Table of Contents
In the age of information overload, data visualization has emerged as a powerful tool for making sense of complex data sets. Whether you’re presenting sales figures, market trends or scientific research findings, effective data visualization can transform raw numbers into meaningful insights. Among the various methods available, charts and graphs stand out as popular choices for creating visually compelling reports. In this article, we will delve into the world of data visualization, exploring the differences between charts and graphs and the tools available for each.
In today’s fast-paced world inundated with data, the art of data visualization has risen as a beacon of clarity amid the information overload. It’s a powerful tool that transcends industries and professions, from business analysts deciphering sales figures to researchers unraveling intricate scientific data. Effective data visualization can perform the remarkable feat of converting raw data into profound insights, making it a cornerstone of informed decision-making.
Among the myriad methods for visualizing data, charts and graphs reign supreme as stalwarts of the trade. They have earned their place as indispensable instruments for crafting visually captivating and comprehensible reports. In this article, we embark on a journey into the captivating realm of data visualization, shedding light on the distinctions between charts and graphs and the diverse array of tools at your disposal for wielding them with finesse.
The Power of Visual Storytelling: In an era where attention spans are at a premium, data visualization leverages the innate human affinity for visual content. It transforms abstract numbers and unwieldy datasets into captivating narratives, allowing you to tell a story with your data. Charts and graphs are the brushstrokes of this visual storytelling canvas, each with its unique strengths and applications.
Charts vs. Graphs: Deciphering the Nuances: While the terms “chart” and “graph” are often used interchangeably, they each have specific connotations in the realm of data visualization. Charts, typically referring to tools like bar charts and pie charts, excel at illustrating categorical data or discrete comparisons. In contrast, graphs encompass a broader spectrum of visual representations, including line graphs and scatter plots, which shine when conveying continuous data trends or relationships. Understanding these nuances is key to selecting the most suitable visualization method for your data.
The Art and Science of Selection: Choosing the right chart or graph for your data is both an art and a science. It involves considering factors such as the nature of your data (categorical or continuous), the message you want to convey (comparison, distribution, correlation, etc.) and the target audience’s familiarity with visualization types. A well-chosen visualization method can elucidate complex data patterns, while an ill-fitting one can lead to confusion.
Tools of the Trade: The arsenal of data visualization tools has expanded dramatically in recent years. From traditional tools like Microsoft Excel and Tableau to open-source platforms like R and Python libraries like Matplotlib and Seaborn, there is a wealth of options at your disposal. Each tool offers a unique blend of features, interactivity and customization, allowing you to tailor your visualizations to your precise needs.
The Quest for Clarity and Impact: Ultimately, the goal of data visualization transcends aesthetics; it’s about clarity and impact. A well-crafted chart or graph should not only be visually appealing but also elucidate the underlying patterns and insights within your data. It should empower your audience to make informed decisions and take meaningful actions based on the information presented.
In the pages that follow, we will embark on an exploratory journey through the world of data visualization. We will delve deeper into the nuances of charts and graphs, examining their individual strengths and applications. We will also navigate the landscape of data visualization tools, equipping you with the knowledge and skills needed to harness the full potential of these visual instruments. So, join us as we unravel the art and science of data visualization, where numbers transform into stories and insights become a beacon in the sea of data.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Visualization types in Power BI – Power BI | Microsoft Learn
The Art of Data Visualization
Data visualization is the practice of representing data in visual formats such as charts, graphs, maps and infographics. Its primary goal is to convey complex information clearly and efficiently, making it easier for audiences to understand and interpret data trends, patterns and outliers. Data visualization is an indispensable tool for decision-makers, analysts, educators and researchers across diverse fields.
Data visualization is not merely a tool; it’s a powerful language that transcends the boundaries of complexity. It serves as a bridge between raw data and meaningful insights, unlocking a world of understanding for those who wield it. Let’s delve deeper into the significance and versatility of data visualization:
Enhanced Comprehension: Data, in its raw form, can be overwhelming. Visualizing data transforms numbers and statistics into accessible visuals. Charts, graphs and maps simplify the interpretation process, enabling individuals to grasp information quickly and accurately.
Detecting Patterns: Data visualization is a detective’s magnifying glass, revealing hidden patterns and correlations that might go unnoticed in rows of numbers. It’s a vital asset for data analysts, as it aids in identifying trends, anomalies and anomalies that can inform strategic decisions.
Effective Communication: As the saying goes, “A picture is worth a thousand words.” Data visualization goes beyond words, conveying complex concepts and findings in a visual language that transcends language barriers. It’s a universal tool for communicating data-driven stories.
Decision Support: Decision-makers across industries rely on data visualization to inform critical choices. Whether it’s a business executive planning a marketing strategy or a healthcare professional analyzing patient outcomes, data visualization provides the insights needed to make informed decisions.
Educational Tool: In the realm of education, data visualization is a dynamic teaching tool. It makes abstract concepts tangible and relatable. Educators use interactive visuals to engage students, making learning a more immersive and enjoyable experience.
Research and Exploration: Researchers leverage data visualization to explore and present their findings. It’s indispensable in fields like environmental science, where maps and geographic visualizations help track phenomena like climate change and deforestation.
Storytelling Medium: Data visualization is a medium for storytelling. It helps narrate data-driven narratives that resonate with audiences. By crafting compelling visuals, communicators can convey the significance of data trends and their real-world implications.
Real-Time Monitoring: In an era of rapid information flow, real-time data visualization is a critical tool for monitoring and responding to dynamic situations. For example, financial analysts rely on real-time stock market visualizations to make split-second decisions.
Data Accessibility: Data visualization democratizes data. It makes information accessible to a broader audience, ensuring that individuals with varying levels of data literacy can engage with and understand data-driven content.
Engagement and Retention: Visual content is inherently more engaging and memorable. Whether it’s a captivating infographic or an interactive dashboard, data visualization captures attention and fosters information retention.
Interdisciplinary Value: Data visualization transcends disciplines. It’s equally valuable in marketing, public health, social sciences and countless other fields, showcasing its versatility and wide-ranging applicability.
In essence, data visualization is the conduit through which data transforms into knowledge. It empowers individuals to explore, understand and act upon information, driving progress in fields as diverse as business, science, education and beyond. As we navigate an increasingly data-driven world, the ability to wield this tool effectively becomes ever more critical, unlocking insights and opportunities that shape our decisions and innovations.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here Data Visualization – How to Pick the Right Chart Type?

Charts vs. Graphs: What’s the Difference?
