerged as a versatile and valuable tool in the medical arsenal.
Statins work by inhibiting an enzyme involved in cholesterol production, thereby reducing the amount of cholesterol circulating in the bloodstream. This mechanism has been shown to be effective in lowering LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, a key contributor to atherosclerosis, the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries. By doing so, statins help to slow or even reverse the progression of arterial narrowing and reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
However, the use of statins is not without its nuances and considerations. Factors such as the type of statin, dosage, and individual patient characteristics play a pivotal role in determining the most appropriate treatment approach. Moreover, ongoing research continues to refine our understanding of who stands to benefit most from statin therapy and under what circumstances.
This article serves as a beacon, guiding us through the labyrinth of scientific studies, clinical trials, and evolving guidelines that shape our understanding of statins and their role in heart health. We aim to shed light on the latest advancements, offering clarity to healthcare providers and patients alike as they navigate the intricate terrain of cardiovascular management.
In our exploration, we’ll unearth the nuances of statin therapy, delve into potential side effects and risks, and shed light on the broader landscape of heart disease prevention and treatment. Through this journey, we strive to empower individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions about their cardiovascular health, ultimately paving the way for a future where heart disease takes a backseat in global health concerns.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: Dyslipidemia – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf
Statins are a group of drugs that inhibit the production of cholesterol in the liver. They primarily target LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, which is a major contributor to the development of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease. By lowering LDL cholesterol levels, statins have been proven to reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
Statins, a remarkable class of medications, play a pivotal role in managing cholesterol levels and promoting heart health. These drugs operate by inhibiting the liver’s production of cholesterol, with a primary focus on LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, commonly known as “bad” cholesterol. This form of cholesterol is notorious for its association with atherosclerosis and the development of coronary artery disease, making it a significant contributor to cardiovascular problems.
The beauty of statins lies in their ability to tackle this harmful LDL cholesterol head-on. By reducing its levels in the bloodstream, these drugs offer a powerful shield against the insidious progression of heart-related issues. Studies and clinical trials have unequivocally demonstrated the efficacy of statins in lowering the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
However, the impact of statins reaches beyond mere cholesterol reduction. They contribute to overall cardiovascular health by stabilizing plaques in arteries, reducing inflammation, and improving blood vessel function. This multifaceted approach is a testament to the significance of statins in modern medicine’s arsenal against heart disease.
Nevertheless, it’s important to note that while statins are highly effective, their use should be guided by a healthcare professional who assesses your individual risk factors and tailors treatment accordingly. With the right guidance, statins can be a vital tool in safeguarding your heart health and ensuring a longer, healthier life.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of …

Recent studies have indicated that statins may offer benefits beyond their cholesterol-lowering effects. They have shown potential in reducing inflammation, stabilizing plaque in blood vessels, and improving endothelial function.
Recent scientific research has unveiled a broader spectrum of benefits associated with statins, transcending their primary role as cholesterol-lowering medications. These studies have shed light on their potential to impact various facets of cardiovascular health and well-being.
One noteworthy revelation is their capacity to reduce inflammation within the body. Chronic inflammation is increasingly recognized as a contributing factor to a range of health issues, including cardiovascular diseases. Statins have demonstrated the ability to quell this inflammatory response, potentially reducing the risk of heart disease and related complications.
Moreover, statins have shown promise in stabilizing arterial plaque, a significant concern in cardiovascular health. Unstable plaque can rupture, leading to blood clots and potentially life-threatening events like heart attacks and strokes. Statins may help fortify this vulnerable plaque, reducing the likelihood of such catastrophic events.
Another fascinating area of research is their impact on endothelial function. Endothelial cells line the inner walls of blood vessels and play a pivotal role in regulating blood flow and vascular health. Statins appear to enhance endothelial function, promoting better blood vessel dilation and overall cardiovascular health.
These findings open up new horizons in the potential applications of statins, hinting at a more comprehensive approach to cardiovascular care. While their primary role remains cholesterol management, their ancillary benefits in reducing inflammation, stabilizing plaque, and improving endothelial function present exciting prospects for individuals at risk of heart disease or related conditions.
