Introduction
Diesel engines have been a driving force behind industrialization and transportation for over a century. Their remarkable efficiency and robust design have made them a staple in various applications, from trucks and ships to generators and heavy machinery. In this article, we delve into the technology that makes diesel engines so efficient and explore their role in the present and future of transportation and industry.
Diesel engines have been a powerhouse driving industrialization and transportation for well over a century. Their remarkable efficiency and robust design have firmly entrenched them as a cornerstone in various critical applications, spanning from the mighty engines of trucks and ships to the reliable generators that keep the lights on and the heavy machinery that shapes our world.
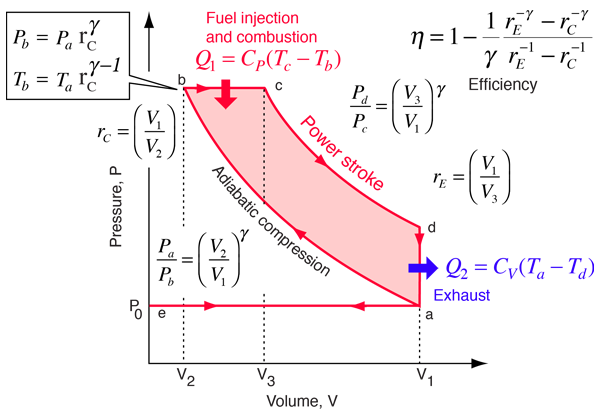
At the heart of diesel engines lies a technology that has withstood the test of time. Their efficiency, often surpassing that of gasoline engines, is a testament to their engineering excellence. The process of compression ignition, where air is compressed to a high temperature, causing the fuel to spontaneously combust, is the secret behind their efficiency. This design not only maximizes fuel economy but also delivers exceptional torque, making diesel engines ideal for heavy-duty work.
In the world of transportation, diesel engines continue to play a pivotal role. Long-haul trucks crisscross continents, carrying goods to meet global demand, and they rely heavily on the power and efficiency of diesel engines. Additionally, marine vessels, from cargo ships to cruise liners, depend on diesel propulsion to navigate the world’s oceans efficiently.
Beyond transportation, diesel generators serve as lifelines during power outages and in remote areas where a stable electricity supply is essential. These generators offer a dependable source of energy, particularly in regions with unreliable grid infrastructure.
Looking ahead, diesel engines are not fading into obsolescence. Instead, they are evolving to meet stringent environmental standards. Advancements in emission control technology, such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and diesel particulate filters (DPF), are reducing their environmental footprint. Furthermore, ongoing research into alternative fuels like biodiesel and synthetic diesel holds promise for a cleaner diesel future.
Diesel engines are poised to continue their journey as an indispensable force in the transportation and industrial sectors. Their longevity, adaptability, and commitment to efficiency make them a vital component of the present and future, ensuring that the wheels of industry keep turning and the world keeps moving forward.
Explore this link for a more extensive examination of the topic: Hydrogen Basics – Alternative Fuels Data Center
the way they ignite fuel. Diesel engines operate on the principle of compression ignition, where air is compressed to a high temperature, causing the injected diesel fuel to spontaneously ignite. This process results in greater thermal efficiency compared to gasoline engines, where a spark plug initiates combustion.
The way engines ignite fuel plays a pivotal role in determining their efficiency and performance. Diesel engines, for instance, operate on the principle of compression ignition. In this ingenious design, air is compressed to an extremely high temperature within the engine cylinder. This intense compression causes the injected diesel fuel to spontaneously ignite upon contact with the superheated air.
This method stands in stark contrast to gasoline engines, where combustion is initiated by a spark plug igniting the air-fuel mixture. This distinct approach to ignition is a defining characteristic of the two engine types and has far-reaching implications.
Compression ignition in diesel engines results in significantly greater thermal efficiency when compared to the spark ignition of gasoline engines. Diesel engines often achieve higher compression ratios, which leads to a more complete and controlled combustion process. This, in turn, translates into improved fuel economy and torque delivery, making diesel engines a preferred choice for applications where efficiency and torque are paramount, such as in heavy-duty trucks and industrial machinery.
On the other hand, gasoline engines excel in situations where high-revving power and responsiveness are key, as the spark ignition allows for precise control of combustion timing. This makes them a common choice for passenger vehicles and sports cars.
Understanding the fundamental difference in ignition methods between diesel and gasoline engines sheds light on the diverse range of applications for each. It also underscores the continuous pursuit of innovation in both engine types, with efforts focused on optimizing efficiency, emissions, and performance to meet the evolving demands of the automotive industry and environmental concerns.
For a comprehensive look at this subject, we invite you to read more on this dedicated page: Pollution from Fossil-Fuel Combustion is the Leading Environmental …
turbocharging and direct injection.
Turbocharging and direct injection represent a dynamic duo in the world of engine technology, contributing significantly to improved efficiency, power output, and reduced emissions.
Turbocharging: Turbochargers are like the lungs of a modern engine. These ingenious devices compress the incoming air before it enters the combustion chamber. By forcing more air into the engine, a turbocharger allows for a higher volume of oxygen to mix with the injected fuel. This compressed air not only enhances power output but also ensures more efficient combustion, resulting in fewer unburned hydrocarbons and reduced emissions.
Furthermore, turbocharging enables smaller, more fuel-efficient engines to produce the power of larger ones, making it a go-to technology for downsizing without sacrificing performance. This is particularly beneficial in passenger cars, where drivers can enjoy both spirited acceleration and fuel economy.
In the world of motorsports, turbocharging has become a staple, enabling race cars to extract astonishing power from compact engines while adhering to strict fuel consumption regulations. In Formula 1, for example, turbocharged hybrid power units have revolutionized the sport, delivering unparalleled power and efficiency.
Direct Injection: Direct injection complements turbocharging by optimizing the delivery of fuel into the combustion chamber. Unlike traditional port fuel injection, where fuel is sprayed into the intake manifold before entering the cylinders, direct injection systems deliver fuel directly into the cylinder at high pressure. This precision results in better atomization, more uniform mixing with air, and improved combustion efficiency.
Direct injection also allows for multiple injections during each combustion cycle, enabling finer control over the combustion process. This, in turn, leads to reduced emissions, improved fuel economy, and enhanced power delivery. In modern diesel engines, especially, direct injection has played a pivotal role in meeting stringent emissions standards while maintaining performance.
Together, turbocharging and direct injection have transformed the automotive landscape, enabling smaller, more fuel-efficient engines to deliver robust power outputs without compromising environmental standards. These technologies continue to evolve, promising even greater gains in efficiency, reduced emissions, and a more sustainable future for transportation.
Don’t stop here; you can continue your exploration by following this link for more details: Global EV Outlook 2020 – Analysis – IEA