Before diving into the tools available for data visualization, it’s important to distinguish between charts and graphs, as they serve slightly different purposes:
Before exploring the array of data visualization tools, it’s crucial to grasp the nuances between charts and graphs, each catering to distinct purposes. Charts primarily represent data using visual elements like bars, lines or pie slices, ideal for comparing and showcasing relationships or trends. On the other hand, graphs employ various types of visualizations such as line graphs, scatter plots and histograms, serving to illustrate patterns, distributions and correlations within data sets. Understanding this fundamental difference sets the stage for choosing the most fitting visualization tool that aligns with your specific data representation needs.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: See 20 Different Types Of Graphs And Charts With Examples
Charts
Charts are primarily used to represent quantitative data and show relationships or comparisons between different data points. Common types of charts include bar charts, pie charts, line charts and scatterplots.
“Charts are invaluable tools in the realm of data visualization, serving as the bridge between raw numbers and meaningful insights. They primarily come into play when we need to represent quantitative data and provide a clear, visual means of conveying information. Here, we delve deeper into the world of charts, exploring their versatility and the common types that help us elucidate relationships and comparisons in our data.
Bar Charts: Bar charts are the workhorses of data representation. They use rectangular bars to depict data values, with the length or height of each bar proportional to the value it represents. Bar charts are ideal for comparing discrete categories or tracking changes over time, making them a favorite for market researchers, statisticians and business analysts.
Pie Charts: If you want to showcase the composition of a whole in relation to its parts, pie charts come into play. These circular charts divide data into slices, with each slice representing a proportion of the whole. They are particularly effective for illustrating percentages and showing how individual components contribute to the whole.
Line Charts: Line charts are the go-to choice for tracking trends and changes over time. They use lines to connect data points, creating a visual representation of how a variable evolves. Line charts are indispensable in fields like finance, where they help investors monitor stock prices or in climate science, where they illustrate temperature fluctuations over the years.
Scatterplots: When you need to uncover patterns, correlations or outliers in your data, scatterplots step in. They scatter data points across a graph, with one variable on the x-axis and another on the y-axis. By examining the distribution and clustering of points, you can discern relationships between variables, making scatterplots invaluable in scientific research, social sciences and quality control.
But these are just the tip of the iceberg. The world of data visualization offers a vast array of chart types, each tailored to specific data representation needs. Heatmaps help visualize complex data distributions, while radar charts come in handy for comparing multiple variables at once. Waterfall charts are perfect for tracking cumulative effects and bubble charts enable the representation of three dimensions of data within a 2D space.
In today’s data-driven world, understanding the strengths and limitations of different chart types is essential for effective communication and decision-making. Choosing the right chart for your data can transform a sea of numbers into a compelling story, allowing you to convey insights with clarity and impact.”
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: See 20 Different Types Of Graphs And Charts With Examples
Graphs
Graphs, on the other hand, are used to display more complex data relationships. They are often employed to showcase the connections, trends or distributions within a dataset. Types of graphs include network graphs, tree diagrams and flowcharts.
Graphs, as a data visualization tool, offer a deeper and more intricate layer of insight into complex data relationships. While charts are excellent for representing simple data sets, graphs come into play when you need to unveil the intricate interplay of data points and their connections. Here’s a closer look at why graphs are essential in data analysis:
Revealing Complex Relationships: Graphs excel at unveiling complex relationships within datasets. Network graphs, for example, showcase the connections between nodes, making them invaluable for social network analysis, transportation planning and even understanding the internet’s structure. These visualizations lay bare the web of interactions that might be challenging to decipher through raw data alone.
Highlighting Trends and Patterns: Graphs are ideal for detecting trends and patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed. By representing data points as nodes and their connections as edges, network graphs can help identify clusters, central hubs and influential nodes within a network. This insight is invaluable in fields like marketing, epidemiology and finance.
Depicting Hierarchical Structures: When dealing with hierarchical data or organizational structures, tree diagrams and flowcharts become indispensable. Tree diagrams visually represent parent-child relationships, allowing you to navigate complex hierarchies with ease. Flowcharts, on the other hand, help map out decision processes, workflows and system architectures, making them a valuable tool in business process analysis and software development.
Understanding Information Flow: Flowcharts, in particular, excel at illustrating the flow of information, materials or processes within a system. They provide a step-by-step representation of how tasks are carried out, decisions are made and inputs and outputs are linked. This clarity is essential in process optimization and quality control.
Enhancing Communication: Graphs serve as a universal language in data communication. Whether you’re sharing research findings, project plans or organizational structures, visual representations like network graphs and flowcharts transcend language barriers and convey complex concepts more effectively than text or tables.
Facilitating Decision-Making: Visualizations like decision trees and flowcharts are instrumental in decision-making processes. They provide a clear framework for evaluating options, considering various scenarios and arriving at informed decisions. Decision trees, for example, are widely used in fields such as finance and healthcare to assess risks and make investment or treatment decisions.
Supporting Project Management: Flowcharts are extensively used in project management to map out project workflows, dependencies and critical paths. They help project managers and teams visualize the project’s timeline and identify potential bottlenecks or areas where resources need allocation.
Enabling Interactive Data Exploration: With the advent of interactive data visualization tools, graphs have taken on a dynamic dimension. Users can explore complex datasets by interacting with network graphs, zooming in on specific nodes and filtering data to reveal deeper insights. This interactivity enhances data exploration and analysis capabilities.
In essence, while charts excel at presenting straightforward data comparisons, graphs elevate data visualization to a new level by revealing intricate relationships, trends, hierarchies and flows within complex datasets. Whether it’s untangling the connections in a social network, optimizing business processes or aiding in decision-making, graphs are a powerful tool in the data analyst’s arsenal, allowing for deeper understanding and more informed action in a data-driven world.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Data Visualization – How to Pick the Right Chart Type?

Choosing the Right Tool
The choice between using charts or graphs depends on the nature of the data and the specific message you want to convey in your report. Here are some considerations when selecting the appropriate tool:
The choice between using charts or graphs depends on the nature of the data and the specific message you want to convey in your report. Here are some important considerations to keep in mind when selecting the appropriate visualization tool:
Data Type and Complexity: Consider the type of data you are dealing with. If you have a dataset with numerical values and want to show trends, relationships or comparisons, charts like line graphs, bar charts and scatterplots are often more suitable. On the other hand, if you are dealing with non-numerical or categorical data, pie charts, stacked bar charts or histograms may be more appropriate.
Message Clarity: Think about the message you want to convey to your audience. Charts are excellent for illustrating trends over time, showing comparisons or highlighting differences. Graphs, on the other hand, are often used to depict data distributions, patterns or proportions. Choose the visualization method that best aligns with your intended message.
Audience Understanding: Consider your audience’s familiarity with data visualization. Charts like bar graphs and line charts are generally more widely understood and easier to interpret for a broad audience. If your audience includes data experts, more complex graphs like heatmaps or box plots may be suitable.
Data Size: The size of your dataset matters. For small datasets, simple charts or graphs are usually sufficient. However, for large datasets, consider using data visualization tools or techniques that can help condense and summarize the information effectively, such as heatmaps or pivot charts.