However, it’s essential to note that the use of statins for these broader purposes may vary from person to person, and discussions with a healthcare provider are crucial for personalized treatment decisions. Nevertheless, the expanding understanding of statins’ multifaceted effects underscores their significance in the pursuit of better heart health and may pave the way for innovative approaches to cardiovascular care in the future.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Statins and Cardiovascular Diseases: From Cholesterol Lowering to …
Research has increasingly focused on the use of statins in older adults. Findings suggest that statins can be beneficial for certain elderly individuals, particularly those with a history of cardiovascular disease or diabetes.
As our population ages and life expectancy increases, the role of statins in promoting the health of older adults has come into sharper focus. The growing body of research suggests that statins can indeed be beneficial for certain elderly individuals, with specific health conditions warranting attention.
One key group that stands to gain from statin therapy in their later years is older adults with a history of cardiovascular disease. For this segment of the population, statins offer a potent tool in managing cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of recurrent heart-related events. By helping to stabilize plaque buildup in arteries and lower LDL cholesterol, statins can contribute significantly to the longevity and quality of life of these individuals.
Similarly, elderly individuals grappling with diabetes can also reap substantial rewards from statin use. Diabetes is a risk factor for heart disease, and the combination of diabetes and aging can exacerbate this risk. Statins not only lower cholesterol but also possess anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit those with diabetes by reducing inflammation in blood vessels, potentially averting complications associated with the disease.
Nevertheless, it’s essential to note that the decision to prescribe statins to older adults should be based on individualized assessments. Factors such as overall health, life expectancy, medication tolerability, and potential interactions must be carefully considered. For some older adults, statin therapy may not provide a significant benefit, while others may stand to gain substantially.
Furthermore, it’s crucial to maintain a patient-centered approach in geriatric statin use. Shared decision-making between healthcare providers and older patients ensures that treatment aligns with individual preferences and values. This approach fosters a holistic view of health, encompassing not just the potential benefits of statins but also the patient’s overall well-being.
In conclusion, as we navigate the complexities of healthcare in an aging society, the role of statins in older adults emerges as a nuanced and increasingly relevant topic. Research continues to refine our understanding of when and for whom statin therapy is most appropriate, emphasizing the need for personalized care. By harnessing the benefits of statins while considering individual circumstances, we can support the health and longevity of our aging population, one tailored decision at a time.
Looking for more insights? You’ll find them right here in our extended coverage: Statins for Primary Prevention in Those Aged 70 Years and Older: A …

The debate over statin use for primary prevention (preventing heart disease in individuals without a history of cardiovascular events) continues. Newer guidelines emphasize individualized risk assessments to determine who may benefit most from statin therapy in this context.
The debate over statin use for primary prevention (preventing heart disease in individuals without a history of cardiovascular events) continues to evolve and is marked by ongoing research and discussions within the medical community. Newer guidelines emphasize individualized risk assessments to determine who may benefit most from statin therapy in this context, and here’s why this personalized approach is gaining prominence:
Precision Medicine: Recognizing that one size doesn’t fit all, modern healthcare is moving towards precision medicine. The idea is to tailor treatments to individuals based on their unique risk factors, genetics, and lifestyle. This approach ensures that those who stand to benefit the most from statins receive them, while minimizing unnecessary medication for others.
Assessing Comprehensive Risk: Beyond just cholesterol levels, contemporary guidelines consider a broader spectrum of risk factors, such as age, gender, family history, smoking status, and blood pressure. This comprehensive risk assessment provides a more accurate picture of an individual’s susceptibility to heart disease.
Balancing Benefits and Risks: Statins are highly effective at reducing cholesterol levels, but they are not without potential side effects. By conducting a thorough risk assessment, healthcare providers can weigh the benefits of statin therapy against the potential risks, ensuring that the treatment plan aligns with the patient’s overall health goals.
Shared Decision-Making: Modern medicine promotes shared decision-making between healthcare providers and patients. In the context of statins for primary prevention, this means involving the patient in discussions about their risk factors, the potential benefits of statins, and any concerns they may have. Informed patients are more likely to adhere to treatment plans.
Monitoring and Adaptation: Regular monitoring of patients on statin therapy allows for adjustments in dosage or medication as needed. This flexibility ensures that treatment remains effective and safe, and it enables healthcare providers to address emerging risk factors over time.
Preventing Overtreatment: Overprescribing medications can lead to unnecessary healthcare costs and potential side effects. Personalized risk assessments help identify individuals who truly need statins, reducing the risk of overtreatment and its associated drawbacks.