Diesel engines have long been the workhorses of the transportation industry, powering commercial trucks, buses, trains, and ships. Their ability to deliver high torque at low RPMs makes them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Diesel’s efficiency also translates to longer ranges and reduced fuel consumption for long-haul vehicles.
In recent years, advancements in diesel engine technology have led to cleaner and more fuel-efficient engines, helping to address environmental concerns. Ultra-low sulfur diesel fuel, advanced exhaust aftertreatment systems, and stricter emissions regulations have contributed to reducing harmful emissions from diesel engines.
Should you desire more in-depth information, it’s available for your perusal on this page: India Energy Outlook 2021 – Analysis – IEA

As the world continues to grapple with climate change and seeks to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, diesel engine technology is evolving to meet these challenges. Manufacturers are developing hybrid diesel-electric systems and exploring alternative fuels like biodiesel and synthetic fuels to further reduce emissions and increase efficiency.
Furthermore, diesel engines are making inroads into passenger vehicles, particularly in Europe, where diesel-powered cars are known for their impressive fuel economy and reduced carbon dioxide emissions. However, the future of diesel in passenger cars is at a crossroads, with electric and hybrid technologies gaining prominence.
To delve further into this matter, we encourage you to check out the additional resources provided here: Battery vs. diesel: Why we need both | CK Power

Diesel engine technology has come a long way since its inception, and its efficiency remains a hallmark in various industries. While diesel engines have faced environmental scrutiny, they continue to adapt and improve, contributing to cleaner and more efficient transportation and industrial operations. As technology advances, diesel engines will likely play a vital role in the transition to greener and more sustainable energy solutions, demonstrating that they are not just engines of the past but also engines of the future.
“The evolution of diesel engine technology has been nothing short of remarkable, and its unparalleled efficiency continues to be a cornerstone in numerous sectors. While diesel engines have encountered increased environmental scrutiny, they have risen to the challenge by embracing innovations that enhance their eco-friendliness. This ongoing adaptation underscores their relevance in today’s pursuit of cleaner and more efficient transportation and industrial processes.
One notable advancement in diesel technology is the development of cleaner-burning fuels and advanced emissions control systems. Ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) and biofuels have significantly reduced the environmental impact of diesel engines, with lower emissions of sulfur and particulate matter. Furthermore, the implementation of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and diesel particulate filters (DPF) has effectively curbed nitrogen oxides and particulate emissions, aligning diesel engines with stringent environmental regulations.
Moreover, the efficiency of diesel engines makes them a compelling candidate for the transition to greener and more sustainable energy solutions. Diesel-hybrid systems and the exploration of alternative fuels, such as synthetic diesel and hydrogen, further expand their potential in achieving a lower carbon footprint. In this context, diesel engines emerge not only as engines of the past but as vital contributors to a sustainable future.
As technology continues to advance, diesel engines are poised to play an integral role in the broader spectrum of energy solutions, bridging the gap between conventional and renewable power sources. Their adaptability and efficiency are testaments to their enduring importance, ensuring that they remain relevant and valuable components of our evolving energy landscape.”
You can also read more about this here: India Energy Outlook 2021 – Analysis – IEA
More links
To expand your knowledge on this subject, make sure to read on at this location: Alternative Fuels and Advanced … – Alternative Fuels Data Center