Temporal Aspects: If your data involves a time dimension, such as tracking trends over months or years, time-series line charts can provide a clear representation of these patterns. On the other hand, if you want to focus on a specific point in time, bar charts or pie charts may be more appropriate.
Interactivity: Consider whether interactivity is necessary for your report. Some charts and graphs can be made interactive, allowing users to explore the data further by hovering over data points or clicking on elements for additional information. Interactive elements can enhance engagement and understanding.
Visual Appeal: Aesthetics matter in data visualization. Choose a chart or graph style that is visually appealing and aligns with your report’s overall design and branding. Clear color choices and proper labeling are essential for making your visualizations attractive and informative.
Context and Storytelling: Think about the context in which your data will be presented. Charts and graphs should be used to support your narrative or story. Ensure that they enhance the overall flow of your report and provide valuable insights to the reader.
In conclusion, the choice between using charts or graphs is not arbitrary but rather a strategic decision based on the nature of your data and the specific message you want to convey. By considering these factors, you can select the most appropriate visualization tool to effectively communicate your data-driven insights to your audience.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: An Overview of the Best Data Visualization Tools | Toptal®

Data Complexity
Charts are suitable for straightforward data comparisons, while graphs are better suited for representing intricate data relationships and structures.
Charts and graphs are indispensable data visualization tools, each offering unique strengths that cater to specific data representation needs:
Charts for Clarity: Charts, such as bar charts and pie charts, excel in presenting straightforward data comparisons. They are ideal for scenarios where you need to highlight individual data points, show proportions or illustrate simple trends. For instance, a bar chart can effectively compare sales figures for different months, making it easy to identify which months had the highest or lowest sales.
Graphs for Complexity: Graphs, on the other hand, are better suited for representing intricate data relationships and structures. Line graphs, scatter plots and network graphs are valuable when dealing with data that has multiple variables, patterns or dependencies. They allow you to visualize how various factors interact and influence one another. For instance, a line graph can show how temperature, humidity and rainfall levels correlate over time, revealing complex weather patterns.
Trend Identification: Charts are excellent for highlighting specific data points and trends that are immediately apparent. They simplify the process of identifying highs, lows and outliers in the data. This is crucial when making quick, data-driven decisions.
Data Exploration: Graphs are essential for in-depth data exploration and analysis. They can uncover hidden patterns, trends and outliers that may not be immediately evident in raw data. Graphs provide a visual landscape where data scientists and analysts can dive deep into complex datasets to extract meaningful insights.
Interactivity: Graphs often offer interactivity features that allow users to explore data dynamically. You can zoom in, filter data points or hover over elements to view additional information. This interactivity enhances the user’s ability to understand the nuances of complex data.
Prediction and Forecasting: Graphs are commonly used in predictive modeling and forecasting. They enable analysts to visualize historical data and extrapolate trends to make informed predictions about future outcomes. For example, a time-series graph can reveal seasonal patterns that help forecast future sales.
Hierarchical Data: When dealing with hierarchical or networked data, such as organizational structures, social networks or supply chains, graphs are indispensable. They visually represent relationships between nodes and edges, making it easier to understand complex networks.
Multiple Variables: Graphs can accommodate multiple variables and dimensions in a single visualization. This is particularly valuable when you want to explore how several factors interact. For instance, a 3D scatter plot can depict relationships between three variables simultaneously.
Customization: Both charts and graphs can be customized to suit specific visualization requirements. You can adjust colors, labels and scales to enhance clarity and visual appeal.
In conclusion, while charts excel in simplifying data for quick comparisons and trend identification, graphs are essential for delving into complex data relationships, uncovering hidden patterns and facilitating in-depth analysis. The choice between charts and graphs depends on the nature of your data and the insights you aim to extract. Leveraging both visualization tools appropriately can help you gain a comprehensive understanding of your data and make informed decisions based on its complexities.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: What is data visualization and why is it important?

Audience Understanding
Consider the level of familiarity your audience has with data visualization. Charts are generally easier for most people to interpret, while graphs may require more expertise.
When it comes to presenting data, tailoring your approach to your audience’s familiarity with data visualization is key to effective communication. It’s crucial to consider the level of expertise and comfort your audience has with interpreting and drawing insights from data. Here’s a deeper exploration of this concept:
Charts for Clarity: Charts, such as bar charts, pie charts and line graphs, are excellent choices when your audience may not have extensive experience with data visualization. These visual representations are generally intuitive and can convey information clearly to a broad audience. They provide a quick, at-a-glance understanding of trends, comparisons and proportions within the data.
Graphs for Depth: On the other hand, if your audience consists of data-savvy individuals or experts in a particular field, using graphs like scatterplots, histograms or heatmaps may be appropriate. Graphs offer more nuanced insights and can reveal complex relationships within the data. However, they often require a deeper level of statistical literacy to interpret accurately.
Audience Proficiency: Gauge your audience’s proficiency in data analysis and visualization. Are they accustomed to dealing with data in their everyday work or is this a less common task for them? Adjust your choice of visualization accordingly to strike the right balance between clarity and depth.
Educational Needs: Consider whether your presentation aims to educate your audience about data visualization or to convey specific data-driven insights. If it’s an educational setting or your audience is relatively new to data analysis, leaning towards simpler chart types can help them grasp fundamental concepts.
Storytelling: Think about the story you want to tell with your data. Charts are often better at conveying straightforward narratives, while graphs can help unveil more complex stories lurking within the data. Tailor your choice to the story you wish to convey.
Interactivity: Some presentations benefit from interactive data visualization tools, allowing the audience to explore the data themselves. This can be particularly effective when presenting to diverse audiences with varying levels of expertise, as it lets individuals engage with the data at their own pace and comfort level.
Visual Appeal: The visual appeal of your data presentation matters. Regardless of your audience’s expertise, a well-designed and aesthetically pleasing data visualization can enhance engagement and understanding. Ensure that your charts or graphs are clear, concise and visually appealing.
Context Matters: Always consider the context in which your data will be presented. Is it a formal business presentation, an academic seminar, a scientific conference or an informal team meeting? The appropriateness of your choice may vary based on the setting.
In conclusion, effective data presentation requires a thoughtful approach that aligns with your audience’s familiarity with data visualization. Whether you opt for charts for simplicity or graphs for depth, the key is to communicate your data clearly and engage your audience effectively, ensuring that the message is conveyed accurately and that insights are gained from the data you present.
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: What Is Data Visualization? Definition & Examples | Tableau

Report Goals
Determine the objectives of your report. If you need to illustrate sales trends over time, a line chart may be ideal. If you’re mapping out organizational hierarchies, a tree diagram could be more appropriate.