Advances in Research: Ongoing research continues to refine our understanding of statin therapy. New insights into the long-term effects and potential benefits are continually emerging, further influencing the decision-making process for primary prevention.
In sum, the shift towards individualized risk assessments for statin use in primary prevention reflects a more patient-centered and evidence-based approach to healthcare. It acknowledges that while statins can be highly effective, their appropriateness varies from person to person. By taking a personalized approach, healthcare providers aim to optimize the balance between the benefits and potential risks of statin therapy, ultimately enhancing heart disease prevention strategies.
You can also read more about this here: Statin Use for the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in …

Genetic research has shed light on how individuals respond to statins differently. Understanding genetic factors can help tailor statin therapy to maximize effectiveness and minimize side effects.
Genetic research has made remarkable strides in elucidating the significant variability in individuals’ responses to statin medications. This newfound knowledge has the potential to revolutionize how we approach cholesterol management and cardiovascular health.
Each person’s genetic makeup influences how their body metabolizes drugs, including statins. Some genetic variations can lead to more efficient statin metabolism, resulting in a greater reduction in LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels. Conversely, other genetic factors may cause slower metabolism or a higher susceptibility to side effects, such as muscle pain or liver abnormalities.
Understanding these genetic factors is akin to having a personalized roadmap for statin therapy. It allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to each patient’s genetic profile, maximizing the effectiveness of the medication while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
For instance, if genetic testing reveals that a patient has a genetic predisposition to metabolize statins slowly, their healthcare provider might choose a lower statin dosage or opt for a different statin altogether to achieve the desired cholesterol-lowering effect without undue side effects.
Furthermore, genetic insights can guide lifestyle recommendations. Individuals with genetic markers indicating a higher risk of statin-related muscle issues may benefit from exercise routines specifically designed to improve muscle health while on statin therapy.
Incorporating genetics into statin therapy decisions represents a significant step towards personalized medicine in cardiovascular care. It empowers both patients and healthcare providers to make more informed choices, potentially leading to better cholesterol control and reduced risks of heart disease. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in genetics or pharmacogenomics to interpret genetic test results accurately and develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your unique genetic profile.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Identifying genetic risk factors for serious adverse drug reactions …
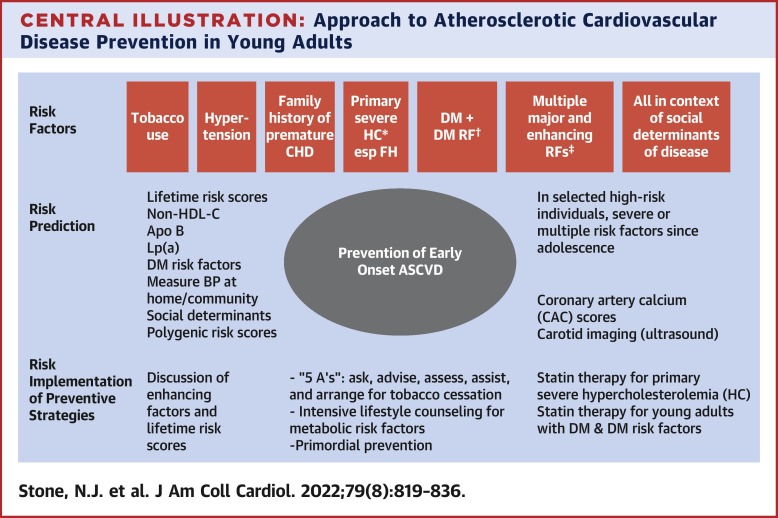
The ACC/AHA guidelines emphasize a more personalized approach to statin therapy. They recommend discussing treatment options with a healthcare provider based on factors such as age, cholesterol levels, and overall cardiovascular risk.
The ACC/AHA guidelines represent a significant shift in how we approach statin therapy, emphasizing a more personalized and patient-centered approach to cardiovascular health. Rather than a one-size-fits-all approach, these guidelines advocate for a thorough assessment of individual risk factors and a shared decision-making process between patients and healthcare providers.
One of the key aspects of this approach is the importance of open and informed discussions. When considering statin therapy, it’s crucial to engage in a meaningful conversation with your healthcare provider. They will take into account various factors, including your age, cholesterol levels, family history, and overall cardiovascular risk, to determine the most suitable treatment plan.