“Determining the objectives of your report is the crucial first step in crafting a compelling and effective document. Once you’ve identified your goals, selecting the right visual representation is paramount to convey your message with clarity and impact. Let’s delve deeper into this process:
Clarifying Objectives: Before diving into chart or diagram selection, it’s essential to clarify the objectives of your report. What story or message are you trying to convey? Are you presenting data, explaining a process or visualizing a complex concept? Understanding the ‘why’ behind your report will guide your choice of visual aids.
Choosing the Right Chart Type: Charts come in various forms, each suited to different types of data and objectives. For instance:
- Line Charts: Ideal for illustrating trends over time, showing the progression of data points, such as sales figures, stock prices or temperature changes.
- Bar Charts: Effective for comparing values across different categories, making them useful for market share comparisons, survey results or budget allocations.
- Pie Charts: Best for showing parts of a whole, like budget distribution, market segments or composition of a portfolio.
- Scatter Plots: Useful for revealing relationships and correlations between two variables, common in scientific research and data analysis.
- Tree Diagrams: Great for visualizing hierarchies, organizational structures or decision-making processes.
- Heatmaps: Effective for displaying large datasets and highlighting patterns or variations within them.
Data Complexity: The complexity of your data is another factor to consider. If your data is straightforward and can be summarized in a single data series, a basic chart type may suffice. However, if you’re dealing with multifaceted data with multiple variables or dimensions, more advanced chart types like radar charts or Sankey diagrams may be required to provide a comprehensive view.
Audience Consideration: Think about your audience’s familiarity with data visualization. If you’re presenting to a data-savvy audience, you can use more complex visualizations. For general audiences, simplicity and clarity should be your guiding principles.
Storytelling Element: Beyond just presenting data, consider how your chart or diagram contributes to the overall narrative of your report. Does it help tell a story, clarify a point or guide the reader’s understanding? The visual aids should seamlessly integrate with your report’s narrative flow.
Aesthetics and Readability: Pay attention to the visual design of your chart or diagram. Ensure that it’s aesthetically pleasing, uses appropriate color schemes and maintains readability. Avoid clutter and unnecessary embellishments that can distract from the main message.
Interactivity (if needed): In digital reports and presentations, consider adding interactive elements to your charts and diagrams, allowing users to explore the data further. Interactive features can enhance engagement and understanding.
Testing and Iteration: Finally, don’t hesitate to test your chosen chart or diagram with a sample audience or colleagues to gather feedback. Iteration based on feedback can lead to refinements that make your report even more effective.
In summary, the choice of visual representation in your report is a pivotal decision. It should align with your report’s objectives, data complexity and audience expectations. By thoughtfully selecting the right chart or diagram type, you enhance your report’s impact, making it a powerful tool for conveying information, insights and stories effectively.”
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: What is data visualization and why is it important?

Tools for Chart Creation
Several software tools are available to create charts, ranging from basic spreadsheet applications to dedicated data visualization software. Here are a few notable options:
Numerous software tools cater to the diverse needs of chart creation, making it easier than ever to transform data into meaningful visual representations. From straightforward spreadsheet applications to specialized data visualization software, the array of options ensures that there’s a tool for everyone. Here’s a closer look at some notable choices that empower users to craft impactful charts:
Microsoft Excel: Excel is a ubiquitous spreadsheet application that offers robust charting capabilities. It’s a go-to choice for creating standard charts like bar graphs, line charts and pie charts. Excel’s user-friendly interface makes it accessible to a wide range of users, from beginners to advanced data analysts.
Google Sheets: Google Sheets, a cloud-based spreadsheet tool, is ideal for collaborative chart creation. It shares many similarities with Excel and provides various chart types. Moreover, it excels in real-time collaboration, allowing multiple users to work on the same spreadsheet simultaneously.
Tableau: Tableau is a powerful data visualization software designed for in-depth analysis and interactive dashboards. It’s particularly well-suited for professionals who require complex visualizations and want to extract insights from large datasets. Tableau offers advanced features for business intelligence and data storytelling.
Power BI: Developed by Microsoft, Power BI is another heavyweight in the data visualization arena. It’s known for its seamless integration with other Microsoft tools and its ability to transform raw data into compelling visual stories. Power BI is a top choice for organizations seeking comprehensive data analytics and reporting.
Plotly: Plotly is an open-source data visualization library that integrates with programming languages like Python and R. It’s favored by data scientists and analysts for its flexibility in creating interactive and customized charts. Plotly’s JavaScript library also facilitates web-based charting.
Canva: Canva is a versatile design platform that simplifies the process of creating visually appealing charts and infographics. It’s an excellent choice for those who prioritize design aesthetics and wish to add a creative touch to their data visualizations. Canva offers a wide array of templates and design elements.
D3.js: D3.js (Data-Driven Documents) is a JavaScript library renowned for its flexibility and control over data visualizations. It allows developers to build custom, interactive charts and data-driven applications. D3.js is ideal for those with programming skills and specific design requirements.
Chart.js: Chart.js is a JavaScript library that simplifies the creation of responsive and interactive charts for web applications. It’s beginner-friendly and offers a range of chart types, making it suitable for web developers and designers looking to add data visualizations to their websites.
Adobe Illustrator: Adobe Illustrator, primarily a vector graphics software, can also be used for chart creation, especially when precise design control is paramount. It’s a favored tool for professionals in design-intensive industries who require custom charts that seamlessly blend into their creative projects.
Infogram: Infogram is an online platform specializing in creating data visualizations, infographics and interactive reports. It’s user-friendly and doesn’t require coding skills. Infogram is ideal for marketing professionals and content creators looking to incorporate compelling visuals into their materials.
In conclusion, the availability of various software tools empowers users with different needs and skill levels to create impactful charts and data visualizations. Whether you’re a spreadsheet enthusiast, a data analyst, a web developer or a design aficionado, there’s a tool that aligns with your goals and helps you communicate data-driven insights effectively. These options ensure that chart creation remains accessible and versatile, catering to the diverse demands of the modern data-driven world.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: Graph Maker – Create online charts & diagrams in minutes | Canva

Microsoft Excel
Excel is a widely used spreadsheet program that offers a variety of chart types and customization options.
Excel, as one of the most ubiquitous spreadsheet programs globally, stands out not only for its versatility but also for its prowess in data visualization. At the core of its appeal lies a rich array of chart types and an extensive set of customization options, making it the go-to choice for professionals across diverse industries.
The diverse chart types available in Excel cater to a wide spectrum of data presentation needs. From classic bar and pie charts to more complex radar and waterfall charts, Excel provides a visual canvas that adapts to the specific nature of your data. Whether you’re tracking financial trends, displaying survey results or analyzing project timelines, you can easily select the chart type that best conveys your message, ensuring that your data is presented in the most comprehensible and engaging manner.