For instance, if you have a history of high cholesterol and a family history of heart disease, your provider may recommend statin therapy as a preventive measure, even if your cholesterol levels are not excessively high. Conversely, if your cholesterol levels are elevated but your overall cardiovascular risk is low due to factors like a healthy lifestyle and no family history of heart disease, your provider might suggest lifestyle changes as a first-line approach, with statins as a secondary option.
These guidelines underscore the importance of treating the person, not just the numbers. By tailoring statin therapy to an individual’s unique risk profile, we can optimize both the benefits and potential risks associated with these medications. This approach allows for a more holistic and patient-centric strategy to prevent and manage cardiovascular disease, ultimately promoting better heart health and well-being for everyone.
In essence, the ACC/AHA guidelines advocate for a partnership between patients and healthcare providers, where informed decisions are made based on a comprehensive evaluation of individual factors. This approach not only enhances the effectiveness of statin therapy but also empowers individuals to take an active role in their cardiovascular health, fostering a stronger commitment to heart-healthy choices and long-term well-being.
If you’d like to dive deeper into this subject, there’s more to discover on this page: 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC …
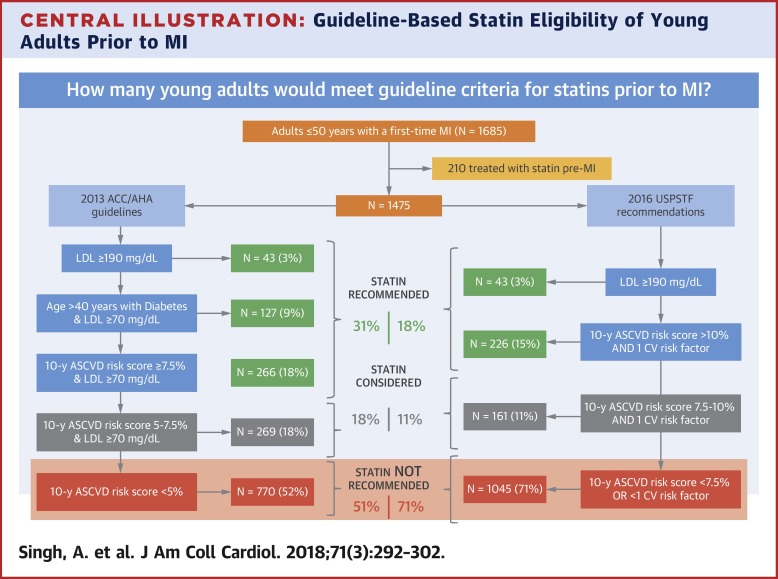
The ESC guidelines also advocate for individualized risk assessment and discuss the importance of lifestyle modifications in conjunction with statin therapy.
The recommendations provided by the ESC guidelines serve as a comprehensive roadmap to cardiovascular health. One significant aspect emphasized in these guidelines is the importance of individualized risk assessment. Recognizing that every person’s cardiovascular risk profile is unique, the guidelines stress the need to tailor treatment plans to each patient’s specific circumstances.
This individualized approach entails a thorough evaluation of various factors, including age, gender, family history, smoking status, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and more. By taking all these elements into account, healthcare professionals can assess the precise level of cardiovascular risk that a patient faces.
Moreover, the ESC guidelines underscore the pivotal role of lifestyle modifications when complemented with statin therapy. Medications alone are not a panacea; they are just one part of the equation. Lifestyle choices, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and abstaining from smoking, play a critical role in preventing and managing cardiovascular disease.
When lifestyle modifications and statin therapy work hand in hand, the results are often more impactful. A balanced, nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, coupled with regular exercise, can help lower cholesterol levels, reduce blood pressure, and improve overall heart health. These lifestyle changes not only enhance the effectiveness of statin treatment but also contribute to the prevention of heart disease in the long term.
In essence, the ESC guidelines encourage a holistic approach to cardiovascular health. They recognize that each patient is unique and that addressing heart health involves more than just prescribing medications. It encompasses personalized risk assessment and the integration of lifestyle changes that empower individuals to take charge of their well-being. By following these guidelines, healthcare professionals and patients alike can collaborate effectively to achieve better heart health outcomes and reduce the burden of cardiovascular disease worldwide.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of …

The latest guidelines underscore the importance of shared decision-making between patients and healthcare providers. This approach allows individuals to actively participate in determining the most appropriate treatment plan based on their unique circumstances and preferences.
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, the latest guidelines are championing a profound shift in the way patients and healthcare providers collaborate in making decisions about treatment. This shift revolves around the concept of shared decision-making, a dynamic and patient-centered approach that empowers individuals to take an active role in their healthcare journey.
This approach acknowledges that each person’s health journey is unique, influenced by a constellation of factors such as their medical history, values, lifestyle, and personal goals. Recognizing this diversity, shared decision-making promotes open and honest communication between patients and healthcare providers. It encourages individuals to share their concerns, preferences, and expectations, allowing them to become informed, engaged partners in their own care.
One of the key benefits of shared decision-making is its capacity to foster a deeper sense of trust and mutual respect between patients and healthcare providers. When individuals feel heard and respected, they are more likely to adhere to treatment plans and actively participate in their healthcare decisions, which can lead to better health outcomes.
Moreover, this approach can be particularly valuable in situations where multiple treatment options exist, each with its own set of benefits and risks. By engaging in shared decision-making, patients gain access to comprehensive information about their treatment choices, enabling them to weigh the pros and cons, ask questions, and ultimately make decisions that align with their values and preferences.
Shared decision-making extends beyond just medical treatment options; it also encompasses broader aspects of healthcare, such as preventive measures, screening tests, and lifestyle modifications. Patients are encouraged to collaborate with their healthcare providers in setting achievable health goals and crafting strategies to attain them.
In essence, shared decision-making represents a significant shift from the traditional model of paternalistic healthcare, where doctors made decisions on behalf of patients. It embodies the idea that healthcare is a partnership, one where the collective wisdom of both patients and providers is harnessed to make well-informed choices that optimize health and well-being.
In conclusion, the latest healthcare guidelines are paving the way for a more patient-centric approach through shared decision-making. This approach respects the uniqueness of each individual’s health journey, empowers patients to actively participate in their care, and ultimately leads to more personalized and effective healthcare decisions. It is a testament to the evolving nature of medicine, where the partnership between patients and healthcare providers takes center stage in shaping a healthier future for all.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: The Evolving View of Coronary Artery Calcium: A Personalized …
While statins have shown significant benefits in reducing heart disease risk, they are not without challenges and considerations:
While statins have shown significant benefits in reducing heart disease risk, they are not without challenges and considerations that merit careful attention. It’s crucial to recognize that, like any medication, statins come with both advantages and potential drawbacks.
Effectiveness in Cardiovascular Health: Statins have been proven effective in lowering LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels, a major contributor to atherosclerosis and heart disease. By reducing LDL cholesterol, statins can help lower the risk of heart attacks and strokes, especially in individuals with high cholesterol levels or preexisting cardiovascular conditions.
Potential Side Effects: However, it’s essential to acknowledge that statins can cause side effects in some individuals. These side effects may include muscle pain, weakness, or cramps, which can range from mild discomfort to more severe conditions like myopathy or rhabdomyolysis. Liver enzyme abnormalities and gastrointestinal symptoms are also possible side effects.
Individual Variability: Not everyone experiences side effects from statins, and for many, the benefits outweigh any potential drawbacks. The response to statins can vary significantly among individuals, and healthcare providers carefully assess each patient’s unique risk factors and medical history before prescribing them.
Monitoring and Communication: Regular monitoring is crucial when taking statins, particularly when first starting the medication or changing the dosage. Patients are encouraged to maintain open communication with their healthcare providers to report any side effects or concerns promptly. Adjustments to the type of statin or its dosage may be necessary to find the most suitable and effective treatment.
Lifestyle Factors: In conjunction with statin therapy, lifestyle changes such as a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation remain essential components of cardiovascular health. These changes can complement the benefits of statins and reduce the overall risk of heart disease.
Long-Term Commitment: Statin therapy is often recommended for the long term to maintain cholesterol levels within a healthy range and minimize cardiovascular risk. Patients are advised to adhere to their prescribed treatment plan consistently.