Customization is where Excel truly shines. It empowers users to tailor their charts and graphs to align perfectly with their intended message or branding. You can fine-tune every element of your charts, from colors and fonts to axis labels and data point markers. This level of control ensures that your charts not only communicate data effectively but also reflect your unique style and preferences.
Excel’s customization options extend beyond aesthetics; they include advanced features for data analysis. You can add trendlines, error bars and data labels to provide deeper insights and context to your audience. The ability to incorporate secondary axes, pivot charts and interactive elements like drop-down lists and slicers further enhances your ability to tell a compelling data-driven story.
Moreover, Excel’s integration with other Microsoft Office applications, such as Word and PowerPoint, simplifies the process of embedding charts and graphs into reports and presentations. This seamless compatibility ensures that your data retains its visual appeal and accuracy when shared across different documents and platforms.
Excel’s capabilities extend beyond the traditional realms of spreadsheet software, allowing you to create dynamic dashboards, perform complex financial modeling and even develop interactive data-driven applications through Power BI integration. Its versatility is a testament to its adaptability, catering not only to data analysts but also to professionals in marketing, finance, engineering and various other fields.
In conclusion, Excel’s wide-ranging chart types and robust customization options make it a versatile tool for data visualization and analysis. Whether you’re crafting financial reports, presenting research findings or creating interactive dashboards, Excel empowers you to transform raw data into meaningful insights that resonate with your audience. Its enduring popularity in the world of spreadsheets is a testament to its ability to evolve and meet the ever-changing demands of data-driven decision-making.
Additionally, you can find further information on this topic by visiting this page: Charts and other visualizations in Power View – Microsoft Support
Google Sheets
Google Sheets provides a collaborative online environment for creating and sharing charts.
Google Sheets is not just a spreadsheet tool; it’s a dynamic platform that fosters collaboration and empowers users to create and share charts in an efficient and interactive online environment. Let’s explore the depth of its capabilities when it comes to chart creation and sharing:
Real-Time Collaboration: Google Sheets excels at real-time collaboration. Multiple users can work on the same sheet simultaneously, including the creation and editing of charts. This collaborative power means that team members can contribute their insights and data to chart creation, resulting in more comprehensive and accurate visualizations.
Wide Range of Chart Types: Google Sheets offers an extensive library of chart types, from basic bar and pie charts to more advanced options like scatter plots, heatmaps and Gantt charts. This variety ensures that you can select the most appropriate chart type to effectively convey your data’s message.
Customization and Styling: Charts created in Google Sheets are highly customizable. You can adjust colors, fonts, labels and other visual elements to match your brand or style preferences. This flexibility allows you to create charts that are not only informative but also visually appealing.
Data Integration: Google Sheets seamlessly integrates with other Google Workspace apps like Google Forms and Google Analytics. This means that data collected through forms or website analytics can be imported directly into Sheets for chart creation, saving time and streamlining data visualization.
Data Validation and Error Checking: Ensuring data accuracy is paramount when creating charts. Google Sheets provides data validation and error checking features, helping you identify and correct any discrepancies or inconsistencies in your data before charting.
Dynamic Data Updates: If your data source changes, Google Sheets charts can update automatically. This feature is especially valuable when dealing with real-time data or when regularly importing new data sets. It ensures that your charts always reflect the most current information.
Sharing and Publishing: Sharing charts is a breeze with Google Sheets. You can share charts with specific collaborators or even publish them on the web as interactive elements that can be embedded in websites, blogs or reports. This makes it easy to disseminate information to a wider audience.
Embedding in Documents and Presentations: Google Sheets allows you to embed charts directly into Google Docs and Google Slides. This integration enhances the visual appeal of your documents and presentations while ensuring that the data remains up to date.
Version History: Just like with other content in Google Workspace, Google Sheets maintains version history for charts. This feature allows you to track changes, revert to previous versions and maintain a clear audit trail of your chart’s development.
Mobile Accessibility: Google Sheets is accessible on mobile devices through the Google Sheets app. This mobility ensures that you can create, edit and share charts while on the go, further enhancing productivity and flexibility.
Data Analysis Tools: In addition to charting, Google Sheets offers various data analysis tools, including functions, pivot tables and statistical analysis. These tools complement your chart creation process by helping you gain deeper insights from your data.
In summary, Google Sheets transcends the traditional role of a spreadsheet tool by providing a collaborative, versatile and user-friendly platform for creating and sharing charts. Its real-time collaboration features, customization options, data integration capabilities and accessibility on multiple devices make it an invaluable tool for professionals across various industries. Whether you’re working on a data-driven report, a project update presentation or an educational resource, Google Sheets empowers you to visualize your data effectively and communicate your insights with precision.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: An Overview of the Best Data Visualization Tools | Toptal®
Tableau
Tableau is a powerful data visualization tool that offers advanced features for creating interactive charts and dashboards.
Tableau stands as a formidable force in the realm of data visualization, thanks to its rich array of advanced features that empower users to craft dynamic charts and dashboards. Here, we’ll explore some of the key attributes that make Tableau a standout choice for data professionals and analysts:
1. Interactive Visualizations: Tableau’s hallmark is its ability to transform static data into interactive visualizations. Users can employ a variety of interactive elements like filters, tooltips and drill-down functionality, enabling stakeholders to engage with data on a deeper level. This interactivity facilitates better insights and decision-making.
2. Diverse Data Source Connectivity: Tableau boasts robust connectivity options, allowing users to connect to a wide range of data sources, from spreadsheets and databases to cloud-based platforms and web services. This versatility ensures that your data remains accessible and up-to-date, regardless of its origin.
3. Drag-and-Drop Interface: A user-friendly drag-and-drop interface makes Tableau accessible to both beginners and seasoned data professionals. Creating charts and dashboards is intuitive, requiring no coding skills. This empowers users to quickly prototype, explore and refine visualizations.
4. Comprehensive Visualization Types: Tableau offers an extensive library of visualization types, including bar charts, scatter plots, maps and more. This versatility enables users to select the most suitable representation for their data, enhancing clarity and understanding.
5. Data Blending and Preparation: Cleaning and shaping data is often a critical step in the data visualization process. Tableau simplifies this with features for data blending and preparation, allowing users to combine, transform and cleanse data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
6. Powerful Analytics: Beyond visualization, Tableau offers built-in analytical capabilities. Users can perform calculations, apply statistical functions and generate forecasts within the tool. This combination of visualization and analytics streamlines the data exploration process.
7. Shareability and Collaboration: Tableau facilitates sharing and collaboration through Tableau Server and Tableau Online. Teams can publish and share dashboards securely, ensuring that stakeholders have access to the latest insights. Real-time collaboration features further enhance teamwork.
8. Scalability: Tableau scales seamlessly with your organization’s growth. Whether you’re a solo analyst or part of a large enterprise, Tableau can adapt to your needs, accommodating more users and data volume as required.
9. Active Community and Support: Tableau boasts a thriving user community that actively shares tips, best practices and resources. Additionally, Tableau offers robust customer support and training resources, ensuring users have the guidance and assistance they need.
10. Integration Ecosystem: Tableau integrates smoothly with a variety of third-party applications and services. Whether it’s connecting to data sources, embedding dashboards in websites or integrating with other analytics tools, Tableau’s ecosystem enhances its versatility and utility.
In summary, Tableau’s reputation as a data visualization powerhouse is well-deserved. Its combination of interactivity, ease of use, data connectivity and analytical capabilities empowers users to transform raw data into actionable insights. Whether you’re visualizing data for business intelligence, reporting or data exploration, Tableau remains a top choice for those seeking to harness the power of data to drive informed decisions.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: What is data visualization and why is it important?
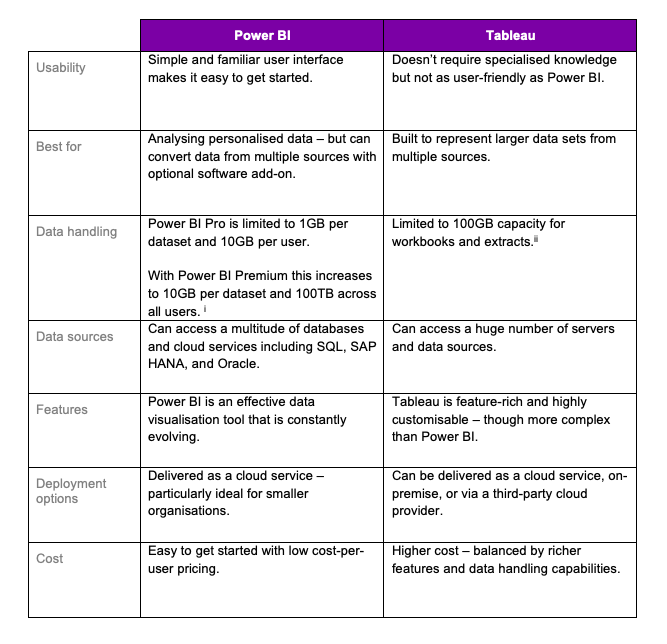
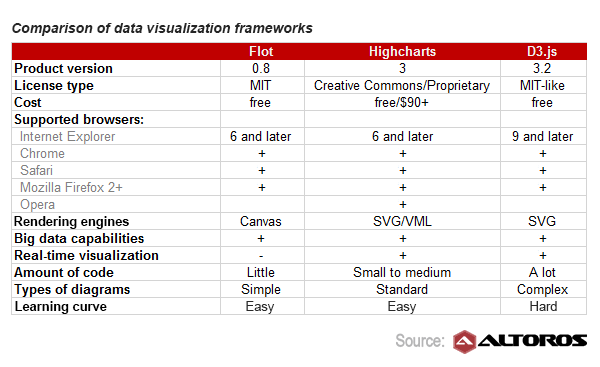
Chart.js
Chart.js is a JavaScript library that enables developers to create dynamic and responsive charts for web applications.
Chart.js is not just a library; it’s a versatile and user-friendly solution that empowers developers to add a layer of interactivity and engagement to their web applications through visually appealing charts. Here’s an extended exploration of the idea:
Chart.js: Transforming Data into Dynamic Visual Stories
Chart.js stands as a testament to the power of modern web development. In an era where data reigns supreme, this JavaScript library has become the go-to choice for developers aiming to breathe life into raw numbers and statistics. Its primary mission? To enable the creation of dynamic and responsive charts that captivate users, convey insights and enhance the overall user experience.
The Art of Data Communication
In the digital age, data is not just about numbers; it’s about telling stories. Chart.js acts as a bridge between data and understanding. Developers harness its capabilities to craft compelling narratives that users can interact with, making complex datasets comprehensible at a glance.
A Canvas of Possibilities
At its core, Chart.js provides a canvas for developers to paint their data-driven visions. Whether you’re visualizing financial trends, survey results or population demographics, the library offers a diverse palette of chart types, from classic bar and line charts to advanced radar and bubble charts. Each chart type comes with a set of customizable options, allowing developers to tailor the visual representation to their specific needs.
Real-Time Data Updates
In a world where information changes at the speed of thought, static charts fall short. Chart.js thrives in this dynamic environment, enabling real-time data updates with seamless animations. Developers can create live charts that respond instantaneously to changing data, providing users with up-to-the-minute insights that guide their decision-making processes.
Responsive Design, Seamless Integration
User experience is paramount in web development and Chart.js understands that implicitly. Its responsive design ensures that charts adapt effortlessly to various screen sizes and devices, whether users access your web application on a desktop computer, tablet or smartphone. Moreover, its integration with other web technologies, such as HTML, CSS and JavaScript frameworks like React and Angular, makes it a valuable asset in any developer’s toolkit.
User Interaction and Exploration
Chart.js goes beyond static visuals; it encourages user interaction and exploration. Developers can implement tooltips, hover effects and click events to enable users to dive deeper into the data. Users can highlight specific data points, reveal additional information or toggle between datasets, fostering a sense of empowerment and discovery.
Enhancing Data-Driven Decision-Making
In a world where data drives decisions in virtually every industry, Chart.js has emerged as a critical ally for developers and businesses alike. It not only elevates the aesthetic appeal of web applications but also empowers users to make informed choices based on clear, digestible insights.
In conclusion, Chart.js is more than just a library; it’s a conduit for transforming raw data into dynamic and responsive visual stories. With its diverse chart types, real-time capabilities, seamless integration and emphasis on user interaction, it enables developers to craft compelling narratives that engage users and facilitate data-driven decision-making. In the ever-evolving landscape of web development, Chart.js stands as a powerful tool that empowers developers to create impactful and visually stunning web applications.
For additional details, consider exploring the related content available here How to Choose the Right Chart for Your Data
Tools for Graph Creation
For more complex data relationships, consider these tools for graph creation:
For more complex data relationships, consider these tools for graph creation:
1. Neo4j: Neo4j is a leading graph database management system. It’s designed specifically for handling and querying graph data, making it an excellent choice for projects that require deep analysis of interconnected data points. Neo4j’s query language, Cypher, simplifies complex graph queries.
2. Gephi: Gephi is an open-source network analysis and visualization software. It’s user-friendly and ideal for exploring and visualizing large-scale graphs. Gephi provides various layout algorithms and customization options to create stunning visual representations of your data.
3. Cytoscape: Cytoscape is a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing complex biological networks, but it can also be applied to other types of graph data. It offers extensive plugins and integrations for data import and analysis, making it versatile for diverse research fields.