In conclusion, statins have emerged as a valuable tool in the prevention and management of heart disease. However, it’s essential to approach their use with awareness of the potential side effects and the need for ongoing monitoring and communication with healthcare providers. By doing so, individuals can make informed decisions about their heart health and work collaboratively with medical professionals to achieve the best possible outcomes.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Women Living with Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Challenges and …

Some individuals may experience side effects, such as muscle pain or liver enzyme elevation, while on statins. Regular monitoring and open communication with healthcare providers are essential to address these concerns.
Some individuals, while reaping the benefits of statin therapy in managing their cholesterol levels, may encounter a few bumps along the way in the form of side effects. These side effects can include muscle pain, liver enzyme elevation, or other discomforts that, while relatively rare, should not be ignored. To navigate this journey successfully, two critical elements come into play: regular monitoring and open communication with your healthcare provider.
Muscle pain, often referred to as myalgia, is one of the more commonly reported side effects of statins. While it can range from mild discomfort to more severe pain, it’s essential to promptly communicate any muscle-related issues to your healthcare provider. Regular check-ins and an open dialogue can help your provider assess the severity and potential causes of the pain, allowing for timely adjustments to your medication regimen if necessary. In some cases, a change in dosage or switching to a different statin may alleviate these concerns, ensuring you continue to benefit from cholesterol management without unnecessary discomfort.
Liver enzyme elevation, another potential side effect, underscores the importance of vigilant monitoring. Statins can occasionally lead to an increase in liver enzymes, which may warrant further investigation. Routine liver function tests are essential to catch and address any concerning trends early on. Your healthcare provider can assess these results, weighing the benefits of statin therapy against any potential risks to your liver health. This careful monitoring helps strike the delicate balance between optimizing cardiovascular health and ensuring overall well-being.
Maintaining open lines of communication with your healthcare provider is paramount. Your provider needs to be informed about any side effects or concerns you experience during statin therapy. This transparency allows them to tailor your treatment plan to your specific needs, potentially exploring alternative medications or dosage adjustments to minimize side effects while effectively managing your cholesterol.
In conclusion, while some individuals may encounter side effects while taking statins, these issues should not deter you from reaping the benefits of cholesterol management. Regular monitoring, including muscle pain assessments and liver function tests, combined with open communication with your healthcare provider, forms the cornerstone of a successful statin regimen. By working collaboratively, you can address concerns promptly, fine-tune your treatment plan, and ensure that your journey to better cardiovascular health remains as smooth and effective as possible.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC …
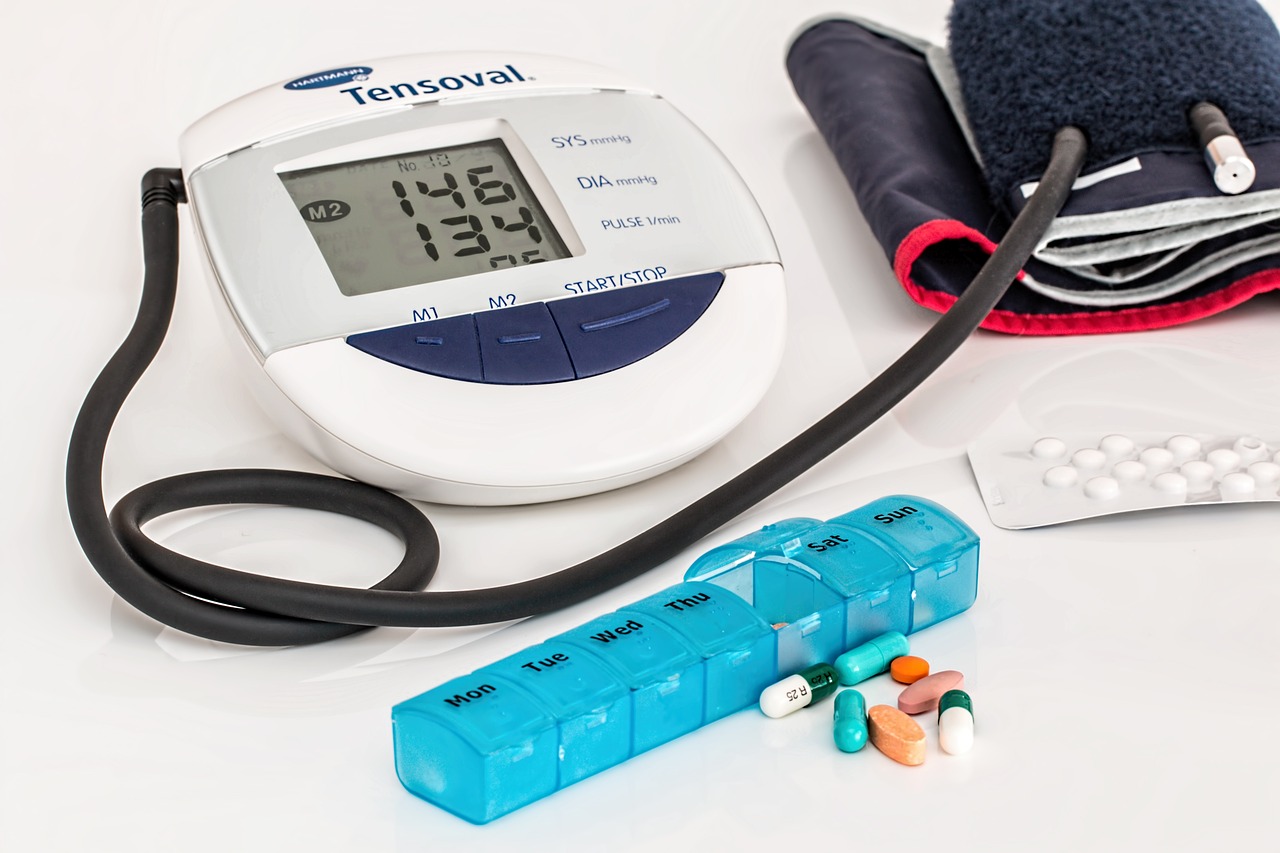
Lifestyle modifications, including a heart-healthy diet and regular exercise, are critical components of heart health. Statins are most effective when used in conjunction with these lifestyle changes.
Embracing a heart-healthy lifestyle is the cornerstone of cardiovascular well-being, and it encompasses more than just taking medications. Lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role in achieving and maintaining optimal heart health. Among these changes, two pillars stand tall: diet and exercise.
A heart-healthy diet is a nutritional roadmap that navigates away from saturated and trans fats, steering towards the bountiful shores of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. This dietary shift is essential, as it helps lower LDL cholesterol levels, the very target of statins. A diet rich in fiber, antioxidants, and unsaturated fats not only supports cholesterol management but also nourishes the heart with essential nutrients.
Regular exercise is the dynamic counterpart to a heart-healthy diet. Physical activity strengthens the heart muscle, enhances blood circulation, and contributes to overall fitness. It plays a starring role in maintaining a healthy weight, reducing blood pressure, and improving cholesterol profiles. Moreover, exercise supports the body’s production of HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, often referred to as “good cholesterol,” which acts as a protective shield for the heart.
When it comes to statins, they are most effective when used in tandem with these lifestyle changes. Statins provide a powerful tool to manage cholesterol levels, but they do not work in isolation. Instead, they complement and amplify the benefits of heart-healthy living. By combining the cholesterol-lowering prowess of statins with a nutritious diet and regular exercise, individuals can create a holistic approach to heart health.
Furthermore, this integrated approach often allows for lower statin dosages, minimizing the risk of potential side effects. It’s a win-win situation: a healthier lifestyle and optimized statin therapy work hand in hand to reduce cardiovascular risk effectively while enhancing overall well-being.
In summary, lifestyle modifications, including a heart-healthy diet and regular exercise, are not just beneficial but critical components of heart health. When coupled with statin therapy, they form a formidable alliance in the fight against heart disease, ensuring that individuals can live their lives to the fullest while protecting their most vital organ—the heart.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC …
Ensuring that patients are well-informed about the benefits and potential risks of statin therapy is crucial for adherence and success.
Ensuring that patients are well-informed about the benefits and potential risks of statin therapy is not just crucial; it’s a cornerstone of successful treatment and improved health outcomes.
Knowledge empowers patients to actively participate in their own healthcare journey. When patients understand why their healthcare provider has recommended statin therapy, the potential benefits, and the associated risks, they are more likely to commit to the treatment plan. This commitment, in turn, enhances medication adherence, which is a critical factor in achieving the desired results.