4. yEd Graph Editor: yEd is a free desktop application for creating high-quality diagrams and graphs. It supports various graph types and layouts, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from flowcharts and organizational diagrams to complex graph visualizations.
5. Sigma.js: Sigma.js is a JavaScript library for creating interactive network graphs in web applications. It’s a lightweight and versatile tool that allows you to embed dynamic graph visualizations directly into your web pages, enhancing user engagement and interactivity.
6. Tulip: Tulip is an open-source graph visualization and analysis software that offers a range of features for graph exploration, analysis and visualization. It’s commonly used in research and academic settings for its flexibility and extensibility.
7. KeyLines: KeyLines is a commercial graph visualization toolkit designed for building interactive and visually engaging applications. It’s particularly well-suited for organizations looking to incorporate graph-based data visualization into their software products.
8. Ggraph (for R): Ggraph is an R package for creating interactive, node-link diagrams using the ggplot2 syntax. It allows data scientists and analysts to leverage R’s statistical capabilities while creating aesthetically pleasing and informative graph visualizations.
9. ArangoDB: ArangoDB is a multi-model database system that supports graph data alongside document and key-value data. It provides a unified querying language, AQL (ArangoDB Query Language), making it a versatile choice for applications requiring both graph and document-oriented data storage.
10. D3.js: While not solely a graph visualization tool, D3.js (Data-Driven Documents) is a powerful JavaScript library for creating custom data visualizations, including network graphs. It offers full control over the design and interactivity of your visualizations and is often used for custom graph projects.
When dealing with complex data relationships and interconnected data sets, these graph creation tools can help you gain insights, uncover patterns and visualize information in ways that are not easily achievable with traditional data visualization methods. The choice of tool depends on the specific requirements of your project and your familiarity with the software ecosystem.
You can also read more about this here: What is data visualization and why is it important?
Gephi
Gephi is an open-source software for visualizing and exploring networks, making it suitable for creating network graphs.
Gephi, as an open-source software for visualizing and exploring networks, is a valuable tool with a wide range of applications in various fields. Its versatility and capabilities extend beyond just creating network graphs, making it an indispensable resource for researchers, analysts and professionals alike.
Network Analysis: Gephi empowers users to delve deep into the structure and dynamics of complex networks. It doesn’t just create static network graphs but provides advanced analytical tools for network exploration. This includes features for measuring network metrics, identifying communities and detecting patterns within your data. Researchers and data scientists often turn to Gephi for its robust network analysis capabilities.
Interactivity and Visualization: Gephi excels in creating interactive and visually stunning network visualizations. It allows you to customize the appearance of nodes and edges, apply various layout algorithms and design aesthetically pleasing graphs. These interactive visualizations help in presenting complex network data in an accessible and comprehensible manner.
Data Import and Integration: Gephi supports various data formats and can seamlessly integrate with data from sources like CSV files, Excel spreadsheets and databases. This flexibility makes it easy to import and work with your data, regardless of where it originates.
Community and Collaboration: Being open-source, Gephi benefits from a passionate and active community of users and developers. This community not only provides support and resources but also contributes to the continuous improvement and expansion of the software’s features. Collaboration and knowledge-sharing within the Gephi community enhance its utility and effectiveness.
Cross-Disciplinary Applications: Gephi’s versatility transcends fields and industries. It is employed in diverse areas, including social network analysis, biology, transportation planning and business analytics. Researchers and professionals across different domains find Gephi to be a valuable tool for uncovering insights and patterns within their specific datasets.
Educational Value: Gephi serves as an educational tool for teaching network analysis concepts. Many academic institutions use it to introduce students to the world of network science and data visualization, helping cultivate skills that are increasingly in demand in today’s data-driven world.
Customization and Automation: For advanced users, Gephi offers extensive customization options and supports automation through scripting. This allows users to tailor the software to their specific research or analysis needs and even automate repetitive tasks.
In summary, Gephi’s role in creating network graphs is just the tip of the iceberg. Its rich set of features for network analysis, visualization and exploration makes it an invaluable resource for anyone dealing with network data. Whether you’re a researcher seeking to uncover hidden connections, an analyst looking for insights within complex datasets or an educator aiming to teach network science, Gephi’s capabilities extend far beyond simple graph creation, offering a comprehensive toolkit for network analysis and visualization.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Visualizing large knowledge graphs: A performance analysis …

Lucidchart
Lucidchart is a versatile online diagramming tool that can be used to create flowcharts, organizational charts and other types of graphs.
Lucidchart is more than just a versatile online diagramming tool; it’s a dynamic canvas for visual thinkers and collaborative teams to bring their ideas to life. With its intuitive interface and powerful features, Lucidchart empowers users to do so much more than create flowcharts and organizational charts.
Mind Mapping Magic: Lucidchart isn’t limited to traditional diagrams. It’s a space where you can unleash your creativity through mind maps. Whether you’re brainstorming ideas, structuring a project or planning a presentation, Lucidchart’s mind mapping capabilities help you visualize and connect concepts effortlessly.
Interactive Prototyping: Designing user interfaces and interactive prototypes becomes a breeze with Lucidchart. You can craft wireframes, mockups and interactive prototypes that give life to your app or website concepts. Collaborate with your team, gather feedback and iterate until your design is perfect.
Process Optimization: Lucidchart isn’t just for depicting processes; it helps you optimize them too. Create process maps and value stream diagrams to identify bottlenecks, streamline workflows and boost productivity. Lucidchart becomes your ally in continuous improvement efforts.
Data Visualization Hub: Transform data into actionable insights with Lucidchart’s data visualization capabilities. Import data from various sources and create informative charts, graphs and dashboards. It’s the perfect tool for making complex data understandable and decision-making easier.
Educational Excellence: Lucidchart extends its utility to the classroom. Teachers and students can use it for educational purposes such as illustrating concepts, creating timelines for history lessons or visualizing scientific processes. Lucidchart becomes an essential educational aid.
Project Planning Powerhouse: Lucidchart doesn’t just draw boxes and arrows; it helps you plan projects from start to finish. Gantt charts, timelines and swimlane diagrams assist in project management. It’s your project planning and execution headquarters, ensuring tasks are completed on time.
Collaborative Catalyst: Collaboration is at the heart of Lucidchart. Real-time collaboration features allow multiple team members to work on diagrams simultaneously, making it perfect for remote teams. Comments, annotations and chat facilitate communication, streamlining your collaborative efforts.
Integration Ecosystem: Lucidchart seamlessly integrates with popular productivity and project management tools like Google Workspace, Microsoft Teams and Trello. This connectivity ensures your diagrams are where you need them, enhancing your workflow.
Cross-Platform Flexibility: Lucidchart’s accessibility extends across devices and platforms. Use it on your web browser, desktop or mobile device. This flexibility means you can work on your diagrams wherever inspiration strikes.
Security and Compliance: Lucidchart takes data security seriously. It offers robust security features and complies with industry standards like GDPR and HIPAA. Your sensitive information is safe while using this tool.
In summary, Lucidchart transcends the boundaries of a mere diagramming tool. It’s a dynamic space where ideas flourish, projects take shape and collaboration thrives. From mind mapping to data visualization and project planning to education, Lucidchart is the canvas that adapts to your needs, making complex information visually engaging and easy to understand.
You can also read more about this here: What is a Data Flow Diagram | Lucidchart
yEd Graph Editor
yEd is a user-friendly graph editor that offers features for creating and editing various types of graphs.
yEd, the user-friendly graph editor, is a versatile tool that empowers users to craft a wide array of graphs with ease. Its extensive feature set makes it invaluable for a range of applications, from academic research to business data visualization. Here’s a deeper exploration of what makes yEd a standout choice for graph creation and editing:
1. Diverse Graph Types: yEd goes beyond simple charting and provides support for a diverse range of graph types. Whether you need to create flowcharts, organizational charts, network diagrams, UML diagrams or more specialized graphs like entity-relationship diagrams (ERD) and mind maps, yEd has you covered. This versatility ensures that the tool can cater to a wide spectrum of user needs.
2. User-Friendly Interface: yEd’s intuitive and user-friendly interface simplifies the graph creation process. Its drag-and-drop functionality, combined with a wide selection of predefined shapes and symbols, ensures that even beginners can start creating professional-looking graphs quickly. The learning curve is gentle, making it accessible to users of all levels.
3. Powerful Layout Algorithms: For complex graphs, arranging and organizing elements can be a challenging task. yEd comes equipped with powerful layout algorithms that automatically position nodes and edges in an aesthetically pleasing and logical manner. This saves users valuable time and ensures that graphs are both visually appealing and comprehensible.
4. Customization Options: While yEd offers automation, it also provides ample customization options. Users can fine-tune graph layouts, adjust styling and add labels and annotations to tailor graphs to their specific requirements. This flexibility allows for creative expression while maintaining clarity.
5. Data Import and Export: yEd supports data-driven graph creation. Users can import data from various sources, such as spreadsheets or databases, to generate graphs automatically. Conversely, data can be exported from created graphs for further analysis or sharing, ensuring data integrity and consistency.
6. Cross-Platform Compatibility: Whether you’re using Windows, macOS or Linux, yEd is available on multiple platforms, ensuring that users can access the tool regardless of their operating system. This cross-platform compatibility promotes collaboration and data sharing among diverse teams.
7. Community and Support: yEd benefits from an active and engaged user community. Users can find resources, tutorials and a responsive support forum where they can seek assistance and exchange ideas. This collaborative environment enhances the user experience and fosters innovation.
8. Regular Updates: The development team behind yEd is committed to enhancing the tool’s capabilities and addressing user feedback. Regular updates and improvements ensure that yEd remains a cutting-edge graph editor that keeps pace with evolving user needs and technological advancements.
In summary, yEd’s user-friendly approach, versatile capabilities and commitment to customization make it an exceptional choice for creating and editing various types of graphs. Whether you’re a student, researcher, data analyst or business professional, yEd empowers you to visually convey complex information, promote understanding and make data-driven decisions with confidence. Its accessibility and rich feature set make it a valuable addition to any toolkit.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: yEd – Graph Editor
Data visualization is a vital component of effective communication and decision-making in today’s data-driven world. Charts and graphs serve as invaluable tools for transforming data into actionable insights, but selecting the right tool for the job is crucial. Whether you choose charts to display data comparisons or graphs to illustrate complex relationships, the availability of various software tools makes it easier than ever to create compelling and informative reports that resonate with your audience. Remember, the choice between charts and graphs should align with your data, your message and the preferences of your audience.
“In the age of big data and information overload, data visualization emerges as the linchpin of effective communication and sound decision-making. The art of transforming raw data into meaningful insights has never been more critical and in this pursuit, charts and graphs become our trusted allies. However, the selection of the right visualization tool is akin to choosing the perfect brush for a masterpiece—essential for conveying your message accurately and engagingly.
The Power of Visual Storytelling:
Data Clarity: Charts and graphs distill complex data into digestible visuals. They unravel intricate patterns, trends and outliers, making it easier for audiences to grasp the essence of the information.
Audience Engagement: Visuals are inherently engaging. They captivate your audience’s attention and facilitate comprehension, especially in a world where attention spans are fleeting.
Informed Decision-Making: Data visualization empowers decision-makers with actionable insights. Whether you’re strategizing in business, conducting research or making policy decisions, visualizations clarify the path forward.
The Art of Choosing: Charts vs. Graphs:
Charts for Comparisons: Charts, such as bar graphs and pie charts, excel at showcasing comparisons. They are your go-to when you need to illustrate proportions, distributions or trends within distinct categories. For example, a bar chart can vividly compare sales figures for different products.
Graphs for Relationships: Graphs, like line graphs and scatter plots, shine when revealing relationships between variables. They help you uncover correlations, trends over time and the impact of one variable on another. For instance, a line graph can chart the progression of stock prices.
The Multitude of Tools at Your Fingertips:
Microsoft Excel: A staple for data visualization, Excel offers a wide range of chart and graph types, making it accessible for beginners and powerful for advanced users.
Tableau: Renowned for its robust data visualization capabilities, Tableau enables you to create interactive and dynamic visuals, perfect for in-depth data exploration.
Google Data Studio: Ideal for collaborative projects, this tool allows you to create and share dynamic reports and dashboards with ease.
Python (Matplotlib and Seaborn): Python libraries like Matplotlib and Seaborn provide programmers with comprehensive control over visualizations, catering to advanced data analysis needs.
Power BI: Microsoft’s Power BI offers extensive visualization options and integrates seamlessly with various data sources, making it a favored choice for data-driven businesses.
Tailoring to Your Audience:
Simplicity for General Audiences: For general audiences, opt for clear and straightforward visuals. Pie charts and bar graphs are universally understood and can effectively convey key points.
Complexity for Experts: When presenting to experts or data-savvy audiences, consider more intricate visuals like heatmaps or scatter plots, which allow for in-depth exploration.
Interactivity for Engagement: Interactive visuals, like those in Tableau or Power BI, enable audiences to explore data on their terms, enhancing engagement and understanding.
Remember, the choice between charts and graphs should harmonize with your data’s nature, the story you wish to tell and your audience’s preferences. It’s the synergy of these elements that transforms data visualization from a mere tool into a compelling and informative means of communication.”
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: See 20 Different Types Of Graphs And Charts With Examples
More links
You can also read more about this here: Graph Maker – Create online charts & diagrams in minutes | Canva