Patients who are well-informed about statin therapy can make informed decisions in collaboration with their healthcare provider. They can discuss any concerns or preferences they have, leading to more personalized treatment plans that align with their individual health goals and lifestyles. This patient-provider partnership fosters trust and confidence in the chosen course of action.
Moreover, awareness of potential risks empowers patients to recognize and report side effects promptly. Early detection of side effects can lead to timely interventions, which may include adjusting the dosage, trying a different statin, or considering alternative cholesterol management strategies. This proactive approach not only minimizes the impact of side effects but also enhances the overall safety and effectiveness of statin therapy.
Furthermore, informed patients are more likely to embrace lifestyle changes that complement their medication. They understand that medication alone is not a magic solution, and that healthy habits like diet and exercise play a significant role in managing cholesterol levels and reducing cardiovascular risk.
In summary, patient education regarding statin therapy is the linchpin of a successful treatment journey. It fosters active participation, informed decision-making, and collaborative partnerships between patients and healthcare providers. Ultimately, it empowers individuals to take charge of their health, adhere to their treatment plan, and work towards achieving the maximum benefits of statin therapy while mitigating potential risks.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Comprehensive Cancer Information – NCI

Conclusion
The latest research and guidelines surrounding statins and heart health underscore the importance of personalized approaches to cholesterol management. While statins continue to be a valuable tool in reducing heart disease risk, healthcare providers are increasingly taking into account individualized risk assessments and shared decision-making to determine the most appropriate treatment plans. It is essential for patients and healthcare providers to collaborate closely to achieve optimal cardiovascular health while considering the latest research findings and guidelines in the context of each individual’s unique health profile.
The evolving landscape of heart health management emphasizes the need for a tailored approach to cholesterol management. Here’s an extended exploration of this idea:
Personalized Medicine in Cholesterol Management: As our understanding of heart disease and cholesterol management deepens, the one-size-fits-all approach to prescribing statins is evolving into a more personalized model. Healthcare providers are recognizing that every patient is unique, with distinct risk factors, genetics, and lifestyle choices that influence their cardiovascular health.
Individualized Risk Assessments: One of the critical shifts in contemporary healthcare is the emphasis on individualized risk assessments. Instead of relying solely on cholesterol levels, healthcare providers now take a comprehensive approach to evaluate a patient’s risk. Factors such as family history, smoking status, blood pressure, and other cardiovascular risk markers are considered. This nuanced evaluation helps determine who stands to benefit the most from statin therapy.
Shared Decision-Making Empowerment: The era of shared decision-making has ushered in a new level of patient empowerment. Patients are encouraged to actively participate in their healthcare journey, including discussions about cholesterol management. Informed patients can engage in productive conversations with their healthcare providers, weighing the potential benefits and risks of statins in light of their unique circumstances and preferences.
Adherence and Monitoring: Achieving optimal cardiovascular health goes beyond just prescribing statins; it involves promoting adherence to medication regimens and lifestyle changes. Patients and providers collaborate closely to monitor the effectiveness of statin therapy, address any side effects, and make necessary adjustments. Regular follow-ups and open communication are key elements of this process.
Lifestyle Integration: While statins are a valuable tool in cholesterol management, they are most effective when integrated with lifestyle modifications. A heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and smoking cessation play a pivotal role in achieving and maintaining optimal heart health. The latest guidelines highlight the synergy between statins and these lifestyle changes, reinforcing the message that both are crucial components of heart disease prevention.
Patient-Centric Outcomes: In this evolving landscape, the focus extends beyond simply lowering cholesterol numbers. The ultimate goal is to improve patient-centric outcomes, such as reducing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and overall cardiovascular mortality. This shift in focus underscores the significance of the individualized approach, where patients and healthcare providers work together to achieve meaningful improvements in health and quality of life.
In conclusion, the latest research and guidelines in cholesterol management and statin therapy promote a patient-centric, personalized approach. Recognizing the diversity of patients’ needs, risk factors, and preferences, healthcare providers are increasingly tailoring treatment plans to individual profiles. This approach fosters a collaborative, informed decision-making process that empowers patients to actively participate in their cardiovascular health journey, ultimately striving for optimal outcomes while considering the latest research findings and guidelines in the context of each individual’s unique health profile.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Flawed cholesterol study makes headlines – Heart Matters magazine …
More links
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC …
